
中国水稻科学 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 325-334.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7122
收稿日期:2017-09-28
修回日期:2018-01-14
出版日期:2018-07-10
发布日期:2018-07-10
通讯作者:
李泽福
基金资助:
Kunneng ZHOU, Jiafa XIA, Tingchen MA, Yuanlei WANG, Zefu LI*( )
)
Received:2017-09-28
Revised:2018-01-14
Online:2018-07-10
Published:2018-07-10
Contact:
Zefu LI
摘要: 【目的】对叶绿体发育相关基因进行克隆和功能分析,为解析叶绿体功能奠定分子基础。【方法】用甲基磺酸乙酯(EMS)处理籼稻9311获得一个条纹叶和白穗突变体slwp,通过色素分析和农艺性状观察分析该突变体的表型,通过图位克隆方法分离该基因,进一步利用定量PCR分析相关基因的表达情况。【结果】突变体slwp从2叶期开始至抽穗期表现出条纹叶表型,抽穗后幼穗白化,光合色素含量明显低于野生型;株高降低、抽穗延迟、产量降低等表型。该突变性状为单隐性核基因控制,该基因定位于水稻第6染色体短臂C6-4和N14标记之间0.91 Mb区间内。基因组测序表明核糖核苷二磷酸还原酶小亚基基因(RNRS1)编码区第776位点发生单碱基替换,导致甘氨酸突变为天冬氨酸;该基因与已报导的水稻基因St1、Gws和St-wp为等位基因。通过对这4个等位基因的突变位点和表型进行分析,总结了该基因不同位点突变对植株表型的影响以及籼粳之间的差异。表达分析显示与叶绿素合成有关的基因受到不同程度调控,叶绿体发育第一和第二阶段基因上调表达,光合作用相关基因均下调表达。【结论】本研究分析了SLWP(RNRS1)基因不同位点的变异对水稻表型的影响,相关结果加深了对RNRS1基因功能的认识,有助于阐明叶绿体发育的分子机制。
中图分类号:
周坤能, 夏加发, 马廷臣, 王元垒, 李泽福. 水稻条纹叶和白穗基因SLWP的定位及变异分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(4): 325-334.
Kunneng ZHOU, Jiafa XIA, Tingchen MA, Yuanlei WANG, Zefu LI. Mapping and Mutation Analysis of Stripe Leaf and White Panicle Gene SLWP in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(4): 325-334.
| 引物用途与名称 Usage and name | 正向引物 Forward sequence(5′-3′) | 反向引物 Reverse sequence(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 定位和测序引物 Primers for mapping and sequencing | ||
| C6-4 | CAGTTAACACCAATCCAATCCA | CCAAATGGGCAGTAGTTTGAA |
| C6-5 | GCTTCTCCCGGAGTATGTCA | TGGTCTGAAAAGTGCCAAAA |
| C6-6 | CCCCAAGCTTGTTTGTCTCT | TTGGGTCTTTGAGCTTCCTC |
| N4 | TCAAGTTGCTAAACCTTATCTG | AGATGAACTGTGCTAAAAGATG |
| N12 | GTAACTTAAAAGCCAATGTTGA | GAGTACTACCATCCATCCCTGT |
| N14 | TCTGTGGACGTAGTAGGTTGA | CCTTCCTTAGGTCTGGCTC |
| slwp-g | ACAACCCCAAATCCCCATCCA | ACCACGCGCATGTATTACTACT |
| 定量PCR引物 Primers for quantitative RT-PCR | ||
| PORA | ATCACCAAGGGCTACGTCTC | GAGTTGTTGTTCCAGCTCCA |
| HEMA1 | CACCAGTCTGAATCATAT | CTACCACTTCTCTAATCC |
| YGL1 | TGGACAGTTGAAGATGTT | GAATAGGACGGTAAGGTT |
| CHLI | AGTAACCTTGGTGCTGTG | AATCCATCAACATTCAACTCTG |
| CHLH | CTATACATTCGCCACACT | TATCACACAACTCCCAAG |
| CHLD | GGAAAGAGAGGGCATTAG | CAATACGATCAAGTAAGTGTT |
| FtsZ | GTTGGTGTTTCTTCCAGCAA | CCTCAATAGACGACCCGATT |
| RpoTp2 | AAGTCTGGCTTACGCTGGTT | AGGATCCTCAGCATTCATCC |
| rpoA | AAATCGTTGATACGGCACAA | ATTCACATTTCGAACAGGCA |
| rpoB | GCATTGTTGGAACTGGATTG | GCCGATGGGTAACTAAAGGA |
| rbcL | GTTGAAAGGGATAAGTTGA | AATGGTTGTGAGTTTACG |
| rbcS | TCATCAGCTTCATCGCCTAC | ACTGGGAACACACGAAACAA |
| psbA | AAGTTTCTCTGATGGTATG | ATAGCACTGAATAGGGAA |
| psaA | GAGATACCACTTCCTCAT | ACTAAGAAATTCTGCGTATT |
| psaB | TTGGTATTGCTACCGCACAT | CCGGACGTCCATAGAAAGAT |
| psbB | TCATATTGCTGCGGGTACAT | AGTTGCTGACCCATACCACA |
| psbC | TACAACCTTGGCAAGAACGA | TACGCCACCCACAGAATTTA |
| SLWP | AGTAATACATGCGCGTGGTG | ACACGGGCAGCTGATACTAA |
| RNRS2 | AGATGTACAACGTCGCCAAC | GACATTACGGACGCCTTCTG |
| Ubq | GCTCCGTGGCGGTATCAT | CGGCAGTTGACAGCCCTAG |
表1 本研究所用引物的序列
Table 1 Primer sequences used in the study.
