
中国水稻科学 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 11-18.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.0503
周天顺1,2, 余东1,3, 刘玲1,2, 欧阳宁1,2, 袁贵龙1,3, 段美娟4,*( ), 袁定阳1,2,3,*(
), 袁定阳1,2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-05-03
修回日期:2020-05-27
出版日期:2021-01-10
发布日期:2021-01-10
通讯作者:
段美娟,袁定阳
基金资助:
Tianshun ZHOU1,2, Dong YU1,3, Ling LIU1,2, Ning OUYANG1,2, Guilong YUAN1,3, Meijuan DUAN4,*( ), Dingyang YUAN1,2,3,*(
), Dingyang YUAN1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2020-05-03
Revised:2020-05-27
Online:2021-01-10
Published:2021-01-10
Contact:
Meijuan DUAN, Dingyang YUAN
摘要: 目的 为鉴定水稻AFP1在非生物胁迫响应中的作用,创制非生物胁迫抗性的水稻新材料。方法 以优异籼稻恢复系华占为转化受体,利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制afp1突变体,并对afp1突变体的耐逆性进行初步鉴定。结果 AFP1靶点1和靶点2的编辑效率分别为66.67%和75.00%。所有突变株系中,突变类型仅有插入和缺失突变,90%突变株系的突变长度为小片段突变(<5bp)。获得了6种无转基因成分的afp1纯合突变体。正常条件下,afp1突变体株高和结实率降低,有效分蘖增加,穗长显著升高,单株产量在-4.06%和11.75%之间变化。和野生型相比,afp1突变体的ABA敏感性和叶片水分散失率降低,耐干旱、热和渗透胁迫能力提高。结论 编辑AFP1基因可提高水稻多种非生物胁迫抗性。
周天顺, 余东, 刘玲, 欧阳宁, 袁贵龙, 段美娟, 袁定阳. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术编辑AFP1基因提高水稻耐逆性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 11-18.
Tianshun ZHOU, Dong YU, Ling LIU, Ning OUYANG, Guilong YUAN, Meijuan DUAN, Dingyang YUAN. CRISPR/Cas9-mediatedEditing of AFP1Improves Rice Stress Tolerance[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(1): 11-18.
| 名称 Name | 正向引物 Forward primer (5' - 3') | 反向引物 Reverse primer (5' - 3') |
|---|---|---|
| AFP1-T1 | ggcaCTGTGCGGCATCGGCAAGGG | aaacCCCTTGCCGATGCCGCACAG |
| AFP1-T2 | gccgCTGTCGCTCGGCGGCCGGTT | aaacAACCGGCCGCCGAGCGACAG |
| AFP1-J | GGCGGATTACTCGCTCGGTCAGTTCT | TGGAGAGAAGCGATGACGCACCTTCAAG |
| Hpt | GACAGCGTCTCCGACCTGAT | CATCGCCTCGCTCCAGTCAAT |
| Cas9 | CTCTTCCTTCCAAGTACGTG | GAAAGGTCGATACGAGTCTC |
| OT1-1 | CAAACGCCAAGGCGGGAATGCAG | GTGCGCCGCGGCGCAGCTGTTG |
| OT1-2 | GATCCATGTGGGCCCCACATGTC | CGCTGGTCCATCCTCTCGATC |
| OT1-3 | GAAGTTCTTGCCGATGACCTCG | GACGAGTGAAGAGGAGGAGAC |
| OT2-1 | CAATCAGTGTAAGCTTGCTCTAG | GGTGAAGTCACACAATTACTG |
| OT2-2 | CTTCTTGCTTGGAGGAGCATG | CTCAGCTGCAACCTGTTAACG |
| OT2-3 | CAAGGAGCGCCGTGTACCTCG | GTAGTCCAGCTTCAGCTTCAC |
表1 本研究所用引物
Table 1 Primers used in this study.
