
中国水稻科学 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (5): 503-512.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.200909
朱春权#, 徐青山#, 曹小闯, 朱练峰, 孔亚丽, 金千瑜, 张均华*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-09-14
修回日期:2020-12-31
出版日期:2021-09-10
发布日期:2021-09-10
通讯作者:
张均华
作者简介:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
Chunquan ZHU#, Qingshan XU#, Xiaochuang CAO, Lianfeng ZHU, Yali KONG, Qianyu JIN, Junhua ZHANG*( )
)
Received:2020-09-14
Revised:2020-12-31
Online:2021-09-10
Published:2021-09-10
Contact:
Junhua ZHANG
About author:#These authors contributed equally to this work
摘要:
【目的】早稻育秧过程中易遭受低温冷害,引起水稻减产。因此,有必要研究不同类型的基质对早稻秧苗耐低温的影响。【方法】以水稻田自然表层土为对照,采用两种代表性基质(无土基质和发酵基质)培育早稻秧苗,在水稻出芽6 d后进行不同低温处理,3 d后测定水稻的基本理化性质指标和基因表达,明确不同基质对早稻秧苗耐低温胁迫的调节作用。【结果】1)无土基质和发酵基质容重均显著低于对照,电导率、通气孔隙、碱解氮、速效磷、速效钾和有机质含量显著高于对照;发酵基质育成的秧苗其根长、百株地上部干质量和百株根部干质量均显著高于对照,无土基质和发酵基质育成的秧苗根系和地上部的氮、磷、钾养分含量显著高于对照。2)随着温度的降低,水稻秧苗的生长和养分吸收均受到抑制。低温对发酵基质上生长的秧苗抑制作用较弱,无土基质次之,对照受抑制较强。3)在低温条件下(白天8℃/晚上4℃),无土基质和发酵基质中育成的秧苗丙二醛含量显著低于对照,说明在寒冷条件下的细胞氧化损伤较少。其中,无土基质和发酵基质育成的秧苗超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶活性,脯氨酸含量和可溶性蛋白含量均高于对照,发酵基质育成的秧苗过氧化物酶活性高于对照,无土基质育成的秧苗谷胱甘肽转移酶活性高于对照。同时,无土基质和发酵基质育成的秧苗OsCold1、OsCOIN、OsP5CS和OsSODB四个基因表达水平均显著高于对照,提高了水稻耐低温能力。【结论】以上结果表明,无土基质和发酵基质通过调控水稻秧苗的生理生化反应和相关基因表达,提高秧苗耐低温胁迫能力。
朱春权, 徐青山, 曹小闯, 朱练峰, 孔亚丽, 金千瑜, 张均华. 不同属性特征基质对早稻秧苗耐低温的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 503-512.
Chunquan ZHU, Qingshan XU, Xiaochuang CAO, Lianfeng ZHU, Yali KONG, Qianyu JIN, Junhua ZHANG. Effects of Substrates with Different Properties on Chilling Tolerance of Early Rice Seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(5): 503-512.
| 处理 Treatment | 基质类型 Substrate type | 温度Temperature/℃ | 时间Time/h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白天 Day | 晚上 Night | 白天 Day | 晚上 Night | |||
| A1 | 无土基质 Soilless substrate | 18 | 10 | 12 | 12 | |
| A2 | 无土基质Soilless substrate | 13 | 7 | 12 | 12 | |
| A3 | 无土基质Soilless substrate | 8 | 4 | 12 | 12 | |
| B1 | 发酵基质Fermentation substrate | 18 | 10 | 12 | 12 | |
| B2 | 发酵基质Fermentation substrate | 13 | 7 | 12 | 12 | |
| B3 | 发酵基质Fermentation substrate | 8 | 4 | 12 | 12 | |
| C1 | 水稻土Paddy soil | 18 | 10 | 12 | 12 | |
| C2 | 水稻土Paddy soil | 13 | 7 | 12 | 12 | |
| C3 | 水稻土Paddy soil | 8 | 4 | 12 | 12 | |
表1 实验设计方案
Table 1 Scheme of experimental design.
