
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (3): 387-398.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240507
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Haiwei, GU Xinyi, CHEN Mingshuai, LI Fukang, SHI Yuecheng, YANG Ting, JIANG Shuochen*( )
)
Received:2024-05-15
Revised:2024-10-08
Online:2025-05-10
Published:2025-05-21
Contact:
*email: 18229920540@163.com
张海维, 顾欣怡, 陈明帅, 李福康, 施玥丞, 杨挺, 姜硕琛*( )
)
通讯作者:
*email: 18229920540@163.com
基金资助:ZHANG Haiwei, GU Xinyi, CHEN Mingshuai, LI Fukang, SHI Yuecheng, YANG Ting, JIANG Shuochen. Effects of Nitrogen Type of Basal Fertilizer on Growth, Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Ratooning Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 387-398.
张海维, 顾欣怡, 陈明帅, 李福康, 施玥丞, 杨挺, 姜硕琛. 基肥氮素类型对再生稻生长、产量和氮素利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 387-398.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240507
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | pH值 pH value | 有机质 Organic matter (g/kg) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g/kg) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g/kg) | 全钾 Total potassium (g/kg) | 碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolyzable nitrogen (mg/kg) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus (mg/kg) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 5.83 | 21.15 | 1.86 | 0.55 | 3.58 | 79.42 | 48.24 | 112.23 | |
| 2021 | N0 | 5.85 | 20.45 | 1.76 | 0.54 | 3.54 | 73.45 | 48.25 | 110.37 |
| CK | 5.85 | 21.12 | 1.87 | 0.55 | 3.59 | 78.29 | 48.27 | 112.14 | |
| T1 | 5.84 | 21.33 | 1.89 | 0.55 | 3.58 | 80.21 | 48.29 | 113.05 | |
| T2 | 6.05 | 23.14 | 2.01 | 0.55 | 3.58 | 79.71 | 48.28 | 113.64 |
Table 1. Soil properties of main season rice before transplanting
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | pH值 pH value | 有机质 Organic matter (g/kg) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g/kg) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g/kg) | 全钾 Total potassium (g/kg) | 碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolyzable nitrogen (mg/kg) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus (mg/kg) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 5.83 | 21.15 | 1.86 | 0.55 | 3.58 | 79.42 | 48.24 | 112.23 | |
| 2021 | N0 | 5.85 | 20.45 | 1.76 | 0.54 | 3.54 | 73.45 | 48.25 | 110.37 |
| CK | 5.85 | 21.12 | 1.87 | 0.55 | 3.59 | 78.29 | 48.27 | 112.14 | |
| T1 | 5.84 | 21.33 | 1.89 | 0.55 | 3.58 | 80.21 | 48.29 | 113.05 | |
| T2 | 6.05 | 23.14 | 2.01 | 0.55 | 3.58 | 79.71 | 48.28 | 113.64 |
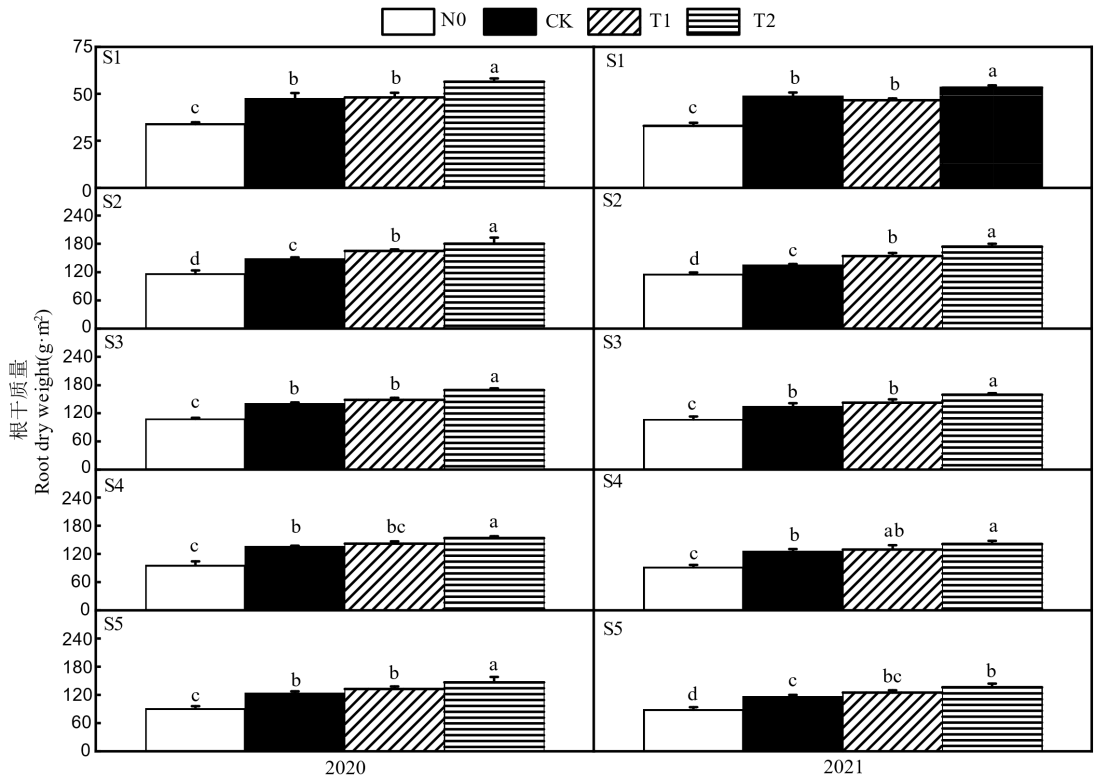
Fig. 2. Effects of different nitrogen fertilizer types on root dry weight at key growth stages of rice N0, CK, T1 and T2 in the figure represent zero nitrogen application, urea, 50% urea+50% controlled release urea and 50% urea+50% livestock manure organic fertilizer, respectively. S1-S5 refer to the tillering stage, heading stage and filling stage of the main season rice, heading stage and filling stage for ratooning rice, respectively. Values are mean ± SD (n=3); Different letters above the bars indicate significant difference among treatments at the 0.05 level (Duncan's new multiple range test).
