
中国水稻科学 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 1-11.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7016
• • 下一篇
刘喜1, 牟昌铃1, 周春雷1, 程治军2, 江玲1,*( ), 万建民1,2
), 万建民1,2
收稿日期:2017-02-07
修回日期:2017-04-20
出版日期:2018-01-10
发布日期:2018-01-10
通讯作者:
江玲
基金资助:
Xi LIU1, Changling MOU1, Chunlei ZHOU1, Zhijun CHENG2, Ling JIANG1,*( ), Jianmin WAN1,2
), Jianmin WAN1,2
Received:2017-02-07
Revised:2017-04-20
Online:2018-01-10
Published:2018-01-10
Contact:
Ling JIANG
摘要:
水稻粒型是影响其产量和品质的重要性状,阐明其遗传调控机理,有助于提高水稻单产和改良品质。水稻粒型性状主要包括粒长、粒宽、粒厚、长/宽比,属于数量性状,受胚、胚乳及母体植株等不同遗传体系的控制。随着水稻功能基因组学和重测序技术的快速发展,目前已经定位超过400个与水稻粒型相关的数量性状位点(QTL),并已克隆了60个水稻粒型基因,涉及植物激素、泛素-蛋白酶体通路、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)信号通路、G蛋白信号通路及表观修饰等多个调控通路。本文对水稻粒型基因克隆及其调控机制的研究进展进行了系统总结和梳理,并对这些基因在育种上的利用价值进行了评价。
中图分类号:
刘喜, 牟昌铃, 周春雷, 程治军, 江玲, 万建民. 水稻粒型基因克隆和调控机制研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(1): 1-11.
Xi LIU, Changling MOU, Chunlei ZHOU, Zhijun CHENG, Ling JIANG, Jianmin WAN. Research Progress on Cloning and Regulation Mechanism of Rice Grain Shape Genes[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(1): 1-11.
| 基因 Gene | Chr. | 功能 Function | 突变体,表型 Mutant, phenotype | 参考文献 Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2/SMG11 | 1 | 细胞色素P450加氧酶,参与BR生物合成 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [10-11] | ||||
| D61/OsBRI1 | 1 | BR受体激酶 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [12-15] | ||||
| RAV6 | 2 | B3 DNA结合结构域蛋白,介导油菜素内酯稳态,受表观遗传修饰调控 | 显性突变体,小粒 | [16] | ||||
| SDG725 | 2 | H3K36 甲基转移酶,参与调节BR相关基因的表达 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [17-18] | ||||
| SMG1 | 2 | 有丝分裂激活的蛋白激酶激酶4,可能作为MAPK通路和BR间连接因子 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [19] | ||||
| TH1/AFD1 | 2 | DUF640结构域的蛋白,影响细胞分裂和扩张 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [20-21] | ||||
| FUWA | 2 | NHL结构域蛋白,限制细胞过度分裂 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [22] | ||||
| GW2 | 2 | 环型E3泛素连接酶,负调节细胞分裂 | 隐性突变体,宽粒 | [23-25] | ||||
| OsGRF4/GS2/GL2 | 2 | 生长调控因子,与BR负调控因子GSK2互作 | 转基因过表达株,大粒 | [26-28] | ||||
| PGL2 | 2 | 非典型的不结合DNA的碱性螺旋-环-螺旋蛋白,与APG互作 | 转基因过表达株,长粒 | [29] | ||||
| BG1 | 3 | 未知蛋白,参与调节生长素的转运 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [30] | ||||
| PGL1 | 3 | 非典型的不结合DNA的碱性螺旋-环-螺旋蛋白 | 转基因过表达株,长粒 | [31] | ||||
| RGB1 | 3 | G蛋白β亚基,正向调控细胞增殖 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [32-33] | ||||
| GS3 | 3 | G蛋白的γ亚基,负调控粒重 | 转基因过表达株,长粒 | [34-38] | ||||
| OsPPKL1/GL3.1 | 3 | 蛋白磷酸酶,调控细胞周期蛋白T1;3 | 转基因干扰株,长粒 | [39-41] | ||||
| BRD1/OsBR6ox | 3 | 细胞色素P450加氧酶,参与BR生物合成 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [42-43] | ||||
| LTS1/OsNaPRT1 | 3 | 烟酸磷酸核糖转移酶,影响烟酰胺的含量 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [44] | ||||
| TUD1 | 3 | U-box家族的E3泛素连接酶,参与BR应答 | 隐性突变体,短粒 | [45] | ||||
| XIAO | 4 | LRR 激酶,调控BR信号传递和动态平衡以及细胞周期 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [46] | ||||
| D11/CPB1 | 4 | 细胞色素P450加氧酶,参与BR生物合成 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [47-48] | ||||
| An-1 | 4 | bHLH转录因子,调控细胞分裂 | 隐性突变体,短粒 | [49] | ||||
| OsBSK3 | 4 | BR信号激酶 | 转基因干扰株,小粒 | [50] | ||||
| Flo2 | 4 | 含TPR结构域蛋白 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [51] | ||||
| GW5/qSW5 | 5 | 核蛋白,调节细胞分裂 | 转基因干扰株,宽粒 | [52-53] | ||||
| GS5 | 5 | 丝氨酸羧肽酶,与 BAK1互作,参与BR信号 | 转基因过表达株,大粒 | [54-55] | ||||
| GSK2 | 5 | 与拟南芥BIN2同源的类GSK3/SHAGGY激酶,BR信号负调控因子 | 转基因干扰株,大粒 | [56] | ||||
| OsCYP51G3 | 5 | 钝叶醇14α-脱甲基酶 | 转基因干扰株,短粒 | [57] | ||||
| OsLAC | 5 | 漆酶蛋白,影响BR信号 | 转基因干扰株,大粒 | [58] | ||||
| SRS3 | 5 | 驱动蛋白13 基因家族成员,影响细胞纵向长度 | 隐性突变体,小圆粒 | [59] | ||||
| OsPPKL2 | 5 | 含有Kelch重复域的蛋白磷酸酶,正向调控粒长 | 转基因过表达株,长粒 | [41] | ||||