| 处理 Treatment | 基质类型 Substrate type | 温度Temperature/℃ | 时间Time/h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白天 Day | 晚上 Night | 白天 Day | 晚上 Night | |||
| A1 | 无土基质 Soilless substrate | 18 | 10 | 12 | 12 | |
| A2 | 无土基质Soilless substrate | 13 | 7 | 12 | 12 | |
| A3 | 无土基质Soilless substrate | 8 | 4 | 12 | 12 | |
| B1 | 发酵基质Fermentation substrate | 18 | 10 | 12 | 12 | |
| B2 | 发酵基质Fermentation substrate | 13 | 7 | 12 | 12 | |
| B3 | 发酵基质Fermentation substrate | 8 | 4 | 12 | 12 | |
| C1 | 水稻土Paddy soil | 18 | 10 | 12 | 12 | |
| C2 | 水稻土Paddy soil | 13 | 7 | 12 | 12 | |
| C3 | 水稻土Paddy soil | 8 | 4 | 12 | 12 | |
| 基质类型 Substrate type | 碱解氮 Alkaline N / (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available P / (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available K / (mg·kg-1) | 总氮 Total N /(g·kg-1) | 总磷 Total P /(g·kg-1) | 总钾 Total P /(g·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter /(g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无土基质Soilless substrate | 1100.63±27.20 a | 87.60±3.84 b | 1899.73±23.10 b | 4.99±0.50 b | 2.65±0.37 b | 11.47±0.79 b | 22.51±0.83 a |
| 发酵基质Fermentation substrate | 477.87±52.20 b | 369.94±2.76 a | 4091.60±119.55 a | 9.22±0.23 a | 9.81±0.17 a | 14.25±0.19 a | 18.49±0.15 b |
| 水稻土Paddy soil | 88.43±3.31 c | 50.70±2.24 c | 499.67±6.00 c | 2.14±0.34 c | 2.45±0.19 b | 14.11±0.15 a | 4.05±1.26 c |
表2 育秧基质养分含量
Table 2 Nutrient contents in seedling raising substrate.
| 基质类型 Substrate type | 碱解氮 Alkaline N / (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available P / (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available K / (mg·kg-1) | 总氮 Total N /(g·kg-1) | 总磷 Total P /(g·kg-1) | 总钾 Total P /(g·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter /(g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无土基质Soilless substrate | 1100.63±27.20 a | 87.60±3.84 b | 1899.73±23.10 b | 4.99±0.50 b | 2.65±0.37 b | 11.47±0.79 b | 22.51±0.83 a |
| 发酵基质Fermentation substrate | 477.87±52.20 b | 369.94±2.76 a | 4091.60±119.55 a | 9.22±0.23 a | 9.81±0.17 a | 14.25±0.19 a | 18.49±0.15 b |
| 水稻土Paddy soil | 88.43±3.31 c | 50.70±2.24 c | 499.67±6.00 c | 2.14±0.34 c | 2.45±0.19 b | 14.11±0.15 a | 4.05±1.26 c |
| 基质类型 Substrate type | pH值 pH value | 电导率 EC/(mS·cm-1) | 容重Bulk density/(g·cm-3) | 总孔隙度 Total porosity /% | 通气孔隙度 Aeration porosity /% | 持水孔隙度 Water-holding porosity/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无土基质Soilless substrate | 6.39±0.02 c | 3.57±0.04 a | 0.29±0.01 c | 71.76±0.56 a | 7.33±0.24 b | 64.44±2.45 a |
| 发酵基质Fermentation substrate | 6.86±0.03 a | 2.50±0.06 b | 0.61±0.01 b | 56.48±0.50 b | 23.70±1.21 a | 32.78±1.81 c |
| 水稻土Paddy soil | 6.78±0.03 b | 0.13±0.00 c | 0.92±0.00 a | 57.57±0.44 b | 6.13±0.44 c | 51.44±1.73 b |
表3 育秧基质理化性质
Table 3 Physical and chemical properties of seedling raising substrate.
