
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 863-872.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.250106
黎星1,2, 张瑞春3, 陈鸽4,5, 解嘉鑫1,5, 肖正午1,5, 曹放波1,5, 陈佳娜1,5,*( ), 黄敏1,5,*(
), 黄敏1,5,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-08
修回日期:2025-04-07
出版日期:2025-11-10
发布日期:2025-11-19
通讯作者:
* email:jianachen@hunau.edu.cn;mhuang@hunau.edu.cn
基金资助:
LI Xing1,2, ZHANG Ruichun3, CHEN Ge4,5, XIE Jiaxin1,5, XIAO Zhengwu1,5, CAO Fangbo1,5, CHEN Jiana1,5,*( ), HUANG Min1,5,*(
), HUANG Min1,5,*( )
)
Received:2025-01-08
Revised:2025-04-07
Online:2025-11-10
Published:2025-11-19
Contact:
* email:jianachen@hunau.edu.cn;mhuang@hunau.edu.cn
摘要:
【目的】探明机插条件下早稻品种作短生育期晚稻品种栽培时的高产形成特点与叶片光合特性,可为短生育期晚稻品种的选育及其规模化高产栽培提供理论依据。【方法】于2021-2023年在湖南省浏阳市永安镇进行大田试验,以两个在早季种植时产量差异较大的品种中嘉早17和中早39为试验材料,测定二者在晚季机插时的产量及其构成因子、干物质积累特性、叶片光合特性和群体特性等。【结果】中早39三年平均产量比中嘉早17高19.76%,其高产形成的主要特点包括:从产量构成来看,中早39的千粒重比中嘉早17高7.60%;在干物质生产方面,中早39的总干物质量比中嘉早17高12.24%,这主要归因于其抽穗前较强的干物质生产能力。中早39表现出较强的早发特性,其抽穗期叶片光合特性与营养生长期群体质量表现优异,具体而言,抽穗期水稻叶片净光合速率、叶绿素a和b含量、叶绿素总含量、叶片氮含量和比叶重较中嘉早17高10.38%~29.04%,而群体质量指标中抽穗前作物生长速率、光合势、辐射利用率以及抽穗期叶面积指数也较中嘉早17高17.80%~25.95%。【结论】机插条件下,千粒重大、早发性强和抽穗期光合能力强的短生育期晚稻品种更容易获得高产。
黎星, 张瑞春, 陈鸽, 解嘉鑫, 肖正午, 曹放波, 陈佳娜, 黄敏. 机插短生育期晚稻产量形成特点与光合特性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 863-872.
LI Xing, ZHANG Ruichun, CHEN Ge, XIE Jiaxin, XIAO Zhengwu, CAO Fangbo, CHEN Jiana, HUANG Min. Yield Formation and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Machine-transplanted Late-season Rice with Short Growth Duration[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(6): 863-872.
| 品种 Variety | 年份 Year | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number per m2 | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 总颖花量 Total spikelets (×104 m-2) | 结实率 Seed setting rate (%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Grain yield (t hm-2) | 生育期 Growth duration (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中嘉早17 | 2021 | 331±15 bc | 116±10 b | 3.83±0.17 c | 79±2 ab | 27.0±0.4 c | 6.89±0.33 b | 104 |
| Zhongjiazao 17 | 2022 | 448±121 a | 101±20 b | 4.35±0.38 abc | 67±9 bc | 27.4±0.2 c | 6.36±0.34 b | 101 |
| 2023 | 354±22 ab | 111±5 b | 3.92±0.14 abc | 79±4 ab | 24.4±0.6 d | 6.94±0.39 b | 102 | |
| 平均 Mean | 377±62 A | 109±8 B | 4.03±0.28 A | 75±7 A | 26.3±1.7 B | 6.73±0.32 B | 102 | |
| 中早39 | 2021 | 291±33 bc | 133±5 b | 3.85±0.42 bc | 84±2 a | 28.7±1.0 a | 7.78±0.71 a | 105 |
| Zhongzao 39 | 2022 | 354±26 ab | 130±19 b | 4.62±0.75 a | 73±12 abc | 27.6±0.4 bc | 8.33±0.05 a | 110 |
| 2023 | 248±17 c | 186±35 a | 4.59±0.57 ab | 62±9 c | 28.5±0.5 ab | 8.08±0.34a | 104 | |
| 平均 Mean | 298±53 B | 150±32 A | 4.35±0.43 A | 73±11 A | 28.3±0.6 A | 8.06±0.27 A | 106 | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance (F-value) | ||||||||
