
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 264-276.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240408
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHAO Yafang, ZHU Dawei, ZHENG Xin, MOU Renxiang, ZHANG Linping, CHEN Mingxue*( )
)
Received:2024-04-17
Revised:2024-05-08
Online:2025-03-10
Published:2025-03-19
Contact:
CHEN Mingxue
邵雅芳, 朱大伟, 郑欣, 牟仁祥, 章林平, 陈铭学*( )
)
通讯作者:
陈铭学
基金资助:SHAO Yafang, ZHU Dawei, ZHENG Xin, MOU Renxiang, ZHANG Linping, CHEN Mingxue. Development Status and Regional Differences of japonica Rice Quality in the Yangtze River Delta Region from 2002 to 2022[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 264-276.
邵雅芳, 朱大伟, 郑欣, 牟仁祥, 章林平, 陈铭学. 2002−2022长三角地区粳稻品质发展状况和地域差异性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 264-276.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240408
| 省份 参数 Province Parameter | 糙米率 Brown rice rate (%) | 精米率 Polished rice rate (%) | 碱消值 Alkali spreading value(grade) | 胶稠度 Gel consistency (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安徽 Anhui | 平均值±标准差Mean±SD | 83.0±0.5 b | 74.4±0.9 b | 6.8±0.1 a | 72.4±3.7 ab |
| 极值Extrema | 82.2~84.1 | 72.4~76.4 | 6.4~7.0 | 63.4~79.5 | |
| 变异系数Variable coefficient(%) | 0.6 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 5.2 | |
| 江苏 Jiangsu | 平均值±标准差Mean±SD | 83.9±0.6 a | 75.4±1.0 a | 6.8±0.1 a | 73.8±2.9 a |
| 极值Extrema | 82.6~84.8 | 73.3~76.7 | 6.6~6.9 | 68.2~77.6 | |
| 变异系数Variable coefficient(%) | 0.8 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 4.0 | |
| 浙江 Zhejiang | 平均值±标准差Mean±SD | 82.8±0.4 b | 73.7±0.7 c | 6.7±0.1 b | 70.1±2.7 b |
| 极值 Extrema | 82.2~83.7 | 72.4~75.0 | 6.4~7.0 | 65.9~76.5 | |
| 变异系数Variable coefficient(%) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.2 | 3.9 | |
Table 1. Statistics and analysis of brown rice rate, polished rice rate, alkali spreading value and gel consistency of japonica rice in Yangtze River Delta area of China during 2002−2022
| 省份 参数 Province Parameter | 糙米率 Brown rice rate (%) | 精米率 Polished rice rate (%) | 碱消值 Alkali spreading value(grade) | 胶稠度 Gel consistency (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安徽 Anhui | 平均值±标准差Mean±SD | 83.0±0.5 b | 74.4±0.9 b | 6.8±0.1 a | 72.4±3.7 ab |
| 极值Extrema | 82.2~84.1 | 72.4~76.4 | 6.4~7.0 | 63.4~79.5 | |
| 变异系数Variable coefficient(%) | 0.6 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 5.2 | |
| 江苏 Jiangsu | 平均值±标准差Mean±SD | 83.9±0.6 a | 75.4±1.0 a | 6.8±0.1 a | 73.8±2.9 a |
| 极值Extrema | 82.6~84.8 | 73.3~76.7 | 6.6~6.9 | 68.2~77.6 | |
| 变异系数Variable coefficient(%) | 0.8 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 4.0 | |
| 浙江 Zhejiang | 平均值±标准差Mean±SD | 82.8±0.4 b | 73.7±0.7 c | 6.7±0.1 b | 70.1±2.7 b |
| 极值 Extrema | 82.2~83.7 | 72.4~75.0 | 6.4~7.0 | 65.9~76.5 | |
| 变异系数Variable coefficient(%) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.2 | 3.9 | |
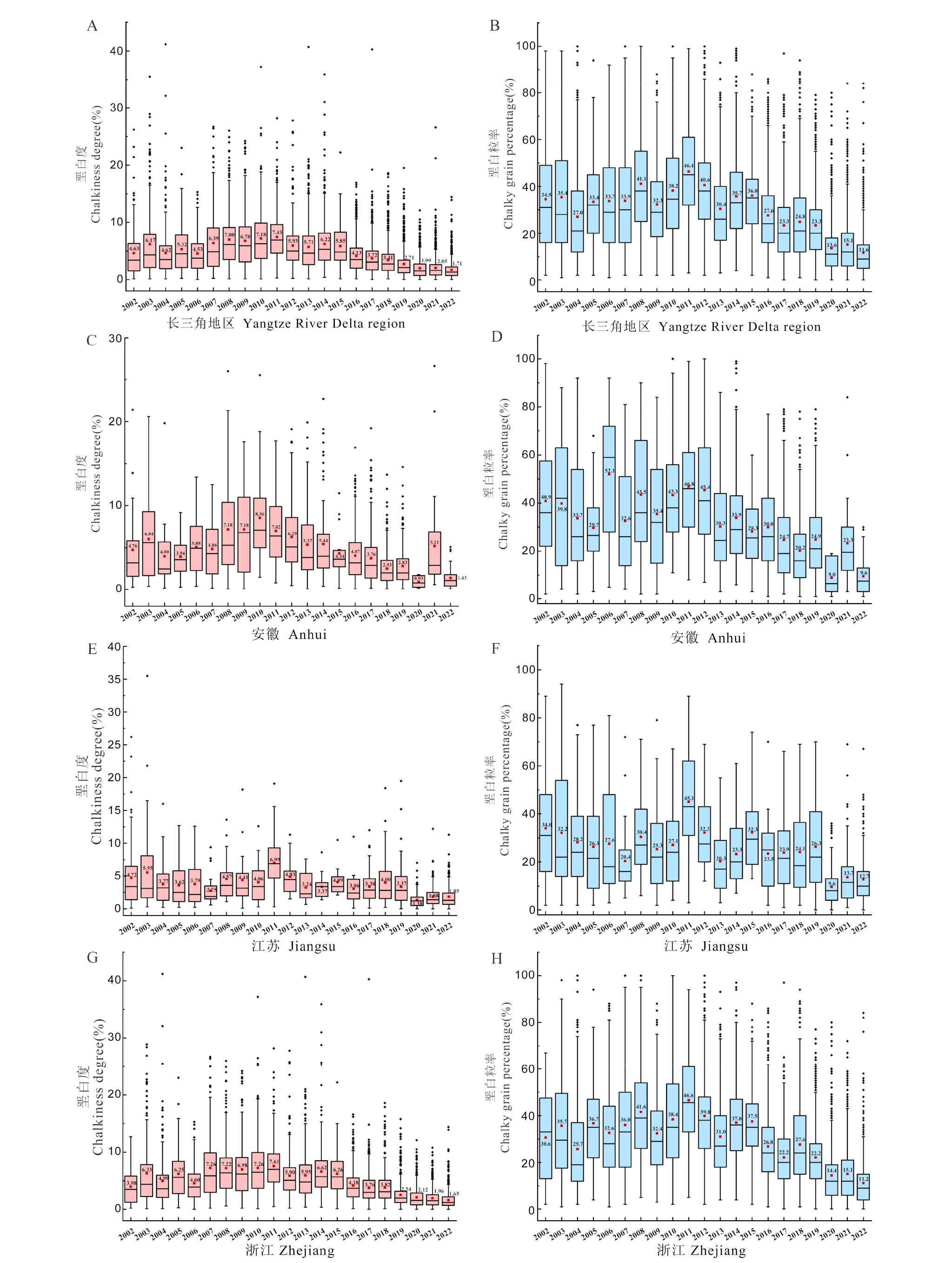
Fig. 2. Statistical analysis of chalkiness degree (A, C, E, G) and chalky grain percentage (B, D, F, H) of japonica rice in the Yangtze River Delta region of China from 2002 to 2022
