
中国水稻科学 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (6): 580-589.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.6152
汪玉琼1, 杨窑龙1, 冷语佳1, 黄李超1, 陈龙1, 代丽萍1, 涂政军1, 高易宏1, 胡江1, 朱丽1, 张光恒1, 任德勇1, 高振宇1, 董国军1, 陈光1, 郭龙彪1, 叶国友2, 钱前1,*( ), 曾大力1,*(
), 曾大力1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-11-05
修回日期:2017-04-03
出版日期:2017-11-25
发布日期:2017-11-10
通讯作者:
钱前,曾大力
基金资助:
Yuqiong WANG1, Yaolong YANG1, Yujia LENG1, Lichao HUANG1, Long CHEN1, Liping DAI1, Zhengjun TU1, Yihong GAO1, Jiang HU1, Li ZHU1, Guangheng ZHANG1, Deyong REN1, Zhenyu GAO1, Guojun DONG1, Guang CHEN1, Longbiao GUO1, Guoyou YE2, Qian QIAN1,*( ), Dali ZENG1,*(
), Dali ZENG1,*( )
)
Received:2017-11-05
Revised:2017-04-03
Online:2017-11-25
Published:2017-11-10
Contact:
Qian QIAN, Dali ZENG
摘要:
【目的】 籽粒大小是决定水稻产量的重要农艺性状之一,开展水稻籽粒大小相关基因的克隆和功能研究对于阐述水稻产量形成的遗传调控机制具有重要意义。【方法】 利用甲基磺酸乙酯诱变粳稻品种中花11,筛选获得一小粒突变体,命名为sg101(small grain 101)。通过形态学、细胞学手段调查了SG101的突变对籽粒大小、穗部主要性状及颖壳细胞数目和大小的影响,通过测定叶夹角和胚芽鞘长度分析其对外施油菜素内酯的差异响应,结合定量PCR技术分析了油菜素内酯合成途径和信号途径相关基因表达情况,并利用图位克隆的手段精细定位了水稻小粒基因SG101。【结果】 与野生型相比,突变体sg101粒长和粒宽均极显著减小,从而导致千粒重极显著降低。此外,sg101还表现出结实率降低、穗长变短、二次枝梗数减少、植株变矮等。细胞学观察发现sg101的颖壳细胞大小没有改变,但细胞数目明显减少。定量PCR检测表明sg101中的细胞周期相关基因表达显著下降。另外,突变体sg101对外施油菜素内酯响应迟钝,其油菜素内酯合成途径和信号途径相关基因表达亦显著降低。【结论】 遗传分析表明sg101突变体由隐性单基因控制,通过图位克隆的方法将SG101精细定位于第1染色体上,物理距离为265 kb的区间内。这为该基因的克隆及深入的功能研究奠定了基础。
中图分类号:
汪玉琼, 杨窑龙, 冷语佳, 黄李超, 陈龙, 代丽萍, 涂政军, 高易宏, 胡江, 朱丽, 张光恒, 任德勇, 高振宇, 董国军, 陈光, 郭龙彪, 叶国友, 钱前, 曾大力. 水稻小粒基因SG101的鉴定和精细定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(6): 580-589.
Yuqiong WANG, Yaolong YANG, Yujia LENG, Lichao HUANG, Long CHEN, Liping DAI, Zhengjun TU, Yihong GAO, Jiang HU, Li ZHU, Guangheng ZHANG, Deyong REN, Zhenyu GAO, Guojun DONG, Guang CHEN, Longbiao GUO, Guoyou YE, Qian QIAN, Dali ZENG. Identification and Fine Mapping of Small Grain Gene SG101 in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(6): 580-589.
