
中国水稻科学 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (5): 437-444.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7154
窦玲玲, 胡海超, 马龙, 柯笑楠, 刘明月, 练旺民, 金珂, 谢玲娟, 刘庆坡*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-12-25
修回日期:2018-02-01
出版日期:2018-09-10
发布日期:2018-09-10
通讯作者:
刘庆坡
基金资助:
Lingling DOU, Haichao HU, Long MA, Xiaonan KE, Mingyue LIU, Wangmin LIAN, Ke JIN, Lingjuan XIE, Qingpo LIU*( )
)
Received:2017-12-25
Revised:2018-02-01
Online:2018-09-10
Published:2018-09-10
Contact:
Qingpo LIU
摘要:
【目的】水稻Os08g44770.1基因编码一个铜锌SOD酶,但其在响应亚砷酸盐[As(Ⅲ)]胁迫中的生物学功能未知。本研究旨在深入揭示由该基因调控水稻砷耐性改变的分子机理并为水稻抗逆育种提供理论参考。【方法】以野生型日本晴(WT)和2个Os08g44770.1过表达转基因株系为试材,通过胁迫处理、生理指标测定和基因表达分析等,系统探究了转基因植株对As(Ⅲ)的耐受性表现,并初步揭示了其调控水稻砷耐性的生理和分子机理。【结果】与WT相比,过表达转基因株系对As(Ⅲ)更加敏感;转基因植株在砷胁迫下的根系相对伸长量、生物量(干质量)、叶绿素含量、根系细胞质膜完整性、叶片抗氧化程度等均显著低于WT;Os08g44770.1在砷处理后的WT和转基因植株叶片中的表达模式略有不同,但均表现为处理24 h时被显著诱导表达。【结论】过度表达Os08g44770.1基因可导致水稻的砷耐受性极显著下降。
中图分类号:
窦玲玲, 胡海超, 马龙, 柯笑楠, 刘明月, 练旺民, 金珂, 谢玲娟, 刘庆坡. 一个水稻铜锌SOD酶基因在应答亚砷酸盐胁迫中的作用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(5): 437-444.
Lingling DOU, Haichao HU, Long MA, Xiaonan KE, Mingyue LIU, Wangmin LIAN, Ke JIN, Lingjuan XIE, Qingpo LIU. Functional Analysis of a Copper/Zinc SOD Encoding Gene in Response to Arsenite Stress in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(5): 437-444.
| 基因名称 Gene symbol | 正向引物 Forward primer(5′-3′) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Os08g44770.1 | GCTTCCACCTCCACGAGTTT | GCCACCCTTCCCCAAATCAT |
| β-actin | TGTGGATTGCCAAGGCTGAG | ACGGCGATAACAGCTCCTC |
Table 1 The real-time RT-PCR primer sequences.
| 基因名称 Gene symbol | 正向引物 Forward primer(5′-3′) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Os08g44770.1 | GCTTCCACCTCCACGAGTTT | GCCACCCTTCCCCAAATCAT |
| β-actin | TGTGGATTGCCAAGGCTGAG | ACGGCGATAACAGCTCCTC |
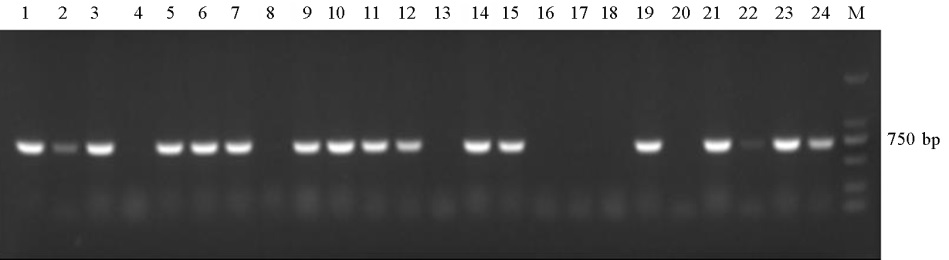
图1 部分转基因水稻的PCR检测 M–DNA标记 2000; 1–阳性对照;2, 3, 5~7, 9~12, 14, 15, 19, 21, 23, 24为转基因阳性植株;4, 8, 13, 16~18, 20, 22为转基因阴性植株。
Fig. 1. PCR analysis of transgenic rice plants carrying overexpressed Os08g44770.1. M–DNA marker 2000; 1, Positive control; 2, 3, 5-7, 9-12, 14, 15, 19, 21, 23, 24 are transformed plants; The others are untransformed plants.