| [1] | Leng Y J, Gao Y H, Chen L, Yang Y L, Huang L C, Dai L P, Ren D Y, Xu Q K, Zhang Y, Ponce K, Hu J, Shen L, Zhang G H, Chen G, Dong G J, Gao Z Y, Guo L B, Ye G Y, Qian Q, Zhu L, Zeng D L. Using heading date 1 preponderant alleles from indica cultivars to breed high-yield, high-quality japonica rice varieties for cultivation in south China[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18(1): 119-128. |
| [2] | Wu M, Liu H, Lin Y, Chen J, Fu Y, Luo J, Zhang Z, Liang K, Chen S, Wang F. In-frame and frame-shift editing of the Ehd1 gene to develop japonica rice with prolonged basic vegetative growth periods[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 307. |
| [3] | 汤述翥, 张宏根, 梁国华, 严长杰, 刘巧泉, 顾铭洪. 三系杂交粳稻发展缓慢的原因及对策[J]. 杂交水稻, 2008, 23(1): 1-5. |
| Tang S Z, Zhang H G, Liang G H, Yan C J, Liu Q Q, Gu M H. Reasons and countermeasures of slow development on three-line japonica hybrid rice[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2008, 23(1): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 朱智伟, 陈能, 王丹英, 章秀福, 姚青, 闵捷, 廖西元. 不同类型水稻品质性状变异特性及差异性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2004, 18 (4): 315-320. |
| Zhu Z W, Chen N, Wang D Y, Zhang X F, Yao Q, Min J, Liao X Y. Analysis on variation and difference for rice quality traits among different types of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2004, 18(4): 315-320. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 王楼楼. 江苏省籼稻改粳稻的发展研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2013. |
| Wang L L. Study on the development of japonica rice instead of indica rice in Jiangsu Province[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 朱大伟, 曾波, 邵雅芳, 章林平, 陈铭学, 于永红. 近10年我国籼稻品种品质特征分析[J]. 粮油食品科技, 2023, 31(6): 10-19. |
| Zhu D W, Zeng B, Shao Y F, Zhang L P, Chen M X, Yu Y H. Analysis of rice quality characteristics of indica rice varieties of China in recent 10 years[J]. Science and Technology of Cereals, Oils and Foods, 2023, 31(6): 10-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 胡贤巧, 张卫星, 邵雅芳, 于永红, 卢林, 陈铭学. 我国近20年稻米品质优质率状况分析[J]. 中国稻米, 2021, 27(4): 84-87. |
| Hu X Q, Zhang W X, Shao Y F, Yu Y H, Lu L, Chen M X. Analysis of high quality rate of rice in China during recent 20 years[J]. China Rice, 2021, 27(4): 84-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 邵雅芳, 郑欣, 朱大伟, 章林平, 牟仁祥, 郑小龙, 陈铭学. 2002—2022年中国籼稻品质的时空分布和发展状况[J]. 浙江大学学报: 农业与生命科学版, 2024, 50(3): 418-430. |
| Shao Y F, Zheng X, Zhu D W, Zhang L P, Mou R X, Zheng X L, Chen M X. Spatio-temporal distribution and development status of indica rice quality in China from 2002 to 2022[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University: Agriculture & Life Sciences, 2024, 50(3): 418-430. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | CODEX STAN 198-1995. Codex standard for rice[S]. Codex Alimentarius Commission, 1995. |
| [10] | 国家粮食局. 大米粒型分类判定: LS/T 6116-2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. |
| National Food and Strategic Reserves Administration. Classification and Judgment of Rice Grain Shape: LS/T 6116-2017[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | Hu J, Wang Y, Fang Y, Zeng L, Xu J, Yu H, Shi Z, Pan J, Zhang D, Kang S. A rare allele of GS2 enhances grain size and grain yield in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2015, 8(10): 1455-1465. |
| [12] | Song X J, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu M Z, Lin H X. A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase[J]. Nature Genetics, 2007, 39(5): 623-630. |
