
中国水稻科学 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 207-218.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7120
• 研究报告 • 下一篇
周梦玉, 宋昕蔚, 徐静, 付雪, 李婷, 朱雨晨, 肖幸运, 毛一剑, 曾大力, 胡江, 朱丽, 任德勇, 高振宇, 郭龙彪, 钱前, 吴明国, 林建荣*( ), 张光恒*(
), 张光恒*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-09-27
修回日期:2018-01-23
出版日期:2018-05-10
发布日期:2018-05-10
通讯作者:
林建荣,张光恒
基金资助:
Mengyu ZHOU, Xinwei SONG, Jing XU, Xue FU, Ting LI, Yuchen ZHU, Xingyun XIAO, Yijian MAO, Dali ZENG, Jiang HU, Li ZHU, Deyong REN, Zhenyu GAO, Longbiao GUO, Qian QIAN, Mingguo WU, Jianrong LIN*( ), Guangheng ZHANG*(
), Guangheng ZHANG*( )
)
Received:2017-09-27
Revised:2018-01-23
Online:2018-05-10
Published:2018-05-10
Contact:
Jianrong LIN, Guangheng ZHANG
摘要:
【目的】本研究旨在挖掘水稻粒型新基因、探索其分子机理,解析籽粒发育调控遗传网络奠定基础,并为通过分子标记聚合有利基因开展超级稻分子设计育种提供理论依据。【方法】以植株和籽粒形态差异较大的晚粳稻品种春江16B(CJ16B)和广亲和中籼稻背景恢复系C84为亲本构建含有188个家系的重组自交系为作图群体,利用158对在双亲中存在多态性差异的分子标记,构建了遗传连锁图谱,总遗传距离为1428.40cM,平均标记间距为9.04cM。在构建遗传图谱的基础上,完成RIL188个株系籽粒的粒长、粒宽、粒厚、长宽比和千粒重等5个性状考查并进行QTL定位。【结果】在海南陵水和浙江杭州两地共检测到籽粒相关主效QTL30个,包括籽粒QTL新座位18个,解释遗传变异3.51%~17.25%。其中粒长、粒宽、粒厚和长宽比QTL位点分别为9个、5个、5个和6个,千粒重QTL位点5个。经基因座位比对,发现有5个QTL区间与已克隆的调控籽粒形态相关基因座位相近,我们通过对双亲目标基因的测序并根据差异位点设计dCAPs分子标记进行验证。【结论】该RIL群体及其遗传图谱可用于水稻重要农艺性状主效QTL基因的定位和克隆,新定位的18个粒型QTL可以为水稻籽粒发育调控网络提供补充和资料积累。
中图分类号:
周梦玉, 宋昕蔚, 徐静, 付雪, 李婷, 朱雨晨, 肖幸运, 毛一剑, 曾大力, 胡江, 朱丽, 任德勇, 高振宇, 郭龙彪, 钱前, 吴明国, 林建荣, 张光恒. 籼稻C84和粳稻春江16B重组自交系遗传图谱构建及籽粒性状QTL定位与验证[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(3): 207-218.
Mengyu ZHOU, Xinwei SONG, Jing XU, Xue FU, Ting LI, Yuchen ZHU, Xingyun XIAO, Yijian MAO, Dali ZENG, Jiang HU, Li ZHU, Deyong REN, Zhenyu GAO, Longbiao GUO, Qian QIAN, Mingguo WU, Jianrong LIN, Guangheng ZHANG. Construction of Genetic Map andMapping andVerification of Grain TraitsQTLs Using Recombinant Inbred LinesDerived from a Cross BetweenindicaC84 andjaponicaCJ16B[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(3): 207-218.
| 性状 Trait | 地点 Site | 亲本Parent | 重组自交系群体RIL population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C84 | 春江16BCJ16B | 平均Mean | 范围Range | ||||
| 粒长 Grain length / mm | 杭州 Hangzhou | 8.2±0.2 | 7.4±0.2** | 7.74 | 6.4~9.0 | ||
| 陵水Lingshui | 7.8±0.1 | 7.0±0.1** | 7.56 | 6.5~8.7 | |||
| 粒宽Grain width / mm | 杭州 Hangzhou | 2.9±0.1 | 3.2±0.0** | 3.11 | 2.6~3.8 | ||
| 陵水Lingshui | 3.1±0.1 | 3.2±0.1* | 3.22 | 2.6~3.7 | |||
| 粒厚Grain thickness / mm | 杭州 Hangzhou | 1.98±0.01 | 2.26±0.04** | 2.06 | 1.79~2.38 | ||
| 陵水Lingshui | 2.03±0.04 | 2.28±0.04** | 2.08 | 1.75~2.34 | |||
| 长宽比Lengthtowidth ratio | 杭州 Hangzhou | 2.8±0.1 | 2.3±0.1* | 2.52 | 2.0~3.4 | ||
| 陵水Lingshui | 2.5±0.3 | 2.2±0.1** | 2.37 | 1.9~3.0 | |||
| 千粒重1000-grain weight / g | 杭州 Hangzhou | 23.7±0.4 | 25.1±0.3* | 22.17 | 13.8~33.2 | ||
| 陵水Lingshui | 24.1±0.1 | 25.2±0.1* | 22.98 | 13.3~30.8 | |||
表1 双亲(C84和春江16B)及其RIL群体2016年在杭州和陵水的粒长、粒宽、粒厚、长宽比及千粒重
Table 1 Grain length, width, thickness, length-to-width ratio and 1000-grain weight inC84 and CJ16Band their recombinant inbred line population in Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province and Lingshui, Hainan Province, China in 2016.
