
中国水稻科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 140-149.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.230502
收稿日期:2023-05-06
修回日期:2023-06-18
出版日期:2024-03-10
发布日期:2024-03-14
通讯作者:
* email: wqli@nwsuaf.edu.cn
基金资助:
GAO Junru, QUAN Hongyu, YUAN Liuzhen, LI Qinying, QIAO Lei, LI Wenqiang( )
)
Received:2023-05-06
Revised:2023-06-18
Online:2024-03-10
Published:2024-03-14
Contact:
* email: wqli@nwsuaf.edu.cn
摘要:
【目的】株高是作物重要的农艺性状,挖掘株高控制基因并解析其分子功能,可为作物高产育种提供更多有用的基因资源。【方法】利用EMS诱变水稻日本晴获得的矮化突变体d1-11为材料,进行表型和细胞学观察,通过图位克隆的方法鉴定d1-11基因并对基因表达、激素含量和抗旱性进行了分析。【结果】d1-11突变体表现出植株矮化、叶片变短变宽和籽粒形态变圆表型;d1-11突变体叶片中脉萎缩,大脉和小脉数量和面积减少,导致叶片形态变异。d1-11基因被定位到水稻5号染色体R5M15.2和R5M15.8两个分子标记之间;图位克隆结果表明d1-11突变体中D1基因第11外显子和内含子交界处单碱基替换导致基因功能缺失。D1基因在苗期各组织中表达量较高,从分蘖期开始表达量降低;外源脱落酸(ABA)处理24 h后诱导D1基因表达,外源赤霉素(GA)处理抑制D1基因表达,盐胁迫处理24 h诱导D1基因剧烈上调表达。d1-11突变体植株GA、油菜素内酯(BR)和生长素(IAA)等激素含量均上升,叶片相对含水量上升、叶片失水速率降低,植株对干旱胁迫抗性显著增强。【结论】鉴定到水稻D1基因新等位突变d1-11,发现d1-11突变体多种内源激素水平上升、叶片含水量增加、植株对干旱胁迫抗性增强。本研究进一步丰富了水稻矮化基因资源并揭示D1基因新的生物学功能。
高郡茹, 权弘羽, 袁刘珍, 李钦颖, 乔磊, 李文强. 水稻D1基因新等位突变体的鉴定与功能分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 140-149.
GAO Junru, QUAN Hongyu, YUAN Liuzhen, LI Qinying, QIAO Lei, LI Wenqiang. Map-based Cloning and Functional Analysis of a New Allele of D1, a Gene Controlling Plant Height in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(2): 140-149.
| 标记名称 Marker name | 正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence(5′-3′) | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence(5′-3′) | 用途 Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| R5M8 | CGAGATGGAGGGATTTGAC | CCCGATGACTAGGGATTAGAG | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M10 | TACAAAATATGCCCGTGTCG | GATCGTTCCGCAAACAGAG | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M12 | GGTAGGAGGTGGAAGAAGG | TTTAGAGGGTCGGGCGATT | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M14 | CGTCAACAGGCTTGAAAGA | TTGCCAGTCCCAAAGAGTA | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M14.5 | AACGCAGTTGTGCTAATCAG | AGATCTTGTTGCCAAAAAAT | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M15 | GACATTTCGTGTGAATTGTT | TTCACAACTTCACTCGAGAC | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M15.2 | ATTAAGGTAGGGGCATGAAT | ATCACAAAGCAGTTTCCAGA | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M15.6 | ACAAAAATATGATGTGGCAA | CAACCCAGAAACCATCTAGT | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M15.8 | CTGAGAATGACTGCTCCGAA | CTTAGCGCATGAGTGGTTTT | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M16 | CCCACTGTATTGGATTCTGC | CCACCAGGTCCCACGTTAT | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M18 | AATGCCCTTCTCATCCGTGTG | GTCTATGCGTGCTGTGGGCTA | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| D1-1 | AAGAGAGAGGCTCAGGCATG | GGAACTCAAAAGCTCAAGGT | 突变位点检测Mutation site detection |
| D1-2 | GGTGCAAAACTGCTGTGAAT | GTGGGCTATGCAAATTAACA | 突变位点检测Mutation site detection |
| CDS-9F/13R | AAACAAAAGAGGTGGAGAGG | TCTCATGCTCTCATCAATCA | cDNA测序 cDNA sequencing |
| CDS-10F/12R | GAATGATGGAGACCAAGGAA | CTGTTTCCCAGGTGCAATAG | cDNA测序 cDNA sequencing |
| UBQ-qPCR | GGACTGGTTAAATCAATCGTCA | CCATATACCACGACCGTCAAAA | qRT-PCR |
| D1-qPCR | CAGGAGGTTGAACATGCATATG | CCTGTGTGACTTACAACCTAGT | qRT-PCR |
表1 本研究所用引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequences used in this study.