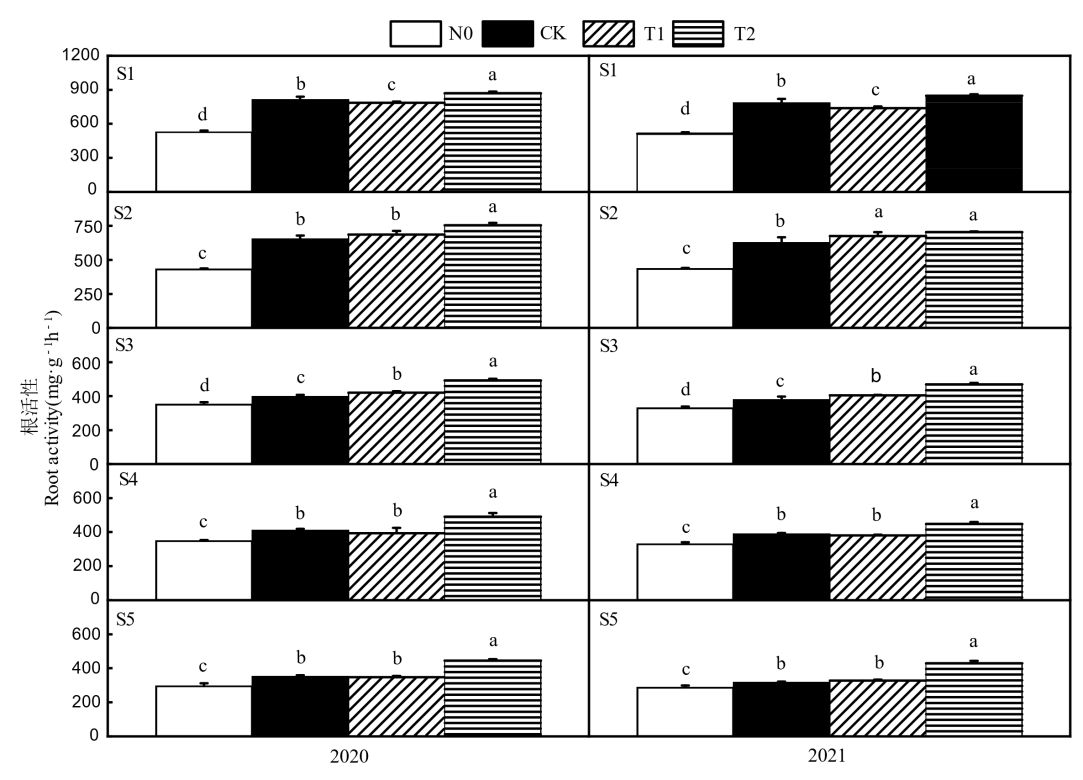
Fig. 3. Effects of different nitrogen fertilizer types on root activity at key growth stages of rice N0, CK, T1 and T2 in the figure represent zero nitrogen application, urea, 50% urea+50% controlled release urea and 50% urea+50% livestock manure organic fertilizer, respectively. S1-S5 referto the tillering stage, heading stage and filling stage of the main season rice, heading stage and filling stage for ratooning rice, respectively. Values are mean ± SD (n=3); Different letters above the bars indicate significant difference among treatments at the 0.05 level (Duncan's new multiple range test).
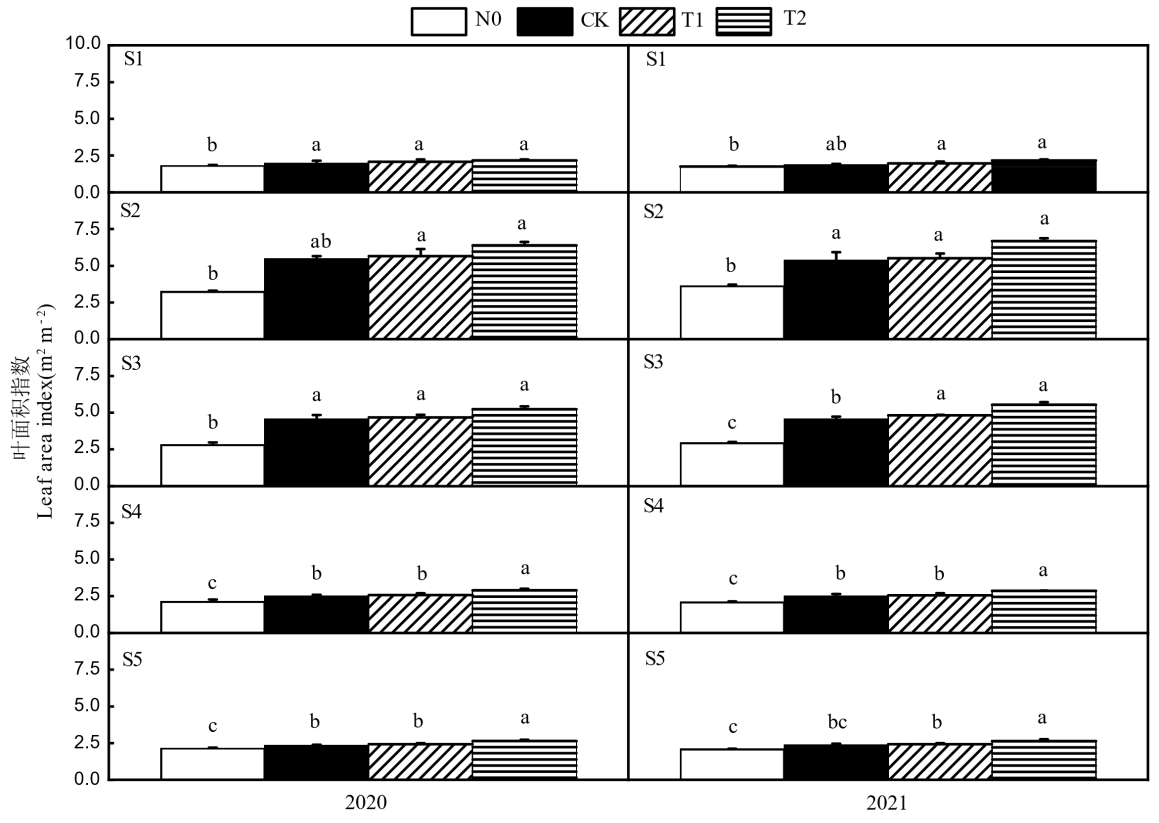
Fig. 4. Effects of different nitrogen fertilizer types on leaf area index at key growth stages of rice N0, CK, T1 and T2 in the figure represent zero nitrogen application, urea, 50% urea+50% controlled release urea and 50% urea+50% livestock manure organic fertilizer, respectively. S1-S5 referto the tillering stage, heading stage and filling stage of the main season rice, heading stage and filling stage for ratooning rice, respectively. Values are mean ± SD (n=3); Different letters above the bars indicate significant difference among treatments at the 0.05 level (Duncan's new multiple range test).