| 年份 Year(Y) | 6.31* | 4.50* | 3.74ns | 3.93ns | 12.43** | 0.35ns | —— | |
| 品种 Variety(V) | 9.94* | 18.97** | 2.69ns | 0.26ns | 68.91** | 50.30** | —— | |
| Y× V | 0.64ns | 3.64ns | 0.92ns | 3.90ns | 22.48** | 3.02ns | —— | |
表1 2021-2023年机插短生育期晚稻产量、产量构成和生育期
Table 1. Grain yield, yield components and growth duration of short growth-duration late rice under machine-transplanted conditions in 2021-2023
| 品种 Variety | 年份 Year | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number per m2 | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number per panicle | 总颖花量 Total spikelets (×104 m-2) | 结实率 Seed setting rate (%) | 千粒重 1000-grain weight (g) | 产量 Grain yield (t hm-2) | 生育期 Growth duration (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中嘉早17 | 2021 | 331±15 bc | 116±10 b | 3.83±0.17 c | 79±2 ab | 27.0±0.4 c | 6.89±0.33 b | 104 |
| Zhongjiazao 17 | 2022 | 448±121 a | 101±20 b | 4.35±0.38 abc | 67±9 bc | 27.4±0.2 c | 6.36±0.34 b | 101 |
| 2023 | 354±22 ab | 111±5 b | 3.92±0.14 abc | 79±4 ab | 24.4±0.6 d | 6.94±0.39 b | 102 | |
| 平均 Mean | 377±62 A | 109±8 B | 4.03±0.28 A | 75±7 A | 26.3±1.7 B | 6.73±0.32 B | 102 | |
| 中早39 | 2021 | 291±33 bc | 133±5 b | 3.85±0.42 bc | 84±2 a | 28.7±1.0 a | 7.78±0.71 a | 105 |
| Zhongzao 39 | 2022 | 354±26 ab | 130±19 b | 4.62±0.75 a | 73±12 abc | 27.6±0.4 bc | 8.33±0.05 a | 110 |
| 2023 | 248±17 c | 186±35 a | 4.59±0.57 ab | 62±9 c | 28.5±0.5 ab | 8.08±0.34a | 104 | |
| 平均 Mean | 298±53 B | 150±32 A | 4.35±0.43 A | 73±11 A | 28.3±0.6 A | 8.06±0.27 A | 106 | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance (F-value) | ||||||||
| 年份 Year(Y) | 6.31* | 4.50* | 3.74ns | 3.93ns | 12.43** | 0.35ns | —— | |
| 品种 Variety(V) | 9.94* | 18.97** | 2.69ns | 0.26ns | 68.91** | 50.30** | —— | |
| Y× V | 0.64ns | 3.64ns | 0.92ns | 3.90ns | 22.48** | 3.02ns | —— | |
| 品种 Variety | 年份 Year | 干物质量 Dry matter production (g m-2) | 收获指数 HI (%) | 作物生长速率 Crop growth rate (g m-2 d-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽穗前 Pre-heading | 抽穗后 Post-heading | 总干物质量 Total | 转运量 DT | 抽穗前 Pre-heading | 抽穗后 Post-heading | |||
| 中嘉早17 | 2021 | 758±22 c | 530±19 a | 1287±6 bc | 159±3 bc | 0.54±0.03 a | 11.8±0.3 bc | 13.2±0.5 b |
| Zhongjiazao 17 | 2022 | 887±233 bc | 555±262 a | 1441±78 ab | 163±6 bc | 0.56±0.01 a | 13.0±3.4 abc | 16.8±0.8 a |
| 2023 | 755±52 c | 463±63 a | 1217±32 c | 185±67 bc | 0.53±0.02 a | 10.6±0.7 c | 14.9±2.0 ab | |
| Mean | 800±75 B | 516±48 A | 1315±115 B | 169±14 B | 0.54±0.01 A | 11.8±1.2 B | 15.0±1.8 A | |
| 中早39 | 2021 | 959±99 ab | 436±175 a | 1395±242 abc | 342±175 ab | 0.55±0.06 a | 13.9±1.4 ab | 12.1±2.1 b |
| Zhongzao 39 | 2022 | 1145±51 a | 428±197 a | 1574±189 a | 404±196 a | 0.47±0.02 b | 15.5±0.7 a | 11.9±2.4 b |
