
中国水稻科学 ›› 2016, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (2): 143-151.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.5154
杨正福1, 张迎信1, 孙廉平1,2, 张沛沛1, 轩丹丹1, 刘嶺1,3, 胡霞1, 李紫荷1, 占小登1, 吴玮勋1, 曹立勇1,*( ), 程式华1,*(
), 程式华1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2015-10-19
修回日期:2015-12-11
出版日期:2016-03-10
发布日期:2016-03-10
通讯作者:
曹立勇,程式华
作者简介:# 共同第一作者;
基金资助:
Zheng-fu YANG1, Ying-xin ZHANG1, Lian-ping SUN1,2, Pei-pei ZHANG1, Dan-dan XUAN1, Ling LIU1,3, Xia HU1, Zi-he LI1, Xiao-deng ZHAN1, Wei-xun WU1, Li-yong CAO1,*( ), Shi-hua CHENG1,*(
), Shi-hua CHENG1,*( )
)
Received:2015-10-19
Revised:2015-12-11
Online:2016-03-10
Published:2016-03-10
Contact:
Li-yong CAO, Shi-hua CHENG
About author:# These authors contributed equally to this work;
摘要:
在60Co-γ射线辐射诱变籼稻中恢8015的突变体库内发现了一个无花粉型雄性不育突变体gamyb5。gamyb5 的株型、株高、分蘖数等农艺性状与野生型中恢8015无差异,而其花药细长且呈白色半透明状,花药中无花粉粒。花药半薄切片观察结果表明,gamyb5的小孢子母细胞减数分裂异常,没有形成正常的四分体和小孢子,并且绒毡层异常伸长,细胞程序性死亡延迟。对以gamyb5 为母本,与野生型中恢8015 和广亲和粳稻品种02428分别配制的杂交组合遗传分析表明,gamyb5 突变性状受一个隐性核基因控制。利用gamyb5 和02428 杂交的F2定位群体,最终将突变基因精细定位于第1染色体长臂的ZF-29和ZF-31两个标记之间,物理距离约16.9 kb。对该区域内2个完整的开放阅读框测序分析发现,编码受赤霉素诱导的MYB转录因子基因LOC_Os01g0812000的第2外显子存在8个碱基的缺失,导致翻译提前终止。qRT-PCR检测到影响花药发育的调控因子UDT1、TDR、CYP703A3和CYP704B2的表达量在突变体中比野生型中极显著降低。进一步证明GAMYB在花药减数分裂和绒毡层细胞程序性死亡过程中起关键作用。
中图分类号:
杨正福, 张迎信, 孙廉平, 张沛沛, 轩丹丹, 刘嶺, 胡霞, 李紫荷, 占小登, 吴玮勋, 曹立勇, 程式华. 水稻雄性不育突变体gamyb5的鉴定与基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(2): 143-151.
Zheng-fu YANG, Ying-xin ZHANG, Lian-ping SUN, Pei-pei ZHANG, Dan-dan XUAN, Ling LIU, Xia HU, Zi-he LI, Xiao-deng ZHAN, Wei-xun WU, Li-yong CAO, Shi-hua CHENG. Identification and Gene Mapping of Male Sterile Mutant gamyb5 in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(2): 143-151.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 上游引物 Forward primer (5'-3') | 下游引物 Reverse primer (5'-3') | 实验目的 Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD0114 | GCTTGTGGCAATTGGG | CGCCTGATGGATGTCG | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-26 | GATCATACCATCATCAGAAGCAGT | CAAGCAGCCCACATCACAGC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-28 | TCTCGCTCCTCTTCGCCCAAAC | ACCCGCACCAGTACGTGACCC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-29 | GGCAGCAGCAATCACAACAC | TCGGCACTTTCTTTACTCAACT | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-31 | CAGCCAGGCACCGCAGCAAA | AAGAAAGGCAGAGCAAGAAGG | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-32 | GCACGCTTCTCGCTACGCTAT | GCTCCAGGAACACCACCAACTC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-38 | TGGGTGCGAGGTTTCTGTGA | AATGAATGCGTGTTTCCTGT | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| InDel15 | CAACCCCTCCAAATACCTGA | ACCGTGTTCATGCCTTTCAC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| GAMYB5 | ACTGGAGCACTGCTGATCTTC | GCACATCTTCTCAGTTGCCAG | gamyb5位点检测gamyb5 deletion site detection |
| cDNA | CCCCTGCGAGTCCAATCTAC | ACCGGCTTATCTCCATGCAC | cDNA测序cDNA sequencing |
表1 精细定位和测序引物
