
中国水稻科学 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (5): 487-494.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.200808
收稿日期:2020-08-11
修回日期:2021-01-01
出版日期:2021-09-10
发布日期:2021-09-10
通讯作者:
王国栋
基金资助:
Yuxiang LI1, Hairong LIN1, Qian LIANG1, Guodong WANG2,*( )
)
Received:2020-08-11
Revised:2021-01-01
Online:2021-09-10
Published:2021-09-10
Contact:
Guodong WANG
摘要:
【目的】探讨多巴胺(Dopamine,DA)引发对盐胁迫下水稻种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响。【方法】 以新疆自育水稻品种新稻17号为研究对象,分别用0(纯水)、0.1、0.5、1、1.5 mg/L的DA溶液(分别用S0、S0.1、S0.5、S1、S1.5表示)引发种子,采用浓度为100 mmol/L的NaCl溶液模拟盐胁迫,以未引发无盐胁迫处理作为对照1(CK),未引发有盐胁迫处理作为对照2(S-CK),研究多巴胺引发对盐胁迫下水稻种子萌发、幼苗生长及生理特性的影响。【结果】与CK相比,盐胁迫下(S-CK)水稻种子的萌发受到明显抑制且萌发速率降低,幼苗长势弱。引发处理不同程度缓解了盐胁迫对种子萌发的抑制,提高发芽率(13.3%~25.8%)和发芽速率,促进幼苗生长;可溶性糖和脯氨酸含量增加(16.4%~51.8%和6.5%~31.2%),超氧化物歧化酶 (28.9%~72.7%)、过氧化物酶 (15.0%~60.1%)和过氧化氢酶 (35.1%~133.0%)活性显著提高,丙二醛 (7.1%~26.8%)含量明显降低。表明对种子进行引发处理,通过增强盐胁迫下水稻种子活力,提高幼苗渗透调节物质含量和抗氧化酶活性,降低丙二醛含量,增强了水稻种子及幼苗的耐盐性,其中1.0 mg/L的多巴胺溶液(S1)引发效果优于水引发(S0)。【结论】对于新疆自育水稻品种新稻17而言,1.0 mg/L多巴胺溶液引发能够有效提高其对盐胁迫的抵抗能力,促进种子萌发和幼苗生长。
李玉祥, 林海荣, 梁倩, 王国栋. 多巴胺引发对盐胁迫下水稻种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 487-494.
Yuxiang LI, Hairong LIN, Qian LIANG, Guodong WANG. Effects of Dopamine Priming on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Rice Under Salt Stress[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(5): 487-494.
| 处理 Treatment | 发芽势 Germination potential/% | 发芽率 Germination rate/% | 发芽指数 Germination index | 活力指数 Activity index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 53.3±1.1 a | 96.7±2.3 a | 30.9±0.3 a | 11.5±0.1 a |
| S-CK | 16.7±0.5 d | 75.0±3.3 d | 18.1±0.3 d | 5.7±0.1 c |
| S0 | 23.3±0.4 c | 86.7±2.2 c | 21.8±0.7 cd | 7.5±0.1 b |
| S0.1 | 23.3±0.3 c | 90.0±1.2 b | 22.2±0.7 bc | 7.1±0.5 bc |
| S0.5 | 30.0±0.5 b | 93.3±2.8 ab | 24.6±0.3 bc | 9.4±0.6 ab |
| S1 | 33.3±0.3 b | 94.3±5.5 ab | 26.6±0.4 ab | 10.0±0.6 a |
| S1.5 | 26.7±0.2 bc | 85.0±4.3 c | 22.8±0.6 bc | 7.7±0.4 b |
表1 多巴胺引发对NaCl胁迫下稻种萌发的影响
Table 1 Effect of dopamine priming on rice seeds germination under NaCl stress.
