
中国水稻科学 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 265-276.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7104
收稿日期:2017-08-29
修回日期:2017-11-09
出版日期:2018-05-10
发布日期:2018-05-10
通讯作者:
江敏
基金资助:
Tongyu ZHOU1, Min JIANG1,2,*( ), Wangliang SUN1, Bin SUN1
), Wangliang SUN1, Bin SUN1
Received:2017-08-29
Revised:2017-11-09
Online:2018-05-10
Published:2018-05-10
Contact:
Min JIANG
摘要:
【目的】气候变化对农业生产的影响日趋明显。分析未来气候变化所产生的影响,模拟调整作物耕作和栽培措施,为有效减轻未来气候变化带来的负效应提供参考。【方法】根据联合国政府间气候变化专门委员会第5次工作报告中未来可能的温室气体排放情况,以BCC_CSM模式模拟未来的气候变化情景,选取RCP4.5和RCP8.5两种典型浓度路径情景,与作物模型CERES-Rice耦合,筛选出了未来气候变化条件下福建省各稻区可能的最佳品种和播期,并研究分析了品种更替和播期调整后的水稻单产、稳产性以及全省水稻总产的变化。【结果】在RCP4.5和RCP8.5情景下,闽东南双季稻区早稻的模拟产量较未作适应性调整分别增加1.6%和1.9%,晚稻的模拟产量依次增加13.5%和9.8%;闽西北双季稻区早稻的模拟产量依次提高1.4%和1.0%,晚稻的模拟产量依次提高11.5%和7.9%;闽西北山地单季稻区一季稻的模拟产量分别增加14.1%和13.7%。在综合考虑两种适应性措施后,福建省各稻区总产也较当前明显提高,在RCP4.5和RCP8.5两种情景下,分别提高9.3%和10.5%。【结论】未来气候变化对福建省水稻产量有不利影响,可采取一定的适应性措施缓解负效应。
中图分类号:
周桐宇, 江敏, 孙汪亮, 孙彬. RCPs情景下福建省水稻生产的适应性调整模拟研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(3): 265-276.
Tongyu ZHOU, Min JIANG, Wangliang SUN, Bin SUN. Simulation of Rice Adaptability Adjustmentin Fujian Province Under RCPs Scenarios[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(3): 265-276.
| 水稻品种Rice combination | 类型Type | P1 | P2R | P5 | P2O | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红优2155Hongyou 2155 | 迟熟早籼EILM | 601.2 | 54.7 | 135.3 | 12.4 | 88.6 | 0.034 | 0.48 | 1.13 |
| 花2优3301 Hua 2 you 3301 | 早熟中籼MIEM | 703.0 | 90.0 | 370.3 | 11.5 | 88.0 | 0.016 | 1.15 | 1.10 |
| 两优667Liangyou 667 | 中熟中籼MIMM | 620.5 | 132.0 | 660.2 | 11.7 | 72.0 | 0.019 | 0.47 | 0.65 |
| 广优2186 Guangyou 2186 | 迟熟中籼MILM | 716.0 | 75.4 | 515.0 | 11.3 | 99.0 | 0.016 | 1.64 | 1.10 |
| 深优9775 Shenyou 9775 | 早熟晚籼LIEM | 505.0 | 204.0 | 124.0 | 11.0 | 59.0 | 0.016 | 0.53 | 1.14 |
| 泰丰优656 Taifengyou 656 | 中熟晚籼LIMM | 696.0 | 130.0 | 439.0 | 11.0 | 77.0 | 0.016 | 0.06 | 0.67 |
| 泰丰优2098 Taifengyou 2098 | 迟熟晚籼LILM | 811.0 | 204.0 | 214.0 | 11.1 | 47.0 | 0.017 | 1.01 | 1.04 |
表1 福建省代表性水稻品种遗传参数
Table 1 Genetic parameters of representative rice combinations in Fujian Province, China.