Table 1 Makers used for fine mapping and sequencing.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 上游引物 Forward primer (5'-3') | 下游引物 Reverse primer (5'-3') | 实验目的 Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD0114 | GCTTGTGGCAATTGGG | CGCCTGATGGATGTCG | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-26 | GATCATACCATCATCAGAAGCAGT | CAAGCAGCCCACATCACAGC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-28 | TCTCGCTCCTCTTCGCCCAAAC | ACCCGCACCAGTACGTGACCC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-29 | GGCAGCAGCAATCACAACAC | TCGGCACTTTCTTTACTCAACT | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-31 | CAGCCAGGCACCGCAGCAAA | AAGAAAGGCAGAGCAAGAAGG | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-32 | GCACGCTTCTCGCTACGCTAT | GCTCCAGGAACACCACCAACTC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| ZF-38 | TGGGTGCGAGGTTTCTGTGA | AATGAATGCGTGTTTCCTGT | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| InDel15 | CAACCCCTCCAAATACCTGA | ACCGTGTTCATGCCTTTCAC | 精细定位Fine mapping |
| GAMYB5 | ACTGGAGCACTGCTGATCTTC | GCACATCTTCTCAGTTGCCAG | gamyb5位点检测gamyb5 deletion site detection |
| cDNA | CCCCTGCGAGTCCAATCTAC | ACCGGCTTATCTCCATGCAC | cDNA测序cDNA sequencing |
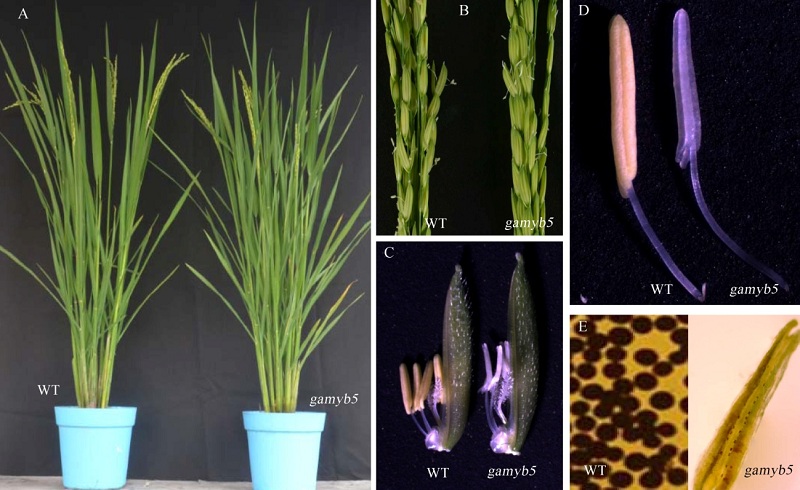

图1 野生型中恢8015(WT)与突变体gamyb5 抽穗期的表型比较 A-中恢8015和突变体gamyb5的植株; B-中恢8015和突变体gamyb5的穗部表型; C-中恢8015和突变体gamyb5的颖花形态;D-中恢8015和突变体gamyb5的花药表型。E-中恢8015和突变体gamyb5的花粉育性。
Fig. 1. Phenotypic comparison of wild type Zhonghui 8015(WT)and gamyb5 . A, Plant of Zhonghui 8015 and the gamyb5 mutant at the heading stage; B, Panicle of Zhonghui 8015 and the gamyb5 mutant; C, Spikelet of the wild type Zhonghui 8015 and gamyb5 ; D, Anther of Zhonghui 8015 and gamyb5 mutant; E, Pollen fertility of Zhonghui 8015 and gamyb5.
| 组合 Cross | Seed-setting rate of F1 /% | F2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生型植株数 Number of wild type plants | 突变体植株数 Number of mutant plants | ||||
| gamyb5/02428 | 86.8 | 1895 | 642 | 0.14 | 3.84 |
| gamyb5/中恢8015 gamyb5/Zhonghui 8015 | 87.2 | 234 | 70 | 0.63 | |
| 中恢8015/02428 Zhonghui 8015/02428 | 87.6 | 960 | 0 | - | |
表2 突变体gamyb5的遗传分析
Table 2 Genetic analysis of the gamyb5 mutant.
| 组合 Cross | Seed-setting rate of F1 /% | F2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生型植株数 Number of wild type plants | 突变体植株数 Number of mutant plants | ||||
| gamyb5/02428 | 86.8 | 1895 | 642 | 0.14 | 3.84 |
| gamyb5/中恢8015 gamyb5/Zhonghui 8015 | 87.2 | 234 | 70 | 0.63 | |
| 中恢8015/02428 Zhonghui 8015/02428 | 87.6 | 960 | 0 | - | |

图2 突变基因的图位克隆 A-突变基因的初步定位; B-突变基因的精细定位; C-精细基因定位区间中的预测基因; D-候选基因 LOC_Os01g0812000 的结构及其在突变体中的突变位点(8个碱基缺失)。
Fig.2. Positional cloning of the gamyb5 mutated gene. A, Preliminary mapping of gamyb5; B, Fine mapping of gamyb5; C, Prediction of the candidate gene within the fine-mapped region; D, The structure of candidate gene LOC_Os01g0812000 and the mutation site in gamyb5 mutant (8 bases deleted).