| 引物用途与名称 Usage and name | 正向引物 Forward sequence(5′-3′) | 反向引物 Reverse sequence(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 定位和测序引物 Primers for mapping and sequencing | ||
| C6-4 | CAGTTAACACCAATCCAATCCA | CCAAATGGGCAGTAGTTTGAA |
| C6-5 | GCTTCTCCCGGAGTATGTCA | TGGTCTGAAAAGTGCCAAAA |
| C6-6 | CCCCAAGCTTGTTTGTCTCT | TTGGGTCTTTGAGCTTCCTC |
| N4 | TCAAGTTGCTAAACCTTATCTG | AGATGAACTGTGCTAAAAGATG |
| N12 | GTAACTTAAAAGCCAATGTTGA | GAGTACTACCATCCATCCCTGT |
| N14 | TCTGTGGACGTAGTAGGTTGA | CCTTCCTTAGGTCTGGCTC |
| slwp-g | ACAACCCCAAATCCCCATCCA | ACCACGCGCATGTATTACTACT |
| 定量PCR引物 Primers for quantitative RT-PCR | ||
| PORA | ATCACCAAGGGCTACGTCTC | GAGTTGTTGTTCCAGCTCCA |
| HEMA1 | CACCAGTCTGAATCATAT | CTACCACTTCTCTAATCC |
| YGL1 | TGGACAGTTGAAGATGTT | GAATAGGACGGTAAGGTT |
| CHLI | AGTAACCTTGGTGCTGTG | AATCCATCAACATTCAACTCTG |
| CHLH | CTATACATTCGCCACACT | TATCACACAACTCCCAAG |
| CHLD | GGAAAGAGAGGGCATTAG | CAATACGATCAAGTAAGTGTT |
| FtsZ | GTTGGTGTTTCTTCCAGCAA | CCTCAATAGACGACCCGATT |
| RpoTp2 | AAGTCTGGCTTACGCTGGTT | AGGATCCTCAGCATTCATCC |
| rpoA | AAATCGTTGATACGGCACAA | ATTCACATTTCGAACAGGCA |
| rpoB | GCATTGTTGGAACTGGATTG | GCCGATGGGTAACTAAAGGA |
| rbcL | GTTGAAAGGGATAAGTTGA | AATGGTTGTGAGTTTACG |
| rbcS | TCATCAGCTTCATCGCCTAC | ACTGGGAACACACGAAACAA |
| psbA | AAGTTTCTCTGATGGTATG | ATAGCACTGAATAGGGAA |
| psaA | GAGATACCACTTCCTCAT | ACTAAGAAATTCTGCGTATT |
| psaB | TTGGTATTGCTACCGCACAT | CCGGACGTCCATAGAAAGAT |
| psbB | TCATATTGCTGCGGGTACAT | AGTTGCTGACCCATACCACA |
| psbC | TACAACCTTGGCAAGAACGA | TACGCCACCCACAGAATTTA |