| 2023 | 875±46 bc | 583±68 a | 1458±22 ab | 110±91 c | 0.48±0.03 b | 12.3±0.6 bc | 17.7±2.1 a | |
| Mean | 993±138 A | 482±87 A | 1476±91 A | 285±155 A | 0.50±0.05 B | 13.9±1.6 A | 13.9±3.3 A | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance (F-value) | ||||||||
| 年份 Year(Y) | 6.05* | 0.10ns | 4.43* | 2.56 ns | 3.68ns | 4.90* | 6.28* | |
| 品种 Variety(V) | 15.20** | 0.19ns | 9.04* | 5.98* | 10.81** | 8.13* | 1.75ns | |
| Y× V | 0.65ns | 1.02ns | 0.59ns | 4.17 ns | 5.01* | 0.09ns | 7.04* | |
表2 2021-2023年机插短生育期晚稻干物质积累量、收获指数和作物生长速率
Table 2. Dry matter production, translocation of pre-heading dry matter to panicles(DT), harvest index (HI), and crop growth rate of short growth-duration late rice under machine-transplanted conditions in 2021-2023
| 品种 Variety | 年份 Year | 干物质量 Dry matter production (g m-2) | 收获指数 HI (%) | 作物生长速率 Crop growth rate (g m-2 d-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽穗前 Pre-heading | 抽穗后 Post-heading | 总干物质量 Total | 转运量 DT | 抽穗前 Pre-heading | 抽穗后 Post-heading | |||
| 中嘉早17 | 2021 | 758±22 c | 530±19 a | 1287±6 bc | 159±3 bc | 0.54±0.03 a | 11.8±0.3 bc | 13.2±0.5 b |
| Zhongjiazao 17 | 2022 | 887±233 bc | 555±262 a | 1441±78 ab | 163±6 bc | 0.56±0.01 a | 13.0±3.4 abc | 16.8±0.8 a |
| 2023 | 755±52 c | 463±63 a | 1217±32 c | 185±67 bc | 0.53±0.02 a | 10.6±0.7 c | 14.9±2.0 ab | |
| Mean | 800±75 B | 516±48 A | 1315±115 B | 169±14 B | 0.54±0.01 A | 11.8±1.2 B | 15.0±1.8 A | |
| 中早39 | 2021 | 959±99 ab | 436±175 a | 1395±242 abc | 342±175 ab | 0.55±0.06 a | 13.9±1.4 ab | 12.1±2.1 b |
| Zhongzao 39 | 2022 | 1145±51 a | 428±197 a | 1574±189 a | 404±196 a | 0.47±0.02 b | 15.5±0.7 a | 11.9±2.4 b |
| 2023 | 875±46 bc | 583±68 a | 1458±22 ab | 110±91 c | 0.48±0.03 b | 12.3±0.6 bc | 17.7±2.1 a | |
| Mean | 993±138 A | 482±87 A | 1476±91 A | 285±155 A | 0.50±0.05 B | 13.9±1.6 A | 13.9±3.3 A | |
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance (F-value) | ||||||||
| 年份 Year(Y) | 6.05* | 0.10ns | 4.43* | 2.56 ns | 3.68ns | 4.90* | 6.28* | |
| 品种 Variety(V) | 15.20** | 0.19ns | 9.04* | 5.98* | 10.81** | 8.13* | 1.75ns | |
| Y× V | 0.65ns | 1.02ns | 0.59ns | 4.17 ns | 5.01* | 0.09ns | 7.04* | |
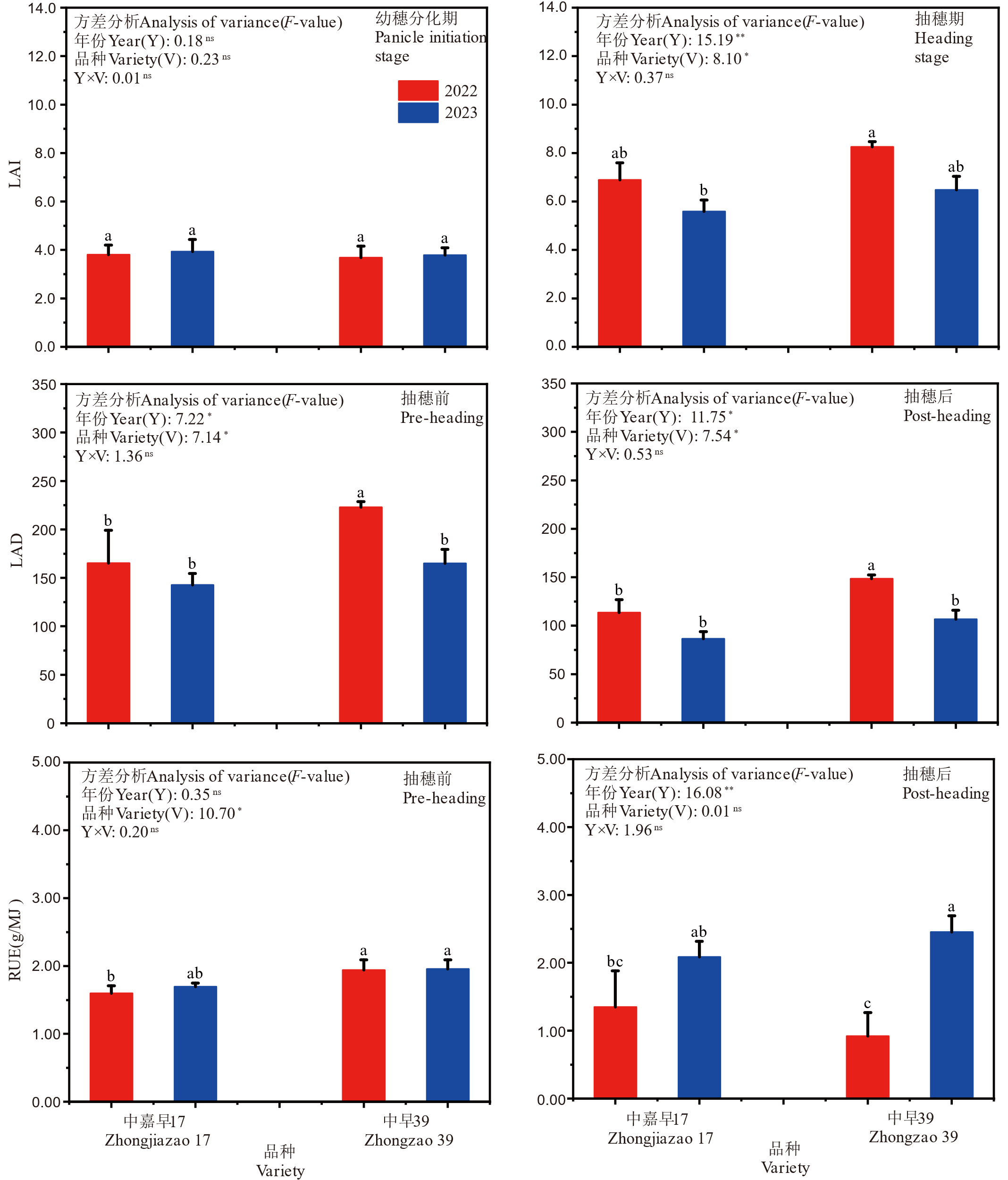
图2 2022-2023年机插短生育期晚稻叶面积指数、光合势和冠层辐射利用率 图中数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。图中柱上不同小写字母表示在0.05水平差异显著。*和**分别表示在0.05和0.01水平下差异显著,ns表示在0.05水平下差异不显著。
Fig. 2. Leaf area index (LAI), leaf area duration (LAD), and radiation use efficiency (RUE) of short growth-duration late rice under machine-transplanted conditions in 2022-2023 Data are means ± standard deviation (n=3). Different letters above the bars indicate significant difference at the 0.05 level. * and ** denote significance at the 0.05 and 0.01 probability levels, respectively; ns denotes non-significance at the 0.05 probability level.
