
中国水稻科学 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (5): 415-426.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.8003
• • 下一篇
李景芳1, 田云录1, 刘喜1, 刘世家1, 陈亮明1, 江玲1, 张文伟1, 徐大勇2, 王益华1,*( ), 万建民1
), 万建民1
收稿日期:2018-01-15
修回日期:2018-03-17
出版日期:2018-09-10
发布日期:2018-09-10
通讯作者:
王益华
基金资助:
Jingfang LI1, Yunlu TIAN1, Xi LIU1, Shijia LIU1, Liangming CHEN1, Ling JIANG1, Wenwei ZHANG1, Dayong XU2, Yihua WANG1,*( ), Jianmin WAN1
), Jianmin WAN1
Received:2018-01-15
Revised:2018-03-17
Online:2018-09-10
Published:2018-09-10
Contact:
Yihua WANG
摘要:
【目的】对水稻粉质皱缩突变体fse2进行表型分析及基因克隆,为阐明水稻淀粉合成机制以及胚的发育奠定基础。【方法】fse2来自粳稻品种滇粳优1号的MNU(N-甲基-N-亚硝基脲)诱变突变体库。本研究考查了突变体fse2籽粒的理化性状,利用扫描电镜和半薄切片观察了淀粉颗粒的结构;构建了fse2与N22的F2群体,通过图位克隆及转基因互补验证确定目标基因;通过qRT-PCR以及GUS活性染色对FSE2进行组织表达分析;免疫印迹分析了突变体中淀粉合成相关基因以及线粒体基因的蛋白变化。【结果】fse2籽粒粉质皱缩,千粒重显著下降;胚乳中淀粉颗粒变小变圆,排列松散,不能形成正常的复合淀粉颗粒;突变体中总淀粉、直链淀粉含量均显著下降,脂肪含量显著上升,突变体淀粉的糊化特性发生明显改变。FSE2编码一个线粒体和质体双定位的鸟苷酸激酶(guanylate kinase),命名为OsGK1。OsGK1在各器官中组成型表达,并在花后6 d的胚乳中表达水平最高。突变体胚乳中淀粉合成相关蛋白水平显著降低,尤其是AGPS2b和PHOI。此外,突变体fse2的胚发育严重受损,导致种子纯合致死;线粒体定位的AOX积累显著增强,而野生型中几乎检测不到,表明线粒体呼吸途径受损。【结论】由于OsGK1的功能缺陷,导致水稻种子中线粒体和造粉体发育异常,进而产生了胚致死以及胚乳粉质皱缩的表型,因此OsGK1对水稻种子的发育至关重要。
中图分类号:
李景芳, 田云录, 刘喜, 刘世家, 陈亮明, 江玲, 张文伟, 徐大勇, 王益华, 万建民. 鸟苷酸激酶OsGK1对水稻种子发育至关重要[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(5): 415-426.
Jingfang LI, Yunlu TIAN, Xi LIU, Shijia LIU, Liangming CHEN, Ling JIANG, Wenwei ZHANG, Dayong XU, Yihua WANG, Jianmin WAN. The Guanylate Kinase OsGK1 is Essential for Seed Development in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(5): 415-426.
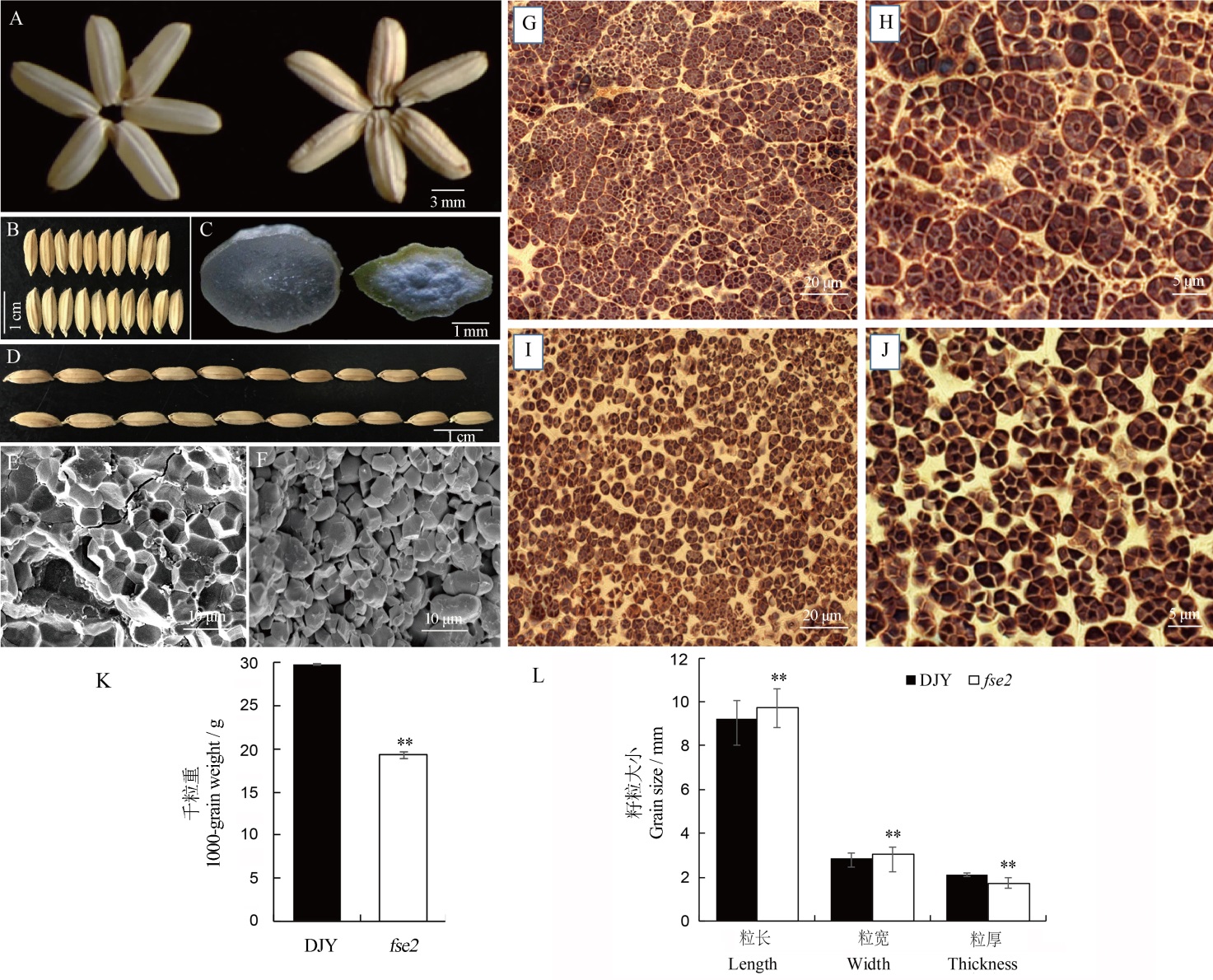