| 水稻品种Rice combination | 类型Type | P1 | P2R | P5 | P2O | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红优2155Hongyou 2155 | 迟熟早籼EILM | 601.2 | 54.7 | 135.3 | 12.4 | 88.6 | 0.034 | 0.48 | 1.13 |
| 花2优3301 Hua 2 you 3301 | 早熟中籼MIEM | 703.0 | 90.0 | 370.3 | 11.5 | 88.0 | 0.016 | 1.15 | 1.10 |
| 两优667Liangyou 667 | 中熟中籼MIMM | 620.5 | 132.0 | 660.2 | 11.7 | 72.0 | 0.019 | 0.47 | 0.65 |
| 广优2186 Guangyou 2186 | 迟熟中籼MILM | 716.0 | 75.4 | 515.0 | 11.3 | 99.0 | 0.016 | 1.64 | 1.10 |
| 深优9775 Shenyou 9775 | 早熟晚籼LIEM | 505.0 | 204.0 | 124.0 | 11.0 | 59.0 | 0.016 | 0.53 | 1.14 |
| 泰丰优656 Taifengyou 656 | 中熟晚籼LIMM | 696.0 | 130.0 | 439.0 | 11.0 | 77.0 | 0.016 | 0.06 | 0.67 |
| 泰丰优2098 Taifengyou 2098 | 迟熟晚籼LILM | 811.0 | 204.0 | 214.0 | 11.1 | 47.0 | 0.017 | 1.01 | 1.04 |
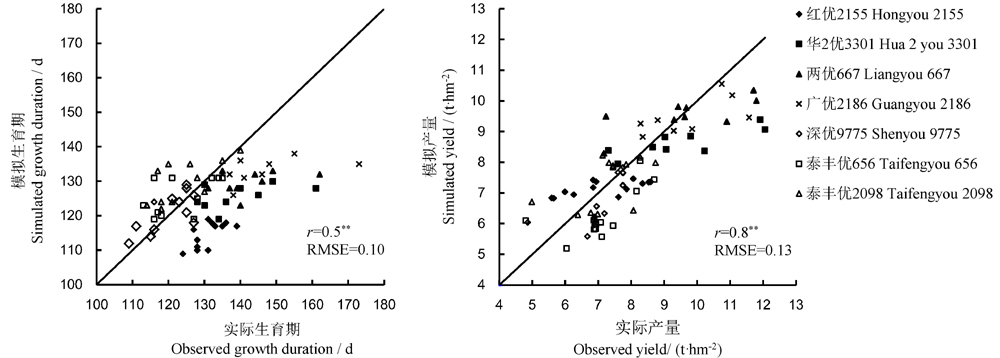
图2 CERES-Rice模型在福建省主要稻区的验证结果**表示在0.01水平上显著相关。
Fig. 2. Verification results of CERES-Rice model in the main ricegrowing regions in Fujian Province, China. **, Significant correlation at 0.01 level.
| 稻区 Rice region | 品种类型 Varietal type | RCP4.5 | RCP8.5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模拟产量 Simulated yield /(kg∙hm-2) | 稳产性指标ΔSD% | 模拟产量 Simulated yield /(kg∙hm-2) | 稳产性指标ΔSD% | |||
| 闽东南双季稻区 Double-cropping rice region in southeastern Fujian | 早熟晚籼 LIEM | 4495.8 | 8.6 | 4842.7 | 11.3 | |
| 中熟晚籼 LIMM | 5533.8 | 9.7 | 5983.0 | 18.4 | ||
| 晚熟晚籼 LILM | 6045.1 | 4.3 | 6133.4 | 5.7 | ||
| 闽西北双季稻区 Double-cropping rice region in northwestern Fujian | 早熟晚籼 LIEM | 4948.1 | 9.5 | 5277.2 | 9.0 | |
| 中熟晚籼 LIMM | 5843.6 | 12.2 | 6235.2 | 18.3 | ||
| 晚熟晚籼 LILM | 6268.4 | 3.2 | 6336.8 | 4.1 | ||
| 闽西北山地单季稻区 Single-cropping rice region In hilly area of northwestern Fujian | 早熟中籼 MIEM | 9305.2 | 1.7 | 9465.4 | 2.4 | |
| 中熟中籼 MIMM | 7429.8 | 11.4 | 7698.0 | 14.6 | ||
| 晚熟中籼 MILM | 10079.3 | 2.0 | 10205.9 | 2.6 | ||
表2 基于两种气候变化情景下福建省各稻区不同品种类型的模拟产量及稳产性指标
Table 2 Simulated yieldsand stability index(ΔSD%) for variousvarietal types under the tworepresentative concentration pathway(RCP) scenarios in different rice growing regions of Fujian Province.