| SLWP | AGTAATACATGCGCGTGGTG | ACACGGGCAGCTGATACTAA |
| RNRS2 | AGATGTACAACGTCGCCAAC | GACATTACGGACGCCTTCTG |
| Ubq | GCTCCGTGGCGGTATCAT | CGGCAGTTGACAGCCCTAG |
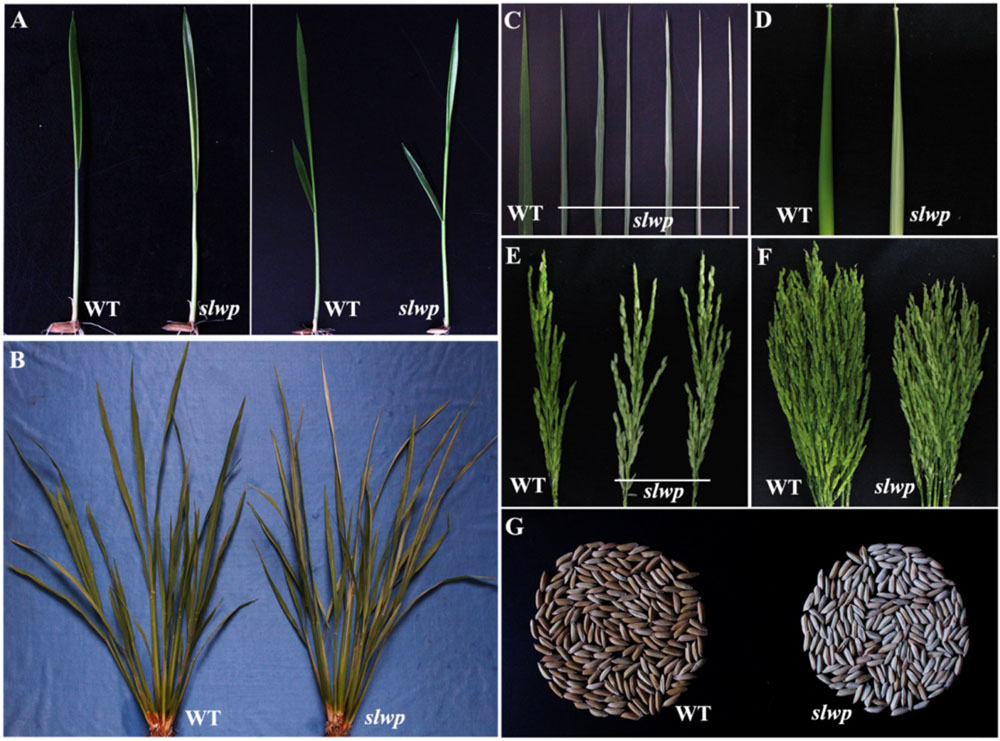
图1 突变体slwp和野生型的表型性状 A—2叶期和3叶期表型;B和C—分蘖期叶片表型;D—孕穗期叶鞘表型;E和F—抽穗期幼穗表型;G—种子表型。
Fig. 1. Phenotypic characteristics of the slwp mutant and its wild type(WT). A, Phenotypes of two- and three-leaf stages; B and C, Leaf phenotype of tillering stage; D, Sheath phenotype of booting stage; E and F—Panicle phenotype of heading stage; G, Seed phenotype.
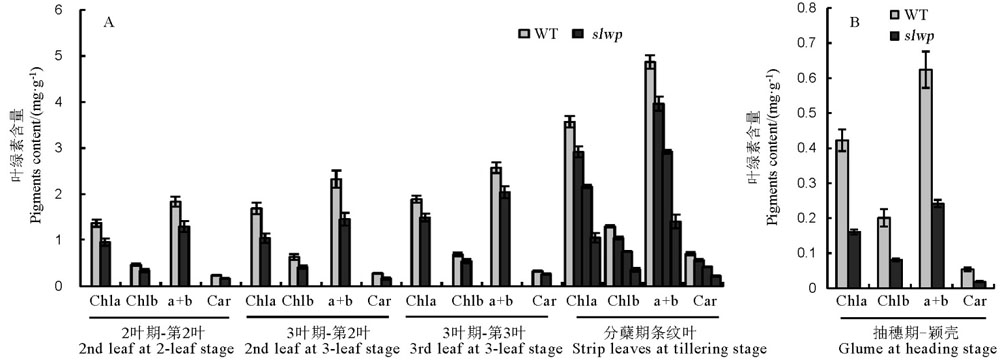
图2 突变体slwp和野生型色素含量测定 chla―叶绿素a;chlb―叶绿素b;a+b―总叶绿素;Car―胡萝卜素。
Fig. 2. Pigments determination of the slwp mutant and its wild type(WT). Chla, Chlorophyll a; chlb, Chlorophyll b; a+b, Total chlorophyll; Car―Carotene.
| 农艺性状 Agronomic trait | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 swlp |
|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height / cm | 124.7±3.4 | 98.2±4.8** |
| 播始历期Days from sowing to heading / d | 98.4±1.2 | 108.3±1.0** |
| 穗长Panicle length / cm | 25.5±1.1 | 22.1±1.3** |
| 有效穗数Number of effective panicles per plant | 7.1±1.4 | 6.6±1.7 |
| 每穗粒数Grain number per panicle | 245.1±32.6 | 145.0±21.0** |
| 结实率Seed-setting rate / % | 88.2±1.3 | 87.9±1.6 |
| 千粒重1000-grain weight / g | 30.8±0.4 | 27.9±0.6** |
| 理论产量Theoretical yield per plot / kg | 10.74±0.23 | 5.34±0.35** |
| 实际产量Actual yield per plot / kg | 9.16±0.26 | 4.43±0.47** |
表2 野生型和突变体的农艺性状分析
Table 2 Agronomic traits of the wild type (WT) and slwp mutant.