| 名称 Name | 正向引物 Forward primer (5' - 3') | 反向引物 Reverse primer (5' - 3') |
|---|---|---|
| AFP1-T1 | ggcaCTGTGCGGCATCGGCAAGGG | aaacCCCTTGCCGATGCCGCACAG |
| AFP1-T2 | gccgCTGTCGCTCGGCGGCCGGTT | aaacAACCGGCCGCCGAGCGACAG |
| AFP1-J | GGCGGATTACTCGCTCGGTCAGTTCT | TGGAGAGAAGCGATGACGCACCTTCAAG |
| Hpt | GACAGCGTCTCCGACCTGAT | CATCGCCTCGCTCCAGTCAAT |
| Cas9 | CTCTTCCTTCCAAGTACGTG | GAAAGGTCGATACGAGTCTC |
| OT1-1 | CAAACGCCAAGGCGGGAATGCAG | GTGCGCCGCGGCGCAGCTGTTG |
| OT1-2 | GATCCATGTGGGCCCCACATGTC | CGCTGGTCCATCCTCTCGATC |
| OT1-3 | GAAGTTCTTGCCGATGACCTCG | GACGAGTGAAGAGGAGGAGAC |
| OT2-1 | CAATCAGTGTAAGCTTGCTCTAG | GGTGAAGTCACACAATTACTG |
| OT2-2 | CTTCTTGCTTGGAGGAGCATG | CTCAGCTGCAACCTGTTAACG |
| OT2-3 | CAAGGAGCGCCGTGTACCTCG | GTAGTCCAGCTTCAGCTTCAC |
| 靶位点 Target | 阳性植株Positive plants | 突变率 Mutant ratio/% | 突变基因型比率Mutant genotype ratio/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纯合突变率 Homozygote ratio | 杂合突变率Heterozygote ratio | 双等位突变率 Bi-allele ratio | 嵌合突变率 Chimera ratio | ||||
| 靶点1 Target 1 | 12 | 66.7 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 75.0 | 0.0 | |
| 靶点2 Target 2 | 12 | 75.0 | 22.2 | 22.2 | 44.4 | 11.1 | |
表2 T0代突变体突变基因型比率
Table 2 Mutant genotype ratios of T0 mutations.
| 靶位点 Target | 阳性植株Positive plants | 突变率 Mutant ratio/% | 突变基因型比率Mutant genotype ratio/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纯合突变率 Homozygote ratio | 杂合突变率Heterozygote ratio | 双等位突变率 Bi-allele ratio | 嵌合突变率 Chimera ratio | ||||
| 靶点1 Target 1 | 12 | 66.7 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 75.0 | 0.0 | |
| 靶点2 Target 2 | 12 | 75.0 | 22.2 | 22.2 | 44.4 | 11.1 | |
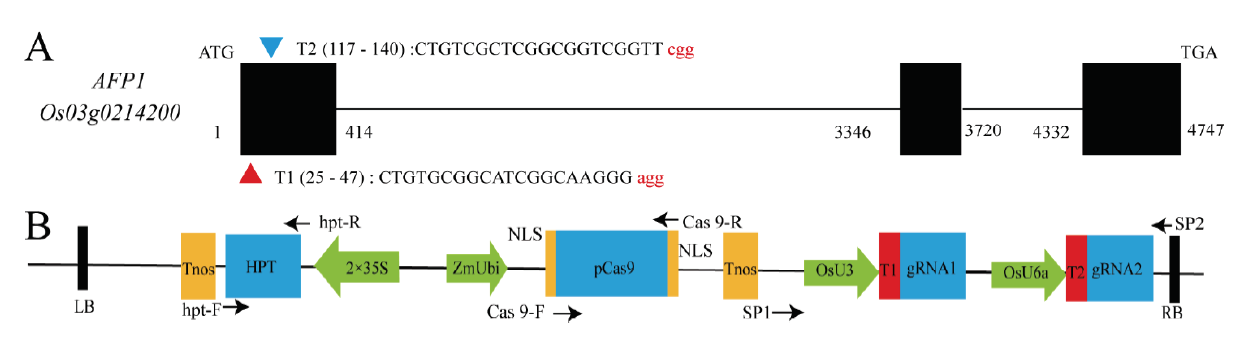
图1 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术定向突变OsAFP1基因 A-敲除靶点设计; B-CRISPR/Cas9敲除载体,箭头代表扩增引物。
Fig. 1. Directed mutation of OsAFP1 using CRISPR/Cas9 technology. A, Design of mutated sites; B, Schematic diagram of CRISPR/Cas9 construction; Arrows represent amplification primers.