| 引物 Marker | 前引物序列 Forward primer (5′-3′) | 后引物序列 Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| UBQ5 | CTCGCCGACTACAACATCCA | TCTTGGGCTTCCTCTACGTCTT |
| E2F2 | TGTTGGTGGCTGCCGATAT | CGCCAGGTGCACCCTTT |
| CYCT1;2 | GCATTTGTTGCAGCTCAAG | TCACCACTTCGCTGACTTATTG |
| CYCD4;1 | GCCATGGAGTTGATACATCCAA | CCAGTAGGGCTCCGTGGAAT |
| CYCD7;1 | CCTTCCACACTGACGGTACAGTT | TGCCGCTGCCAAATAGACA |
| CYCB2;2 | CTCAAGGCTGCACAATCTGACA | GCATTGACGGCTGGAATTTG |
| D2 | TTCAACCCATGGAGGTGGAA | GCACGGTGGGGAAGTTGACGA |
| OsCPOD | TTCTTCTCCATCCCCTTTCCTCTCGCCA | CACCCTCCGCCTCAAGAAGCTCCTCAA |
| DWARF4Q | GAGATGGTTTTCACGCAATGTG | ACCCTTGTAGTGCACGTCCTTG |
| BU1 | GTAGCCAGCTTGATCTCATCTC | GGGACGACTCTACTGCATCA |
| BZRF | CTCGGCAGCGTCGAGGTGC | AGGAATTGTTGCTGAGCTTC |
| D61 | CTCGGCAGCGTCGAGGTGC-3' | AGGAATTGTTGCTGAGCTTC |
| PAVL1 | GCACTCCTCGTTGGATCTCGAT | GCAGCAGACGGAAGATGGATT |
| OsLIC | GGAGTTTCGAGCGTATCTGGAA | TGGACAGAGGAAGCAGGAGACT |
| OsMDP1 | TTATTGACCGGTACAACTCGCA | TCCAGTCCATCGATCTCATCC |
表1 本研究用于RT-PCR分析的引物
Table 1 Primers used for real-time RT-PCR in the study.
| 引物 Marker | 前引物序列 Forward primer (5′-3′) | 后引物序列 Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| UBQ5 | CTCGCCGACTACAACATCCA | TCTTGGGCTTCCTCTACGTCTT |
| E2F2 | TGTTGGTGGCTGCCGATAT | CGCCAGGTGCACCCTTT |
| CYCT1;2 | GCATTTGTTGCAGCTCAAG | TCACCACTTCGCTGACTTATTG |
| CYCD4;1 | GCCATGGAGTTGATACATCCAA | CCAGTAGGGCTCCGTGGAAT |
| CYCD7;1 | CCTTCCACACTGACGGTACAGTT | TGCCGCTGCCAAATAGACA |
| CYCB2;2 | CTCAAGGCTGCACAATCTGACA | GCATTGACGGCTGGAATTTG |
| D2 | TTCAACCCATGGAGGTGGAA | GCACGGTGGGGAAGTTGACGA |
| OsCPOD | TTCTTCTCCATCCCCTTTCCTCTCGCCA | CACCCTCCGCCTCAAGAAGCTCCTCAA |
| DWARF4Q | GAGATGGTTTTCACGCAATGTG | ACCCTTGTAGTGCACGTCCTTG |
| BU1 | GTAGCCAGCTTGATCTCATCTC | GGGACGACTCTACTGCATCA |
| BZRF | CTCGGCAGCGTCGAGGTGC | AGGAATTGTTGCTGAGCTTC |
| D61 | CTCGGCAGCGTCGAGGTGC-3' | AGGAATTGTTGCTGAGCTTC |
| PAVL1 | GCACTCCTCGTTGGATCTCGAT | GCAGCAGACGGAAGATGGATT |
| OsLIC | GGAGTTTCGAGCGTATCTGGAA | TGGACAGAGGAAGCAGGAGACT |