| 农艺性状 Agronomic trait | 野生型 Wild type | 突变体 swlp |
|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height / cm | 124.7±3.4 | 98.2±4.8** |
| 播始历期Days from sowing to heading / d | 98.4±1.2 | 108.3±1.0** |
| 穗长Panicle length / cm | 25.5±1.1 | 22.1±1.3** |
| 有效穗数Number of effective panicles per plant | 7.1±1.4 | 6.6±1.7 |
| 每穗粒数Grain number per panicle | 245.1±32.6 | 145.0±21.0** |
| 结实率Seed-setting rate / % | 88.2±1.3 | 87.9±1.6 |
| 千粒重1000-grain weight / g | 30.8±0.4 | 27.9±0.6** |
| 理论产量Theoretical yield per plot / kg | 10.74±0.23 | 5.34±0.35** |
| 实际产量Actual yield per plot / kg | 9.16±0.26 | 4.43±0.47** |
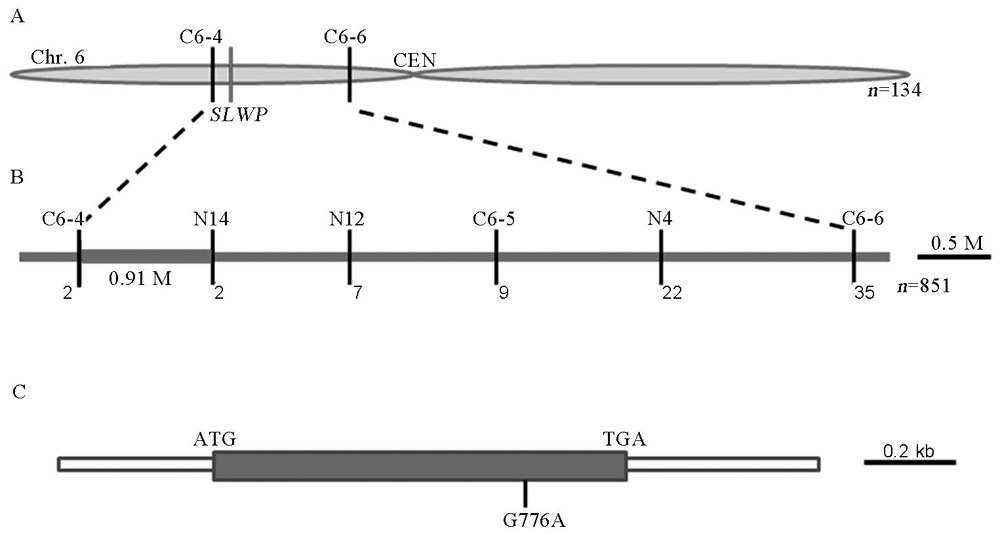
图3 SLWP基因的图位克隆 A—SLWP基因初定位;B—SLWP基因精细定位;C—SLWP基因结构和突变位点;ATG和TGA分别代表起始密码子和终止密码子。
Fig. 3. Map-based cloning of the SLWP gene. A, Initial mapping of the SLWP gene; B, Fine mapping of the SLWP gene; C, Structure and mutant site of the SLWP gene; ATG and TGA indicate initiation codon and termination codon, respectively.
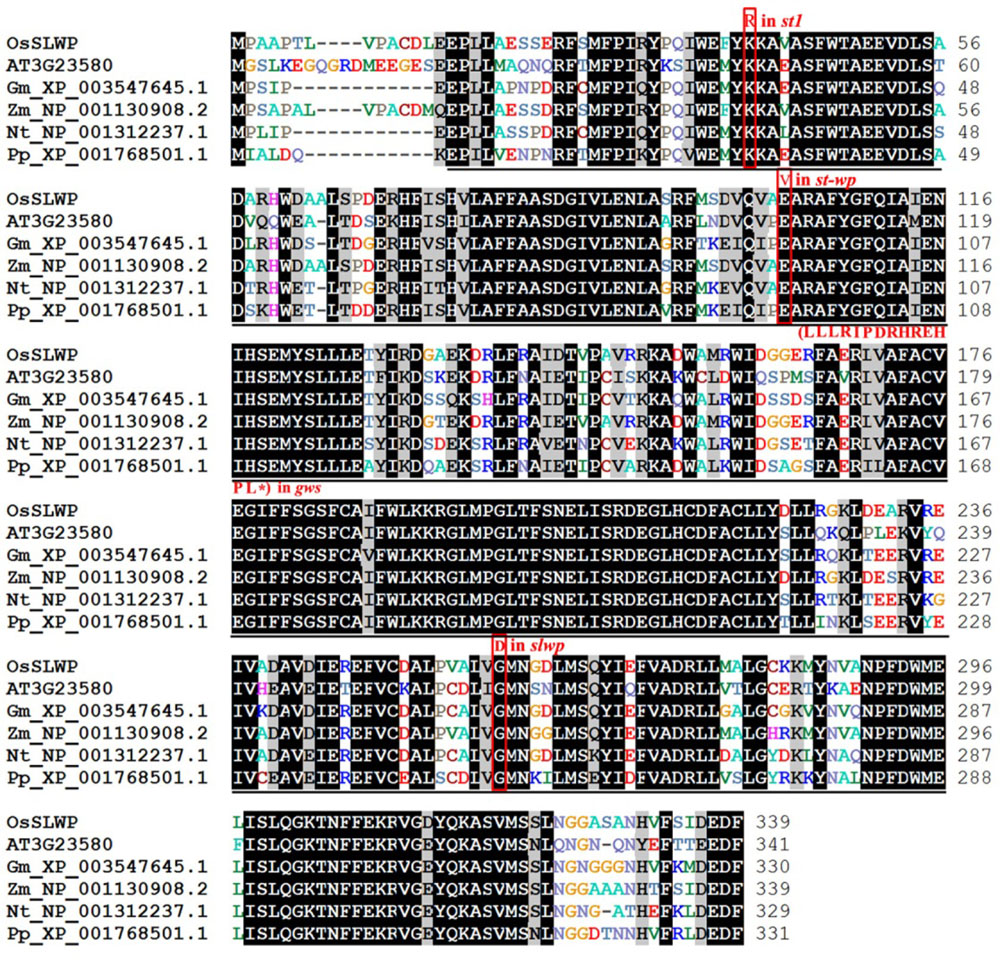
图4 SLWP及其同源蛋白的序列比对序列来源于水稻LOC_Os06g14620(SLWP)、拟南芥At3g23580、大豆XP_003547645.1、玉米NP_001130908.2、烟草NP_001312237.1和小立碗藓XP_001768501.1;下划线代表核糖核苷酸还原酶结构域;ST1、STWP、GWS和SLWP蛋白突变位点以红色字体和线框标出。
Fig. 4. Alignment of SLWP and SLWP-related proteins of different organisms. Sequences are for Oryza sativa LOC_Os06g14620(SLWP), Arabidopsis thaliana At3g23580, Glycine max XP_003547645.1, Zea mays NP_001130908.2, Nicotiana tabacum NP_001312237.1 and Physcomitrella patens XP_001768501.1; Underline represents nucleotide reductase domain; Red font and frame indicate mutant sites of ST1, STWP, GWS and SLWP.
