
中国水稻科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (2): 166-177.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220414
陈丽明1,#, 杨陶陶2,#, 熊若愚1, 谭雪明1, 黄山1, 曾勇军1, 潘晓华1, 石庆华1, 张俊3, 曾研华1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-29
修回日期:2022-07-23
出版日期:2023-03-10
发布日期:2023-03-10
通讯作者:
曾研华
作者简介:第一联系人:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
CHEN Liming1,#, YANG Taotao2,#, XIONG Ruoyu1, TAN Xueming1, HUANG Shang1, ZENG Yongjun1, PAN Xiaohua1, SHI Qinghua1, ZHANG Jun3, ZENG Yanhua1,*( )
)
Received:2022-04-29
Revised:2022-07-23
Online:2023-03-10
Published:2023-03-10
Contact:
ZENG Yanhua
About author:First author contact:#These authors contributed equally to this work
摘要:
【目的】明确未来气候变暖条件下双季籼稻品质形成的淀粉积累特征。【方法】早稻以湘早籼45号(常规籼稻)和柒两优2012(杂交籼稻),晚稻以九香粘(常规籼稻)和泰优398(杂交籼稻)为试验材料,利用开放式主动增温系统,设置全生育期增温(早稻增温1.4~1.5 ℃,晚稻增温2.0~2.3 ℃)和不增温2个处理,探明全生育期增温对双季籼稻籽粒淀粉合成及其关键酶活性的影响。【结果】开放式增温条件下,稻米中总淀粉和支链淀粉含量无显著变化,直链淀粉含量和直链淀粉占总淀粉比例降低,其中,柒两优2012和九香粘的直链淀粉含量分别显著降低了4.2%和3.4%。与不增温处理相比,增温提高了灌浆前期(抽穗后7~14 d)籽粒中总淀粉和直链淀粉积累量,但对晚稻籽粒直链淀粉积累量的影响持续时间要大于早稻,主要与淀粉合成关键酶活性不同程度升高有关。增温条件下,早稻灌浆结实期籽粒中二磷酸腺苷葡萄糖焦磷酸化酶(ADGPase)活性呈先升高后降低趋势,而晚稻呈逐渐升高趋势;增温降低了早稻抽穗后14 d和晚稻抽穗后7 d籽粒中结合态淀粉合成酶(GBSS)活性,但显著增加晚稻抽穗后期(抽穗后21、28 d)籽粒中GBSS活性;同时显著提高了柒两优2012和九香粘抽穗后7和14 d 籽粒中可溶性淀粉合成酶(SSS)活性,晚稻籽粒中淀粉分支酶(SBE)活性有升高趋势。总体上,增温对晚稻籽粒中ADGPase、GBSS活性的影响显著大于早稻。【结论】开放式主动增温显著提升双季籼稻灌浆前期(抽穗后7~14 d)籽粒中ADGPase、GBSS和SSS的活性,进而提高双季籼稻灌浆前期籽粒总淀粉及其组分的合成和积累。增温对淀粉合成关键酶的影响因季别和品种而异。
陈丽明, 杨陶陶, 熊若愚, 谭雪明, 黄山, 曾勇军, 潘晓华, 石庆华, 张俊, 曾研华. 开放式主动增温对双季优质籼稻籽粒淀粉积累及其关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 166-177.
CHEN Liming, YANG Taotao, XIONG Ruoyu, TAN Xueming, HUANG Shang, ZENG Yongjun, PAN Xiaohua, SHI Qinghua, ZHANG Jun, ZENG Yanhua. Effect of Free-air Temperature Increasing on Activities of Enzymes Involved in Starch Synthesis and Accumulation of Double-cropping indica Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(2): 166-177.
