
中国水稻科学 ›› 2015, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (4): 431-438.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001G7216.2015.04.013
收稿日期:2015-02-26
修回日期:2015-04-24
出版日期:2015-07-10
发布日期:2015-07-10
通讯作者:
刘巧泉
基金资助:
Ji-hui ZHU, Chang-quan ZHANG, Ming-hong GU, Qiao-quan LIU*( )
)
Received:2015-02-26
Revised:2015-04-24
Online:2015-07-10
Published:2015-07-10
Contact:
Qiao-quan LIU
摘要:
胚乳中直链淀粉含量是决定稻米蒸煮与食味品质的最重要指标,其在不同品种间变异范围较大。蜡质基因(Waxy,Wx)控制着稻米中直链淀粉的合成,是影响稻米蒸煮与食味品质的最重要基因。目前,在栽培稻中已鉴定了Wx基因的多个复等位变异,包括Wxa、Wxb、wx、Wxop、Wxin、Wxmq、Wxmp、Wxhp等,这些等位变异是造成稻米品质差异的主要原因。综述了目前已发现的Wx基因的主要等位变异类型及变异所产生的效应,简要回顾了各Wx等位基因在育种上的利用,展望了今后Wx基因的主要研究方向。
中图分类号:
朱霁晖, 张昌泉, 顾铭洪, 刘巧泉. 水稻Wx基因的等位变异及育种利用研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(4): 431-438.
Ji-hui ZHU, Chang-quan ZHANG, Ming-hong GU, Qiao-quan LIU. Progress in the Allelic Variation of Wx Gene and Its Application in Rice Breeding[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2015, 29(4): 431-438.
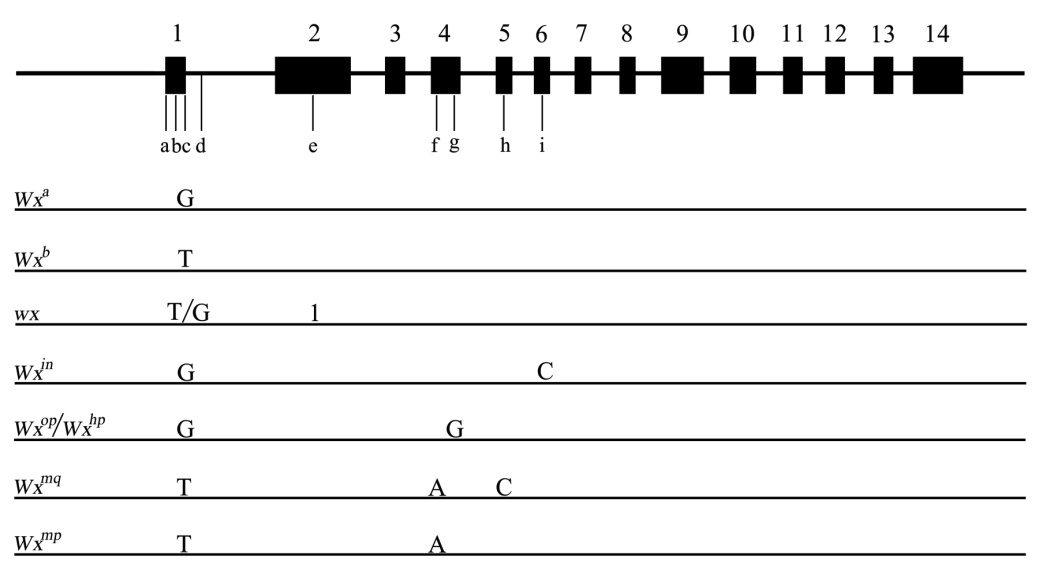
图1 Wx基因结构及等位基因变异类型(a,转录开始的碱基位点;b,第1外显子(CT)n,位于第1外显子中部;c,第一内含子5'端SNP;d,第1内含子(AATT)n,位于第1内含子起始位点;e, 糯稻23 bp插入,位于第2外显子中前部位点;f,第4外显子(共99 bp)第53位碱基;g,第4外显子(共99 bp)第77位碱基;h,第5外显子(共90 bp)第52位碱基;i,第6外显子(共64 bp)第62位碱基。)
Fig.1. The structure and different alleles of the Wx gene in rice. (a, Transcription start site(TSS); b, Exon 1 (CT)n, in the middle of the exon 1; c, Leader intron 5' SNP; d, Intron1 (AATT)n, in the start position of the intron 1; e, The 23 bp insertional locus of glutinous rice, in the front of the exon 2; f, 53th base in the exon 4(99 bp in all); g, 77th base in the exon 4(99 bp in all); h, 52th base in the exon 5(90 bp in all); i, 62th base in the exon 6(64 bp in all). )
| [1] | Khush G S.Origin, dispersal,cultivation and variation of rice.Plant Mol Biol, 1997, 35: 25-34. |
| [2] | 包劲松. 稻米淀粉品质遗传与改良研究进展. 分子植物育种,2007, 5(6s): 1-20. |
| [3] | James M G, Denyer K, Myers A M.Starch synthesis in the cereal endosperm.Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2003, 6: 215-222. |
| [4] | Juliano B O.Criteria and test for rice grain quality//Juliano B O. Rice Chemistry and Technology. St. Paul, Minnesota: American Association of Cereal Chemists, Inc., 1985: 443-513. |
| [5] | Wang Z Y, Zheng F Q, Shen G Z, et al.The amylose content in rice endosperm is related to the post-transcriptional regulation of the waxy gene.Plant J, 1995, 7(4): 613-622. |
| [6] | Smith A M, Denyer K, Martin C.The synthesis of the starch granule.Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol, 1997, 48: 67-87. |
| [7] | Steven G Ball, Marion H B J, van de Wal, et al. Progress in understanding the biosynthesis of amylose.Trends Plant Sci, 1998, 3: 462-467. |
| [8] | Gu M H, Liu Q Q, Yan C J, et al.Grain quality of hybrid rice: Genetic variation and molecular improvement// Xie F, Hardy B. Accelerating Hybrid Rice Development. Los Banos: IRRI, 2009: 345-356. |
| [9] | Tian Z X, Qian Q, Liu Q Q, et al.Allelic diversity in rice starch biosynthesis pathway leads to a diverse array of rice eating and cooking qualities.Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2009, 106: 21760-21765. |