| 基质类型 Substrate type | pH值 pH value | 电导率 EC/(mS·cm-1) | 容重Bulk density/(g·cm-3) | 总孔隙度 Total porosity /% | 通气孔隙度 Aeration porosity /% | 持水孔隙度 Water-holding porosity/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无土基质Soilless substrate | 6.39±0.02 c | 3.57±0.04 a | 0.29±0.01 c | 71.76±0.56 a | 7.33±0.24 b | 64.44±2.45 a |
| 发酵基质Fermentation substrate | 6.86±0.03 a | 2.50±0.06 b | 0.61±0.01 b | 56.48±0.50 b | 23.70±1.21 a | 32.78±1.81 c |
| 水稻土Paddy soil | 6.78±0.03 b | 0.13±0.00 c | 0.92±0.00 a | 57.57±0.44 b | 6.13±0.44 c | 51.44±1.73 b |
| 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height /cm | 根长 Root height /cm | 叶龄 Leaf age /d | 百株地上部干质量 Shoot weight per 100 plants/g | 百株根部干质量 Root weight per 100 plants/g | 茎基宽 Width of shoot base per 10 plants/cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 7.82±0.26 a | 6.75±0.26 d | 1.98±0.10 a | 1.04±0.04 a | 0.21±0.01 cd | 1.54±0.02 a |
| A2 | 5.93±0.27 c | 5.44±0.22 f | 1.90±0.00 b | 0.61±0.02 d | 0.16±0.01 e | 1.48±0.05 ab |
| A3 | 4.81±0.25 e | 5.38±0.23 f | 1.90±0.00 b | 0.59±0.01 d | 0.14±0.01 e | 1.37±0.01 c |
| B1 | 7.39±0.29 b | 10.44±0.54 a | 1.91±0.06 b | 0.90±0.11 b | 0.32±0.01 a | 1.53±0.04 a |
| B2 | 5.65±0.24 c | 8.13±0.31 b | 1.90±0.00 b | 0.64±0.02 d | 0.27±0.01 b | 1.50±0.01 ab |
| B3 | 5.23±0.27 d | 7.18±0.28 c | 1.90±0.00 b | 0.56±0.02 d | 0.23±0.02 cd | 1.40±0.02 bc |
| C1 | 7.24±0.42 b | 7.33±0.41 c | 1.93±0.07 b | 0.79±0.01 c | 0.27±0.01 b | 1.48±0.03 ab |
| C2 | 5.20±0.30 d | 6.41±0.35 de | 1.90±0.00 b | 0.62±0.02 d | 0.24±0.02 c | 1.45±0.01 abc |
| C3 | 4.44±0.20 f | 6.07±0.31 e | 1.90±0.00 b | 0.53±0.01 d | 0.20±0.01 d | 1.36±0.01 c |
表4 不同温度处理对水稻根系和地上部生长特征的影响
Table 4 Effects of different temperature treatments on rice roots and aboveground part growth characteristics.
| 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height /cm | 根长 Root height /cm | 叶龄 Leaf age /d | 百株地上部干质量 Shoot weight per 100 plants/g | 百株根部干质量 Root weight per 100 plants/g | 茎基宽 Width of shoot base per 10 plants/cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 7.82±0.26 a | 6.75±0.26 d | 1.98±0.10 a | 1.04±0.04 a | 0.21±0.01 cd | 1.54±0.02 a |
| A2 | 5.93±0.27 c | 5.44±0.22 f | 1.90±0.00 b | 0.61±0.02 d | 0.16±0.01 e | 1.48±0.05 ab |
| A3 | 4.81±0.25 e | 5.38±0.23 f | 1.90±0.00 b | 0.59±0.01 d | 0.14±0.01 e | 1.37±0.01 c |
| B1 | 7.39±0.29 b | 10.44±0.54 a | 1.91±0.06 b | 0.90±0.11 b | 0.32±0.01 a | 1.53±0.04 a |
| B2 | 5.65±0.24 c | 8.13±0.31 b | 1.90±0.00 b | 0.64±0.02 d | 0.27±0.01 b | 1.50±0.01 ab |
| B3 | 5.23±0.27 d | 7.18±0.28 c | 1.90±0.00 b | 0.56±0.02 d | 0.23±0.02 cd | 1.40±0.02 bc |
| C1 | 7.24±0.42 b | 7.33±0.41 c | 1.93±0.07 b | 0.79±0.01 c | 0.27±0.01 b | 1.48±0.03 ab |
| C2 | 5.20±0.30 d | 6.41±0.35 de | 1.90±0.00 b | 0.62±0.02 d | 0.24±0.02 c | 1.45±0.01 abc |
| C3 | 4.44±0.20 f | 6.07±0.31 e | 1.90±0.00 b | 0.53±0.01 d | 0.20±0.01 d | 1.36±0.01 c |