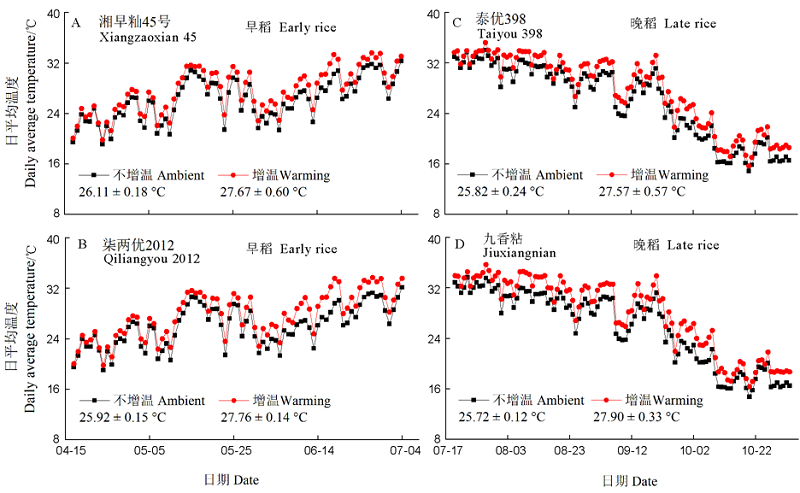
图1 不增温和增温处理水稻冠层日平均温度动态 图中数据为平均值±标准误。
Fig. 1. Rice canopy daily average temperature changes of rice canopy in ambient and warming treatments. The data in the table are average values ± standard error.
| 季别 Season | 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 抽穗-成熟 Heading to maturity | 移栽-成熟 Transplanting to maturity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最高 Max | 最低 Min | 日较差 Range | 最高 Max | 最低 Min | 日较差 Range | |||
| 早稻 | 湘早籼45号 | 不增温 Ambient | 36.9 | 23.5 | 13.4 | 34.6 | 21.5 | 12.6 |
| Early rice | Xiangzaoxian 45 | 增温Warming | 37.9 | 25.0 | 12.9 | 35.0 | 23.2 | 12.0 |
| 差值 Difference | 1.0 | 1.5 | −0.5 | 0.4 | 1.7 | −0.6 | ||
| 柒两优2012 | 不增温 Ambient | 37.7 | 23.6 | 13.6 | 34.2 | 21.6 | 12.7 | |
| Qiliangyou 2012 | 增温Warming | 38.5 | 25.3 | 13.2 | 35.0 | 23.2 | 12.0 | |
| 差值 Difference | 0.8 | 1.7 | −0.4 | 0.8 | 1.6 | −0.7 | ||
| 晚稻 | 九香粘 | 不增温 Ambient | 31.1 | 15.5 | 15.6 | 35.2 | 20.3 | 15.0 |
| Late rice | Jiuxiangnian | 增温Warming | 32.3 | 18.2 | 14.1 | 36.6 | 23.0 | 13.6 |
| 差值 Difference | 1.2 | 2.7 | −1.5 | 1.4 | 2.7 | −1.4 | ||
| 泰优398 | 不增温 Ambient | 35.2 | 19.9 | 15.3 | 37.5 | 22.5 | 15.0 | |
| Taiyou 398 | 增温Warming | 35.9 | 21.9 | 13.8 | 38.5 | 24.9 | 13.6 | |
| 差值 Difference | 0.7 | 2.0 | −1.5 | 1.0 | 2.4 | −1.4 | ||
表1 不增温和增温处理水稻冠层最高温度、最低温度和日较差
Table 1. Max, min and range temperature of rice canopy under ambient and warming treatments. ℃
| 季别 Season | 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 抽穗-成熟 Heading to maturity | 移栽-成熟 Transplanting to maturity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最高 Max | 最低 Min | 日较差 Range | 最高 Max | 最低 Min | 日较差 Range | |||
| 早稻 | 湘早籼45号 | 不增温 Ambient | 36.9 | 23.5 | 13.4 | 34.6 | 21.5 | 12.6 |
| Early rice | Xiangzaoxian 45 | 增温Warming | 37.9 | 25.0 | 12.9 | 35.0 | 23.2 | 12.0 |
| 差值 Difference | 1.0 | 1.5 | −0.5 | 0.4 | 1.7 | −0.6 | ||