| 处理 Treatment | 发芽势 Germination potential/% | 发芽率 Germination rate/% | 发芽指数 Germination index | 活力指数 Activity index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 53.3±1.1 a | 96.7±2.3 a | 30.9±0.3 a | 11.5±0.1 a |
| S-CK | 16.7±0.5 d | 75.0±3.3 d | 18.1±0.3 d | 5.7±0.1 c |
| S0 | 23.3±0.4 c | 86.7±2.2 c | 21.8±0.7 cd | 7.5±0.1 b |
| S0.1 | 23.3±0.3 c | 90.0±1.2 b | 22.2±0.7 bc | 7.1±0.5 bc |
| S0.5 | 30.0±0.5 b | 93.3±2.8 ab | 24.6±0.3 bc | 9.4±0.6 ab |
| S1 | 33.3±0.3 b | 94.3±5.5 ab | 26.6±0.4 ab | 10.0±0.6 a |
| S1.5 | 26.7±0.2 bc | 85.0±4.3 c | 22.8±0.6 bc | 7.7±0.4 b |
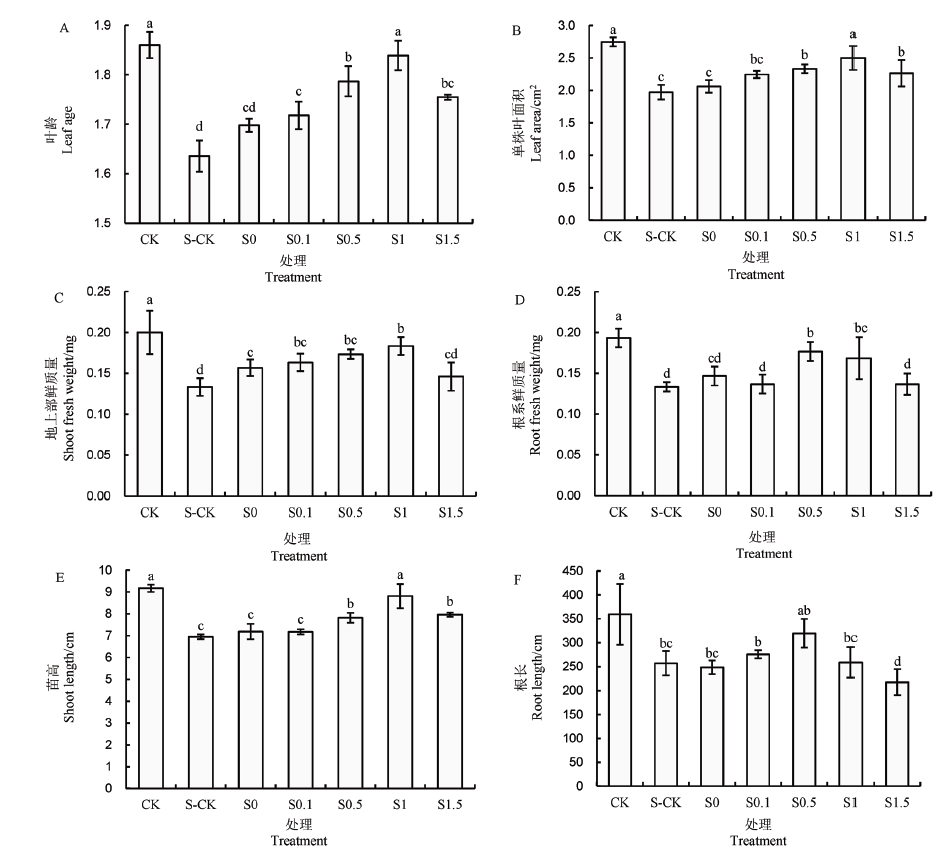
图2 多巴胺引发对NaCl胁迫下水稻幼苗生长的影响柱上相同小写字母表示在5%水平上差异不显著(n=3,最小显著差数法)。下同。
Fig. 2. Effect of dopamine priming on growth of rice seedlings under NaCl stress.Common lowercase letters above the bars mean no significant difference at P<0.05 (n =3, LSD). The same as below.