| 处理 Treatment | 地上部氮含量 Shoot N content /(g kg-1) | 根系氮含量 Root N content /(g·kg-1) | 地上部磷含量 Shoot P content /(g kg-1) | 根系磷含量 Root P content /(g kg-1) | 地上部钾含量 Shoot K content /(g kg-1) | 根系钾含量 Root K content /(g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 47.93±0.58 a | 30.56±0.25 a | 5.86±0.07 bc | 3.98±0.11 b | 23.42±0.26 c | 24.32±0.23 c |
| A2 | 42.21±0.11 c | 26.64±0.58 b | 5.54±0.07 c | 3.85±0.77 b | 20.89±0.32 de | 20.52±0.13 e |
| A3 | 43.86±0.34 b | 26.20±0.04 b | 5.19±0.04 d | 3.71±0.21 bc | 20.23±0.18 e | 18.40±0.74 f |
| B1 | 34.60±0.36 d | 16.89±0.47 c | 6.19±0.23 a | 4.69±0.16 a | 31.97±0.61 a | 35.24±0.19 a |
| B2 | 34.69±0.18 d | 16.11±0.48 cd | 6.13±0.13 ab | 4.83±0.27 a | 31.24±0.58 a | 29.14±0.47 b |
| B3 | 29.77±0.67 e | 15.49±0.47 de | 6.02±0.07 ab | 4.91±0.24 a | 29.11±0.79 b | 22.14±0.07 d |
| C1 | 29.09±0.46 e | 14.69±0.38 ef | 5.08±0.03 d | 3.23±0.13 bc | 24.32±0.26 c | 20.00±0.24 e |
| C2 | 29.62±0.26 e | 13.13±0.46 g | 5.06±0.05 d | 3.05±0.16 c | 21.61±0.36 d | 17.27±0.11 g |
| C3 | 26.82±0.57 f | 13.87±0.25 fg | 4.98±0.13 d | 3.24±0.12 bc | 17.50±0.21 f | 15.80±0.23 h |
表5 不同温度处理后水稻植株养分含量
Table 5 Nutrient contents in rice under different temperature treatments.
| 处理 Treatment | 地上部氮含量 Shoot N content /(g kg-1) | 根系氮含量 Root N content /(g·kg-1) | 地上部磷含量 Shoot P content /(g kg-1) | 根系磷含量 Root P content /(g kg-1) | 地上部钾含量 Shoot K content /(g kg-1) | 根系钾含量 Root K content /(g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 47.93±0.58 a | 30.56±0.25 a | 5.86±0.07 bc | 3.98±0.11 b | 23.42±0.26 c | 24.32±0.23 c |
| A2 | 42.21±0.11 c | 26.64±0.58 b | 5.54±0.07 c | 3.85±0.77 b | 20.89±0.32 de | 20.52±0.13 e |
| A3 | 43.86±0.34 b | 26.20±0.04 b | 5.19±0.04 d | 3.71±0.21 bc | 20.23±0.18 e | 18.40±0.74 f |
| B1 | 34.60±0.36 d | 16.89±0.47 c | 6.19±0.23 a | 4.69±0.16 a | 31.97±0.61 a | 35.24±0.19 a |
| B2 | 34.69±0.18 d | 16.11±0.48 cd | 6.13±0.13 ab | 4.83±0.27 a | 31.24±0.58 a | 29.14±0.47 b |
| B3 | 29.77±0.67 e | 15.49±0.47 de | 6.02±0.07 ab | 4.91±0.24 a | 29.11±0.79 b | 22.14±0.07 d |
| C1 | 29.09±0.46 e | 14.69±0.38 ef | 5.08±0.03 d | 3.23±0.13 bc | 24.32±0.26 c | 20.00±0.24 e |
| C2 | 29.62±0.26 e | 13.13±0.46 g | 5.06±0.05 d | 3.05±0.16 c | 21.61±0.36 d | 17.27±0.11 g |
| C3 | 26.82±0.57 f | 13.87±0.25 fg | 4.98±0.13 d | 3.24±0.12 bc | 17.50±0.21 f | 15.80±0.23 h |
| 养分含量 Nutrient content | 碱解氮 Alkaline N content | 速效磷 Available P content | 速效钾 Available K content |
|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部氮Shoot N content | 0.947** | - | - |
| 根系氮Root N content | 0.948** | - | - |
| 地上部磷Shoot P content | - | 0.858** | - |
| 根系磷Root P content | - | 0.903** | - |
| 地上部钾Shoot K content | - | - | 0.856** |
| 根系钾Root K content | - | - | 0.791** |
表6 基质速效养分与水稻植株内养分含量的相关性分析
Table 6 Correlation of nutrient contents between seedling raising substrate and rice seedlings.