| 柒两优2012 | 不增温 Ambient | 37.7 | 23.6 | 13.6 | 34.2 | 21.6 | 12.7 | |
| Qiliangyou 2012 | 增温Warming | 38.5 | 25.3 | 13.2 | 35.0 | 23.2 | 12.0 | |
| 差值 Difference | 0.8 | 1.7 | −0.4 | 0.8 | 1.6 | −0.7 | ||
| 晚稻 | 九香粘 | 不增温 Ambient | 31.1 | 15.5 | 15.6 | 35.2 | 20.3 | 15.0 |
| Late rice | Jiuxiangnian | 增温Warming | 32.3 | 18.2 | 14.1 | 36.6 | 23.0 | 13.6 |
| 差值 Difference | 1.2 | 2.7 | −1.5 | 1.4 | 2.7 | −1.4 | ||
| 泰优398 | 不增温 Ambient | 35.2 | 19.9 | 15.3 | 37.5 | 22.5 | 15.0 | |
| Taiyou 398 | 增温Warming | 35.9 | 21.9 | 13.8 | 38.5 | 24.9 | 13.6 | |
| 差值 Difference | 0.7 | 2.0 | −1.5 | 1.0 | 2.4 | −1.4 | ||
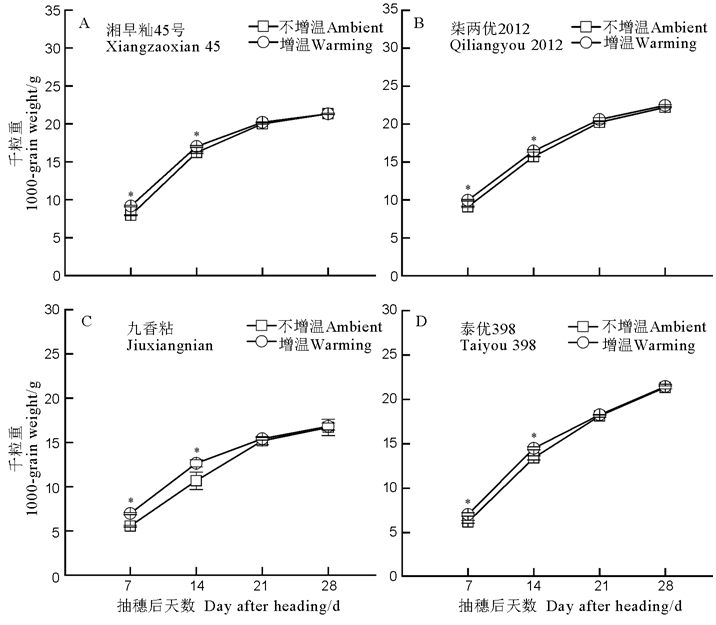
图3 增温对水稻籽粒粒重的影响 误差线表示标准误(n = 3)。*表示处理在0.05水平上差异显著。下同。
Fig. 3. Effects of warming on rice grain weight. Error bars represent the standard errors (n = 3). * means significance at 0.05 level. The same below.
| 季别 Season | 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 总淀粉含量 Starch contents/% | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 直链淀粉 占总淀粉比例 Proportion of amylose/% | 支链淀粉含量 Amylopectin content/% | 支链淀粉 占总淀粉比例 Proportion of amylopectin/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻 Early rice | 湘早籼45号 | 不增温 Ambient | 87.6 a | 15.4 a | 17.6 a | 72.2 a | 82.4 a |
| Xiangzaoxian 45 | 增温Warming | 87.2 a | 15.1 a | 17.3 a | 72.1 a | 82.7 a | |
| 柒两优2012 | 不增温 Ambient | 89.2 a | 14.2 a | 15.9 a | 75.0 a | 84.1 a | |
| Qiliangyou 2012 | 增温Warming | 88.4 a | 13.6 b | 15.4 b | 74.8 a | 84.6 a | |
| 晚稻 Late rice | 九香粘 | 不增温 Ambient | 90.1 a | 14.6 a | 16.2 a | 75.6 a | 83.9 a |
| Jiuxiangnian | 增温Warming | 89.7 a | 14.1 b | 15.7 b | 75.6 a | 84.3 a | |
| 泰优398 | 不增温 Ambient | 87.8 a | 14.6 a | 16.6 a | 73.1 a | 83.3 a | |
| Taiyou 398 | 增温Warming | 86.7 a | 14.4 a | 16.6 a | 72.3 a | 83.4 a |
表2 增温对水稻籽粒中总淀粉含量及其组分含量的影响
Table 2. Effects of warming on starch content and its component contents in rice grain.