| 品种 Variety | 年份 Year | 净光合速率 Net photosynthetic rate (μmol·m−2s-1) | 叶绿素a含量 Chlorophyll a content (mg g-1) | 叶绿素b含量 Chlorophyll b content (mg g-1) | 叶绿素总含量 Total chlorophyll content (mg g-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 幼穗分化期 PI | 抽穗期 HD | 幼穗分化期 PI | 抽穗期 HD | 幼穗分化期 PI | 抽穗期 HD | 幼穗分化期 PI | 抽穗期 HD | |||||
| 中嘉早17 Zhongjiazao 17 | 2022 | 26.5±0.6 a | 20.8±1.3 d | 2.69±0.52 a | 2.68±0.09 b | 1.32±0.70 a | 1.04±0.20 ab | 4.02±1.22 a | 3.71±0.25 b | |||
| 2023 | 25.0±1.0 a | 22.1±1.3 c | 2.52±0.24 a | 2.77±0.27 b | 1.07±0.46 a | 0.84±0.12 b | 3.59±0.32 a | 3.61±0.39 b | ||||
| Mean | 25.8±1.1 A | 21.5±0.9 B | 2.61±0.12 A | 2.72±0.06 B | 1.20±0.18 A | 0.94±0.14 B | 3.80±0.30 A | 3.66±0.07 B | ||||
| 中早39 Zhongzao 39 | 2022 | 27.0±0.9 a | 24.1±0.9 b | 2.92±0.43 a | 3.45±0.12 a | 1.04±0.05 a | 1.19±0.06 a | 3.96±0.48 a | 4.64±0.17 a | |||
| 2023 | 26.8±1.2 a | 26.5±1.1 a | 2.69±0.39 a | 3.57±0.15 a | 0.86±0.13 a | 1.08±0.14 ab | 3.55±0.52 a | 4.66±0.28 a | ||||
| Mean | 26.9±0.1 A | 25.3±1.7 A | 2.80±0.16 A | 3.51±0.09 A | 0.95±0.13 A | 1.14±0.08 A | 3.75±0.29 A | 4.65±0.01 A | ||||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance (F-value) | ||||||||||||
| 年份 Year(Y) | 1.92ns | 39.77** | 0.73ns | 2.28ns | 0.98ns | 4.56ns | 0.99ns | 0.13ns | ||||
| 品种 Variety(V) | 3.27ns | 173.70** | 0.71ns | 124.20** | 1.21ns | 8.04* | 0.01ns | 64.60** | ||||
| Y×V | 1.18ns | 3.44ns | 0.01ns | 0.05ns | 0.02ns | 0.36ns | 0.01ns | 0.22ns | ||||
| 品种 Variety | 年份 Year | 叶绿素a/b Chl a/Chl b | 叶片N含量 Leaf N content(%) | 比叶重 Specific leaf weight(mg cm-2) | ||||||||
| 幼穗分化期 PI | 抽穗期 HD | 幼穗分化期 PI | 抽穗期 HD | 幼穗分化期 PI | 抽穗期 HD | |||||||
| 中嘉早17 Zhongjiazao 17 | 2022 | 2.25±0.63 a | 2.64±0.45 b | 1.54±0.28 ab | 1.00±0.01 b | 3.23±0.17 b | 3.29±0.01 b | |||||
| 2023 | 2.66±1.06 a | 3.30±0.21 a | 1.54±0.28 ab | 1.08±0.09 b | 3.04±0.02 b | 3.06±0.16 c | ||||||
| Mean | 2.46±0.29 A | 2.97±0.47 A | 1.54±0.12 A | 1.04±0.06 B | 3.13±0.13 B | 3.18±0.17 B | ||||||
| 中早39 Zhongzao 39 | 2022 | 2.78±0.29 a | 2.89±0.07 ab | 1.63±0.06 a | 1.11±0.07 ab | 3.89±0.05 a | 3.78±0.08 a | |||||
| 2023 | 3.14±0.20 a | 3.32±0.36 a | 1.35±0.24 b | 1.23±0.02 a | 3.07±0.20 b | 3.23±0.12 bc | ||||||
| Mean | 2.96±0.25 A | 3.11±0.30 A | 1.49±0.20 A | 1.17±0.09 A | 3.48±0.58 A | 3.51±0.39 A | ||||||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance (F-value) | ||||||||||||
| 年份 Year(Y) | 1.47ns | 9.95* | 3.14ns | 7.74* | 49.99** | 34.86** | ||||||
| 品种 Variety(V) | 2.54ns | 0.63ns | 0.39ns | 12.18* | 23.75** | 24.57** | ||||||
| Y×V | 0.01ns | 0.44ns | 3.14ns | 0.40ns | 19.73** | 5.79ns | ||||||
表3 2022-2023年机插短生育期晚稻净光合速率、叶绿素含量、叶片N含量和比叶重
Table 3. Net photosynthetic rate, chlorophyll content, leaf N content, and specific leaf weight of short growth-duration late rice under machine-transplanted conditions in 2022-2023
| 品种 Variety | 年份 Year | 净光合速率 Net photosynthetic rate (μmol·m−2s-1) | 叶绿素a含量 Chlorophyll a content (mg g-1) | 叶绿素b含量 Chlorophyll b content (mg g-1) | 叶绿素总含量 Total chlorophyll content (mg g-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 幼穗分化期 PI | 抽穗期 HD | 幼穗分化期 PI | 抽穗期 HD | 幼穗分化期 PI | 抽穗期 HD | 幼穗分化期 PI | 抽穗期 HD | |||||
| 中嘉早17 Zhongjiazao 17 | 2022 | 26.5±0.6 a | 20.8±1.3 d | 2.69±0.52 a | 2.68±0.09 b | 1.32±0.70 a | 1.04±0.20 ab | 4.02±1.22 a | 3.71±0.25 b | |||
| 2023 | 25.0±1.0 a | 22.1±1.3 c | 2.52±0.24 a | 2.77±0.27 b | 1.07±0.46 a | 0.84±0.12 b | 3.59±0.32 a | 3.61±0.39 b | ||||
| Mean | 25.8±1.1 A | 21.5±0.9 B | 2.61±0.12 A | 2.72±0.06 B | 1.20±0.18 A | 0.94±0.14 B | 3.80±0.30 A | 3.66±0.07 B | ||||
| 中早39 Zhongzao 39 | 2022 | 27.0±0.9 a | 24.1±0.9 b | 2.92±0.43 a | 3.45±0.12 a | 1.04±0.05 a | 1.19±0.06 a | 3.96±0.48 a | 4.64±0.17 a | |||