| 标记名称 Marker name | 正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence(5′-3′) | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence(5′-3′) | 用途 Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| R5M8 | CGAGATGGAGGGATTTGAC | CCCGATGACTAGGGATTAGAG | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M10 | TACAAAATATGCCCGTGTCG | GATCGTTCCGCAAACAGAG | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M12 | GGTAGGAGGTGGAAGAAGG | TTTAGAGGGTCGGGCGATT | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M14 | CGTCAACAGGCTTGAAAGA | TTGCCAGTCCCAAAGAGTA | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M14.5 | AACGCAGTTGTGCTAATCAG | AGATCTTGTTGCCAAAAAAT | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M15 | GACATTTCGTGTGAATTGTT | TTCACAACTTCACTCGAGAC | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M15.2 | ATTAAGGTAGGGGCATGAAT | ATCACAAAGCAGTTTCCAGA | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M15.6 | ACAAAAATATGATGTGGCAA | CAACCCAGAAACCATCTAGT | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M15.8 | CTGAGAATGACTGCTCCGAA | CTTAGCGCATGAGTGGTTTT | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M16 | CCCACTGTATTGGATTCTGC | CCACCAGGTCCCACGTTAT | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| R5M18 | AATGCCCTTCTCATCCGTGTG | GTCTATGCGTGCTGTGGGCTA | 基因定位Gene mapping |
| D1-1 | AAGAGAGAGGCTCAGGCATG | GGAACTCAAAAGCTCAAGGT | 突变位点检测Mutation site detection |
| D1-2 | GGTGCAAAACTGCTGTGAAT | GTGGGCTATGCAAATTAACA | 突变位点检测Mutation site detection |
| CDS-9F/13R | AAACAAAAGAGGTGGAGAGG | TCTCATGCTCTCATCAATCA | cDNA测序 cDNA sequencing |
| CDS-10F/12R | GAATGATGGAGACCAAGGAA | CTGTTTCCCAGGTGCAATAG | cDNA测序 cDNA sequencing |
| UBQ-qPCR | GGACTGGTTAAATCAATCGTCA | CCATATACCACGACCGTCAAAA | qRT-PCR |
| D1-qPCR | CAGGAGGTTGAACATGCATATG | CCTGTGTGACTTACAACCTAGT | qRT-PCR |
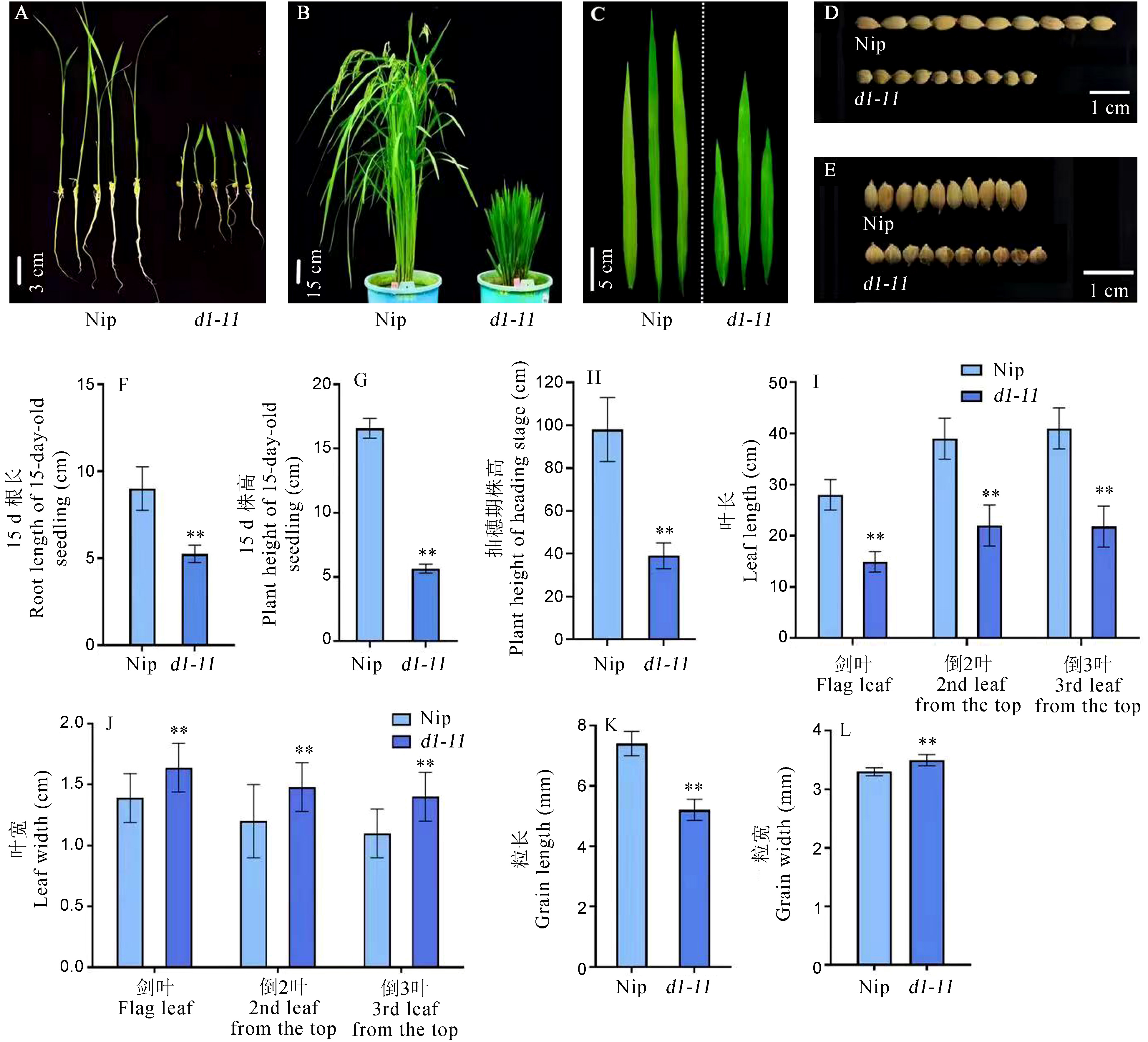
图1 野生型与突变体d1-11的表型特征 A:生长15 d的野生型和突变体幼苗;B:抽穗期的野生型和突变体植株;C:抽穗期叶片,从左向右依次为剑叶、倒2叶、倒3叶;D、E分别为野生型和突变体籽粒表型;F~L分别为生长15 d的野生型和突变体幼苗的根长(F)、株高(G),抽穗期株高(H)、叶长(I)、叶宽(J)、粒长(K)和粒宽(L)比较。误差线表示平均值±标准差(n=20)。** P<0.01(t检验)。
Fig. 1. Phenotypic characterization of WT and d1-11 mutant A, Seedlings of 15-day-old WT and d1-11; B, Morphology of WT and d1-11 at the heading stage; C, Phenotypes of WT and d1-11 leaves