图1 野生型与突变体fse2成熟种子表型比较 A,B,D—滇粳优1号(DJY)与fse2的成熟种子的外观表型;A,DJY(左),fse2(右)。B和D,DJY(上),fse2(下)。C—DJY(左)与fse2(右)种子的横切面。E,F—DJY(E)和fse2(F)成熟种子横切面的SEM观察。G~J—花后10 d I2-KI染色的DJY(G,H)和fse2(I,J)胚乳半薄切片。K—DJY和fse2的千粒重比较,n=3;L—DJY和fse2的粒长、粒宽和粒厚,n=20。所有数值为平均值±标准差;**野生型与突变体间的差异达0.01显著水平(t测验)。
Fig. 1. Phenotypic comparison of mature seeds of wild type and fse2 mutant. A, B, D, Mature seeds of Dianjingyou 1(DJY) and fse2. A, DJY (left), fse2 (right). B, D, DJY (upper), fse2 (lower). C, Cross-sections of mature seeds of DJY(left) and fse2 (right). E, F, Scanning electron microscopic (SEM) analysis of cross-sections of mature seeds of DJY (E) and fse2 (F). G-J, Semi-thin sections of DJY (G, H) and fse2 (I, J) endosperm at 10 days after pollination (DAP) stained with I2-KI. K, The 1000-grain weight of DJY and fse2. n=3. L, Grain length, width and thickness in DJY and fse2. n=20. All values are expressed as mean±SD. **means significant difference at 0.01 level (Student’s t-test).
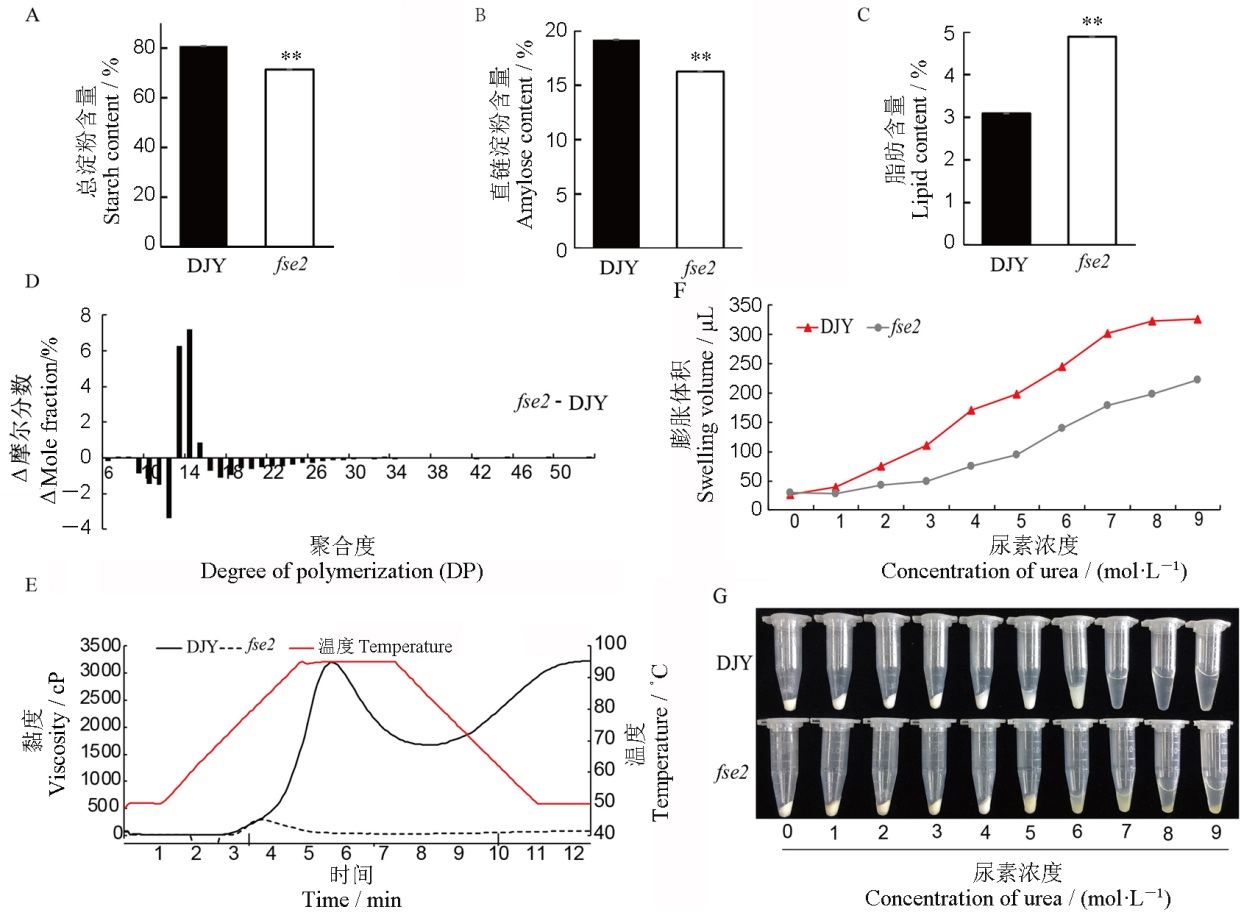
图2 野生型与突变体fse2成熟种子理化特性分析 A~C—滇粳优1号(DJY)和fse2胚乳中总淀粉(A)、直链淀粉(B)和脂肪(C)含量的测定,n=3,取平均值±标准差,采用t测验,**P<0.01;D—DJY和fse2支链淀粉链长分布;E—DJY和fse2淀粉的RVA谱分析;F—DJY与fse2米粉的膨胀体积比较(n=3);G—DJY与fse2的尿素膨胀。
Fig. 2. Physicochemical characteristics of mature seeds of fse2 and its wild type. A~C, The contents of total starch (A), amylose (B), and lipid (C) in the endosperm of Dianjingyou(DJY) and fse2. n=3, Values are means±SD, Student’s t-test, **P<0.01. D, Amylopectin chain length distributions of DJY and fse2. E, Analysis of RVA characteristic of starch in DJY and fse2. F, The swollen volume of DJY and fse2 starch in urea solution (n=3). G, Starch expansion of DJY and fse2 in urea solutions.