| 2023 | 26.8±1.2 a | 26.5±1.1 a | 2.69±0.39 a | 3.57±0.15 a | 0.86±0.13 a | 1.08±0.14 ab | 3.55±0.52 a | 4.66±0.28 a | ||||
| Mean | 26.9±0.1 A | 25.3±1.7 A | 2.80±0.16 A | 3.51±0.09 A | 0.95±0.13 A | 1.14±0.08 A | 3.75±0.29 A | 4.65±0.01 A | ||||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance (F-value) | ||||||||||||
| 年份 Year(Y) | 1.92ns | 39.77** | 0.73ns | 2.28ns | 0.98ns | 4.56ns | 0.99ns | 0.13ns | ||||
| 品种 Variety(V) | 3.27ns | 173.70** | 0.71ns | 124.20** | 1.21ns | 8.04* | 0.01ns | 64.60** | ||||
| Y×V | 1.18ns | 3.44ns | 0.01ns | 0.05ns | 0.02ns | 0.36ns | 0.01ns | 0.22ns | ||||
| 品种 Variety | 年份 Year | 叶绿素a/b Chl a/Chl b | 叶片N含量 Leaf N content(%) | 比叶重 Specific leaf weight(mg cm-2) | ||||||||
| 幼穗分化期 PI | 抽穗期 HD | 幼穗分化期 PI | 抽穗期 HD | 幼穗分化期 PI | 抽穗期 HD | |||||||
| 中嘉早17 Zhongjiazao 17 | 2022 | 2.25±0.63 a | 2.64±0.45 b | 1.54±0.28 ab | 1.00±0.01 b | 3.23±0.17 b | 3.29±0.01 b | |||||
| 2023 | 2.66±1.06 a | 3.30±0.21 a | 1.54±0.28 ab | 1.08±0.09 b | 3.04±0.02 b | 3.06±0.16 c | ||||||
| Mean | 2.46±0.29 A | 2.97±0.47 A | 1.54±0.12 A | 1.04±0.06 B | 3.13±0.13 B | 3.18±0.17 B | ||||||
| 中早39 Zhongzao 39 | 2022 | 2.78±0.29 a | 2.89±0.07 ab | 1.63±0.06 a | 1.11±0.07 ab | 3.89±0.05 a | 3.78±0.08 a | |||||
| 2023 | 3.14±0.20 a | 3.32±0.36 a | 1.35±0.24 b | 1.23±0.02 a | 3.07±0.20 b | 3.23±0.12 bc | ||||||
| Mean | 2.96±0.25 A | 3.11±0.30 A | 1.49±0.20 A | 1.17±0.09 A | 3.48±0.58 A | 3.51±0.39 A | ||||||
| 方差分析 Analysis of variance (F-value) | ||||||||||||
| 年份 Year(Y) | 1.47ns | 9.95* | 3.14ns | 7.74* | 49.99** | 34.86** | ||||||
| 品种 Variety(V) | 2.54ns | 0.63ns | 0.39ns | 12.18* | 23.75** | 24.57** | ||||||
| Y×V | 0.01ns | 0.44ns | 3.14ns | 0.40ns | 19.73** | 5.79ns | ||||||
| [1] | Qian Q. Genomics-assisted germplasm improvement[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2018, 60(2): 82-84. |
| [2] | 蒋鹏, 张林, 周兴兵, 郭晓艺, 朱永川, 刘茂, 郭长春, 熊洪, 徐富贤. 冬水田轻简化栽培杂交稻蓄留再生稻产量形成特点[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(5): 544-554. |
| Jiang P, Zhang L, Zhang X B, Guo X Y, Zhu Y C, Liu M, Guo C C, Xiong H, Xu F X. Yield formation characteristics of ratooning hybrid rice under simplified cultivation practices in winter paddy fields[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 544-554. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Yin X, Huang M, Zou Y. Changes in rice yield stability in Southern China from 1949 to 2015[J]. Agricultural & Environmental Letters, 2018, 3(1): 170038. |
| [4] | Peng S B, Zheng C, Yu X. Progress and challenges of rice ratooning technology in China[J]. Crop and Environment, 2023, 2(1): 5-11. |
| [5] | 彭少兵. 对转型时期水稻生产的战略思考[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2014, 44(8): 845-850. |
| Peng S B. Reflection on China's rice production strategies during the transition period[J]. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 2014, 44(8): 845-850. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 应俊杰, 朱贵平, 顾天飞, 何豪豪, 泮崇新, 曾孝元, 秦叶波. 不同种植方式对双季稻生产的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2023, 64(2): 297-299. |
| Ying J J, Zhu G P, Gu T F, He H H, Pan C X, Zeng X Y, Qin Y B. Effects of different Cultivation methods on double-cropping rice production[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 64(2): 297-299. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 张卫建, 陈长青, 江瑜, 张俊, 钱浩宇. 气候变暖对我国水稻生产的综合影响及其应对策略[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(4): 805-811. |
| Zhang W J, Chen C Q, Jiang Y, Zhang J, Qian H Y. Comprehensive influence of climate warming on rice production and countermeasure for food security in China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(4): 805-811. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Huang M, Zou Y B. Integrating mechanization with agronomy and breeding to ensure food security in China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2018, 224: 22-27. |