| 稻区 Rice region | 品种类型 Varietal type | RCP4.5 | RCP8.5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模拟产量 Simulated yield /(kg∙hm-2) | 稳产性指标ΔSD% | 模拟产量 Simulated yield /(kg∙hm-2) | 稳产性指标ΔSD% | |||
| 闽东南双季稻区 Double-cropping rice region in southeastern Fujian | 早熟晚籼 LIEM | 4495.8 | 8.6 | 4842.7 | 11.3 | |
| 中熟晚籼 LIMM | 5533.8 | 9.7 | 5983.0 | 18.4 | ||
| 晚熟晚籼 LILM | 6045.1 | 4.3 | 6133.4 | 5.7 | ||
| 闽西北双季稻区 Double-cropping rice region in northwestern Fujian | 早熟晚籼 LIEM | 4948.1 | 9.5 | 5277.2 | 9.0 | |
| 中熟晚籼 LIMM | 5843.6 | 12.2 | 6235.2 | 18.3 | ||
| 晚熟晚籼 LILM | 6268.4 | 3.2 | 6336.8 | 4.1 | ||
| 闽西北山地单季稻区 Single-cropping rice region In hilly area of northwestern Fujian | 早熟中籼 MIEM | 9305.2 | 1.7 | 9465.4 | 2.4 | |
| 中熟中籼 MIMM | 7429.8 | 11.4 | 7698.0 | 14.6 | ||
| 晚熟中籼 MILM | 10079.3 | 2.0 | 10205.9 | 2.6 | ||
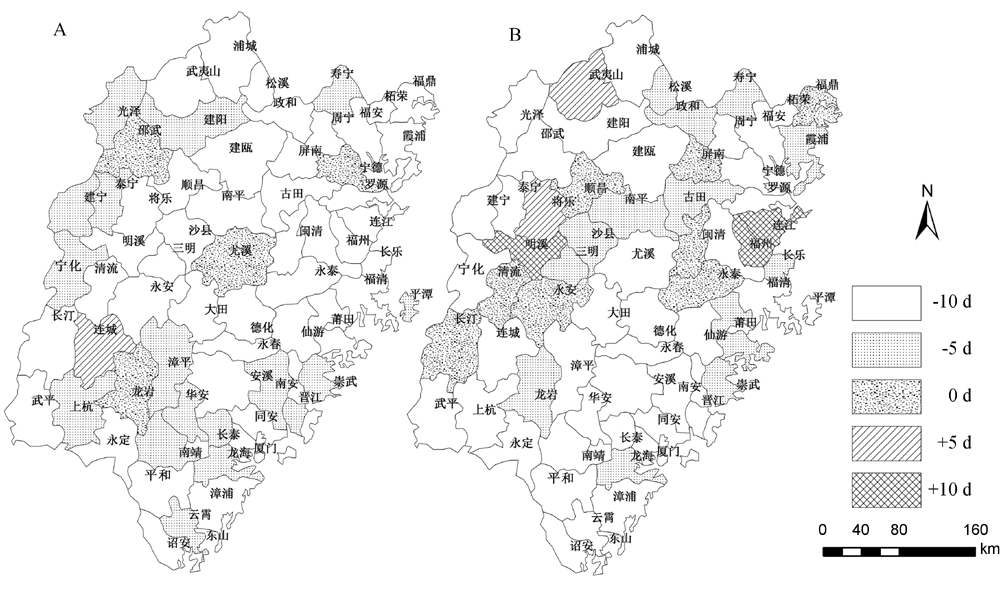
图3 基于两种气候变化情景下福建省早稻和单季稻区各样点最佳播期的可能改变 A–RCP4.5情景; B–RCP8.5情景;–10d, –5d, 0d, +5d和+10d分别指播期提前10d、提前5d、与当前相同、推迟5d和推迟10d。图4中的缩写与图3相同。
Fig. 3. Changes in proper sowing dates of early rice and single-cropping rice under the two representative concentration pathway(RCP) scenarios in Fujian Province, China. A, RCP4.5 scenario; B, RCP8.5 scenario; –10d,–5d, 0d, +5d and +10d represent 10 days advanced, 5 days advanced, the same with the baseline, 5 days delayed and 10 days delayed, respectively. The same as those in Fig. 4.
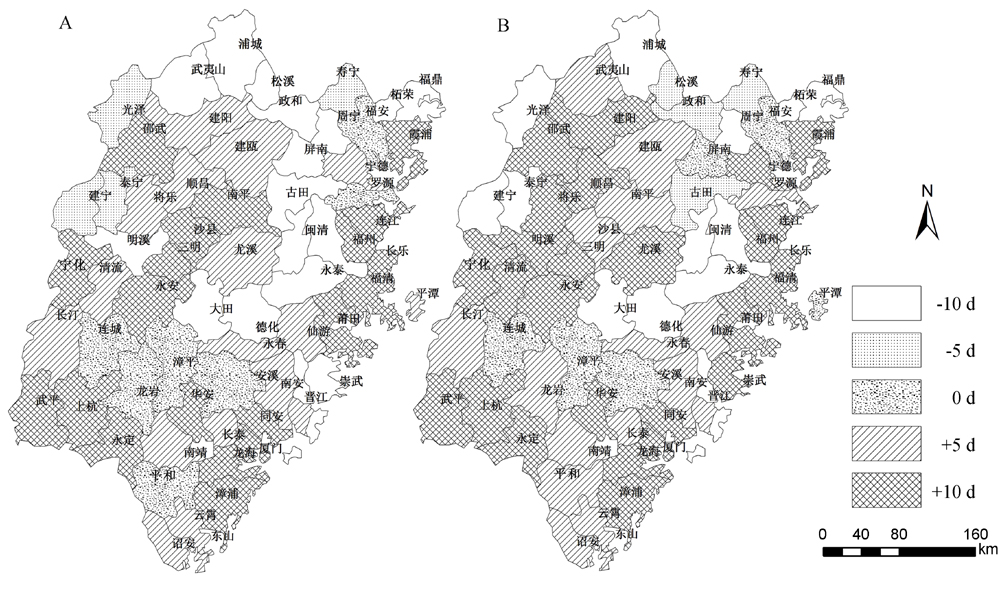
图4 基于两种气候变化情景下福建省晚稻和单季稻区各样点最佳播期的可能改变
Fig. 4. Changes in proper sowing dates of late rice and single-cropping rice under the two representative concentration pathway(RCP) scenarios in Fujian Province, China.