| APG | 5 | bHLH蛋白,PGL1拮抗因子 | 转基因干扰株,长粒 | [29] | ||||
| D1 | 5 | G蛋白亚基,调控细胞分裂 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [60-63] | ||||
| TGW6 | 6 | IAA-葡萄糖水解酶,水解IAA-葡萄糖成IAA和葡萄糖 | 转基因干扰株,大粒 | [64] | ||||
| GW6a | 6 | 组蛋白乙酰转移酶,增加细胞数和加速灌浆速率,增大颖壳 | 转基因干扰株,小粒 | [65] | ||||
| GS6/DLT | 6 | GRAS基因家族,BR信号基因 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [66-67] | ||||
| BU1 | 6 | 螺旋-环-螺旋蛋白,BR信号基因 | 转基因过表达株,大粒 | [68] | ||||
| OsARF19 | 6 | 生长素响应因子 | 转基因过表达株,瘪粒 | [69] | ||||
| HGW | 6 | 泛素相关结构域蛋白,可能直接通过GIF1 控制水稻籽粒和质量 | 隐性突变体,细长粒 | [70] | ||||
| OsMAPK6/DSG1 | 6 | 有丝分裂激活的蛋白激酶,影响细胞增殖以及BR信号和稳态 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [71] | ||||
| GL7/GW7/SLG7 | 7 | TONNEAU1募集基序蛋白 | 转基因过表达株,长粒 | [72-74] | ||||
| GLW7 | 7 | SPL家族转录因子 | 转基因过表达株,长粒 | [75] | ||||
| OsBZR1 | 7 | BR信号因子 | 转基因过表达株,大粒 | [76] | ||||
| BG2/GE | 7 | 细胞色素P450加氧酶,促进细胞增殖 | 显性突变体,大粒 | [77-78] | ||||
| SRS1/EP2 | 7 | 未知蛋白 | 隐性突变体,小圆粒 | [79-80] | ||||
| SLG | 8 | 类BAHD酰基转移酶,调控BR的稳态 | 半显性突变体,细长粒 | [81] | ||||
| BAK1 | 8 | BR信号受体BRI1的激酶,BR共受体 | 转基因过表达株,小粒 | [82] | ||||
| qGW8/OsSPL16 | 8 | 含SBP结构域的转录因子,结合GW7启动子,抑制其表达 | 转基因过表达株,细长粒 | [83] | ||||
| OsFIE1 | 8 | 多梳蛋白抑制复合体的类Esc核心元件,参与H3K27me3介导的基因抑制过程 | 显性突变体,小粒 | [84] | ||||
| OsFEI2 | 8 | 具有特异的组蛋白H3甲基转移酶活性,负责组蛋白H3第27位赖氨酸上三甲基化的形成 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [85] | ||||
| GAD1 | 8 | 一个表皮模式因子类蛋白EPFL1,促进细胞分裂 | 转基因干扰株,短粒 | [86] | ||||
| GDD1 | 9 | 驱动蛋白4家族基因,控制水稻细胞周期进程和细胞壁的属性 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [87] | ||||
| SG1 | 9 | 未知蛋白,与BR相关 | 转基因干扰株,短粒 | [88] | ||||
| DEP1/DN1/qNGR9 | 9 | G蛋白γ亚基 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [89-93] | ||||
| BRD2 | 10 | 拟南芥DIM1/DWF1同源基因,参与BR生物合成 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [94] | ||||
| SRS5/TID1 | 11 | 微管蛋白 | 隐性突变体,小圆粒 | [95-96] | ||||
| OsGIF1 | 11 | GRF互作因子 | 转基因过表达株,大粒 | [27] | ||||
| OsPPKL3 | 12 | 含有Kelch重复域的蛋白磷酸酶,负向调控粒长 | 转基因过表达株,短粒 | [41] | ||||
| miR1848 | 调控靶基因OsCYP51G3 | 转基因过表达株,短粒 | [57] | |||||
| miR397 | 调控靶基因OsLAC | 转基因过表达株,大粒 | [58] | |||||
| miR396 | 调控靶基因GS2 | 转基因过表达株,小粒 | [27] | |||||
表1 已克隆的控制水稻粒型的基因
Table 1 Cloned genes for grain shape in rice.
| 基因 Gene | Chr. | 功能 Function | 突变体,表型 Mutant, phenotype | 参考文献 Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2/SMG11 | 1 | 细胞色素P450加氧酶,参与BR生物合成 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [10-11] | ||||
| D61/OsBRI1 | 1 | BR受体激酶 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [12-15] | ||||
| RAV6 | 2 | B3 DNA结合结构域蛋白,介导油菜素内酯稳态,受表观遗传修饰调控 | 显性突变体,小粒 | [16] | ||||
| SDG725 | 2 | H3K36 甲基转移酶,参与调节BR相关基因的表达 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [17-18] | ||||
| SMG1 | 2 | 有丝分裂激活的蛋白激酶激酶4,可能作为MAPK通路和BR间连接因子 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [19] | ||||
| TH1/AFD1 | 2 | DUF640结构域的蛋白,影响细胞分裂和扩张 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [20-21] | ||||
| FUWA | 2 | NHL结构域蛋白,限制细胞过度分裂 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [22] | ||||
| GW2 | 2 | 环型E3泛素连接酶,负调节细胞分裂 | 隐性突变体,宽粒 | [23-25] | ||||
| OsGRF4/GS2/GL2 | 2 | 生长调控因子,与BR负调控因子GSK2互作 | 转基因过表达株,大粒 | [26-28] | ||||
| PGL2 | 2 | 非典型的不结合DNA的碱性螺旋-环-螺旋蛋白,与APG互作 | 转基因过表达株,长粒 | [29] | ||||
| BG1 | 3 | 未知蛋白,参与调节生长素的转运 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [30] | ||||
| PGL1 | 3 | 非典型的不结合DNA的碱性螺旋-环-螺旋蛋白 | 转基因过表达株,长粒 | [31] | ||||
| RGB1 | 3 | G蛋白β亚基,正向调控细胞增殖 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [32-33] | ||||
| GS3 | 3 | G蛋白的γ亚基,负调控粒重 | 转基因过表达株,长粒 | [34-38] | ||||
| OsPPKL1/GL3.1 | 3 | 蛋白磷酸酶,调控细胞周期蛋白T1;3 | 转基因干扰株,长粒 | [39-41] | ||||
| BRD1/OsBR6ox | 3 | 细胞色素P450加氧酶,参与BR生物合成 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [42-43] | ||||