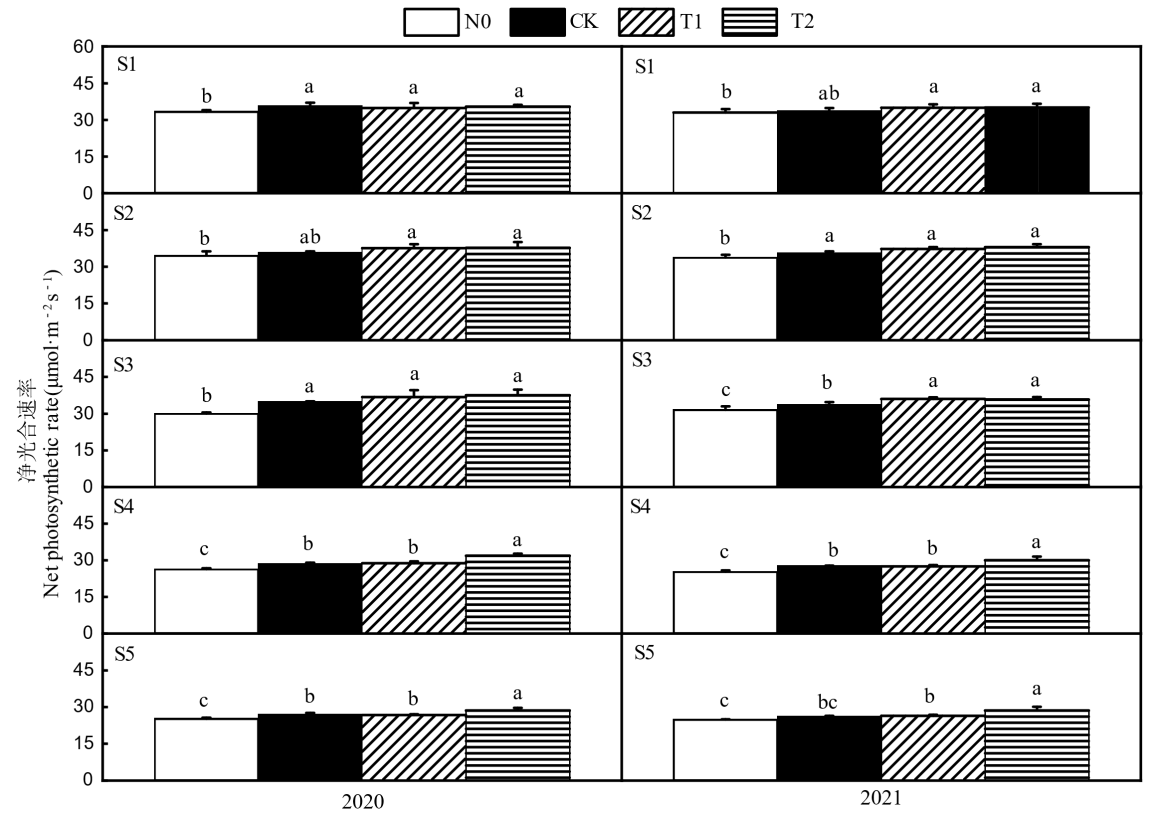
Fig. 5. Effects of different nitrogen fertilizer types on net photosynthetic rate at key growth stages of rice N0, CK, T1 and T2 in the figure represent zero nitrogen application, urea, 50% urea+50% controlled release urea and 50% urea+50% livestock manure organic fertilizer, respectively. S1-S5 referto the tillering stage, heading stage and filling stage of the main season rice, heading stage and filling stage for ratooning rice, respectively. Values are mean ± SD (n=3); Different letters above the bars indicate significant difference among treatments at the 0.05 level (Duncan's new multiple range test).
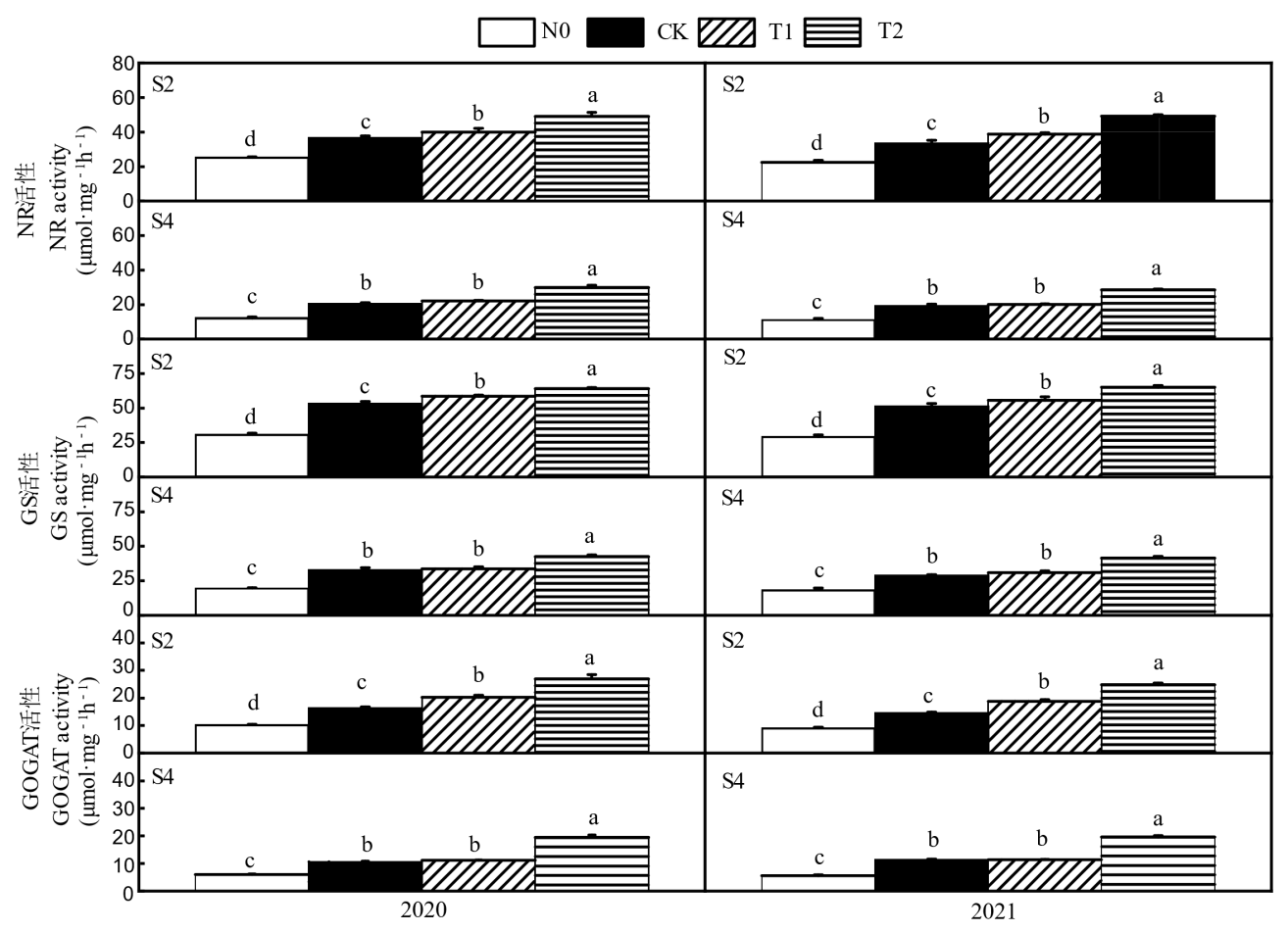
Fig. 6. Effects of different nitrogen fertilizer types on nitrogen metabolizing enzyme of rice N0, CK, T1 and T2 in the figure represent zero nitrogen application, urea, 50% urea+50% controlled release urea and 50% urea+50% livestock manure organic fertilizer, respectively. S2 and S4 referto the heading stage of main season rice and heading stage of ratooning rice, respectively. Values are mean±SD(n=3); Different letters above the bars indicate significant difference among treatments at the 0.05 level (Duncan's new multiple range test).
