
中国水稻科学 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 259-268.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.01204
邓雪梅1,#, 胡鹏1,#, 王月影1, 文艺1, 谭义青1, 伍豪2, 吴凯雄1, 王俊格1, 侯琳琳1, 朱黎欣1, 朱丽1, 陈光1, 曾大力1, 张光恒1, 郭龙彪1, 高振宇1, 任德勇1, 钱前1,*( ), 胡江1,*(
), 胡江1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-06-10
修回日期:2020-08-06
出版日期:2021-05-10
发布日期:2021-05-10
通讯作者:
钱前,胡江
作者简介:#共同第一作者;
基金资助:
Xuemei DENG1,#, Peng HU1,#, Yueying WANG1, Yi WEN1, Yiqing TAN1, Hao WU2, Kaixiong WU1, Junge WANG1, Linlin HOU1, Lixin ZHU1, Li ZHU1, Guang CHEN1, Dali ZENG1, Guangheng ZHANG1, Longbiao GUO1, Zhenyu GAO1, Deyong REN1, Qian QIAN1,*( ), Jiang HU1,*(
), Jiang HU1,*( )
)
Received:2020-06-10
Revised:2020-08-06
Online:2021-05-10
Published:2021-05-10
Contact:
Qian QIAN, Jiang HU
About author:#These authors contributed equally to this work;
摘要:
【目的】水稻粒形是影响水稻产量和决定稻米外观品质的主要性状之一。筛选和鉴定新的粒形突变材料,可为研究水稻籽粒发育的调控机制奠定基础。【方法】粳稻品种中花11经1%的EMS处理,在诱变群体中获得一份窄粒突变体gw4(grain width on chromosome 4);分析粒形和其他主要农艺性状,在扫描电镜下观察颖壳细胞变化;利用突变体与籼稻品种台中本地1号配组的F2分离群体,选择隐性个体完成基因的精细定位;开展生物信息和测序分析,确定定位区间的候选基因;采用RT-PCR分析该基因在根、茎、叶、鞘、穗等组织中的表达模式及其他粒形相关基因的表达水平。【结果】与野生型相比,除了表现窄粒外,gw4的粒长、千粒重、每穗粒数、一次枝梗数和二次枝梗数等显著下降;扫描电镜发现gw4的颖壳内外表皮细胞均小于野生型;遗传分析表明该窄粒表型受一对单隐性核基因控制;通过开发的新标记最终将该基因定位在第4染色体BS6与EX49两个标记之间约31.74 kb的范围内;测序结果发现在LOC_Os04g01590基因编码区发生了一个由G至A的单碱基突变,导致原来编码的甘氨酸变成了天冬氨酸;qRT-PCR结果表明,LOC_Os04g01590主要在幼穗中表达,且在突变体中表达显著下降。【结论】GW4主要调控水稻粒宽的发育,预测LOC_Os04g01590为其候选基因。这为进一步丰富粒形的遗传调控网络打下了基础。
邓雪梅, 胡鹏, 王月影, 文艺, 谭义青, 伍豪, 吴凯雄, 王俊格, 侯琳琳, 朱黎欣, 朱丽, 陈光, 曾大力, 张光恒, 郭龙彪, 高振宇, 任德勇, 钱前, 胡江. 水稻粒宽突变体gw4的鉴定与基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(3): 259-268.
Xuemei DENG, Peng HU, Yueying WANG, Yi WEN, Yiqing TAN, Hao WU, Kaixiong WU, Junge WANG, Linlin HOU, Lixin ZHU, Li ZHU, Guang CHEN, Dali ZENG, Guangheng ZHANG, Longbiao GUO, Zhenyu GAO, Deyong REN, Qian QIAN, Jiang HU. Identification and Fine Mapping of a Grain Width Mutant gw4 in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(3): 259-268.
