
中国水稻科学 ›› 2015, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (3): 319-326.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001G7216.2015.03.012
倪海平1,2, 徐秋芳2, 兰莹2, 陈晴晴2, 张金凤2, 周益军1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2014-12-01
修回日期:2015-01-29
出版日期:2015-05-10
发布日期:2015-05-10
通讯作者:
周益军
基金资助:
Hai-ping NI1,2, Qiu-fang XU2, Ying LAN2, Qing-qing CHEN2, Jin-feng ZHANG2, Yi-jun ZHOU1,2,*( )
)
Received:2014-12-01
Revised:2015-01-29
Online:2015-05-10
Published:2015-05-10
Contact:
Yi-jun ZHOU
摘要:
为明确水稻黑条矮缩病毒(Rice black streaked dwarf virus,RBSDV)侵染对水稻脱落酸(abscisic acid,ABA)含量的影响,通过灰飞虱在水稻日本晴和淮稻5号两个品种上人工接种RBSDV,待接种的水稻表现明显矮缩症状时,采用ELISA方法测定ABA含量。结果显示,在接种RBSDV的日本晴和淮稻5号中,ABA含量均明显增加。接种病毒的日本晴植株中ABA含量为111.04 ng/g,而对照中仅为60.86 ng/g;淮稻5号对照植物ABA含量为70.61 ng/g,而病株中ABA的含量为102.60 ng/g。为进一步明确病毒侵染如何调控ABA的含量,采用荧光定量PCR方法分析了日本晴接种RBSDV 8 d,12 d,16 d和60 d时ABA合成关键基因(OsZEP、OsNCED1、OsNCED2、OsNCED3、OsNCED4和OsNCED5)及分解关键基因(OsABA8ox1、OsABA8ox2和OsABA8ox3)mRNA相对表达量的变化。结果显示,病毒侵染 8 d,ABA合成和分解代谢基因的表达量均高于对照,其中OsNCED4和OsNCED5的表达量随病毒侵染时间的延长而增加,至60 d时OsNCED3、OsNCED4和OsNCED5的表达量为对照的3.97、7.66和2.99倍,而OsZEP,OsABA8ox1和OsABA8ox2的表达量则随侵染时间的延长而降低。RBSDV侵染后可能既影响了ABA合成也影响了其分解,两者共同作用导致了ABA含量增加。
倪海平, 徐秋芳, 兰莹, 陈晴晴, 张金凤, 周益军. RBSDV侵染对水稻ABA代谢相关基因表达的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(3): 319-326.
Hai-ping NI, Qiu-fang XU, Ying LAN, Qing-qing CHEN, Jin-feng ZHANG, Yi-jun ZHOU. Effect of RBSDV Infection on Transcriptional Expression of Abscisic Acid Metabolism Related Genes in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2015, 29(3): 319-326.
| 基因名称 Gene name | 基因登录号 Accession No. | 引物序列 Primer sequence | 产物大小 Amplification length/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| OsUBQ5 | AK061988 | F:5’-ACCACTTCGACCGCCACTACT-3’ | 69 |
| R:5’-ACGCCTAAGCCTGCTGGTT-3’ | |||
| OsZEP | AB050884 | F:5’-GGATGCCATTGAGTTTGGTT-3’ | 133 |
| R:5’-TGGCTGACTGAAGTCTCTCG-3’ | |||
| OsNCED1 | AY838897 | F:5’-CTCACCATGAAGTCCATGAGGCTT-3’ | 126 |
| R:5’-GTTCTCGTAGTCTTGGTCTTGGCT-3’ | |||
| OsNCED2 | AY838898 | F:5’-GGTATGGAAACGAGGATAGTGGTT-3’ | 100 |
| R:5’-TGCTTATTGTTGTGCGAGAAGTTC-3’ | |||
| OsNCED3 | AY838899 | F:5’-CCCCTCCCAAACCATCCAAACCGA-3’ | 132 |
| R:5’-TGTGAGCATATCCTGGCGTCGTGA-3’ | |||
| OsNCED4 | AY838900 | F:5’-TCGCGCTCAGCTACAATGTC-3’ | 88 |
| R:5’-ATGTCGACGTCTCGGGACTT-3’ | |||
| OsNCED5 | AY838901 | F:5’-ACATCCGAGCTCCTCGTCGTGAA-3’ | 184 |
| R:5’-TTGGAAGGTGTTTTGGAATGAACCA-3’ | |||
| OsABA8ox1 | NM_001054390 | F:5’-CCAAGAACCCCAACGTGTTC-3’ | 101 |
| R:5’-CGGGCTGGACACCATCA-3’ | |||
| OsABA8ox2 | NM_001068556 | F:5’-GCGAGACGCTCCAGCTCTA-3’ | 100 |
| R:5’-GGGCACCCCAGCAGATTC-3’ | |||
| OsABA8ox3 | NM_001069901 | F:5’-TCCAGCGACGAGGTTGAGTA-3’ | 100 |
| R:5’-AACCATCTGTTTCCACACTGACA-3’ |
表1 ABA合成和代谢基因的荧光定量PCR引物
Table 1 Primers of ABA synthesis- and metabolism-related genes for qRT-PCR.