| 性状 Trait | 地点 Site | 亲本Parent | 重组自交系群体RIL population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C84 | 春江16BCJ16B | 平均Mean | 范围Range | ||||
| 粒长 Grain length / mm | 杭州 Hangzhou | 8.2±0.2 | 7.4±0.2** | 7.74 | 6.4~9.0 | ||
| 陵水Lingshui | 7.8±0.1 | 7.0±0.1** | 7.56 | 6.5~8.7 | |||
| 粒宽Grain width / mm | 杭州 Hangzhou | 2.9±0.1 | 3.2±0.0** | 3.11 | 2.6~3.8 | ||
| 陵水Lingshui | 3.1±0.1 | 3.2±0.1* | 3.22 | 2.6~3.7 | |||
| 粒厚Grain thickness / mm | 杭州 Hangzhou | 1.98±0.01 | 2.26±0.04** | 2.06 | 1.79~2.38 | ||
| 陵水Lingshui | 2.03±0.04 | 2.28±0.04** | 2.08 | 1.75~2.34 | |||
| 长宽比Lengthtowidth ratio | 杭州 Hangzhou | 2.8±0.1 | 2.3±0.1* | 2.52 | 2.0~3.4 | ||
| 陵水Lingshui | 2.5±0.3 | 2.2±0.1** | 2.37 | 1.9~3.0 | |||
| 千粒重1000-grain weight / g | 杭州 Hangzhou | 23.7±0.4 | 25.1±0.3* | 22.17 | 13.8~33.2 | ||
| 陵水Lingshui | 24.1±0.1 | 25.2±0.1* | 22.98 | 13.3~30.8 | |||
| 地点Site 性状Trait | HZ-GL | HZ-GW | HZ-GT | HZ-LWR | HZ-TGW | LS-GL | LS-GW | LS-GT | LS-LWR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 杭州 | 粒宽 GW | –0.104** | ||||||||
| Hangzhou | 粒厚 GT | 0.073** | 0.396** | |||||||
| (HZ) | 长宽比LWR | 0.672** | –0.801** | –0.248** | ||||||
| 千粒重TGW | 0.441** | 0.443** | 0.404** | –0.066** | ||||||
| 陵水 | 粒长 GL | 0.809** | ||||||||
| Lingshui | 粒宽 GW | 0.817** | –0.016** | |||||||
| (LS) | 粒厚 GT | 0.270** | 0.117** | 0.164** | ||||||
| 长宽比LWR | 0.854** | 0.660** | –0.758** | –0.030** | ||||||
| 千粒重 TGW | 0.529** | 0.438** | 0.508** | 0.287** | –0.094** | |||||
表2 C84/CJ16B重组自交系群体粒型性状间相关性分析
Table 2 Correlationship analysis on grain shape traits in C84/CJ16B recombinant inbred lines.
| 地点Site 性状Trait | HZ-GL | HZ-GW | HZ-GT | HZ-LWR | HZ-TGW | LS-GL | LS-GW | LS-GT | LS-LWR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 杭州 | 粒宽 GW | –0.104** | ||||||||
| Hangzhou | 粒厚 GT | 0.073** | 0.396** | |||||||
| (HZ) | 长宽比LWR | 0.672** | –0.801** | –0.248** | ||||||
| 千粒重TGW | 0.441** | 0.443** | 0.404** | –0.066** | ||||||
| 陵水 | 粒长 GL | 0.809** | ||||||||
| Lingshui | 粒宽 GW | 0.817** | –0.016** | |||||||
| (LS) | 粒厚 GT | 0.270** | 0.117** | 0.164** | ||||||
| 长宽比LWR | 0.854** | 0.660** | –0.758** | –0.030** | ||||||
| 千粒重 TGW | 0.529** | 0.438** | 0.508** | 0.287** | –0.094** | |||||
| 染色体 Chromosome | 物理距离 Physical distance/Mb | 遗传距离 Genetic distance /cM | 平均物理距离 Mean physical distance /Mb | 平均遗传距离 Mean genetic distance /cM | 标记数 Number of markers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 46.15 | 192.8 | 2.71 | 11.34 | 17 |
| 2 | 35.93 | 128.0 | 2.57 | 9.14 | 14 |
| 3 | 36.41 | 145.9 | 2.28 | 9.12 | 16 |
| 4 | 35.28 | 148.5 | 1.96 | 8.25 | 18 |
| 5 | 29.89 | 106.9 | 1.99 | 7.13 | 15 |
| 6 | 31.25 | 104.8 | 2.84 | 9.53 | 11 |
| 7 | 29.69 | 128.5 | 2.12 | 9.18 | 14 |
| 8 | 28.44 | 107.2 | 2.59 | 9.75 | 11 |
| 9 | 23.01 | 77.5 | 2.30 | 7.75 | 10 |
| 10 | 23.13 | 72.5 | 2.57 | 8.06 | 9 |
| 11 | 28.51 | 115.5 | 2.38 | 9.63 | 12 |
| 12 | 27.49 | 100.3 | 2.50 | 9.12 | 11 |
| 合计 Total | 375.18 | 1428.4 | 2.40 | 9.04 | 158 |
表3 本研究所用的标记在水稻12条染色体上分布
Table 3 Distribution of the markers used in the study on 12chromosomes of rice.