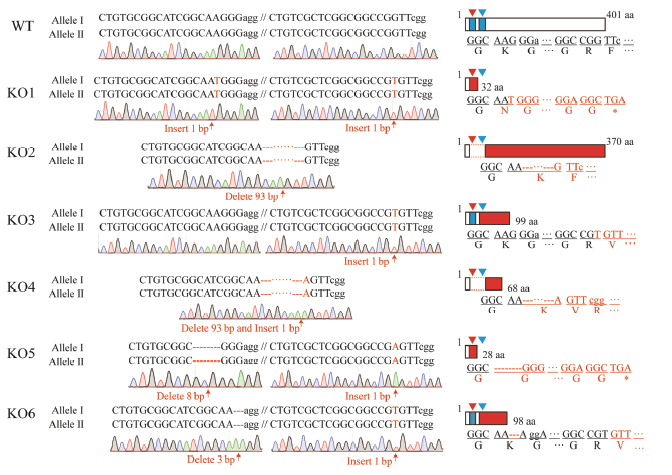
图3 T2代纯合敲除突变体的突变类型 长方形代表推测蛋白;红色区域为突变蛋白序列,下方为相应蛋白序列;倒三角形和蓝色区域均表示靶位点。WT-野生型;KO1~KO6代表6个不含外源基因的纯合突变株系。
Fig. 3. Mutated types of T2 homozygous mutants. Rectangles are putative mutated proteins; Red shades indicate mutated protein regions and letters below are putative protein sequences;Inverted triangle and blue area represent target sites.WT, Wild type; KO1-KO6 indicate six homozygous mutants without exogenous genes.
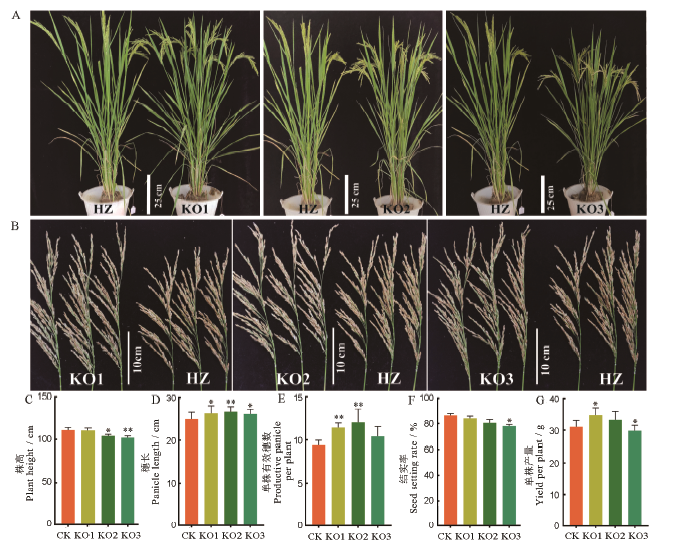
图 4 afp1敲除突变体和野生型的表型比较 A-整体株型;B-穗部性状;C-株高;D-穗长;E-有效分蘖数;F-结实率;G-单株产量;均值±标准误,n=3;*和**分别表示突变体与野生型的差异达0.05和0.01显著水平(t检验)。HZ代表野生型华占,KO代表敲除突变体。
Fig. 4. Phenotypic comparisons of afp1 knockdown mutants and the wildtype. A, Plant architectures; B, Panicle traits; C, Plant height; D, Panicle length; E, Effecttivepanicle per plant; F, Seed setting rate; G, Yield per plant;Mean±SE, n=3; * and ** represent significant difference between the mutant and the wild type at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels by t-test, respectively.HZ, Wild type Huazhan; KO, afp1knockdown mutants.
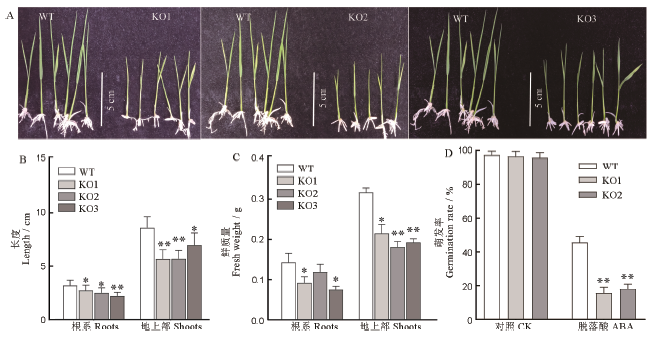
图5 野生型和突变体ABA敏感性分析 A-3μmol/L ABA处理后的幼苗; B-ABA处理后幼苗的株高和根长; C-ABA处理后幼苗根和地上部分的鲜质量; D-3μmol/L ABA处理后种子的萌发率;均值±标准误,n=3;*和**表示在0.05和0.01水平上的差异(t检验)。
Fig. 5. ABA sensitivity of WT and mutants. A, Phenotype of seedlingsafter 3μmol/L ABA treatment; B, Length of root and shootafter 3μmol/L ABA treatment; C, Fresh weight of seedlings after 3μmol/L ABA treatment; D, Germination rate of seeds after 3μmol/L ABA treatment;Mean±SE, n=3; * and ** represent significant difference at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels by t-test, respectively.