| 基因名称 Gene name | 基因登录号 Accession No. | 引物序列 Primer sequence | 产物大小 Amplification length/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| OsUBQ5 | AK061988 | F:5’-ACCACTTCGACCGCCACTACT-3’ | 69 |
| R:5’-ACGCCTAAGCCTGCTGGTT-3’ | |||
| OsZEP | AB050884 | F:5’-GGATGCCATTGAGTTTGGTT-3’ | 133 |
| R:5’-TGGCTGACTGAAGTCTCTCG-3’ | |||
| OsNCED1 | AY838897 | F:5’-CTCACCATGAAGTCCATGAGGCTT-3’ | 126 |
| R:5’-GTTCTCGTAGTCTTGGTCTTGGCT-3’ | |||
| OsNCED2 | AY838898 | F:5’-GGTATGGAAACGAGGATAGTGGTT-3’ | 100 |
| R:5’-TGCTTATTGTTGTGCGAGAAGTTC-3’ | |||
| OsNCED3 | AY838899 | F:5’-CCCCTCCCAAACCATCCAAACCGA-3’ | 132 |
| R:5’-TGTGAGCATATCCTGGCGTCGTGA-3’ | |||
| OsNCED4 | AY838900 | F:5’-TCGCGCTCAGCTACAATGTC-3’ | 88 |
| R:5’-ATGTCGACGTCTCGGGACTT-3’ | |||
| OsNCED5 | AY838901 | F:5’-ACATCCGAGCTCCTCGTCGTGAA-3’ | 184 |
| R:5’-TTGGAAGGTGTTTTGGAATGAACCA-3’ | |||
| OsABA8ox1 | NM_001054390 | F:5’-CCAAGAACCCCAACGTGTTC-3’ | 101 |
| R:5’-CGGGCTGGACACCATCA-3’ | |||
| OsABA8ox2 | NM_001068556 | F:5’-GCGAGACGCTCCAGCTCTA-3’ | 100 |
| R:5’-GGGCACCCCAGCAGATTC-3’ | |||
| OsABA8ox3 | NM_001069901 | F:5’-TCCAGCGACGAGGTTGAGTA-3’ | 100 |
| R:5’-AACCATCTGTTTCCACACTGACA-3’ |
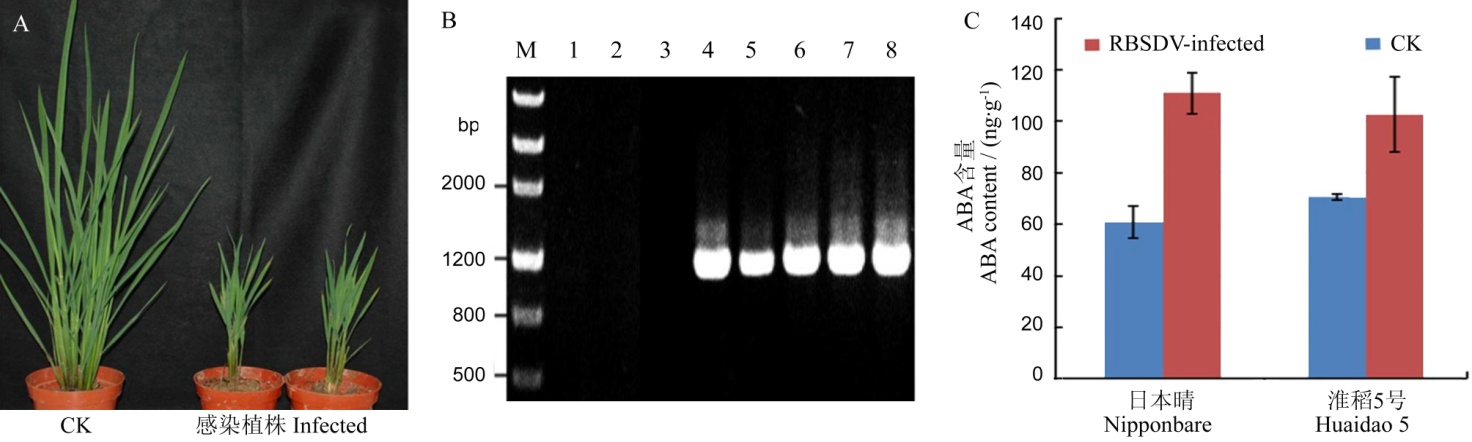
图1 RBSDV侵染导致水稻中ABA含量增加(A-水稻感染RBSDV后的症状; B-RT-PCR检测对照(泳道1~3)和接种RBSDV的水稻(泳道4~8); C-RBSDV侵染后水稻ABA含量。)
Fig. 1. RBSDV infection resulted in an increase of ABA in rice. (A, Phenotype of RBSDV-infected rice plant; B, RT-PCR analysis of the RBSDV infection in mock-inoculated rice (lanes 1-3) and in RBSDV-inoculated rice (lanes 4-8); C, Content of endogenous ABA in RBSDV- and mock-inoculated rice. )
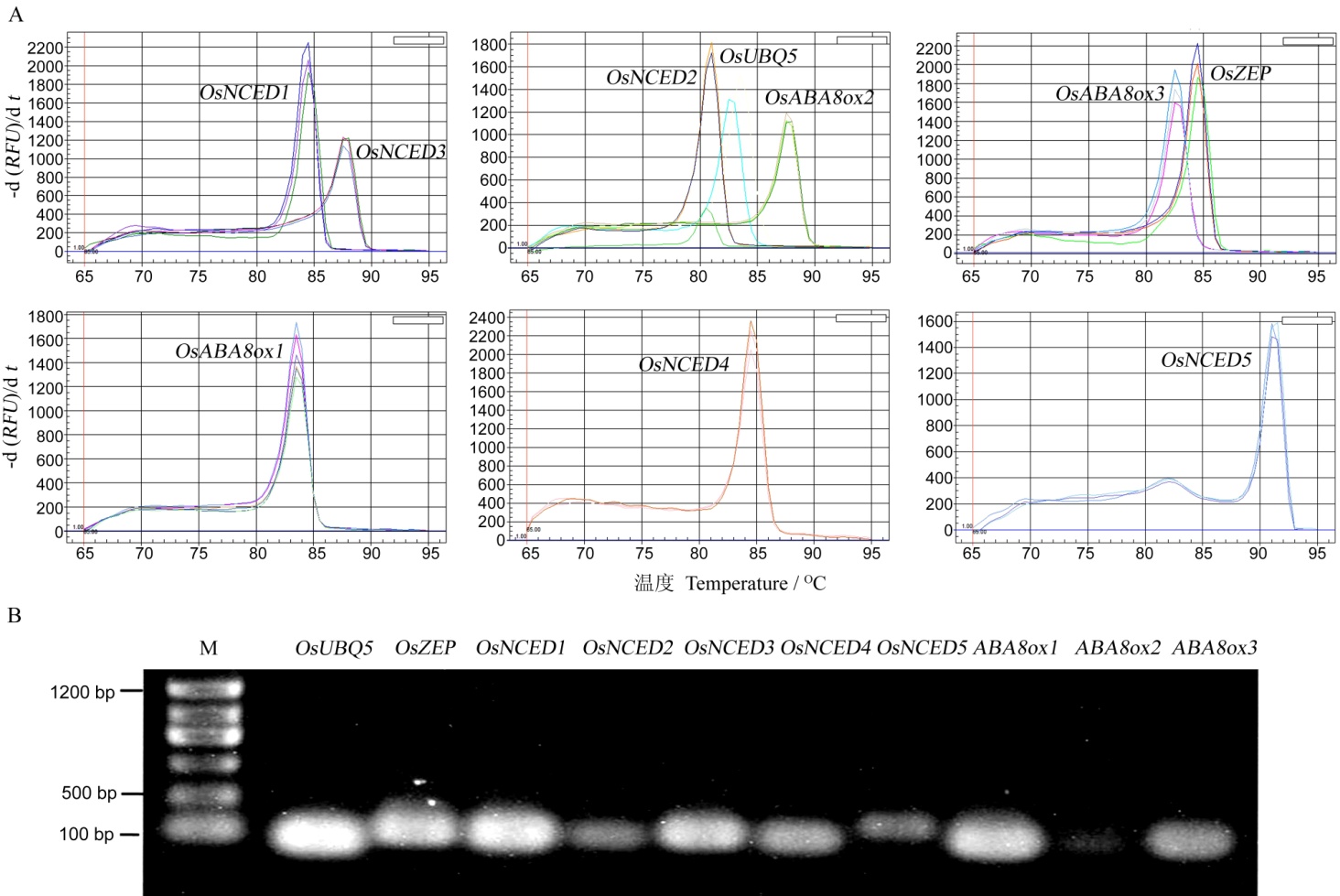
图2 荧光定量PCR引物特异性分析(A-qRT-PCR扩增后的融解曲线; B-采用qRT-PCR引物进行常规PCR的扩增产物。)
Fig. 2. Specific verification of primers used for qRT-PCR. (A, Dissociation curves of amplified products; B, The PCR products amplified by the specific primers. )
| 基因名称 Gene name | 侵染后天数Days after infection/d | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 12 | 16 | 60 | |