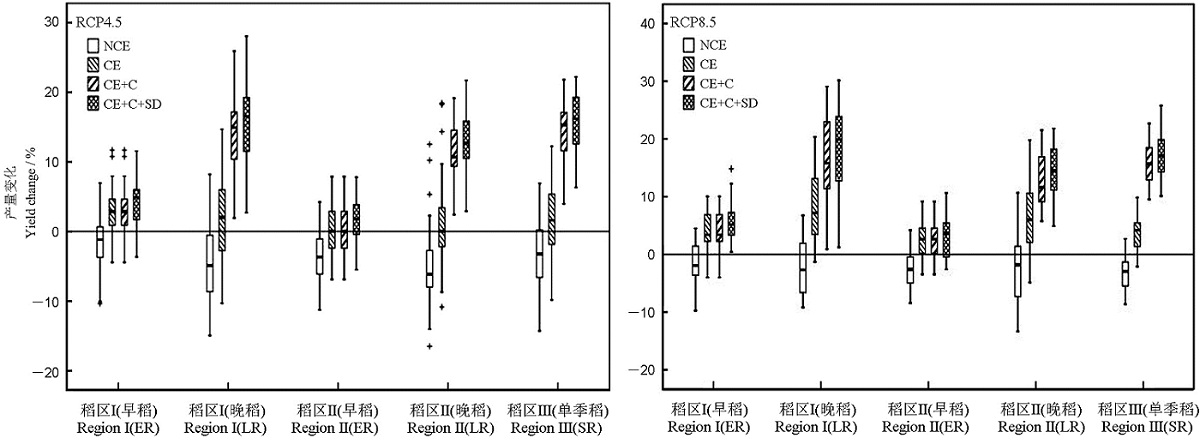
图5 两种气候变化情景下福建省不同稻区在适应性调整后水稻模拟产量相对于基准时段的变化稻区Ⅰ–闽东南双季稻区; 稻区Ⅱ–闽西北双季稻区; 稻区Ⅲ–闽西北山地单季稻区; ER–早稻; LR–晚稻; SR–单季稻; NCE–不考虑CO2肥效作用时气候变化的影响;CE–考虑CO2肥效作用时气候变化的影响;CE+C–考虑CO2肥效作用时气候变化影响+优化品种;CE+C+SD–考虑CO2肥效作用时气候变化影响+优化品种+播期调整。
Fig. 5. Change in rice yields under the tworepresentative concentration pathway(RCP) scenarioswithadaptive adjustments compared with the base yields in different rice growing regions in Fujian Province, China. RegionⅠ, Double-cropping rice region in Southeastern Fujian;RegionⅡ, Double-cropping rice region in Northwestern Fujian; Region Ⅲ, Single-cropping rice region in mountain area of Northwestern Fujian; ER, Early rice; LR, Late rice; SR, Single-cropping rice;NCE, Without taking into consideration CO2 fertilization effect; CE, Taking into consideration CO2 fertilization effect; CE+C, Combined effects of CE and optimized in cultivar; CE+C+SD, Combined effects of CE+C and adjustments in sowing date
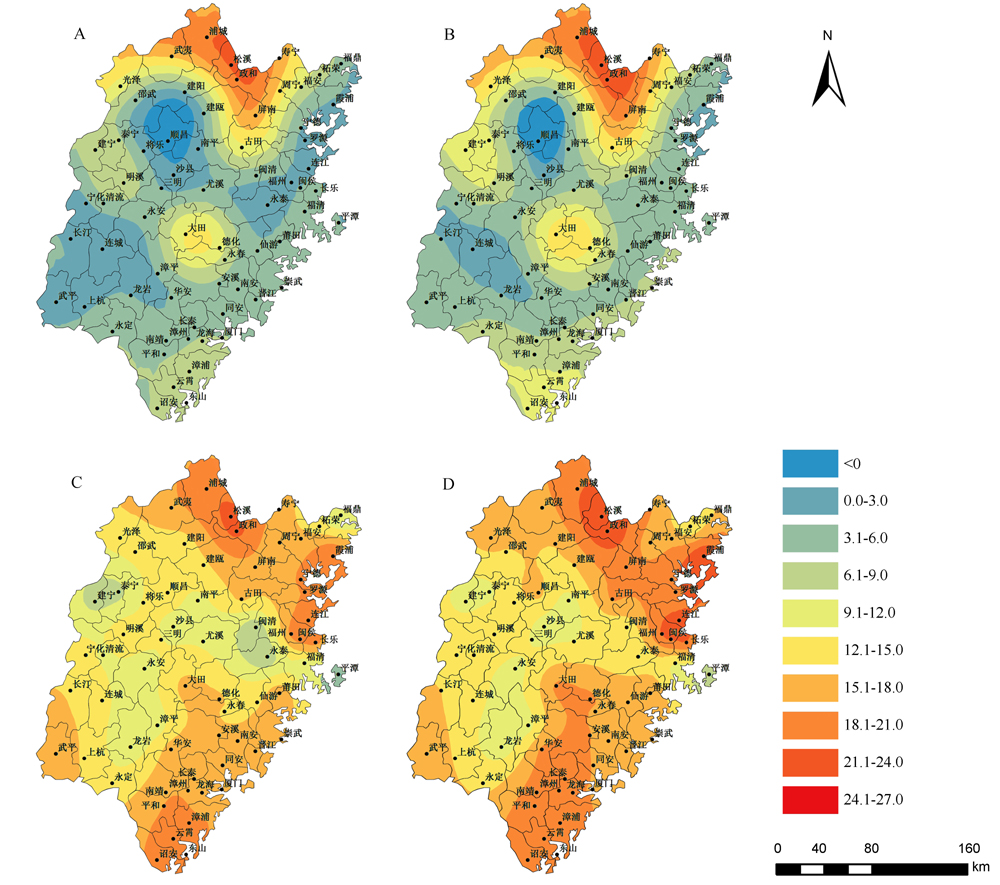
图6 两种排放情景下福建省各稻区水稻在考虑适应调整前后的产量相较基准时段产量的变化 A和B–早稻和单季稻种植区;C和D–晚稻和单季稻种植区;其中A和C是RCP4.5情景,B、D是RCP8.5情景。
Fig. 6. Change in rice yields underthe two representative concentration pathway(RCP) scenarioswith adaptive adjustments compared with the base yieldsin different rice growing regions in Fujian Province, China. A and B, Early rice and single-cropping rice region; C and D, Late rice and single-cropping rice region; A and C, RCP4.5 scenario; B and D, RCP8.5 scenario.