| 试材 Test material | 最高黏度 Peak viscosity | 热浆黏度 Hot pasting viscosity | 崩解值Breakdown viscosity | 冷胶黏度 Cool pasting viscosity | 消减值 Setback viscosity | 峰值时间 Peak time / min | 糊化温度 Gelatinization temperature /℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DJY | 3197 | 1677 | 1520 | 3225 | 28 | 5.67 | 76.00 |
| fse2 | 293 | 34 | 259 | 83 | -210 | 3.80 | 75.95 |
表1 野生型和突变体fse2淀粉的RVA谱特征分析
Table 1 Analysis of RVA characteristic values of starch in wild type and fse2 mutant.
| 试材 Test material | 最高黏度 Peak viscosity | 热浆黏度 Hot pasting viscosity | 崩解值Breakdown viscosity | 冷胶黏度 Cool pasting viscosity | 消减值 Setback viscosity | 峰值时间 Peak time / min | 糊化温度 Gelatinization temperature /℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DJY | 3197 | 1677 | 1520 | 3225 | 28 | 5.67 | 76.00 |
| fse2 | 293 | 34 | 259 | 83 | -210 | 3.80 | 75.95 |
| 年份 Year | 透明种子数 Number of normal seeds | 粉质皱缩种子数 Number of floury and shrunken seeds | χ2(3:1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 681 | 208 | 1.508 |
| 2016 | 573 | 172 | 1.612 |
表2 fse2遗传分析
Table 2 Genetic analysis of fse2.
| 年份 Year | 透明种子数 Number of normal seeds | 粉质皱缩种子数 Number of floury and shrunken seeds | χ2(3:1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 681 | 208 | 1.508 |
| 2016 | 573 | 172 | 1.612 |
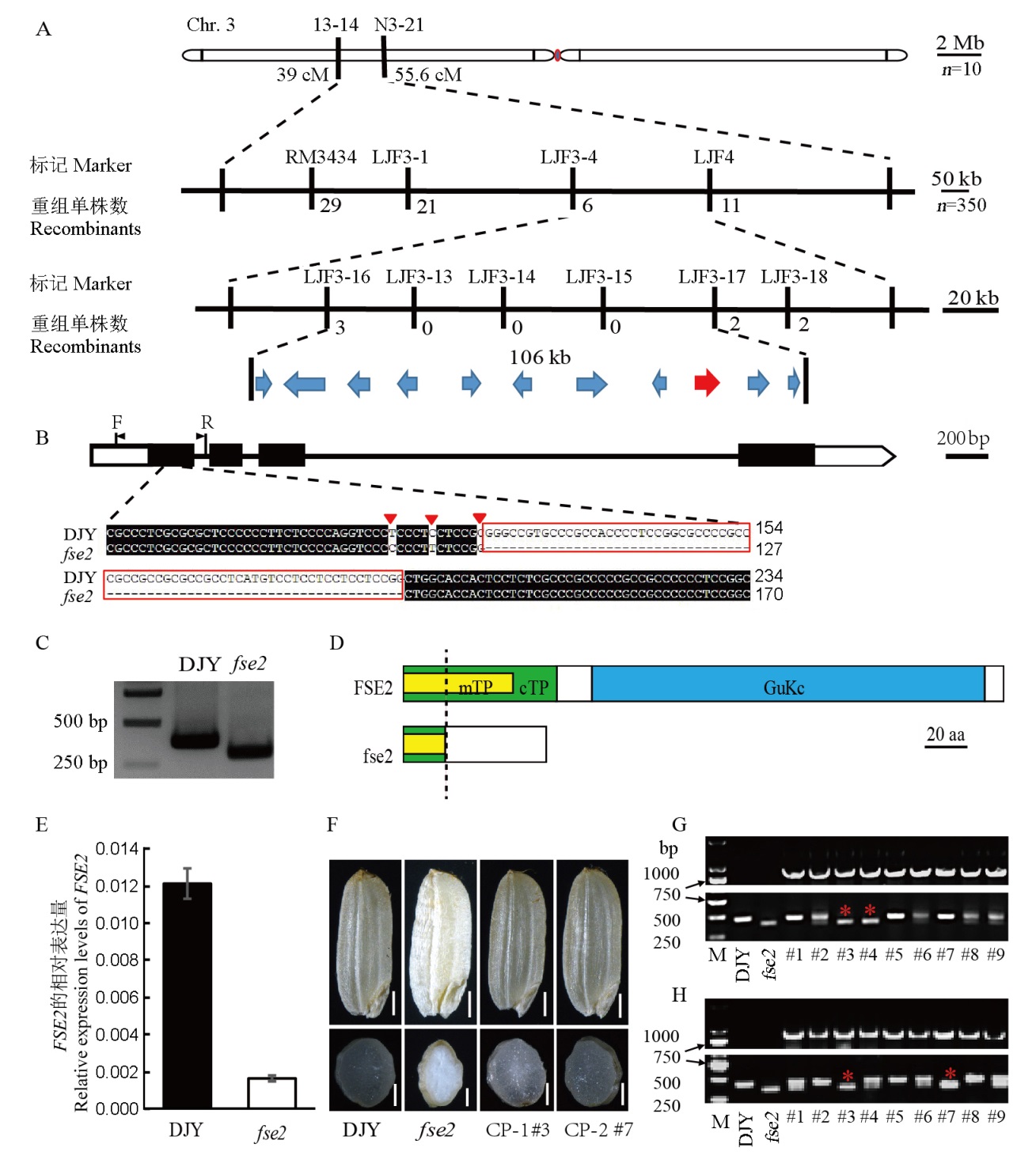