| 季别 Season | 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 总淀粉含量 Starch contents/% | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content/% | 直链淀粉 占总淀粉比例 Proportion of amylose/% | 支链淀粉含量 Amylopectin content/% | 支链淀粉 占总淀粉比例 Proportion of amylopectin/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻 Early rice | 湘早籼45号 | 不增温 Ambient | 87.6 a | 15.4 a | 17.6 a | 72.2 a | 82.4 a |
| Xiangzaoxian 45 | 增温Warming | 87.2 a | 15.1 a | 17.3 a | 72.1 a | 82.7 a | |
| 柒两优2012 | 不增温 Ambient | 89.2 a | 14.2 a | 15.9 a | 75.0 a | 84.1 a | |
| Qiliangyou 2012 | 增温Warming | 88.4 a | 13.6 b | 15.4 b | 74.8 a | 84.6 a | |
| 晚稻 Late rice | 九香粘 | 不增温 Ambient | 90.1 a | 14.6 a | 16.2 a | 75.6 a | 83.9 a |
| Jiuxiangnian | 增温Warming | 89.7 a | 14.1 b | 15.7 b | 75.6 a | 84.3 a | |
| 泰优398 | 不增温 Ambient | 87.8 a | 14.6 a | 16.6 a | 73.1 a | 83.3 a | |
| Taiyou 398 | 增温Warming | 86.7 a | 14.4 a | 16.6 a | 72.3 a | 83.4 a |
| [1] | FAO. The FAO Statistical Database-Agriculture[DB/OL]. (2018-11-06)[2022-04-02]http://www.fao.org/economic/the-statistics-division-ess/publitions-studies/statistical-yearbook/fao-statistical-year book-2018/en/. |
| [2] | 中国国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2018. |
| NBSC. China Statistical Yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2018. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | Yang T T, Tan X M, Huang S, Pan X H, Zeng Y J. Effects of experimental warming on physicochemical properties of indica rice starch in a double rice cropping system[J]. Food Chemistry, 2019, 310: 125981. |
| [4] | 程方民, 丁元树, 朱碧岩. 稻米直链淀粉含量的形成及其与灌浆结实期温度的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2000(4): 646-652. |
| Cheng F M, Ding Y S, Zhu B Y. The formation of amylose content in rice grain and its relation with field temperature[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2000(4): 646-652. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Ratnayake W S, Jackson D S. A new insight into the gelatinization process of native starches[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2007, 67(4): 511-529. |
| [6] |
Li H Y, Prakash S, Nicholson T M, Fitzgerald M A, Gilbert R G. The importance of amylose and amylopectin fine structure for textural properties of cooked rice grains[J]. Food Chemistry, 2016, 196: 702-711.
PMID |
| [7] | 成臣, 曾勇军, 程慧煌, 谭雪明, 商庆银, 曾研华, 石庆华. 齐穗至乳熟期不同温度对水稻南粳9108籽粒激素含量、淀粉积累及其合成关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(1): 57-67. |
| Chen C, Zeng Y J, Chen H H, Tan X M, Shan Q Y, Zeng Y H, Shi Q H. Effects of Different temperature from full heading to milking on grain filling stage on grain hormones concentrations, activities of enzymes involved in starch synthesis and accumulation in rice Nanjing 9108[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(1): 57-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 程方民, 钟连进, 孙宗修. 灌浆结实期温度对早籼水稻籽粒淀粉合成代谢的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2003, 36 (5): 492-501. |
| Cheng F M, Zhong L J, Sun Z X. Effect of temperature at grain-filling stage on starch biosynthetic metabolism in developing rice grains of early-indica[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2003, 36(5): 492-501. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 李木英, 石庆华, 胡志红, 潘晓华, 谭雪明. 高温胁迫对不同早稻品种胚乳淀粉合成酶类活性的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2007, 40(8): 1622-1629. |
| Li M Y, Shi Q H, Hu Z H, Pan X H, Tan X M. Effects of high temperature stress on activity of amylosynthease in endosperm of early Indica rice varieties[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2007, 40(8): 1622-1629. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Cheng F M, Zhong L J, Zhao N C, Liu Y, Zhang G P. Temperature induced changes in the starch components and biosynthetic enzymes of two rice varieties[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2005, 46(1): 87-95. |
| [11] | 董文军, 田云录, 张彬, 陈金, 张卫建. 非对称性增温对水稻品种南粳44米质及关键酶活性的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2011, 37(5): 832-841. |
| Dong W J, Tian Y L, Zhang B, Chen J, Zhang W J. Effects of asymmetric warming on grain quality and related key enzymes activities for japonica rice (Nanjing 44) under FATI facility[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2011, 37(5): 832-841. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] |
Yang Z Y, Zhang Z L, Zhang T, Fahad S, Cui K H, Nie L X, Peng S B, Huang J L. The Effect of season-long temperature increases on rice cultivars grown in the central and southern regions of China[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1908.