| [10] | Tran D S, Tran T T H, Nguyen T L H, et al. Variation on grain quality in Vietnamese rice cultivars collected from Central Vietnam.J Fac Agric Kyushu Univ, 2012, 57: 365-371. |
| [11] | Ikeno S.Über die Bestäubung und die Bastardierung von Reis.ZPflanzenzücht, 1914, 2: 495-503. |
| [12] | Nagao S,Takahashi M E.Genetical studies on rice plant: XXVII. Trial construction of twelve linkage groups in Japanese rice. J Fac Agric,Hokkaido Univ, 1963, 53: 72-130. |
| [13] | Iwata N, Omura T.Linkage analysis by reciprocal translocation method in rice plants(Oryza sativa L.).Jpn J Breed, 1971, 21: 19-28. |
| [14] | International Rice Research Institute. Annual Report for 1975. Los Banos, Philippines: International Rice Research Institute, 1976: 85-86. |
| [15] | Wang Z Y, Wu Z L, Xing Y Y, et al.Nucleotide sequence of rice waxy gene.Nucleic Acids Res, 1990, 18: 58-98. |
| [16] | Cai X L, Wang Z Y, Xing Y Y, et al.Aberrant splicing of intron 1 leads to the heterogeneous 5’UTR and decreased expression of waxy gene in rice cultivars of intermediate amylose content.Plant J, 1998, 14: 459-465. |
| [17] | Sano Y.Differential regulation of waxy gene expression in rice endosperm.Theor Appl Genet, 1984, 68: 467-473. |
| [18] | Bligh H F J, Till R I, Jones C A. A microsatellite sequence closely linked to the Waxy gene of Oryza sativa.Euphytica, 1995, 86: 83-85. |
| [19] | Ayres N M, McClung A M, Larkin P D, et al. Microsatellites and a single-nucleotide polymorphism differentiate apparent amylose classes in an extended pedigree of US rice germplasm.Theor Appl Genet, 1997, 94: 773-781. |
| [20] | 舒庆尧, 吴殿星, 夏英武, 等. 籼稻和粳稻中蜡质基因座位上微卫星标记的多态性及其与直链淀粉含量的关系. 遗传学报, 1999, 26(4): 350-358. |
| [21] | Tan Y F, Zhang Q F.Correlation of simple sequence repeat (SSR) variants in the leader sequence of the waxy gene with amylose content of the grain in rice.Acta Bot Sin, 2001, 43(2): 146-150. |
| [22] | 曾瑞珍, 张泽民, 张桂权. 利用微卫星标记鉴定水稻Wx座位上的复等位基因//中国作物学会.作物科学研究理论与实践——2000作物科学学术研讨会文集.北京:[出版者不详], 2001: 230-235. |
| [23] | Mikami I, Uwatoko N, Ikeda Y, et al.Allelic diversification at the wx locus in landraces of Asian rice.Theor Appl Genet, 2008, 116(7): 979-989. |
| [24] | Sato H, Yasuhiro S, Sakai M, et al.Molecular characterization of Wx-mq, a novel mutant gene for low-amylose content in endosperm of rice (Oryza sativa L.).Breeding Sci, 2002, 52: 131-135. |
| [25] | Yang J, Wang J, Fan F J, et al.Development of AS-PCR marker based on a key mutation confirmed by resequencing of Wx-mp in Milky Princess and its application in japonica soft rice (Oryza sativa L.)breeding.Plant Breeding, 2013, 132: 595-603. |
| [26] | Liu L L, Ma X D, Liu S J, et al.Identification and characterization of a novel Waxy allele from a Yunnan rice landrace.Plant Mol Biol, 2009, 71: 609-626. |
| [27] | Sano Y, Maekawa M, Kikuchi H.Temperature effects on the Wx protein level and amylose content in the endosperm of rice.J Hered, 1985, 76: 221-222. |
| [28] | Sano Y, Katsumata M, Okuno K.Genetic studies of speciation in cultivated rice: Inter and intra-specific differentiation in the waxy gene expression.Euphytica, 1986, 35: 1-9. |
