
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (3): 257-268.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.8102
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yaozhu YIN, Changchun GUO, Yongjian SUN*( ), Yunxia WU, Huaqing YU, Zhibai SUN, Qiao ZHANG, Haiyue WANG, Zhiyuan YANG, Jun MA
), Yunxia WU, Huaqing YU, Zhibai SUN, Qiao ZHANG, Haiyue WANG, Zhiyuan YANG, Jun MA
Received:2018-09-13
Revised:2019-02-26
Online:2019-05-10
Published:2019-05-10
Contact:
Yongjian SUN
殷尧翥, 郭长春, 孙永健*( ), 武云霞, 余华清, 孙知白, 张桥, 王海月, 杨志远, 马均
), 武云霞, 余华清, 孙知白, 张桥, 王海月, 杨志远, 马均
通讯作者:
孙永健
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yaozhu YIN, Changchun GUO, Yongjian SUN, Yunxia WU, Huaqing YU, Zhibai SUN, Qiao ZHANG, Haiyue WANG, Zhiyuan YANG, Jun MA. Effects of Rape Straw Retention and Water and Nitrogen Management on Population Quality and Yield of Hybrid Rice Under Rice-rape Rotation[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(3): 257-268.
殷尧翥, 郭长春, 孙永健, 武云霞, 余华清, 孙知白, 张桥, 王海月, 杨志远, 马均. 稻油轮作下油菜秸秆还田与水氮管理对杂交稻群体质量和产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(3): 257-268.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.8102
| 年份 Year | 全氮 Total N/(g·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter/(g·kg-1) | 速效养分 Available nutrient/(mg·kg-1) | pH | 秸秆量 Rape straw amount/(t·hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | |||||
| 2017 | 1.17 | 19.3 | 91.3 | 31.3 | 86.3 | 6.4 | 10.34 |
| 2018 | 1.81 | 24.8 | 112.5 | 22.8 | 107.1 | 5.9 | 11.18 |
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of soil (0-20 cm) in the experiments.
| 年份 Year | 全氮 Total N/(g·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter/(g·kg-1) | 速效养分 Available nutrient/(mg·kg-1) | pH | 秸秆量 Rape straw amount/(t·hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | |||||
| 2017 | 1.17 | 19.3 | 91.3 | 31.3 | 86.3 | 6.4 | 10.34 |
| 2018 | 1.81 | 24.8 | 112.5 | 22.8 | 107.1 | 5.9 | 11.18 |
| 处理 Treatment | 籽粒产量 Grain yield | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number | 每穗粒数 Number of grains per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate | 千粒重 1000-grain weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 秸秆还田 Straw returning (A) | 153.42** | 379.85** | 49.41* | 28.89* | 35.12* |
| 灌水方式 Irrigation method (W) | 66.16** | 52.91** | 30.51** | 34.13** | 0.95 |
| 施氮量 N rate(N) | 520.95** | 227.84** | 2153.67** | 43.10** | 25.02** |
| A×W | 0.34 | 3.55 | 20.21* | 1.12 | 1.77 |
| A×N | 19.38** | 13.90** | 176.09** | 2.46 | 9.29** |
| W×N | 6.70* | 0.57 | 17.81** | 2.47 | 3.29* |
| A×W×N | 9.70* | 1.94 | 15.90** | 1.42 | 7.17** |
Table 2 Analysis of variance for yield index of rice between straw returning and water and N management patterns (F values).
| 处理 Treatment | 籽粒产量 Grain yield | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number | 每穗粒数 Number of grains per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate | 千粒重 1000-grain weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 秸秆还田 Straw returning (A) | 153.42** | 379.85** | 49.41* | 28.89* | 35.12* |
| 灌水方式 Irrigation method (W) | 66.16** | 52.91** | 30.51** | 34.13** | 0.95 |
| 施氮量 N rate(N) | 520.95** | 227.84** | 2153.67** | 43.10** | 25.02** |
| A×W | 0.34 | 3.55 | 20.21* | 1.12 | 1.77 |
| A×N | 19.38** | 13.90** | 176.09** | 2.46 | 9.29** |
| W×N | 6.70* | 0.57 | 17.81** | 2.47 | 3.29* |
| A×W×N | 9.70* | 1.94 | 15.90** | 1.42 | 7.17** |
| 处理 Treatment | 结实期干物 质积累量 Dry matter accumulation during filling stage | 结实期 群体生长率 Population growth rate during filling stage | 成熟期 单茎干物质量 Total weight per stem at maturity | 拔节期 总叶面积 Total LAI during jointing | 齐穗期 总叶面积 Total LAI at full heading | 齐穗期 高效叶面积 Efficient LAI at full heading | 拔节至齐穗 叶面积衰减率 Decreasing rate of leaf area at jointing-full heading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 秸秆还田Straw returning (A) | 611.60** | 608.96** | 627.66** | 42.58* | 35.48* | 96.09* | 28.16* |
| 灌水方式Irrigation method (W) | 9.56* | 9.65* | 118.58** | 0.58 | 0.04 | 46.83** | 8.56* |
| 施氮量 N rate(N) | 305.48** | 305.41** | 480.07** | 255.04** | 346.73** | 868.59** | 1185.76** |
| A×W | 0.67 | 0.68 | 7.03* | 8.73* | 0.78 | 0.17 | 5.30 |
| A×N | 11.31** | 11.32** | 0.99 | 9.31** | 4.60* | 3.94* | 4.29* |
| W×N | 7.43* | 7.39** | 1.07 | 0.43 | 0.67 | 2.47 | 7.58** |
| A×W×N | 2.73 | 2.75* | 0.80 | 0.66 | 0.17 | 1.84 | 3.95* |
Table 3 Analysis of variance for population quality index of rice between straw returning and water and N management patterns (F values).
| 处理 Treatment | 结实期干物 质积累量 Dry matter accumulation during filling stage | 结实期 群体生长率 Population growth rate during filling stage | 成熟期 单茎干物质量 Total weight per stem at maturity | 拔节期 总叶面积 Total LAI during jointing | 齐穗期 总叶面积 Total LAI at full heading | 齐穗期 高效叶面积 Efficient LAI at full heading | 拔节至齐穗 叶面积衰减率 Decreasing rate of leaf area at jointing-full heading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 秸秆还田Straw returning (A) | 611.60** | 608.96** | 627.66** | 42.58* | 35.48* | 96.09* | 28.16* |
| 灌水方式Irrigation method (W) | 9.56* | 9.65* | 118.58** | 0.58 | 0.04 | 46.83** | 8.56* |
| 施氮量 N rate(N) | 305.48** | 305.41** | 480.07** | 255.04** | 346.73** | 868.59** | 1185.76** |
| A×W | 0.67 | 0.68 | 7.03* | 8.73* | 0.78 | 0.17 | 5.30 |
| A×N | 11.31** | 11.32** | 0.99 | 9.31** | 4.60* | 3.94* | 4.29* |
| W×N | 7.43* | 7.39** | 1.07 | 0.43 | 0.67 | 2.47 | 7.58** |
| A×W×N | 2.73 | 2.75* | 0.80 | 0.66 | 0.17 | 1.84 | 3.95* |
| 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicles (×104/hm2) | 每穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 实际产量 Grain yield /(kg·hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | W1 | N0 | 144.30 d | 149.20 d | 92.00 a | 37.37 a | 7057.2 d |
| N1 | 162.53 c | 180.34 c | 91.52 a | 35.55 b | 8472.1 c | ||
| N2 | 177.06 a | 195.27 a | 90.81 a | 37.71 a | 9855.9 a | ||
| N3 | 166.18 b | 186.07 b | 86.78 b | 37.63 a | 9312.1 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 162.52 | 177.72 | 90.28 | 37.07 | 8674.3 | ||
| W2 | N0 | 148.37 d | 157.38 d | 93.68 a | 36.93 bd | 7275.9 d | |
| N1 | 163.91 c | 183.48 c | 92.35 a | 37.53 ab | 8603.4 c | ||
| N2 | 181.60 a | 200.45 a | 93.53 a | 37.52 abc | 10328.1 a | ||
| N3 | 170.71 b | 189.05 b | 88.33 b | 37.86 a | 9444.1 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 166.15 | 182.59 | 91.97 | 37.46 | 8912.9 | ||
| A2 | W1 | N0 | 137.48 c | 154.16 d | 90.17 a | 36.29 c | 6697.5 c |
| N1 | 142.38 b | 167.84 c | 89.63 a | 37.07 a | 7797.7 b | ||
| N2 | 155.18 a | 207.93 a | 89.22 a | 36.54 bc | 8680.3 a | ||
| N3 | 151.30 a | 179.29 b | 85.64 b | 36.61 b | 8542.4 a | ||
| 平均 Average | 146.58 | 177.31 | 88.67 | 36.63 | 7929.48 | ||
| W2 | N0 | 140.99 c | 159.29 d | 92.24 a | 36.13 c | 6937.8 c | |
| N1 | 151.77 b | 168.92 c | 88.75 c | 36.87 b | 8059.3 b | ||
| N2 | 163.09 a | 199.24 a | 90.09 b | 37.25 a | 8855.3 a | ||
| N3 | 155.18 b | 183.77 b | 88.29 c | 36.02 c | 8692.8 a | ||
| 平均 Average | 152.76 | 177.81 | 89.84 | 36.57 | 8136.3 | ||
Table 4 Effects of water and N management on yield and its components in hybrid rice under direct straw returning(2017).