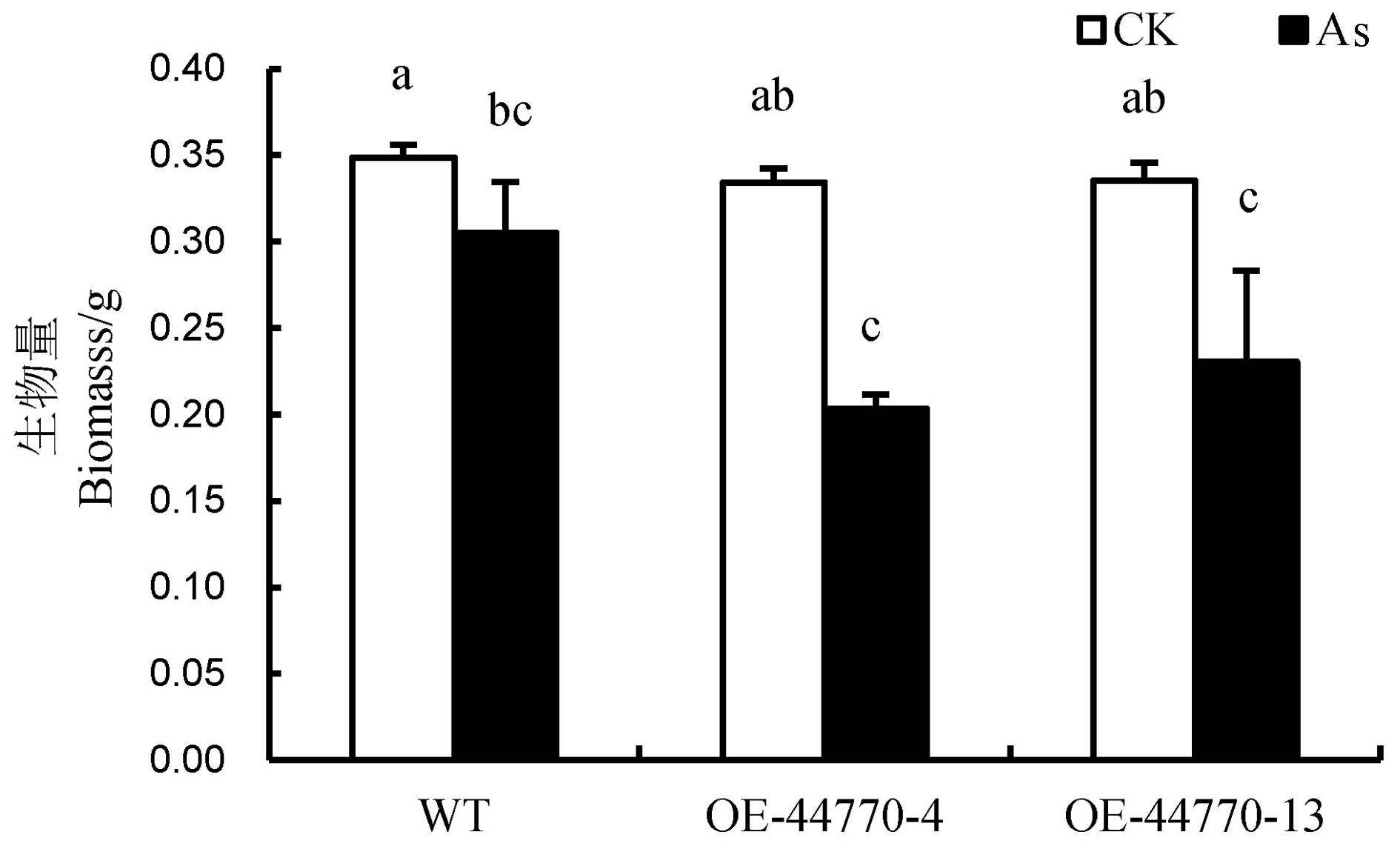
图4 亚砷酸盐处理6 d后WT和各转基因株系的生物量相同小写字母表示不同材料不同处理间差异未达0.05显著水平。
Fig. 4. Comparison of biomass of WT and transgenic rice plants after 6-day As(Ⅲ) treatment(n=8). Common lowercase letters above the bars indicate no significant difference among treatments or materials (P≤0.05).