| OsMDP1 | TTATTGACCGGTACAACTCGCA | TCCAGTCCATCGATCTCATCC |
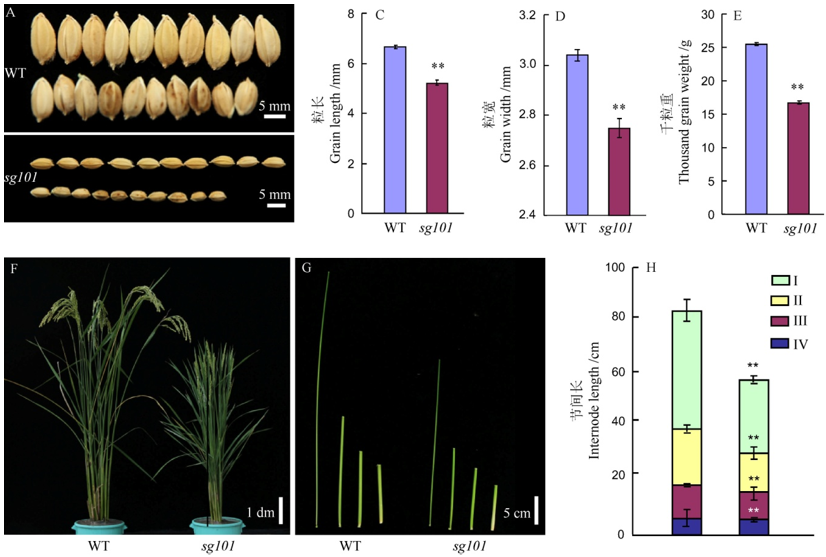
图1 野生型中花11和突变体sg101的表型比较**代表突变体与野生型之间差异达0.01显著水平。图2和图3同。
Fig. 1. Phenotypes of Zhonghua 11(WT) and sg101. **Significant difference at 0.01 level between wild type and mutant sg101. The same as that in Fig. 2 and Fig. 3.
| 性状 Trait | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 sg101 |
|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height/cm | 88.8±2.4 | 67.6±6.1 |
| 穗长Panicle length/cm | 22.7±1.1 | 17.1±1.2 |
| 着粒密度Spikelet density | 11.8±1.3 | 9.9±1.4 |
| 一次枝梗数Primary rachis branch number per panicle | 15.0±1.0 | 13.0±3.0 |
| 二次枝梗数Secondary rachis branch number per panicle | 51.3±11.1 | 33.6±7.1 |
| 每穗颖花数Spikelet number per panicle | 270.0±40.0 | 170.0±29.3 |
| 结实率Seed setting rate/% | 70.0±4.3 | 5.0±3.2 |
表2 野生型中花11和突变体sg101的穗部性状比较
Table 2 Comparison of panicle-related traits between Zhonghua 11 and sg101.
| 性状 Trait | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 sg101 |
|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height/cm | 88.8±2.4 | 67.6±6.1 |
| 穗长Panicle length/cm | 22.7±1.1 | 17.1±1.2 |
| 着粒密度Spikelet density | 11.8±1.3 | 9.9±1.4 |
| 一次枝梗数Primary rachis branch number per panicle | 15.0±1.0 | 13.0±3.0 |
| 二次枝梗数Secondary rachis branch number per panicle | 51.3±11.1 | 33.6±7.1 |
| 每穗颖花数Spikelet number per panicle | 270.0±40.0 | 170.0±29.3 |
| 结实率Seed setting rate/% | 70.0±4.3 | 5.0±3.2 |
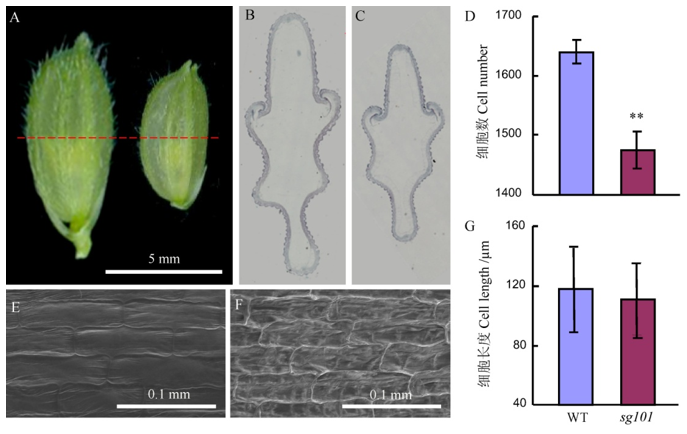
图2 野生型中花11和突变体sg101籽粒的比较 A–野生型和sg101发育成熟的颖;B,C分别为野生型和sg101颖壳石蜡切片;D–野生型和sg101横切面细胞数目的比较;E,F分别为野生型和sg101颖壳内表皮的扫描电镜图;G–野生型和sg101颖壳细胞长度的比较。
Fig. 2. The comparison of grain between Zhonghua 11(WT) and sg101. A, Developed lemma; B and C, Paraffin section of the lemmas of wild-type and sg101, respectively. D, Cell number of the lemma; E and F, SEM analysis of the lemma outer surface of wild-type and sg101, respectively. G, Cell length of the outer epidermal lemma.