图3 FSE2的图位克隆 A―FSE2位点的图位克隆,FSE2定位在第3染色体短臂标记LJF3-16与LJF3-17之间约106 kb区域内,包含11个预测基因;B―Os03g0320900基因结构和突变位点,序列中存在3处单碱基替换(红色三角)和70 bp的缺失(红色方框)。引物F/R用于鉴定转基因家系CP-1、CP-2中透明种子的遗传背景;C―PCR鉴定FSE2基因中70 bp的缺失;D―FSE2蛋白的定位信号及结构域,在fse2中共有68个氨基酸,但只有N端20个氨基酸与野生型保持一致(虚线左边);mTP―线粒体转运肽;cTP―叶绿体转运肽;aa―氨基酸;E―FSE2在DJY和fse2发育种子中(开花10 d后)的相对表达量;F―具突变体背景的阳性转基因种子(CP-1 #3和CP-2 #7)恢复为正常表型,CP-1和CP-2为具有杂合突变体背景的转基因阳性家系,标尺为1 cm;G,H―CP-1家系(G)和CP-2家系(H)后代透明种子的PCR鉴定。G和H中上图均为转基因阳性鉴定结果,下图均为遗传背景检测结果,红色星号表示纯合突变体背景的阳性转基因种子。DJY―滇粳优1号。
Fig. 3. Map-based cloning of FSE2. A, Map-based cloning of the FSE2 locus. The FSE2 locus was mapped to a 106 kb region by markers LJF3-16 and LJF3-17 on the short arm of chromosome 3, which contains 11 predicted open reading frames (ORFs). B, The structure of Os03g0320900 and the mutation site. Three nucleotide substitutions (red triangles) and a 70 bp deletion (red box) in the sequence are indicated. The genetic background was identified with the primer pair F/R in transgenic lines. C, PCR analysis of the 70 bp deletion in the genomic region of Os03g0320900. D, Target peptides and functional domain of FSE2 protein. A total of 68 amino acids in fse2, and only the first 20 amino acids in the N-terminus are consistent with the wild type (left of the dotted line). mTP, Mitochondrial transit peptide; cTP, Chloroplast transit peptide; aa, amino acids. E, The relative expression levels of developing seeds (10 days post-pollination) in DJY and fse2. F, Positive transgenic seeds with homozygous fse2 background (CP-1 #3 and CP-2 #7) showed transparent endosperm. CP-1 and CP-2 are two positive transgenic lines with heterozygous background. Bar=1 cm. G-H, PCR