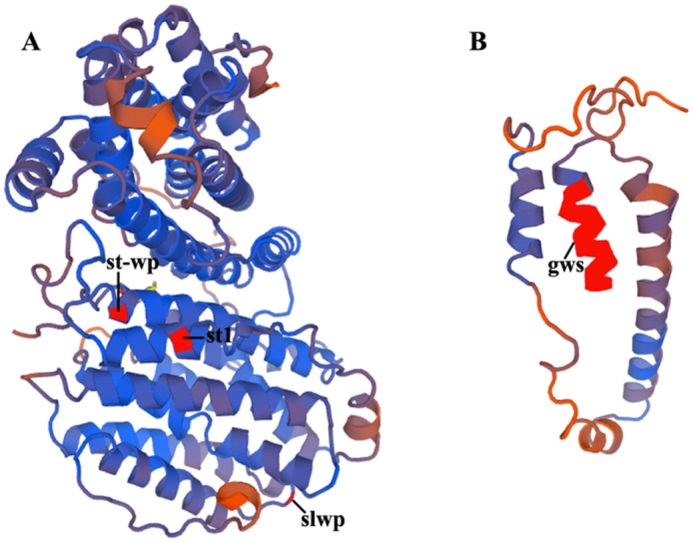
图5 蛋白三维结构预测 A—st1、st-wp和slwp;B—突变蛋白gws;红色表示突变位点。
Fig. 5. Prediction of 3D structure model. A—st1, st-wp and slwp; B—Mutant protein gws; The red regions represent mutant sites.
| 突变体 Mutant | 野生型 Wild type | 氨基酸突变位点 Mutant site of amino acid | 叶片表型 Leaf phenotype | 穗部表型 Panicle phenotype | 主要农艺性状变化 Agronomic trait change compared with its wild type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| st1 | FL176 | p. Lys40Arg | 4或5叶期至分蘖期出现条纹;抽穗后表型恢复Display stripe from 4- or 5-leaf stage to tillering, then revert to normal after heading | 无 None | 无 None |
| gws | 日本晴 Nipponbare | 104原有+插入14个氨基酸 104 original+Inserted 14 amino acid residues | 苗期至抽穗期叶片均出现条纹Display stripe from the seedling to heading stage | 无 None | 株高、穗长、有效分蘖数、结实率、千粒重、单株生物量均降低Decreased plant height, panicle length, tiller number, seed-setting rate, 1000-grain weight, and plant biomass per plant |
| st-wp | 9311 | p. Glu103Val | 苗期至抽穗期叶片均出现条纹Display stripe from the seedling to heading stage | 白穗 White panicle | 株高、穗长、每穗粒数、结实率、千粒重降低,抽穗期延长,有效穗数不变 Decreased plant height, panicle length, grain number per panicle, seed-setting rate, and 1000-grain weight; prolonged heading date; similar tiller number |
| slwp | 9311 | p. Gly259Asp | 苗期至抽穗期叶片出现条纹 Display stripe from the seedling to heading stage | 白穗 White panicle | 株高、穗长、每穗粒数、千粒重、理论产量、实际产量下降,抽穗期延长,有效穗数和结实率不变 Decreased plant height, panicle length, grain number per panicle, 1000-grain weight, theoretical yield, and actual yield; prolonged heading date, similar tiller number and seed-setting rate |
表3 SLWP变异分析
Table 3 Mutation analysis of SLWP.