| 处理 Treatment | 根数 Root number | 根投影面积 Root projected area/cm2 | 根表面积 Root surface area/cm2 | 根系直径 Roots diameter/mm | 根系体积 Roots volume/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 4.83±0.33 a | 8.98±1.03 a | 28.20±3.22 a | 0.25±0.02 b | 0.18±0.02 a |
| S-CK | 4.39±0.10 ab | 6.91±0.61 bc | 21.70±1.93 abc | 0.27±0.02 ab | 0.15±0.01 ab |
| S0 | 4.44±0.11 ab | 6.39±0.52 bc | 20.09±1.62 abc | 0.26±0.01 ab | 0.13±0.01 ab |
| S0.1 | 4.12±0.25 b | 6.12±0.53 bc | 19.23±1.66 abc | 0.26±0.01 ab | 0.14±0.02 ab |
| S0.5 | 4.56±0.13 ab | 7.60±0.65 ab | 23.87±2.05 ab | 0.28±0.02 a | 0.16±0.01 ab |
| S1 | 4.67±0.44 a | 6.58±0.78 bc | 20.67±2.45 bc | 0.25±0.01 b | 0.13±0.03 ab |
| S1.5 | 4.56±0.15 ab | 6.27±0.85 c | 19.71±2.66 c | 0.25±0.03 b | 0.11±0.02 b |
表2 多巴胺引发对NaCl胁迫下水稻根系形态特征的影响
Table 2 .Effects of dopamine priming on rice root morphological characters under NaCl stress.
| 处理 Treatment | 根数 Root number | 根投影面积 Root projected area/cm2 | 根表面积 Root surface area/cm2 | 根系直径 Roots diameter/mm | 根系体积 Roots volume/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 4.83±0.33 a | 8.98±1.03 a | 28.20±3.22 a | 0.25±0.02 b | 0.18±0.02 a |
| S-CK | 4.39±0.10 ab | 6.91±0.61 bc | 21.70±1.93 abc | 0.27±0.02 ab | 0.15±0.01 ab |
| S0 | 4.44±0.11 ab | 6.39±0.52 bc | 20.09±1.62 abc | 0.26±0.01 ab | 0.13±0.01 ab |
| S0.1 | 4.12±0.25 b | 6.12±0.53 bc | 19.23±1.66 abc | 0.26±0.01 ab | 0.14±0.02 ab |
| S0.5 | 4.56±0.13 ab | 7.60±0.65 ab | 23.87±2.05 ab | 0.28±0.02 a | 0.16±0.01 ab |
| S1 | 4.67±0.44 a | 6.58±0.78 bc | 20.67±2.45 bc | 0.25±0.01 b | 0.13±0.03 ab |
| S1.5 | 4.56±0.15 ab | 6.27±0.85 c | 19.71±2.66 c | 0.25±0.03 b | 0.11±0.02 b |
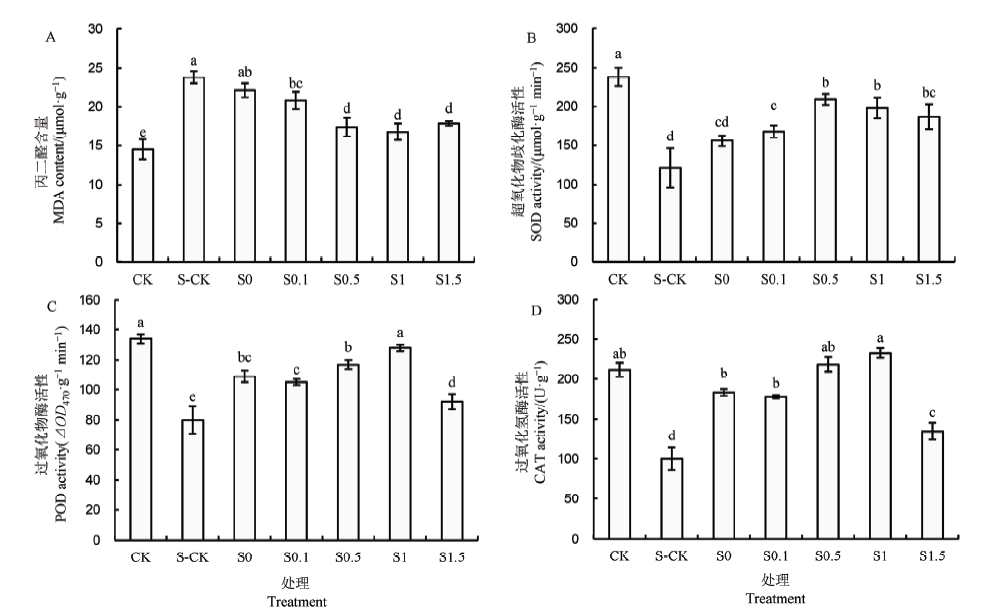
图4 多巴胺引发对NaCl胁迫下水稻叶片MDA含量及抗氧化酶活性的影响
Fig. 4. Effect of DA priming on MDA content and antioxidant enzyme activities of rice seedling leaves under NaCl stress.