| 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicles (×104/hm2) | 每穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 实际产量 Grain yield /(kg·hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | W1 | N0 | 144.30 d | 149.20 d | 92.00 a | 37.37 a | 7057.2 d |
| N1 | 162.53 c | 180.34 c | 91.52 a | 35.55 b | 8472.1 c | ||
| N2 | 177.06 a | 195.27 a | 90.81 a | 37.71 a | 9855.9 a | ||
| N3 | 166.18 b | 186.07 b | 86.78 b | 37.63 a | 9312.1 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 162.52 | 177.72 | 90.28 | 37.07 | 8674.3 | ||
| W2 | N0 | 148.37 d | 157.38 d | 93.68 a | 36.93 bd | 7275.9 d | |
| N1 | 163.91 c | 183.48 c | 92.35 a | 37.53 ab | 8603.4 c | ||
| N2 | 181.60 a | 200.45 a | 93.53 a | 37.52 abc | 10328.1 a | ||
| N3 | 170.71 b | 189.05 b | 88.33 b | 37.86 a | 9444.1 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 166.15 | 182.59 | 91.97 | 37.46 | 8912.9 | ||
| A2 | W1 | N0 | 137.48 c | 154.16 d | 90.17 a | 36.29 c | 6697.5 c |
| N1 | 142.38 b | 167.84 c | 89.63 a | 37.07 a | 7797.7 b | ||
| N2 | 155.18 a | 207.93 a | 89.22 a | 36.54 bc | 8680.3 a | ||
| N3 | 151.30 a | 179.29 b | 85.64 b | 36.61 b | 8542.4 a | ||
| 平均 Average | 146.58 | 177.31 | 88.67 | 36.63 | 7929.48 | ||
| W2 | N0 | 140.99 c | 159.29 d | 92.24 a | 36.13 c | 6937.8 c | |
| N1 | 151.77 b | 168.92 c | 88.75 c | 36.87 b | 8059.3 b | ||
| N2 | 163.09 a | 199.24 a | 90.09 b | 37.25 a | 8855.3 a | ||
| N3 | 155.18 b | 183.77 b | 88.29 c | 36.02 c | 8692.8 a | ||
| 平均 Average | 152.76 | 177.81 | 89.84 | 36.57 | 8136.3 | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 有效穗 Effective panicles (×104/hm2) | 每穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 实际产量 Grain yield /(kg·hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | W1 | N0 | 163.90 c | 153.61 d | 93.02 b | 36.36 b | 8473.9 d |
| N1 | 177.78 b | 163.27 c | 94.85 a | 36.42 b | 9501.4 c | ||
| N2 | 212.11 a | 178.36 a | 88.60 c | 37.08 a | 11876.3 a | ||
| N3 | 206.34 a | 170.72 b | 86.32 d | 36.51 b | 10547.1 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 190.03 | 166.49 | 90.70 | 36.59 | 10099.7 | ||
| W2 | N0 | 167.67 d | 156.82 d | 93.73 a | 36.10 b | 8819.4 d | |
| N1 | 180.21 c | 165.80 c | 95.97 a | 37.12 a | 10142.2 c | ||
| N2 | 220.88 a | 180.82 a | 89.78 b | 36.06 b | 12464.1 a | ||
| N3 | 209.42 b | 175.65 b | 86.70 c | 36.42 b | 11026.9 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 194.54 | 169.77 | 91.55 | 36.42 | 10613.1 | ||
| A2 | W1 | N0 | 159.76 c | 148.48 c | 92.20 b | 37.39 a | 7783.1 d |
| N1 | 167.49 b | 157.32 b | 94.35 a | 36.44 ab | 8581.6 c | ||
| N2 | 198.66 a | 164.80 a | 89.13 c | 36.41 ab | 10063.7 a | ||
| N3 | 192.91 a | 162.24 a | 86.04 d | 36.28 b | 9534.4 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 179.71 | 158.21 | 90.43 | 36.63 | 8990.7 | ||
| W2 | N0 | 161.19 d | 151.76 d | 93.51 a | 37.29 a | 8038.6 d | |
| N1 | 171.19 c | 159.11 c | 95.28 a | 36.48 ab | 8868.4 c | ||
| N2 | 204.56 a | 169.32 a | 89.24 b | 36.19 b | 10380.5 a | ||
| N3 | 196.12 b | 165.08 b | 85.68 c | 36.36 ab | 9782.0 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 183.27 | 161.32 | 90.93 | 36.58 | 9267.4 | ||
Table 5 Effects of water and N management on yield and its components in hybrid rice under direct straw returning(2018).
| 处理 Treatment | 有效穗 Effective panicles (×104/hm2) | 每穗粒数 Grain number per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate /% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 实际产量 Grain yield /(kg·hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | W1 | N0 | 163.90 c | 153.61 d | 93.02 b | 36.36 b | 8473.9 d |
| N1 | 177.78 b | 163.27 c | 94.85 a | 36.42 b | 9501.4 c | ||
| N2 | 212.11 a | 178.36 a | 88.60 c | 37.08 a | 11876.3 a | ||
| N3 | 206.34 a | 170.72 b | 86.32 d | 36.51 b | 10547.1 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 190.03 | 166.49 | 90.70 | 36.59 | 10099.7 | ||
| W2 | N0 | 167.67 d | 156.82 d | 93.73 a | 36.10 b | 8819.4 d | |
| N1 | 180.21 c | 165.80 c | 95.97 a | 37.12 a | 10142.2 c | ||
| N2 | 220.88 a | 180.82 a | 89.78 b | 36.06 b | 12464.1 a | ||
| N3 | 209.42 b | 175.65 b | 86.70 c | 36.42 b | 11026.9 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 194.54 | 169.77 | 91.55 | 36.42 | 10613.1 | ||
| A2 | W1 | N0 | 159.76 c | 148.48 c | 92.20 b | 37.39 a | 7783.1 d |
| N1 | 167.49 b | 157.32 b | 94.35 a | 36.44 ab | 8581.6 c | ||
| N2 | 198.66 a | 164.80 a | 89.13 c | 36.41 ab | 10063.7 a | ||
| N3 | 192.91 a | 162.24 a | 86.04 d | 36.28 b | 9534.4 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 179.71 | 158.21 | 90.43 | 36.63 | 8990.7 | ||
| W2 | N0 | 161.19 d | 151.76 d | 93.51 a | 37.29 a | 8038.6 d | |
| N1 | 171.19 c | 159.11 c | 95.28 a | 36.48 ab | 8868.4 c | ||
| N2 | 204.56 a | 169.32 a | 89.24 b | 36.19 b | 10380.5 a | ||
| N3 | 196.12 b | 165.08 b | 85.68 c | 36.36 ab | 9782.0 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 183.27 | 161.32 | 90.93 | 36.58 | 9267.4 | ||
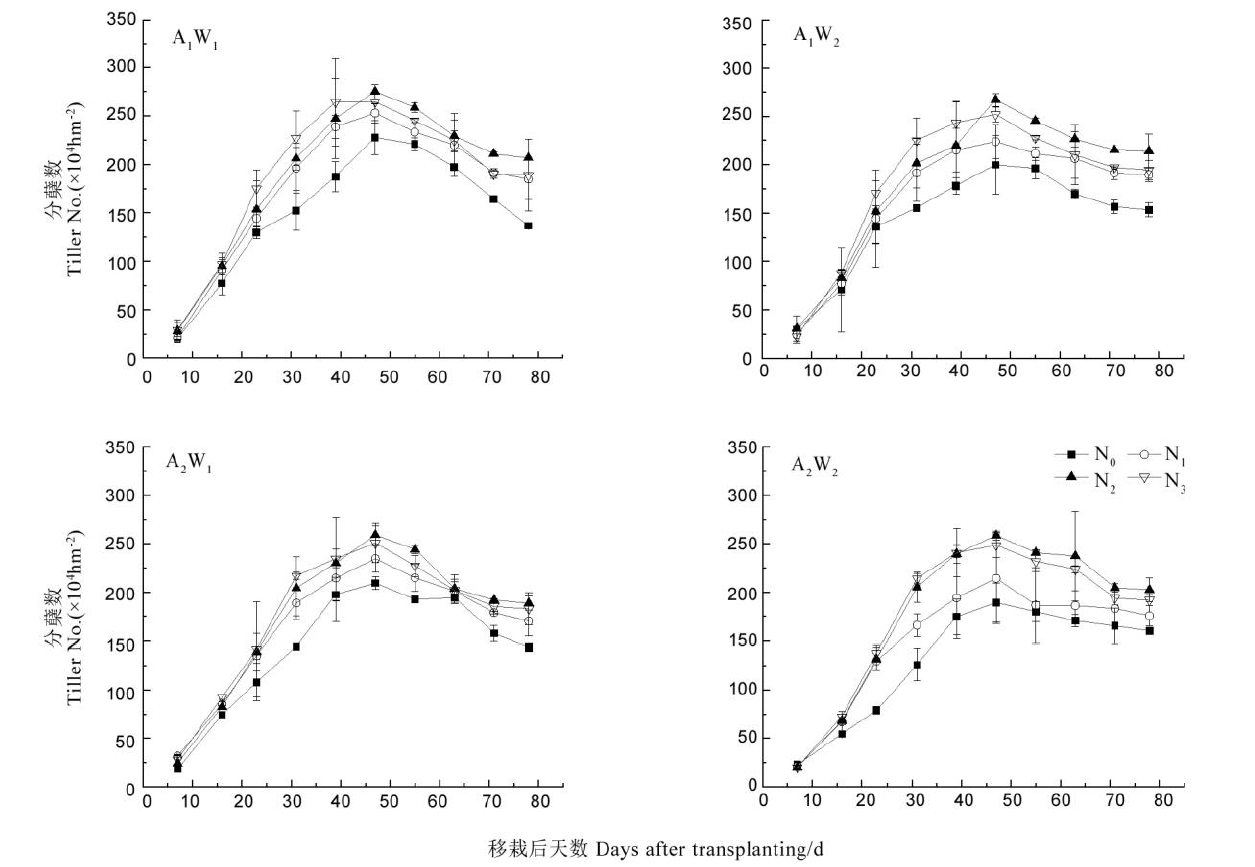
Fig. 1. Effects of water and N management on dynamic changes of stem and tiller in hybrid rice under different straw returning modes(2017). A1, Straw composting; A2, Direct straw returning; W1, Submerged irrigation; W2, Alternate irrigation.