| OsZEP | 4.28±0.43 | 3.03±0.39 | 0.89±0.18 | 0.40±0.06 |
| OsNCED1 | 2.00±0.11 | 2.78±0.30 | 2.72±0.58 | 0.23±0.06 |
| OsNCED2 | 1.55±0.17 | 0.93±0.08 | 1.43±0.32 | 0.43±0.06 |
| OsNCED3 | 1.22±0.34 | 3.03±0.31 | 1.07±0.32 | 3.97±0.81 |
| OsNCED4 | 1.63±0.29 | 2.58±0.34 | 3.13±0.65 | 7.66±1.46 |
| OsNCED5 | 1.66±0.30 | 1.67±0.28 | 2.44±0.72 | 2.99±0.44 |
| OsABA8ox1 | 3.37±0.52 | 2.37±0.21 | 0.91±0.22 | 0.57±0.23 |
| OsABA8ox2 | 3.30±0.44 | 2.62±0.48 | 1.30±0.26 | 0.60±0.09 |
| OsABA8ox3 | 2.36±0.27 | 1.61±0.23 | 0.54±0.11 | 1.11±0.31 |
表2 水稻感染RBSDV后ABA代谢基因相对表达量
Table 2 Relative expression levels of ABA metabolism-related genes in RBSDV-infected rice.
| 基因名称 Gene name | 侵染后天数Days after infection/d | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 12 | 16 | 60 | |
| OsZEP | 4.28±0.43 | 3.03±0.39 | 0.89±0.18 | 0.40±0.06 |
| OsNCED1 | 2.00±0.11 | 2.78±0.30 | 2.72±0.58 | 0.23±0.06 |
| OsNCED2 | 1.55±0.17 | 0.93±0.08 | 1.43±0.32 | 0.43±0.06 |
| OsNCED3 | 1.22±0.34 | 3.03±0.31 | 1.07±0.32 | 3.97±0.81 |
| OsNCED4 | 1.63±0.29 | 2.58±0.34 | 3.13±0.65 | 7.66±1.46 |
| OsNCED5 | 1.66±0.30 | 1.67±0.28 | 2.44±0.72 | 2.99±0.44 |
| OsABA8ox1 | 3.37±0.52 | 2.37±0.21 | 0.91±0.22 | 0.57±0.23 |
| OsABA8ox2 | 3.30±0.44 | 2.62±0.48 | 1.30±0.26 | 0.60±0.09 |
| OsABA8ox3 | 2.36±0.27 | 1.61±0.23 | 0.54±0.11 | 1.11±0.31 |
| [1] | Fang S, Yu J, Feng J, et al.Identification of rice black-streaked dwarf fijivirus in maize with rough dwarf disease in China.Arch Virol, 2001, 146(1): 167-170. |
| [2] | Zhang H, Chen J, Lei J, et al.Sequence analysis shows that a dwarfing disease on rice, wheat and maize in China is caused by Rice black-streaked dwarf virus.Eur J Plant Pathol, 2001, 107(5): 563-567. |
| [3] | Bai F, Yan J, Qu Z, et al.Phylogenetic analysis reveals that a dwarfing disease on different cereal crops in China is due to rice black streaked dwarf virus (RBSDV).Virus Genes, 2002, 25(2): 201-206. |
| [4] | 季英华, 任春梅, 程兆榜, 等. 江苏省近年来新发生的一种水稻矮缩病害病原初步鉴定. 江苏农业学报, 2009, 25(6): 1263-1267. |