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicles number (No.·m-2) | 每穗粒数 Spikelets per panicle | 结实率 Grain-filling rate (%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Yield (t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | N0 | 206.45±13.56 b | 161.83±2.75 c | 75.20±2.51 b | 21.96±0.36 c | 5.34±0.28 c |
| CK | 230.64±13.71 a | 216.74±14.36 b | 80.55±4.00 ab | 24.70±0.23 b | 9.44±0.47 b | |
| T1 | 242.62±13.94 a | 231.64±10.77 ab | 84.24±1.21 a | 24.90±0.54 b | 11.29±1.10 a | |
| T2 | 237.39±3.90 a | 247.17±5.65 a | 82.38±1.60 ab | 26.13±0.25 a | 12.23±0.11 a | |
| 2021 | N0 | 207.02±10.64 b | 175.41±17.69 c | 76.62±0.92 b | 22.04±0.67 c | 6.00±0.38 d |
| CK | 236.05±2.53 a | 224.84±7.98 b | 76.27±1.58 b | 25.36±0.35 b | 9.81±0.65 c | |
| T1 | 230.45±12.78 a | 253.72±7.95 a | 77.06±5.06 b | 25.88±0.59 ab | 11.22±0.52 b | |
| T2 | 238.06±18.59 a | 261.61±8.84 a | 82.60±2.75 a | 26.48±0.48 a | 13.15±0.63 a |
Table 2. Grain yield and yield components of main season rice
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicles number (No.·m-2) | 每穗粒数 Spikelets per panicle | 结实率 Grain-filling rate (%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Yield (t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | N0 | 206.45±13.56 b | 161.83±2.75 c | 75.20±2.51 b | 21.96±0.36 c | 5.34±0.28 c |
| CK | 230.64±13.71 a | 216.74±14.36 b | 80.55±4.00 ab | 24.70±0.23 b | 9.44±0.47 b | |
| T1 | 242.62±13.94 a | 231.64±10.77 ab | 84.24±1.21 a | 24.90±0.54 b | 11.29±1.10 a | |
| T2 | 237.39±3.90 a | 247.17±5.65 a | 82.38±1.60 ab | 26.13±0.25 a | 12.23±0.11 a | |
| 2021 | N0 | 207.02±10.64 b | 175.41±17.69 c | 76.62±0.92 b | 22.04±0.67 c | 6.00±0.38 d |
| CK | 236.05±2.53 a | 224.84±7.98 b | 76.27±1.58 b | 25.36±0.35 b | 9.81±0.65 c | |
| T1 | 230.45±12.78 a | 253.72±7.95 a | 77.06±5.06 b | 25.88±0.59 ab | 11.22±0.52 b | |
| T2 | 238.06±18.59 a | 261.61±8.84 a | 82.60±2.75 a | 26.48±0.48 a | 13.15±0.63 a |
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicles number spike (No.·m-2) | 每穗粒数 Spikelets per panicle | 结实率 Grain-filling rate (%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Yield (t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | N0 | 214.54±13.38 b | 72.52±2.67 d | 54.66±2.80 b | 19.76±0.49 b | 1.66±0.27 c |