| 养分含量 Nutrient content | 碱解氮 Alkaline N content | 速效磷 Available P content | 速效钾 Available K content |
|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部氮Shoot N content | 0.947** | - | - |
| 根系氮Root N content | 0.948** | - | - |
| 地上部磷Shoot P content | - | 0.858** | - |
| 根系磷Root P content | - | 0.903** | - |
| 地上部钾Shoot K content | - | - | 0.856** |
| 根系钾Root K content | - | - | 0.791** |
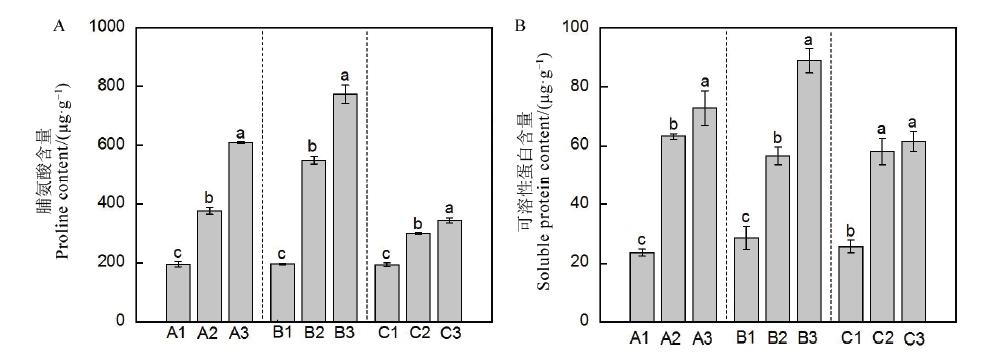
图1 不同温度处理后水稻植株脯氨酸含量(A)和可溶性蛋白含量(B)柱上不同字母表示处理间在P<0.05水平上差异显著。
Fig. 1. Proline content (A) and soluble protein contents (B) in rice under different temperature treatments.Different letters above the columns indicate significant difference at P<0.05.
| 处理 Treatment | 超氧化物歧化酶 SOD/(U·g-1) | 过氧化物酶 POD/(U·g-1) | 过氧化氢酶 CAT/(nmol·min-1g-1) | 谷胱甘肽转移酶 GST/(nmol·min-1g-1) | 丙二醛 MDA/(nmol·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 874.81±15.74 b | 25 658.80±560.06 g | 71.43±1.61 g | 1 685.03±12.29 b | 17.63±0.71 de |
| A2 | 951.64±8.78 a | 30 529.72±677.72 f | 241.67±9.35 e | 1 658.03±45.42 b | 18.50±0.26 cde |
| A3 | 951.64±10.51 a | 46 423.71±343.76 c | 443.59±16.32 b | 1 842.49±27.30 a | 21.42±0.48 b |
| B1 | 870.96±20.39 b | 34 879.49±412.25 e | 96.63±2.74 g | 1 020.68±40.80 d | 17.42±0.51 e |
| B2 | 972.06±7.44 a | 39 903.96±436.82 d | 389.94±6.45 c | 1 396.50±76.34 c | 17.56±0.52 de |
| B3 | 951.08±25.08 a | 67 467.43±754.67 a | 608.51±13.69 a | 1 404.21±24.02 c | 19.14±0.20 cd |
| C1 | 870.88±18.74 b | 28 890.89±426.78 f | 75.65±1.05 g | 1 408.21±52.31 c | 17.53±0.68 e |
| C2 | 855.95±19.74 b | 40 492.02±786.14 d | 200.78±11.55 f | 1 445.14±6.09 c | 19.38±0.62 c |
| C3 | 897.51±22.83 b | 57 541.67±594.53 b | 291.15±15.03 d | 1 411.59±12.33 c | 24.06±0.77 a |
表7 不同温度处理后水稻体内抗氧化酶活性
Table 7 Activities of anti-oxidase in rice under different temperature treatments.