| 参数 Parameter | 可溶性糖含量 SS content | 脯氨酸含量 Proline content | MDA含量 MDA content | SOD活性 SOD activity | POD活性 POD activity | CAT活性 CAT activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶龄Leaf age | 0.189 | 0.046 | -0.967** | 0.951** | 0.897** | 0.822** |
| 单株叶面积 Leaf area per plant | -0.060 | -0.177 | -0.967** | 0.954** | 0.853* | 0.711 |
| 地上部鲜质量 Shoot fresh weight | -0.011 | 0.036 | -0.833* | 0.880** | 0.978** | 0.889** |
| 根系鲜质量 Root fresh weight | -0.015 | -0.081 | -0.818* | 0.863* | 0.888** | 0.791* |
| 苗高 Shoot length | 0.009 | -0.188 | -0.934** | 0.872* | 0.795* | 0.645 |
| 根长 Root length | -0.329 | -0.267 | -0.552 | 0.654 | 0.666 | 0.547 |
| 根数Root number | -0.070 | -0.329 | 0.765* | 0.705 | 0.599 | 0.436 |
| 根投影面积Root projected area | -0.469 | -0.548 | -0.604 | 0.649 | 0.559 | 0.359 |
| 根表面积Root surface area | -0.469 | -0.548 | -0.604 | 0.650 | 0.559 | 0.359 |
| 根直径Root diameter | 0.217 | 0.282 | 0.413 | -0.318 | -0.302 | -0.126 |
| 根体积Root volume | -0.625 | -0.575 | -0.349 | 0.418 | 0.412 | 0.213 |
表3 水稻幼苗长势与生理指标的相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation between growing state and physiological indexes of rice seedlings.
| 参数 Parameter | 可溶性糖含量 SS content | 脯氨酸含量 Proline content | MDA含量 MDA content | SOD活性 SOD activity | POD活性 POD activity | CAT活性 CAT activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶龄Leaf age | 0.189 | 0.046 | -0.967** | 0.951** | 0.897** | 0.822** |
| 单株叶面积 Leaf area per plant | -0.060 | -0.177 | -0.967** | 0.954** | 0.853* | 0.711 |
| 地上部鲜质量 Shoot fresh weight | -0.011 | 0.036 | -0.833* | 0.880** | 0.978** | 0.889** |
| 根系鲜质量 Root fresh weight | -0.015 | -0.081 | -0.818* | 0.863* | 0.888** | 0.791* |
| 苗高 Shoot length | 0.009 | -0.188 | -0.934** | 0.872* | 0.795* | 0.645 |
| 根长 Root length | -0.329 | -0.267 | -0.552 | 0.654 | 0.666 | 0.547 |
| 根数Root number | -0.070 | -0.329 | 0.765* | 0.705 | 0.599 | 0.436 |
| 根投影面积Root projected area | -0.469 | -0.548 | -0.604 | 0.649 | 0.559 | 0.359 |
| 根表面积Root surface area | -0.469 | -0.548 | -0.604 | 0.650 | 0.559 | 0.359 |
| 根直径Root diameter | 0.217 | 0.282 | 0.413 | -0.318 | -0.302 | -0.126 |
| 根体积Root volume | -0.625 | -0.575 | -0.349 | 0.418 | 0.412 | 0.213 |
| [1] | Heydecker W. Germination of an Idea: The priming of seeds[R]. School of Agriculture, University of Nottingham, 1974: 50-67. |
| [2] | Heydecker W, Coolbear P. Seed treatments for improved performance survey and attempted prognosis[J]. Seed Science and Technology, 1977(5): 353-425. |
| [3] | Bailly C, Benamar A, Corbineau F, Come D. Antioxidant systems in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L. ) seed as affected by priming[J]. Seed Science Research, 2000 (10): 35-42. |
| [4] | Jisha K C, Vijayakumari K, Puthur J T. Seed priming for abiotic stress tolerance: An overview[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2013, 35: 1381-1396. |
| [5] | Ehab A I. Seed priming to alleviate salinity stress in germinating seeds[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2016, 192: 38-46. |
| [6] | Sivritepe H O, Dourado A M. The effete of priming treatments on the viability and accumulation of chromosomal damage in aged pea seeds[J]. Annals of Botany, 1995, 75: 165-171. |
| [7] | Siri B, Vichitphan K, Kaewnaree P, Vichitphan S, Klanrit P. Improvement of quality, membrane integrity and antioxidant systems in sweet pepper(Capsicum annuum Linn.) seeds affected by osmopriming[J]. Australian Journal of Crop Science, 2013(7): 2068-2073. |
| [8] | 赵玥, 辛霞, 王宗礼, 卢新雄. 种子引发机理研究进展及牧草种子引发研究展望[J]. 中国草地学报, 2012, 34(3): 102-108. |
| Zhao Y, Xin X, Wang Z L, Lu X X. Research progress and prospects in the mechanism of seed priming[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2012, 34(3): 102-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 周小梅, 赵运林, 文彤, 李小湘. 亚精胺引发对水分胁迫下水稻种子活力及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2013, 27(2): 247-252. |