| [5] | Fraser R S S, Whenham R J. Plant growth regulators and virus infection: A critical review.Plant Growth Requl, 1982, 1(1): 37-59. |
| [6] | 吴建国, 王萍, 谢荔岩. 水稻矮缩病毒对3种內源激素含量及代谢相关基因转录水平的影响. 植物病理学报, 2010, 40(2): 151-158. |
| [7] | Zhu S F, Gao F, Gao X S, et al.The rice dwarf virus P2 protein interacts with ent-kaurene oxidases in vivo, leading to reduced biosynthesis of gibberellins and rice dwarf symptoms.Plant Physiol, 2005, 139(4): 1935-1945. |
| [8] | Mauch-Mani B, Mauch F.The role of abscisic acid in plant-pathogen interactions.Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2005, 8(4): 409-414. |
| [9] | Mohr P G, Cahill D M.Suppression by ABA of salicylic acid and lignin accumulation and the expression of multiple genes, in Arabidopsis infected with Pseudomonas syringae pv. Tomato.Funct Integr Genom, 2007, 7(3): 181-191. |
| [10] | de Torres-Zabala M, Truman W, Bennett M H, et al. Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato hijacks the Arabidopsis abscisic acid signaling pathway to cause disease.EMBO J, 2007, 26(5): 1434-1443. |
| [11] | Adie B A, Pérez-Pérez J, Pérez-Pérez M M, et al. ABA is an essential signal for plant resistance to pathogens affecting JA biosynthesis and the activation of defenses in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell, 2007, 19(5): 1665-1681. |
| [12] | Ton J, Flors V, Mauch-Mani B, et al.The multifaceted role of ABA in disease resistance.Trends Plant Sci, 2009, 14(6): 310-317. |
| [13] | 张海保, 朱西儒, 刘鸿先. 香蕉束顶病毒(BBTV)侵染对寄主內源激素的影响. 植物病理学报, 1997, 27(1): 79-83. |
| [14] | 吴建宇,盖钧镒. 接种玉米矮花叶病毒对抗性不同的玉米自交系内源激素的影响. 植物病理学报, 2001, 31(3): 286-287. |
| [15] | 丁新伦, 谢荔岩, 林奇英, 等. 水稻条纹病毒与不同抗性水稻互作中的脱落酸调控. 福建农林大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 42(5): 466-470. |
| [16] | 张爱红, 任萍, 邸垫平, 等. RBSDV所致玉米粗缩病不同病级植株内源激素水平变化研究. 华北农学报, 2012, 26(6): 217-220. |
| [17] | Nambara E, Marion-Poll A.Abscisic acid biosynthesis and catabolism.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 2005, 56: 165-185. |