| [13] | Fan C, Xing Y, Mao H, Lu T, Han B, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q. GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2006, 112(6): 1164-1171. |
| [14] | Wu W, Liu X, Wang M, Meyer R S, Luo X, Ndjiondjop M N, Tan L, Zhang J, Wu J, Cai H, Sun C, Wang X, Wing R A, Zhu Z. A single-nucleotide polymorphism causes smaller grain size and loss of seed shattering during African rice domestication[J]. Nature Plants, 2017, 3(6): 17064. |
| [15] | Li Y, Fan C, Xing Y, Jiang Y, Luo L, Sun L, Shao D, Xu C, Li X, Xiao J, He Y, Zhang Q. Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2011, 43: 1266-1269. |
| [16] | Wang Y, Xiong G, Hu J, Jiang L, Yu H, Xu J, Fang Y, Zeng L, Xu E, Xu J, Ye W, Meng X, Liu R, Chen H, Jing Y, Wang Y, Zhu X, Li J, Qian Q. Copy number variation at the GL7 locus contributes to grain size diversity in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2015, 47(8): 944-948. |
| [17] | Wang S, Wu K, Yuan Q, Liu X, Liu Z, Lin X, Zeng R, Zhu H, Dong G, Qian Q, Zhang G, Fu X. Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2012, 44(8): 950-954. |
| [18] | 黄海祥, 钱前. 水稻粒形遗传与长粒型优质粳稻育种进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(6): 665-672. |
| Huang H X, Qian Q. Progress in genetic research of rice grain shape and breeding achievements of long-grain shape and good quality japonica rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(6): 665-672. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 倪昊东. 水稻品质相关性状分析及QTL定位[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2022. |
| Ni H D. Analysis and QTL mapping of quality related traits in rice[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 程新杰, 施伟, 张梦龙, 岳红亮, 代金英, 胡蕾, 朱国永. 水稻垩白形成机制的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(2): 1-7. |
| Cheng X J, Shi W, Zhang M L, Yue H L, Dai J Y, Hu L, Zhu G Y. Research progress on chalkiness formation mechanism[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2024, 40(2): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | Li Y B, Fan C C, Xing Y Z, Yun P, Luo L J, Yan B, Peng B, Xie W B, Wang G W, Li X H, Xiao J H, Xu C G, He Y Q. Chalk5 encodes a vacuolar H+-translocating pyrophosphatase influencing grain chalkiness in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2014, 46(4): 398-404. |
| [22] | Kang H G, Park S, Matsuoka M, An G. White-core endosperm floury endosperm-4 in rice is generated by knockout mutations in the C4-type pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase gene (OsPPDKB)[J]. The Plant Journal, 2005, 42(6): 901-911. |
| [23] | She K C, Kusano H, Koizumi K, Yamakawa H, Hiroaki S. A novel factor FLOURY ENDOSPERM2 is involved in regulation of rice grain size and starch quality[J]. The Plant Cell, 2010, 22(10): 3280-3294. |
| [24] | 徐富贤, 郑家奎, 朱永川, 王贵雄. 川东南高温伏旱区杂交中稻品种库源结构对稻米整精米率与垩白粒率的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2004(5): 432-437. |
| Xu F X, Zheng J K, Zhu Y C, Wang G X. Effect of ratio source to sink on percentage of head milled rice and chalky rice of combinations of mid-season hybrid rice in the south-east districts of Sichuan under high temperature and summer drought[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2004(5): 432-437. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 习敏, 许有尊, 孙雪原, 吴文革, 周永进. 氮素穗肥对水稻垩白籽粒灌浆影响及与加工品质的关系[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(9): 144-151. |