analyses of the transparent seeds from CP-1 and CP-2 lines. The upper panels in G and H represent positive transgenic individuals. The lower panels of G and H show the backgrounds of these positive transgenic individuals. The red asterisks indicate the positive transgenic seeds with homozygous fse2 background. DJY, Dianjingyou 1.
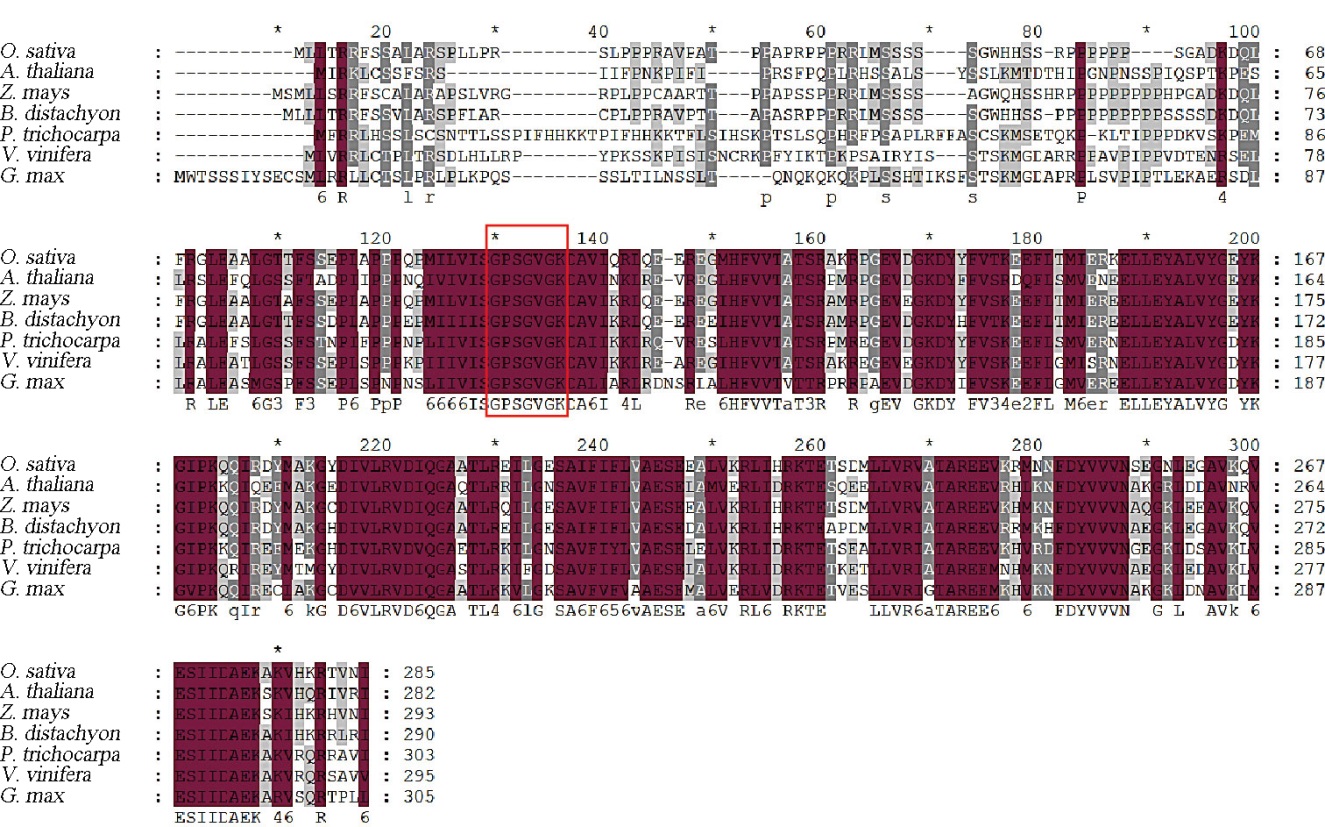
图4 FSE2及其同源蛋白序列比对红色方框区域代表鸟苷酸激酶催化位点;GenBank蛋白质登录号:水稻,XP_051628708.1;拟南芥,NP_566276.1;玉米,NP_001149581.1;二穗短柄草,XP_003561683.1;毛果杨,XP_006380050.1;葡萄,XP_002279802.1;大豆,XP_003542897.2。
Fig. 4. Protein sequence alignment of FSE2 and its homologs. The red box indicates the catalytic site of GK; GenBank protein accession number are as follows O. sativa, XP_051628708.1; A. thaliana, NP_566276.1; Z. mays, NP_001149581.1; B. distachyon, XP_003561683.1; P. trichocarpa, XP_006380050.1; V. vinifera, XP_002279802.1; G. max, XP_003542897.2.
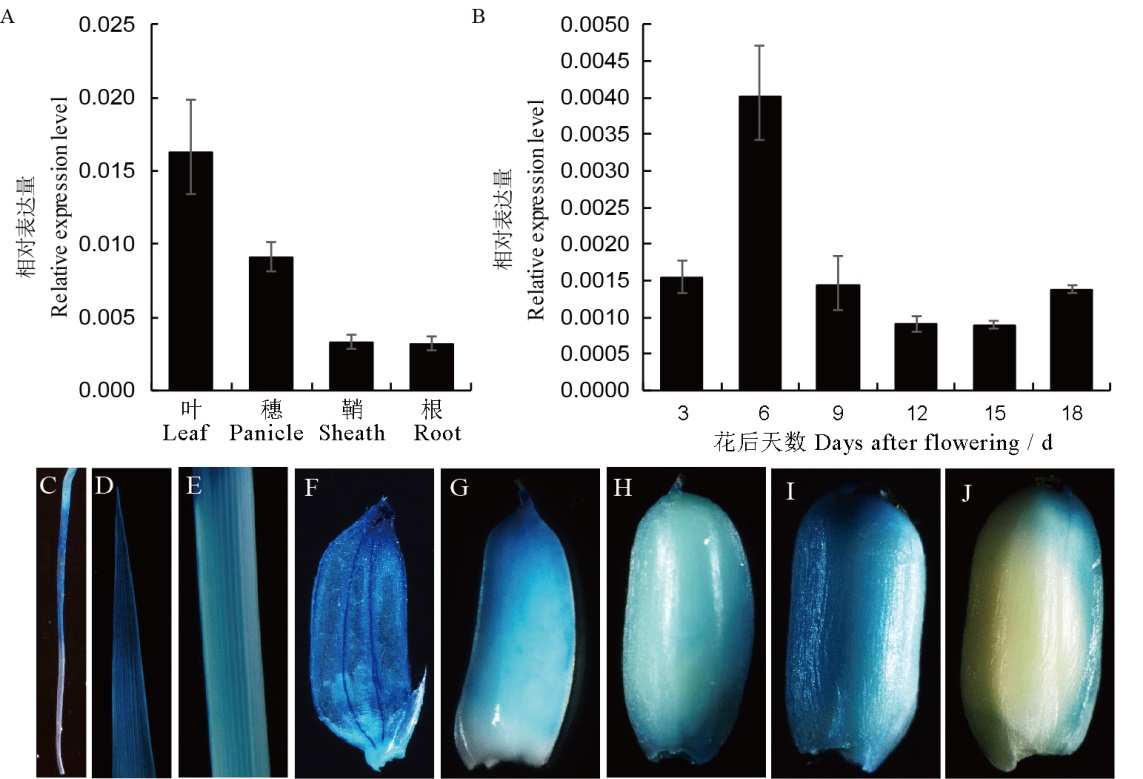
图5 FSE2的表达模式 A—FSE2在叶、穗子、鞘、根中的表达量;B—FSE2在花后3、6、9、12、15和18 d的发育胚乳中的表达量;C~F—根(C)、叶(D)、鞘(E)、小花(F)的GUS染色;G~J—开花后6(G)、9(H)、12(I)和15 d(J)的发育胚乳的GUS染色。
Fig. 5. The expression patterns of FSE2. A, Expression levels of FSE 2 in leaf, panicle, sheath and root of wild type. B, Expression levels of FSE2 in the developing endosperms of 3, 6, 9, 12, 15 and 18 days after flowering. C-F, GUS staining patterns in root (C), leaf (D), sheath (E) and panicle (F); G-J, GUS staining patterns in developing endosperm of 6 (G), 9 (H), 12 (I) and 15 days after flowering (J).