| 稻区 Rice region growing | 样点 Site | RCP4.5 | RCP8.5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 品种搭配 Variety collocation | 播种日期 Sowing date | 品种搭配 Variety collocation | 播种日期 Sowing date | ||||||
| 闽东南双季稻区 Double-cropping rice region in southeastern Fujian | 闽清、永泰 Minqing,Yongtai | 晚熟早籼+中熟晚籼 EILM+LIMM | 提前10d+提前10d 10 days advanced +10 days advanced | 晚熟早籼+中熟晚籼 EILM+LIMM | 提前10d+提前10d 10 days advanced +10 days advanced | ||||
| 其余样点 The rest sites | 晚熟早籼+晚熟晚籼 EILM+LILM | 提前10d+推迟10d 10 days advanced +10 days delayed | 晚熟早籼+晚熟晚籼 EILM+LILM | 提前10d+推迟10d 10 days advanced +10 days delayed | |||||
| 闽西北双季稻区 Double-cropping rice region in northwestern Fujian | 福鼎 Fuding | 晚熟早籼+中熟晚籼 EILM+LIMM | 提前10d+提前10d 10 days advanced +10 days advanced | 晚熟早籼+中熟晚籼 EILM+LIMM | 提前10d+提前10d 10 days advanced +10 days advanced | ||||
| 其余样点 The rest sites | 晚熟早籼+晚熟晚籼 EILM+LILM | 提前10d+推迟10d 10 days advanced +10 days delayed | 晚熟早籼+晚熟晚籼 EILM+LILM | 提前10d+推迟10d 10 days advanced +10 days delayed | |||||
| 闽西北山地单季稻区 SCR | 所有样点 All sites | 晚熟中籼 MILM | 提前10d 10 days advanced | 晚熟中籼 MILM | 提前10d 10 days advanced | ||||
表3 未来两种气候变化情景下福建省适应性调整后的水稻生产方式及管理措施
Table 3 Rice production patterns and managements with adaptive adjustments under the two representative concentration pathway(RCP) scenarios in different rice growing regions of Fujian Province, China.