| 处理 Treatment | 单茎叶片干质量 Dry weight of leaves per stem/g | 单茎茎鞘干质量 Dry weight of Culm and sheath per stem/g | 单茎干物质量 Dry matter weight per stem/g | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖盛期 Tillering | 拔节期 Jointing | 齐穗期 Full heading | 成熟期 Maturity | 分蘖盛期Tillering | 拔节期Jointing | 齐穗期 Full heading | 成熟期Maturity | 分蘖盛期Tillering | 拔节期Jointing | 齐穗期 Full heading | 成熟期Maturity | |||||
| A1 | W1 | N0 | 0.12 c | 0.40 c | 1.17 d | 0.87 d | 0.14 d | 0.53 c | 3.19 b | 2.07 d | 0.26 d | 0.93 c | 5.10 d | 8.11 d | ||
| N1 | 0.14 b | 0.49 b | 1.22 c | 1.06 c | 0.16 c | 0.58 b | 3.31 a | 2.26 c | 0.30 c | 1.07 b | 5.33 c | 9.14 c | ||||
| N2 | 0.19 a | 0.55 a | 1.39 a | 1.23 a | 0.22 a | 0.64 a | 3.35 a | 2.41 a | 0.40 a | 1.19 a | 5.59 a | 10.15 a | ||||
| N3 | 0.18 a | 0.49 b | 1.33 b | 1.11 b | 0.20 b | 0.59 b | 3.34 a | 2.35 b | 0.38 b | 1.07 b | 5.51 b | 9.82 b | ||||
| 平均 Average | 0.16 | 0.48 | 1.28 | 1.07 | 0.18 | 0.59 | 3.3 | 2.27 | 0.34 | 1.07 | 5.38 | 9.31 | ||||
| W2 | N0 | 0.14 c | 0.43 d | 1.13 c | 0.91 d | 0.17 c | 0.55 d | 3.15 c | 2.10 d | 0.31 c | 0.98 d | 5.02 c | 8.32 d | |||
| N1 | 0.16 b | 0.45 c | 1.26 b | 1.07 c | 0.19 b | 0.57 c | 3.31 b | 2.30 c | 0.35 b | 1.02 c | 5.38 b | 9.39 c | ||||
| N2 | 0.18 a | 0.57 a | 1.39 a | 1.24 a | 0.21 a | 0.67 a | 3.43 a | 2.45 a | 0.39 a | 1.24 a | 5.68 a | 10.35 a | ||||
| N3 | 0.17 ab | 0.51 b | 1.38 a | 1.13 b | 0.19 b | 0.62 b | 3.40 a | 2.35 b | 0.36 b | 1.13 b | 5.63 a | 9.95 b | ||||
| 平均 Average | 0.16 | 0.49 | 1.29 | 1.09 | 0.19 | 0.61 | 3.32 | 2.3 | 0.35 | 1.09 | 5.43 | 9.5 | ||||
| A2 | W1 | N0 | 0.12 d | 0.39 d | 1.12 d | 0.81 c | 0.13 d | 0.52 c | 3.15 c | 2.02 d | 0.25 d | 0.91 d | 4.99 c | 7.83 d | ||
| N1 | 0.13 c | 0.42 c | 1.18 c | 1.04 b | 0.14 c | 0.56 bc | 3.24 b | 2.20 c | 0.27 c | 0.99 c | 5.20 b | 8.85 c | ||||
| N2 | 0.16 a | 0.52 a | 1.36 a | 1.17 a | 0.19 a | 0.63 a | 3.31 a | 2.35 a | 0.36 a | 1.16 a | 5.51 a | 9.78 a | ||||
| N3 | 0.14 b | 0.48 b | 1.32 b | 1.04 b | 0.17 b | 0.58 ab | 3.29 a | 2.30 b | 0.31 b | 1.06 b | 5.45 a | 9.43 b | ||||
| 平均 Average | 0.14 | 0.45 | 1.25 | 1.02 | 0.16 | 0.57 | 3.25 | 2.22 | 0.29 | 1.03 | 5.29 | 8.97 | ||||
| W2 | N0 | 0.10 c | 0.40 d | 1.12 c | 0.84 c | 0.12 c | 0.53 c | 3.12 c | 2.05 d | 0.23 c | 0.94 d | 4.97 c | 8.01 c | |||
| N1 | 0.14 b | 0.45 c | 1.26 b | 1.13 b | 0.15 b | 0.59 b | 3.29 b | 2.23 c | 0.29 b | 1.04 c | 5.33 b | 9.35 b | ||||
| N2 | 0.16 a | 0.55 a | 1.37 a | 1.21 a | 0.17 a | 0.65 a | 3.36 a | 2.33 a | 0.33 a | 1.20 a | 5.59 a | 10.01 a | ||||
| N3 | 0.15 a | 0.49 b | 1.34 a | 1.14 b | 0.17 a | 0.61 ab | 3.32 a | 2.29 b | 0.32 a | 1.10 b | 5.51 a | 9.80 a | ||||
| 平均Average | 0.14 | 0.47 | 1.27 | 1.08 | 0.15 | 0.59 | 3.27 | 2.22 | 0.3 | 1.07 | 5.35 | 9.29 | ||||
Table 6 Effects of water and N management on leaves, culm and sheath per shoot and dry matter weight of stem under straw returning(2017).