| 突变体 Mutant | 野生型 Wild type | 氨基酸突变位点 Mutant site of amino acid | 叶片表型 Leaf phenotype | 穗部表型 Panicle phenotype | 主要农艺性状变化 Agronomic trait change compared with its wild type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| st1 | FL176 | p. Lys40Arg | 4或5叶期至分蘖期出现条纹;抽穗后表型恢复Display stripe from 4- or 5-leaf stage to tillering, then revert to normal after heading | 无 None | 无 None |
| gws | 日本晴 Nipponbare | 104原有+插入14个氨基酸 104 original+Inserted 14 amino acid residues | 苗期至抽穗期叶片均出现条纹Display stripe from the seedling to heading stage | 无 None | 株高、穗长、有效分蘖数、结实率、千粒重、单株生物量均降低Decreased plant height, panicle length, tiller number, seed-setting rate, 1000-grain weight, and plant biomass per plant |
| st-wp | 9311 | p. Glu103Val | 苗期至抽穗期叶片均出现条纹Display stripe from the seedling to heading stage | 白穗 White panicle | 株高、穗长、每穗粒数、结实率、千粒重降低,抽穗期延长,有效穗数不变 Decreased plant height, panicle length, grain number per panicle, seed-setting rate, and 1000-grain weight; prolonged heading date; similar tiller number |
| slwp | 9311 | p. Gly259Asp | 苗期至抽穗期叶片出现条纹 Display stripe from the seedling to heading stage | 白穗 White panicle | 株高、穗长、每穗粒数、千粒重、理论产量、实际产量下降,抽穗期延长,有效穗数和结实率不变 Decreased plant height, panicle length, grain number per panicle, 1000-grain weight, theoretical yield, and actual yield; prolonged heading date, similar tiller number and seed-setting rate |
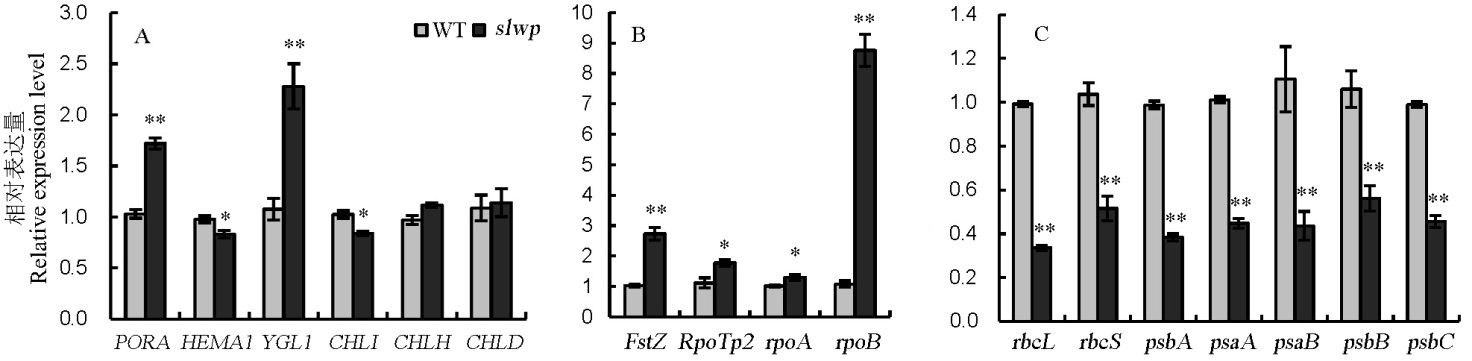
图6 野生型和突变体中叶绿素合成、叶绿体发育和光合作用相关基因的表达分析 A—叶绿素合成相关基因表达分析;B—叶绿体发育相关基因表达分析;C—光合作用相关基因表达分析。*和**分别表示5%和1%显著水平。
Fig. 6. Expression analysis of genes involved in chlorophyll biosynthesis, chloroplast development and photosynthesis between wild type(WT) and mutant. A, Expression analysis of genes associated with chlorophyll biosynthesis; B, Expression analysis of genes associated with chloroplast development; C, Expression analysis of genes associated with photosynthesis. * and ** represent significant difference at 5% and 1% levels, respectively.