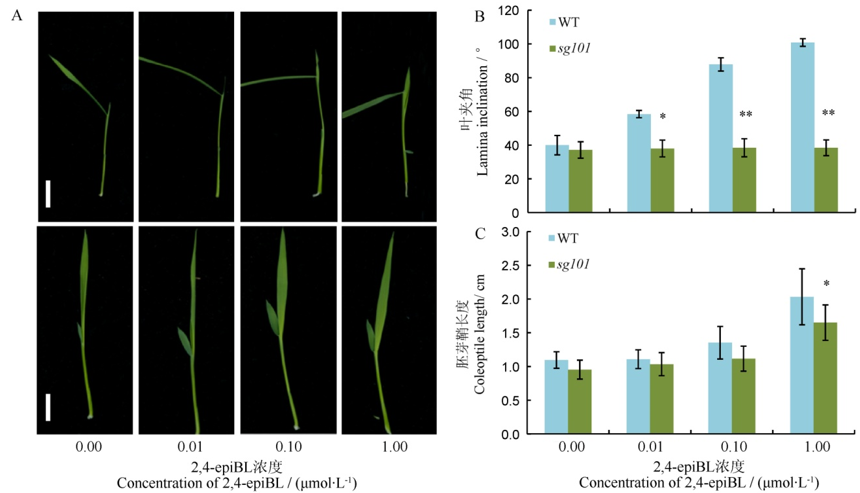
图4 中花11和突变体sg101对2,4-epiBL处理的响应 A–不同2,4-epiBL浓度处理,上面为中花11,下面为sg101,bar=2 cm;B, C分别为不同2,4-epiBL浓度处理叶夹角和胚芽鞘长度的变化。*,**分别代表突变体与野生型之间差异达0.05,0.01显著水平。
Fig. 4. Lamina joint test to 2,4-epiBL in Zhonghua 11(WT) and sg101. A, Performance of lamina joint to 2,4-epiBL in wild-type(up) and sg101(down). Scale bars, 2.0 cm; B and C, Changes of lamina inclination and coleoptile length to 2,4-epiBL, respectively. *, **Significant difference at 0.05 and 0.01 level between wild type and mutant sg101, respectively.
| 分离群体 Segregation population | F1 | F2 | χ2 (3:1) | P值 P-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常表型 Wild-type phenotype | 突变表型 sg101 phenotype | 正常表型 Wild-type phenotype | 突变表型 sg101 phenotype | ||||
| sg101/TN1 | 4 | 0 | 116 | 34 | 0.436 | 0.509 | |
| sg101/南京6号 sg101/Nanjing 6号 | 8 | 0 | 258 | 74 | 1.301 | 0.254 | |
| sg101/9311 | 5 | 0 | 154 | 43 | 1.058 | 0.304 | |
| TN1/sg101 | 4 | 0 | 128 | 38 | 0.394 | 0.530 | |
| 南京6号/sg101 Nanjing 6/sg101 | 3 | 0 | 102 | 29 | 0.573 | 0.449 | |
| 9311/sg101 | 6 | 0 | 178 | 56 | 0.143 | 0.076 | |
表3 SG101的遗传分析
Table 3 Genetic analysis of SG101.