| 稻区 Rice region growing | 样点 Site | RCP4.5 | RCP8.5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 品种搭配 Variety collocation | 播种日期 Sowing date | 品种搭配 Variety collocation | 播种日期 Sowing date | ||||||
| 闽东南双季稻区 Double-cropping rice region in southeastern Fujian | 闽清、永泰 Minqing,Yongtai | 晚熟早籼+中熟晚籼 EILM+LIMM | 提前10d+提前10d 10 days advanced +10 days advanced | 晚熟早籼+中熟晚籼 EILM+LIMM | 提前10d+提前10d 10 days advanced +10 days advanced | ||||
| 其余样点 The rest sites | 晚熟早籼+晚熟晚籼 EILM+LILM | 提前10d+推迟10d 10 days advanced +10 days delayed | 晚熟早籼+晚熟晚籼 EILM+LILM | 提前10d+推迟10d 10 days advanced +10 days delayed | |||||
| 闽西北双季稻区 Double-cropping rice region in northwestern Fujian | 福鼎 Fuding | 晚熟早籼+中熟晚籼 EILM+LIMM | 提前10d+提前10d 10 days advanced +10 days advanced | 晚熟早籼+中熟晚籼 EILM+LIMM | 提前10d+提前10d 10 days advanced +10 days advanced | ||||
| 其余样点 The rest sites | 晚熟早籼+晚熟晚籼 EILM+LILM | 提前10d+推迟10d 10 days advanced +10 days delayed | 晚熟早籼+晚熟晚籼 EILM+LILM | 提前10d+推迟10d 10 days advanced +10 days delayed | |||||
| 闽西北山地单季稻区 SCR | 所有样点 All sites | 晚熟中籼 MILM | 提前10d 10 days advanced | 晚熟中籼 MILM | 提前10d 10 days advanced | ||||
| 稻区 Rice region | 稻作类型 Rice pattern | RCP4.5 | RCP8.5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不考虑适应性调整 Without adaptive adjustment | 考虑适应性调整 With adaptive adjustment | 不考虑适应性调整 Without adaptive adjustment | 考虑适应性调整 With adaptive adjustment | ||||||
| 对总产量变化的贡献率 Contribution to change in overall rice output / % | |||||||||
| 闽东南双季稻区 Double-cropping rice region in southeastern Fujian | 早稻Early rice | 0.31 | 0.50 | 0.45 | 0.67 | ||||
| 后季稻Late rice | 0.20 | 1.53 | 0.75 | 1.73 | |||||
| 闽西北双季稻区 Double-cropping rice region in northwestern Fujian | 早稻Early rice | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.33 | ||||
| 后季稻Late rice | 0.25 | 2.04 | 0.98 | 2.21 | |||||
| 闽西北山地单季稻区 Single-cropping rice region in hilly area of northwestern Fujian | 单季稻Single rice | –0.16 | 5.00 | 0.63 | 5.60 | ||||
| 总产量变化Change in overall rice output / % | 0.66 | 9.25 | 3.05 | 10.54 | |||||
表4 两种气候变化情景下考虑与不考虑适应性调整各稻区水稻模拟总产对全省水稻总产的贡献
Table 4 Contribution of overall rice output of rice growing regions toFujian Province with adaptive adjustment and without adaptive adjustment under the tworepresentative concentration pathway(RCP) scenarios.
| 稻区 Rice region | 稻作类型 Rice pattern | RCP4.5 | RCP8.5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不考虑适应性调整 Without adaptive adjustment | 考虑适应性调整 With adaptive adjustment | 不考虑适应性调整 Without adaptive adjustment | 考虑适应性调整 With adaptive adjustment | ||||||
| 对总产量变化的贡献率 Contribution to change in overall rice output / % | |||||||||
| 闽东南双季稻区 Double-cropping rice region in southeastern Fujian | 早稻Early rice | 0.31 | 0.50 | 0.45 | 0.67 | ||||
| 后季稻Late rice | 0.20 | 1.53 | 0.75 | 1.73 | |||||
| 闽西北双季稻区 Double-cropping rice region in northwestern Fujian | 早稻Early rice | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.33 | ||||
| 后季稻Late rice | 0.25 | 2.04 | 0.98 | 2.21 | |||||
| 闽西北山地单季稻区 Single-cropping rice region in hilly area of northwestern Fujian | 单季稻Single rice | –0.16 | 5.00 | 0.63 | 5.60 | ||||
| 总产量变化Change in overall rice output / % | 0.66 | 9.25 | 3.05 | 10.54 | |||||
| [1] | IPCC. Climate Change 2014:Impacts,adaptation,and vulnerability.Cambridge:Cambridge University Press,2014. |
| [2] | Rosenzweig C,Elliott J, Deryng D, Ruane A C, Muller C, Arneth A, Boote K J, Folberth C, Glotter M, Khabarov N, Neumann K, Piontek F, Thomas A M, Schmid E, Stehfest E, Yang H, Jones J W.Assessing agricultural risks of climate change in the 21st century in a global gridded crop model intercomparison.Proc NatlAcadSci USA,2014, 111(9):3268-3273. |
| [3] | 张建平,赵艳霞,王春乙,何勇. 未来气候变化情景下中国主要粮食作物产量变化模拟. 干旱地区农业研究,2007,25(5):208-213. |