| LTS1/OsNaPRT1 | 3 | 烟酸磷酸核糖转移酶,影响烟酰胺的含量 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [44] | ||||
| TUD1 | 3 | U-box家族的E3泛素连接酶,参与BR应答 | 隐性突变体,短粒 | [45] | ||||
| XIAO | 4 | LRR 激酶,调控BR信号传递和动态平衡以及细胞周期 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [46] | ||||
| D11/CPB1 | 4 | 细胞色素P450加氧酶,参与BR生物合成 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [47-48] | ||||
| An-1 | 4 | bHLH转录因子,调控细胞分裂 | 隐性突变体,短粒 | [49] | ||||
| OsBSK3 | 4 | BR信号激酶 | 转基因干扰株,小粒 | [50] | ||||
| Flo2 | 4 | 含TPR结构域蛋白 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [51] | ||||
| GW5/qSW5 | 5 | 核蛋白,调节细胞分裂 | 转基因干扰株,宽粒 | [52-53] | ||||
| GS5 | 5 | 丝氨酸羧肽酶,与 BAK1互作,参与BR信号 | 转基因过表达株,大粒 | [54-55] | ||||
| GSK2 | 5 | 与拟南芥BIN2同源的类GSK3/SHAGGY激酶,BR信号负调控因子 | 转基因干扰株,大粒 | [56] | ||||
| OsCYP51G3 | 5 | 钝叶醇14α-脱甲基酶 | 转基因干扰株,短粒 | [57] | ||||
| OsLAC | 5 | 漆酶蛋白,影响BR信号 | 转基因干扰株,大粒 | [58] | ||||
| SRS3 | 5 | 驱动蛋白13 基因家族成员,影响细胞纵向长度 | 隐性突变体,小圆粒 | [59] | ||||
| OsPPKL2 | 5 | 含有Kelch重复域的蛋白磷酸酶,正向调控粒长 | 转基因过表达株,长粒 | [41] | ||||
| APG | 5 | bHLH蛋白,PGL1拮抗因子 | 转基因干扰株,长粒 | [29] | ||||
| D1 | 5 | G蛋白亚基,调控细胞分裂 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [60-63] | ||||
| TGW6 | 6 | IAA-葡萄糖水解酶,水解IAA-葡萄糖成IAA和葡萄糖 | 转基因干扰株,大粒 | [64] | ||||
| GW6a | 6 | 组蛋白乙酰转移酶,增加细胞数和加速灌浆速率,增大颖壳 | 转基因干扰株,小粒 | [65] | ||||
| GS6/DLT | 6 | GRAS基因家族,BR信号基因 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [66-67] | ||||
| BU1 | 6 | 螺旋-环-螺旋蛋白,BR信号基因 | 转基因过表达株,大粒 | [68] | ||||
| OsARF19 | 6 | 生长素响应因子 | 转基因过表达株,瘪粒 | [69] | ||||
| HGW | 6 | 泛素相关结构域蛋白,可能直接通过GIF1 控制水稻籽粒和质量 | 隐性突变体,细长粒 | [70] | ||||
| OsMAPK6/DSG1 | 6 | 有丝分裂激活的蛋白激酶,影响细胞增殖以及BR信号和稳态 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [71] | ||||
| GL7/GW7/SLG7 | 7 | TONNEAU1募集基序蛋白 | 转基因过表达株,长粒 | [72-74] | ||||
| GLW7 | 7 | SPL家族转录因子 | 转基因过表达株,长粒 | [75] | ||||
| OsBZR1 | 7 | BR信号因子 | 转基因过表达株,大粒 | [76] | ||||
| BG2/GE | 7 | 细胞色素P450加氧酶,促进细胞增殖 | 显性突变体,大粒 | [77-78] | ||||
| SRS1/EP2 | 7 | 未知蛋白 | 隐性突变体,小圆粒 | [79-80] | ||||
| SLG | 8 | 类BAHD酰基转移酶,调控BR的稳态 | 半显性突变体,细长粒 | [81] | ||||
| BAK1 | 8 | BR信号受体BRI1的激酶,BR共受体 | 转基因过表达株,小粒 | [82] | ||||
| qGW8/OsSPL16 | 8 | 含SBP结构域的转录因子,结合GW7启动子,抑制其表达 | 转基因过表达株,细长粒 | [83] | ||||
| OsFIE1 | 8 | 多梳蛋白抑制复合体的类Esc核心元件,参与H3K27me3介导的基因抑制过程 | 显性突变体,小粒 | [84] | ||||
| OsFEI2 | 8 | 具有特异的组蛋白H3甲基转移酶活性,负责组蛋白H3第27位赖氨酸上三甲基化的形成 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [85] | ||||
| GAD1 | 8 | 一个表皮模式因子类蛋白EPFL1,促进细胞分裂 | 转基因干扰株,短粒 | [86] | ||||
| GDD1 | 9 | 驱动蛋白4家族基因,控制水稻细胞周期进程和细胞壁的属性 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [87] | ||||
| SG1 | 9 | 未知蛋白,与BR相关 | 转基因干扰株,短粒 | [88] | ||||
| DEP1/DN1/qNGR9 | 9 | G蛋白γ亚基 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [89-93] | ||||
| BRD2 | 10 | 拟南芥DIM1/DWF1同源基因,参与BR生物合成 | 隐性突变体,小粒 | [94] | ||||
| SRS5/TID1 | 11 | 微管蛋白 | 隐性突变体,小圆粒 | [95-96] | ||||
| OsGIF1 | 11 | GRF互作因子 | 转基因过表达株,大粒 | [27] | ||||
| OsPPKL3 | 12 | 含有Kelch重复域的蛋白磷酸酶,负向调控粒长 | 转基因过表达株,短粒 | [41] | ||||
| miR1848 | 调控靶基因OsCYP51G3 | 转基因过表达株,短粒 | [57] | |||||
| miR397 | 调控靶基因OsLAC | 转基因过表达株,大粒 | [58] | |||||
| miR396 | 调控靶基因GS2 | 转基因过表达株,小粒 | [27] | |||||
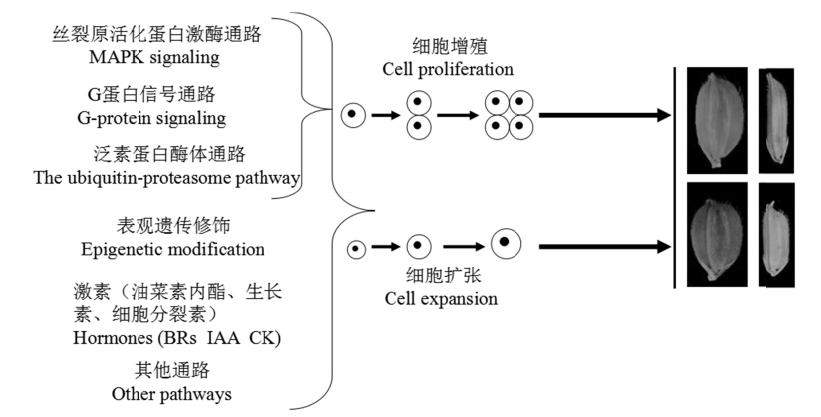
图2 水稻粒型主要调控通路水稻粒型是由5个主要的信号途径调控,包括激素、泛素-蛋白酶体通路、MAPK信号、表观修饰与G蛋白信号转导。这些调控因子通过影响细胞增殖和扩张来控制粒型。
Fig. 2. Major pathways of rice grain shape regulation. Grain shape is regulated by five major signaling pathways in rice, including phytohormones, the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, MAPK signaling, epigenetic modification and G-protein signaling. These regulators control grain shape by influencing cell proliferation and expansion in grain development.