| 处理 Treatment | 单茎叶片干质量 Dry weight of leaves per stem/g | 单茎茎鞘干质量 Dry weight of Culm and sheath per stem/g | 单茎干物质量 Dry matter weight per stem/g | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖盛期 Tillering | 拔节期 Jointing | 齐穗期 Full heading | 成熟期 Maturity | 分蘖盛期Tillering | 拔节期Jointing | 齐穗期 Full heading | 成熟期Maturity | 分蘖盛期Tillering | 拔节期Jointing | 齐穗期 Full heading | 成熟期Maturity | |||||
| A1 | W1 | N0 | 0.12 c | 0.40 c | 1.17 d | 0.87 d | 0.14 d | 0.53 c | 3.19 b | 2.07 d | 0.26 d | 0.93 c | 5.10 d | 8.11 d | ||
| N1 | 0.14 b | 0.49 b | 1.22 c | 1.06 c | 0.16 c | 0.58 b | 3.31 a | 2.26 c | 0.30 c | 1.07 b | 5.33 c | 9.14 c | ||||
| N2 | 0.19 a | 0.55 a | 1.39 a | 1.23 a | 0.22 a | 0.64 a | 3.35 a | 2.41 a | 0.40 a | 1.19 a | 5.59 a | 10.15 a | ||||
| N3 | 0.18 a | 0.49 b | 1.33 b | 1.11 b | 0.20 b | 0.59 b | 3.34 a | 2.35 b | 0.38 b | 1.07 b | 5.51 b | 9.82 b | ||||
| 平均 Average | 0.16 | 0.48 | 1.28 | 1.07 | 0.18 | 0.59 | 3.3 | 2.27 | 0.34 | 1.07 | 5.38 | 9.31 | ||||
| W2 | N0 | 0.14 c | 0.43 d | 1.13 c | 0.91 d | 0.17 c | 0.55 d | 3.15 c | 2.10 d | 0.31 c | 0.98 d | 5.02 c | 8.32 d | |||
| N1 | 0.16 b | 0.45 c | 1.26 b | 1.07 c | 0.19 b | 0.57 c | 3.31 b | 2.30 c | 0.35 b | 1.02 c | 5.38 b | 9.39 c | ||||
| N2 | 0.18 a | 0.57 a | 1.39 a | 1.24 a | 0.21 a | 0.67 a | 3.43 a | 2.45 a | 0.39 a | 1.24 a | 5.68 a | 10.35 a | ||||
| N3 | 0.17 ab | 0.51 b | 1.38 a | 1.13 b | 0.19 b | 0.62 b | 3.40 a | 2.35 b | 0.36 b | 1.13 b | 5.63 a | 9.95 b | ||||
| 平均 Average | 0.16 | 0.49 | 1.29 | 1.09 | 0.19 | 0.61 | 3.32 | 2.3 | 0.35 | 1.09 | 5.43 | 9.5 | ||||
| A2 | W1 | N0 | 0.12 d | 0.39 d | 1.12 d | 0.81 c | 0.13 d | 0.52 c | 3.15 c | 2.02 d | 0.25 d | 0.91 d | 4.99 c | 7.83 d | ||
| N1 | 0.13 c | 0.42 c | 1.18 c | 1.04 b | 0.14 c | 0.56 bc | 3.24 b | 2.20 c | 0.27 c | 0.99 c | 5.20 b | 8.85 c | ||||
| N2 | 0.16 a | 0.52 a | 1.36 a | 1.17 a | 0.19 a | 0.63 a | 3.31 a | 2.35 a | 0.36 a | 1.16 a | 5.51 a | 9.78 a | ||||
| N3 | 0.14 b | 0.48 b | 1.32 b | 1.04 b | 0.17 b | 0.58 ab | 3.29 a | 2.30 b | 0.31 b | 1.06 b | 5.45 a | 9.43 b | ||||
| 平均 Average | 0.14 | 0.45 | 1.25 | 1.02 | 0.16 | 0.57 | 3.25 | 2.22 | 0.29 | 1.03 | 5.29 | 8.97 | ||||
| W2 | N0 | 0.10 c | 0.40 d | 1.12 c | 0.84 c | 0.12 c | 0.53 c | 3.12 c | 2.05 d | 0.23 c | 0.94 d | 4.97 c | 8.01 c | |||
| N1 | 0.14 b | 0.45 c | 1.26 b | 1.13 b | 0.15 b | 0.59 b | 3.29 b | 2.23 c | 0.29 b | 1.04 c | 5.33 b | 9.35 b | ||||
| N2 | 0.16 a | 0.55 a | 1.37 a | 1.21 a | 0.17 a | 0.65 a | 3.36 a | 2.33 a | 0.33 a | 1.20 a | 5.59 a | 10.01 a | ||||
| N3 | 0.15 a | 0.49 b | 1.34 a | 1.14 b | 0.17 a | 0.61 ab | 3.32 a | 2.29 b | 0.32 a | 1.10 b | 5.51 a | 9.80 a | ||||
| 平均Average | 0.14 | 0.47 | 1.27 | 1.08 | 0.15 | 0.59 | 3.27 | 2.22 | 0.3 | 1.07 | 5.35 | 9.29 | ||||
| 处理 Treatment | 群体干物质量 Dry matter weight of population/(t·hm-2) | 不同生育阶段干物质积累量 Phase accumulation/(t·hm-2) | 群体生长率 Population growth rate/(g·m-2d-1) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖盛期Tillering | 拔节期Jointing | 齐穗期 Full heading | 成熟期Maturity | 分蘖盛期- 拔节期 Tillering- jointing | 拔节期- 齐穗期 Jointing- full heading | 齐穗期- 成熟期 Full heading- maturity | 分蘖盛期- 拔节期 Tillering- jointing | 拔节期- 齐穗期 Jointing- full heading | 齐穗期- 成熟期 Full heading- maturity | |||||
| A1 | W1 | N0 | 0.62 c | 2.41 c | 7.22 d | 11.71 d | 1.79 c | 4.84 c | 4.49 d | 13.78 c | 13.84 c | 10.68 d | ||
| N1 | 1.00 b | 3.50 b | 9.83 c | 14.85 c | 2.50 b | 6.33 b | 5.02 c | 19.27 b | 18.07 b | 11.95 c | ||||
| N2 | 1.19 a | 3.97 a | 11.42 a | 17.98 a | 2.78 a | 7.46 a | 6.56 a | 21.36 a | 21.30 a | 15.61 a | ||||
| N3 | 1.21 a | 3.93 a | 10.32 b | 16.35 b | 2.72 a | 6.40 b | 6.03 b | 20.95 a | 18.30 b | 14.35 b | ||||
| 平均 Average | 1.00 | 3.81 | 9.70 | 15.22 | 2.45 | 6.26 | 5.52 | 18.84 | 17.88 | 13.15 | ||||
| W2 | N0 | 0.79 c | 2.99 c | 7.86 d | 12.34 d | 2.20 c | 4.87 d | 4.48 d | 16.93 c | 13.92 d | 10.67 d | |||
| N1 | 1.04 b | 3.78 b | 10.17 c | 15.39 c | 2.74 b | 6.39 c | 5.22 c | 21.08 b | 18.26 c | 12.42 c | ||||
| N2 | 1.26 a | 4.28 a | 11.85 a | 18.79 a | 3.02 a | 7.57 a | 6.94 a | 23.24 a | 21.62 a | 16.53 a | ||||
| N3 | 1.31 a | 4.20 a | 11.03 b | 16.98 b | 2.89 ab | 6.86 b | 5.95 b | 22.24 ab | 19.60 b | 14.17 b | ||||
| 平均 Average | 1.10 | 3.81 | 10.23 | 15.87 | 2.71 | 6.42 | 5.65 | 20.87 | 18.35 | 13.45 | ||||
| A2 | W1 | N0 | 0.51 c | 2.31 c | 7.54 d | 10.77 d | 1.80 c | 5.23 c | 3.23 c | 13.80 c | 14.95 c | 7.69 c | ||
| N1 | 0.95 b | 3.18 b | 8.76 c | 12.59 c | 2.23 b | 5.58 c | 3.80 b | 17.12 b | 15.95 c | 9.05 b | ||||
| N2 | 1.10 a | 3.71 a | 10.49 a | 15.18 a | 2.61 a | 6.78 a | 4.68 a | 20.11 a | 19.37 a | 11.16 a | ||||
| N3 | 1.14 a | 3.62 a | 9.82 b | 14.27 b | 2.48 a | 6.20 b | 4.45 a | 19.11 a | 17.71 b | 10.60 a | ||||
| 平均 Average | 0.93 | 3.21 | 9.15 | 13.20 | 2.28 | 5.95 | 4.04 | 17.54 | 17.00 | 9.63 | ||||
| W2 | N0 | 0.56 c | 2.65 c | 8.42 d | 11.29 d | 2.09 c | 5.77 c | 2.87 c | 16.10 c | 16.48 c | 6.84 c | |||
| N1 | 0.96 b | 3.43 b | 9.80 c | 14.19 c | 2.47 b | 6.37 b | 4.38 b | 19.01 b | 18.21 b | 10.44 b | ||||
| N2 | 1.13 a | 3.85 a | 11.23 a | 16.33 a | 2.72 a | 7.39 a | 5.09 a | 20.91 a | 21.10 a | 12.12 a | ||||
| N3 | 1.15 a | 3.80 a | 10.51 b | 15.20 b | 2.65 ab | 6.71 b | 4.69 b | 20.39 ab | 19.17 b | 11.16 b | ||||
| 平均 Average | 0.95 | 3.43 | 9.99 | 14.25 | 2.48 | 6.56 | 4.26 | 19.10 | 18.74 | 10.14 | ||||
Table 7 Effects of water and N management on dry matter accumulation characteristics of population under straw returning(2017).