| 染色体 Chromosome | 物理距离 Physical distance/Mb | 遗传距离 Genetic distance /cM | 平均物理距离 Mean physical distance /Mb | 平均遗传距离 Mean genetic distance /cM | 标记数 Number of markers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 46.15 | 192.8 | 2.71 | 11.34 | 17 |
| 2 | 35.93 | 128.0 | 2.57 | 9.14 | 14 |
| 3 | 36.41 | 145.9 | 2.28 | 9.12 | 16 |
| 4 | 35.28 | 148.5 | 1.96 | 8.25 | 18 |
| 5 | 29.89 | 106.9 | 1.99 | 7.13 | 15 |
| 6 | 31.25 | 104.8 | 2.84 | 9.53 | 11 |
| 7 | 29.69 | 128.5 | 2.12 | 9.18 | 14 |
| 8 | 28.44 | 107.2 | 2.59 | 9.75 | 11 |
| 9 | 23.01 | 77.5 | 2.30 | 7.75 | 10 |
| 10 | 23.13 | 72.5 | 2.57 | 8.06 | 9 |
| 11 | 28.51 | 115.5 | 2.38 | 9.63 | 12 |
| 12 | 27.49 | 100.3 | 2.50 | 9.12 | 11 |
| 合计 Total | 375.18 | 1428.4 | 2.40 | 9.04 | 158 |
| 性状 Trait | QTL | 标记区间 Marker interval | 位置 Position | 加性效应 Additive effect | 贡献率 EPV/% | 已克隆基因 Genecloned | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZ | LS | HZ | LS | HZ | LS | |||||||||||
| 粒长 | qGL1 | RM3252 | –RM1247 | 2.0 | 0.0925 | 5.75 | ||||||||||
| Grain length | qGL2.1 | H2-2 | –H2-3 | 28.1 | –0.1539 | 9.01 | FUWA | |||||||||
| qGL2.2 | H2-5 | –H2-6 | 39.8 | –0.0804 | 7.05 | |||||||||||
| qGL5 | M17954R | –H5-7 | 32.5 | –0.1272 | 7.52 | JMJ703;SRS3/ OsKinesin-13A/sar1 | ||||||||||
| qGL7.1 | RM11 | –RM3826 | 81.0 | –0.1675 | 10.09 | |||||||||||
| qGL7.2 | RM3826 | –RM1132 | 90.7 | –0.1868 | 14.40 | |||||||||||
| qGL10 | RM6370 | –RM5689 | 14.0 | 18.0 | –0.1912 | –0.1794 | 11.97 | 10.33 | OsPCR1 | |||||||
| qGL11 | H11 | –4-H11-5 | 59.7 | 0.0768 | 5.89 | |||||||||||
| qGL12 | RM1337 | –RM3739 | 59.7 | 0.2160 | 11.04 | |||||||||||
| 粒宽 | qGW1 | H1-5 | –RM8097 | 141.6 | –0.0396 | 3.51 | ||||||||||
| Grain width | qGW2.1 | H2-6 | –H2-7 | 47.0 | 0.1134 | 9.58 | ||||||||||
| qGW2.2 | H2-7 | –RM262 | 52.7 | 0.0977 | 9.34 | |||||||||||
| qGW5 | RM17954 | –H5-7 | 27.5 | 23.5 | 0.1202 | 0.1143 | 12.28 | 11.44 | qGW5;JMJ703 | |||||||
| qGW6 | H6-2 | –RM3496 | 47.0 | 0.0728 | 7.06 | |||||||||||
| 粒厚 | qGT1 | RM8097 | –RM6703 | 163.5 | 163.5 | –0.1074 | –0.0907 | 12.75 | 12.59 | |||||||
| Grain thickness | qGT2.1 | H2-3 | –H2-4 | 33.2 | 0.0919 | 9.01 | ||||||||||
| qGT2.2 | H2-5 | –H2-6 | 41.8 | 0.0823 | 9.51 | |||||||||||
| qGT6 | wgwl | –RM3183 | 35.2 | 0.0708 | 8.21 | |||||||||||
| qGT9 | RM242 | –H9-6 | 69.3 | 0.0830 | 9.69 | |||||||||||
| 长宽比 | qGLW2.1 | H2-4 | –RM300 | 34.9 | –0.0787 | 13.88 | ||||||||||
| Length to width | qGLW2.2 | H2-5 | –H2-6 | 42.8 | –0.1332 | 15.61 | ||||||||||
| qGLW2 | H2-6 | –H2-7 | 50.0 | –0.0496 | 12.95 | |||||||||||
| qGLW5 | RM17954 | –H5-7 | 28.5 | 27.5 | –0.1598 | –0.1302 | 17.25 | 12.75 | ||||||||
| qGLW11 | RM167 | –H11-2 | 30.9 | 0.0519 | 7.79 | |||||||||||
| qGLW12 | RM1337 | –RM3739 | 51.7 | 0.0975 | 6.25 | |||||||||||
| 千粒重 | qTGW1.1 | H1-5 | –RM8097 | 144.6 | –1.1430 | 8.17 | OsTRBF3 | |||||||||
| 1000-grain | qTGW1.2 | RM8097 | –RM6703 | 148.5 | –1.0656 | 8.43 | ||||||||||
| weight | qTGW4 | RM317 | –RM5879 | 113.5 | 1.1454 | 7.41 | ||||||||||
| qTGW5 | RM18751 | –RM3476 | 85.1 | –1.2472 | 10.55 | |||||||||||
| qTGW9 | H9-4 | –RM3700 | 52.6 | –0.8719 | 4.55 | |||||||||||
表4 RILs的粒型相关性状的QTL定位结果
Table 4 QTLs for grain shape-related traits of recombinant inbred lines.