| [1] | Bai X,Luo L,Yan W,Kovi M R,Zhan W,Xing Y.Genetic dissection of rice grain shape using a recombinant inbred line population derived from two contrasting parents and fine mapping a pleiotropic quantitative trait locusqGL7. BMC Genet,2010,11: 16. |
| [2] | Shao G N,Tang S Q,Luo J,Jiao G,Wei X,Tang A,Wu J,Zhuang J,Hu P.Mapping ofqGL7-2, a grain length QTL on chromosome 7 of rice. J Genet Genom,2010,37(8):523-531. |
| [3] | Harberd N P.Shaping Taste: The molecular discovery of rice genes improving grain size, shape and quality.J Genet Genom,2015,42(11):597-599. |
| [4] | Meyer R S,Purugganan M D.Evolution of crop species: genetics of domestication and diversification.Nat Rev Genet,2013,14(12):840-852. |
| [5] | Xing Y,Zhang Q.Genetic and molecular bases of rice yield.Ann Rev Plant Biol,2010,61: 421-442. |
| [6] | Sakamoto T,Matsuoka M.Identifying and exploiting grain yield genes in rice.Curr Opin Plant Biol,2008,11(2):209-214. |
| [7] | Huang R Y,Jiang L R,Zheng J S,Wang T,Wang H,Huang Y,Hong Z.Genetic bases of rice grain shape: so many genes, so little known.Trends Plant Sci,2013,18(4):218-226. |
| [8] | Kesavan M,Song J T,Seo H S.Seed size: a priority trait in cereal crops.Physiol Plant,2013,147(2):113-120. |
| [9] | Li N,Li Y.Signaling pathways of seed size control in plants.Curr Opin Plant Biol,2016,33: 23-32. |
| [10] | Fang N,Xu R,Huang L,Zhang B,Duan P,Li N,Luo Y,Li Y.SMALL GRAIN 11 controls grain size, grain number and grain yield in rice. Rice,2016,9: 64. |
| [11] | Hong Z,Ueguchi-Tanaka M,Umemura K,Uozu S,Fujioka S,Takatsuto S,Yoshida S,Ashikari M,Kitano H,Matsuoka M.A rice brassinosteroid-deficient mutant,ebisu dwarf (d2), is caused by a loss of function of a new member of cytochrome P450.Plant Cell,2003,15(12):2900-2910. |
| [12] | Liu J M,Park S J,Huang J,Lee E J,Xuan Y H,Je B I,Kumar V,Priatama R A,Raj K V,Kim S H,Min M K,Cho J H,Kim T H,Chandran A K,Jung K H,Takatsuto S,Fujioka S,Han C D.Loose Plant Architecture1 (LPA1) determines lamina joint bending by suppressing auxin signalling that interacts with C-22-hydroxylated and 6-deoxo brassinosteroids in rice. J Exp Bot,2016,67(6):1883-1895. |
| [13] | Nakamura A,Fujioka S,Sunohara H,Kamiya N,Hong Z,Inukai Y,Miura K,Takatsuto S,Yoshida S,Ueguchi- Tanaka M,Hasegawa Y,Kitano H,Matsuoka M.The role ofOsBRI1 and its homologous genes, OsBRL1 and OsBRL3, in rice. Plant Physiol,2006,140(2):580-590. |
| [14] | Zhao J,Wu C,Yuan S,Yin L,Sun W,Zhao Q,Zhao B,Li X.Kinase activity of OsBRI1 is essential for brassinosteroids to regulate rice growth and development.Plant Sci, 2013(199-200):113-120. |
| [15] | Yamamuro C,Ihara Y,Wu X,Kamiya N,Hong Z,Inukai Y,Miura K,Takatsuto S,Yoshida S,Ueguchi-Tanaka M,Hasegawa Y,Kitano H,Matsuoka M.Loss of function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint.Plant Cell,2000,12(9):1591-1605. |
| [16] | Zhang X,Sun J,Cao X,Song X.Epigenetic mutation ofRAV6 affects leaf angle and seed size in rice. Plant Physiol,2015,169(3):2118-2128. |
| [17] | Sui P,Shi J,Gao X,Shen W H,Dong A.H3K36 methylation is involved in promoting rice flowering. Mol Plant,2013,6(3):975-977. |
| [18] | Sui P,Jin J,Ye S,Mu C,Gao J,Feng H,Shen W H,Yu Y,Dong A.H3K36 methylation is critical for brassinosteroid-regulated plant growth and development in rice.Plant J,2012,70(2):340-347. |
| [19] | Duan P,Rao Y,Zeng D,Yang Y,Xu R,Zhang B,Dong G,Qian Q,Li Y.SMALL GRAIN 1, which encodes a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4, influences grain size in rice. Plant J,2014,77(4):547-557. |
| [20] | Ren D,Rao Y,Wu L,Xu Q,Li Z,Yu H,Zhang Y,Leng Y,Hu J,Zhu L,Gao Z,Dong G,Zhang G,Guo L,Zeng D,Qian Q.The pleiotropicABNORMAL FLOWER AND DWARF1 affects plant height, floral development and grain yield in rice. J Integr Plant Biol,2016,58(6):529-539. |
| [21] | Li X,Sun L,Tan L,Liu F,Zhu Z,Fu Y,Sun X,Sun X,Xie D,Sun C.TH1, a DUF640 domain-like gene controls lemma and palea development in rice. Plant Mol Biol,2012,78(4-5):351-359. |
| [22] | Chen J,Gao H,Zheng X M,Jin M,Weng J F,Ma J,Ren Y,Zhou K,Wang Q,Wang J,Wang J L,Zhang X,Cheng Z,Wu C,Wang H,Wan J M.An evolutionarily conserved gene,FUWA, plays a role in determining panicle architecture, grain shape and weight in rice. Plant J,2015,83(3):427-438. |
| [23] | Song X J,Huang W,Shi M,Zhu M Z,Lin H X.A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown ring-type E3 ubiquitin ligase.Nat Genet,2007,39(5):623-630. |
| [24] | Xia T,Li N,Dumenil J,Kamenski A,Bevan M W,Gao F,Li Y.The ubiquitin receptor DA1 interacts with the E3 ubiquitin ligase DA2 to regulate seed and organ size inArabidopsis. Plant Cell,2013,25(9):3347-3359. |
| [25] | Bednarek J,Boulaflous A,Girousse C,Ravel C,Tassy C,Barret P,Bouzidi M F,Mouzeyar S.Down-regulation of theTaGW2 gene by RNA interference results in decreased grain size and weight in wheat. J Exp Bot,2012,63(16):5945-5955. |