| 处理 Treatment | 群体干物质量 Dry matter weight of population/(t·hm-2) | 不同生育阶段干物质积累量 Phase accumulation/(t·hm-2) | 群体生长率 Population growth rate/(g·m-2d-1) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖盛期Tillering | 拔节期Jointing | 齐穗期 Full heading | 成熟期Maturity | 分蘖盛期- 拔节期 Tillering- jointing | 拔节期- 齐穗期 Jointing- full heading | 齐穗期- 成熟期 Full heading- maturity | 分蘖盛期- 拔节期 Tillering- jointing | 拔节期- 齐穗期 Jointing- full heading | 齐穗期- 成熟期 Full heading- maturity | |||||
| A1 | W1 | N0 | 0.62 c | 2.41 c | 7.22 d | 11.71 d | 1.79 c | 4.84 c | 4.49 d | 13.78 c | 13.84 c | 10.68 d | ||
| N1 | 1.00 b | 3.50 b | 9.83 c | 14.85 c | 2.50 b | 6.33 b | 5.02 c | 19.27 b | 18.07 b | 11.95 c | ||||
| N2 | 1.19 a | 3.97 a | 11.42 a | 17.98 a | 2.78 a | 7.46 a | 6.56 a | 21.36 a | 21.30 a | 15.61 a | ||||
| N3 | 1.21 a | 3.93 a | 10.32 b | 16.35 b | 2.72 a | 6.40 b | 6.03 b | 20.95 a | 18.30 b | 14.35 b | ||||
| 平均 Average | 1.00 | 3.81 | 9.70 | 15.22 | 2.45 | 6.26 | 5.52 | 18.84 | 17.88 | 13.15 | ||||
| W2 | N0 | 0.79 c | 2.99 c | 7.86 d | 12.34 d | 2.20 c | 4.87 d | 4.48 d | 16.93 c | 13.92 d | 10.67 d | |||
| N1 | 1.04 b | 3.78 b | 10.17 c | 15.39 c | 2.74 b | 6.39 c | 5.22 c | 21.08 b | 18.26 c | 12.42 c | ||||
| N2 | 1.26 a | 4.28 a | 11.85 a | 18.79 a | 3.02 a | 7.57 a | 6.94 a | 23.24 a | 21.62 a | 16.53 a | ||||
| N3 | 1.31 a | 4.20 a | 11.03 b | 16.98 b | 2.89 ab | 6.86 b | 5.95 b | 22.24 ab | 19.60 b | 14.17 b | ||||
| 平均 Average | 1.10 | 3.81 | 10.23 | 15.87 | 2.71 | 6.42 | 5.65 | 20.87 | 18.35 | 13.45 | ||||
| A2 | W1 | N0 | 0.51 c | 2.31 c | 7.54 d | 10.77 d | 1.80 c | 5.23 c | 3.23 c | 13.80 c | 14.95 c | 7.69 c | ||
| N1 | 0.95 b | 3.18 b | 8.76 c | 12.59 c | 2.23 b | 5.58 c | 3.80 b | 17.12 b | 15.95 c | 9.05 b | ||||
| N2 | 1.10 a | 3.71 a | 10.49 a | 15.18 a | 2.61 a | 6.78 a | 4.68 a | 20.11 a | 19.37 a | 11.16 a | ||||
| N3 | 1.14 a | 3.62 a | 9.82 b | 14.27 b | 2.48 a | 6.20 b | 4.45 a | 19.11 a | 17.71 b | 10.60 a | ||||
| 平均 Average | 0.93 | 3.21 | 9.15 | 13.20 | 2.28 | 5.95 | 4.04 | 17.54 | 17.00 | 9.63 | ||||
| W2 | N0 | 0.56 c | 2.65 c | 8.42 d | 11.29 d | 2.09 c | 5.77 c | 2.87 c | 16.10 c | 16.48 c | 6.84 c | |||
| N1 | 0.96 b | 3.43 b | 9.80 c | 14.19 c | 2.47 b | 6.37 b | 4.38 b | 19.01 b | 18.21 b | 10.44 b | ||||
| N2 | 1.13 a | 3.85 a | 11.23 a | 16.33 a | 2.72 a | 7.39 a | 5.09 a | 20.91 a | 21.10 a | 12.12 a | ||||
| N3 | 1.15 a | 3.80 a | 10.51 b | 15.20 b | 2.65 ab | 6.71 b | 4.69 b | 20.39 ab | 19.17 b | 11.16 b | ||||
| 平均 Average | 0.95 | 3.43 | 9.99 | 14.25 | 2.48 | 6.56 | 4.26 | 19.10 | 18.74 | 10.14 | ||||
| 处理 Treatment | 群体干物质量 Dry matter weight of population/(t·hm-2) | 不同生育阶段干物质积累量 Phase accumulation/(t·hm-2) | 群体生长率 Population growth rate/(g·m-2d-1) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖盛期Tillering | 拔节期Jointing | 齐穗期 Full heading | 成熟期Maturity | 分蘖盛期- 拔节期 Tillering- jointing | 拔节期- 齐穗期 Jointing- full heading | 齐穗期- 成熟期 Full heading- maturity | 分蘖盛期- 拔节期 Tillering- jointing | 拔节期- 齐穗期 Jointing- full heading | 齐穗期- 成熟期 Full heading- maturity | |||||
| A1 | W1 | N0 | 1.10 b | 2.95 c | 8.10 d | 13.30 d | 1.85 c | 5.15 d | 5.20 c | 12.34 c | 14.71 d | 9.99 c | ||
| N1 | 1.33 b | 3.88 b | 10.23 c | 16.24 c | 2.55 b | 6.79 c | 6.01 b | 17.01 b | 19.40 c | 11.56 b | ||||
| N2 | 2.16 a | 6.03 a | 14.53 a | 21.54 a | 3.86 a | 8.50 a | 7.01 a | 25.77 a | 24.28 a | 13.48 a | ||||
| N3 | 2.39 a | 5.84 a | 13.53 b | 20.26 b | 3.44 a | 7.69 b | 6.73 a | 22.96 a | 21.97 b | 12.94 a | ||||
| 平均 Average | 1.75 | 4.67 | 11.60 | 17.83 | 2.93 | 7.03 | 6.24 | 19.52 | 20.09 | 11.99 | ||||
| W2 | N0 | 1.16 c | 3.16 c | 8.46 d | 13.95 d | 2.00 b | 5.31 d | 5.48 d | 16.59 b | 15.16 d | 10.54 d | |||
| N1 | 1.68 b | 4.17 b | 10.67 c | 16.92 c | 2.49 b | 6.18 c | 6.25 c | 13.31 b | 17.66 c | 12.02 c | ||||
| N2 | 2.31 a | 6.62 a | 15.49 a | 22.85 a | 4.31 a | 8.87 a | 7.36 a | 24.29 a | 25.35 a | 14.15 a | ||||
| N3 | 2.58 a | 6.22 a | 14.00 b | 20.83 b | 3.64 a | 7.78 b | 6.83 b | 28.72 a | 22.23 b | 13.13 b | ||||
| 平均 Average | 1.93 | 5.04 | 12.16 | 18.64 | 3.11 | 7.04 | 6.48 | 20.73 | 20.10 | 12.46 | ||||
| A2 | W1 | N0 | 0.91 b | 2.50 c | 7.50 d | 12.51 d | 1.60 c | 4.99 d | 5.02 b | 10.64 c | 14.26 d | 9.65 b | ||
| N1 | 1.27 b | 3.77 b | 9.56 c | 14.82 c | 2.50 b | 6.46 c | 5.26 b | 16.70 b | 18.45 c | 10.11 b | ||||
| N2 | 2.20 a | 6.05 a | 13.48 a | 19.43 a | 3.85 a | 7.44 a | 5.95 a | 25.66 a | 21.25 a | 11.44 a | ||||
| N3 | 2.33 a | 5.67 a | 12.41 b | 18.20 b | 3.34 a | 6.75 b | 5.79 a | 22.26 a | 19.27 b | 11.13 a | ||||
| 平均 Average | 1.68 | 4.50 | 10.74 | 16.24 | 2.82 | 6.41 | 5.50 | 18.81 | 18.31 | 10.58 | ||||
| W2 | N0 | 1.14 c | 2.81 c | 7.90 d | 12.91 d | 1.66 c | 5.09 d | 5.01 c | 14.88 b | 14.55 d | 9.64 c | |||
| N1 | 1.61 b | 3.84 b | 10.35 c | 16.01 c | 2.23 b | 5.72 c | 5.66 b | 11.08 c | 16.34 c | 10.88 b | ||||
| N2 | 2.23 a | 6.13 a | 14.01 a | 20.48 a | 3.90 a | 7.88 a | 6.47 a | 23.89 a | 22.52 a | 12.44 a | ||||
| N3 | 2.41 a | 5.99 a | 13.15 b | 19.21 b | 3.58 a | 7.16 b | 6.06 a | 25.99 a | 20.45 b | 11.66 a | ||||
| 平均 Average | 1.85 | 4.69 | 11.35 | 17.15 | 2.84 | 6.46 | 5.80 | 18.96 | 18.46 | 11.16 | ||||
Table 8 Effects of water and N management on dry matter accumulation characteristics of population under straw returning(2018).