| 分子标记 | 正向引物序列(5'-3') | 反向引物序列(5'-3') | 实验目的 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marker | Forward primer sequence (5'-3') | Reverse primer sequence (5'-3') | Purpose | |
| BS6 | AGTACACATGGGGAGTAGTTGG | GATGGCAATTGAAAAGTGACC | 定位Mapping | |
| BS11 | TGCAGGTACACACACATACCC | GGAAGTAGCATCCATGCAACTA | 定位Mapping | |
| BS15 | TTTGCAGCTGGCTAGCTTA | ACTTCCATAATTACGGGTCCT | 定位Mapping | |
| BS16 | GGCAAATAATTAATAGCATGGTCC | TGGATGATTTCTGTTAGTGGTTCA | 定位Mapping | |
| BS18 | TGGTTACAACGACACAACTGC | TCACTCATACCAACCTTGCG | 定位Mapping | |
| EX49 | GTGCCTCCTTTTCTTGGAGAT | CACAGTCATCTCACTTGCAATC | 定位Mapping | |
| BS19 | ACGTGTCTTGGGGCTGTGTC | TCCCTACACTTATTGCCCCTCT | 测序Sequencing | |
| BS20 | TCCTCATTACATGTCCCCATCC | CCCTATCTGAACGCAAGTGCT | 测序Sequencing | |
| BS21 | GTGGTAGCATGTGCTCTCCCT | AGGGTTGGCAGAGTTGTCAGA | 测序Sequencing | |
| BS22 | TACCATGTTGCACCTGAATACCT | CAACCCTCCTGGTGATTCCC | 测序Sequencing | |
| BS23 | CCAGTTGTTAGGGCTGTGTCTG | AGATTAGGGAGCCAATGCGA | 测序Sequencing | |
| BS24 | GATGCTCTGTTTGGACAGCCT | TGTCGTCAGCATGTTGCCTG | 测序Sequencing | |
| BS25 | ACCAACCAACCCCTTGAGTCT | TGGAAATCGGAGAGATTATACGTAC | 测序Sequencing | |
| Histon | GGTCAACTTGTTGATTCCCCTCT | AACCGCAAAATCCAAAGAACG | RT-PCR | |
| RT-GW2 | ATCGTGGACAAGGGCACCTGC | CCGTCCCGCTCGCGAGGCATG | RT-PCR | |
| RT-GW5 | AATCCAGACGGCATTCAGAG | CTTCACCAGCGCCTTGAG | RT-PCR | |
| RT-GW7 | CCCTAGCATCGACACCAAGT | TCGAGGACAGAGATGGGACT | RT-PCR | |
| RT-GW8 | ACAGCCAGATCCCATGAACT | GCGTGTAGTATGGGCTCTCC | RT-PCR | |
| RT-GS2 | TGCGTCCCTTCTTTGATGAGT | ACAGTTGGGTGCCTGAGAATG | RT-PCR | |
| RT-GS3 | CGGAAGAACTCCTGATCCATTC | CACTTGCTCTGCACAAACAGC | RT-PCR | |
| RT-GS5 | GTTCTCGGTACTGCGTGGAAG | ACTCCACAAACCTCCCAGCA | RT-PCR | |
| RT-GL6 | TCCAAACCAGATGTTGGTGA | GCCGTCGACTACATCTCGTT | RT-PCR | |
| RT-LOC_Os04g01590 | TTGGTGATGTCCCCATACAA | ACCAAATCTCTTCCCCTGCT | RT-PCR | |
表1 用于基因定位和定量分析的分子标记 Table 1. Markers developed for mapping of gw4 and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT- PCR) analysis.
Table 1. Markers developed for mapping of gw4 and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT- PCR) analysis.
| 分子标记 | 正向引物序列(5'-3') | 反向引物序列(5'-3') | 实验目的 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marker | Forward primer sequence (5'-3') | Reverse primer sequence (5'-3') | Purpose | |
| BS6 | AGTACACATGGGGAGTAGTTGG | GATGGCAATTGAAAAGTGACC | 定位Mapping | |
| BS11 | TGCAGGTACACACACATACCC | GGAAGTAGCATCCATGCAACTA | 定位Mapping | |