| 性状 Trait | QTL | 标记区间 Marker interval | 位置 Position | 加性效应 Additive effect | 贡献率 EPV/% | 已克隆基因 Genecloned | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZ | LS | HZ | LS | HZ | LS | |||||||||||
| 粒长 | qGL1 | RM3252 | –RM1247 | 2.0 | 0.0925 | 5.75 | ||||||||||
| Grain length | qGL2.1 | H2-2 | –H2-3 | 28.1 | –0.1539 | 9.01 | FUWA | |||||||||
| qGL2.2 | H2-5 | –H2-6 | 39.8 | –0.0804 | 7.05 | |||||||||||
| qGL5 | M17954R | –H5-7 | 32.5 | –0.1272 | 7.52 | JMJ703;SRS3/ OsKinesin-13A/sar1 | ||||||||||
| qGL7.1 | RM11 | –RM3826 | 81.0 | –0.1675 | 10.09 | |||||||||||
| qGL7.2 | RM3826 | –RM1132 | 90.7 | –0.1868 | 14.40 | |||||||||||
| qGL10 | RM6370 | –RM5689 | 14.0 | 18.0 | –0.1912 | –0.1794 | 11.97 | 10.33 | OsPCR1 | |||||||
| qGL11 | H11 | –4-H11-5 | 59.7 | 0.0768 | 5.89 | |||||||||||
| qGL12 | RM1337 | –RM3739 | 59.7 | 0.2160 | 11.04 | |||||||||||
| 粒宽 | qGW1 | H1-5 | –RM8097 | 141.6 | –0.0396 | 3.51 | ||||||||||
| Grain width | qGW2.1 | H2-6 | –H2-7 | 47.0 | 0.1134 | 9.58 | ||||||||||
| qGW2.2 | H2-7 | –RM262 | 52.7 | 0.0977 | 9.34 | |||||||||||
| qGW5 | RM17954 | –H5-7 | 27.5 | 23.5 | 0.1202 | 0.1143 | 12.28 | 11.44 | qGW5;JMJ703 | |||||||
| qGW6 | H6-2 | –RM3496 | 47.0 | 0.0728 | 7.06 | |||||||||||
| 粒厚 | qGT1 | RM8097 | –RM6703 | 163.5 | 163.5 | –0.1074 | –0.0907 | 12.75 | 12.59 | |||||||
| Grain thickness | qGT2.1 | H2-3 | –H2-4 | 33.2 | 0.0919 | 9.01 | ||||||||||
| qGT2.2 | H2-5 | –H2-6 | 41.8 | 0.0823 | 9.51 | |||||||||||
| qGT6 | wgwl | –RM3183 | 35.2 | 0.0708 | 8.21 | |||||||||||
| qGT9 | RM242 | –H9-6 | 69.3 | 0.0830 | 9.69 | |||||||||||
| 长宽比 | qGLW2.1 | H2-4 | –RM300 | 34.9 | –0.0787 | 13.88 | ||||||||||
| Length to width | qGLW2.2 | H2-5 | –H2-6 | 42.8 | –0.1332 | 15.61 | ||||||||||
| qGLW2 | H2-6 | –H2-7 | 50.0 | –0.0496 | 12.95 | |||||||||||
| qGLW5 | RM17954 | –H5-7 | 28.5 | 27.5 | –0.1598 | –0.1302 | 17.25 | 12.75 | ||||||||
| qGLW11 | RM167 | –H11-2 | 30.9 | 0.0519 | 7.79 | |||||||||||
| qGLW12 | RM1337 | –RM3739 | 51.7 | 0.0975 | 6.25 | |||||||||||
| 千粒重 | qTGW1.1 | H1-5 | –RM8097 | 144.6 | –1.1430 | 8.17 | OsTRBF3 | |||||||||
| 1000-grain | qTGW1.2 | RM8097 | –RM6703 | 148.5 | –1.0656 | 8.43 | ||||||||||
| weight | qTGW4 | RM317 | –RM5879 | 113.5 | 1.1454 | 7.41 | ||||||||||
| qTGW5 | RM18751 | –RM3476 | 85.1 | –1.2472 | 10.55 | |||||||||||
| qTGW9 | H9-4 | –RM3700 | 52.6 | –0.8719 | 4.55 | |||||||||||
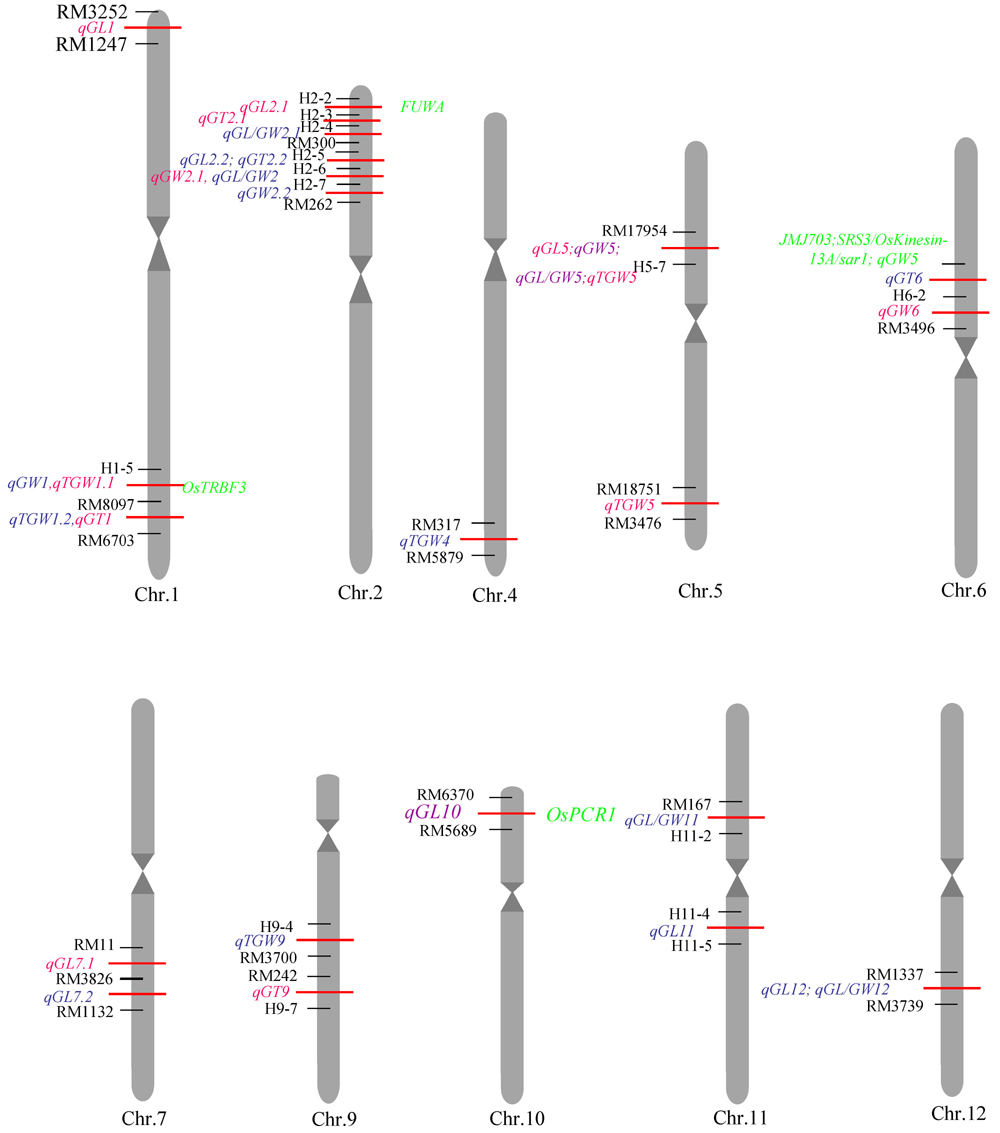
图2 水稻粒型相关性状QTL在染色体上的分布染色体左端红色标注为2016年杭州检测到的QTL位点;蓝色标注为2016年陵水检测到的QTL位点;右侧绿色标注为该区间内已报道水稻相关克隆基因。
Fig.2. Distribution of QTLs related to grain shape traits in rice chromosome. Red labels indicated the QTLs detected in Hangzhou in 2016, and the blue labelsthe QTLs detected in Lingshui in 2016, the green labels indicated rice-related cloned genes in the interval.