| [9] | 邹应斌, 黄敏. 转型期作物生产发展的机遇与挑战[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(6): 791-795. |
| Zou Y B, Huang M. Opportunities and challenges for crop production in China during the transition period[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2018, 44(6): 791-795. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Vargas-Perez H, Kee R T, Walton C H, Hansen D M, Razavi R, Clarke L, Bufalino M R, Allison D W, Steffensen S C, van der Kooy D. Ventral tegmental area BDNF induces an opiate-dependent-like reward state in naive rats[J]. Science, 2009, 324(5935): 1732-1734. |
| [11] | Chen J N, Zhang R C, Cao F B, Yin X H, Zou Y B, Huang M, Abou-Elwafa S F. Evaluation of late-season short- and long-duration rice cultivars for potential yield under mechanical transplanting conditions[J]. Agronomy, 2020, 10(9): 1307. |
| [12] | 潘想成, 杨国栋, 符迎迎, 王昕钰, 熊渠, 徐乐, 彭少兵. 新育成超短生育期品系在双季稻双直播下的产量表现及农艺特性[J]. 作物学报, 2023, 49(10): 2738-2752. |
| Pan X C, Yang G D, Fu Y Y, Wang X Y, Xiong Q, Xu L, Peng S B. Yield performance and agronomic characteristics of a newly developed ultrashort-duration line in direct-seeded double-season rice system[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2023, 49(10): 2738-2752. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Wang X Y, Yang G D, Xu L, Xiang H S, Yang C, Wang F, Peng S B. Grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of an ultrashort-duration variety grown under different nitrogen and seeding rates in direct-seeded and double-season rice in Central China[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2023, 22(4): 1009-1020. |
| [14] | Wang X Y, Xu L, Li X X, Yang G D, Wang F, Peng S B. Grain yield and lodging-related traits of ultrashort-duration varieties for direct-seeded and double-season rice in Central China[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2022, 21(10): 2888-2899. |
| [15] | 吴建平, 程建平, 赵锋, 蔡海亚, 汪本福, 吴德军, 李亮, 游爱兵. 湖北省早稻秋种产量形成特性及其相关因素[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2012, 51(23): 5279-5282. |
| Wu J P, Chen J P, Zhao F, Cai H Y, Wang B F, Wu D J, Li L, You A B. Yield development characteristics and relative factors of autumn planting-early rice in Hubei[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 51(23): 5279-5282. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Chen J N, Cao F B, Yin X H, Huang M, Zou Y B. Yield performance of early-season rice cultivars grown in the late season of double-season crop production under machine-transplanted conditions[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(3): e0213075. |
| [17] | Chen J N, Zhang R C, Cao F B, Yin X H, Liang T F, Huang M, Zou Y B. Critical yield factors for achieving high grain yield in early-season rice grown under mechanical transplanting conditions[J]. Phyton, 2020, 89(4): 1043-1057. |
| [18] | 陈佳娜, 曹放波, 谢小兵, 单双吕, 高伟, 李志斌, 黄敏, 邹应斌. 机插条件下低氮密植栽培对“早晚兼用”双季稻产量和氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(8): 1176-1187. |
| Chen J N, Cao F B, Xie X B, Shan S L, Gao W, Li Z B, Huang M, Zou Y B. Effect of low nitrogen rate combined with high plant density on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of machine-transplanted early-late season double cropping rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(8): 1176-1187. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 陈苏, 谢建坤, 黄文新, 陈登云, 彭晓剑, 付学琴. 根际促生细菌对干旱胁迫下水稻生理特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(5): 485-492. |