| BS15 | TTTGCAGCTGGCTAGCTTA | ACTTCCATAATTACGGGTCCT | 定位Mapping | |
| BS16 | GGCAAATAATTAATAGCATGGTCC | TGGATGATTTCTGTTAGTGGTTCA | 定位Mapping | |
| BS18 | TGGTTACAACGACACAACTGC | TCACTCATACCAACCTTGCG | 定位Mapping | |
| EX49 | GTGCCTCCTTTTCTTGGAGAT | CACAGTCATCTCACTTGCAATC | 定位Mapping | |
| BS19 | ACGTGTCTTGGGGCTGTGTC | TCCCTACACTTATTGCCCCTCT | 测序Sequencing | |
| BS20 | TCCTCATTACATGTCCCCATCC | CCCTATCTGAACGCAAGTGCT | 测序Sequencing | |
| BS21 | GTGGTAGCATGTGCTCTCCCT | AGGGTTGGCAGAGTTGTCAGA | 测序Sequencing | |
| BS22 | TACCATGTTGCACCTGAATACCT | CAACCCTCCTGGTGATTCCC | 测序Sequencing | |
| BS23 | CCAGTTGTTAGGGCTGTGTCTG | AGATTAGGGAGCCAATGCGA | 测序Sequencing | |
| BS24 | GATGCTCTGTTTGGACAGCCT | TGTCGTCAGCATGTTGCCTG | 测序Sequencing | |
| BS25 | ACCAACCAACCCCTTGAGTCT | TGGAAATCGGAGAGATTATACGTAC | 测序Sequencing | |
| Histon | GGTCAACTTGTTGATTCCCCTCT | AACCGCAAAATCCAAAGAACG | RT-PCR | |
| RT-GW2 | ATCGTGGACAAGGGCACCTGC | CCGTCCCGCTCGCGAGGCATG | RT-PCR | |
| RT-GW5 | AATCCAGACGGCATTCAGAG | CTTCACCAGCGCCTTGAG | RT-PCR | |
| RT-GW7 | CCCTAGCATCGACACCAAGT | TCGAGGACAGAGATGGGACT | RT-PCR | |
| RT-GW8 | ACAGCCAGATCCCATGAACT | GCGTGTAGTATGGGCTCTCC | RT-PCR | |
| RT-GS2 | TGCGTCCCTTCTTTGATGAGT | ACAGTTGGGTGCCTGAGAATG | RT-PCR | |
| RT-GS3 | CGGAAGAACTCCTGATCCATTC | CACTTGCTCTGCACAAACAGC | RT-PCR | |
| RT-GS5 | GTTCTCGGTACTGCGTGGAAG | ACTCCACAAACCTCCCAGCA | RT-PCR | |
| RT-GL6 | TCCAAACCAGATGTTGGTGA | GCCGTCGACTACATCTCGTT | RT-PCR | |
| RT-LOC_Os04g01590 | TTGGTGATGTCCCCATACAA | ACCAAATCTCTTCCCCTGCT | RT-PCR | |
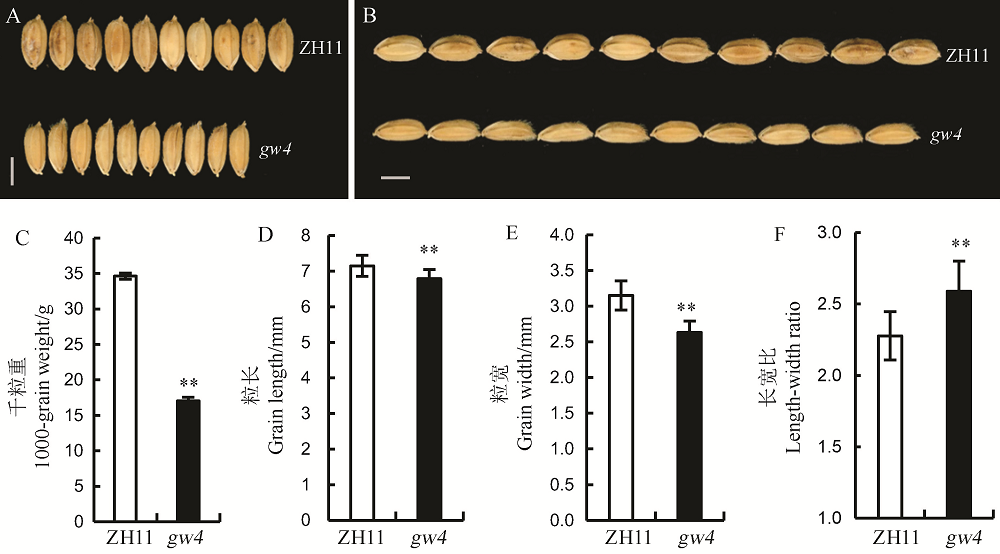
图1 野生型中花11与突变体gw4的粒形 A, B-野生型和gw4成熟籽粒,标尺=0.25 cm;C~F图中误差值代表标准误(n=13),**表示0.01显著水平。ZH11-中花11。
Fig. 1. Grains size of the wild type Zhonghua 11(ZH11) and its mutant gw4. A and B, Mature grain of WT and gw4, bar= 0.25 cm; C-F, Bars represent standard error(n=13). **indicate significant difference between WT and gw4 by t-test(P<0.01). ZH11, Zhonghua 11.
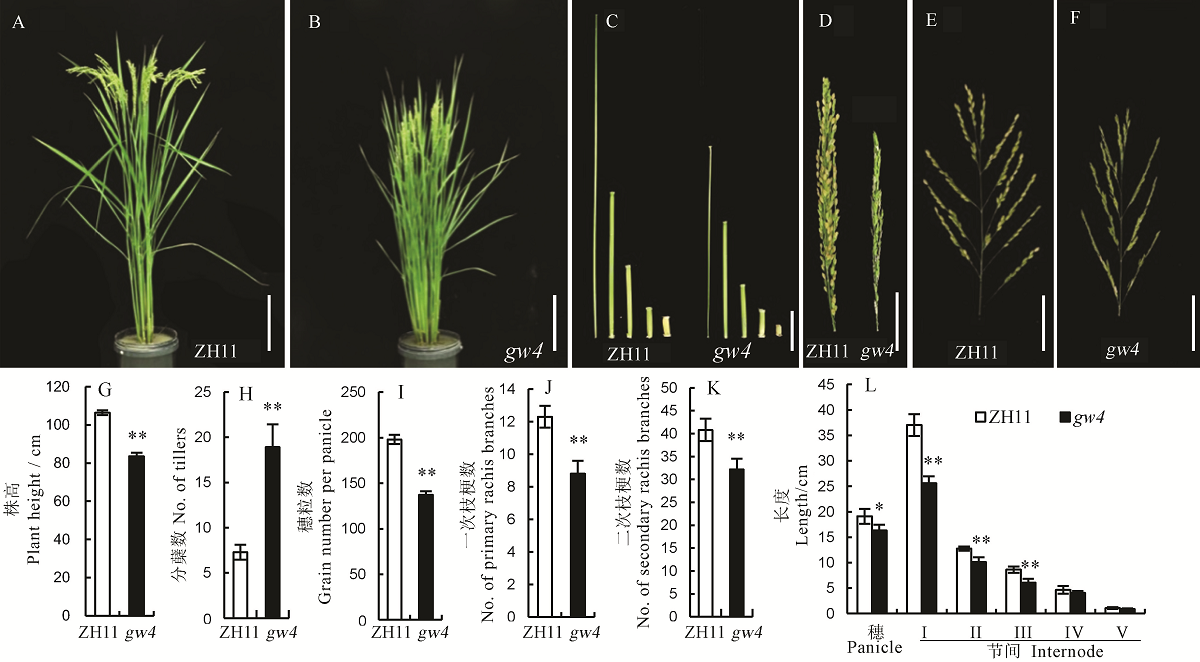
图2 野生型中花11(ZH11)和突变体gw4的表型 A, B-植株表型, 标尺=20 cm;C-茎秆节间,标尺=5 cm;D, E, F-穗,标尺=5 cm。G~L中Bar值代表标准误(n=10),**表示0.01极显著水平,*表示0.05显著差异。
Fig. 2. Phenotype of the wild type Zhonghua 11(ZH11) and its mutant gw4. A and B, Phenotype of Zhonghua 11(ZH11) and gw4, bar=20 cm; C, Internodes, bar=5 cm; D, E and F, Panicles, bar=5 cm; G-L, Bars represent standard error (n=10). ** and * indicate significant difference between WT and gw4 by t-test(P<0.01, P<0.05), respectively.