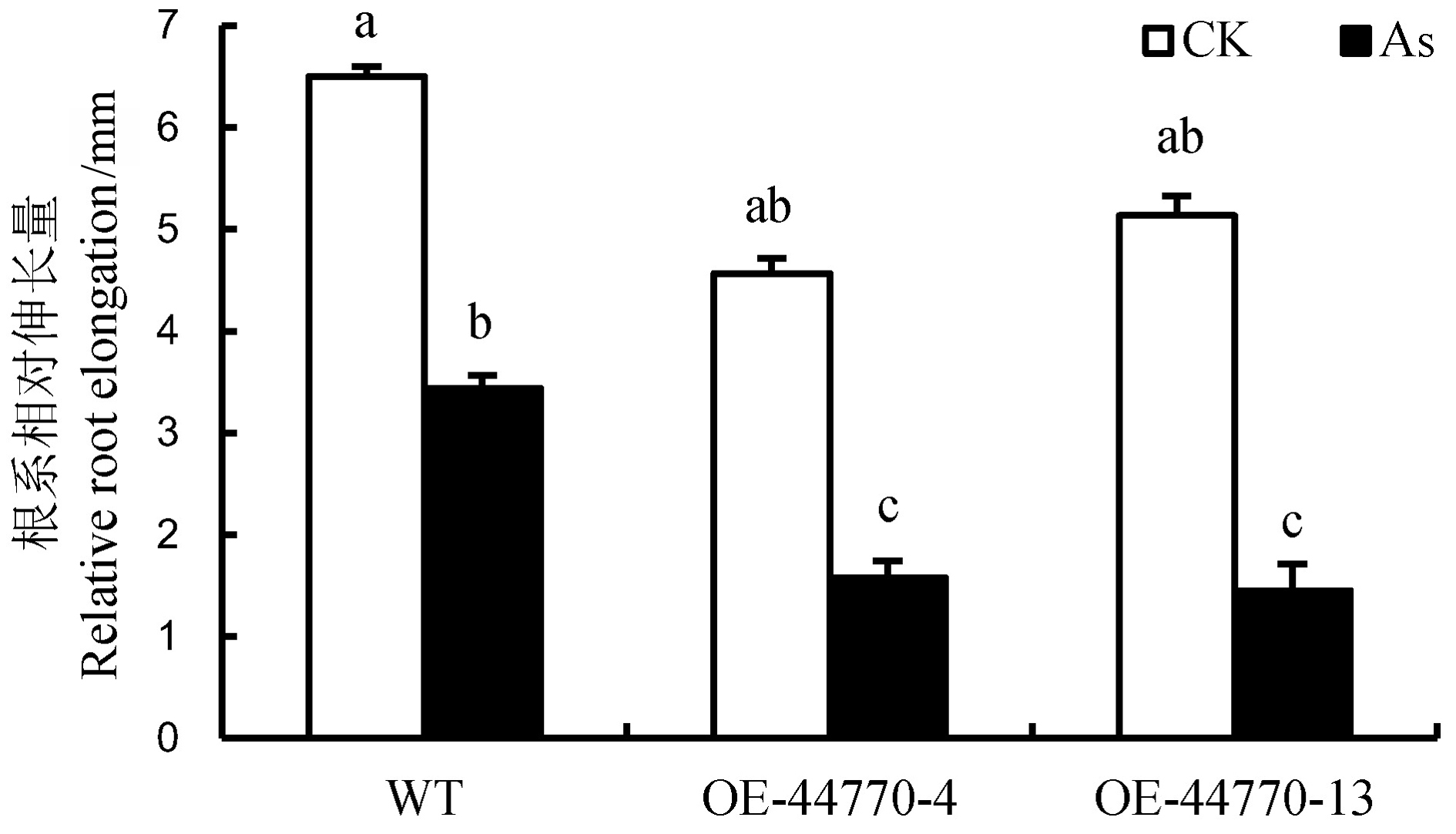
图5 亚砷酸盐处理6 d后WT和各转基因株系根系相对伸长量的比较(n=8) 相同小写字母表示不同材料不同处理间差异未达0.05显著水平。
Fig. 5. Comparison of relative root elongation of WT and transgenic rice plants under As(Ⅲ) stress for 6 days (n=8). Common lowercase letters above the bars indicate no significant difference among treatments or materials (P≤0.05).