at the heading stage. From left to right, three leaves represent flag leaf, the second leaf and the third leaf; D and E, Seed morphology; F-L, Agronomic comparison between WT and mutant. Bars represent mean ± SD (n=20). **P<0.01(the Student’s t-test).
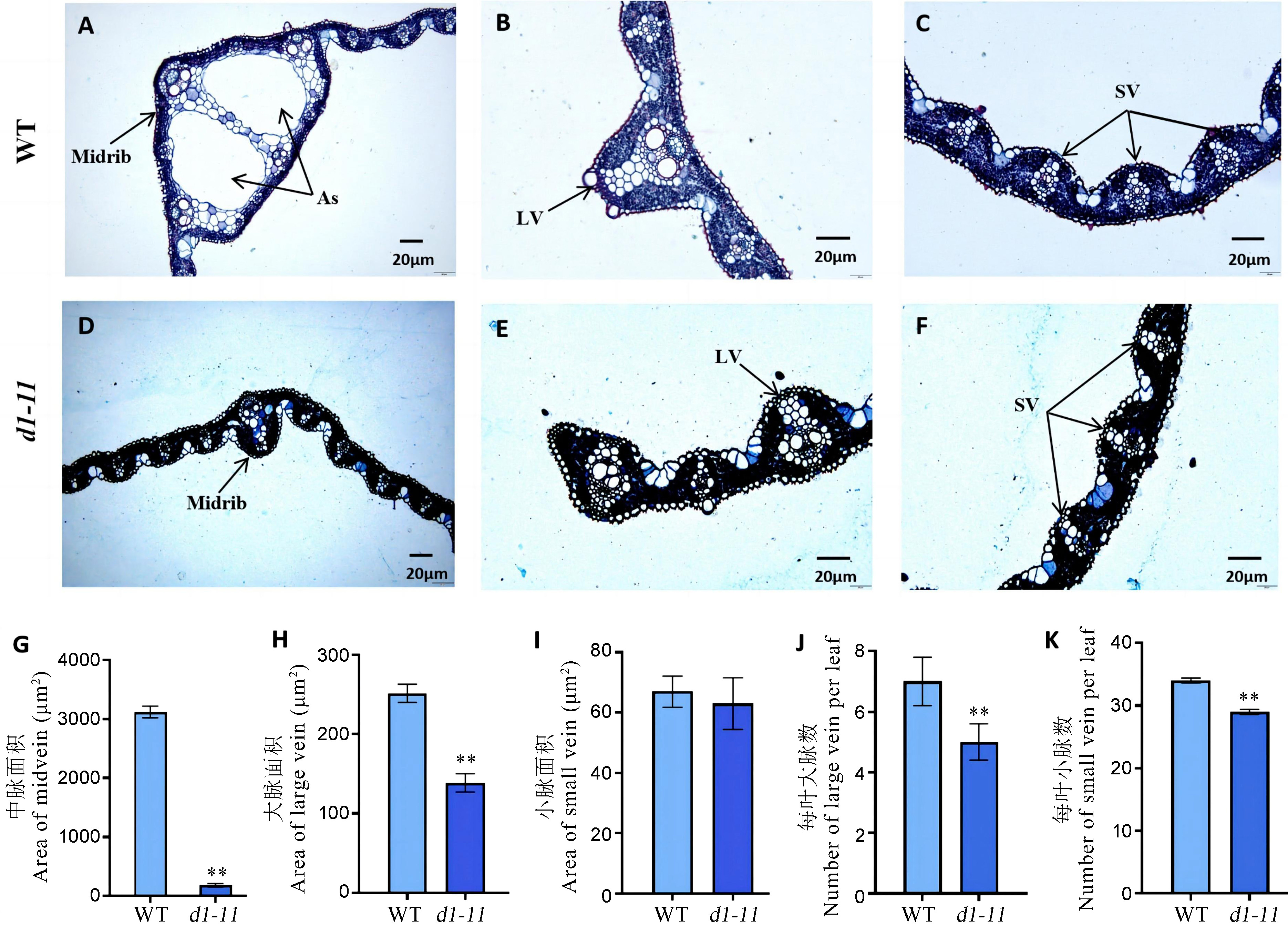
图2 野生型和突变体叶片横切面石蜡切片观察 A~C: 野生型叶片中脉、大脉和小脉的横切面;D~F: 突变体叶片中脉、大脉和小脉的横切面;G~I: 野生型和突变体叶片中脉、大脉和小脉的面积统计;J~K: 野生型和突变体每叶大脉和小脉数目统计。LV: 大脉;SV: 小脉;As: 气腔。图中误差线表示平均数±标准差(n=9)。**P<0.01(t检验)。
Fig. 2. Cross section of leaves of the wild type and the mutant A-C, Leaf midrib, large vein and small vein in WT; D-F, Leaf midrib, large vein and small vein in mutant; G-I, Area of leaf midrib, large vein and small vein in WT and mutant; J-K, Number of large and small veins per leaf in WT and mutant. LV, large vein; SV, small vein; As, Air space. Bars represent mean ± SD (n=9). **P<0.01(the Student’s t-test)
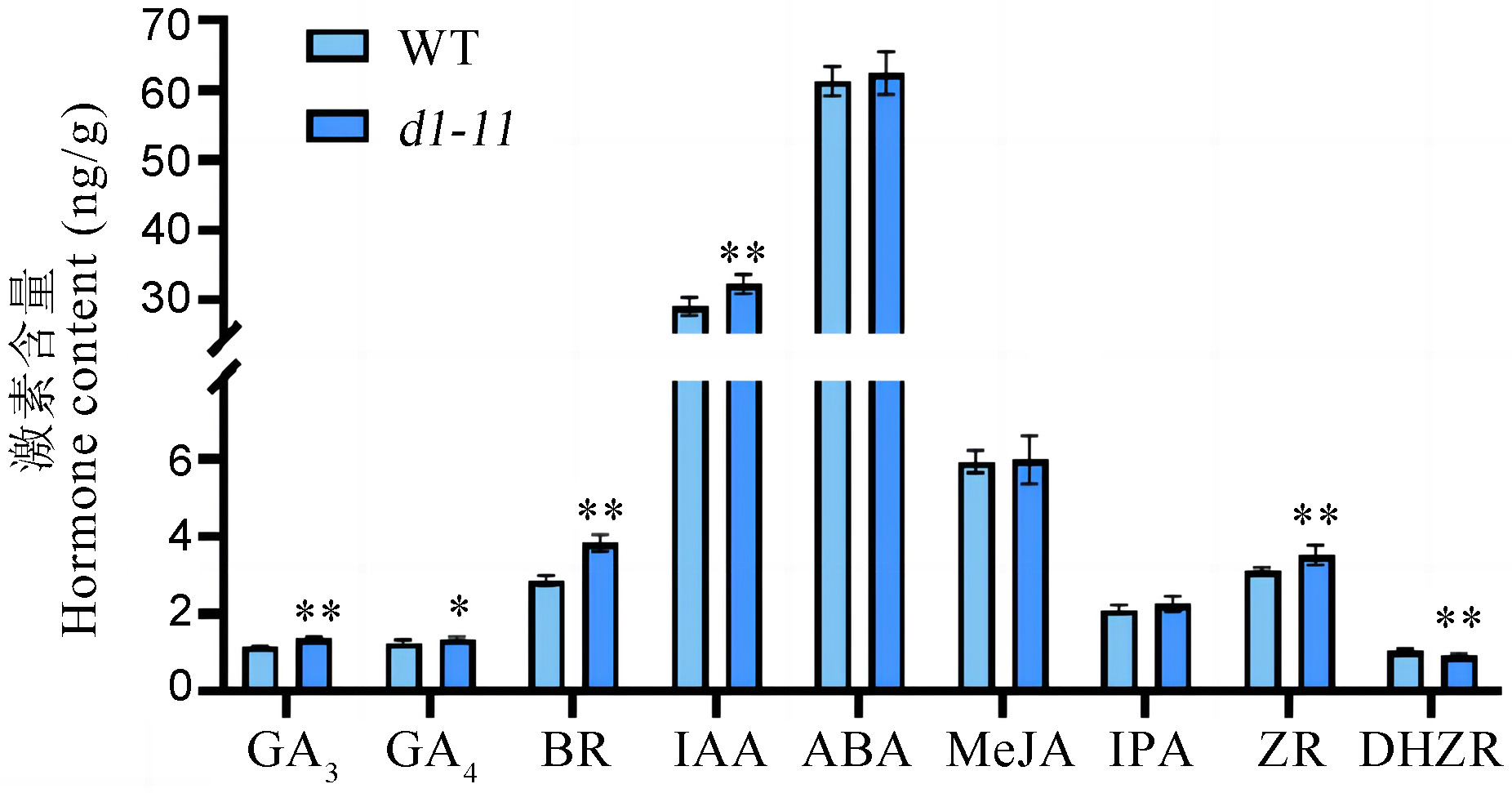
图3 野生型和d1-11突变体内源性激素水平比较 图中误差线表示平均数±标准差(n=9)。*P<0.05; **P<0.01(t检验)。
Fig. 3. Comparison of hormone levels in the wild type and the d1-11 mutant Bars represent mean ± SD (n=9). *P<0.05; **P<0.01(t-test).