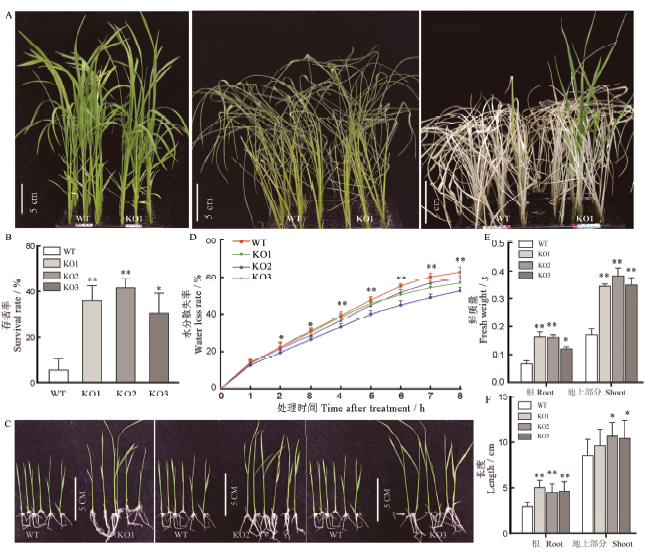
图6 耐旱性和耐渗透性鉴定 A-干旱处理后幼苗表型;B-干旱处理后存活率;C-渗透胁迫处理后幼苗表型;D-水稻离体叶片水分散失率;E-渗透胁迫处理后幼苗鲜重;F-渗透胁迫处理后幼苗株高和根长;均值±标准误,n=3;*和**分别表示在0.05和0.01水平上的差异(t检验)。
Fig. 6. Identification of drought and osmotic stress tolerances. A, Phenotype of seedlings after drought treatment; B, Survival rate of seedlings after drought treatment; C, Phenotype of seedlings after osmotic stress treatment;D, Water loss rate of rice detached leaves;E, Fresh weight of seedlings after osmotic stress treatment; F, Length of root and shoot after osmotic stress treatment;Mean±SE, n=3; * and ** represent significant difference at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels by t-test, respectively.
| [1] | Akram R, Fahad S, Masood N, Fahad S, Masood N, Rasool A, Ijaz M, Ihsan M Z, Maqbool M M, Ahmad S, Hussain S, Ahmed M, Kaleem S, Sultana S R, Mubeen M, Saud S, Kamran M, Nasim W.Advances in Rice Research for Abiotic Stress Tolerance[M]. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing, 2019: 69-85. |
| [2] | Boyer J S.Plant productivity and environment[J]. Science, 1982, 218: 443-448. |
| [3] | Pauwels L, Barbero G F, Geerinck J, Tilleman S, Grunewald W, Pérez A C, Chico J M, Bossche R V, Sewell J, Gil E, García-Casado G, Witters E, Inzé D, Long J A, De Jaeger G, Solano R, Goossens A.NINJA connects the co-repressor TOPLESS to jasmonatesignaling[J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7289): 788-791. |
| [4] | Huang M D, Wu W L.Overexpression of TMAC2, a novel negative regulator of abscisic acid and salinity responses, has pleiotropic effects in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2007, 63(4): 557-569. |
| [5] | Chang G X, Wang C T, Kong X X, Chen Q, Yang Y P, Hu X Y.AFP2 as the novel regulator breaks high-temperature-induced seeds secondary dormancy through ABI5 and SOM in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2018, 501(1): 232-238. |
| [6] | Chang G X, Yang W J, Zhang Q L, Huang J L, Yang Y P, Hu X Y. ABI5-BINDING PROTEIN2coordinates CONSTANS to delay flowering by recruiting the transcriptional corepressor TPR2[J]. Plant Physiology, 2019, 179(2): 477-490. |
| [7] | 安敏敏, 杨立明, 罗玉明. AFP2基因调控拟南芥茉莉酸合成与开花时间的分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2019, 17(10): 3259-3266. |
| An M M, Y L M, Luo Y M. Analysis of the role of AFP2gene in regulating jasmonic acid biosynthesis and flowering time of Arabidopsis[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2019, 17(10): 3259-3266. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Tang N, Ma S Q, Zong W, Yang N, Lv Y, Yan C, Guo Z, Li J, Li X, Xiang Y, Song H Z, Xiao J H, Li X H, Xiong L Z.MODD mediates deactivation and degradation of OsbZIP46 to negatively regulate ABA signaling and drought resistance in rice[J]. The Plant Cell, 2016, 28(9): 2161-2177. |
| [9] | Ma S, Tang N, Li X, Xie Y J, Xiang D H, Fu J, Shen J Q, Yang J, Tu H F, Li X H, Hu H H, Xiong L Z.Reversible histone H2BMonoubiquitinationfine-tunes abscisic acid signaling and drought response in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 12(2): 263-277. |