| 处理 Treatment | 供试材料 Tested material | 叶绿素a含量 Chlorophyll a content / (mg∙g-1) | 叶绿素b含量 Chlorophyll b content / (mg∙g-1) | 总叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll a+b content / (mg∙g-1) | 类胡萝卜素含量 Carotenoid content / (mg∙g-1) | 叶绿素a /叶绿素b Chlorophyll a/ Chlorophyll b | 类胡萝卜素 /总叶绿素 Carotenoid/ Chlorophyll a+b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照CK | WT | 24.25±1.16 a | 8.14±1.16 a | 32.39±1.79 a | 4.69±0.30 abc | 2.98±0.35 a | 0.14±0.02 b |
| OE-44770-4 | 22.90±1.30 b | 6.20±1.30 ab | 29.21±2.68 ab | 4.94±0.25 ab | 3.67±0.50 a | 0.17±0.01 ab | |
| OE-44770-13 | 23.90±1.34 a | 7.27±1.34 ab | 31.20±2.44 a | 5.20±0.07 a | 3.30±0.49 a | 0.17±0.01 ab | |
| 亚砷酸处理As(Ⅲ) stress | WT | 23.83±0.44 a | 7.03±0.20 ab | 30.86±0.59 a | 4.23±0.07 cd | 3.38±0.07 a | 0.14±0.00 b |
| OE-44770-4 | 22.05±0.89 b | 5.41±0.07 b | 25.13±0.77 b | 3.78±0.07 d | 3.64±0.16 a | 0.15±0.00 ab | |
| OE-44770-13 | 23.00±0.30 b | 5.33±0.16 b | 24.81±0.48 b | 4.50±0.29 bc | 3.65±0.17 a | 0.18±0.00 a |
Table 2 Effects of As(Ⅲ) stress on chlorophyll contents of wild type(WT) and transgenic rice plants (n=3).