| 基因名称基因登录号 Gene name Gene ID | 位置 Location | 春江16B CJ16B | 春江16B-AA CJ16B-AA | C84 | C84-AA | 变异类型 Variation type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FUWALOC_Os02g13950 | 9-11 | CCT | Pro | F | ||
| 120 | A | AAA/Lys | G | AAG/Lys | Si | |
| qSW5 LOC_Os05g09520 | 986 | C | CCG/Pro | T | CTG/Leu | S |
| 1014 | G | CGC/Arg | T | CTC/Leu | S | |
| 1072 | G | GCG/Ala | A | ACG/Thr | S | |
| 1100 | C | GCG/Ala | T | GTG/Val | S | |
| OsPCR1 LOC_Os10g02300 | 172 | G | GCC/Ala | T | TCC/Ser | S |
| 467 | A | CAC/His | T | CTC/Leu | S | |
| 507-509 | GAG | F | ||||
| 559-561 | TAA | STOP | CAC | His | S | |
| SRS3LOC_Os05g06280 /Kinesin-13A /Sar1 | 1189 | C | CTG/Leu | T | TTG/Leu | Si |
| 2420 | G | CGT/Arg | A | CAT/His | S | |
| 2505 | A | GAA/Glu | C | GAC/Asp | S | |
| OsTRBF3 LOC_Os01g51154 | 542 | G | TGA/STOP | T | TTA/Leu | S |
| 547-548 | CC | CCA/Pro | AG | AGA/Arg | S | |
| 554 | T | TTT/Phe | A | TAT/Tyr | S | |
| 556-557 | TG | TGG/Trp | GT | GTG/Val | S | |
| 561 | T | CAT/His | G | CAG/Gln | S | |
| 565 | G | GGG/Gly | A | AGG/Arg | S |
表5 双亲(C84和春江16B)已克隆粒型主效QTL等位基因序列差异分析
Table 5 Sequence variance analysis of the cloned grain shape main effect QTL allele in the two parents (C84 and CJ16B).
| 基因名称基因登录号 Gene name Gene ID | 位置 Location | 春江16B CJ16B | 春江16B-AA CJ16B-AA | C84 | C84-AA | 变异类型 Variation type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FUWALOC_Os02g13950 | 9-11 | CCT | Pro | F | ||
| 120 | A | AAA/Lys | G | AAG/Lys | Si | |
| qSW5 LOC_Os05g09520 | 986 | C | CCG/Pro | T | CTG/Leu | S |
| 1014 | G | CGC/Arg | T | CTC/Leu | S | |
| 1072 | G | GCG/Ala | A | ACG/Thr | S | |
| 1100 | C | GCG/Ala | T | GTG/Val | S | |
| OsPCR1 LOC_Os10g02300 | 172 | G | GCC/Ala | T | TCC/Ser | S |
| 467 | A | CAC/His | T | CTC/Leu | S | |
| 507-509 | GAG | F | ||||
| 559-561 | TAA | STOP | CAC | His | S | |
| SRS3LOC_Os05g06280 /Kinesin-13A /Sar1 | 1189 | C | CTG/Leu | T | TTG/Leu | Si |
| 2420 | G | CGT/Arg | A | CAT/His | S | |
| 2505 | A | GAA/Glu | C | GAC/Asp | S | |
| OsTRBF3 LOC_Os01g51154 | 542 | G | TGA/STOP | T | TTA/Leu | S |
| 547-548 | CC | CCA/Pro | AG | AGA/Arg | S | |
| 554 | T | TTT/Phe | A | TAT/Tyr | S | |
| 556-557 | TG | TGG/Trp | GT | GTG/Val | S | |
| 561 | T | CAT/His | G | CAG/Gln | S | |
| 565 | G | GGG/Gly | A | AGG/Arg | S |
| 基因名称 Gene name | 位置 Location | 限制性内切酶Restriction enzyme | 酶切位点Enzyme cutting site | 引物Primer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FUWA | 120 | SalⅠ | GTCGAC | F: ACGACGACGACGACGACGAAGGAACCCGCGTCGA |
| R: CCTCCTCCTCCTCCTCCTC | ||||
| OsPCR1 | 467 | StuⅠ | AGGCCT | F: TCGCACAGATGCACCGTGAGCTCAAGAACCGAGGCC |
| R: GTGTTGGGGAGGAGTCATCA | ||||
| OsTRBF3 | 565 | MaeⅡ | ACGT | F: ATCCTTCTTTGGACTTGGAGACTTATTTGCTTACG |
| R: TGCTTCTAGGGCAGGACTCG | ||||
| qGW5 | 986 | HaeⅢ | GGCC | F: CGAGGACTGGTGCGCCAACTCCATGTCGTGGC |
| R: GTTGGACATGTAGTTCGGGC | ||||
| SRS3/OsKinesin-13A/sar1 | 1189 | HindⅢ | AAGCTT | F: CGCCGCGCAGCTCGAGCTCTAAAGCT |
| R: GGTTTCAGCATCGCCTCAAA |
表6 双亲目标基因差异位点dCAPs分子标记引物设计
Table 6 dCAPsmolecular marker designed according totarget gene differencesite of the two parents C84 and CJ16B.