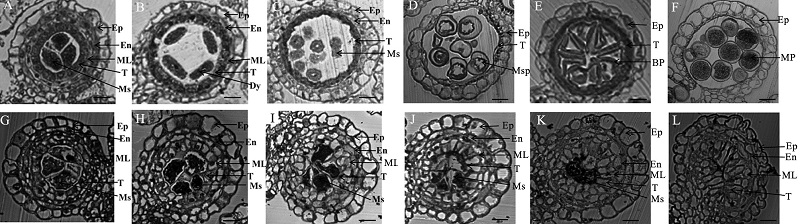
图3 gamyb5突变体和中恢8015野生型不同发育时期花药半薄横切观察 A到F为野生型,G到L为突变体gamyb5。A和G为花药发育第7阶段时的横切; B和H为第8a阶段时花药横切; C和I为第9阶段时花药横切; D和J为第10阶段时花药横切; E和K为第11阶段时花药横切; F和L为第12阶段时花药横切。Ep-表皮层; En-内皮层; ML-中层; T-绒毡层; Ms-小孢子母细胞; Dy-二分体; Msp-小孢子; BP-二孢花粉; MP-成熟花粉。标尺为20 μm。
Fig. 3. Transverse section analyses of the wild type and gamyb5 anthers in various of developmental stages. A to E, Wild type; G to L, The gamyb5 mutant. A and G, Cross-section of anthers at the stage 7; B and H, Cross-section of anthers at the stage 8; C and I, Cross-section of anthers at the stage 9; D and J, Cross-section of anthers at the stage 10; E and K, Cross-section of anthers at the stage 11; F and L, Cross-section of anthers at the stage 12. Ep, Epidermis; En, Endothecium; ML, Middle layer; T, Tapetum; Ms, Microsporocyte; Dy, Dyad cell; Msp, Microspore; BP, Biceullar pollen; MP, Mature pollen. Bars = 20 μm.
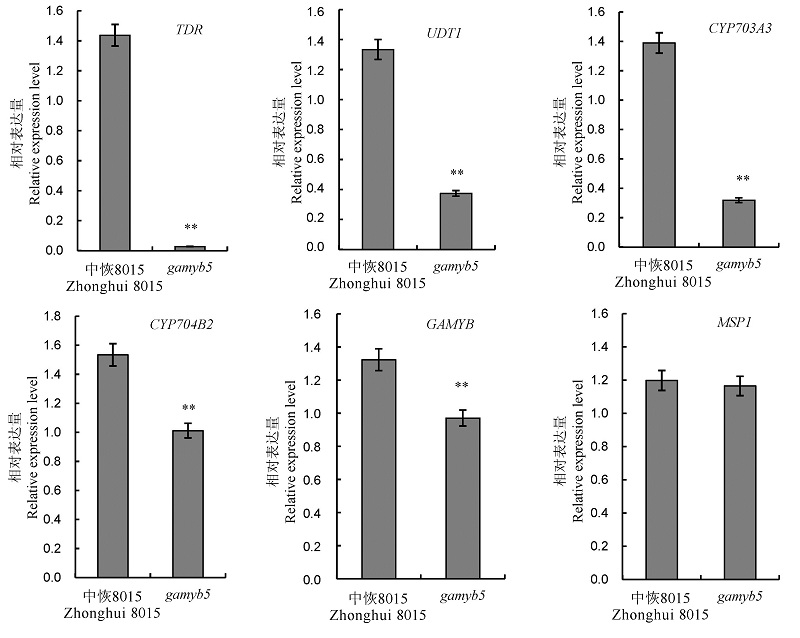
图4 实时荧光定量 PCR 分析野生型与突变体中水稻隐性核雄性不育相关基因的表达 **在P=0.01水平上差异显著。
Fig. 4. Expression analysis of male sterility-associated genes of the wild type and the mutant. **significant at P=0.01.