| [26] | Hu J,Wang Y,Fang Y,Zeng L,Xu J,Yu H,Shi Z,Pan J,Zhang D,Kang S,Zhu L,Dong G,Guo L,Zeng D,Zhang G,Xie L,Xiong G,Li J,Qian Q.A rare allele ofGS2 enhances grain size and grain yield in rice. Mol Plant,2015,8(10):1455-1465. |
| [27] | Che R,Tong H,Shi B,Liu Y,Fang S,Liu D,Xiao Y,Hu B,Liu L,Wang H,Zhao M,Chu C.Control of grain size and rice yield byGL2-mediated brassinosteroid responses. Nat Plants,2015,2: 15195. |
| [28] | Duan P,Ni S,Wang J,Zhang B,Xu R,Wang Y,Chen H,Zhu X,Li Y.Regulation ofOsGRF4 by OsmiR396 controls grain size and yield in rice. Nat Plants,2015,2: 15203. |
| [29] | Heang D,Sassa H.An atypical bHLH protein encoded byPOSITIVE REGULATOR OF GRAIN LENGTH 2 is involved in controlling grain length and weight of rice through interaction with a typical bHLH protein APG. Breeding Sci,2012,62(2):133-141. |
| [30] | Liu L,Tong H,Xiao Y,Che R,Xu F,Hu B,Liang C,Chu J,Li J,Chu C.Activation ofbig grain1 significantly improves grain size by regulating auxin transport in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci,2015,112(35):11102-11107. |
| [31] | Heang D,Sassa H.Antagonistic actions of HLH/bHLH proteins are involved in grain length and weight in rice.PLoS ONE,2012,7(2):e31325. |
| [32] | Zhang D P,Zhou Y,Yin J F,Yan X J,Lin S,Xu WF,Baluška F,Wang Y P,Xia YJ,Liang G H,Liang J S.Rice G-protein subunits qPE9-1 and RGB1 play distinct roles in abscisic acid responses and drought adaptation.J Exp Bot,2015,66(20):6371-6384. |
| [33] | Utsunomiya Y,Samejima C,Takayanagi Y,Izawa Y,Yoshida T,Sawada Y,Fujisawa Y,Kato H,Iwasaki Y.Suppression of the rice heterotrimeric G protein beta-subunit gene, RGB1, causes dwarfism and browning of internodes and lamina joint regions. Plant J,2011,67(5):907-916. |
| [34] | Fan C,Xing Y,Mao H,Lu T,Han B,Xu C,Li X,Zhang Q.GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet,2006,112(6):1164-1171. |
| [35] | Mao H,Sun S,Yao J,Wang C,Yu S,Xu C,Li X,Zhang Q.Linking differential domain functions of the GS3 protein to natural variation of grain size in rice.Theor Appl Genet,2010,107(45):19579-19584. |
| [36] | Takano-Kai N,Jiang H,Kubo T,Wang C,Yu S,Xu C,Li X,Zhang Q.Evolutionary history ofGS3, a gene conferring grain length in rice. Genetics,2009,182(4):1323-1334. |
| [37] | Fan C,Yu S,Wang C,Xing Y.A causal C-A mutation in the second exon ofGS3 highly associated with rice grain length and validated as a functional marker. Theor Appl Genet,2009,118(3):465-472. |
| [38] | Yan S,Zou G,Li S,Wang H,Liu H,Zhai G,Guo P,Song H,Yan C,Tao Y.Seed size is determined by the combinations of the genes controlling different seed characteristics in rice.Theor Appl Genet,2011,123(7):1173-1181. |
| [39] | Hu Z,He H,Zhang S,Sun F,Xin X,Wang W,Qian X,Yang J,Luo X.A kelch motif-containing serine/threonine protein phosphatase determines the large grain QTL trait in rice.J Integ Plant Biol,2012,54(12):979-990. |
| [40] | Qi P,Lin Y S,Song X J,Shen J B,Huang W,Shan J X,Zhu M Z,Jiang L,Gao J P,Lin H X.The novel quantitative trait locusGL3.1 controls rice grain size and yield by regulating Cyclin-T1;3. Cell Res,2012,22(12):1666-1680. |
| [41] | Zhang X J,Wang J F,Huang J,Lan H,Wang C,Yin C,Wu Y,Tang H,Qian Q,Li J,Zhang H.Rare allele ofOsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci,2012,109(52):21534-21539. |
| [42] | Hong Z,Ueguchi-Tanaka M,Shimizu-Sato S,Inukai Y,Fujioka S,Shimada Y,Takatsuto S,Agetsuma M,Yoshida S,Watanabe Y,Uozu S,Kitano H,Ashikari M,Matsuoka M.Loss-of-function of a rice brassinosteroid biosynthetic enzyme, C-6 oxidase, prevents theorganized arrangement and polar elongation of cells in the leaves and stem.Plant J,2002,32(4):495-508. |
| [43] | Mori M,Nomura T,Ooka H,Ishizaka M,Yokota T,Sugimoto K,Okabe K,Kajiwara H,Satoh K,Yamamoto K,Hirochika H,Kikuchi S.Isolation and characterization of a rice dwarf mutant with a defect in brassinosteroid biosynthesis.Plant Physiol,2002,130(3):1152-1161. |
| [44] | Wu L,Ren D,Hu S,Li G,Dong G,Jiang L,Hu X,Ye W,Cui Y,Zhu L,Hu J,Zhang G,Gao Z,Zeng D,Qian Q,Guo L.Down-regulation of a nicotinate phosphoribosyl- transferase gene,OsNaPRT1, leads to withered leaf tips. Plant Physiol,2016,171(2):1085-1098. |
| [45] | Hu X,Qian Q,Xu T,Zhang Y,Dong G,Gao T,Xie Q,Xue Y.The U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase TUD1 functions with a heterotrimeric G α subunit to regulate brassinosteroid-mediated growth in rice.PLoS Genet,2013,9(3):e1003391. |
| [46] | Jiang Y,Bao L,Jeong S Y,Kim S K,Xu C,Li X,Zhang Q.XIAO is involved in the control of organ size by contributing to the regulation of signaling and homeostasis of brassinosteroids and cell cycling in rice.Plant J,2012,70(3):398-408. |
| [47] | Wu Y,Fu Y,Zhao S,Gu P,Zhu Z,Sun C,Tan L.CLUSTERED PRIMARY BRANCH 1, a new allele of DWARF11, controls panicle architecture and seed size in rice. Plant Biotechnol J,2016,14(1):377-386. |