| [29] | Bligh H F J, Larkin P D, Roach P S, et al. Use of alternate splice sites in granule-bound starch synthase mRNA from low-amylose rice varieties.Plant Mol Biol, 1998, 38: 407-415. |
| [30] | Hirano H Y, Eiguchi M, Sano Y.A single base change altered the regulation of the Waxy gene at the posttranscriptional level during domestication of rice.Mol Biol Evol, 1998, 15: 978-987. |
| [31] | Isshiki M, Morino K, Nakajima M, et al.A naturally occurring functional allele of the waxy locus has a GT to TT mutation at the 50 splice site of the first intron.Plant J, 1998, 15: 133-138. |
| [32] | Inukai T, Sako A, Hirano H Y, et al.Analysis of intragenic recombination at wx in rice: Correlation between the molecular and genetic maps within the locus.Genome, 2000, 43: 589-596. |
| [33] | Wanchana S, Toojinda T, Tragoonrung S, et al.Duplicated coding sequence in the waxy allele of tropical glutinous rice (Oryza sativa L.).Plant Sci, 2003, 165: 1193-1199. |
| [34] | Hori Y, Fujimoto R, Sato Y, et al.A novel wx mutation caused by insertion of a retrotransposon-like sequence in a glutinous cultivar of rice (Oryza sativa).Theor Appl Genet, 2007, 115: 217-224. |
| [35] | Mikami I, Dung LV, Hirano H Y, et al.Effects of the two most common Wx alleles on different genetic backgrounds in rice.Plant Breed, 2000, 119: 505-508. |
| [36] | Dung L V, Mikami I, Amano E, et al.Study on the response of dull endosperm 2-2, du2-2, to two Wx alleles in rice.Breed Sci, 2000, 50: 215-219. |
| [37] | Wessler S R, Baran G, Varagona M, et al.Excision of Ds produces waxy proteins with a range of enzymatic activities.EMBO J, 1986, 5: 2427-2432. |
| [38] | Garris A J, Tai T H, Coburn J, et al.Genetic structure and diversity in Oryza sativa L.Genetics, 2005, 169: 1631-1638. |
| [39] | Heu M H.Inheritance of chalkiness of brown rice found in a non glutinous cultivar “Pokhareli Mashino”.Korean J Breed, 1986, 18: 162-166. |
| [40] | Heu M H, Kim Y K.Inheritance of an opaque endosperm derived from Nepali Indica rice cultivar ‘Pokhareli Machino’. Proceedings of the 6th international congress of SABRAO, August 21-25,1989.Tsukuba,1989:321-324. |
| [41] | Mikami I, Aikawa M, Hirano H Y, et al.Altered tissue-specific expression at the Wx gene of the opaque mutants in rice.Euphytica, 1999, 105: 91-99. |
| [42] | Baba T, Nishihara M, Mizuno K, et al.Identification cDNA cloning and gene expression of soluble starch synthase in rice (Oryza sativa L.) immature seeds.Plant Physiol, 1993, 103: 565-573. |
| [43] | Furukawa K, Tagaya M, Inouye M, et al.Identification of lysine 15 at the active site in Escherichia coli glycogen synthase.J Biol Chem, 1990, 265: 2086-2090. |
| [44] | Suto M, Ando I, Numaguchi K, et al.Breeding of low amylose content paddy rice variety “Milky Queen”with good eating quality.Jpn J Breed, 1996, 46(suppl 1): 221. |
| [45] | Sato H, Suzuki Y, Okumo K, et al.Genetic analysis of low-amylose content in a rice variety, ‘Milky Queen’.Breeding Res, 2001, 3: 13-19. |
| [46] | Shu Q Y, Wu D X, Xia Y W, et al.Microsatellites polymorphism on the Waxy gene locus and their relationship to amylose content in indica and japonica rice, Oryza sativa L.Acta Genet Sin, 1999, 26(4): 350-358. |