| 分离群体 Segregation population | F1 | F2 | χ2 (3:1) | P值 P-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常表型 Wild-type phenotype | 突变表型 sg101 phenotype | 正常表型 Wild-type phenotype | 突变表型 sg101 phenotype | ||||
| sg101/TN1 | 4 | 0 | 116 | 34 | 0.436 | 0.509 | |
| sg101/南京6号 sg101/Nanjing 6号 | 8 | 0 | 258 | 74 | 1.301 | 0.254 | |
| sg101/9311 | 5 | 0 | 154 | 43 | 1.058 | 0.304 | |
| TN1/sg101 | 4 | 0 | 128 | 38 | 0.394 | 0.530 | |
| 南京6号/sg101 Nanjing 6/sg101 | 3 | 0 | 102 | 29 | 0.573 | 0.449 | |
| 9311/sg101 | 6 | 0 | 178 | 56 | 0.143 | 0.076 | |
| 引物 Marker | 前引物序列 Forward primer(5′-3′) | 后引物序列 Reverse primer(5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | GCTAGGCTTGATCCGAGAGA | GTCCCGCTTCTTCCCCTA | |
| M2 | GACCACGTCAAGCATAAGTTCA | AGCCTTTCAGGGAGGAAGAA | |
| M3 | CTCCCTACTTCTCCTCTTCG | CATACGCAACACCGCATCTT | |
| M4 | GGTGTTTGATCCCATTTGCT | TGGATGAAGAACTGCGCATA | |
| S1 | GGAACGGGGTGACAATTCTA | GCCTGTTTGAGGGAATGGTA | |
| S2 | ATTCTTACTTAATAATCAATAC | TACCTAGCTCGACTCAGACCCA | |
| S3 | GAGCAGGCAGACCTGCATAA | AAAACACTGCCTGTGATTCTGT | |
| S4 | CGACGGTGGGAGCAGAAGAAA | TCGGACTATCTCTGCTGGAATT | |
| S5 | ACTCCTATGTTTCAACCTG | GTGACCATCAATGAACCTT | |
| S6 | AAATCTAGTCAACACGCCGT | ACATGAGTTTAATTCCAAAATT | |
表4 本研究中SG101定位所用引物
Table 4 Primers used for fine mapping of SG101 in this study.
| 引物 Marker | 前引物序列 Forward primer(5′-3′) | 后引物序列 Reverse primer(5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | GCTAGGCTTGATCCGAGAGA | GTCCCGCTTCTTCCCCTA | |
| M2 | GACCACGTCAAGCATAAGTTCA | AGCCTTTCAGGGAGGAAGAA | |
| M3 | CTCCCTACTTCTCCTCTTCG | CATACGCAACACCGCATCTT | |
| M4 | GGTGTTTGATCCCATTTGCT | TGGATGAAGAACTGCGCATA | |
| S1 | GGAACGGGGTGACAATTCTA | GCCTGTTTGAGGGAATGGTA | |
| S2 | ATTCTTACTTAATAATCAATAC | TACCTAGCTCGACTCAGACCCA | |
| S3 | GAGCAGGCAGACCTGCATAA | AAAACACTGCCTGTGATTCTGT | |
| S4 | CGACGGTGGGAGCAGAAGAAA | TCGGACTATCTCTGCTGGAATT | |
| S5 | ACTCCTATGTTTCAACCTG | GTGACCATCAATGAACCTT | |
| S6 | AAATCTAGTCAACACGCCGT | ACATGAGTTTAATTCCAAAATT | |
| [1] | Xing Y, Zhang Q.Genetic and molecular bases of rice yield.Ann Rev Plant Biol, 2010, 61: 421-442. |
| [2] | Li W, Wu J, Weng S, Zhang Y, Zhang D, Shi C.Identification and characterization ofdwarf 62, a loss-of-function mutation in DLT/OsGRAS-32 affecting gibberellin metabolism in rice. Planta, 2010, 232(6): 1383-1396. |
| [3] | Mao H, Sun S, Yao J, Wang C, Yu S, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q.Linking differential domain functions of theGS3 protein to natural variation of grain size in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2010, 107(45): 19579-19584. |
| [4] | 茆海亮. 水稻粒形基因GS3的功能研究. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2010. |
| Mao H L.Functional study of rice grain shape gene GS3. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 石珍源. 水稻粒型QTL qGW12的精细定位和粒长调控基因SG4的克隆与功能验证. 北京:中国农业科学院, 2015. |
| Shi Z Y.Fine mapping of rice width locus GW12 and functional verification of a grain length gene SG4 in rice. Beijing: Chinese Academic of Agricultural Sciences, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Zuo J, Li J.Molecular genetic dissection of quantitative trait loci regulating rice grain size.Ann Rev Genet, 2014, 48: 99-118. |
| [7] | Zhang X, Wang J, Huang J, Lan H, Wang C, Yin C, Wu Y, Tang H, Qian Q, Li J, Zhang H.Rare allele ofOsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2012, 109(52): 21534-21539. |