| [10] | Liu X, Baird W V.Identification of a novel gene, HaABRC5, from Helianthus annuus (Asteraceae) that is upregulated in response to drought, salinity, and abscisic acid[J]. American Journal of Botany, 2004, 91(2): 184-191. |
| [11] | Wu J, Seng S S, Carianopol C, Sui J J, Yang Q Y, Zhang F Q, Jiang H R, He J N, Yi M F.Cloning and characterization of a novel Gladiolus hybridusAFP family gene (GhAFP-like) related to corm dormancy[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2016, 471(1): 198-204. |
| [12] | Miao C B, Xiao L H, Hua K, Zou C S, Zhao Y, Bressan R A, Zhu J K.Mutations in a subfamily of abscisic acid receptor genes promote rice growth and productivity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2018, 115(23): 6058-6063. |
| [13] | Lou D J, Wang H P, Liang G, Yu D Q.OsSAPK2 confers abscisic acid sensitivity and tolerance to drought stress in rice[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 993. |
| [14] | Cui Y T, Hu X M, Liang G H, Feng A H, Wang F M, Ruan S, Dong G J, Shen L, Zhang B, Chen D D,Zhu L,Hu J,Lin Y J,Guo L B,Matsuoka M,Qian Q. Production of novel beneficial alleles of a rice yield-related QTL by CRISPR/Cas9[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18(10): 1987-1989. |
| [15] | Zhou T S, Yu D, Dong H, Sun Z Z, Tan Y N, Sun X W, Sheng X B, Duan M J, Yuan D Y.Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profile of NINJA and AFP Genes in Rice[J]. International Journal of Advances in Biology, 2020, 23(1): 171-182. |
| [16] | Ma X L, Zhang Q Y, Zhu Q L, Liu W, Chen Y, Qiu R, Wang B, Yang Z F, Li H Y, Lin Y R, Xie Y Y, Shen R X, Chen S F, Wang Z, Chen Y L, Guo J X, Chen L T, Zhao X C, Dong Z C, Liu Y G.A robust CRISPR/Cas9 system for convenient, high-efficiency multiplex genome editing in monocot and dicot plants[J]. Molecular Plant, 2015, 8(8): 1274-1284. |
| [17] | Liang G, Zhang H M, Lou D J, Yu D Q.Selection of highly efficient sgRNAs for CRISPR/Cas9-based plant genome editing[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 21451. |
| [18] | Wang Y P, Cheng X, Shan Q W, Zhang Y, Liu J X, Gao C X.Simultaneous editing of three homoeoalleles in hexaploid bread wheat confers heritable resistance to powdery mildew[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2014, 32(9): 947-951. |
| [19] | Li J Y, Sun Y W, Du J L, Zhao Y D, Xia L Q.Generation of targeted point mutations in rice by a modified CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10(3): 526-529. |
| [20] | 王影, 李相敢, 邱丽娟. CRISPR/Cas9基因组定点编辑中脱靶现象的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(4): 521-541. |
| Wang Y, Li X G, Qiu L J.Research progress in off-target in CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(4): 521-541. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | Garcia M E, Lynch T, Peeters J, Snowden C, Finkelstein R.A small plant-specific protein family of ABI five binding proteins (AFPs) regulates stress response in germinating Arabidopsis seeds and seedlings[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2008, 67(6): 643-658. |
| [22] | Lopez-Molina L, Mongrand S, Kinoshita N, Chua N H.AFP is a novel negative regulator of ABA signaling that promotes ABI5 protein degradation[J]. Genes & Development, 2003, 17(3): 410-418. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||