| [1] | McCormick S. Male gametophyte development.Plant Cell,1993, 5: 1265-1275. |
| [2] | Scott R J, Spielman M, Dickinson H G.Stamen structure and function.Plant Cell, 2004,16(Suppl): 46-60. |
| [3] | Ma H.Molecular genetic analyses of microsporogenesis and microgametogenesis in flowering plants.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 2005, 56: 393-434. |
| [4] | Zhang D B, Wilson Z A.Stamen specification and anther development in rice.Chin Sci Bull, 2009, 54: 2342-2353. |
| [5] | Zhang D B, Luo X, Zhu L, et al.Cytological analysis and genetic control of rice anther development.J Genet Genom, 2011, 38: 379-390. |
| [6] | Zhang D B, Yang L.Specification of tapetum and microsporocyte cells within the anther.Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2014, 17C: 49-55. |
| [7] | 马西青, 方才臣, 邓联武, 等. 水稻隐性核雄性不育基因研究进展及育种应用探讨. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(5): 511-520. |
| Ma X Q, Fang C C, Deng L W, et al.Research progress and breeding application of recessive genic male sterility genes in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2012, 26(5): 511-520. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Nonomura K, Miyoshi K.The MSP1 gene is necessary to restrict the number of cells entering into male and female sporogenesis and to initiate anther wall formation in rice.Plant Cell, 2003, 15(8): 1728-1739. |
| [9] | Ken-Ichi N, Mutsuko N, Toshiyuki F, et al.The novel gene HOMOLOGOUS PAIRING ABERRATION IN RICE MEIOSIS1 of rice encodes a putative coiled-coil protein required for homologous chromosome pairing in meiosis.Plant J, 2004, 16(4): 1008-1020. |
| [10] | Nonomura K I, Nakano M, Murata K, et al.An insertional mutation in the rice PAIR2 gene, the ortholog of Arabidopsis ASY1, results in a defect in homologous chromosome pairing during meiosis.Mol Genet Genom, 2004, 271(2): 121-129. |
| [11] | Yuan W Y, Li X W, Chang Y X, et al.Mutation of the rice gene PAIR3 results in lack of bivalent formation in meiosis.Plant J, 2009, 59(2): 303-315. |
| [12] | Sandra N Ol, Elizabeth S D, Rudy D.ABA regulates apoplastic sugar transport and is a potential signal for cold-induced pollen sterility in rice.Plant Cell Physiol, 2007, 48(9): 1319-1330. |
| [13] | Ken-Ichi N, Akane M, Mutsuko N, et al.A germ cell-specific gene of the ARGONAUTE family is essential for the progression of premeiotic mitosis and meiosis during sporogenesis in rice.Plant Cell, 2007, 19(8): 2583-2594. |
| [14] | Wang C, Huang W, Ying Y H, et al.Functional characterization of the rice SPX-MFS family reveals a key role of OsSPX-MFS1 in controlling phosphate homeostasis in leaves.New Phytol, 2012, 196(1): 139-148. |
| [15] | Li L, Li Y X, Song S F.An anther development F-box (ADF) protein regulated by tapetum degeneration retardation (TDR) controls rice anther development.Planta, 2015, 241(1): 157-166. |
| [16] | Jung K H, Han M J, Lee Y S.Rice undeveloped tapetum1 is a major regulator of early tapetum development.Plant Cell, 2005, 17(10): 2705-2722. |
| [17] | Liu Z H, Bao W J.Identification of gamyb-4 and analysis of the regulatory role of GAMYB in rice anther development.J Integ Plant Biol, 2010, 52(7): 670-678. |
| [18] | Li H, Yuan Z.PERSISTENT TAPETAL CELL1 Encodes a PHD-finger protein that is required for tapetal cell death and pollen development in rice.Plant Physiol, 2011, 156(2): 615-630. |
| [19] | Li X W, Gao X Q.Rice APOPTOSIS INHIBITOR5 coupled with two DEAD-box adenosine 5'-triphosphate-dependent RNA helicases regulates tapetum degeneration.Plant Cell, 2011, 23(4): 1416-1434. |
| [20] | Jung K H, Han M J.Wax-deficient anther1 is involved in cuticle and wax production in rice anther walls and is required for pollen development.Plant Cell, 2006, 18(11): 3015-3032. |
| [21] | Shi J, Tan H X.Defective pollen wall is required for anther and microspore development in rice and encodes a fatty acyl carrier protein reductase.Plant Cell, 2011, 23(6): 2225-2246. |