| [48] | Tanabe S,Ashikari M,Fujioka S,Takatsuto S,Yoshida S,Yano M,Yoshimura A,Kitano H,Matsuoka M,Fujisawa Y,Kato H,Iwasaki Y.A novel cytochrome P450 is implicated in brassinosteroid biosynthesis via the characterization of a rice dwarf mutant,dwarf11, with reduced seed length.Plant Cell,2005,17(3):776-790. |
| [49] | Luo J,Liu H,Zhou T,Huang X,Shangguan Y,Zhu J,Li Y,Zhao Y,Wang Y,Zhao Q,Wang A,Wang Z,Sang T,Wang Z,Han B.An-1 encodes a basic helix-loop-helix protein that regulates awn development, grain size, and grain number in rice. Plant Cell,2013,25(9):3360-3376. |
| [50] | Zhang B W,Wang X L,Zhao Z Y,Wang R,Huang X,Zhu Y,Yuan L,Wang Y,Xu X,Burlingame A L,Gao Y,Sun Y,Tang W.OsBRI1 activates BR signaling by preventing binding between the TPR and kinase domains of OsBSK3 via phosphorylation. Plant Physiol,2016,170(2):1149-1161. |
| [51] | She K C,Kusano H,Koizumi K,Yamakawa H,Hakata M,Imamura T,Fukuda M,Naito N,Tsurumaki Y,Yaeshima M,Tsuge T,Matsumoto K,Kudoh M,Itoh E,Kikuchi S,Kishimoto N,Yazaki J,Ando T,Yano M,Aoyama T,Sasaki T,Satoh H,Shimada H.A novel factorfloury endosperm 2 is involved in regulation of rice grain size and starch quality. Plant Cell,2010,22(10):3280-3294. |
| [52] | Weng J F,Gu S,Wan X,Gao H,Guo T,Su N,Lei C,Zhang X,Cheng Z,Guo X,Wang J,Jiang L,Zhai H,Wan J M.Isolation and initial characterization of GW5, a major QTL associated with rice grain width and weight. Cell Res,2008,18(12):1199-1209. |
| [53] | Shomura A,Izawa T,Ebana K,Ebitani T,Kanegae H,Konishi S,Yano M.Deletion in a gene associated with grain size increased yields during rice domestication.Nat Genet,2008,40(8):1023-1028. |
| [54] | Li Y,Fan C,Xing Y,Jiang Y,Luo L,Sun L,Shao D,Xu C,Li X,Xiao J,He Y,Zhang Q.Natural variation inGS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat Genet,2011,43(12):1266-1269. |
| [55] | Xu C,Liu Y,Li Y,Xu X,Xu C,Li X,Xiao J,Zhang Q.Differential expression ofGS5 regulates grain size in rice. J Exp Bot,2015,66(9):2611-2623. |
| [56] | Tong H,Liu L,Jin Y,Du L,Yin Y,Qian Q,Zhu L,Chu C.DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING acts as a direct downstream target of a GSK3/SHAGGY-Like kinase to mediate brassinosteroid responses in rice.Plant Cell,2012,24(6):2562-2577. |
| [57] | Xia K F,Ou X J,Tang H D,Wang R,Wu P,Jia Y,Wei X,Xu X,Kang S H,Kim S K,Zhang M.Rice microRNA osa-miR1848 targets the obtusifoliol 14 ademethylase geneOsCYP51G3 and mediates the biosynthesis of phytosterols and brassinosteroids during development and in response to stress.New Phytol,2015,208(3):790-802. |
| [58] | Zhang Y C,Yu Y,Wang C Y,Li Z Y,Liu Q,Xu J,Liao J Y,Wang X J,Qu L H,Chen F,Xin P,Yan C,Chu J,Li H Q,Chen Y Q.Overexpression of microRNA OsmiR397 improves rice yield by increasing grain size and promoting panicle branching.Nat Biotechnol,2013,31(9):848-852. |
| [59] | Kitagawa K,Kurinami S,Oki K,Abe Y,Ando T,Kono I,Yano M,Kitano H,Iwasaki Y.A novel kinesin 13 protein regulating rice seed length.Plant Cell & Physiol,2010,51(8):1315-1329. |
| [60] | Miura K,Agetsuma M,Kitano H,Yoshimura A,Matsuoka M,Jacobsen S E,Ashikari M.A metastableDWARF1 epigenetic mutant affecting plant stature in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci,2009,106(27):11218-11223. |
| [61] | Izawa Y,Takayanagi Y,Inaba N,Abe Y,Minami M,Fujisawa Y,Kato H,Ohki S,Kitano H,Iwasaki Y.Function and expression pattern of the α subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein in rice. Plant&Cell Physiol,2010,51(2):271-281. |
| [62] | Ashikari M,Wu J,Yano M,Sasaki T,Yoshimura A.Rice gibberellin-insensitive dwarf mutant geneDwarf 1 encodes the alpha-subunit of GTP-binding protein. The Proc Natl Acad Sci,1999,96(18):10284-10289. |
| [63] | Wang L,Xu Y Y,Ma Q B,Li D,Xu Z H,Chong K.Heterotiomeric G protein alpha subunit is involved in rice brassinosteroid response.Cell Res,2006,16(12):916-922. |
| [64] | Ishimaru K,Hirotsu N,Madoka Y,Murakami N,Hara N,Onodera H,Kashiwagi T,Ujiie K,Shimizu B,Onishi A,Miyagawa H,Katoh E.Loss of function of the IAA-glucose hydrolase geneTGW6 enhances rice grain weight and increases yield.Nat Genet,2013,45(6):707-711. |
| [65] | Song X J,Kuroha T,Ayano M,Furuta T,Nagai K,Komeda N,Segami S,Miura K,Ogawa D,Kamura T,Suzuki T,Higashiyama T,Yamasaki M,Mori H,Inukai Y,Wu J,Kitano H,Sakakibara H,Jacobsen S E,Ashikari M.Rare allele of a previously unidentified histone H4 acetyltransferase enhances grain weight, yield, and plant biomass in rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci,2015,112(1):76-81. |
| [66] | Tong H,Jin Y,Liu W,Li F,Fang J,Yin Y,Qian Q,Zhu L,Chu C.DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING, a new member of the GRAS family,plays positive roles in brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Plant J,2009,58(5):803-816. |