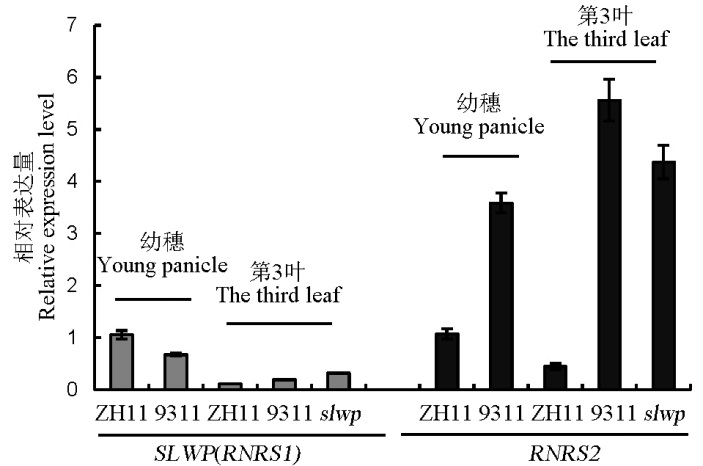
图7 SLWP(RNRS1)和RNRS2在中花11(ZH11)、9311和slwp突变体不同组织中的表达分析
Fig. 7. Expression analysis of SLWP (RNRS1) and RNRS2 in different tissues of ZH11, 9311 and slwp mutant.
| [1] | Fromme P, Melkozernov A, Jordan P, Krauss N.Structure and function of photosystem I: interaction with its soluble electron carriers and external antenna systems.FEBS Lett, 2003, 555: 40-44. |
| [2] | Lokstein H, Tian L, Polle J E W, DellaPenna D. Xanthophyll biosynthetic mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana: Altered nonphotochemical quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence is due to changes in Photosystem II antenna size and stability.Biochim Biophys Acta, 2002, 1553: 309-319. |
| [3] | Lv M Z, Chao D Y, Shan J X, Zhu M Z, Shi M, Gao J P, Lin H X.Rice carotenoid b-ring hydroxylase CYP97A4 is involved in lutein biosynthesis.Plant Cell Physiol, 2012, 53: 987-1002. |
| [4] | Nagata N, Tanaka R, Satoh S, Tanaka A.Identification of a vinyl reductase gene for chlorophyll synthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana and implications for the evolution of Prochlorococcus species. Plant Cell, 2005, 17(1): 233-240. |
| [5] | Yoo S C, Cho S H, Sugimoto H, Li J, Kusumi K, Koh H J, Iba K, Paek N C.Rice Virescent3 and Stripe1 encoding the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase are required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development. Plant Physiol, 2009, 150: 388-401. |
| [6] | Kusumi K, Mizutani A, Nishimura M, Iba K.A virescent gene V1 determines the expression timing of plastid genes for transcription/translation apparatus during early leaf development in rice. Plant J, 1997, 12: 1241-1250. |
| [7] | Kusumi K, Sakata C, Nakamura T, Kawasaki S, Yoshimura A, Iba K.A plastid protein NUS1 is essential for build-up of the genetic system for early chloroplast development under cold stress conditions.Plant J, 2011, 68: 1039-1050. |
| [8] | Sugimoto H, Kusumi K, Tozawa Y, Yazaki J, Kishimoto N, Kikuchi S, Iba K.The virescent-2 mutation inhibits translation of plastid transcripts for the plastid genetic system at an early stage of chloroplast differentiation. Plant Cell Physiol, 2004, 45: 985-996. |
| [9] | Sugimoto H, Kusumi K, Noguchi K, Yano M, Yoshimura A, Iba K.The rice nuclear gene, VIRESCENT 2 , is essential for chloroplast development and encodes a novel type of guanylate kinase targeted to plastids and mitochondria. Plant J, 2007, 52: 512-527. |
| [10] | Dong H, Fei G L, Wu C Y, Wu F Q, Sun Y Y, Chen M J, Ren Y L, Zhou K N, Cheng Z J, Wang J L, Jiang L, Zhang X, Guo X P, Lei C L, Su N, Wang H Y, Wan J M. A rice virescent-yellow leaf mutant reveals new insights into the role and assembly of plastid caseinolytic protease in higher plants. Plant Physiol, 2013, 162: 1867-1880. |
| [11] | Tan J, Tan Z, Wu F, Sheng P, Heng Y, Wang X, Ren Y, Wang J, Guo X, Zhang X, Cheng Z, Jiang L, Liu X, Wang H, Wan J.A novel chloroplast-localized pentatricopeptide repeat protein involved in splicing affects chloroplast development and abiotic stress response in rice.Mol Plant, 2014, 7: 1329-1349. |
| [12] | Wang Y, Ren Y, Zhou K, Liu L, Wang J, Xu Y, Zhang H, Zhang L, Feng Z, Wang L, Ma W, Wang Y, Guo X, Zhang X, Lei C, Cheng Z, Wan J.WHITE STRIPE LEAF4 encodes a novel P-type PPR protein required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development. Front Plant Sci, 2017, 8: 1116. |
| [13] | Wang L, Wang C, Wang Y, Niu M, Ren Y, Zhou K, Zhang H, Lin Q, Wu F, Cheng Z, Wang J, Zhang X, Guo X, Jiang L, Lei C, Wang J, Zhu S, Zhao Z, Wan J.WSL3, a component of the plastid-encoded plastid RNA polymerase, is essential for early chloroplast development in rice.Plant Mol Biol, 2016, 92: 581-595. |