| 处理 Treatment | 供试材料 Tested material | 叶绿素a含量 Chlorophyll a content / (mg∙g-1) | 叶绿素b含量 Chlorophyll b content / (mg∙g-1) | 总叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll a+b content / (mg∙g-1) | 类胡萝卜素含量 Carotenoid content / (mg∙g-1) | 叶绿素a /叶绿素b Chlorophyll a/ Chlorophyll b | 类胡萝卜素 /总叶绿素 Carotenoid/ Chlorophyll a+b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照CK | WT | 24.25±1.16 a | 8.14±1.16 a | 32.39±1.79 a | 4.69±0.30 abc | 2.98±0.35 a | 0.14±0.02 b |
| OE-44770-4 | 22.90±1.30 b | 6.20±1.30 ab | 29.21±2.68 ab | 4.94±0.25 ab | 3.67±0.50 a | 0.17±0.01 ab | |
| OE-44770-13 | 23.90±1.34 a | 7.27±1.34 ab | 31.20±2.44 a | 5.20±0.07 a | 3.30±0.49 a | 0.17±0.01 ab | |
| 亚砷酸处理As(Ⅲ) stress | WT | 23.83±0.44 a | 7.03±0.20 ab | 30.86±0.59 a | 4.23±0.07 cd | 3.38±0.07 a | 0.14±0.00 b |
| OE-44770-4 | 22.05±0.89 b | 5.41±0.07 b | 25.13±0.77 b | 3.78±0.07 d | 3.64±0.16 a | 0.15±0.00 ab | |
| OE-44770-13 | 23.00±0.30 b | 5.33±0.16 b | 24.81±0.48 b | 4.50±0.29 bc | 3.65±0.17 a | 0.18±0.00 a |
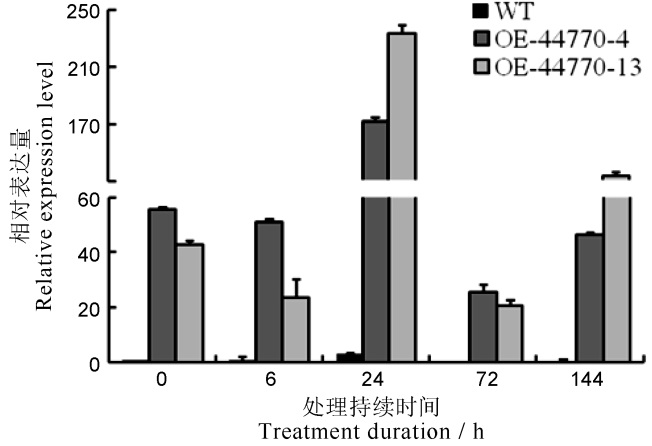
图8 亚砷酸盐处理后Os08g44770.1在WT和转基因植株叶片中的表达变化
Fig. 8. Temporal expression profiles of Os08g44770.1 in the leaves of As(Ⅲ)-treated WT and transgenic rice plants.
| [1] | 刘雪琴, 仝瑞建, 宋睿. 植物的砷污染研究进展. 湖北农业科学, 2014, 53(15): 3477-3481. |
| Liu X Q, Tong R J, Song R.Arsenic contamination of plant.Hubei Agric Sci, 2014, 53(15): 3477-3481. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Brammer H, Ravenscroft P.Arsenic in groundwater: A threat to sustainable agriculture in South and South-east Asia. Environ Int, 2009, 35(3): 647-654. |
| [3] | Su Y H, Mcgrath S P, Zhao F J.Rice is more efficient in arsenite uptake and translocation than wheat and barley. Plant Soil, 2010, 328(1-2): 27-34. |
| [4] | 段桂兰. 植物体内砷酸盐还原的生物化学与分子生物学研究. 北京: 中国科学院生态环境研究中心, 2006. |
| Duan G L.The biochemical and biomolecular mechanisms of arsenate reduction in plants. Beijing: Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Duan G L, Zhou Y, Tong Y R, Mukhopadhyay R, Rosen B P, Zhu Y G.A CDC25 homologue from rice functions as an arsenate reductase. New Phytol, 2007, 174(2): 311-321. |
| [6] | Dhankher O P, Rosen B P, Mckinney E C, Meagher R B.Hyperaccumulation of arsenic in the shoots of Arabidopsis silenced for arsenate reductase (ACR2). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2006, 103(14): 5413-5418. |
| [7] | Zhao F J, Ma J F, Ma J F, Meharg A A, Mcgrath S P.Arsenic uptake and metabolism in plants.New Phytol, 2009, 181(4): 777-794. |
| [8] | Chen Y, Sun S K, Tang Z, Liu G, Moore K L, Maathuis F J M, Miller A J, Mcgrath S P, Zhao F J. The Nodulin 26-like intrinsic membrane protein OsNIP3;2 is involved in arsenite uptake by lateral roots in rice.J Exp Bot, 2017, 68(11): 3007-3016. |
| [9] | Zhao X Q, Mitani N, Yamaji N, Shen R F, Ma J F.Involvement of silicon influx transporter OsNIP2;1 in selenite uptake in rice.Plant Physiol, 2010, 153(4): 1871-1877. |
| [10] | Ma J F, Yamaji N, Mitani N, Tamai K, Saeko K, Fujiwara T, Katsuhara M, Yano M.An efflux transporter of silicon in rice.Nature, 2007, 448(7150): 209-212. |