| CK | 256.20±9.97 a | 100.01±7.69 bc | 58.23±3.73 b | 21.99±0.25 a | 3.15±0.39 b | |
| T1 | 270.59±3.63 a | 98.60±5.55 c | 56.34±5.61 b | 22.18±0.56 a | 3.17±0.20 b | |
| T2 | 266.86±12.17 a | 120.34±4.94 a | 70.42±2.24 a | 22.48±0.55 a | 4.91±0.14 a | |
| 2021 | N0 | 203.32±9.58 b | 66.52±0.61 c | 59.23±3.30 bc | 20.25±0.52 b | 1.60±0.22 d |
| CK | 266.48±11.61 a | 93.22±4.87 b | 59.75±4.55 bc | 22.59±0.90 a | 3.17±0.03 c | |
| T1 | 259.81±9.54 a | 98.36±3.10 b | 57.34±2.27 c | 22.66±0.66 a | 3.13±0.08 b | |
| T2 | 268.29±5.36 a | 110.58±0.50 a | 67.96±2.11 a | 22.82±0.54 a | 4.42±0.02 b |
Table 3. Grain yield and yield components of ratooning rice
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicles number spike (No.·m-2) | 每穗粒数 Spikelets per panicle | 结实率 Grain-filling rate (%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Yield (t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | N0 | 214.54±13.38 b | 72.52±2.67 d | 54.66±2.80 b | 19.76±0.49 b | 1.66±0.27 c |
| CK | 256.20±9.97 a | 100.01±7.69 bc | 58.23±3.73 b | 21.99±0.25 a | 3.15±0.39 b | |
| T1 | 270.59±3.63 a | 98.60±5.55 c | 56.34±5.61 b | 22.18±0.56 a | 3.17±0.20 b | |
| T2 | 266.86±12.17 a | 120.34±4.94 a | 70.42±2.24 a | 22.48±0.55 a | 4.91±0.14 a | |
| 2021 | N0 | 203.32±9.58 b | 66.52±0.61 c | 59.23±3.30 bc | 20.25±0.52 b | 1.60±0.22 d |
| CK | 266.48±11.61 a | 93.22±4.87 b | 59.75±4.55 bc | 22.59±0.90 a | 3.17±0.03 c | |
| T1 | 259.81±9.54 a | 98.36±3.10 b | 57.34±2.27 c | 22.66±0.66 a | 3.13±0.08 b | |
| T2 | 268.29±5.36 a | 110.58±0.50 a | 67.96±2.11 a | 22.82±0.54 a | 4.42±0.02 b |
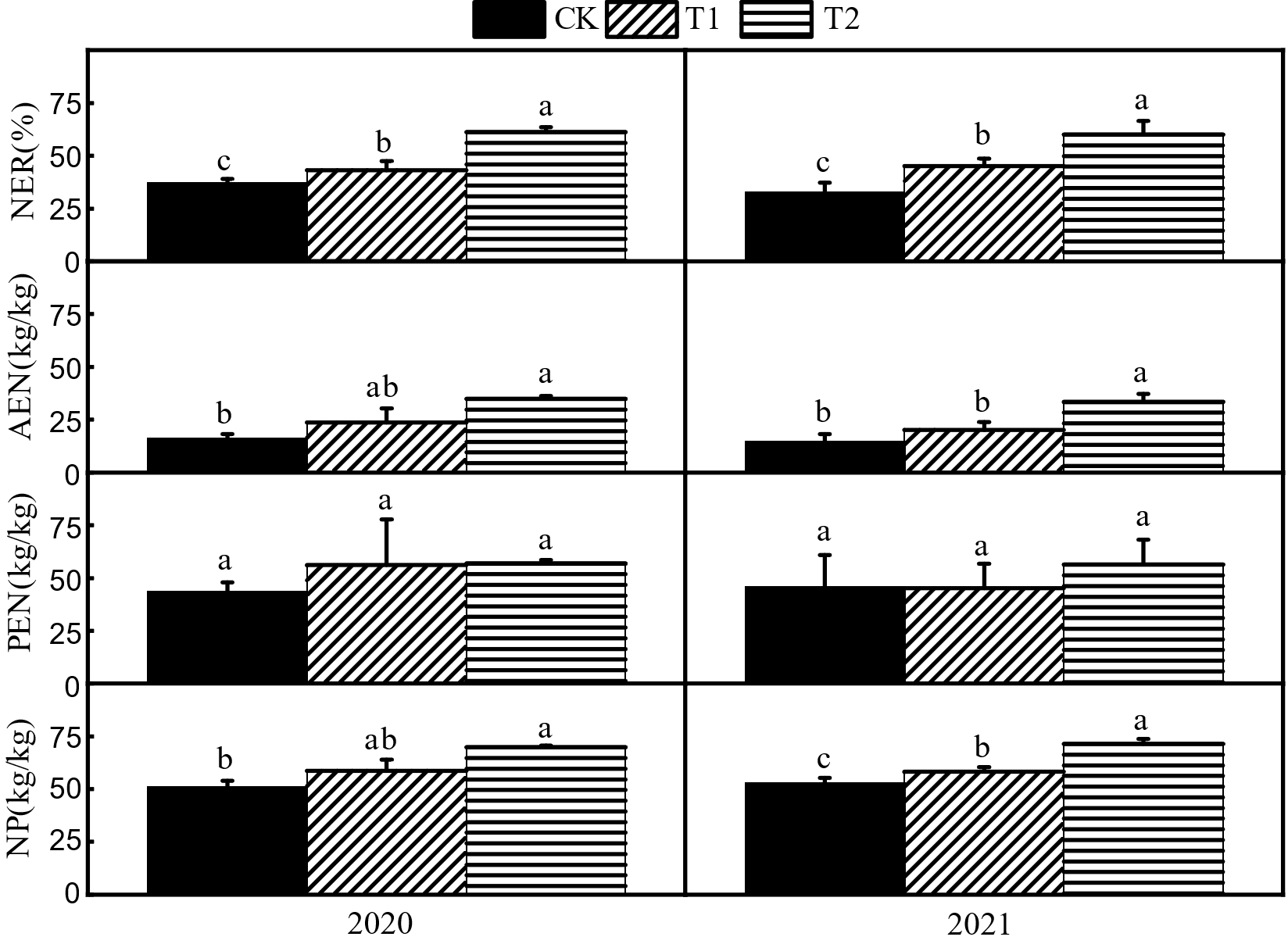
Fig. 7. Effect of different nitrogen fertilizer types on nitrogen utilization efficiency CK, T1 and T2 in the figure represent urea, 50% urea+50% controlled release urea and 50% urea+50% livestock manure organic fertilizer. NER represents nitrogen recovery efficiency, AEN represents agronomic nitrogen use efficiency, PEN represents physiological nitrogen efficiency, and NP represents nitrogen partial productivity. Values are mean±SD(n=3); Different letters above the bars indicate significant difference among treatments at the 0.05 level (Duncan's new multiple range test).