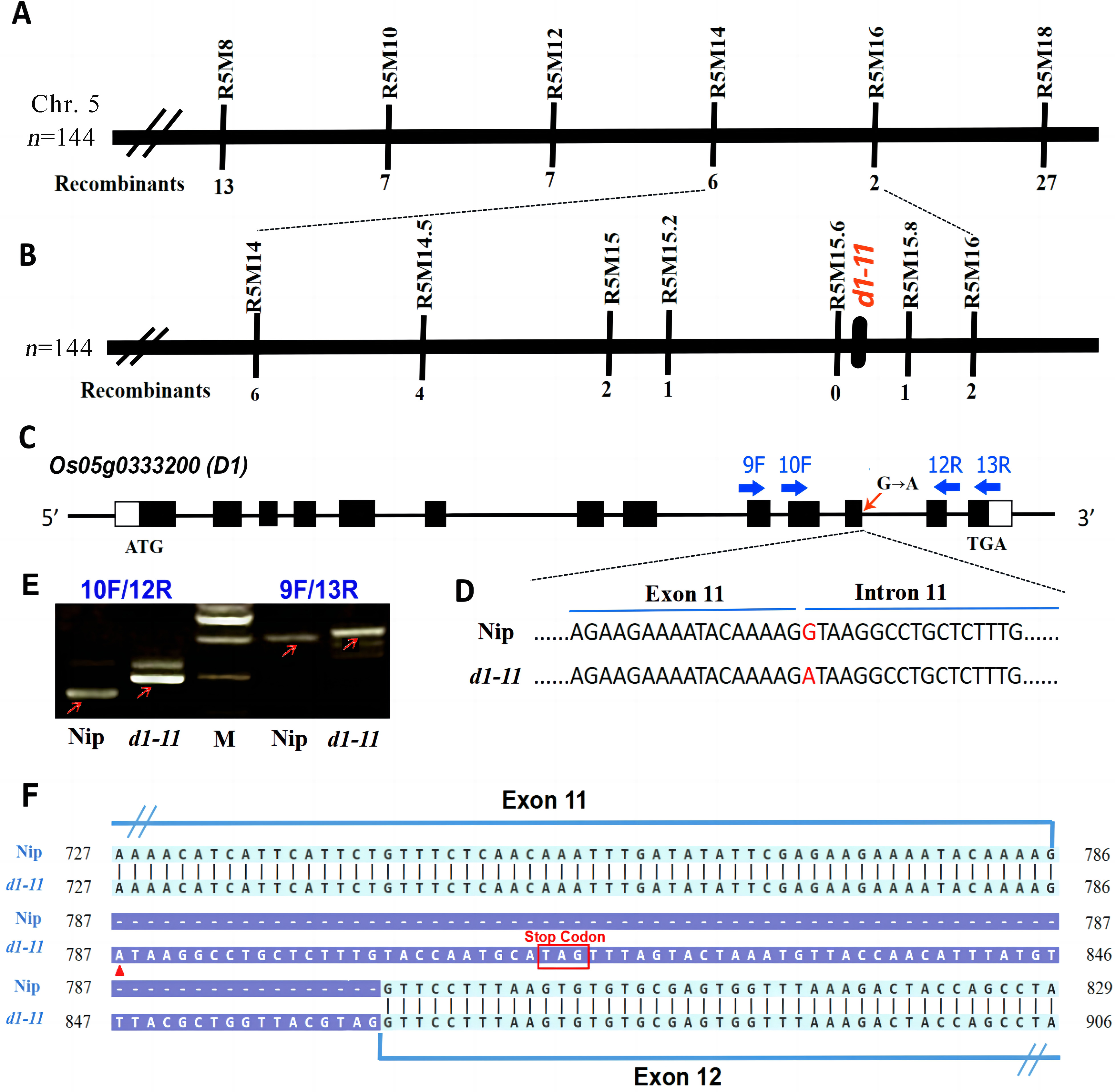
图4 d1-11基因的遗传定位与图位克隆 A、B:d1-11的分子标记定位;C:D1基因结构及突变位点分析;D:野生型和d1-11突变体测序结果;E:野生型和d1-11的 RT-PCR扩增结果, M为标记, 从上至下依次为1000 bp、750 bp、500 bp、250 bp;F:野生型和d1-11突变体中D1基因CDS区cDNA序列比对。
Fig. 4. Genetic mapping and map-based cloning of the d1-11 gene A and B, Genetic mapping of d1-11; C, Gene structure of D1; D, Sequence comparison between WT and d1-11; E, RT-PCR analysis of D1 gene in WT and the d1-11 mutant. M, DNA marker; F, Alignments of D1 gene cDNA sequence in WT and d1-11.