| Xi M, Xu Y Z, Sun X Y, Wu W G, Zhou Y J. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer topdressing on grain filling and milling quality of the rice with high grain chalkiness[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(9): 144-151. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 陈培峰, 董明辉, 顾俊荣, 惠锋, 乔中英, 杨代凤, 刘腾飞. 麦秸还田与氮肥运筹对超级稻强弱势粒粒重与品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(6): 715-722. |
| Chen P F, Dong M H, Gu J R, Hui F, Qiao Z Y, Yang D F, Liu T F. Effects of returning wheat-residue to field and nitrogen management on grain weight and quality of superior and inferior grains in super rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2012, 26(6): 715-722. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | Chen J L, Tang L, Shi P H, Yang B H, Sun T, Cao W X, Zhu Y. Effects of short-term high temperature on grain quality and starch granules of rice at post-anthesis stage[J]. Protoplasma, 2017, 254(2): 935-943. |
| [28] | Xie Q, Xu J K, Huang K, Su Y, Tong J H, Huang Z G, Huang C, Wei M L, Lin W H, Xiao L T. Dynamic formation and transcriptional regulation mediated by phytohormones during chalkiness formation in rice[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2021, 21(1): 308. |
| [29] | 冯向前, 殷敏, 王孟佳, 马横宇, 褚光, 刘元辉, 徐春梅, 章秀福, 张运波, 王丹英, 陈松. 南方稻区“早籼晚粳”栽培模式晚季灌浆期气象因子对晚粳稻品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2023, 56(1): 46-63. |
| Feng X Q, Yin M, Wang M J, Ma H Y, Chu G, Liu Y H, Xu C M, Zhang X F, Zhang Y B, Wang D Y, Chen S. Effects of meteorological factors on quality of late japonica rice during late season grain filling stage under ‘early indica and late japonica’ cultivation pattern in southern China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2023, 56(1): 46-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 史玉良, 杨勇, 李雪飞, 李钱峰, 黄李春, 张昌泉, 宋学堂, 刘巧泉. 不同直链淀粉含量软米品种品质性状的比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 601-610. |
| Shi Y L, Yang Y, Li X F, Li Q F, Huang L C, Zhang C Q, Song X T, Liu Q Q. Comparison of grain quality profiles of japonica soft rice varieties with different amylose content[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2022, 36(6): 601-610. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 朱霁晖, 张昌泉, 顾铭洪, 刘巧泉. 水稻Wx基因的等位变异及育种利用研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(4): 431-438. |
| Zhu J H, Zhang C Q, Gu M H, Liu Q Q. Progress in the allelic variation of Wx gene and its application in rice breeding[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2015, 29(4): 431-438. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | Chen Z, Lu Y, Feng L, Hao W, Li C, Yang Y, Fan X, Li Q, Zhang C, Liu Q. Genetic dissection and functional differentiation of ALKa and ALKb, two natural alleles of the ALK/SSIIa gene, responding to low gelatinization temperature in rice[J]. Rice, 2020, 13: 39. |
| [33] | 王才林, 张亚东, 朱镇, 赵春芳, 魏晓东, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 赵凌, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 路凯, 梁文化. 优良食味半糯粳稻品质标准的研制与应用[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2022, 38(1): 1-8. |