| [67] | Sun L J,Li X J,Fu Y C,Zhu Z,Tan L,Liu F,Sun X,Sun X,Sun C. GS6, a member of the GRAS gene family, negatively regulates grain size in rice. J Integr Plant Biol,2013,55(10):938-949. |
| [68] | Tanaka A,Nakagawa H,Tomita C,Shimatani Z,Ohtake M,Nomura T,Jiang CJ,Dubouzet JG,Kikuchi S,Sekimoto H,Yokota T,Asami T,Kamakura T,Mori M.BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1, encoding a helix-loop-helix protein, is a novel gene involved in brassinosteroid signaling and controls bending of the lamina joint in rice. Plant Physiol,2009,151(2):669-680. |
| [69] | Zhang S,Wang S,Xu Y,Yu C,Shen C,Qian Q,Geisler M, Jiang de A, Qi Y. The auxin response factor,OsARF19, controls rice leaf angles through positively regulating OsGH3-5 and OsBRI1.Plant, Cell & Environ,2015,38(4):638-654. |
| [70] | Li J,Chu H,Zhang Y,Mou T,Mou T,Wu C,Zhang Q,Xu J.The riceHGW gene encodes an ubiquitin- associated (UBA) domain protein that regulates heading date and grain weight. PLoS ONE,2012,7(3):e34231. |
| [71] | Liu S,Hua L,Dong S,Chen H,Zhu X,Jiang J,Zhang F,Li Y,Fang X,Chen F.OsMAPK6, a mitogen-activated protein kinase, influences rice grain size and biomass production.Plant J,2015,84(4):672-681. |
| [72] | Wang Y,Xiong G,Hu J,Jiang L,Yu H,Xu J,Fang Y,Zeng L,Xu E,Xu J,Ye W,Meng X,Liu R,Chen H,Jing Y,Wang Y,Zhu X,Li J,Qian Q.Copy number variation at theGL7locus contributes to grain size diversity in rice.Nat Genet,2015,47(8):944-948. |
| [73] | Wang S,Li S,Liu Q,Wu K,Zhang J,Wang S,Wang Y,Chen X,Zhang Y,Gao C,Wang F,Huang H,Fu X.TheOsSPL16-GW7 regulatory module determines grain shape and simultaneously improves rice yield and grain quality.Nat Genet,2015,47(8):949-954. |
| [74] | Zhou Y,Miao J,Gu H,Peng X,Leburu M,Yuan F,Gu H,Gao Y,Tao Y,Zhu J,Gong Z,Yi C,Gu M,Yang Z,Liang G.Natural variations inSLG7 regulate grain shape in rice.Genetics,2015,201(4):1591-1599. |
| [75] | Si L,Chen J,Huang X,Gong H,Luo J,Hou Q,Zhou T,Lu T,Zhu J,Shangguan Y,Chen E,Gong C,Zhao Q,Jing Y,Zhao Y,Li Y,Cui L,Fan D,Lu Y,Weng Q,Wang Y,Zhan Q,Liu K,Wei X,An K,An G,Han B.OsSPL13 controls grain size in cultivated rice. Nat Genet,2016,48(4):447-456. |
| [76] | Bai M Y,Zhang L Y,Gampala S S,Zhu S W,Song W Y,Chong K,Wang Z Y.Functions of OsBZR1 and 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signaling in rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci,2007,104(34):13839-13844. |
| [77] | Xu F,Fang J,Ou S,Gao S,Zhang F,Du L,Xiao Y,Wang H,Sun X,Chu J,Wang G,Chu C.Variations inCYP78A13 coding region influence grain size and yield in rice. Plant, Cell & Environ,2015,38(4):800-811. |
| [78] | Yang W,Gao M,Yin X,Liu J,Xu Y,Zeng L,Li Q,Zhang S,Wang J,Zhang X,He Z.Control of rice embryo development, shoot apical meristem maintenance, and grain yield by a novel cytochrome P450.Mol Plant,2013,6(6):1945-1960. |
| [79] | Tanabe S,Mieda K,Ashikari M,Kitano H,Iwasaki Y.Mapping of small and round seed 1 gene in rice.Rice Genet Newsl,2007,23: 44-47. |
| [80] | Zhu K,Tang D,Yan C,Chi Z,Yu H,Chen J,Liang J,Gu M,Cheng Z.ERECT PANICLE2 encodes a novel protein that regulates panicle erectness in indica rice. Genetics,2010,184(2):343-350. |
| [81] | Feng Z M,Wu C,Wang C,Roh J,Zhang L,Chen J,Zhang S,Zhang H,Yang C,Hu J,You X,Liu X,Yang X,Guo X,Zhang X,Wu F,Terzaghi W,Kim S K,Jiang L,Wan J M.SLG controls grain size and leaf angle by modulating brassinosteroid homeostasis in rice. J Exp Bot,2016,67: 4241-4253. |
| [82] | Li D,Wang L,Wang M,Xu Y Y,Luo W,Liu Y J,Xu Z H,Li J,Chong K.EngineeringOsBAK1 gene as a molecular tool to improve rice architecture for high yield. Plant Biotechnol J,2009,7(14):791-806. |
| [83] | Wang S,Wu K,Yuan Q,Liu X,Liu Z,Lin X,Zeng R,Zhu H,Dong G,Qian Q,Zhang G,Fu X.Control of grain size, shape and quality byOsSPL16 in rice. Nat Genet,2012,44(8):950-954. |
| [84] | Zhang L G,Cheng Z,Qin R,Qiu Y,Wang J L,Cui X,Gu L,Zhang X,Guo X,Wang D,Jiang L,Wu C Y,Wang H,Cao X,Wan J M.Identification and characterization of an epi-allele of FIE1 reveals a regulatory linkage between two epigenetic marks in rice. Plant Cell,2012,24(11):4407-4421. |
| [85] | Li S,Zhou B,Peng X,Kuang Q,Huang X,Yao J,Du B,Sun M X.OsFIE2 plays an essential role in the regulation of rice vegetative and reproductive development. New Phytol,2014,201(1):66-79. |
| [86] | Jin J,Hua L,Zhu Z,Tan L,Zhao X,Zhang W,Liu F,Fu Y,Cai H,Sun X,Gu P,Xie D,Sun C.GAD1 encodes a secreted peptide that regulates grain number, grain length and awn development in rice domestication. Plant Cell,2016,28(10):2453-2463. |
| [87] | Li J,Jiang J,Qian Q,Xu Y,Zhang C,Xiao J,Du C,Luo W,Zou G,Chen M,Huang Y,Feng Y,Cheng Z,Yuan M,Chong K.Mutation of riceBC12/GDD1, which encodes a kinesin-like protein that binds to a GA biosynthesis gene promoter, leads to dwarfism with impaired cell elongation. Plant Cell,2011,23(2):628-640. |