图7 d1-11突变体对干旱胁迫的抗性分析 A: 野生型和突变体干旱胁迫前、胁迫后和复水5 d后的表型特征;B: 野生型和突变体干旱胁迫后存活率比较;干旱胁迫数据来源于3次独立实验;C、D: 正常条件下野生型和突变体的叶片相对含水量(C)和失水速率(D)比较。图中误差线表示平均数±标准差(n=9)。*表示P<0.05,显著差异,**表示P<0.01,极显著差异(t检验)。
Fig. 7. Analysis of drought resistance in the d1-11 mutant A, Phenotypes of WT and mutant under drought stress; B, Survival rate of WT and the mutant after recovery for 5 days; C and D, Relative water content (RWC) and rate of water loss (RWL) in WT and the mutant under non-stressed conditions. Bars represent mean ± SD(n=9). * and ** indicate significant difference between WT and the d1-11 mutant by the Student’s t-test (P<0.05, P<0.01), respectively.
| [1] | Wing R A, Purugganan M D, Zhang Q. The rice genome revolution: From an ancient grain to Green Super Rice[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2018, 19(8): 505-517. |
| [2] | Peng J, Richards D E, Hartley N M, Murphy G P, Devos K M, Flintham J E, Beales J, Fish L J, Worland A J, Pelica F, Sudhakar D, Christou P. Green revolution genes encode mutant gibberellin response modulators[J]. Nature, 1999, 400(6741): 256-261. |
| [3] | Khush G S. Green revolution: The way forward[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2001, 2(10): 815-822. |
| [4] | Sasaki A, Ashikari M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Itoh H, Nishimura A, Swapan D, Ishiyama K, Saito T. Green revolution: a mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice[J]. Nature, 2002, 416(6882): 701-702. |
| [5] | Sasaki A, Itoh H, Gomi K, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Ishiyama K, Kobayashi M, Jeong D H, An G, Kitano H, Ashikari M. Accumulation of phosphorylated repressor for gibberellin signaling in an F-box mutant[J]. Science, 2003, 299(5614): 1896-1898. |
| [6] | Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Umemura K, Uozu S, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S. A rice brassinosteroid- deficient mutant, ebisu dwarf(d2), is caused by a loss of function of a new member of cytochrome P450[J]. Plant Cell, 2003, 15(12): 2900-2910. |
| [7] | Itoh H, Tatsumi T, Sakamoto T, Otomo K, Toyomasu T, Kitano H, Ashikari M, Ichihara S, Matsuoka M. A rice semi-dwarf gene, Tan-Ginbozu (D35), encodes the gibberellin biosynthesis enzyme[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2004, 54(4): 533-547. |
| [8] | Tanabe S, Ashikari M, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Yano M, Yoshimura A, Kitano H, Matsuoka M, Fujisawa Y, Kato H, Iwasaki Y. A novel cytochrome P450 is implicated in brassinosteroid biosynthesis via the characterization of a rice dwarf mutant, dwarfll, with reduced seed length[J]. Plant Cell, 2005, 17(3): 776-790. |
| [9] | Ferrero-Serrano Á, Cantos C, Assmann S M. The role of dwarfing traits in historical and modern agriculture with a focus on rice[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2019, 11(11): a034645. |
| [10] | Ishikawa A, Tsubouchi H, Iwasaki Y, Asahi T. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA for the alpha subunit of a G protein from rice[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 1995, 36(2): 353-359. |
| [11] | Ashikari M, Wu J, Yano M, Sasaki T, Yoshimura A. Rice gibberellin-insensitive dwarf mutant gene dwar1 encodes the alpha-subunit of GTP-binding protein[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1999, 96(18): 10284. |
| [12] | Fujisawa Y, Kato T, Ohki S, Ishikawa A, Kitano H, Sasaki T, Asahi T, Iwasaki Y. Suppression of the heterotrimeric G protein causes abnormal morphology, including dwarfism in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1999, 96(13): 7575-7580. |
| [13] | Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Fujisawa Y, Kobayashi M, Ashikari M, Iwasaki Y, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. Rice dwarf mutant d1, which is defective in the alpha subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein, affects gibberellin signal transduction[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2000, 97(21): 11638-11643. |
| [14] | Oki K, Inaba N, Kitagawa K, Fujioka S, Kitano H, Fujisawa Y, Kato H, Iwasaki Y. Function of the a subunit of rice heterotrimeric G protein in brassinosteroid signaling[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2009, 50(1): 161-172. |