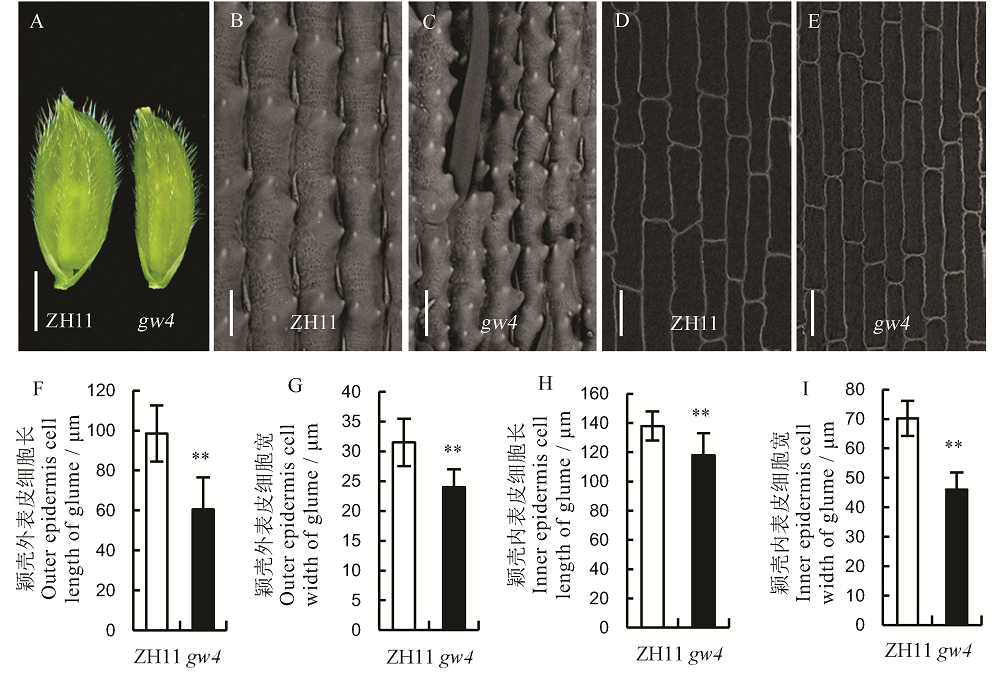
图3 野生型中花11(ZH11)和突变体gw4的颖壳 A-颖壳, 标尺=0.25 cm; B和C-颖壳外表皮, 标尺=50 μm; D和E-颖壳内表皮, 标尺=50 μm; Bar值代表标准误(n=10); **表示0.01显著水平。
Fig. 3. Glumes of the wild type(ZH11) and its mutant gw4. A, Glume, bar=0.25 cm; B and C, Outer epidermis of glume, bar=50 μm; D and E, Inner epidermis of glume; bar=50 μm; Bars represent standard error (n=10). **indicate significant difference between WT and gw4 by t-test(P<0.01).
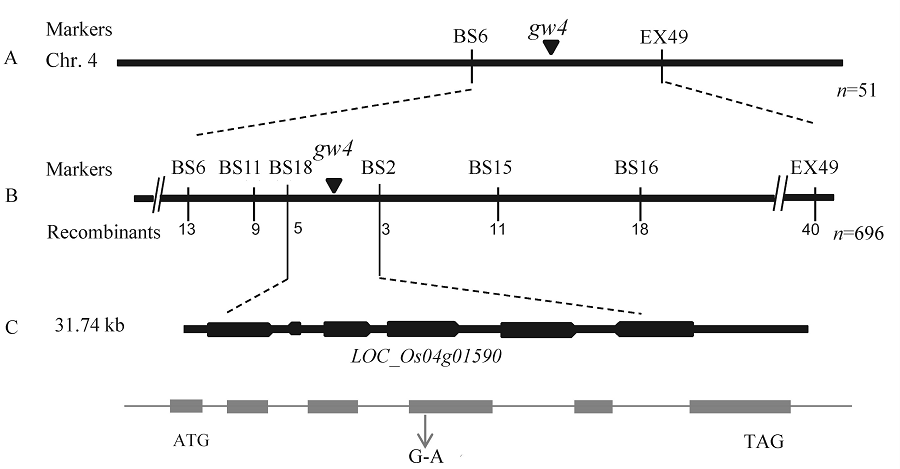
图4 突变体gw4的精细定位 A-gw4初定位在第4染色体;B-gw4精细定位在31.74 kb的范围内;C-定位区间的6个预测基因。
Fig. 4. Fine mapping of gw4. A, gw4 was primarily mapped on chromosome 4; B, gw4 was narrowed to a 31.74 kb genomic region; C, Total six genes was predicted in this region.