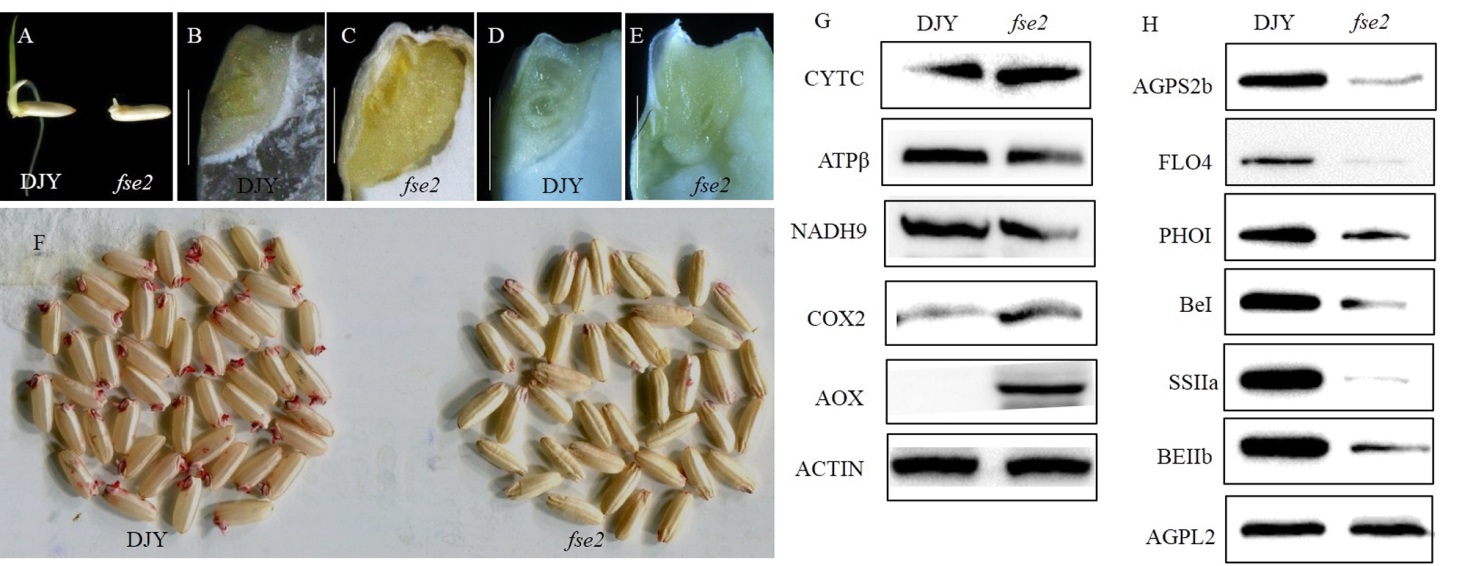
图6 突变体fse2的胚和胚乳发育异常 A—野生型和突变体fse2种子萌发后2 d的表型;B,C—野生型和突变体fse2种子吸胀后的胚(30℃下吸胀9 h),比例尺为1 mm;D,E—花后15 d野生型和突变体的胚,比例尺为1 mm;F—TTC法测定种子活力;G—Western blotting检测野生型和突变体成熟种子中的线粒体相关蛋白含量。CytC―细胞色素c合成酶C;COX2―细胞色素c氧化酶亚基2;NADH9―NADH脱氢酶亚基9;ATPβ―ATP合酶F0亚基6;AOX―交替氧化酶;H—Western blotting检测野生型和突变体成熟种子中淀粉合成相关酶蛋白含量,AGPL2―腺苷葡萄糖焦磷酸化酶大亚基2;AGPS2b―腺苷葡萄糖焦磷酸化酶小亚基2b;PPDKB―胞质丙酮酸磷酸双激酶B;PHOⅠ―质体磷酸化酶Ⅰ;BEⅠ―淀粉分支酶Ⅰ;BEⅡb―淀粉分支酶Ⅱb;SSⅡa―淀粉合酶Ⅱa;G,H中以ACTIN作为内参。DJY―滇粳优1号。
Fig. 6. The abnormal development of embryo and endosperm in the fse2 mutant. A, Comparison of the seed of wild type and fse2 after germinating for two days. B,C, Embryos of wild type and fse2 mutant seeds after imbibition (30℃, 9 h). Bars=1 mm. D, E, Developing embryos of 15 DAP seeds of wild type and fse2. Bars=1 mm. F, The determination of seed viability by TTC staining. G, Western blotting analysis of mitochondrial proteins in mature seeds of wild type and mutant. CytC, Cytochrome c biogenesis C; COX2, Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 2; NADH9, NADH dehydrogenase subunit 9; ATPβ, ATP synthase F0 subunit 6; AOX, Alternative oxidase. H, Western blotting analysis of starch synthesis enzymes in mature seeds of wild type and mutant. AGPL2, ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase large subunit 2; AGPS2b, ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase small subunit 2b; PPDKB, Cytosolic pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase B; PHOⅠ, Plastid phosphorylaseⅠ; BEⅠ, Starch-branching enzyme; BEⅡb, Starch-branching enzymeⅡb; SSⅡa, Starch synthaseⅡa. ACTIN antibody was used as a loading control in G and H. DJY, Dianjingyou 1.