| Zhou X M, Zhao Y L, Wen T, Li X X. Effects of spd priming on seed vigor and seedling physiological characteristics of rice under water stress[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 27(2): 247-252. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Harris D, Joshi A, Khan P A, Gothkar P, Sodhi P S. On-farm seed priming in semi-arid agriculture- development and evaluation in maize, rice and chickpea in India using participatory methods[J]. Experimental Agriculture, 1999, 35(1): 15-29. |
| [11] | Imran M, Mahmood A, Romheld V, Neumann G. Nutrient seed priming improves seedling development of maize exposed to low root zone temperatures during early growth[J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 2013, 49: 141-148. |
| [12] | Shafiq F, Batool H, Raza S H. Effect of Potassium nitrate seed priming on allometry of drought-stressed cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)[J]. Journal of Crop Science and Biotechnology, 2015, 18(3): 195-204. |
| [13] | 阮松林, 薛庆中, 王清华. 种子引发对杂交水稻幼苗耐盐性的生理效应[J]. 中国农业科学, 2003, 36(4): 463-468. |
| Ruan S L, Xue Q Z, Wang Q H. Physiological effects of seed priming on salt-tolerance of seedlings in hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2003, 36(4): 463-468. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | Salama K, Mansour M M F. Choline priming-induced plasma membrane lipid alterations contributed to improved wheat salt tolerance[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2015, 37: 1-7. |
| [15] | Yan K, Xu H L, Cao W, Chen X B. Salt priming improved salt tolerance in sweet sorghum by enhancing osmotic resistance and reducing root Na+ uptake[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2015, 203(37): 1-10 |
| [16] | Rehman H U, Kamran M, Basra S M A, Afzal I, Farooq M. Influence of seed priming on performance and water productivity of direct seeded rice in alternating wetting and drying[J]. Rice Science, 2015, 22(4): 189-196. |
| [17] | Ruttanaruangboworn A, Chanprasert W, Tobunluepop P, Onwimol D. Effect of seed priming with different concentrations of potassium nitrate on the pattern of seed imbibition and germination of rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2017, 16(3): 605-613. |
| [18] | Farooq M, Basre S M A, Tabassum R, Afzal I. Enhancing the performance for direct seeded fine rice by seed priming[J]. Plant Production Science, 2006, 9(4): 446-456. |
| [19] | Goswami A, Banerjee R, Sangh A R. Drought resistance in rice seedlings conferred by seed priming[J]. Protoplasma, 2013, 250: 1115-1129. |
| [20] | Zheng M M, Tao Y, Hussain S, Jiang Q W, Peng S B, Huang J L, Cui K H, Nie L X. Seed priming in dry direct-seeded rice: Consequences for emergence, seedling growth and associated metabolic events under drought stress[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2016, 78: 167-178. |
| [21] | Sarkar R K. Seed priming improves agronomic trait performance under flooded and non-flooded conditions in rice with SUB1 QTL[J]. Rice Science, 2012 (4): 286-294. |
| [22] | 万春光. 不同引发处理对水稻苗期耐冷性及老化水稻种子萌发的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江大学, 2011 |
| Wang C G. Effects of different priming treatments on cold tolerance of rice seedlings and germination of aged rice seeds[D]. Haerbin: Heilongjiang University, 2011. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | Khaliq A, Aslam F, Hussain A M S, Geng M, Wahid A, Rehman H. Seed priming with selenium: Consequences for emergence, seedling growth, and biochemical attributes of rice[J]. Biological Trace Element Research, 2015, 166: 236-244. |