PMID |
| [13] | 艾治勇, 郭夏宇, 刘文祥, 马国辉, 青先国. 农业气候资源变化对双季稻生产的可能影响分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 2014, 29(12): 2089-2102. |
| Ai Z Y, Guo X Y, Liu W X, Ma G H, Qin X G. Analysis on possible influences of agricultural climate resources change on double-season rice production[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2014, 29(12): 2089-2102. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Dou Z, Tang S, Chen W Z, Zhang H X, Li G H, Liu Z H, Ding C Q, Chen L, Wang S H, Zhang H C, Ding Y F. Effects of open-field warming during grain-filling stage on grain quality of two japonica rice cultivars in lower reaches of Yangtze River delta[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2018, 81: 118-126. |
| [15] | 杨陶陶. 双季籼稻产量和稻米品质对增温的响应特征及其机理[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2020. |
| Yang T T. Response of indica grain yield and grain quality to experimental warming in a double rice cropping system and its mechanism[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Yasunori N, Kazuhiro Y, Shin-Young P, Toshihide O. Carbohydrate metabolism in the developing endosperm of rice grains[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 1989, 30: 833-839. |
| [17] |
Ahmed N, Tetlow I J, Nawaz S, Ahsan , Muhammad M, Muhammad S N R, Aisha B, David A L, Masahiko M. Effect of high temperature on grain filling period, yield, amylose content and activity of starch biosynthesis enzymes in endosperm of basmati rice[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2015, 95(11): 2237-2243.
PMID |
| [18] | Tester R F, John K, Qi X. Starch-composition, fine structure and architecture[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2004, 39(2): 151-165. |
| [19] | 陈海生, 陶龙兴, 王熹, 黄效林, 谈惠娟, 程式华, 闵绍楷. 灌水方式对水稻灌浆期光合物质运转与分配的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2005(4): 678-683. |
| Chen H S, TAO L X, Wang X, Huang X L, Tan H J, Cheng S H, Min S K. Effect of different irrigation modes during grain filling of rice on translocation and allocation of carbohydrate in rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2005(4): 678-683. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Ball S G, van de M H, Wal B J, Visser R G F. Progress in understanding the biosynthesis of amylase[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 1998, 3: 462-467. |
| [21] |
Ahmed N, Tetlow I J, Nawaz S, Iqbal A, Mubin M, Rehman M, Butt A, Lightfoot D A, Maekawa M. Effect of high temperature on grain filling period, yield, amylose content and activity of starch biosynthesis enzymes in endosperm of Basmati rice[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2015, 95(11): 2237-2243.
PMID |
| [22] | 沈泓, 姚栋萍, 吴俊, 罗秋红, 吴志鹏, 雷东阳, 邓启云, 柏斌. 灌浆期不同时段高温对稻米淀粉理化特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学: 2022, 36(4): 367-376. |
| Shen H, Yao D P, Wu J, Luo Q H, Wu Z P, Lei D Y, Deng Q Y, Bai B. Effects of high temperature at different times during grain filling stage on rice starch physicochemical properties[J]. Journal of Rice Science, 2022, 36(4): 367-376. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Yamakawa H, Hirose T, Kuroda M, Yamaguchi T. Comprehensive expression profiling of rice grain filling-related genes under high temperature using DNA microarray[J]. Plant Physiology, 2007, 144(5): 258-277. |
| [24] | 金正勋, 杨静, 钱春荣, 刘海英, 金学泳, 秋太权. 灌浆成熟期温度对水稻籽粒淀粉合成关键酶活性及品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2005(4): 377-380. |
| Jin Z X, Yang J, Qian C R, Liu H Y, Jin X Y, Qiu T Q. Effects of temperature during grain filling period on activities of key enzymes for starch synthesis and rice grain quality[J]. Journal of Rice Science, 2005(4): 377-380. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 沈波, 陈能, 李太贵, 罗玉坤. 温度对早籼稻米垩白发生与胚乳物质形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 1997, 11(3): 183-186. |
| Shen B, Chen N, Li T G, Luo Y K. Effect of temperature on rice chalkiness formation and changes of materials in endosperm[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Sciences, 1997, 11(3): 183-186. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 张桂莲, 廖斌, 武小金, 肖应辉, 肖浪涛, 陈立云. 高温对水稻胚乳淀粉合成关键酶活性及内源激素含量的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 2014, 50(12): 1840-1844. |
| Zhang G L, Liao B, Wu X J, Xiao Y H, Xiao L T, Chen L Y. Effect of high temperature on activities of enzymes associated with starch synthesis and hormones contents in endosperm of rice[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2014, 50 (12): 1840-1844. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] |
Jiang H W, Dian W M, Wu P. Effect of high temperature on fine structure of amylopectin in rice endosperm by reducing the activity of the starch branching enzyme[J]. Phytochemistry, 2003, 63(1): 53-59.