| Zhang J P, Zhao Y X, Wang C Y, He Y.Simulation of the yields change of China' main crops under climate change scenario. Agric Res Arid Areas,2007,25(5):208-213. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 杨沈斌, 申双和, 赵小艳, 赵艳霞, 许吟隆, 王主玉, 刘娟, 张玮玮. 气候变化对长江中下游稻区水稻产量的影响. 作物学报, 2010,36(9):1519-1528. |
| Yang S B, Shen S H, Zhao X Y, Zhao Y X, Xu Y L, Wang Z Y, Liu J, Zhang W W.Impacts of climate changes on rice production in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River.ActaAgron Sin, 2010,36(9):1519-1528. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Chun J A, Li S, Wang Q, Lee W S, Lee E J.Assessing rice productivity and adaptation strategies for Southeast Asia under climate change though multi-scale crop modeling.AgricSyst,2016,143:14-21. |
| [6] | 周曙东, 周文魁, 朱红根, 王传星, 王艳. 气候变化对农业的影响及应对措施. 南京农业大学学报: 社会科学版, 2010,10(1):34-39. |
| Zhou S D, Zhou W K, Zhu H G, Wang C X, Wang Y.Impact of climate change on agriculture and its countermeasures.J Nanjing AgricUniv: SociSci Ed, 2010, 10(1): 34-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 杨晓光, 刘志娟, 陈阜. 全球气候变暖对中国种植制度可能影响: Ⅰ. 气候变暖对中国种植制度北界和粮食产量的可能影响分析. 中国农业科学, 2010,43(2):329-336. |
| Yang X G, Liu Z J, Chen F,.The possible effects of global warming on cropping systems in China:Ⅰ. The possible effects of climatic warming on northern limits of cropping systems and crop yields in China.SciAgricSin,2010,43(2):329-336. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 肖风劲, 张海东, 王春乙. 气候变化对我国农业的可能影响及适应性对策. 自然灾害学报, 2006,15(6):327-331. |
| Xiao F J, Zhang H D, Wang C Y.Impact of climatic change on agriculture and its adaptation countermeasures in China. JNat Disas,2006,15(6):327-331. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 孙白妮, 门艳忠, 姚凤梅. 气候变化对农业影响评价方法研究进展. 环境科学与管理, 2007,32(6):165-168. |
| Sun B N, Men Y Z, Yao F M.Advancement of study on assessing impacts of climate change on agriculture.Environ SciManag, 2007, 32(6): 165-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 房世波, 沈斌, 谭凯炎, 高西宁. 大气CO2和温度升高对农作物生理及生产的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2010, 15(5):1116-1124. |
| Fang S B, Shen B, Tan K Y, Gao X N.Effect of elevated CO2 concentration and increased temperature on physiology and production of crops.Chin J Eco-Agric, 2010, 15(5):1116-1124. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 秦鹏程, 姚凤梅, 曹秀霞, 张佳华, 曹倩. 利用作物模型研究气候变化对农业影响的发展过程. 中国农业气象, 2011,32(2):240-245. |
| Qin P C, Yao F M, Cao X X, Zhang J H, Cao Q.Development process of modeling impacts of climate change on agricultural productivity based on crop models.Chin J Agrometeorol, 2011, 32(2): 240-245. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 石春林, 冯慧慧, 金之庆, 王华. 水稻发育期模型的比较. 中国水稻科学, 2010,24(3):303-308. |
| Shi C L, Feng H H, Jin Z Q, Wang H.Comparison of phasic development models in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2010, 24(3): 303-308. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 姚凤梅, 秦鹏程, 张佳华, 林而达, Boken V.基于模型模拟气候变化对农业影响评估的不确定性及处理方法. 科学通报,2011, 56(8):547-555. |
| Yao F M, Qin P C, Zhang J H, Lin E D, Boken V.Uncertainties in assessing the effect of climate change on agriculture using model simulation and uncertainty processing methods.Chin Sci Bull, 2011,56(8):547-555. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 江敏,金之庆. CERES-Rice模型区域应用中遗传参数升尺度的一种方法. 中国水稻科学,2009, 23(2): 172-178. |
| Jiang M, Jin Z Q.A method to upscale the genetic parameters of CERES-Rice in regional applications.Chin J Rice Sci, 2009, 23(2): 172-178. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 叶宏宝, 石晓燕, 李东, 华珊, 徐志福. 气候变化对浙江水稻生产影响的集合模拟分析. 浙江农业学报, 2016, 28(7):1183-1192. |