| [18] | Schwartz S H, Qin X, Zeevaart J A D. Elucidation of the indirect pathway of abscisic acid biosynthesis by mutants, genes, and enzymes.Plant Physiol, 2003, 131(4): 1591-1601. |
| [19] | Nakashima K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K.ABA signaling in stress-response and seed development.Plant Cell Rep, 2013, 32(7): 959-970. |
| [20] | Gillard D F, Walton D C.Abscisic acid metabolism by a cell-free preparation from echinocystis lobata liquid endoserum.Plant Physiol, 1976, 58(6): 790-795. |
| [21] | Krochko J E, Abrams G D, Loewen M K, et al.(+)-abscisic acid 8’-hydroxylase is a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase.Plant Physiol, 1998, 118(3): 849-860. |
| [22] | Cutler A J, Krochko J E.Formation and breakdown of ABA.Trends Plant Sci, 1999, 4(12): 472-478. |
| [23] | 周彤, 吴丽娟, 王英, 等. 灰飞虱从冷冻病叶获得水稻黑条矮缩病毒方法的研究初报. 中国水稻科学, 2010, 24(4): 425-428. |
| [24] | 季英华, 高瑞珍, 张野, 等. 一种快速同步检测水稻黑条矮缩病毒和南方水稻黑条矮缩病毒的方法. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(1): 91-94. |
| [25] | Whenham R J, Fraser R S S. Effect of systermic and local-lesion-forming strains of tobacco mosaic virus on abscisic acid concentration in tobacco leaves consequences for the control of leaf growth.Physiol Plant Pathol, 1981, 18: 267-278. |
| [26] | Xiong L, Lee H, Ishitani M, et al.Regulation of osmotic stress-responsive gene expression by the LOS6/ABA1 locus in Arabidopsis.J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(10): 8588-8596. |
| [27] | 王淑敏, 侯喜林, 李英, 等. 芜菁花叶病毒对不结球白菜内源激素含量及代谢相关基因转录水平的影响. 南京农业大学学报, 2011, 34(5): 13-19. |
| [28] | Alazem M,Lin K Y, Lin N S.The abscisic acid pathway has multifaceted effects on the accumulation of bamboo mosaic virus.Mol Plant Microbe Interact, 2014, 27(2): 177-189. |
| [29] | Frey A, Audran C, Marin E, et al.Engineering seed dormancy by the modification of zeaxanthin epoxidase gene expression.Plant Mol Biol, 1999, 39(6): 1267-1274. |
| [30] | Xiong L M, Zhu J K.Regulation of abscisic acid biosynthesis.Plant Physiol, 2003, 133(1): 29-36. |