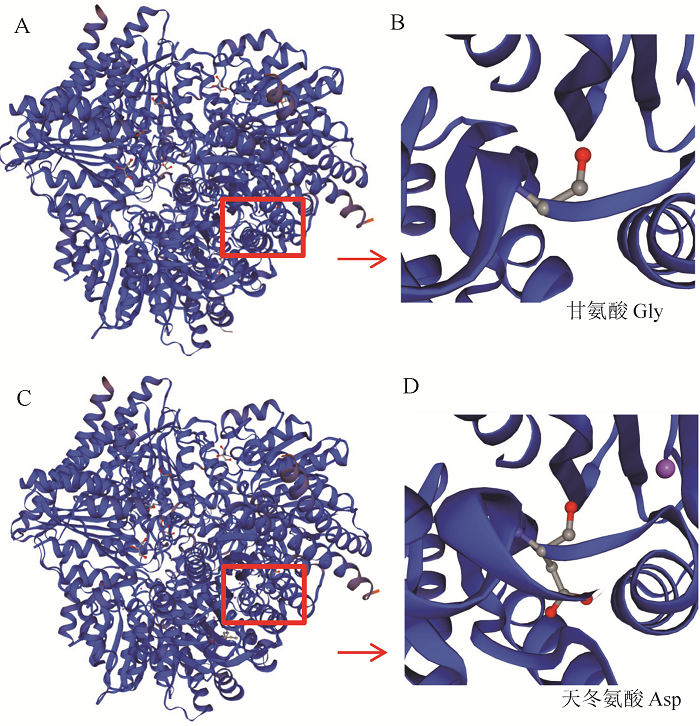
图5 GW4和gw4蛋白的三维结构 A, B-GW4蛋白的三维结构;C, D-gw4蛋白的三维结构;B和D为A和C的放大图;红框表示蛋白折叠差异位置。
Fig. 5. Three-dimensional structures of proteins GW4 and gw4. A and B, Protein domain of GW4; C and D, Protein domain of gw4; B and D, Enlarged size of A and C; The red box indicate the differences in protein folding.
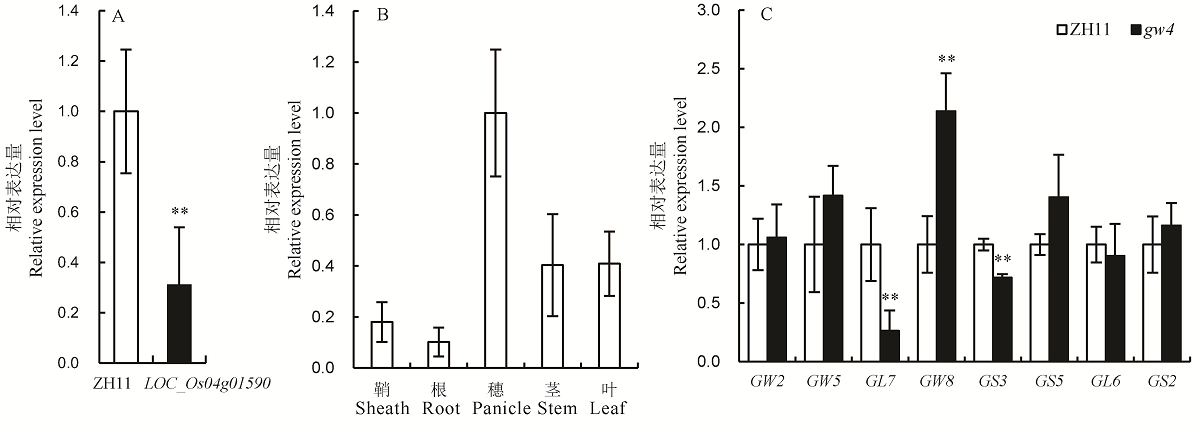
图6 LOC_Os04g01590及粒形相关基因的表达分析 A-LOC_Os04g01590在中花11(ZH11)和gw4中的表达分析;B-LOC_Os04g01590在不同组织中的相对转录水平;C-粒形相关基因的表达分析。将ZH11的穗中的转录水平设置为1.0,Bar值表示3个生物学重复的平均值±SD;**表示0.01极显著水平。
Fig. 6. Expression analysis of LOC_Os04g01590 and grain shape genes. A, Expression analysis of LOC_Os04g01590 in Zhonghua 11(ZH11) and gw4; B, Relative transcript levels of LOC_Os04g01590 in various organs; C, Expression analysis of grain shape genes in the ZH11 and gw4. Set the transcription level in the panicle of ZH11 to 1.0. Bars represent standard deviation (n=3). ** indicates significant difference between ZH11 and gw4 by t-test (P<0.01).