| [24] | Rehman A U, Farooq M, Cheema Z A, Wahid A. Seed priming with boron improves growth and yield of fine grain aromatic rice[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2012, 68: 189-201. |
| [25] | Wei L X, Lv B S, Xiao W, Li M M, Wang H Y, Ma H Y, Yang R F, Yang Z Z, Piao Z H, Wang J H, Lou C J, Jiang Z, Liang W. Priming of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings with abscisic acid enhances seedling survival, plant growth, and grain yield in saline-alkaline paddy fields[J]. Field Crops Research, 2017, 203: 86-93. |
| [26] | 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. |
| Li H S. Principles and Technology of Plant Physiology and Biochemistry[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000. | |
| [27] | 王学奎. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. |
| Wang X K. The Principle and Technology of Plant Physiology and Biochemistry Experiment[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. | |
| [28] | 王素平, 李娟, 郭世荣, 胡晓辉, 李璟, 汪天. NaCl 胁迫对黄瓜幼苗植株生长和光合特性的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2006, 26(3): 455-461. |
| Wand S P, Li J, Guo, S R, Hu X H, Li J, Wang T. Effects of NaCl stress on growth and photosynthetic characteristics of cucumber (Cucumber sativus L.) seedlings[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-occidentalia Sinica, 2006, 26(3): 455-461. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Bohnert H J, Shen B. Transformation and compatible solutes[J]. Scientia Hortculturaae, 1999, 78: 237-260. |
| [30] | 刘慧霞, 王彦荣. 水引发对紫花苜蓿种子萌发及其生理活动的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2008, 17(4): 78-84. |
| Liu H X, Wang Y R. Effect of hydro-priming on seed germination and physiological activities in medicago sativa[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2008, 17(4): 78-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | Ellis R H, Butcher P D. The effect of priming and‘natural’difference in quality amongst onion seed lots on the response the rate of germination to temperature and the identification of the characteristics under genotypic control[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 1988, 39: 935-950. |
| [32] | Sami F, Yusuf M, Faizan M, Faraz A, Hayat S. Role of sugars under abiotic stress[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2016, 109(12): 54-61. |
| [33] | 孙园园, 孙永健, 王明田, 李旭毅, 郭翔, 胡蓉, 马均. 种子引发对水分胁迫下水稻发芽及幼苗生理性状的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2010, 36(11): 1931-1940. |
| Sun Y Y, Sun Y J, Wang M T, Li X Y, Guo X, Hu R, Ma J. Effects of seed priming on germination and seedling growth of rice under water stress[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2010, 36(11): 1931-1940. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 郑光华, 燕义唐, 张庆昌. 大豆种子吸胀冷害与“修补”过程的探讨[J]. 中国科学: B辑, 1988(4): 395-402. |
| Zheng G H, Tan Y T, Zhang Q C. Discussion on Soybean Seed Imbibition and Chilling Damage and "Mending" Process[J]. Science in China: Series B, 1988(4): 395-402. (in Chinese) | |
| [35] | Bailly C, Benamar A, Corbineau F. Antioxidant systems in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) seeds as affected by priming[J]. Seed Science Research, 2000, 10: 35-42. |
| [36] | Chen K, Arora R. Priming memory invokes seed stress-tolerance[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2013, 94: 33-45. |
| [37] | Bailly C. Active oxygen species and antioxidants in seed biology[J]. Seed Science Research, 2004, 14: 93-107. |
| [38] | 李洁, 徐军桂, 林程, 关亚静, 胡晋. 引发对低温胁迫下不同类型玉米种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 2016, 52(2): 157-166. |
| LI J, Xu J G, Lin C, Guan Y J, Hu J. Effect of priming on germination and physiological characteristics of different types of corn seeds under low-temperature stress[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2016, 52(2): 157-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||