| [31] | Tan B C, Joseph L M, Deng W T, et al.Molecular characterization of the Arabidopsis 9-cisepoxycarotenoid dioxygenase gene family.Plant J, 2003, 35(1): 44-56. |
| [32] | Zhu G, Ye N, Zhang J.Glucose-induced delay of seed germination in rice is mediated by the suppression of ABA catabolism rather than an enhancement of ABA biosynthesis.Plant Cell Physiol, 2009, 50(3): 644-65. |
| [33] | Ye N, Zhu G, Liu Y, et al.ABA Controls H2O2 accumulation through the induction of OsCATB in rice leaves under water stress.Plant Cell Physiol, 2011, 52(4): 689-698. |
| [34] | Tian L, DellaPenna D, Zeevaart J A D. Effects of hydroxylated carotenoid deficiency on ABA accumulation in Arabidopsis.Physiol Plant, 2004, 122(3): 314-320. |
| [35] | 任慧波, 范意娟, 魏开发, 等. NCED3基因的持续诱导及ABA合成与代谢的协同调控在拟南芥ABA 信号积累中的作用. 科学通报, 2007, 52(1): 59-66. |
| [36] | Hwang S G, Chen H C, Huang W Y, et al.Ectopic expression of rice OsNCED3 in Arabidopsis increases ABA level and alters leaf morphology.Plant Sci, 2010, 178(1): 12-22. |
| [37] | Wong C E, Li Y, Labbe A, et al.Transcriptional profiling implicates novel interactions between abiotic stress and hormonal responses in Thellungiella, a close relative of Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol, 2006, 140(4): 1437-1450. |
| [38] | Saika H, Okamoto M, Miyoshi K, et al.Ethylene promotes submergence-induced expression of OsABA8ox1, a gene that encodes ABA 8'-hydroxylase in rice.Plant Cell Physiol, 2007, 48(2): 287-298. |
| [39] | Millar A, Jacobsen J, Ross J, et al.Seed dormancy and ABA metabolism in Arabidopsis and barley: The role of ABA 8'-hydroxylase.Plant J, 2006, 45: 942-954. |
| [40] | Okamoto M, Kuwahara A, Seo M, et al.CYP707A1 and CYP707A2, which encode abscisic acid 8'-hydroxylases, are indispensable for proper control of seed dormancy and germination in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol, 2006, 141: 97-107. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||