| 基因 Gene | 功能注释 Function annotation |
|---|---|
| LOC_Os04g01560 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein |
| LOC_Os04g01570 | 蔗糖酶/果胶甲基酯酶抑制剂家族蛋白Invertase/Pectin methylesterase inhibitor family protein |
| LOC_Os04g01580 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein |
| LOC_Os04g01590 | 精氨酸酶Arginase |
| LOC_Os04g01600 | 赤藓酸-4-磷酸脱氢酶结构域蛋白Erythroate-4-phosphate dehydrogenase domain protein |
| LOC_Os04g01610 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein |
表2 候选基因分析
Table 2 Predicted genes in fine-mapping region.
| 基因 Gene | 功能注释 Function annotation |
|---|---|
| LOC_Os04g01560 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein |
| LOC_Os04g01570 | 蔗糖酶/果胶甲基酯酶抑制剂家族蛋白Invertase/Pectin methylesterase inhibitor family protein |
| LOC_Os04g01580 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein |
| LOC_Os04g01590 | 精氨酸酶Arginase |
| LOC_Os04g01600 | 赤藓酸-4-磷酸脱氢酶结构域蛋白Erythroate-4-phosphate dehydrogenase domain protein |
| LOC_Os04g01610 | 表达蛋白Expressed protein |
| [1] | Wang Y, Xiong G, Hu J, Jiang L, Yu H, Xu J, Fang Y, Zeng L, Xu E, Xu J, Ye W, Meng X, Liu R, Chen H, Jing Y, Wang Y, Zhu X, Li J, Qian Q.Copy number variation at the GL7 locus contributes to grain size diversity in rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2015, 47(8): 944-948. |
| [2] | 尉鑫, 曾智锋, 杨维丰, 韩婧, 柯善文. 水稻粒形遗传调控研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2019, 47(5): 21-28. |
| Wei X, Zeng Z F, Yang Wei F, Han J, Ke S W.Research progress on genetic regulation of rice grain shape[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(5): 21-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Yan S, Zou G, Li S, Wang H, Liu H, Zhai G, Guo P, Song H, Yan C, Tao Y.Seed size is determined by the combinations of the genes controlling different seed characteristics in rice[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2011, 123: 1173-1181. |
| [4] | Huang K, Wang D, Duan P, Zhang B, Xu R, Li N, Li Y.WIDE AND THICK GRAIN 1, which encodes an otubain-like protease with deubiquitination activity, influences grain size and shape in rice[J]. Plant Journal, 2017, 91(5): 849-860. |
| [5] | Shi C, Ren Y, Liu L, Wang F, Zhang H, Tian P, Pan T, Wang Y, Jing R, Liu T, Wu F, Lin Q, Lei C, Zhang X, Zhu S, Guo X, Wang J, Zhao Z, Wang J, Zhai H, Cheng Z, Wan J.Ubiquitin Specific Protease 15 has an important role in regulating grain width and size in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2019, 180(1): 381-391. |
| [6] | Chen Y, Xu Y, Luo W, Li W, Chen N, Zhang D, Chong K.The F-box protein OsFBK12 targets OsSAMS1 for degradation and affects pleiotropic phenotypes, including leaf senescence, in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2013, 163(4): 1673-1685. |
| [7] | Hu X, Qian Q, Xu T, Zhang Y, Dong G, Gao T, Xie Q, Xue Y.The U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase TUD1 functions with a heterotrimeric Gα subunit to regulate Brassinosteroid-mediated growth in rice[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2013, 9(3): e1003391. |
| [8] | Liu Q, Han R, Wu K, Zhang J, Ye Y, Wang S, Chen J, Pan Y, Li Q, Xu X, Zhou J, Tao D, Wu Y, Fu X.G-protein βγ subunits determine grain size through interaction with MADS-domain transcription factors in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 852. |
| [9] | Zhang D P, Zhou Y, Yin J F, Yan X J, Lin S, Xu W F, Baluška F, Wang Y P, Xia Y J, Liang G H, Liang J S. Rice G-protein subunits qPE9-1 and RGB1 play distinct roles in abscisic acid responses and drought adaptation[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015(20): 6371. |
| [10] | Swain D M, Sahoo R K, Srivastava V K, Tripathy B C, Tuteja R, Tuteja N.Function of heterotrimeric G-protein γ subunit RGG1 in providing salinity stress tolerance in rice by elevating detoxification of ROS[J]. Planta, 2017, 245(2): 367-383. |
| [11] | Yadav D K, Islam S M, Tuteja N.Rice heterotrimeric G-protein gamma subunits (RGG1 and RGG2) are differentially regulated under abiotic stress[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2012, 7(7): 733-740. |
| [12] | Xu R, Duan P, Yu H, Zhou Z, Zhang B, Wang R, Li J, Zhang G, Zhuang S, Lü J, Li N, Chai T, Tian Z, Yao S, Li Y.Control of grain size and weight by the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4-OsMAPK6 signaling pathway in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11(6): 860-873. |