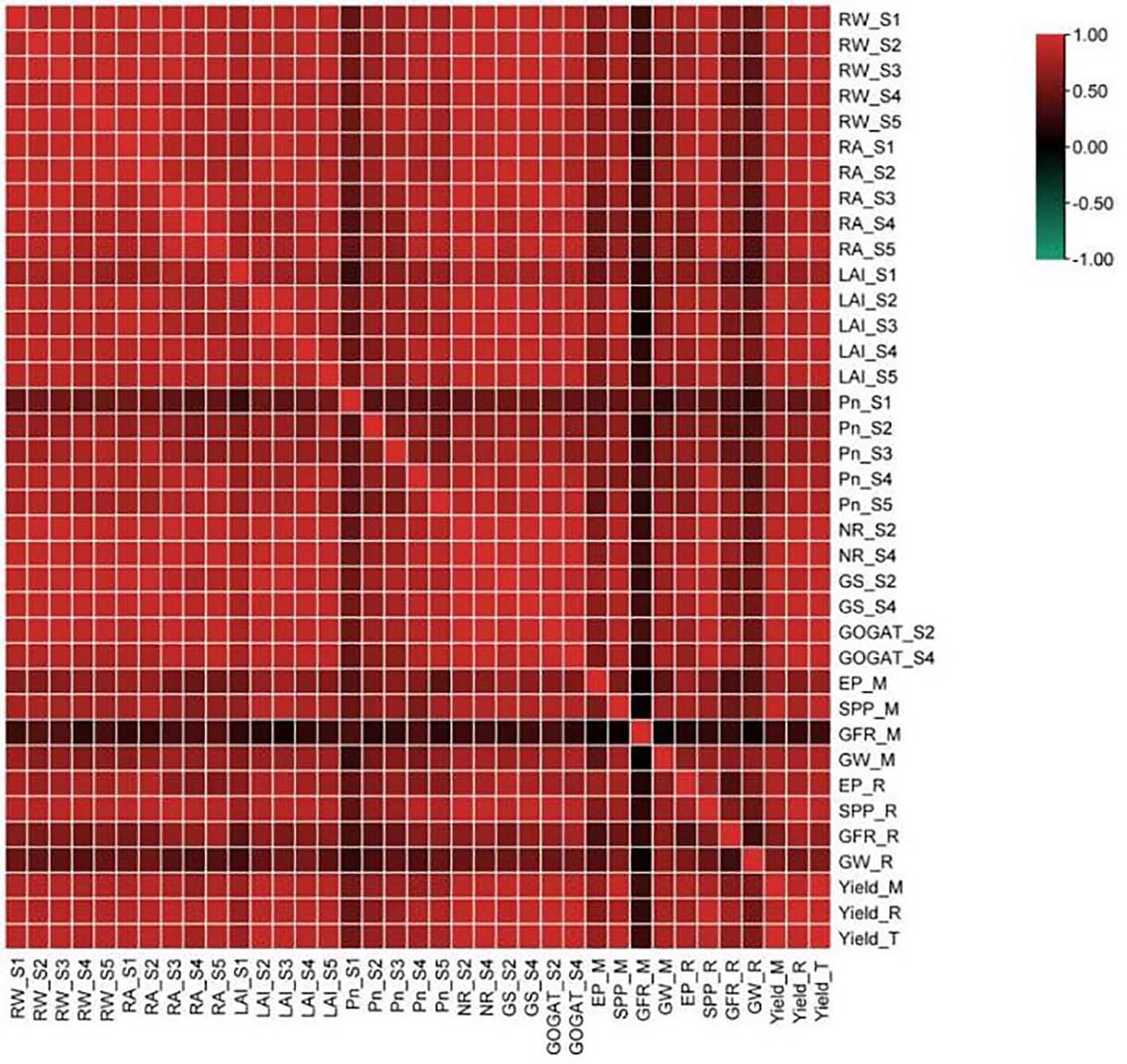
Fig. 8. Heat map of correlation analysis between grain yield and various indicators RW, Root dry weight; RA, Root activity; LAI, Leaf area index; Pn, Net photosynthetic rate; NR, Nitrate reductase activity; GS, Glutamine synthetase activity; GOGAT, Glutamate synthase activity; EP, Effective panicle number; SPP, Spikelets per panicle; GFR, Grain filling rate; GW, 1000-grain weight. _S1 to _S5 represent the tillering stage, heading stage and filling stage of main season rice, heading stage and filling stage of ratooning rice, respectively. _M and _R represent main season rice and ratooning rice, respectively, while Yield_T represents the total yield of two-season rice.
| [1] | Wang Y C, Li X F, Lee T, Peng S B, Dou F G. Effects of nitrogen management on the ratoon crop yield and head rice yield in South USA[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2021, 20(6): 1457-1464. |
| [2] | 费震江, 董华林, 武晓智, 周鹏. 湖北省再生稻发展的现状及潜力[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2013, 52(24): 5977-5978. |
| Fei Z J, Dong H L, Wu X Z, Zhou P. The development status and potential of ratoon rice in Hubei Province[J], Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 52(24): 5977-5978. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 丁紫娟, 胡仁, 李锦涛, 曹玉贤, 田应兵, 侯俊. 一次性根区施氮促进再生稻生长及增产的研究[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2023, 51(9): 112-119. |
| Ding Z J, Hu R, Li J T, Cao Y X, Tian Y B, Hou J. Study on promoting growth and increasing yield of ratooning rice by one-off nitrogen application in root zone[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 2023, 51(9): 112-119. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | Wang W Q, He A, Jiang G L, Sun H J, Jiang M, Man J G, Ling X X, Cui K H, Huang J L, Peng S B. Ratoon rice technology: A green and resource-efficient way for rice production[J]. Advances in Agronomy, 2020, 159: 135-167. |
| [5] | Wang Y C, Zheng C, Xiao S, Sun Y T, Huang J L, Peng S B. Agronomic responses of ratoon rice to nitrogen management in Central China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2019, 241: 107569. |
| [6] | 赵灿, 刘光明, 戴其根, 许轲, 高辉, 霍中洋. 氮肥对水稻产量, 品质和氮利用效率的影响研究进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2022, 28(1): 48. |
| Zhao C, Liu G M, Dai Q G, Xu K, Gao H, Huo Z Y. Research progress on the effects of nitrogen fertilizer on rice yield, quality and nitrogen use efficiency[J]. China Rice, 2022, 28(1): 48. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 杨德生, 黄冠军, 李勇, 黄见良, 王飞. 水稻氮高效栽培技术、品种改良和生理机制研究进展[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2022, 41(1): 62-75. |
| Yang D S, Huang G J, Li Y, Huang J L, Wang F. Progress on cultivation technologies, variety improvements and physiological mechanisms of rice with high nitrogen utilization efficiency[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022, 41(1): 62-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Ata-Ul-Karim S T, Liu X J, Lu Z Z, Zheng H B, Cao W X, Zhu Y. Estimation of nitrogen fertilizer requirement for rice crop using critical nitrogen dilution curve[J]. Field Crops Research, 2017, 201: 32-40. |
| [9] | Tayefeh M, Sadeghi S M, Ali Noorhosseini S, Bacenetti J, Damalas C A. Environmental impact of rice production based on nitrogen fertilizer use[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2018, 25(16): 15885-15895. |
| [10] | Vejan P, Khadiran T, Abdullah R, Ahmad N. Controlled release fertilizer: A review on developments, applications and potential in agriculture[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2021, 339: 321-334. |
| [11] | Pan F X, Li Y Y, Chapman S J, Khan S, Yao H Y. Microbial utilization of rice straw and its derived biochar in a paddy soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 559: 15-23. |
| [12] | Dinesh K B, Kiranvir B, Amardeep S T, Shivani S. Sensitivity of labile soil organic carbon pools to long-term fertilizer, straw and manure management in rice-wheat system[J]. Pedosphere, 2015, 25(4): 534-545. |
| [13] | Jiang Z W, Yang S H, Chen X, Pang Q Q, Xu Y, Qi S T, Yu W Q, Dai H D. Controlled release urea improves rice production and reduces environmental pollution: A research based on meta-analysis and machine learning[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2022, 29(3): 3587-3599. |
| [14] | Ding W C, Xu X P, He P, Ullah S, Zhang J J, Cui Z L, Zhou W. Improving yield and nitrogen use efficiency through alternative fertilization options for rice in China: A meta-analysis[J]. Field Crops Research, 2018, 227: 11-18. |
| [15] | Ali I, Ullah S, He L, Zhao Q, Iqbal A, Wei S, Shah T, Ali N, Bo Y, Adnan M, Amanullah, Jiang L. Combined application of biochar and nitrogen fertilizer improves rice yield, microbial activity and N-metabolism in a pot experiment[J]. PeerJ, 2020, 8: e10311. |
| [16] | AL Aasmi A, Li J, Hamoud Y A, Lan Y, Alordzinu K E, Appiah S A, Shaghaleh H, Sheteiwy M, Wang H, Qiao S. Impacts of slow-release nitrogen fertilizer rates on the morpho-physiological traits, yield, and nitrogen use efficiency of rice under different water regimes[J]. Agriculture, 2022, 12(1): 86. |