| [15] | Hu X, Qian Q, Xu T, Zhang Y, Dong G, Gao T, Xie Q, Xue Y. The U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase TUD1 functions with a heterotrimeric G α subunit to regulate brassinosteroid-mediated growth in rice[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2013, 9(3): e1003391. |
| [16] | Ferrero-Serrano Á, Assmann S M. The alpha-subunit of the rice heterotrimeric G protein, RGA1, regulates drought tolerance during the vegetative phase in the dwarf rice mutant d1[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(11): 3433-3443. |
| [17] | Gaur, V S, Channappa G, Chakraborti M, Sharma T R, Mondal T K. ‘Green revolution’ dwarf gene sd1 of rice has gigantic impact[J]. Briefings in Functional Genomics, 2020, 19(5): 390-409. |
| [18] | 李刚, 赵静, 王保民, 李召虎, 周成明, 何钟佩, 董学会. 植物生长物质对栽培甘草幼苗根内源激素变化动态研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2005(14): 1118-1120. |
| Li G, Zhao J, Wang B M, Li Z H, Zhou C M, He Z P, Dong X H. Dynamic study on changes of endogenous hormones in roots of cultivated Glycyrrhiza uralensis seedlings affected by plant growth substances[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2005(14): 1118-1120. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | Du H, Guo Z R, Xiong L Z. Determination of rice leaf water content[J]. Bio-Protocol, 2018: e1010157. |
| [20] | Mao B, Cheng Z, Lei C, Xu F, Gao S, Ren Y, Wang J, Zhang X, Wang J, Wu F, Guo X, Liu X, Wu C, Wang H, Wan J. Wax crystal-sparse leaf2, a rice homologue of WAX2/GL1, is involved in synthesis of leaf cuticular wax[J]. Planta, 2012, 235(1): 39-52. |
| [21] | Murray M G, Thompson W F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1980, 8(19): 4321-4325. |
| [22] | Michelmore R W, Paran I. Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA, 1991, 88(21): 9828-9832. |
| [23] | 张敏娟, 李帅军, 陈琼琼, 景秀清, 陈坤明, 石春海, 李文强. 水稻矮化少蘖突变体dlt3的基因定位和白质组学分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 529-537. |
| Zhang M J, Li S J, Chen Q Q, Jing X Q, Chen K M, Shi C H, Li W Q. Genetic Mapping and proteomic analysis of the dwarf and low-tillering mutant dlt3 in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(6): 529-537. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Li W Q, Zhang M J, Qiao L, Chen Y B, Zhang D P, Jing X Q, Gan P F, Huang Y B, Gao J R, Liu W T, Shi C H, Cui H C, Chen K M. Characterization of wavy root 1, an agravitropism allele, reveals the functions of OsPIN2 in fine regulation of auxin transport and distribution and in ABA biosynthesis and response in rice[J]. Crop Journal, 2022, 10(4): 980-992. |
| [25] | Spielmeyer W, Ellis M H, Chandler P M. Semidwarf (sd-1), contains a defective gibberellin 20-oxidase gene. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 2002, 99(13): 9043-9048. |
| [26] | Monna L, Kitazawa N, Yoshino R, Suzuki J, Masuda H, Maehara Y, Tanji M, Sato M, Nasu S, Minobe Y. Positional cloning of rice semidwarfing gene, sd-1: Rice "Green Revolution Gene" encodes a mutant enzyme involved in gibberellin synthesis[J]. DNA Research, 2002, 9(1): 11-17. |
| [27] | Ishikawa S, Mackawa M, Arite T, Onishi K, Takamure I, Kyozuka J. Suppression of tiller bud activity in tillering dwarf mutants of rice[J]. Plant Cell and Physiology, 2005, 46(1): 79-86. |
| [28] | Choi J, Lee T, Cho J, Servante EK, Pucker B, Summers W, Bowden S, Rahimi M, An K, An G, Bouwmeester H J, Oldroyd G, Paszkowski U. The negative regulator SMAX1 controls mycorrhizal symbiosis and strigolactone biosynthesis in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1521-1524. |
| [29] | Zheng J, Hong K, Zeng L, Wang L, Kang S, Qu M, Dai J, Zou L, Zhu L, Tang Z, Meng X, Wang B, Qian Q, Wang Y, Li J, Xiong G. Karrikin signaling acts parallel to and additively with strigolactone signaling to regulate rice mesocotyl elongation in darkness[J]. The Plant Cell, 2020, 32(9): 2780-2805. |
| [30] | Liu F, Wang P, Zhang X, Li X, Yan X, Fu D, Wu G. The genetic and molecular basis of crop height based on a rice model[J]. Planta, 2017, 247(1): 1-26. |
| [31] | Ferrero-Serrano N, Cantos C, Assmann S M. The role of dwarfing traits in historical and modern agriculture with a focus on rice[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2019, 11(11): 1943-1964. |