| 基因名称 Gene name | 位置 Location | 限制性内切酶Restriction enzyme | 酶切位点Enzyme cutting site | 引物Primer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FUWA | 120 | SalⅠ | GTCGAC | F: ACGACGACGACGACGACGAAGGAACCCGCGTCGA |
| R: CCTCCTCCTCCTCCTCCTC | ||||
| OsPCR1 | 467 | StuⅠ | AGGCCT | F: TCGCACAGATGCACCGTGAGCTCAAGAACCGAGGCC |
| R: GTGTTGGGGAGGAGTCATCA | ||||
| OsTRBF3 | 565 | MaeⅡ | ACGT | F: ATCCTTCTTTGGACTTGGAGACTTATTTGCTTACG |
| R: TGCTTCTAGGGCAGGACTCG | ||||
| qGW5 | 986 | HaeⅢ | GGCC | F: CGAGGACTGGTGCGCCAACTCCATGTCGTGGC |
| R: GTTGGACATGTAGTTCGGGC | ||||
| SRS3/OsKinesin-13A/sar1 | 1189 | HindⅢ | AAGCTT | F: CGCCGCGCAGCTCGAGCTCTAAAGCT |
| R: GGTTTCAGCATCGCCTCAAA |
| [1] | TianZ X,QianQ, LiuQ Q, YanM X, LiuX F, Yan C J, Liu G F, Gao Z Y, Tang S Z, Zeng D L, Wang Y H, Yu J M, Li J Y.Allelic diversities in rice starch biosynthesis lead to a diverse array of rice eating and cooking qualities.Proc NatlAcadSciUSA,2009, 106(51): 21760-21765. |
| [2] | 李孝琼, 韦宇, 高国庆, 邓国富, 郭嗣斌. 水稻遗传图谱构建及粒形相关性状的QTL定位. 南方农业学报, 2014, 45(7): 1154-1159. |
| Li X Q, Wei Y, Gao G Q, Deng G F, Guo C B.Construction of genetic map and mapping quantitative trait loci for grain shape-related traits in rice.JSouthAgric,2014, 45(7):1154-1159.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | McCouch S R,Teytelman L,Xu Y,Lobos K B, Clare K,Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z, Xing Y, Zhang Q, Kono L, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, DeClerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L.Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.) .DNA Res, 2002, 9(6):257-279. |
| [4] | Xu J C,Zhu L, Chen Y,LuC F, CaiH W.Construction of a rice molecular linkage map using a double hploid (DH) population.JGenGenom, 1994,21(3):205-214. |
| [5] | 张启军, 叶少平, 虞德容, 李平, 吕川根, 邹江石. 六张水稻遗传连锁图谱的比较分析. 西南农业学报,2005, 18(5): 584-592. |
| Zhang Q J, Ye S P, Yu D R, Li P, Lu C G, Zou J S.Comparison of six rice genetic linkage maps.Southwest China JAgricSci, 2005, 18(5): 584-592.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 庄杰云, 施勇烽, 应杰政, 鄂志国, 曾瑞珍, 陈洁, 朱智伟. 中国主栽水稻品种微卫星标记数据库的初步构建. 中国水稻科学, 2006, 20(5):460-468. |
| Zhuang J Y, Shi Y F, Ying J Z, Dong Z G, Zeng R Z, Chen J, Zhu Z W.Construction and testing of primary microsatellite database of major rice varieties in China.Chin J Rice Sci, 2006, 20(5): 460-468.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Xu J J, Zhao Q, Du P N, Xu C W,LiuQ Q, FengQ, WangB H, Tang S Z, Gu M H, Han B, Liang G H. Developing high throughput genotyped chromosome segment substitution lines based on population whole-genome re-sequencing in rice (Oryza sativa L.).BMC Genomics, 2010,11(1): 656. |
| [8] | 沈利爽, 何平, 徐云碧, 谭震波, 陆朝福, 朱立煌.水稻DH群体的分子连锁图谱及基因组分析. 植物生态学报,1998, 40(12):1115-1122. |
| Shen L S, He P, Xu Y B, Tan Z B, Lu C F, Zhu L H.Genetic molecular linkage map construction and genome analysis of rice doubled.Plant ActaEcol Sin, 1998, 40(12):1115-1122. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | Huang R Y, Jiang L G, Zheng J S, Wang T S, Huang Y M, Wang H C, Hong Z L.Genetic bases of rice grain shape: So many genes, so little known.TrendsPlant Sci, 2013, 18(4):218-226. |
| [10] | 方先文,张云辉, 肖西林,张所兵,林静,汪迎节.基于重组自交系群体的水稻粒形QTL定位. 江苏农业学报, 2017, 33(2): 241-247. |
| Fang X W, Zhang Y H, Xiao X L, Zhang S B, Lin J, Wang Y J.Mapping of QTLs for grain shape using recombinant inbred lines in rice ( Oryza sativa L.).ActaAgric Jiangsu, 2017,33(2): 241-247.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | Xia D, Zhou H, Qiu L, Jiang H, Zhang Q L, Gao G J, He Y Q.Mapping and verification of grain shape QTLs based on an advanced backcross population in rice.PloS One, 2017, 12(11):e0187553. |
| [12] | Zhao D, Li P B, Wang L Q, Sun L, Xia D, Luo L J, Gao G J, He Y Q, Zhang Q L.Genetic dissection of large grain shape in rice cultivar ‘Nanyangzhan’ and validation of a grain thickness QTL (qGT3.1) and a grain length QTL(qGL3.4).MolBreed, 2017, 37(3):42. |
| [13] | Zhou L Q,Wang Y P, Li S G.Genetic analysis and physical mapping of Lk-4 (t), a major gene controlling grain length in rice, with a BC2F2 population.Acta GenSin, 2006,33(1):72-79. |