| 处理 Treatment | 超氧化物歧化酶 SOD/(U·g-1) | 过氧化物酶 POD/(U·g-1) | 过氧化氢酶 CAT/(nmol·min-1g-1) | 谷胱甘肽转移酶 GST/(nmol·min-1g-1) | 丙二醛 MDA/(nmol·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 874.81±15.74 b | 25 658.80±560.06 g | 71.43±1.61 g | 1 685.03±12.29 b | 17.63±0.71 de |
| A2 | 951.64±8.78 a | 30 529.72±677.72 f | 241.67±9.35 e | 1 658.03±45.42 b | 18.50±0.26 cde |
| A3 | 951.64±10.51 a | 46 423.71±343.76 c | 443.59±16.32 b | 1 842.49±27.30 a | 21.42±0.48 b |
| B1 | 870.96±20.39 b | 34 879.49±412.25 e | 96.63±2.74 g | 1 020.68±40.80 d | 17.42±0.51 e |
| B2 | 972.06±7.44 a | 39 903.96±436.82 d | 389.94±6.45 c | 1 396.50±76.34 c | 17.56±0.52 de |
| B3 | 951.08±25.08 a | 67 467.43±754.67 a | 608.51±13.69 a | 1 404.21±24.02 c | 19.14±0.20 cd |
| C1 | 870.88±18.74 b | 28 890.89±426.78 f | 75.65±1.05 g | 1 408.21±52.31 c | 17.53±0.68 e |
| C2 | 855.95±19.74 b | 40 492.02±786.14 d | 200.78±11.55 f | 1 445.14±6.09 c | 19.38±0.62 c |
| C3 | 897.51±22.83 b | 57 541.67±594.53 b | 291.15±15.03 d | 1 411.59±12.33 c | 24.06±0.77 a |
| [1] | Sasaki T, Burr B. International rice genome sequencing project: The effort to completely sequence the rice genome[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2000, 3(2): 138-141. |
| [2] | 万春光. 不同引发处理对水稻苗期耐冷性及老化水稻种子萌发的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江大学, 2011. |
| Wan C G. Effects of different initiation treatments on cold tolerance and germination of aged rice seeds in seedling stage[D]. Harbin: Heilongjiang University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 程式华. 2019年中国水稻产业发展报告[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2019: 147. |
| Chen S H. China Rice Industry Development Report in 2019[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2019: 147. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 王一帆, 赵海岩. 北方粳稻高产新技术[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2006: 1-10. |
| Wang Y F, Zhao H Y. New Technology for High Yield of japonica Rice in North China[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2006: 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Cruz R, Duarte I, Cabreira C. Inheritance of rice cold tolerance at the seedling stage[J]. Scientia Agricola, 2010, 67(6): 669-674. |
| [6] | 赵利辉, 刘友良. 冷胁迫对水稻幼苗根系液泡膜质子泵的伤害及钙的调节作用[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2000, 23(3): 5-8. |
| Zhao L H, Liu Y L. Injury of chilling stress to vacuolar proton pumps in roots of rice seedlings and Ca2+ regulation[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2000, 23(3): 5-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 郭确, 潘瑞炽. ABA对水稻幼苗抗冷性的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 1984, 10(4): 295-303. |
| Guo Q, Pan R C. Effects of ABA on cold resistance of rice seedlings[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 1984, 10(4): 295-303. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 吴旺嫔, 周伟江, 唐才宝, 刘坤, 曾红丽, 王悦. 2, 4- 表油菜素内酯对低温胁迫下水稻种子萌发及生理特性的影响[J]. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(13): 4427-4434. |
| Wu W P, Zhou W J, Tang C B, Liu K, Zeng H L, Wang Y. Effects of exogenous 2, 4-epibrassinolide on germination and physiological characteristics of rice seeds under chilling stress[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(13): 4427-4434. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 饶玉春, 杨窑龙, 黄李超, 潘建伟, 马伯军, 钱前, 曾大力. 水稻耐冷胁迫的研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2013, 11(3): 443-450. |
| Rao Y C, Yang Y L, Huang L C, Pan J W, Ma B J, Qian Q, Zeng D L. Research progress on cold stress in rice[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2013, 11(3): 443-450. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Liu K M, Wang L, Xu Y Y, Chen N, Ma Q B, Li F, Chong K. Overexpression of OsCOIN, a putative cold inducible zinc finger protein, increased tolerance to chilling, salt and drought, and enhanced proline level in rice[J]. Planta, 2007, 226: 1007-1016. |
| [11] | 文中华, 刘喜雨, 孟军, 刘遵奇, 史国宏. 生物炭和腐熟秸秆组配基质对水稻幼苗生长的影响[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2020, 51(1): 10-17. |
| Wen Z H, Liu X Y, Meng J, Liu Z Q, Shi G H. Research on biochar and rotten straw-based matrix on the growth of rice seedlings[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2020, 51(1): 10-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 戚秀秀, 魏畅, 刘晓丹, 张林利, 姜瑛, 张登晓. 根际促生菌应用于基质对水稻幼苗生长的影响[J]. 土壤, 2020, 52(5): 1025-1032. |