| [8] | Qi P, Lin Y, Song X, Shen J, Huang W, Shan J, Zhu M, Jiang L, Gao J, Lin H.The novel quantitative trait locusGL3.1 controls rice grain size and yield by regulating Cyclin-T1;3. Cell Res, 2012, 22(12): 1666-1680. |
| [9] | Wang Y, Xiong G, Hu J, Jiang L, Yu H, Xu J, Fang Y, Zeng L, Xu E, Xu J, Ye W, Meng X, Liu R, Chen H, Jing Y, Wang Y, Zhu X, Li J, Qian Q.Copy number variation at theGL7 locus contributes to grain size diversity in rice. Nat Genet, 2015, 47(8): 944-948. |
| [10] | Hu, Wang Y, Fang Y, Zeng L, Xu J, Yu H, Shi Z, Pan J, Zhang D, Kang S, Zhu L, Dong G, Guo L, Zeng D, Zhang G, Xie L, Xiong G, Li J, Qian Q. A rare allele ofGS2 Enhances grain size and grain yield in rice. Mol Plant, 2015, 8(10): 1455-1465. |
| [11] | Song X, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu M, Lin H,. A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase.Nat Genet, 2007, 39: 623-630. |
| [12] | Yan S, Zou G, Li S, Wang H, Liu H, Zhai G, Guo P, Song H, Yan C, Tao Y.Seed size is determined by the combinations of the genes controlling different seed characteristics in rice.Theor Appl Genet, 2011, 123(7): 1173-1181. |
| [13] | Weng J F, Gu S H, Wan X Y, Gao H, Guo T, Su N, Lei C L, Zhang X, Cheng Z J, Guo X P, Wang J L, Jiang L, Zhai H Q, Wan J M.Isolation and initial characterization ofGW5, a major QTL associated with rice grain width and weight. Cell Res, 2008, 18(12): 1199-1209. |
| [14] | Li Y, Fan Ch, Xing Y, Jiang Y, Luo L, Sun L, Shao D, Xu C, Li X, Xiao J, He Y, Zhang Q.Natural variation inGS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat Genet, 2011, 43(12): 1266-1269. |
| [15] | Wang S, Wu K, Yuan Q, Liu X, Liu Z, Lin X, Zeng R, Zhu H, Dong G, Qian Q, Zhang G, Fu X.Control of grain size, shape and quality byOsSPL16 in rice. Nat Genet, 2012, 44: 950-954. |
| [16] | Yamamuro C, Ihara Y, Wu X, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M.Loss of function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint.Plant Cell, 2000, 12(9): 1591-1605. |
| [17] | Tanaka A, Nakagawa H, Tomita C, Shimatani Z, Ohtake M, Nomura T, Jiang , Dubouzet J, Kikuchi S, Sekimoto H, Yokota T, Asami T, Kamakura T, Mori M.BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1, encoding a helix-loop-helix protein, is a novel gene involved in brassinosteroid signaling and controls bending of the lamina joint in rice. Plant Physiol, 2009, 151(2): 669-680. |
| [18] | Duan P, Rao Y, Zeng D, Yang Y, Xu R, Zhang B, Dong G, Qian Q, Li Y.SMALL GRAIN 1, which encodes a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4, influences grain size in rice. Plant J, 2014, 77(4): 547-557. |
| [19] | Liu S, Hua L, Dong S, Chen H, Zhu X, Jiang J, Zhang F, Li Y, Fang X, Chen F.OsMAPK6, a mitogen-activated protein kinase, influences rice grain size and biomass production. Plant J, 2015, 84(4): 672-681. |
| [20] | Liu L, Tong H, Xiao Y, Che R, Xu F, Hu B, Liang C, Chu J, Li J, Chu C.Activation ofBig Grain1 significantly improves grain size by regulating auxin transport in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2015, 112(35): 11102-11107. |
| [21] | Murray M G, Thompson W F.Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA.Nucleic Acids Res, 1980, 8(19): 4321-4326. |