| 处理 Treatment | 群体干物质量 Dry matter weight of population/(t·hm-2) | 不同生育阶段干物质积累量 Phase accumulation/(t·hm-2) | 群体生长率 Population growth rate/(g·m-2d-1) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖盛期Tillering | 拔节期Jointing | 齐穗期 Full heading | 成熟期Maturity | 分蘖盛期- 拔节期 Tillering- jointing | 拔节期- 齐穗期 Jointing- full heading | 齐穗期- 成熟期 Full heading- maturity | 分蘖盛期- 拔节期 Tillering- jointing | 拔节期- 齐穗期 Jointing- full heading | 齐穗期- 成熟期 Full heading- maturity | |||||
| A1 | W1 | N0 | 1.10 b | 2.95 c | 8.10 d | 13.30 d | 1.85 c | 5.15 d | 5.20 c | 12.34 c | 14.71 d | 9.99 c | ||
| N1 | 1.33 b | 3.88 b | 10.23 c | 16.24 c | 2.55 b | 6.79 c | 6.01 b | 17.01 b | 19.40 c | 11.56 b | ||||
| N2 | 2.16 a | 6.03 a | 14.53 a | 21.54 a | 3.86 a | 8.50 a | 7.01 a | 25.77 a | 24.28 a | 13.48 a | ||||
| N3 | 2.39 a | 5.84 a | 13.53 b | 20.26 b | 3.44 a | 7.69 b | 6.73 a | 22.96 a | 21.97 b | 12.94 a | ||||
| 平均 Average | 1.75 | 4.67 | 11.60 | 17.83 | 2.93 | 7.03 | 6.24 | 19.52 | 20.09 | 11.99 | ||||
| W2 | N0 | 1.16 c | 3.16 c | 8.46 d | 13.95 d | 2.00 b | 5.31 d | 5.48 d | 16.59 b | 15.16 d | 10.54 d | |||
| N1 | 1.68 b | 4.17 b | 10.67 c | 16.92 c | 2.49 b | 6.18 c | 6.25 c | 13.31 b | 17.66 c | 12.02 c | ||||
| N2 | 2.31 a | 6.62 a | 15.49 a | 22.85 a | 4.31 a | 8.87 a | 7.36 a | 24.29 a | 25.35 a | 14.15 a | ||||
| N3 | 2.58 a | 6.22 a | 14.00 b | 20.83 b | 3.64 a | 7.78 b | 6.83 b | 28.72 a | 22.23 b | 13.13 b | ||||
| 平均 Average | 1.93 | 5.04 | 12.16 | 18.64 | 3.11 | 7.04 | 6.48 | 20.73 | 20.10 | 12.46 | ||||
| A2 | W1 | N0 | 0.91 b | 2.50 c | 7.50 d | 12.51 d | 1.60 c | 4.99 d | 5.02 b | 10.64 c | 14.26 d | 9.65 b | ||
| N1 | 1.27 b | 3.77 b | 9.56 c | 14.82 c | 2.50 b | 6.46 c | 5.26 b | 16.70 b | 18.45 c | 10.11 b | ||||
| N2 | 2.20 a | 6.05 a | 13.48 a | 19.43 a | 3.85 a | 7.44 a | 5.95 a | 25.66 a | 21.25 a | 11.44 a | ||||
| N3 | 2.33 a | 5.67 a | 12.41 b | 18.20 b | 3.34 a | 6.75 b | 5.79 a | 22.26 a | 19.27 b | 11.13 a | ||||
| 平均 Average | 1.68 | 4.50 | 10.74 | 16.24 | 2.82 | 6.41 | 5.50 | 18.81 | 18.31 | 10.58 | ||||
| W2 | N0 | 1.14 c | 2.81 c | 7.90 d | 12.91 d | 1.66 c | 5.09 d | 5.01 c | 14.88 b | 14.55 d | 9.64 c | |||
| N1 | 1.61 b | 3.84 b | 10.35 c | 16.01 c | 2.23 b | 5.72 c | 5.66 b | 11.08 c | 16.34 c | 10.88 b | ||||
| N2 | 2.23 a | 6.13 a | 14.01 a | 20.48 a | 3.90 a | 7.88 a | 6.47 a | 23.89 a | 22.52 a | 12.44 a | ||||
| N3 | 2.41 a | 5.99 a | 13.15 b | 19.21 b | 3.58 a | 7.16 b | 6.06 a | 25.99 a | 20.45 b | 11.66 a | ||||
| 平均 Average | 1.85 | 4.69 | 11.35 | 17.15 | 2.84 | 6.46 | 5.80 | 18.96 | 18.46 | 11.16 | ||||
| 处理 Treatment | 分蘖盛期 Tillering | 拔节期 Jointing | 齐穂期 Full heading | 高效叶面积指数H-LAI | 叶面积衰减率 R-LAI/(LAI·d-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | |||||||
| A1 | W1 | N0 | 1.74 d | 2.49 c | 4.53 c | 3.11 c | 3.58 c | 0.0585 d |
| N1 | 2.31 c | 3.06 b | 5.97 b | 4.25 b | 4.78 b | 0.0832 b | ||
| N2 | 2.67 b | 3.99 a | 6.98 a | 4.61 a | 5.18 a | 0.0855 a | ||
| N3 | 2.92 a | 4.01 a | 6.86 a | 4.50 a | 5.09 a | 0.0814 c | ||
| 平均 Average | 2.41 | 3.39 | 6.09 | 4.12 | 4.66 | 0.0772 | ||
| W2 | N0 | 1.44 d | 2.40 c | 4.45 c | 3.26 c | 3.70 c | 0.0586 c | |
| N1 | 2.13 c | 3.24 b | 6.15 b | 4.49 b | 5.00 b | 0.0830 b | ||
| N2 | 2.52 b | 4.04 a | 7.16 a | 4.80 a | 5.35 a | 0.0891 a | ||
| N3 | 2.77 a | 4.02 a | 6.97 a | 4.74 a | 5.32 a | 0.0845 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 2.22 | 3.43 | 6.18 | 4.32 | 4.84 | 0.0788 | ||
| A2 | W1 | N0 | 1.30 d | 2.10 c | 4.08 c | 2.85 c | 3.28 c | 0.0567 c |
| N1 | 2.09 c | 3.46 b | 6.22 b | 4.10 b | 4.27 b | 0.0787 b | ||
| N2 | 2.33 b | 3.77 a | 6.70 a | 4.41 a | 4.93 a | 0.0839 a | ||
| N3 | 2.52a | 3.83 a | 6.74 a | 4.38 a | 4.61 a | 0.0830 a | ||
| 平均 Average | 2.06 | 3.29 | 5.94 | 3.94 | 4.27 | 0.0756 | ||
| W2 | N0 | 1.44 d | 2.12 c | 3.95 c | 2.88 c | 3.32 c | 0.0525 c | |
| N1 | 2.15 c | 3.41 b | 6.25 b | 4.18 b | 4.73 b | 0.0813 b | ||
| N2 | 2.52 b | 3.72 a | 6.75 a | 4.72 a | 5.27 a | 0.0867 a | ||
| N3 | 2.74 a | 3.65 a | 6.55 ab | 4.68 a | 5.25 a | 0.0827 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 2.21 | 3.23 | 5.88 | 4.12 | 4.65 | 0.0758 | ||
Table 9 Effects of water and N management on LAI in hybrid rice under straw returning.
| 处理 Treatment | 分蘖盛期 Tillering | 拔节期 Jointing | 齐穂期 Full heading | 高效叶面积指数H-LAI | 叶面积衰减率 R-LAI/(LAI·d-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | |||||||
| A1 | W1 | N0 | 1.74 d | 2.49 c | 4.53 c | 3.11 c | 3.58 c | 0.0585 d |
| N1 | 2.31 c | 3.06 b | 5.97 b | 4.25 b | 4.78 b | 0.0832 b | ||
| N2 | 2.67 b | 3.99 a | 6.98 a | 4.61 a | 5.18 a | 0.0855 a | ||
| N3 | 2.92 a | 4.01 a | 6.86 a | 4.50 a | 5.09 a | 0.0814 c | ||
| 平均 Average | 2.41 | 3.39 | 6.09 | 4.12 | 4.66 | 0.0772 | ||
| W2 | N0 | 1.44 d | 2.40 c | 4.45 c | 3.26 c | 3.70 c | 0.0586 c | |
| N1 | 2.13 c | 3.24 b | 6.15 b | 4.49 b | 5.00 b | 0.0830 b | ||
| N2 | 2.52 b | 4.04 a | 7.16 a | 4.80 a | 5.35 a | 0.0891 a | ||
| N3 | 2.77 a | 4.02 a | 6.97 a | 4.74 a | 5.32 a | 0.0845 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 2.22 | 3.43 | 6.18 | 4.32 | 4.84 | 0.0788 | ||
| A2 | W1 | N0 | 1.30 d | 2.10 c | 4.08 c | 2.85 c | 3.28 c | 0.0567 c |
| N1 | 2.09 c | 3.46 b | 6.22 b | 4.10 b | 4.27 b | 0.0787 b | ||
| N2 | 2.33 b | 3.77 a | 6.70 a | 4.41 a | 4.93 a | 0.0839 a | ||
| N3 | 2.52a | 3.83 a | 6.74 a | 4.38 a | 4.61 a | 0.0830 a | ||
| 平均 Average | 2.06 | 3.29 | 5.94 | 3.94 | 4.27 | 0.0756 | ||
| W2 | N0 | 1.44 d | 2.12 c | 3.95 c | 2.88 c | 3.32 c | 0.0525 c | |
| N1 | 2.15 c | 3.41 b | 6.25 b | 4.18 b | 4.73 b | 0.0813 b | ||
| N2 | 2.52 b | 3.72 a | 6.75 a | 4.72 a | 5.27 a | 0.0867 a | ||
| N3 | 2.74 a | 3.65 a | 6.55 ab | 4.68 a | 5.25 a | 0.0827 b | ||
| 平均 Average | 2.21 | 3.23 | 5.88 | 4.12 | 4.65 | 0.0758 | ||
| 指标 Index | 生育期 Growth stage | 单茎干物质 Single stem dry weight | 总干物质量 Dry matter amount | 有效穗 Effective panicles | 每穗粒数 Spikelet no. per panicle | 产量 Grain yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAI | JS | 0.89** | 0.82** | 0.72* | 0.90** | 0.75* |
| FHS | 0.95** | 0.88** | 0.75* | 0.89** | 0.80** | |
| MS | 0.94** | 0.89** | 0.77* | 0.85** | 0.80** | |
| H-LAI | FHS | 0.94** | 0.86** | 0.75* | 0.74* | 0.78* |
| PGR | FHS | 0.93** | 0.93** | 0.90** | 0.65* | 0.95** |
| JS-FHS | 0.92** | 0.91** | 0.83** | 0.59* | 0.81** | |
| FHS-MS | 0.82** | 0.93** | 0.94** | 0.49* | 0.92** |
Table 10 orrelation coefficients of LAI and population rate with dry matter amount and grain yield.