| [17] | Yang L X, Wang Y L, Kobayashi K, Zhu J G, Huang J Y, Yang H J, Wang Y X, Dong G C, Liu G, Han Y, Shan Y, Hu J, Zhou J. Seasonal changes in the effects of free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) on growth, morphology and physiology of rice root at three levels of nitrogen fertilization[J]. Global Change Biology, 2008, 14(8): 1844-1853. |
| [18] | Ramasamy S ten Berge, Hein F M, Purushothaman S. Yield formation in rice in response to drainage and nitrogen application[J]. Field Crops Research, 1997, 51(1/2): 65-82. |
| [19] | Jiang S C, Du B, Wu Q X, Zhang H W, Zhu J Q. Increasing pit-planting density of rice varieties with different panicle types to improves sink characteristics and rice yield under alternate wetting and drying irrigation[J]. Food and Energy Security, 2023, 12(1): e335. |
| [20] | Iqbal A, He L, Ali I, Ullah S, Khan A, Akhtar K, Wei S, Fahad S, Khan R, Jiang L. Co-incorporation of manure and inorganic fertilizer improves leaf physiological traits, rice production and soil functionality in a paddy field[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 10048. |
| [21] | 张思懿, 崔博文, 王佳玲, 蔺吉祥, 杨青杰. 非生物胁迫下植物根系的生理与分子响应研究进展[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(10):2391-2401. |
| Zhang S Y, Cui B W, Wang J L, Lin J X, Yang Q J. Research progress on physiogical and molecular responses of plant roots under abiotic stress[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(10): 2391-2401. (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [22] | Iqbal A, He L, Khan A, Wei S, Akhtar K, Ali I, Ullah S, Munsif F, Zhao Q, Jiang L. Organic manure coupled with inorganic fertilizer: An approach for the sustainable production of rice by improving soil properties and nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Agronomy, 2019, 9(10): 651. |
| [23] | Liu L Y, Li H Y, Zhu S H, Gao Y, Zheng X Q, Xu Y. The response of agronomic characters and rice yield to organic fertilization in subtropical China: A three-level meta-analysis[J]. Field Crops Research, 2021, 263: 108049. |
| [24] | Yuan G Y, Huan W W, Song H, Lu D J, Chen X Q, Wang H Y, Zhou J M. Effects of straw incorporation and potassium fertilizer on crop yields, soil organic carbon, and active carbon in the rice-wheat system[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2021, 209: 104958. |
| [25] | Wang Y D, Hu N, Xu M G, Li Z F, Lou Y L, Chen Y, Wu C Y, Wang Z L. 23-year manure and fertilizer application increases soil organic carbon sequestration of a rice-barley cropping system[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2015, 51(5): 583-591. |
| [26] | Liu B T, Li H L, Li H B, Zhang A P, Rengel Z. Long-term biochar application promotes rice productivity by regulating root dynamic development and reducing nitrogen leaching[J]. GCB Bioenergy, 2021, 13(1): 257-268. |
| [27] | Iqbal A, He L, Ali I, Ullah S, Ahmad K, Aziz K, Akhtar K, Wei S, Zhao Q, Zhang J, Jiang L. Manure combined with chemical fertilizer increases rice productivity by improving soil health, post-anthesis biomass yield, and nitrogen metabolism[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(10): e0238934. |
| [28] | Huang M, Fan L, Jiang L G, Yang S Y, Zou Y B, Uphoff N. Continuous applications of biochar to rice: Effects on grain yield and yield attributes[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2019, 18(3): 563-570. |
| [29] | Xu D, Zhu Y, Zhu H B, Hu Q, Liu G D, Wei H Y, Zhang H C. Effects of a one-time application of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer on yield and nitrogen accumulation and utilization of late japonica rice in China[J]. Agriculture, 2021, 11(11): 1041. |
| [30] | Kishorekumar R, Bulle M, Wany A, Gupta K J. An overview of important enzymes involved in nitrogen assimilation of plants[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2020, 2057: 1-13. |
| [31] | Dong D, Feng Q B, Mcgrouther K, Yang M, Wang H L, Wu W X. Effects of biochar amendment on rice growth and nitrogen retention in a waterlogged paddy field[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2015, 15(1): 153-162. |
| [32] | Wany A, Gupta A K, Kumari A, Mishra S, Singh N, Pandey S, Vanvari R, Igamberdiev A U, Fernie A R, Gupta K J. Nitrate nutrition influences multiple factors in order to increase energy efficiency under hypoxia in Arabidopsis[J]. Annals of Botany, 2019, 123(4): 691-705. |
| [33] | Planchet E, Gupta K J, Sonoda M, Kaiser W M. Nitric oxide emission from tobacco leaves and cell suspensions: Rate limiting factors and evidence for the involvement of mitochondrial electron transport[J]. The Plant Journal, 2005, 41(5): 732-743. |
| [34] | Yi Q Q, Liang B Q, Nan Q, Wang H, Zhang W, Wu W X. Temporal physicochemical changes and transformation of biochar in a rice paddy: Insights from a 9-year field experiment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 721: 137670. |