| Ye H B, Shi X Y, Li D, Hua S, Xu Z F.Ensemble simulation of impacts of climate change on rice production in Zhejiang Province.ActaAgric Zhejiang, 2016, 28(7): 1183-1192. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 熊伟, 林而达, 蒋金荷, 李岩, 许吟隆. 中国粮食生产的综合影响因素分析. 地理学报,2010, 65(4):397-406. |
| Xiong W, Lin E D, Jiang J H, Li Y, Xu Y L.An integrated analysis of impact factors in determining China’s future grain production.ActaGeol Sin,2010, 65(4): 397-406. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | Osbome TM, Lawrence DM, Challinor AJ, Slingo J M, Wheeler T R.Development and assessment of a coupled crop-climate model.Global Change Biol, 2007, 13(1):169-183. |
| [18] | 马锐, 江敏, 薛昌颖, 孙彬, 周桐宇. 基于适应性调整的豫南地区水稻生产对未来气候变化的相应. 中国水稻科学, 2016,30(4):417-430. |
| Ma R, Jiang M, Xue C Y, Sun B, Zhou T Y.Response of rice to future climate change based on adaptive adjustment in southern Henan Province,Chin J Rice Sci, 2016,30(4):417-430. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 王连喜, 刘静, 李琪, 钱蕊. 气候变化对宁夏水稻的影响及适应性研究. 地球科学进展, 2013,28(11):1248-1256. |
| Wang L X, Liu J, Li Q, Qian R.Simulation study of the climate change impact on the rice and its adaptability in Ningxia.Adv Earth Sci, 2013,28(11):1248-1256. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Moss R H, Edmonds J A, Hibbard K A, Manning M R, Rose S K.The next generation of scenarios for climate research and assessment.Nature,2010, 463:747-756. |
| [21] | HoogenboomG, Jones J W,Wilkens P W, Porter C Q, Boote K, Hunt L D, Singh U. Decision Support System for Agrotechnology Transfer (DSSAT) Version 4. 6. Washington:DSSAT Foundation,Prosser,2014. |
| [22] | JonesJW, Hoogenboom G,Porter C H, Boote K J, Batchelor W D. DSSAT Cropping System Model.Eur JAgron,2003,18(3/4):235-265. |
| [23] | Ritchie JT, Alocilja EC, Uehara G.IBSNAT/CERES-Rice model.Agrotechnol Transfer, 1986, 3:1-5. |
| [24] | He J Q,Jones J W,Graham W D, et al.Influence of likelihood function choice for estimating crop model parameters using the generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation method.AgricSyst,2010,103(5):256-264. |
| [25] | 孙睿, 梁璐, 杨玲. 基于气象站资料的中国地区太阳日辐射量算法研究. 气象与环境科学, 2007,30(1):24-27. |
| Sun R, Liang L, Yang L.Estimation of daily solar radiation in China based on weather station data.Meteorol Environ Sci, 2007,30(1):24-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | Long S P, Ainsworth E A, Leakey A D B,Nosberger J, Ort D R. Food for thought: lower-than-expected crop yield simulation with rising CO2 concentrations.Science,2006,312:1918-1921. |
| [27] | 谢立勇,林而达. 二氧化碳浓度增高对稻、麦品质影响研究进展. 应用生态学报,2007,18(3):659-664. |
| Xie L Y, Lin E D.Effects of CO2 enrichment on grain quality of rice and wheat: A research review.Chin J ApplEcol, 2007,18(3): 659-664. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 郭尔静, 杨晓光, 王晓煜, 张天一, 黄晚华, 刘子琪, Tao L.湖南省双季稻产量差时空分布特征. 中国农业科学, 2017,50(2):399-412. |
| Guo E J, Yang X G, Wang X Y, Zhang T Y, Liu Z Q, Tao L.Spatial-temporal distribution of double cropping rice’s yield gap in Hunan Province.SciAgric Sin, 2017, 50(2): 399-412. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 张强, 邓振镛, 赵映东, 乔娟. 全球气候变化对中国西北地区农业的影响. 生态学报,2008, 28(3):1210-1218. |
| Zhang Q, Deng Z Y, Zhao Y D, Qiao J.The impacts of global climatic change on the agriculture in northwest China.ActaEcol Sin, 2008, 28(3): 1210-1218. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 江敏, 金之庆, 石春林, 林文雄. 福建省基于自适应调整的水稻生产对未来气候变化的响应. 作物学报, 2012,38(12):2246-2257. |
| Jiang M, Jin Z Q, Shi C L, Lin W X.Response of rice production based on self-adaption to climate change in Fujian Province.ActaAgron Sin, 2012,38(12):2246-2257. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||