| 指标 Index | 生育期 Growth stage | 单茎干物质 Single stem dry weight | 总干物质量 Dry matter amount | 有效穗 Effective panicles | 每穗粒数 Spikelet no. per panicle | 产量 Grain yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAI | JS | 0.89** | 0.82** | 0.72* | 0.90** | 0.75* |
| FHS | 0.95** | 0.88** | 0.75* | 0.89** | 0.80** | |
| MS | 0.94** | 0.89** | 0.77* | 0.85** | 0.80** | |
| H-LAI | FHS | 0.94** | 0.86** | 0.75* | 0.74* | 0.78* |
| PGR | FHS | 0.93** | 0.93** | 0.90** | 0.65* | 0.95** |
| JS-FHS | 0.92** | 0.91** | 0.83** | 0.59* | 0.81** | |
| FHS-MS | 0.82** | 0.93** | 0.94** | 0.49* | 0.92** |
| [1] | 廖伯寿, 殷艳, 马霓. 中国油料作物产业发展回顾与展望. 农学学报, 2018, 8(1): 107-112. |
| Liao B S, Yin Y, Ma N.Review and future prospects of oil crops industry development in China.J Agric, 2018, 8(1): 107-112. | |
| [2] | Kousterna E.The effect of covering and mulching on the temperature and moisture of soil and broccoli yield.Acta Agrophys, 2014, 21(2): 165-178. |
| [3] | Su W, Lu J W, Wang W N, Li X K, Ren T, Cong R H.Influence of rice straw mulching on seed yield and nitrogen use efficiency of winter oilseed rape in intensive rice oilseed rape cropping system.Field Crop Res, 2014, 159: 53-61. |
| [4] | Jawson M D, Elliott L F.Carbon and nitrogen transformations during wheat straw and root decomposition.Soil Bio Chem, 1986, 18: 15-22. |
| [5] | 马宗国, 卢绪奎, 万丽, 陈祖光, 左辉. 小麦秸秆还田对水稻生长及土壤肥力的影响. 作物杂志, 2003(5): 37-38. |
| Ma Z G, Lu X K, Wan L, Chen Z G, Zuo H.Effects of wheat straw returning on rice growth and soil fertility.Crops, 2003(5): 37-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 孙永健, 马均, 孙园园, 徐徽, 严奉君, 代邹, 蒋明金, 李玥. 水氮管理模式对杂交籼稻冈优527群体质量和产量的影响. 中国农业科学, 2014, 47(10): 2047-2061. |
| Sun Y J, Ma J, Sun Y Y, Xu H, Yan F J, Dai Z, Jiang M J, Li Y.Effects of water and nitrogen management patterns on population quality and yield of hybrid rice Gangyou 527.Sci Agric Sin, 2014, 47(10): 2047-2061. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 严奉君, 孙永健, 马均, 徐徽, 李玥, 代邹, 杨志远, 蒋明金, 孙园园. 灌溉方式与秸秆覆盖优化施氮模式对秸秆腐熟特征及水稻氮素利用的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(11): 1435-1444. |
| Yan F J, Sun Y J, Ma J, Xu H, Li Y, Dai Z, Yang Z Y, Jiang M J, Sun Y Y.Effects of irrigation method and straw mulch-nitrogen management pattern on straw decomposition characteristics and nitrogen utilization of hybrid rice. Chin J Eco-Agric, 2016, 24(11): 1435-1444. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 赵建红, 李玥, 孙永健, 李应洪, 孙加威, 代邹, 谢华英, 徐徽, 马均. 灌溉方式和氮肥运筹对免耕厢沟栽培杂交稻氮素利用及产量的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(3): 609-617. |
| [9] | Zhao J H, Li Y, Sun Y J, Li Y H, Sun J W, Dai Z, Xie H Y, Xu H, Ma J.Effects of irrigation and nitrogen management on nitrogen use efficiency and yield of hybrid rice cultivated in ditches under no-tillage.Plant Nutr Fert Sci, 2016, 22(3): 609-617. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [10] | Wang Z Q, Zhang W Y, Beebout S S, Hao Z, Liu L.Grain yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies of rice as influenced by irrigation regimes and their interaction with nitrogen rates.Field Crops Res, 2016: 193, 54-69. |
| [11] | 常勇, 黄忠勤, 周兴根, 孙克新, 周涧楠, 丁震乾, 王波, 李小珊. 不同麦秸还田量对水稻生长发育、产量及品质的影响田. 江苏农业科学, 2018, 46(20): 47-51. |
| Chang Y, Huang Z Q, Zhou X G, Sun K X, Zhou J N, Ding Z Q, Wang B, Li X S.Different amount of wheat straw counters-field impact on rice growth, yield and quality.Jiangsu Agric Sci, 2018, 46(20): 47-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 刘玲玲, 刘婷, 狄霖, 吴文祥, 盛海君, 余彬彬, 杨艳菊, 钱晓晴, 王娟娟. 秸秆全量还田对水稻生长及土壤理化性质的影响. 扬州大学学报, 2018, 39(3): 81-85. |
| Liu L L, Liu T, Di L, Wu W X, Sheng H J, Yu B B, Yang Y J, Qian X Q, Wang J J.Influences of total straw returning on rice growth and soil physiochemical properties.J Yangzhou Univ, 2018, 39(3): 81-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Zeng X M, Han B J, Xu F S, Huang J L, Cai H M, Shi L.Effects of modified fertilization technology of on the grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of midseason rice.Field Crop Res, 2012, 137: 203-212. |
| [14] | 李旭毅, 孙永健, 程洪彪, 郑宏祯, 刘树金, 胡蓉, 马均. 两种生态条件下氮素调控对不同栽培方式水稻干物质积累和产量的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(4): 773-781. |
| Li X Y, Sun Y J, Cheng H B, Zhen H Z, Liu S J, Hu R, Ma Jet al. Effects of nitrogen application strategy and cultivation model on the performances of canopy apparent photosynthesis of Indica hybrid rice Eryou 498 during filling stage.Plant Nutr Fert Sci, 2011, 17(4): 773-781. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 张军, 张洪程, 段祥茂. 地力与施氮量对超级稻产量、品质及氮素利用率的影响. 作物学报, 2011, 37(11): 2020-2029. |
| Zhang T, Zhang H C, Duan X M.Effects of soil fertility and nitrogen application rates on super rice yield quality, and nitrogen use efficiency.Acta Agron Sin, 2011, 37(11): 2020-2029. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 魏海燕, 工亚江, 孟天瑶, 徐宗进, 杨波, 郭保卫,杜斌,戴其根, 许轲, 霍中洋, 魏海燕,. 机插超级粳稻产量、品质及氮肥利用率对氮肥的响应. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(2): 488-496. |
| Wei H Y, Wang Y J, Meng T Y, Xu Z J, Yang B, Guo B W, Du B, Dai Q G, Xu K, Huo Z Y, Wei H Y,.Response of yield, quality and nitrogen use efficiency to nitrogen fertilizer from mechanical transplanting super japonica rice.Chin J Appl Ecol, 2014, 25(2): 488-496. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 于林惠, 李刚华, 徐晶晶, 凌启鸿, 丁艳锋. 基于高产示范方的机插水稻群体特征研究. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 26(4): 451-456. |
| Yu L H, Li G H, Xu J J, Ling Q H, Ding Y F.Population characteristics of machine-transplanted japonica rice based on high-yield demonstration fields. Chin J Rice Sci, 2011, 26(4): 451-456. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Zhang H, Chen T T, Liu L J, Wang Z Q, Yang J C, Zhang J.Performance in grain yield and physiological traits of rice in the Yangtze River basin of China during the last 60 yr. J Integr Agric, 2013, 12(1):57-66. |
| [19] | 严奉君, 孙永健, 马均, 徐徽, 李玥, 杨志远, 蒋明金, 吕腾飞等. 秸秆覆盖与氮肥运筹对杂交稻根系生长及氮素利用的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(1): 23-55. |
| Yan F J, Sun Y J, Ma J, Xu H, Li Y, Yang Z Y, Jiang M J, LÜ T F.Effects of straw mulch and nitrogen management on root growth and nitrogen utilization characteristics of hybrid rice.Plant Nutr Fert Sci, 2015, 21(1): 23-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 陈培峰, 董明辉, 顾俊荣, 惠锋, 乔中英, 杨代凤, 刘腾飞. 麦秸还田与氮肥运筹对超级稻强弱势粒粒重与品质的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(6): 715-722. |
| Chen P F, Dong M H, Gu J R, Hui F, Qiao Z Y, Yang D F, Liu T F.Effects of returning wheat residue to field and nitrogen management on grain weight and quality of superior and inferior grain in super rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2012, 26(6): 715-722. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 朱萍, 顾艾节, 王华, 顾建芹. 稻麦秸秆连续还田配施腐熟剂对土壤性状和水稻产量的影响. 上海农业学报, 2018, 34(2): 60-64. |
| Zhu P, Gu A J, Wang H, Gu J Q, Gu J Q,.Effects of continuous rice and wheat straw returning to field with decomposing agent on soil properties and rice yield.Acta Agric Shanghai, 2018, 34(2):60-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 怀燕, 潘建清, 陈一定, 陆若辉, 朱伟锋. 腐熟剂作用下油菜秸秆还田对土壤性状与单季稻产量的影响. 浙江农业科学, 2014(5): 636-638. |