| [35] | Ke J, Xing X M, Li G H, Ding Y F, Dou F G, Wang S H, Liu Z H, Tang S, Ding C Q, Chen L. Effects of different controlled-release nitrogen fertilisers on ammonia volatilisation, nitrogen use efficiency and yield of blanket-seedling machine-transplanted rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2017, 205: 147-156. |
| [36] | 丁紫娟, 李锦涛, 胡仁, 徐洲, 张丁月, 曹玉贤, 田应兵, 侯俊. 一次性根区施控释尿素对再生稻生长及产量的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022(2): 106-115. |
| Ding Z J, Li J T, Hu R, Xu Z, Zhang D Y, Cao Y X, Tian Y B, Hou J. Effect of one-time root zone application of controlled release urea on the growth and yield of ratoon rice[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2022(2): 106-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | Li S C, Zhang Y L, Guo L H, Li X F. Impact of tillage and straw treatment methods on rice growth and yields in a rice-ratoon rice cropping system[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(15): 9290. |
| [1] | WU Meng, NI Chuan, KANG Yuying, MAO Yuxin, YE Miao, ZHANG Zujian. Inter-varietal Differences in Early Tillering Characteristics and Their Responses to Nitrogen [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(1): 101-114. |
| [2] | Jinwen HUANG, Jiayi WU, Hongfei CHEN, Zhixing ZHANG, Changxun FANG, Caihong SHAO, Weiwei LIN, Peiying WENG, Wenxiong LIN. Nitrogen Fertilizer Management for Main Crop Rice and Its Carrying-over Effect on Rhizosphere Function and Yield of Ratoon Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(4): 383-395. |
| [3] | Menjun DUAN, Yucong TIAN, Yunzi WU, Tao JIN, Fu CHEN, Zhangyong LIU. Effect of Foliar Application of Na2SeO3 on the Yield and Quality of Ratooning Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(1): 96-102. |
| [4] | Yue WU, Jing HU, Chen CHEN, Jiaxing ZHANG, Wanyuan LI, Dongnan TANG, Jun ZHONG, Bin YANG, Zhengkang ZHU, Youli YAO, Yulong WANG, Guichun DONG. Nitrogen Absorption and Utilization Characteristics of the Newly Approved Early-Maturity Late japonica Rice Cultivars in Jiangsu Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(6): 619-630. |
| [5] | Jin-dan WU, Qian CHEN, Xiao-xi LIU, Fu-cheng LIN, Qi-kang GAO, Bing-gan LOU. Preliminary Study on Mechanisms of Growth Promotion in Rice Colonized by Piriformospora indica [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2015, 29(2): 200-207. |
| [6] | FU Jing1,2, WANG Zhiqin1, YUAN Limin1, WANG Xueming1, YANG Jianchang1,*. Effect of Nitrogen Rates on Grain Yield and Some Physiological Traits of Super Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2014, 28(4): 391-400. |
| [7] | ZHEN Xiaohui1,SHEN Weijun 1,ZHANG Xiaojuan1,XU Jingang1,ZHANG Qijun2,LU Chuangen2,CHEN Guoxiang1,3,*, GAO Zhiping1,*. Senescent Characteristics of Flag Leaf Photosynthesis in a White Stripe Rice Mutant 6001 [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2014, 28(1): 49-56. |
| [8] | ZHANG Jian-fu ,ZHU Yong-sheng,CAI Qiu-hua,ZHUO Chuan-ying,ZHANG Shang-shou,ZHENG Rong-he ,XIE Hua-an . Analysis on Correlationship of Net Photosynthetic Rate with Yield and Its Components of Ratooning Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(1): 103-106 . |
| [9] | YE Shi-chao,#,LIN Zhong-cheng,#,DAI Qi-gen,JIA Yu-shu,GU Hai-yan,CHEN Jing-dou,XU Lu-sheng,WU Fu-guan,ZHANG Hong-cheng,HUO Zhong-yang,XU Ke,WEI Hai-yan. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate on Ammonia Volatilization and Nitrogen Utilization in Rice Growing Season [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(1): 71-78 . |
| [10] | YI Zhen-xie,ZHOU Wen-xin,TU Nai-mei*. Effects of Stubble Height of the Main Crop on SourceSink Characteristics and Assimilates Transportation in Ratooning Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2009, 23(5): 509-516 . |
| [11] | XU Fuxian,XIONG Hong,ZHU Yongchuan,ZHANG Lin,GUO Xiaoyi. Estimation of Efficient Rate of Nitrogen Application for Promoting Ratooning Bud Development Using Chlorophyll Meter Reading(SPAD Value) of Flag Leaf at the Full Heading Stage of Main Crop in MidSeason Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2009, 23(1): 51-51~56 . |
| [12] | YANG Fu ,LIANG Zheng-wei ,WANG Zhi-chun ,CHEN Yuan . Relationship Between Diurnal Changes of Net Photosynthetic Rate and Affecting Factors in Flag Leaves of Rice under Saline Sodic Stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2007, 21(4): 386-390 . |
| [13] | XU Hong-xing ,LU Zhong-xian ,JIANG Xue-hui ,YU Xiao-ping ,CHEN Jian-ming ,ZHENG Xu-song. Some Physiological Changes of Rice Plants Damaged by Striped Stem Borer,Chilo suppressalis [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2007, 21(3): 316-318 . |
| [14] | LI Ji-hang ,XIANG Xun-chao ,HE Li-bin ,LI Ping. Source-Sink Characteristics of Intersubspecific F1 in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2006, 20(3): 301-305 . |
| [15] | CHEN Gai-ping ,ZHU Jian-guo ,PANG Jing ,CHENG Lei ,XIE Zu-bin ,ZENG Qing. Effects of Free-Air Carbon Dioxide Enrichment(FACE) on Some Traits and C/N Ratio of Rice Root at the Heading Stage [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2006, 20(1): 53-57 . |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||