| [88] | Nakagawa H,Tanaka A,Tanabata T,Ohtake M,Fujioka S,Nakamura H,Ichikawa H,Mori M.SHORT GRAIN1 decreases organ elongation and brassinosteroid response in rice.Plant Physiol,2012,158(3):1208-1219. |
| [89] | Yan C J,Zhou J H,Yan S,Chen F,Yeboah M,Tang S Z,Liang G H,Gu M H.Identification and characterization of a major QTL responsible for erect panicle trait injaponica rice(Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet,2007,115(8):1093-1100. |
| [90] | Huang X,Qian Q,Liu Z,Sun H,He S,Luo D,Xia G,Chu C,Li J,Fu X.Natural variation at theDEP1 locus enhances grain yield in rice. Nat Genet,2009,41(4):494-497. |
| [91] | Fumio T S,Yasushi K,Hiroshi K,Haruko O,Akemi T,Naho H,Akio M,Hirohiko H,Hidemi K,Masahiro Y,Seiichi T.A loss-of-function mutation of riceDENSE PANICLE 1 causes semi-dwarfness and slightly increased number of spikelets. Breeding Sci,2011,61(1):17-25. |
| [92] | Sun H,Qian Q,Wu K,Luo J,Wang S,Zhang C,Ma Y,Liu Q,Huang X,Yuan Q,Han R,Zhao M,Dong G,Guo L,Zhu X,Gou Z,Wang W,Wu Y,Lin H,Fu X.Heterotrimeric G proteins regulate nitrogen-use efficiency in rice.Nat Genet,2014,46(4):652-656. |
| [93] | Li M,Li X,Zhou Z,Wu P,Fang M,Pan X,Lin Q,Luo W,Wu G,Li H.Reassessment of the four yield-related genesGn1a, DEP1, GS3, and IPA1 in rice using a CRISPR/Cas9 system. Front Plant Sci,2016,7: 377. |
| [94] | Hong Z,Ueguchi-Tanaka M,Fujioka S,Takatsuto S,Yoshida S,Hasegawa Y,Ashikari M,Kitano H,Matsuoka M.The ricebrassinosteroid-deficient dwarf2 mutant, defective in the rice homolog of Arabidopsis DIMINUTO/DWARF1, is rescued by the endogenously accumulated alternative bioactive brassinosteroid, dolichosterone. Plant Cell,2005,17(8):2243-2254. |
| [95] | Segami S,Kono I,Ando T,Yano M,Kitano H,Miura K,Iwasaki Y.Small and round seed 5 gene encodes alpha-tubulin regulating seed cell elongation in rice.Rice,2012,5(1):4. |
| [96] | Sunohara H,Kawai T,Shimizu-Sato S,Sato Y,Sato K,Kitano H.A dominant mutation ofTWISTED DWARF 1 encoding an α-tubulin protein causes severe dwarfism and right helical growth in rice. Genes & Genetic Systems,2009,84(3):209-218. |
| [97] | Fujioka S,Yokota T.Biosynthesis and metabolism of brassinosteroids. Ann Rev Plant Biol,2003,54: 137-164. |
| [98] | Moon J,Parry G,Estelle M.The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and plant development.Plant Cell,2004,16: 3181-3195. |
| [99] | Bent A F.Plant mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades: Negative regulatory roles turn out positive.Proc Natl Acad Sci,2001,98(3):784-786. |
| [100] | Khan M,Rozhon W,Bigeard J,Pflieger D,Husar S,Pitzschke A,Teige M,Jonak C,Hirt H,Poppenberger B.Brassinosteroid-regulated GSK3/Shaggy-like kinases phosphorylate mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinases, which control stomata development inArabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem,2013,288(11):7519-7527. |
| [101] | Boosani C S,Agrawal D K.Methylation and microRNA- mediated epigenetic regulation of SOCS3.Mol Biol Rep,2015,42(4):853-872. |
| [102] | Chaudhury A M,Koltunow A,Payne T,Luo M,Tucker M R,Dennis E S,Peacock W J.Control of early seed development.Ann Rev Cell & Dev Biol,2001,17(3):677-699. |
| [103] | Urano D,Chen J G,Botella J R,Jones A M.Heterotrimeric G protein signalling in the plant kingdom.Open Biol,2013,3: 120-186. |
| [104] | Ullah H,Chen J G,Young J C,Im K H,Sussman M R,Jones A M.Modulation of cell proliferation by heterotrimeric G protein inArabidopsis.Science,2001,292(5524):2066-2069. |
| [105] | Lease K A,Wen J,Li J,Doke J T,Liscum E,Walker J C.A mutantArabidopsis heterotrimeric G-protein beta subunit affects leaf, flower, and fruit development.Plant Cell,2001,13(12):2631-2641. |
| [106] | Li S,Liu Y,Zheng L,Chen L,Li N,Corke F,Lu Y,Fu X,Zhu Z,Bevan M W,Li Y.The plant-specific G protein gamma subunit AGG3 influences organ size and shape inArabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol,2012,194(3):690-703. |
| [107] | Gao X,Zhang X,Lan H,Huang J,Wang J,Zhang H S.The additive effects ofGS3 and qGL3 on rice grain length regulation revealed by genetic and transcriptome comparisons. BMC Plant Biol,2015,15: 156. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 伏荣桃, 陈诚, 王剑, 赵黎宇, 陈雪娟, 卢代华. 转录组和代谢组联合分析揭示稻曲病菌的致病因子[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 375-385. |
| [5] | 丁正权, 潘月云, 施扬, 黄海祥. 基于基因芯片的嘉禾系列长粒优质食味粳稻综合评价与比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | 吕宙, 易秉怀, 陈平平, 周文新, 唐文帮, 易镇邪. 施氮量与移栽密度对小粒型杂交水稻产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [10] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [11] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [12] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [13] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [14] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [15] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||