| [1] | Khush G S.What it will take to feed 5.0 billion rice consumers in 2030.Plant Mol Biol, 2005, 59(1): 1-6. |
| [2] | Zhou Z, Robards K, Heliwell S, Blanchard C.Composition and functional properties of rice.Int J Food Sci Technol, 2002, 37(8): 849-868. |
| [3] | Demirkesen I, Sumnu G, Sahin S.Image analysis of gluten-free breads prepared with chestnut and rice flour and baked in different ovens.Food Bioprocess Technol, 2013, 6(7): 1749-1758. |
| [4] | Patindol J, Wang Y J.Fine structures and physicochemical properties of starches from chalky and translucent rice kernels.J Agric Food Chem, 2003, 51(9): 2777-2784. |
| [5] | Martin C, Smith A M.Starch biosynthesis.Plant Cell, 1995, 7(7): 971-985. |
| [6] | Nakamura Y.Towards a better understanding of the metabolic system for amylopectin biosynthesis in plants: Rice endosperm as a model tissue.Plant & Cell Physiol, 2002, 43(7): 718-725. |
| [7] | Hirose T, Terao T.A comprehensive expression analysis of the starch synthase gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Planta, 2004, 220(1): 9-16. |
| [8] | Ball S G, Morell M K.From bacterial glycogen to starch: Understanding the biogenesis of the plant starch granule.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 2003, 54(1): 207-233. |
| [9] | Colleoni C, Dauvillée D, Mouille G, Morell M, Samuel M, Slomiany M C, Lienard L, Wattebled F, d’Hulst C, Ball S. Biochemical characterization of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii α-1,4 glucanotransferase supports a direct function in amylopectin biosynthesis. Plant Physiol, 1999, 120(4): 1005-1014. |
| [10] | Dauvillée D, Chochois V, Steup M, Haebel S, Eckermann N, Ritte G, Ral J P, Colleoni C, Hicks G, Wattebled F O, Deschamps P, d’Hulst C O, Liénard L, Cournac L O, Putaux J L O, Dupeyre D, Ball S G O. Plastidial phosphorylase is required for normal starch synthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J, 2006, 48(2): 274-285. |
| [11] | Dong X, Zhang D, Liu J, Liu Q Q, Liu H, Tian L, Jiang L, Qu le Q. Plastidial disproportionating enzyme participates in starch synthesis in rice endosperm by transferring maltooligosyl groups from amylose and amylopectin to amylopectin.Plant Physiol, 2015, 169(4): 2496-2512. |
| [12] | Schupp N, Ziegler P.The relation of starch phosphorylases to starch metabolism in wheat.Plant & Cell Physiol, 2004, 45(10): 1471-1484. |
| [13] | Satoh H, Shibahara K, Tokunaga T, Nishi A, Tasaki M, Hwang S K, Okita T W, Kaneko N, Fujita N, Yoshida M, Hosaka Y, Sato A, Utsumi Y, Ohdan T, Nakamura Y.Mutation of the plastidial a-glucan phosphorylase gene in rice affects the synthesis and structure of starch in the endosperm.Plant Cell, 2008, 20(7): 1833-1849. |
| [14] | Pfeilmeier S, Saur I M, Rathjen J P, Zipfel C, Malone J G.High levels of cyclic-di-GMP in plant-associated Pseudomonas correlate with evasion of plant immunity.Mol Plant Pathol, 2016, 17(4): 521-531. |
| [15] | Zrenner R, Stitt M, Sonnewald U, Boldt R.Pyrimidine and purine biosynthesis and degradation in plants.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 2006, 57: 805-836. |
| [16] | Green R, Noller H F.Ribosomes and translation.Annu Rev Biochem, 1997, 66: 679-716. |
| [17] | Sumita K, Lo Y H, Takeuchi K, Senda M, Kofuj S, Ikeda Y, Terakawa J, Sasaki M, Yoshino H, Majd N, Zheng Y X, Kahoud E R, Yokota T, Emerling B M, Asara J M, Ishida T, Locasale J W, Daikoku T, Anastasiou D, Senda T, Sasaki A T.The lipid kinase PI5P4Kβ is an intracellular GTP sensor for metabolism and tumorigenesis.Mol Cell, 2016, 61(2): 187-198. |
| [18] | Caro L G, Palade G E.Protein synthesis, storage, and discharge in the pancreatic exocrine cell. An autoradiographic study. J Cell Biol, 1946, 20(3): 473-495. |
| [19] | Havel P J.Control of energy homeostasis and insulin action by adipocyte hormones: Leptin, acylation stimulating protein, and adiponectin.Curr Opin Lipidol, 2002, 13(1): 51-59. |
| [20] | Stasolla C, Katahira R, Thorpe T A, Ashihara H.Purine and pyrimidine nucleotide metabolism in higher plants.J Plant Physiol, 2003, 160(11): 1271-1295. |
| [21] | Gaidarov I O, Suslov O N, Abdulaev N G.Enzymes of the cyclic GMP metabolism in Bovine retina: I. Cloning and expression of the gene for guanylate kinase. FEBS Lett, 1993, 335(1): 81-84. |
| [22] | Brady W A, Kokoris M S, Fitzgibbon M, Black M E.Cloning, characterization, and modeling of mouse and human guanylate kinases.J Biol Chem, 1996, 271(28): 16734-16740. |
| [23] | Stolworthy T S, Krabbenhoft E, Black M E.A novel Escherichia coli strain allows functional analysis of guanylate kinase drug resistance and sensitivity.Anal Biochem, 2003, 322(1): 40-47. |
| [24] | Beck B J, Huelsmeyer M, Paul S, Downs D M.A mutation in the essential gene gmk(encoding guanylate kinase) generates a requirement for adenine at low temperature in Salmonella enteric. J Bacteriol, 2003, 185(22): 6732-6735. |
| [25] | Gentry D, Bengra C, Ikehara K, Cashel M.Guanylate kinase of Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem, 1993, 268(19): 14316-14321. |