| Chen S, Xie J K, Huang W X, Chen D Y, Peng X J, Fu X Q. Effects of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on physiological characteristics of rice under drought stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(5): 485-492. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 袁继超, 刘从军, 蔡光泽, 朱庆森, 李俊青, 杨建昌. 攀西地区优质稻产量构成因素的变异及其构成特点[J]. 西南农业学报, 2005, 18(2): 144-148. |
| Yuan J C, Liu C J, Cai G Z, Zhu Q S, Li J Q, Yang J C. Study on variation and its characteristics of yield components of high-quality rice in Panxi region[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2005, 18(2): 144-148. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 曾勇军, 石庆华, 潘晓华, 韩涛. 长江中下游双季稻高产株型特征初步研究[J]. 作物学报, 2009, 35(3): 546-551. |
| Zeng Y J, Shi Q H, Pan X H, Han T. Preliminary study on the plant type characteristics of double cropping rice in Middle and Lower Reaches of Changjiang River[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2009, 35(3): 546-551. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Zhong X M, Peng J W, Kang X R, Wu Y F, Luo G W, Hu W F, Zhou X. Optimizing agronomic traits and increasing economic returns of machine-transplanted rice with side-deep fertilization of double-cropping rice system in Southern China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2021, 270: 108191. |
| [23] | 曹放波, 陈佳娜, 谢小兵, 单双吕, 邹应斌. 双季晚稻机插品种筛选[J]. 中国稻米, 2015, 21(4): 205-207. |
| Cao F B, Chen J N, Xie X B, Shan S L, Zou Y B. Cultivars screening of late season machine transplanting rice[J]. China Rice, 2015, 21(4): 205-207. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Fu Y Q, Lu C S, Zhong X H, Liang K M, Pan J F, Liu Y Z, Hu X Y, Hu R, Li M J, Wang X Y, Ye Q H, Yin Y H, Huang J C, Huang N R. Post-heading dry-matter transport and nutrient uptake differentiate hybrid and inbred indica rice in the double-cropping system in South China[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2024, 15: 1433402. |
| [25] | Peng S B, Cassman K G, Virmani S S, Sheehy J, Khush G S. Yield potential trends of tropical rice since the release of IR8 and the challenge of increasing rice yield potential[J]. Crop Science, 1999, 39(6): 1552-1559. |
| [26] | 王伟妮, 鲁剑巍, 何予卿, 李小坤, 李慧. 氮、磷、钾肥对水稻产量、品质及养分吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(6): 645-653. |
| Wang W N, Lu J W, He Y Q, Li X K, Li H. Effects of N, P, K fertilizer application on grain yield, quality, nutrient uptake and utilization of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(6): 645-653. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | Huang M, Yin X H, Jiang L G, Zou Y B, Deng G F. Raising potential yield of short-duration rice cultivars is possible by increasing harvest index[J]. Biotechnology, Agronomy and Society and Environment, 2015, 19(2): 153-159. |
| [28] | 吕伟生, 曾勇军, 石庆华, 潘晓华, 黄山, 商庆银, 谭雪明, 李木英, 胡水秀, 曾研华. 双季机插稻叶龄模式参数及高产品种特征[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(12): 1844-1857. |
| Lü W S, Zeng Y J, Shi Q H, Pan X H, Huang S, Shang Q Y, Tan X M, Li M Y, Hu S X, Zeng Y H. Leaf-age-model parameters and characteristics of high-yield cultivars of machine-transplanted double cropping rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2018, 44(12): 1844-1857. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Huang M, Fang S L, Cao F B, Chen J N, Shan S L, Liu Y, Lei T, Tian A L, Tao Z, Zou Y B. Early sowing increases grain yield of machine-transplanted late-season rice under single-seed sowing[J]. Field Crops Research, 2020, 253: 107832. |
| [30] | Ao H J, Peng S B, Zou Y B, Tang Q Y, Visperas R M. Reduction of unproductive tillers did not increase the grain yield of irrigated rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2010, 116(1/2): 108-115. |