| [14] | Wang Y X, Xiong G S, Hu J, JiangL, YuH, Fang Y X, Xu E B, Ye W J, Liu R F, Jing Y H, Zhu X D, Qian Q, Jing Y H, Xu J, Zeng L J, Xu J, Meng X B, Chen H Q, Wang Y H, Li J Y. Copy number variation at the GL7 locus contributes to grain size diversity in rice.NatGenet, 2015, 47(8):944-948. |
| [15] | Wu T, Shen Y Y, Zheng M, ChenY L, FengZ M, Liu X, Chen Z J, Wang J L, Wan J M, Yang C Y, Liu S J, Lei C L, Jiang L. Gene SGL SGL.Plant Cell Rep, 2014, 33(2):235-244. |
| [16] | Takano-Kai N, Doi K, Yoshimura A. GS3# participates in stigma exsertion as well as seed length in rice. BreedSci#, 2011, 61(3):244-250. |
| [17] | Qi P, Lin Y S, Song X J, ShenJB, HuangW, Shan J X, Zhu M Z, Jiang L W, Gao J P, Lin H X. The novel quantitative trait locus GL3.1 controls rice grain size and yield by regulating Cyclin-T1;3.Cell Res, 2012, 22(12):1666-1680. |
| [18] | Wu W,Liu X, Wang M,MeyerRS, LuoX, NdjiondjopMN, Tan L, Zhang J, Wu J, Cai H, Sun C, Wang X, Wing R A, Zhu Z.A single-nucleotide polymorphism causes smaller grain size and loss of seed shattering during African rice domestication.NatPlants, 2017, 3:17064. |
| [19] | Li Y B, Fan C C, Xing Y Z, JiangY H, LuoL J,SunL, Shao D, Xu C J, Li X H, Xiao J X, He Y Q, Zhang Q F.Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice.NatGenet,2011, 43(12):1266-1292. |
| [20] | Song X J, Huang W, Shi M, ZhuMZ, LinHX.A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase.NatGenet, 2007, 39(5):623-630. |
| [21] | Yan S, Zou G H, Li S J, Wang H, LiuH Q, ZhaiG W, Guo P, Song H M, Yan C J, Tao Y Z. Seed size is determined by the combinations of the genes controlling different seed characteristics in rice.TheorApplGenet, 2011, 123(7):1173-1181. |
| [22] | Liu J F, Chen J, Zheng X M, Wu F Q, Lin Q B, Heng Y Q, Tian Peng, Cheng Z J, Yu X W, Zhou K N, Zhang X, Guo X P, Wang J L, Wang H Y, Wan J M.GW5 acts in the brassinosteroidsignalling pathway to regulate grain width and weight in rice. NatPlants, 2017, 3:17043. |
| [23] | Xue W Y, Xing Y Z, Weng X Y, Zhao Y, Tang W J, Zhou H J, Yu S B, Xu C B, Li X H, Zhang Q F.Natural variation in Ghd7 is an important regulator of heading date and yield potential in rice.NatGenet, 2009, 40(6):761-767. |
| [24] | LiJ,ThomsonM, McCouchSR. Fine mapping of a grain-weight quantitative trait locus in the pericentromeric region of rice chromosome 3.Genetics, 2004,168(4): 2187. |
| [25] | Bai X F, Luo L J, Yan W H,Mallikarjuna R K, Zhan W, Xing Y Z.Genetic dissection of rice grain shape using a recombinant inbred line population derived from two contrasting parents and fine mapping a pleiotropic quantitative trait locus qGL7.BMC Genet, 2010, 11(1): 16. |
| [26] | Shao G N, Tang S Q, Luo J, Jiao G A, Wei X J, Tang A, Wu J L, Zhuang J Y, Hu P S.Mapping of qGL7-2, a grain length QTL on chromosome 7 of rice.JGenGenom, 2010, 37(8):523-531. |
| [27] | Liu T M, Shao D, Kovi M R, Zhong X Y.Mapping and validation of quantitative trait loci for spikelets per panicle and 1,000-grain weight in rice ( Oryza sativa L.).TheorApplGenet, 2010, 120(5):933-942. |
| [28] | Xie X, Jin F, Song M H, Suh J P, Hwang H G.Fine mapping of a yield-enhancing QTL cluster associated with transgressive variation in an Oryza sativa ×O. rufipogoncross. TheorApplGenet, 2008, 116(5):613-622. |
| [29] | 陈建华, 姚青, 谢绍军,孙成效,朱智伟. 机器视觉在稻米粒型检测中的应用.中国水稻科学, 2007, 21(6):669-672. |
| Chen J H,Yao Q, Xie S J,Sun C X, Zhu Z W.Detection of rice shape based on machine vision.Chin J Rice Sci, 2007, 21(6):669-672. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 刘仁虎, 孟金陵. MapDraw在Excel中绘制遗传连锁图的宏.遗传, 2003, 25(3):317-321. |
| Liu R H, Meng J L.MapDraw: Amicro for drawing genetic linkage maps based on given genetic linkage data.Hereditas, 2003, 25(3):317-321. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | McCouch S R. Genenomenclaturesystem forrice.Rice,2008, 1(1):72-84. |
| [32] | Song W Y, Lee H S, Jin S R, KoD, Martinoia E, LeeY. RicePCR1 influences grain weight and Zn accumulation in grains. Plant Cell & Environ,2015, 38(11):2327-2339. |