| [13] | Guo T, Chen K, Dong N Q, Shi C L, Ye W W, Gao J P, Shan J X, Lin H X.GRAIN SIZE AND NUMBER1 negatively regulates the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4-OsMPK6 cascade to coordinate the trade-off between grain number per panicle and grain size in rice[J]. Plant Cell, 2018, 30(4): 871-888. |
| [14] | Yi J, Lee Y S, Lee D Y, Cho M H, Jeon J S, An G. OsMPK6 plays a critical role in cell differentiation during early embryogenesis in Oryza sativa[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016(8): 2425-2437. |
| [15] | Xia D, Zhou H, Liu R, Dan W, Li P, Wu B, Chen J, Wang L, Gao G, Zhang Q, He Y.GL3.3, a novel QTL encoding a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase, epistatically interacts with GS3 to produce extra-long grains in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11(5): 754-756. |
| [16] | 梁文化, 赵春芳, 张善磊, 张亚东, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 陈涛, 王才林. 水稻粒型基因GLW7的功能标记开发与鉴定//江苏省遗传学会. 2017年学术研讨会—“技术创新与遗传学发展”论文摘要集[C]. 南京: 江苏省遗传学会, 2017: 1. |
| Liang W H, Zhao C F, Zhang S L, Zhang Y D, Zhu Z, Zhao Q Y, Chen T, Wang C L.Development and identification of functional markers of rice grain type gene GLW7//Jiangsu Society of Genetics. Academic Seminar of Jiangsu Society of Genetics in 2017 Meeting—“Technology Innovation and Genetics Development” Abstracts Collection[C]. Nanjing: Jiangsu Genetics Society, 2017: 1. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | Hu J, Wang Y, Fang Y, Zeng L, Xu J, Yu H, Shi Z, Pan J, Zhang D, Kang S, Zhu L, Dong G, Guo L, Zeng D, Zhang G, Xie L, Xiong G, Li J, Qian Q.A Rare allele of GS2 enhances grain size and grain yield in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2015: 1455-1465. |
| [18] | Wang S, Li S, Liu Q, Wu K, Zhang J, Wang S, Wang Y, Chen X, Zhang Y, Gao C, Wang F, Huang H, Fu X.The OsSPL16-GW7 regulatory module determines grain shape and simultaneously improves rice yield and grain quality[J]. Nature Genetics, 2015, 47(8): 949. |
| [19] | 徐乾坤, 余海平, 夏赛赛, 崔元江, 俞晓琦, 刘贺,曾大力, 胡江, 张强, 高振宇, 张光恒, 朱丽, 沈兰, 郭龙彪, 饶玉春, 钱前, 任德勇. C2H2锌指蛋白LRG1调控水稻小穗的发育[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(9): 753-764. |
| Xu Q K, Yu H P, Xia S S, Cui Y J, Yu X Q, Liu H, Zeng D L, Hu J, Zhang Q, Gao Z Y, Zhang G H, Zhu L, Shen L, Guo L B, Rao Y C, Qian Q, Ren D Y.C2H2 zinc finger protein LRG1 regulates the development of rice spikelets[J]. Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(9): 753-764. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Mori M, Tomita C, Sugimoto K, Hasegawa M, Hayashi N, Dubouzet JG, Ochiai H, Sekimoto H, Hirochika H, Kikuchi S.Isolation and molecular characterization of a Spotted leaf 18 mutant by modified activation-tagging in rice[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2007, 63(6): 847-860. |
| [21] | Yan S, Zou G, Li S, Wang H, Liu H, Zhai G, Guo P, Song H, Yan C, Tao Y.Seed size is determined by the combinations of the genes controlling different seed characteristics in rice[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2011, 123(7): 1173-1181. |
| [22] | Jia S, Xiong Y, Xiao P, Wang X, Yao J.OsNF-YC10, a seed preferentially expressed gene regulates grain width by affecting cell proliferation in rice[J]. Plant Science, 2019, 280: 219-227. |
| [23] | Prasad K, Parameswaran S, Vijayraghavan U.OsMADS1, a rice MADS-box factor, controls differentiation of specific cell types in the lemma and palea and is an early-acting regulator of inner floral organs[J]. Plant Journal, 2010, 43(6): 915-928. |
| [24] | Zhao M, Liu B, Wu K, Ye Y, Huang S, Wang S, Wang Y, Han R, Liu Q, Fu X, Wu Y.Regulation of OsmiR156h through alternative polyadenylation improves grain yield in rice[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(5): e0126154. |
| [25] | Miao C, Wang D, He R, Liu S, Zhu J K.Mutations in MIR396e and MIR396f increase grain size and modulate shoot architecture in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18(2): 491-501. |
| [26] | Zhang Y C, Yu Y, Wang C Y, Li Z Y, Liu Q, Xu J, Liao J Y, Wang X J, Qu L H, Chen F, Xin P, Yan C, Chu J, Li H Q, Chen Y Q.Overexpression of microRNA OsmiR397 improves rice yield by increasing grain size and promoting panicle branching[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(9): 848-852. |