| Wang C L, Zhang Y D, Zhu Z, Zhao C F, Wei X D, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Zhao L, Yao S, Zhou L H, Lu K, Liang W H. Development and application of quality standard for semi-glutinous japonica rice with good taste[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 38(1): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 朱大伟, 章林平, 陈铭学, 方长云, 于永红, 郑小龙, 邵雅芳. 中国优质稻品种品质及食味感官评分值的特征[J]. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(7): 1271-1283. |
| Zhu D W, Zhang L P, Chen M X, Fang C Y, Yu Y H, Zheng X L, Shao Y F. Characteristics of high-quality rice varieties and taste sensory evaluation values in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(7): 1271-1283. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | Liu Z J, Li P H, Yu L, Hu Y Z, Du A P, Fu X Y, Wu C L, Luo D G, Hu B H, Dong H, Jiang H B, Ma X R, Huang W Z, Tu S B, Li H. OsMADS1 regulates grain quality, gene expressions, and regulatory networks of starch and storage protein metabolisms in rice[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(9): 8017. |
| [36] | Wang X, Wang K, Yin T, Zhao Y, Liu W, Shen Y, Ding Y, Tang S. Nitrogen fertilizer regulated grain storage protein synthesis and reduced chalkiness of rice under actual field warming[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 715436. |
| [37] | Xi M, Wu W G, Xu Y Z, Zhou Y J, Chen G, Ji Y L, Sun X Y. Grain chalkiness traits is affected by the synthesis and dynamic accumulation of the storage protein in rice[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2021, 101(14): 6125-6133. |
| [38] | Shi S, Pan K, Zhang G, Zhao D, Zhou H, Liu J, Cao C, Jiang Y. Differences in grain protein content and regional distribution of 706 rice accessions[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2023, 103: 1593-1599. |
| [1] | YANG Chuanming, WANG Lizhi, ZHANG Xijuan, YANG Xianli, WANG Yangyang, HOU Benfu, CUI Shize, LI Qingchao, LIU Kai, MA Rui, FENG Yanjiang, LAI Yongcai, LI Hongyu, JIANG Shukun. Analysis of QTL Controlling Cold Tolerance at Seedling Stage by Using a High-Density SNP Linkage Map in japonica Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(1): 82-91. |
| [2] | WANG Xiaoxi, CAI Chuang, SONG Lian, ZHOU Wei, YANG Xiong, GU Xinyue, ZHU Chunwu. Effect of Free-air CO2 Enrichment and Temperature Increase on Grain Quality of Rice Cultivar Yangdao 6 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(1): 115-127. |
| [3] | DU Yanxiu, SUN Wenyu, YUAN Zeke, ZHANG Qianqian, LI Fuhao, LI Junzhou, SUN Hongzheng. Mapping of qChalk8 Controlling Chalky Rice Rate in japonica Rice by Combining QTL-Seq with Molecular Markers [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(6): 665-671. |
| [4] | LIU Junfeng, MOU Jingyi, ZHAO Hongyan, GUO Shimeng, LI Yimeng, LIANG Chao, ZHOU Chanchan, WANG Shu, HUANG Yuancai. Effects of Nitrogen Application Practice and Row Spacing on Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in japonica Rice With Different Panicle Types [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(6): 672-684. |
| [5] | YAO Shu, CHEN Tao, ZHAO Chunfang, ZHOU Lihui, ZHAO Ling, LIANG Wenhua, HAO Lei, LU Kai, ZHU Zhen, ZHAO Qingyong, GUAN Ju, WANG Cailin, ZHANG Yadong. Analysis on Appearance and Cooking Taste Quality Characteristics of Different Types of japonica Rice in Jianghuai Rice-growing Area [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(6): 709-718. |