| [47] | Bergman C J, Delgado J T, McClung A M, et al. An improved method for using a microsatellite in the rice Waxy gene to determine amylose class.Cereal Chem, 2001, 78: 257-260. |
| [48] | Bao J S, Corke H, Sun M.Microsatellites in starch-synthesizing genes in relation to starch physicochemical properties in waxy rice (Oryza sativa L.).Theor Appl Genet, 2002, 105: 898-905. |
| [49] | Bao J S, Corke H, Sun M.Microsatellites, single nucleotide polymorphisms and a sequence tagged site in starch-synthesizing genes in relation to starch physicochemical properties in nonwaxy rice (Oryza sativa L.).Theor Appl Genet, 2006, 113: 1185-1196. |
| [50] | Zeng R Z, Zhang Z M, He F H, et al.Identification of multiple alleles at the Wx Locus and development of single segment substitution lines for the alleles in rice.Rice Sci, 2006, 13(1): 9-14. |
| [51] | Teng B, Zeng R Z, Wang Y C, et al.Detection of allelic variation at the Wx locus with single-segment substitution lines in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Mol Breeding, 2012, 30: 583-595. |
| [52] | Liu D R, Wang W, Cai X L.Modulation of amylose content by structure-based modification of OsGBSS1 activity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Biotechnol J, 2012, 12(9): 1297-1307. |
| [53] | 蔡秀玲, 刘巧泉, 汤述翥, 等.用于筛选直链淀粉含量为中等的籼稻品种的分子标记. 植物生理与分子生物学学报, 2002, 28(2): 137-144. |
| [54] | 万映秀, 邓其明, 王世全, 等.水稻Wx基因的遗传多态性及其与主要米质指标的相关性分析. 中国水稻科学, 2006, 20(6): 603-609. |
| [55] | Jin L, Lu Y, Shao Y F, et al.Molecular marker assisted selection for improvement of the eating, cooking and sensory quality of rice (Oryza sativa L.).J Cereal Sci, 2010, 51: 159-164. |
| [56] | Liu Q Q, Li Q F, Cai X L, et al.Molecular marker-assisted selection for improved cooking and eating quality of two elite parents of hybrid rice.Crop Sci, 2006, 46: 2354-2360. |
| [57] | 刘巧泉, 蔡秀玲, 李钱锋, 等.分子标记辅助选择改良特青及其杂交稻米的蒸煮食味品质. 作物学报, 2006, 32(1): 64-69. |
| [58] | Ni D H, Zhang S L, Chen S N, et al.Improving cooking and eating quality of Xieyou 57, an elite indica hybrid rice, by marker-assisted selection of the Wx locus.Euphytica, 2011, 179: 355-362. |
| [59] | Myint Y, Khin T N, Vanavichit A, et al.Marker assisted backcross breeding to improve cooking quality traits in Myanmar rice cultivar Manawthukha.Field Crops Res, 2009, 113: 178-186. |
| [60] | Caffagni A, Albertazzi G, Gavina G, et al.Characterization of an Italian rice germplasm collection with genetic markers useful for breeding to improve eating and cooking quality.Euphytica, 2013, 194: 383-399. |
| [61] | 姚姝, 陈涛, 张亚东, 等. 分子标记辅助选择聚合水稻暗胚乳突变基因Wx-mq和抗条纹叶枯病基因Stv-bi. 中国水稻科学, 2010, 24(4): 341-347. |
| [62] | Asaoka M, Okuno K, Konishi Y, et al.The effects of endosperm mutations and environmental temperature during development on the distribution of molecular weight of amylose in rice endosperm.Agric Biol Chem, 1987, 51: 3451-3453. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 肖正午, 方升亮, 曹威, 胡丽琴, 黎星, 解嘉鑫, 廖成静, 康玉灵, 胡玉萍, 张珂骞, 曹放波, 陈佳娜, 黄敏. 米粉质构特性与稻米理化性状的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 316-323. |
| [14] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [15] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||