| [26] | Konrad M.Cloning and expression of the essential gene for guanylate kinase from yeast.J Biol Chem, 1992, 267(36): 25652-25655. |
| [27] | Ray B D, Jarori G K, Raghunathan V, Yan H, Rao B D N. Conformations of nucleotides bound to wild type and Y78 F mutant yeast guanylate kinase: Proton two-dimensional transferred NOESY measurements. Biochemistry, 2005, 44(42): 13762 13770. |
| [28] | Kumar V.Cloning and sequence analysis of lily and tobacco guanylate kinases.Mol Biol Rep, 2000, 27(1): 45 49. |
| [29] | Kumar V, Spangenberg O, Konrad M.Cloning of the guanylate kinase homologues AGK-1 and AGK-2 from Arabidopsis thaliana and characterization of AGK-1. Eur J Biochem, 2000, 267(2): 606-615 |
| [30] | Sugimoto H, Kusumi K, Tozawa Y, Yazaki H, Kishimoto N, Kikuchi S, Iba K.The virescent-2 mutation inhibits translation of plastid transcripts for the plastid genetic system at an early stage of chloroplast differentiation. Plant & Cell Physiol, 2004, 45(8): 985-996. |
| [31] | Sugimoto H, Kusumi K, Noguchi K, Yano M, Yoshimura A, Iba K.The rice nuclear gene,VIRESCENT 2, is essential for chloroplast development and encodes a novel type of guanylate kinase targeted to plastids and mitochondria. Plant J, 2007, 52(3): 512-527. |
| [32] | Kang H G, Park S, Matsuoka M, An G.White-core endosperm floury endosperm-4 in rice is generated by knockout mutations in the C-type pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase gene (OsPPDKB). Plant J, 2005, 42(6): 901-911. |
| [33] | Peng C, Wang Y, Liu F, Ren Y, Zhou K, Lv J, Zheng M, Zhao M, Zhao S, Zhang L, Wang C, Jiang L, Zhang X, Guo X, Wan J M.FLOURY ENDOSPERM 6 encodes a CBM48 domain-containing protein involved in compound granule formation and starch synthesis in rice endosperm. Plant J, 2014, 77(6): 917-930. |
| [34] | Nishi A, Nakamura Y, Tanaka N, Satoh H.Biochemical and genetic analysis of the effects of Amylose-Extender mutation in rice endosperm. Plant Physiol, 2001, 127(2): 459-472 |
| [35] | Ohdan T, Francisco P B Jr, Sawada T, Hirose T, Saltoh H, Nakamura Y. Expression profiling of genes involved in starch synthesis in sink and source organs of rice. J Exp Bot, 2005, 56(422): 3229-3244. |
| [36] | Akihiro T, Mizuno K, Fujimura T.Gene expression of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and starch contents in rice cultured cells are cooperatively regulated by sucrose and ABA.Plant & Cell Physiol, 2005, 46(6): 937-946. |
| [37] | Finnegan P M, Soole K L, Umbach A L.Alternative mitochondrial electron transport proteins in higher plants. //Day D A, Millar A H, Whelan J. Plant Mitochondria: From Genome to Function. The Netherlands: Springer, 2004: 163-230. |
| [38] | Selinshi J, Hartmann A, Kordes A, Deckers-Hebestreit G, Whelan J, Scheibe R.Analysis of post-translational activation of alternative oxidase isoforms.Plant Physiol, 2017, 174(4): 2113-2127. |
| [39] | Zhang Y F, Suzuki M, Sun F, Tan B C.The mitochondrion-targeted PENTATRICOPEPTIDE REPEAT78 protein is required fornad5 mature mRNA stability and seed development in maize. Mol Plant, 2017, 10(10): 1321-1333 |
| [40] | Li X J, Zhang Y F, Hou M M, Sun F, Shen Y, Xiu Z H, Wang X, Chen Z L, Sun S S, Small I, Tan B C.Small kernel 1 encodes a pentatricopeptide repeat protein required for mitochondrial nad7 transcript editing and seed development in maize(Zea mays) and rice, 2014, 79(5): 797-809. |
| [41] | Liu Y J, Xiu Z H, Meeley R, Tan B C.Empty Pericarp5 encodes a pentatricopeptide repeat protein that is required for mitochondrial RNA editing and seed development in maize. Plant Cell, 2013, 25(3): 868-883. |
| [42] | Yang Y Z, Ding S, Wang H C, Sun F, Huang W L, Song S, Xu C, Tan B C.The pentatricopeptide repeat protein EMP9 is required for mitochondrial ccmB and rps4 transcript editing, mitochondrial complex biogenesis and seed development in maize. New Phytol, 2017, 214(2): 782-795. |
| [43] | Cai M J, Li S Z, Sun F, Sun Q, Zhao H, Ren X, Zhao Y, Tan B C, Zhang Z, Qiu F.Emp10 encodes a mitochondrial PPR protein that affects the cis-splicing of nad2 intron 1 and seed development in maize. Plant J, 2017, 91(1): 132-144. |
| [44] | Ren X M, Pan Z Y, Zhao H L, Zhao J L, Cai M J, Li J, Zhang Z X, Qiu F Z.EMPTY PERICARP11 serves as a factor for splicing of mitochondrial nad1 intron and is required to ensure proper seed development in maize. J Exp Bot, 2017, 68(16): 4571-4581. |
| [45] | Jiang P F, Wang S L, Jiang H Y, Cheng B J, Wu K Q, Ding Y.The COMPASS-like complex promotes flowering and panicle branching in rice. Plant Physiol, 176(4): 01749.2017. DOI:10.1104/pp.17.01749. |
| [46] | Minkenberg B, Xie K, Yang Y N.Discovery of rice essential genes by characterizing a CRISPR-edited mutation of closely related rice MAP kinase genes.Plant J, 2017, 89(3): 636-648. |
| [47] | Huang X, Peng X, Sun M X.OsGCD1 is essential for rice fertility and required for embryo dorsal-ventral pattern formation and endosperm development.New Phytol, 2017, 215(9): 1039-1058. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||