| Qi X X, Wei C, Liu X D, Zhang L L, Jiang Y, Zhang D X. Effects of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria added in seedling substrate on rice growth[J]. Soils, 2020, 52(5): 1025-1032. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 王德伟. 工厂化大棚水稻育苗不同基质对比[J]. 农技服务, 2019, 36(7): 23-24. |
| Wang D W. Comparison of different substrates of rice seedling in factory greenhouse[J]. Agricultural Extension Service, 2019, 36(7): 23-24. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 钱银飞, 张洪程, 钱宗华, 刘艳阳, 李杰, 郭振华, 陈烨, 张强. 我国水稻机插秧发展问题的探讨[J]. 农机化研究, 2009, 31(10): 1-5. |
| Qian Y F, Zhang H C, Qian Z H, Liu Y Y, Li J, Guo Z H, Chen Y, Zhang Q. Discussion on development of mechanical-transplanting rice in China[J]. Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2009, 31(10): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 徐安平. 新常态下中国农业机械化发展问题探讨[J]. 北京农业, 2015(20): 130-131. |
| Xu A P. Discussion on the development of agricultural mechanization in China under the new normal conditions[J]. Beijing Agricultural, 2015(20): 130-131. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 丁桂珍, 王显, 李亚伟. 姜堰市水稻基质育秧存在的问题及对策[J]. 中国稻米, 2013, 19(6): 96-97. |
| Ding G Z, Wang X, Li Y W. Problems and countermeasures of rice matric seedling raising in Jiangyan City[J]. China Rice, 2013, 19(6): 96-97. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 张楠, 孙彬, 于洪久, 钟鹏, 郭炜, 刘杰. 不同育秧基质对寒地水稻秧苗素质的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2018, 46(1): 39-41. |
| Zhang N, Sun B, Yu H J, Zhong P, Guo Y W, Liu J. Influence of different raising substrate on quality of rice seedling in cold region[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science, 2018, 46(1): 39-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 郭世荣. 无土栽培学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2003. |
| Guo S R. Soilless Culture[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2003. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 南京: 河海大学出版社, 2000. |
| Lu R K. Methods of Soil Agricultural Chemical Analysis[M]. Nanjing: Hehai University Press, 2000. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 林育炯, 张均华, 胡继杰, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 禹盛苗, 金千瑜. 不同类型基质对机插水稻秧苗生理特征及产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016(8): 18-26. |
| Lin Y J, Zhang J H, Hu J J, Zhu L F, Cao X C, Yu S M, Jin Q Y. Effects of different seedling substrates on physiological characters and grain yield of mechanized-transplanted rice[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 2016(8): 18-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | Stoscheck C M. Quantitation of protein[J]. Methods Enzymology, 1990, 182: 50-68. |
| [22] | Bates L S, Waldren R P, Teare I D. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies[J]. Plant and Soil, 1973, 39(1): 205-207. |
| [23] | Wang H H, Hou J J, Li Y, Zhang Y Y, Huang J J, Liang W H. Nitric oxide-mediated cytosolic glucose-6 -phosphate dehydrogenase is involved in aluminum toxicity of soybean under high aluminum concentration[J]. Plant and Soil, 2017, 416(1-2): 39-52. |
| [24] | Beauchamp C, Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase: Improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 1971, 44(1): 276-287. |
| [25] | Dhindsa R S, Plumbdhindsa P, Thorpe T A. Leaf senescence: Correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 1981, 32(126): 93-101. |
| [26] | Chen J, Wang W H, Wu F H, You C Y, Liu T W, Dong X J, He J X, Zheng H L. Hydrogen sulfide alleviates aluminum toxicity in barley seedlings[J]. Plant and Soil, 2013, 362(1-2): 301-318. |
| [27] | Chen J, Duan R X, Hu W J, Zhang N N, Lin X Y, Zhang J H, Zheng H L. Unravelling calcium-alleviated aluminium toxicity in Arabidopsis thaliana: Insights into regulatory mechanisms using proteomics[J]. Journal of Proteomics, 2019, 199: 15-30. |
| [28] | Ma Y, Dai X Y, Xu Y Y, Luo W, Zheng X M, Zeng D, Pan Y J, Lin X L, Liu H H, Zhang D J, Xiao J, Guo X Y, Xu S J, Niu Y D, Jin J B, Zhang H, Xu X, Li L G, Wang W, Qian Q, Ge S, Chong K. COLD1 confers chilling tolerance in rice[J]. Cell, 2015, 6(160): 1209-1221. |