PMID |
| [28] | 钟连进, 董虎, 蔡小波, 封言柠, 任凭, 程方民. 控制水稻胚乳淀粉合成代谢若干关键酶基因对花后高温的响应表达[J]. 应用生态学报, 2012, 23(3): 745-750. |
| Zhong L J, Dong H, Cai X B, Feng Y N, Ren P, Cheng F M. Gene expression of the key enzymes controlling starch synthesis and metabolism in rice grain endosperm under effects of high temperature after anthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2012, 23(3): 745-750. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Mizuno K, Kimura K, Arai Y. Starch branching enzymes from immature rice seeds[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1992, 112: 643-651. |
| [30] |
Mizuno K, Kawasaki T, Shimada H, Satoh H, Kobayashi E, Okumura S, Arai Y, Baba T. Alteration of the structural properties of starch components by the lack of an isoform of starch branching enzyme in rice seeds[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1993, 268: 19084-19091.
PMID |
| [1] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [2] | 吴子牛, 何丽梅, 熊莹, 陈凯瑞, 杨志远, 孙永健, 吕旭, 马均. 氮素穗肥对杂交籼稻籽粒灌浆影响及其与淀粉合成关键酶活性间关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 48-56. |
| [3] | 杨陶陶, 邹积祥, 伍龙梅, 包晓哲, 江瑜, 张楠, 张彬. 开放式增温对华南双季稻稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 66-77. |
| [4] | 陈红阳, 贾琰, 赵宏伟, 瞿炤珺, 王新鹏, 段雨阳, 杨蕊, 白旭, 王常丞. 结实期低温胁迫对水稻强、弱势粒淀粉形成与积累的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(5): 487-504. |
| [5] | 姚姝, 张亚东, 路凯, 王才林. 水稻可溶性淀粉合成酶基因SSⅡa和SSⅢa的功能、等位变异及其互作研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 227-236. |
| [6] | 姚姝, 张亚东, 刘燕清, 赵春芳, 周丽慧, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, Balakrishna PILLAY, 王才林. Wxmp基因背景下可溶性淀粉合成酶基因SSⅡa和去分支酶基因PUL对水稻蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(3): 217-227. |
| [7] | 杜溢墨 潘天 田云录 刘世家 刘喜 江玲 张文伟 王益华* 万建民. 水稻粉质皱缩胚乳突变体fse4的表型分析与基因克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 499-512. |
| [8] | 成臣, 曾勇军, 程慧煌, 谭雪明, 商庆银, 曾研华, 石庆华. 齐穗至乳熟期不同温度对水稻南粳9108籽粒激素含量、淀粉积累及其合成关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(1): 57-67. |
| [9] | 陈中督, 徐春春, 纪龙, 方福平. 基于农户调查的长江中游地区双季稻生产碳足迹及其构成[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 601-609. |
| [10] | 陈中督 徐春春 纪龙 方福平*. 基于农户调查的长江中游地区双季稻生产碳足迹及其构成[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 601-609. |
| [11] | 杨陶陶, 胡启星, 黄山, 曾研华, 谭雪明, 曾勇军, 潘晓华, 石庆华, 张俊. 双季优质稻产量和品质形成对开放式主动增温的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 572-580. |
| [12] | 孙涛, 同拉嘎, 赵书宇, 王海微, 韩云飞, 张忠臣, 金正勋. 氮肥对水稻胚乳淀粉品质、相关酶活性及基因表达量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(5): 475-484. |
| [13] | 李景芳, 田云录, 刘喜, 刘世家, 陈亮明, 江玲, 张文伟, 徐大勇, 王益华, 万建民. 鸟苷酸激酶OsGK1对水稻种子发育至关重要[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(5): 415-426. |
| [14] | 张习春, 鲁菲菲, 吕育松, 罗荣剑, 焦桂爱, 邬亚文, 唐绍清, 胡培松, 魏祥进. 两个垩白突变体的鉴定及突变基因的图位克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(6): 568-579. |
| [15] | 陈雅玲, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关酶的结构、功能及其互作研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(1): 1-12. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||