| [14] | Zhou K N, Ren Y L, Zhou F, Wang Y, Zhang L, Lyu J, Wang Y H, Zhao S L, Ma W W, Zhang H, Wang L W, Wang C M, Wu F Q, Zhang X, Guo X P, Cheng Z J, Wang J L, Lei C L, Jiang L, Li Z F, Wan J M.Young Seedling Stripe1 encodes a chloroplast nucleoid- associated protein required for chloroplast development in rice seedlings. Planta, 2017, 245: 45-60. |
| [15] | Sheng P, Tan J, Jin M, Wu F, Zhou K, Ma W, Heng Y, Wang J, Guo X, Zhang X, Cheng Z, Liu L, Wang C, Liu X, Wan J.Albino midrib 1 , encoding a putative potassium efflux antiporter, affects chloroplast development and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Cell Rep, 2014, 33: 1581-1594. |
| [16] | 李红昌, 钱前, 王赟, 李晓波, 朱立煌, 徐吉臣. 水稻白穗突变体基因的鉴定和染色体定位. 科学通报, 2003, 48(3): 268-270. |
| Li H C, Qian Q, Wang Y, Li X B, Zhu L H, Xu J C.Identification and gene mapping of white panicle mutant in rice.Chin Sci Bull, 2003, 48(3): 268-270. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 金怡, 刘合芹, 汪得凯, 陶跃之. 一个水稻苗期白条纹及抽穗期白穗突变体的鉴定和基因定位. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(5): 461-466. |
| Jin Y, Liu H Q, Wang D K, Tao Y Z.Genetic analysis and gene mapping of a white striped leaf and white panicle mutant in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2011, 25(5): 461-466. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 王晓雯, 蒋钰东, 廖红香, 杨波, 邹帅宇, 朱小燕, 何光华, 桑贤春. 水稻白穗突变体wp4的鉴定与基因精细定位. 作物学报, 2015, 41(6): 838-844. |
| Wang X W, Jiang Y D, Niao H X, Yang B, Zou S Y, Zhu X Y, He G H, Sang X C.Identification and gene mapping of white panicle mutant wp4 in Oryza sativa. Acta Agron Sin, 2015, 41(6): 838-844. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | Song J, Wei X J, Shao G N, Sheng Z H, Cheng D, Liu C, Jiao G A, Xie L H, Tang S Q, Hu P S.The rice nuclear gene WLP1 encoding a chloroplast ribosome L13 protein is needed for chloroplast development in rice grown under low temperature conditions. Plant Mol Biol, 2014, 84: 301-314. |
| [20] | Wang Y L, Wang C M, Zheng M, Lyu J, Xu Y, Li X H, Niu M, Long W H, Wang D, Wang H Y, Terzaghi W, Wang Y H, Wan J M.WHITE PANICLE1 , a Val-tRNA synthetase regulating chloroplast ribosome biogenesis in rice, is essential for early chloroplast development. Plant Physiol, 2016, 170: 2120-2123. |
| [21] | Zhou K N, Xia J F, Wang Y L, Ma T C, Li Z F.A Young Seedling Stripe2 phenotype in rice is caused by mutation of a chloroplast-localized nucleoside diphosphate kinase 2 required for chloroplast biogenesis. Genet Mol Biol, 2017, 40: 630-642. |
| [22] | 许凤华, 程治军, 王久林, 吴自明, 孙伟, 张欣, 雷财林, 王洁, 吴赴清, 郭秀平, 刘玲珑, 万建民. 水稻白条纹叶Gws基因的精细定位与遗传分析. 作物学报, 2010, 36(5): 713-720. |
| Xu F H, Cheng Z J, Wang J L, Wu Z M, Sun W, Zhang X, Lei C L, Wang J, Wu F Q, Guo X P, Liu L L, Wan J M.Genetic analysis and fine-mapping of Gws gene using green-white-stripe rice mutant. Acta Agron Sin, 2010, 36(5): 713-720. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 陈叶平, 翟哲, 杨文君, 孙健, 舒小丽, 吴殿星. 水稻条白叶和白穗突变基因St-wp的遗传分析与精细定位. 核农学报, 2015, 29(7): 1246-1252. |
| Chen Y P, Zhai Z, Yang W J, Sun J, Shu X L, Wu D X.Genetic analysis and fine mapping of St-wp gene in mutant rice with stripe white leaf and white panicle. Acta Agric Nucl Sin, 2015, 29(7): 1246-1252. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Eriksson M, Uhlin U, Ramaswamy S, Ekberg M, Regnström K, Sjöberg B M, Eklund H.Binding of allosteric effectors to ribonucleotide reductase protein R1: reduction of active-site cysteines promotes substrate binding.Structure, 1997, 5: 1077-1092. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||