| [29] | Tian Y, Zhang H W, Pan X W, Chen X L, Zhang Z J, Lu X Y, Huang R F. Overexpression of ethylene response factor TERF2 confers cold tolerance in rice seedlings[J]. Transgenic Research, 2011, 20(4): 857-866. |
| [30] | 周跃华, 聂艳丽, 赵永红, 李永梅, 何飞飞. 国内外固体基质研究概况[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2005(4): 46-49. |
| Zhou Y H, Nie Y L, Zhao Y H, Li Y M, He F F. Research on solid substrate in the whole world[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2005(4): 46-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 田曦. 几种有机物料堆肥的腐熟度评价及复配基质的筛选[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2012. |
| Tian X. Study on evaluating the rotten degree of several organic decomposing matter and choosing the complex medium [D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 仲海洲. 利用废弃生物质开发水稻育秧基质及其应用效果研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013. |
| Zhong H Z. Study on utilization of biomass waste to develop rice seedling substrate[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | Bahuguna R N, Jagadish K S V. Temperature regulation of plant phenological development[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2015, 111: 83-90. |
| [34] | Farrell T C, Fox K M, Williams R L, Fukai S. Genotypic variation for cold tolerance during reproductive development in rice: Screening with cold air and cold water[J]. Field Crops Research, 2006, 98(2-3): 178-194. |
| [35] | Shimono H, Hasegawa T, Fujimura S, Iwama K. Responses of leaf photosynthesis and plant water status in rice to low water temperature at different growth stages[J]. Field Crops Research, 2004, 89(1): 70-83. |
| [36] | 曲辉辉, 姜丽霞, 朱海霞, 闫平, 宫丽娟, 吕佳佳, 王晾晾, 纪仰慧. 孕穗期低温对黑龙江省主栽水稻品种空壳率的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2011, 30(3): 489-493. |
| Qu H H, Jiang L X, Zhu H X, Yan P, Gong L J, Lü J J, Wang L L, Ji Y H. Effects of low temperature at booting stage on the percentage of unfilled grains of major rice varieties in Heilongjiang Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2011, 30(3): 489-493. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 王国莉, 郭振飞. 低温对水稻不同耐冷品种幼苗光合速率和叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(4): 381-383. |
| Wang G L, Guo Z F. Effects of chilling stress on photosynthetic rate and the parameters of chlorophyll fluorescence in two rice varieties differing in sensitivity[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2005, 19(4): 381-383. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 丁彦. 水稻材料WDl的抗寒研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2006. |
| Ding Y. Research on cold tolerance in WD1 of rice[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 王淼. 不同基因型水稻苗期耐冷性与硅的关系[D]. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江大学, 2012. |
| Wang M. Relationship between cold tolerance and silicon in rice seedling with different genotypes[D]. Harbin: Heilongjiang University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | Igarashi Y, Yoshiba Y, Sanada Y, Yamaguchi-shinozaki K, Wada K, Shinozaki K. Characterization of the gene for Δ1 -pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase and correlation between the expression of the gene and salt tolerance in Oryza sativa L[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 1997, 33(5): 857-865. |
| [41] | 宋广树, 孙忠富, 王夏, 刘妍. 不同生育时期低温处理对水稻品质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(18): 174-179. |
| Song G S, Sun Z F, Wang X, Liu Y. Effect of low temperature on rice quality in different growth period[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(18): 174-179. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 陈思思. 苗期和拔节期低温胁迫对扬麦16产量和生理特性的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2010. |
| Chen S S. Effects of low temperature at seedling stage and jointing stage on grain yield and physiological parameters in wheat Yangmai 16[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | Apel K, Hirt H. Reactive oxygen species: Metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2004, 55: 373-399. |
| [44] | 祝涛, 杨美英. 低温处理对不同品种水稻苗期保护酶活性的影响[J]. 吉林农业, 2010(7): 95. |
| Zhu T, Yang M Y. Effect of low temperature treatment on protective enzyme activity of different rice varieties at seedling stage[J]. Agriculture of Jilin, 2010(7): 95. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||