| [11] | Mosa K A, Kumar K, Chhikara S, Mcdermott J, Liu Z, Musante C, White J C, Dhankher O P.Members of rice plasma membrane intrinsic proteins subfamily are involved in arsenite permeability and tolerance in plants.Transg Res, 2012, 21(6): 1265-1277. |
| [12] | Tiwari M, Sharma D, Dwivedi S, Singh M, Tripathi R D, Trivedi P K.Expression in Arabidopsis and cellular localization reveal involvement of rice NRAMP, OsNRAMP1, in arsenic transport and tolerance. Plant Cell Environ, 2014, 37(1): 140-152. |
| [13] | Cao Y, Sun D, Ai H, Mei H, Liu X, Sun S, Xu G, Liu Y, Chen Y, Ma L Q.Knocking out OsPT4 gene decreases arsenate uptake by rice plants and inorganic arsenic accumulation in rice grains. Environ Sci Technol, 2017, 51(21): 12131-12138. |
| [14] | Wang P, Zhang W, Mao C, Xu G, Zhao F J.The role of OsPT8 in arsenate uptake and varietal difference in arsenate tolerance in rice. J Exp Bot, 2016, 67(21): 6051-6059. |
| [15] | Xu J, Shi S, Wang L, Tang Z, Lü T, Zhu X L, Ding X M, Wang Y F, Zhao F J, Wu Z C. OsHAC4 is critical for arsenate tolerance and regulates arsenic accumulation in rice. New Phytol, 2017, 215(3): 1090-1101. |
| [16] | Liu Q, Hu H, Zhu L, Li R, Feng Y, Zhang L, Yang Y, Liu X, Zhang H.Involvement of miR528 in the regulation of arsenite tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Agric Food Chem, 2015, 63(40): 8849-8861. |
| [17] | 张丽清, 陈霞, 胡海超, 张俊艇, 官慧谦, 刘庆坡. miR3979在水稻砷耐受性中的作用. 浙江农林大学学报, 2016, 33(4): 571-580. |
| Zhang L Q, Chen X, Hu H C, Zhang J T, Liu Q P. miR3979-mediated arsenite tolerance in rice. J Zhejiang A & F Univ, 2016, 33(4): 571-580. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 王建华, 刘鸿先, 徐同. 超氧物歧化酶(SOD)在植物逆境和衰老生理中的作用. 植物生理学报, 1989(1): 1-7. |
| Wang J H, Liu H X, Xu T.The role of superoxide dismutase (SOD) in stress physiology and senescence physiology of plant.Plant Physiol Commun, 1989(1): 1-7. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | Kaminaka H, Morita S, Yokoi H, Masumura T, Tanaka K.Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA for plastidic copper/zinc-superoxide dismutase in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Physiol, 1997, 38(1): 65-69. |
| [20] | Kaminaka H, Morita S, Tokumoto M, Masumura T, Tanaka K.Differential gene expressions of rice superoxide dismutase isoforms to oxidative and environmental stresses.Free Radic Res, 1999, 31: S219-S225. |
| [21] | Murray M G, Thompson W F.Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA.Nucl Acids Res, 1980, 8(19): 4321-4325. |
| [22] | 刘全吉, 孙学成, 胡承孝. 砷对小麦生长和光合作用特性的影响. 生态学报, 2009, 29(2): 854-859. |
| Liu Q J, Sun X C, Hu C X.Growth and photosynthesis characteristics of wheat (Triticum aestivun L.) under arsenic stress condition. Acta Ecol Sin, 2009, 29(2): 854-859. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 詹洁, 余永昌, 何龙飞. 逆境条件下的植物细胞程序性死亡. 南方农业学报, 2006, 37(1): 13-16. |
| Zhan J, Yu Y C, He L F.Programmed cell death of plant in adversity conditions. J Southern Agric, 2006, 37(1): 13-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 桑子阳, 马履一, 陈发菊. 干旱胁迫对红花玉兰幼苗生长和生理特性的影响. 西北植物学报, 2011, 31(1): 109-115. |