| [22] | Li H, Pinot F.Cytochrome P450 family member CYP704B2 catalyzes the ω -Hydroxylation of fatty acids and is required for anther cutin biosynthesis and pollen exine formation in rice.Plant Cell, 2010, 22(1): 173-190. |
| [23] | Yang X J, Wu D. rice CYP703A3, a cytochrome P450 hydroxylase, is essential for development of anther cuticle and pollen exine.J Integ Plant Biol, 2014, 56(10): 979-994. |
| [24] | Zhu Q H, Ramm K, Shivakkumar R, et al.The ANTHER INDEHISCENCE1 gene encoding a single MYB domain protein is involved in anther development in rice.Plant Physiol, 2004, 135(3): 1514-1525. |
| [25] | 初明光, 李双成, 王世全, 等. 一个水稻雄性不育突变体的遗传分析和基因定位. 作物学报, 2009, 35(6): 1151-1155. |
| Chu G M, Li S C, Wang S Q, et al.Genetic analysis and molecular mapping of a male sterile mutant in rice.Crop J, 2004, 135(3): 1514-1525. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 卢扬江, 郑康乐. 提取水稻DNA 的一种简易方法. 中国水稻科学, 1992, 6(1): 47-48. |
| Lu Y J, Zheng K L.A simple method for isolation of rice DNA.Chin J Rice Sci, 1992, 6(1): 47-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | Orjuela J, Garavito A, Bouniol M.A universal core genetic map for rice.Theor Appl Genet, 2010,120,563-572. |
| [28] | Rychlik W.Oligo primer analysis software version 7.0. 2nd ed. Molecular Biology Insights, Inc, Cascade, Co, 2008. |
| [29] | Aya K, Miyako Ueguchi-Tanaka M. Gibberellin modulates anther development in rice via the transcriptional regulation of GAMYB.Plant Cell, 2009, 21(5): 1453-1472. |
| [30] | Gocal, Sheldon G F. GAMYB-like genes, flowering and gibberellin signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol, 2001,127, 1682-1693. |
| [31] | Gubler F, Kalla R, Roberts J K, et al.Gibberellin-regulated expression of a MYB gene in barley aleurone cells: Evidence for Myb transactivation of a high-pI α-amylase gene promoter.Plant Cell, 1995, 7: 1879-1891. |
| [32] | Fiona J, Woodger A M, Murray F, et al.The role of GAMYB transcription factors in GA-regulated gene expression.J Plant Growth Regul, 2003, 22, 176-184. |
| [33] | Kaneko M, Inukai Y, Ueguchi-Tanaka M. loss-of-function mutations of the rice GAMYB gene impair α-amylase expression in aleurone and flower development.Plant Cell, 2004,16:1473-1487. |
| [34] | Aya K, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Kondo M, et al.Gibberellin modulates anther development in rice via the transcriptional regulation of GAMYB.Plant Cell, 2009, 21:1453-1472. |
| [35] | Wang Y, Wang Y F, Zhang D B.Identification of the rice (Oryza sativa L.) mutant msp1-4 and expression analysis of its UDT1 and GAMYB genes.J Plant Physiol Mol Biol, 2006 , 32: 527-534. |
| [36] | Morant M, Jorgensen K, Schaller H.CYP703 is an ancient cytochrome P450 in land plants catalyzing in-chain hydroxylation of lauric acid to provide building blocks for sporopollenin synthesis in pollen.Plant Cell, 2007, 19:1473-1487. |
| [37] | Dobritsa A A, Shrestha J, Morant M.CYP704B1 is a long-chain fatty acid ω-hydroxylase essential for sporopollenin synthesis in pollen of Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol, 2009, 151: 574-589. |
| [38] | Bouquin L, Pinot R, Benveniste F, et al.Cloning and functional characterization of CYP94A2, a medium chain fatty acid hydroxylase from Vicia sativa. Biochem. Biophys.Res Commun, 1999, 261: 156-162. |
| [39] | Kurdyukov S, Faust A, Trenkamp S.Genetic and biochemical evidence for involvement of HOTHEAD in the biosynthesis of long-chain alpha-omega-dicarboxylic fatty acids and formation of extracellular matrix.Planta, 2006, 224: 315-329. |
| [40] | Kandel S, Sauveplane V, Compagnon V.Characterization of a methyl jasmonate and wounding-responsive cytochrome P450 of Arabidopsis thaliana catalyzing dicarboxylic fatty acid formation in vitro.FEBS J, 2007, 274: 5116-5127. |
| [41] | Sauveplane V, Kandel S, Kastner P E.Arabidopsis thaliana CYP77A4 is the first cytochrome P450 able to catalyze the epoxidation of free fatty acids in plants.FEBS J, 2009, 276: 719-735. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||