| Huan Y, Pan J Q, Chen Y D, Lu R H, Zhu W F.Rotten agent under the action of rape straw returned to soil properties and the effect of single harvesting yield.Zhejiang Agric Sci, 2014(5): 636-638. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Cabangon R J, Tuong T P, Castillo E G, Bao L X, Lu G A, Wang G H, Cui Y L, Bouman B A M, Li Y H, Chen C D, Wang J Z. Effect of irrigation method and N-fertilizer management on rice yield, water productivity and nutrient-use efficiencies in typical lowland rice conditions in China.Paddy Water Environ, 2004, 2: 195-206. |
| [24] | 杨建昌, 王志琴, 朱庆森. 不同土壤水分状况下氮素营养对水稻产量的影响及其生理机制的研究. 中国农业科学, 1996, 29(4): 58-66. |
| Yang J C, Wang Z Q, Zhu Q S.Effect of nitrogen nutrition on rice yield and its physiological mechanism under different status of soil moisture.Sci Agric Sin, 1996, 29(4): 58-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Sun Y J, Ma J, Sun Y Y, Xu H, Yang Z Y, Liu S J, Jia X W, Zheng H Z.The effects of different water and nitrogen managements on yield and nitrogen use efficiency in hybrid rice of China.Field Crops Res, 2012, 127(27): 85-98. |
| [26] | 吴登, 黄世礽, 李明灌, 谢毅栋, 梁玉祥, 陈智慧. 稻草还田免耕抛秧的增产效果及节水效应. 杂交水稻, 2006(S1): 109-112. |
| Wu D, Huang S R, Li M G, Xie Y D, Liang Y X, Chen Z H.Straw counters-field increase yield and some water-saving effect.Hybrid Rice, 2006(S1): 109-112. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 任万军, 刘代银, 伍菊仙, 杨文钰, 樊高琼. 免耕高留茬抛秧稻的产量及若干生理特性研究. 作物学报, 2008, 34(11): 1994-2002. |
| Ren W J, Liu D Y, Wu J X, Yang W Y, Fan G Q.Effect of broadcasting rice seedlings in the field with high stand- ing-stubbles under no-tillage condition on yield and some physiological characteristics.Acta Agron Sin, 2008, 34(11): 1994-2002. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 叶文培, 谢小立, 王凯荣, 李志国. 不同时期秸秆还田对水稻生长发育及产量的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2008, 22(1): 65-70. |
| Ye W P, Xie X L, Wang K R, Li Z G.Effects of rice straw maturing in different periods on growth and yield of rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2008, 22(1): 65-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Jawson M D, Elliott L F.Carbon and nitrogen transformations during wheat straw and root decomposition.Soil Biol Chem, 1986, 18: 15-22. |
| [30] | 张杰, 刘正柱, 将井军, 陈凤英. 小麦留高茬还田的效果. 土壤通报, 2001(4): 34-36. |
| Zhang J, Liu Z Z, Jiang J J, Chen F Y.The Effect and methods of returning the high stubble of wheat stubble into field.Chin J Soil Sci, 2001(4): 34-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 钱洪兵, 韩春贵, 钱存进, 严桂珠. 稻麦秸秆直接还田技术研究. 土壤通报, 1998(2): 26-29. |
| Qian H B, Han C G, Qian C J, Yan G Z.Rice and wheat straw counters-field technology research.Chin J Soil Sci, 1998(2): 26-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 张自常, 李鸿伟, 曹转勤, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 施氮量和灌溉方式的交互作用对水稻产量和品质影响. 作物学报, 2013, 39(1): 84-92. |
| Zhang Z C, Li H W, Cao Z Q, Wang Z Q, Yang J C.Effect of interaction between nitrogen rate and irrigation regime on grain yield and quality of rice.Acta Agron Sin, 2013, 39(1): 84-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 孙永健, 孙园园, 刘树金, 杨志远, 程洪彪, 贾现文, 马均. 水分管理和氮肥运筹对水稻养分吸收、转运及分配的影响. 作物学报, 2011, 37(12): 2221-2232. |
| Sun Y J, Sun Y Y, Liu S J, Yang Z Y, Cheng H B, Jia X W, Ma J.Effects of water management and nitrogen application strategies on nutrient absorption, transfer, and distribution in rice.Acta Agron Sin, 2011, 37(12): 2221-2232. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | Ishii R.Leaf photosynthesis in rice in relation to grain yields//Abrol Y P, Govindjee M P. Photosynthesis -Photoreactions to Plant Productivity . Kluwer, Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1993: 561-569. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [4] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [5] | ZHAO Yiting, XIE Keran, GAO Ti, CUI Kehui. Effects of Drought Priming During Tillering Stage on Panicle Development and Yield Formation Under High Temperature During Panicle Initiation Stage in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [6] | ZHOU Tian, WU Shaohua, KANG Jianhong, WU Hongliang, YANG Shenglong, WANG Xingqiang, LI Yu, HUANG Yufeng. Effects of Planting Patterns on Starch Content and Activities of Key Starch Enzymes in Rice Grains [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [7] | LIU Zhongqi, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai, GUI Jinxin. Genome-wide Association Analysis of Rice Seed Dehydration Rate at Maturity Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(2): 150-159. |
| [8] | LIU Huimin, ZHOU Jieqiang, HU Yuanyi, TIAN Yan, LEI Bin, LI Jianwu, WEI Zhongwei, TANG Wenbang. Super-high Yield Characteristics of Two-line Hybrid Rice Zhuoliangyou 1126 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(2): 160-171. |
| [9] | PENG Xianlong, DONG Qiang, ZHANG Chen, LI Pengfei, LI Bolin, LIU Zhilei, YU Cailian. Effects of Straw Return Rate on Soil Reducing Substances and Rice Growth Under Different Soil Conditions [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(2): 198-210. |
| [10] | ZHU Wang, ZHANG Xiang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Zhe, CHEN Yinglong, WEI Huanhe, DAI Qigen, XU Ke, ZHU Guanglong, ZHOU Guisheng, MENG Tianyao. Morphological and Physiological Characteristics of Rice Roots Under Combined Salinity-Drought Stress and Their Relationships with Yield Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(6): 617-627. |
| [11] | ZOU Yuao, WU Qixia, ZHOU Qianshun, ZHU Jianqiang, YAN Jun. Response of Middle-season Hybrid Rice to Flooding Stress at the Booting Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(6): 642-656. |
| [12] | YUAN Pei, ZHOU Xuan, YANG Wei, YIN Lingjie, JIN Tuo, PENG Jianwei, RONG Xiangmin, TIAN Chang. Effects of Combined Application of Chemical Fertilizers and Nitrogen Reduction on the Yield of Double-cropping Rice and the Risk of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss in Field Water in Dongting Lake Area [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(5): 518-528. |
| [13] | XIAO Dakang, HU Ren, HAN Tianfu, ZHANG Weifeng, HOU Jun, REN Keyu. Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer Consumption and Operation on Rice Yield and Its Components in China:A Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(5): 529-542. |
| [14] | HUANG Yaru, XU Peng, WANG Lele, HE Yizhe, WANG Hui, KE Jian, HE Haibing, WU Liquan, YOU Cuicui. Effects of Exogenous Trehalose on Grain Filling Characteristics and Yield Formation of japonica Rice Cultivar W1844 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| [15] | DONG Liqiang, YANG Tiexin, LI Rui, SHANG Wenqi, MA Liang, LI Yuedong, SUI Guomin. Effect of Plant-row Spacing on Rice Yield and Root Morphological and Physiological Characteristics in Super High Yield Field [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(4): 392-404. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||