| [27] | Sun W, Xu X H, Li Y, Xie L, He Y, Li W, Lu X, Sun H, Xie X.OsmiR530 acts downstream of OsPIL15 to regulate grain yield in rice[J]. New Phytology, 2019, 226(3): 823-837. |
| [28] | Chen J, Gao H, Zheng X M, Jin M, Weng J F, Ma J, Ren Y, Zhou K, Wang Q, Wang J, Wang J L, Zhang X, Cheng Z, Wu C, Wang H, Wan J M.An evolutionarily conserved gene, FUWA, plays a role in determining panicle architecture, grain shape and grain weight in rice[J]. Plant Journal, 2015, 83(3): 427-438. |
| [29] | Abe Y, Mieda K, Ando T, Kono I, Yano M, Kitano H, Iwasaki Y.The SMALL AND ROUND SEED1 (SRS1/DEP2) gene is involved in the regulation of seed size in rice[J]. Genes & Genetic Systems, 2011, 85(5): 327-339. |
| [30] | Wu T, Shen Y, Zheng M, Yang C, Chen Y, Feng Z, Liu X, Liu S, Chen Z, Lei C, Wang J, Jiang L, Wan J.Gene SGL, encoding a kinesin-like protein with transactivation activity, is involved in grain length and plant height in rice[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2014, 33(2): 235-244. |
| [31] | Segami S, Kono I, Ando T, Yano M, Kitano H, Miura K, Iwasaki Y.Small and round seed 5 gene encodes alpha-tubulin regulating seed cell elongation in rice[J]. Rice, 2011, 5(1): 4. |
| [32] | Wu L, Ren D, Hu S, Li G, Dong G, Jiang L, Hu X, Ye W, Cui Y, Zhu L, Hu J, Zhang G, Gao Z, Zeng D, Qian Q, Guo L.Down-regulation of a nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase gene, OsNaPRT1, leads to withered leaf tips[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 171(2): 1085. |
| [33] | Hu Z, Lu S J, Wang M J, He H, Sun L, Wang H, Liu X H, Jiang L, Sun J L, Xin X, Kong W, Chu C, Xue H W, Yang J, Luo X, Liu J X. A novel QTL qTGW3 encodes the GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase OsGSK5/OsSK41 that interacts with OsARF4 to negatively regulate grain size and weight in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2018(5): 736-749. |
| [34] | Xiong H, Yu J, Miao J, Li J, Zhang H, Wang X, Liu P, Zhao Y, Jiang C, Yin Z, Li Y, Guo Y, Fu B, Wang W, Li Z, Ali J, Li Z,. Natural variation in OsLG3 increases drought tolerance in rice by inducing ROS scavenging[J]. Plant Physiology, 2018, 178(1): 451-467. |
| [35] | Gao X, Zhang J Q, Zhang X, Zhou J, Jiang Z, Huang P, Tang Z, Bao Y, Cheng J, Tang H, Zhang W, Zhang H, Huang J.Rice qGL3/OsPPKL1 functions with the GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase OsGSK3 to modulate brassinosteroid signaling[J]. Plant Cell, 2019, 31(5): 1077-1093. |
| [36] | Zhao D S, Li Q F, Zhang C Q, Zhang C, Yang Q Q, Pan L X, Ren X Y, Lu J, Gu M H, Liu Q Q.GS9 acts as a transcriptional activator to regulate rice grain shape and appearance quality[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1240. |
| [37] | Xu C, Liu Y, Li Y, Xu X, Xu C, Li X, Xiao J, Zhang Q.Differential expression of GS5 regulates grain size in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015, 66(9): 2611-2623. |
| [38] | Weng J, Gu S, Wan X, Gao H, Guo T, Su N, Lei C, Zhang X, Cheng Z, Guo X, Wang J, Jiang L, Zhai H, Wan J.Isolation and initial characterization of GW5, a major QTL associated with rice grain width and weight[J]. Cell Research, 2008, 18(12): 1199-1209. |
| [39] | Ma X, Cheng Z, Qin R, Qiu Y, Heng Y, Yang H, Ren Y, Wang X, Bi J, Ma X, Zhang X, Wang J, Lei C, Guo X, Wang J, Wu F, Jiang L, Wang H, Wan J.OsARG encodes an arginase that plays critical roles in panicle development and grain production in rice[J]. Plant Journal, 2013, 73(2): 190-200. |
| [40] | Hang L?, Yu H, Ma B, Liu G, Wang J, Wang J, Gao R, Li J, Liu J, Xu J, Zhang Y, Li Q, Huang X, Xu J, Li J, Qian Q, Han B, He Z, Li J,. A natural tandem array alleviates epigenetic repression of IPA1 and leads to superior yielding rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 14789. |
| [41] | Wang Y, Shang L, Yu H, Zeng L, Hu J, Ni S, Rao Y, Li S, Chu J, Meng X, Wang L, Hu P, Yan J, Kang S, Qu M, Lin H, Wang T, Wang Q, Hu X, Chen H, Wang B, Gao Z, Guo L, Zeng D, Zhu X, Xiong G, Li J, Qian Q.A strigolactone biosynthesis gene contributed to the green revolution in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(6): 923-932. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||