| [6] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [7] | JING Xiu, ZHOU Miao, WANG Jing, WANG Yan, WANG Wang, WANG Kai, GUO Baowei, HU Yajie, XING Zhipeng, XU Ke, ZHANG Hongcheng. Effect of Drought Stress on Root Morphology and Leaf Photosynthetic Characteristics of Good Taste japonica Rice from Late Stage of Panicle Differentiation to Early Stage of Grain Filling [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(1): 33-47. |
| [8] | HUANG Yaru, XU Peng, WANG Lele, HE Yizhe, WANG Hui, KE Jian, HE Haibing, WU Liquan, YOU Cuicui. Effects of Exogenous Trehalose on Grain Filling Characteristics and Yield Formation of japonica Rice Cultivar W1844 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| [9] | MA Zhaohui, SHI Yihan, CHENG Haitao, SONG Wenwen, LU Lianji, LIU Renguang, LÜ Wenyan. Effects of Embryo Morphology and Endosperm Composition on Embryo-remaining Characteristics in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(3): 265-275. |
| [10] | WANG Yu, SUN Quanyi, DU Haibo, XU Zhiwen, WU Keting, YIN Li, FENG Zhiming, HU Keming, CHEN Zongxiang, ZUO Shimin. Improvement of the Resistance of Nanjing 9108 to Blast and Sheath Blight by Pyramiding Resistance Gene Pigm and Quantitative Trait Genes qSB-9TQ and qSB-11HJX [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(2): 125-132. |
| [11] | PEI Feng, WANG Guangda, GAO Peng, FENG Zhiming, HU Keming, CHEN Zongxiang, CHEN Hongqi, CUI Ao, ZUO Shimin. Evaluation of New japonica Rice Lines with Low Cadmium Accumulation and Good Quality Generated by Knocking Out OsNramp5 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 16-28. |
| [12] | WANG Shiguang, LU Zhanhua, LIU Wei, LU Dongbai, WANG Xiaofei, FANG Zhiqiang, WU Haoxiang, HE Xiuying. Generating Guangdong Simiao Rice Germplasms by Applying CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing and Marker-assisted Selection Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 29-36. |
| [13] | CHEN Tao, ZHAO Qingyong, ZHU Zhen, ZHAO Ling, YAO Shu, ZHOU Lihui, ZHAO Chunfang, ZHANG Yadong, WANG Cailin. Development of New Low Glutelin Content japonica Rice Lines with Good Eating Quality and Fragrance by Molecular Marker-Assisted Selection [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 55-65. |
| [14] | ZHANG Xiaoxiang, SHAO Shimei, ZHAO Buhong, ZHANG Hao, JI Hongjuan, XIAO Ning, PAN Cunhong, LI Yuhong, WU Yunyu, CAI Yue, LIU Jianju, JI Chunming, ZHANG Xiuqin, LIU Guangqing, ZHOU Changhai, HUANG Niansheng, LI Aihong. Effects of Nitrogen Reduction Model on Yield and Nitrogen Absorption and Utilization of Late-maturing Mid-japonica Rice with Different Panicle Types [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 278-294. |
| [15] | HUANG Tao, WANG Yanning, ZHONG Qi, CHENG Qin, YANG Mengmeng, WANG Peng, WU Guangliang, HUANG Shiying, LI Caijing, YU Jianfeng, HE Haohua, BIAN Jianmin. Mapping and Analysis of QTLs for Rice Grain Weight and Grain Shape Using Chromosome Segment Substitution Line Population [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(2): 159-170. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||