| [33] | Chen J, Gao H, Zheng X M, JinM, WengJF, MaJ. An evolutionarily conserved gene, FUWA, plays a role in determining panicle architecture, grain shape and grain weight in rice.Plant J, 2015, 83(3):427-438. |
| [34] | Liu X Y, Zhou S L, Wang W T, YeY R, ZhaoY, XuQ T, Zhou C, Tan F, Cheng S F, Zhou D X.Regulation ofhistone methylation and reprogramming of gene expression in the rice inflorescence meristem. Plant Cell, 2015, 27(5):1428-1444. |
| [35] | ZhuYD,LingTL,TangL, SongY, BaiJK, ShanJH, Chang J Y, Tai W.OsKinesin-13A is an active microtubule depolymerase involved in glume length regulation via affecting cell elongation.SciRep, 2015, 5(10):9457. |
| [36] | Byun M Y, Hong J P, KimW T. Identification and characterization of three telomere repeat-binding factors in rice.BiochemBiophyResComm, 2008, 372(1):85-90. |
| [37] | Cui X K, Jin P, Cui X,Gu L F, Lu Z K, Xue Y M, Wei L Y, Qi J F, Song X W, Luo M, An G, Cao X F.Control of transposon activity by a histone H3K4 demethylase in rice.Proc NatlAcadSci USA, 2013, 110(5):1953-1958. |
| [38] | Kitagawa K, Kurinami S, Oki K, Abe Y, Ando T, Kono I, Yano M, Kitano H, Iwasaki Y.A novel Kinesin 13 protein regulating rice seed length.Plant & Cell Physiol, 2010, 51(8):1315-1329. |
| [39] | Yoshida S, Ikegami M, Kuze J, Sawada K, Nashimoto Z, Nakamura C, Ishii T, Kamijima O.QTL analysis for plant and grain characters of sake-brewing rice using a doubled haploid population.Breed Sci, 2002, 52(4):309-317. |
| [40] | Li Z F, Wan J M, Xia J F,Zhai H Q.Mapping quantitative trait loci underlying appearance quality of rice grains (Oryza sativa L.). JGenGenom,2003, 30(3):251-259. |
| [41] | Huang N, Parco A, Mew T,Magpantay G, McCouch S, Guiderdoni E, Xu J, Subudhi P, Angeles E R, Khush G S. RFLP mapping of isozymes, RAPD and QTLs for grain shape, brown planthopper resistance in a doubled haploid rice population.MolBreed, 1997, 3(2):105-113. |
| [42] | Wan X Y, Wan J M, Weng J F,Jiang L, Bi J C, Wang C M, Zhai H Q.Stability of QTLs for rice grain dimension and endosperm chalkiness characteristics across eight environments.TheorApplGenet, 2005, 110(7):1334. |
| [43] | Hittalmani S, Huang N, Courtois B,Venuprassad R, Shashidhar H E, Zhuang J Y, Zheng K L, Liu G F, Wang G C, Sidhu J S, Srivantaneeyakul S, Sinqh V P, Baqali P G, Prasanna H C, McLaren G, Khush G S. Identification of QTL for growth- and grain yield-related traits in rice across nine locations of Asia.TheorApplGenet, 2003, 107(4):679-690. |
| [44] | GaoYM, ZhuJ, SongYS, He C X, Shi C H, Xing Y Z. Analysis of digenic epistatic effects and QE interaction effects QTL controlling grain weight in rice.JZhejiang UnivSci, 2004, 5(4):371-377. |
| [45] | Lin H X, Qian H R, Zhuang J Y, Lu J, Min S K, Xiong Z M, Huang N, Zheng K L.RFLP mapping of QTLs for yield and related characters in rice ( Oryza sativa L.).TheorApplGenet, 1996, 92(8):920-927. |
| [46] | ChoYC, SuhJP, ChoiIS, Hong H C, Baek M K, Hong H C, Kim Y G, Choi H, Moon H P, Hwang G H. QTLs analysis of yield and its related traits in wild rice relative Oryzarufipogon.TreatCropRes, 2003(4): 19-29. |
| [47] | Hua J, Xing Y, Wu W, Xu C, Sun X, Yu S, Zhang Q.Single-locus heterotic effects and dominance by dominance interactions can adequately explain the genetic basis of heterosis in an elite rice hybrid.Proc NatlAcadSciUSA, 2003, 100(5):2574. |
| [48] | Zhuang J Y, Fan Y Y, Rao Z M, Wu J L, Xia Y W, Zheng K L.Analysis on additive effects and additive-by-additive epistatic effects of QTLs for yield traits in a recombinant inbred line population of rice.TheorApplGenet, 2002, 105(8):1137-1145. |
| [49] | Hua J P, Xing Y Z, Xu C G, Sun X L, Yu S B, Zhang Q.Genetic dissection of an elite rice hybrid revealed that heterozygotes are not always advantageous for performance.Genetics, 2003, 162(4):1885-1895. |
| [50] | 谭震波, 沈利爽, 陆朝福, 陈英, 朱立煌, 周开达, 袁祚廉. 水稻再生能力和头季稻产量性状的QTL定位及其遗传效应分析. 作物学报, 1997, 23(3): 289-295. |
| Tan Z B,Shen L S, Yuan Z L, Lu C F, Chen Y, Zhou K D, Zhu L H, Zuo W X B. Identification of QTLs for ratooning ability and grain yield traits of rice and analysis of their genetic effects.ActaAgronSin, 1997, 23(3):289-295. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||