| [22] | Horiguchi G, Ferjani A, Fujikura U, Tsukaya H.Coordination of cell proliferation and cell expansion in the control of leaf size inArabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Res, 2006,119: 37-42. |
| [23] | Horvath BM, Magyar Z, Zhang Y, Hamburger AW, Bako L, Visser RG, Bachem CW, Bogre L.EBP1 regulates organ size through cell growth and proliferation in plants. EMBO J. 2006, 25: 4909-4920. |
| [24] | Ishimaru K, Hirotsu N, Madoka Y, Murakami N, Hara N, Onodera H, Kashiwagi T, Ujiie K, Shimizu B, Onishi A, Miyagawa H, Katoh E.Loss of function of the IAA-glucose hydrolase geneTGW6 enhances rice grain weight and increases yield. Nat Genet, 2013, 45(6): 707-711. |
| [25] | Ashikari M, Wu J, Yano M, Sasaki T, Yoshimura A.Rice gibberellin-insensitive dwarf mutant geneDwarf 1 encodes the α-subunit of GTP-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 1999, 96(18): 10284-10289. |
| [26] | Fujisawa Y, Kato T, Ohki S, Ishikawa A, Kitano H, Sasaki T, Asahi T, Iwasaki Y.Suppression of the heterotrimeric G protein causes abnormal morphology, including dwarfism, in rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci, 1999, 96(13): 7575-7580. |
| [27] | Andrzej B.Metabolism of brassinosteroids in plants.Plant Physiol Biochem, 2007, 45(2): 95-107. |
| [28] | Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Shimizu-Sato S, Inukai Y, Fujioka S, Shimada Y, Takatsuto S, Agetsuma M, Yoshida S, Watanabe Y, Uozu S, Kitano H, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M.Loss-of-function of a rice brassinosteroid biosynthetic enzyme, C-6 oxidase, prevents the organized arrangement and polar elongation of cells in the leaves and stem.Plant J, 2002, 32(4): 495-508. |
| [29] | Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Umemura K, Uozu S, Fujiok S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M.A rice brassinosteroid-deficient mutant, ebisudwarf (d2), is caused by a loss of function of a new member of cytochrome P450. Plant Cell, 2003, 15(12): 2900-2910. |
| [30] | Tanabe S, Ashikari M, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Yano M, Yoshimura A, Kitano H, Matsuoka M, Fujisawa Y, Kato H, Iwasaki Y.A novel cytochrome P450 is implicated in brassinosteroid biosynthesis via the characterization of a rice dwarf mutant,dwarf11, with reduced seed length. Plant Cell, 2005, 17(3): 776-790. |
| [31] | Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Hasegawa Y, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M.The rice brassinosteroid deficientdwarf2 mutant, defective in the rice homolog of Arabidopsis DWARF1, is rescued by the endogenously accumulated alternative bioactive brassinosteroid, dolichosterone. Plant Cell, 2005, 17(8): 2243-2254. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [6] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [7] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [8] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [9] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [10] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [11] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [12] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [13] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [14] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [15] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||