| [31] | Huang M, Tao Z, Lei T, Cao F B, Chen J N, Yin X H, Zou Y B, Liang T F. Improving lodging resistance while maintaining high grain yield by promoting pre-heading growth in rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2021, 270: 108212. |
| [32] | Wang W X, Du J, Zhou Y Z, Zeng Y J, Tan X M, Pan X H, Shi Q H, Wu Z M, Zeng Y H. Effects of different mechanical direct seeding methods on grain yield and lodging resistance of early indica rice in South China[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2021, 20(5): 1204-1215. |
| [33] | 刘涛, 杨晓光, 高继卿, 何斌, 白帆, 张方亮, 刘志娟, 王晓煜, 孙爽, 万能涵, 陈曦, 黄秋婉, 柳晓庆. 不同粮食作物光能利用效率研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(24): 186-193. |
| Liu T, Yang X G, Gao J Q, He B, Bai F, Zhang F L, Liu Z J, Wang X Y, Sun S, Wan N H, Chen X, Huang Q W, Liu X Q. Radiation use efficiency of different grain crops in Northeast China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(24): 186-193. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 朱从桦, 孙永健, 杨志远, 贾现文, 徐徽, 马均. 晒田强度和穗期氮素运筹对不同氮效率水稻根系、叶片生长及产量的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(6): 196-203, 256. |
| Zhu C H, Sun Y J, Yang Z Y, Jia X W, Xu W, Ma J. Effect of paddy field drainage and panicle nitrogen fertilizer management on rice root system, leaf growth and yield with different nitrogen efficiency[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 31(6): 196-203, 256. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 陈玲, 林文英, 梁丽梅, 欧阳由男, 叶胜海, 季芝娟. 水稻开花习性及其在粳型三系不育系选育中的应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 731-743. |
| [2] | 卞金龙, 任高磊, 裘实, 许方甫, 胡忠磊, 张洪程, 魏海燕. 不同机插方式下控混肥施用方式对淮北地区优质食味粳稻产量及氮素利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(6): 847-862. |
| [3] | 陆婷婷, 闫文惠, 苏新全, 曾罗华, 华丽琴, 谌江华, 奉保华, 王跃星, 胡江, 符冠富. 多年生稻产量品质抗逆响应形成的生理生态机制及其调控途径研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 586-600. |
| [4] | 曹云, 陈雪芳, 黄兴海, 何咨霆, 汤菁莎, 陈坤, 汪爱羚, 罗贯洲, 廖琴, 孙园园, 郭翔, 杨志远, 马均, 孙永健. 播种量和取秧量对精量条播机插杂交稻高产群体构建及能效的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 477-490. |
| [5] | 唐承翰, 陈惠哲, 怀燕, 孙良, 张玉屏, 向镜, 张义凯, 王志刚, 徐逸文, 王亚梁. 杂交稻钵毯苗机插质量及产量形成对钵深的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 491-500. |
| [6] | 朱鹏, 凌溪铁, 王金彦, 张保龙, 杨郁文, 许轲, 裘实. 机直播条件下不同控草方式对抗除草剂水稻产量和品质差异性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 501-515. |
| [7] | 董立强, 张义凯, 杨铁鑫, 冯莹莹, 马亮, 梁潇, 张玉屏, 李跃东. 北方粳稻密苗机插育秧对秧苗素质及取秧特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 516-528. |
| [8] | 韦还和, 汪璐璐, 马唯一, 张翔, 左博源, 耿孝宇, 朱旺, 朱济邹, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 戴其根. 盐−旱复合胁迫下粳稻品种南粳9108籽粒灌浆特性及其与产量形成的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 373-386. |
| [9] | 沈智达, 余秋华, 张斌, 曹玉东, 王少华, 王红飞, 伍永清, 戴志刚, 李小坤. 磷肥施用量对湖北省直播水稻产量、磷素积累及利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 399-411. |
| [10] | 何勇, 张诗骞, 王志成, 詹逍康, 丁一可, 刘晓瑞, 马素素, 田志宏. 印度梨形孢与复合肥组合施用对水稻机插秧秧苗素质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 412-422. |
| [11] | 徐月梅, 彭诗燕, 孙志伟, 王志琴, 朱宽宇, 杨建昌. 不同耐低磷水稻品种的内源激素水平差异及其与产量和磷利用率的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 231-244. |
| [12] | 唐承翰, 王晶卿, 陈惠哲, 张玉屏, 向镜, 张义凯, 王志刚, 怀燕, 陈佳峰, 王亚梁. 杂交稻条播育秧机插秧苗素质对产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 245-254. |
| [13] | 舒傲, 解嘉鑫, 曹威, 周传名, 李蓓蕾, 陈嘉馨, 李莉, 曹放波, 陈佳娜, 黄敏. 氮肥运筹对优质杂交中稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 255-263. |
| [14] | 陈书融, 朱练峰, 秦碧蓉, 王婕, 朱旭华, 田文昊, 朱春权, 曹小闯, 孔亚丽, 张均华, 金千瑜. 增氧灌溉下配施硝化抑制剂对水稻生长、产量和氮肥利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 92-100. |
| [15] | 冯向前, 王爱冬, 洪卫源, 李子秋, 覃金华, 詹丽钏, 陈里鹏, 张运波, 王丹英, 陈松. 基于低空无人机遥感的水稻产量估测方法研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 604-616. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||