| [32] | Yang D W, Zheng X H, Cheng C P, Wang W D, Ye X F. A dwarfing mutant caused by deactivation function of alpha subunit of the heterotrimeric G-protein in rice[J]. Euphytica, 2014, 197(1): 145-159. |
| [33] | Gilman A G. Proteins: Transducers of receptor- generated signals[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 1986, 56(1): 615-649. |
| [34] | Miura K, Agetsuma M, Kitano H, Yoshimura A, Matsuoka M, Jacobsen S, Ashikari M. A metastable DWARF1 epigenetic mutant affecting plant stature in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA, 2009, 106(27): 11218-11223. |
| [35] | Sun S, Wang L, Mao H, Shao L, Li X, Xiao J, Ouyang Y. A G-protein pathway determines grain size in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 851-861. |
| [36] | 罗茂春, 赵政, 夏令, 郭迟鸣, 陈亮. 水稻矮秆基因d-ss的遗传分析与克隆[J]. 厦门大学学报, 2013, 52(5): 684-689. |
| Luo M C, Zhao Z, Xia L, Guo C M, Chen L. Genetic analysis and cloning of the rice dwarf mutant d-ss[J]. Journal of Xiamen University, 2013, 52(5): 684-689. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 纪现军, 叶胜海, 周涯, 修芬连, 邓晓梅, 尚海漩, 刘继云, 陈萍萍, 李小华, 金庆生, 张小明. 水稻矮秆突变体zj88d的鉴定与基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(1): 35-40. |
| Ji X J, Ye S H, Zhou Y, Xiu F L, Deng X M, Shang H X, Liu J Y, Chen P P, Li X H, Jin Q S, Zhang X M. Characterization and gene mapping of a dwarf mutant zj88d in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2013, 27(1): 35-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | Wang J, Wang J, Yang J, Zhao X Q, Zhu J Y, Fan F J, Li W Q, Wang F Q, Zhong W G. Genetic analysis and gene fine mapping of a midrib-deficient mutant dl-6[J]. Agricultural Science&Technology, 2015, 16(12): 2672. |
| [39] | Nagasawa N, Miyoshi M, Sano Y, Satoh H, Hirano H, Sakai H, Nagato Y. SUPERWOMAN1 and DROOPING LEAF genes control floral organ identity in rice[J]. Development, 2003, 130(4): 705-718. |
| [40] | Kang G, Zhang N, Tan T H, Zhang Z, Wang R, Wu L T. Leaf microstructure and photosynthetic characteristics of a rice midvein-deficient mutant dl-14[J]. Biologia Plantarum, 2022, 66(9): 172-177. |
| [41] | Tanguilig V, Yambao E, O’toole J, Datta S. Water stress effects on leaf elongation, leaf water potential, transpiration, and nutrient uptake of rice, maize, and soybean[J]. Plant and Soil, 1987, 103(2): 155-168. |
| [42] | Miyamoto N, Steudle E, Hirasawa T, Lafitte R. Hydraulic conductivity of rice roots[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2001, 52(362): 1835-1840. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [3] | 景秀, 周苗, 王晶, 王岩, 王旺, 王开, 郭保卫, 胡雅杰, 邢志鹏, 许轲, 张洪程. 穗分化末期-灌浆初期干旱胁迫对优质食味粳稻根系形态和叶片光合特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 33-47. |
| [4] | 裘霖琳, 刘窍, 付亚萍, 刘文真, 胡国成, 翟玉凤, 庞礴, 汪得凯. 水稻矮化小穗基因DSP2的鉴定与克隆[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(2): 150-158. |
| [5] | 杨晓龙, 程建平, 汪本福, 李阳, 张枝盛, 李进兰, 李萍. 灌浆期干旱胁迫对水稻生理性状和产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 38-46. |
| [6] | 李斌, 黄进, 王丽, 李瑾, 梁越洋, 陈稷. 环境胁迫及相关植物激素在水稻根毛发育过程中的作用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(4): 287-299. |
| [7] | 许赵蒙, 李利华, 高晓庆, 袁正杰, 李莘, 田旭丹, 王岚岚, 瞿绍洪. 转Pi9抗稻瘟病基因水稻株系的比较转录组分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(3): 245-255. |
| [8] | 张敏娟, 李帅军, 陈琼琼, 景秀清, 陈坤明, 石春海, 李文强. 水稻矮化少蘖突变体dlt3的基因定位和蛋白质组学分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 529-537. |
| [9] | 陈苏, 谢建坤, 黄文新, 陈登云, 彭晓剑, 付学琴. 根际促生细菌对干旱胁迫下水稻生理特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(5): 485-492. |
| [10] | 杨永杰, 杨雪芹, 张彩霞, 符冠富, 陈婷婷, 陶龙兴. 干旱胁迫下NO 对水稻日本晴叶片生理特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(1): 65-72. |
| [11] | 丁雷1,李英瑞1,李勇2 ,沈其荣1 ,郭世伟1,*. 梯度干旱胁迫对水稻叶片光合和水分状况的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(1): 65-70. |
| [12] | 陈俊宇,王凯,龚俊义,樊叶杨,黄得润,庄杰云*. RFT1与Hd1所在区间对水稻抽穗期、株高和千粒重的作用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(2): 117-121. |
| [13] | 付坚1,Linkun GU2 ,郭怡卿1,Liyuan ZHANG 2,王玲仙1,李定琴1,王波1 ,Jeff Qingxi SHEN2,*,程在全1,*. 干旱胁迫的水稻根高效酵母双杂交体系建立[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(2): 198-202. |
| [14] | 江建华1,2 ,陈兰1 ,刘强明1 ,赫英俊1 ,洪德林1,* . 利用基于条件表型值的关联分析发掘粳稻生育期和单株有效穗数有利等位变异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(5): 542-548. |
| [15] | 罗炬#,邵高能#,魏祥进,陈明亮,唐绍清,焦桂爱,谢黎虹,胡培松* . 一个控制水稻株高QTL qPH3的遗传分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(4): 417-422. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||