| Sang Z Y, Ma L Y, Chen F J.Growth and physiological characteristics ofMagnolia wufengensis seedlings under drought stress. Acta Bot Bor-Occid Sin, 2011, 31(1): 109-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Srivastava M, Ma L Q, Rathinasabapathi B, Srivastava P.Effects of selenium on arsenic uptake in arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata L. Bioresour Technol, 2009, 100(3): 1115-1121. |
| [26] | 谢亚军, 王兵, 梁新华, 韩招迪. 干旱胁迫对甘草幼苗活性氧代谢及保护酶活性的影响. 农业科学研究, 2008, 29(4): 19-22. |
| Xie Y J, Wang B, Liang X H, Han Z D.Effect of drought stress on active oxygen metabolism and activities of protective enzymes of licorice seedlings.J Agric Sci, 2008, 29(4): 19-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | Tripathi P, Tripathi R D, Singh R P, Dwivedi S, Chakrabarty D, Trivedi P K, Adhikari B.Arsenite tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) involves coordinated role of metabolic pathways of thiols and amino acids. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 2013, 20(2): 884-896. |
| [28] | 李黎, 宋帅杰, 方小梅. 高温干旱及复水对毛竹实生苗保护酶和脂质过氧化的影响. 浙江农林大学学报, 2017, 34(2): 268-275. |
| Li L, Song S J, Fang X M.Protection enzymes and lipid peroxidation in Phyllostachys edulis seedlings with temperature and water stresses. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2017, 34(2): 268-275. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 汪攀, 陈奶莲, 邹显花. 植物根系解剖结构对逆境胁迫响应的研究进展. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(2): 550-556. |
| Wang P, Chen N L, Zou X H.Research progress on adaptive responses of anatomical structure of plant roots to stress.Chin J Ecol, 2015, 34(2): 550-556. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 袁菊红, 胡绵好. 彩叶草根系对亚硒酸钠胁迫的适应机制研究. 西南农业学报, 2015, 28(5): 2009-2015. |
| Yuan J H, Hu M H.Study on adaptive mechanisms of Coleus blumei roots to Na2SeO3 stress. Southwest China J Agric Sci, 2015, 28(5): 2009-2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | Zgallai H, Steppe K, Lemeur R.Effects of different levels of water stress on leaf water potential, stomatal, stomatal resistance, protein and chlorophyll content and certain anti-oxidative enzymes in tomato plants.J Integr Plant Biol, 2006, 48(6): 679-685. |
| [32] | 常思敏, 马新明, 蒋媛媛, 贺德先, 张贵龙. 土壤砷污染及其对作物的毒害研究进展. 河南农业大学学报, 2005, 39(2): 161-186. |
| Chang S M, Ma X M, Jiang Y Y, He D L, Zhang G L.Research progress on arsenic contamination in soils and arsenic toxicity in crops.J Henan Agric Univ, 2005, 39(2): 161-186. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 蒋明义, 郭绍川. 水分亏缺诱导的氧化胁迫和植物的抗氧化作用. 植物生理学报, 1996, 32(2): 144-150. |
| Jiang M Y, Guo S C.Oxidative stress and antioxidation induced by water deficiency in plants.Acta Phytophysiol Sin, 1996, 32(2): 144-150. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 林阳, 王世忠. 4 种油松混交灌木树种的耐阴性研究. 河北林果研究, 2014, 29(3): 258-262. |
| Lin Y, Wang S Z.Research on the shade tolerance of 4 shrub tree species mixed with Chinese pine. Hebei J For Orch Res, 2014, 29(3): 258-262. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 肖姣娣. 3种刺篱植物对干旱胁迫的生理生化响. 西北农林科技大学学报, 2015, 43(7): 155-160. |
| Xiao J D.Physiological and biochemical responses of three spiny plants to drought stress.J Northwest A & F Univ, 2015, 43(7): 155-160. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||