
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (2): 166-176.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.0914
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Wenxia WANG, Liming CHEN, Haixia WANG, Youqing LIU, Ziming WU, Yongjun ZENG, Xueming TAN, Xiaohua PAN, Qinghua SHI, Yanhua ZENG*( )
)
Received:2020-09-23
Revised:2020-12-19
Online:2021-03-10
Published:2021-03-10
Contact:
Yanhua ZENG
王文霞, 陈丽明, 王海霞, 刘有清, 吴自明, 曾勇军, 谭雪明, 潘晓华, 石庆华, 曾研华*( )
)
通讯作者:
曾研华
基金资助:Wenxia WANG, Liming CHEN, Haixia WANG, Youqing LIU, Ziming WU, Yongjun ZENG, Xueming TAN, Xiaohua PAN, Qinghua SHI, Yanhua ZENG. Study on Physiological Characteristics Behind Mitigative Effects of Flooding on Low Temperature-caused Chilling Damage to Direct Seeded Early indica Rice at the Seedling Stage[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(2): 166-176.
王文霞, 陈丽明, 王海霞, 刘有清, 吴自明, 曾勇军, 谭雪明, 潘晓华, 石庆华, 曾研华. 淹水缓解直播早籼稻苗期低温冷害的生理特性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(2): 166-176.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.0914
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 苗高 Seedling height /cm | 单株根数 Root number per plant | 最大根长 Maximum root length /cm | 百株鲜质量 Fresh weight per 100 plants/mg | 百株干质量 Dry weight per 100 plants/mg | 叶长Leaf length / cm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | |||||||
| 湘早籼6号 XZX6 | Pre-T | 20.3 d | 10.9 e | 6.6 d | 182.5 f | 26.1 f | 3.5 d | 12.1 c | 6.4 d |
| LT | 19.7 e | 10.8 e | 6.6 d | 206.4 e | 30.5 e | 2.8 f | 11.0 d | 5.0 e | |
| LTF | 20.6 d | 11.5 de | 7.2 c | 209.0 d | 32.1 cd | 3.0 e | 12.0 cd | 5.8 d | |
| CK | 28.2 b | 14.3 b | 9.2 b | 229.5 a | 33.4 b | 4.4 b | 13.4 b | 9.3 b | |
| Re-LT | 22.3 c | 12.6 cd | 7.5 cd | 211.5 c | 31.4 de | 3.6 d | 11.9 cd | 7.8 c | |
| Re-LTF | 22.9 c | 13.1 c | 7.9 c | 216.4 b | 32.6 bc | 3.8 c | 13.0 b | 8.2 c | |
| Re-CK | 31.4 a | 18.0 a | 11.4 a | 231.2 a | 35.4 a | 4.9 a | 14.9 a | 11.0 a | |
| 中嘉早17 ZJZ17 | Pre-T | 23.1 c | 10.7 d | 5.2 d | 175.1 g | 25.3 f | 3.1 c | 9.2 d | 9.0 d |
| LT | 18.9 e | 10.7 d | 5.3 d | 186.0 f | 27.2 e | 2.4 e | 9.3 e | 7.1 f | |
| LTF | 19.9 d | 11.0 c | 5.5 d | 212.4 d | 32.5 d | 2.4 e | 9.8 de | 8.1 e | |
| CK | 28.4 b | 14.1 b | 7.9 b | 253.5 b | 36.4 b | 3.7 b | 10.6 c | 10.5 b | |
| Re-LT | 20.6 d | 12.6 bc | 6.6 c | 194.8 e | 33.5 d | 2.8 d | 10.8 c | 9.8 c | |
| Re-LTF | 22.6 c | 12.3 bcd | 7.0 c | 232.0 c | 35.1 c | 3.0 d | 11.3 b | 10.0 bc | |
| Re-CK | 33.2 a | 17.1 a | 10.9 a | 278.0 a | 40.2 a | 4.2 a | 12.4 a | 12.1 a | |
Table 1 Effects of flooding on agronomic characters of direct-seeded early indica rice subjected to chilling at seedling stage.
| 品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 苗高 Seedling height /cm | 单株根数 Root number per plant | 最大根长 Maximum root length /cm | 百株鲜质量 Fresh weight per 100 plants/mg | 百株干质量 Dry weight per 100 plants/mg | 叶长Leaf length / cm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | |||||||
| 湘早籼6号 XZX6 | Pre-T | 20.3 d | 10.9 e | 6.6 d | 182.5 f | 26.1 f | 3.5 d | 12.1 c | 6.4 d |
| LT | 19.7 e | 10.8 e | 6.6 d | 206.4 e | 30.5 e | 2.8 f | 11.0 d | 5.0 e | |
| LTF | 20.6 d | 11.5 de | 7.2 c | 209.0 d | 32.1 cd | 3.0 e | 12.0 cd | 5.8 d | |
| CK | 28.2 b | 14.3 b | 9.2 b | 229.5 a | 33.4 b | 4.4 b | 13.4 b | 9.3 b | |
| Re-LT | 22.3 c | 12.6 cd | 7.5 cd | 211.5 c | 31.4 de | 3.6 d | 11.9 cd | 7.8 c | |
| Re-LTF | 22.9 c | 13.1 c | 7.9 c | 216.4 b | 32.6 bc | 3.8 c | 13.0 b | 8.2 c | |
| Re-CK | 31.4 a | 18.0 a | 11.4 a | 231.2 a | 35.4 a | 4.9 a | 14.9 a | 11.0 a | |
| 中嘉早17 ZJZ17 | Pre-T | 23.1 c | 10.7 d | 5.2 d | 175.1 g | 25.3 f | 3.1 c | 9.2 d | 9.0 d |
| LT | 18.9 e | 10.7 d | 5.3 d | 186.0 f | 27.2 e | 2.4 e | 9.3 e | 7.1 f | |
| LTF | 19.9 d | 11.0 c | 5.5 d | 212.4 d | 32.5 d | 2.4 e | 9.8 de | 8.1 e | |
| CK | 28.4 b | 14.1 b | 7.9 b | 253.5 b | 36.4 b | 3.7 b | 10.6 c | 10.5 b | |
| Re-LT | 20.6 d | 12.6 bc | 6.6 c | 194.8 e | 33.5 d | 2.8 d | 10.8 c | 9.8 c | |
| Re-LTF | 22.6 c | 12.3 bcd | 7.0 c | 232.0 c | 35.1 c | 3.0 d | 11.3 b | 10.0 bc | |
| Re-CK | 33.2 a | 17.1 a | 10.9 a | 278.0 a | 40.2 a | 4.2 a | 12.4 a | 12.1 a | |
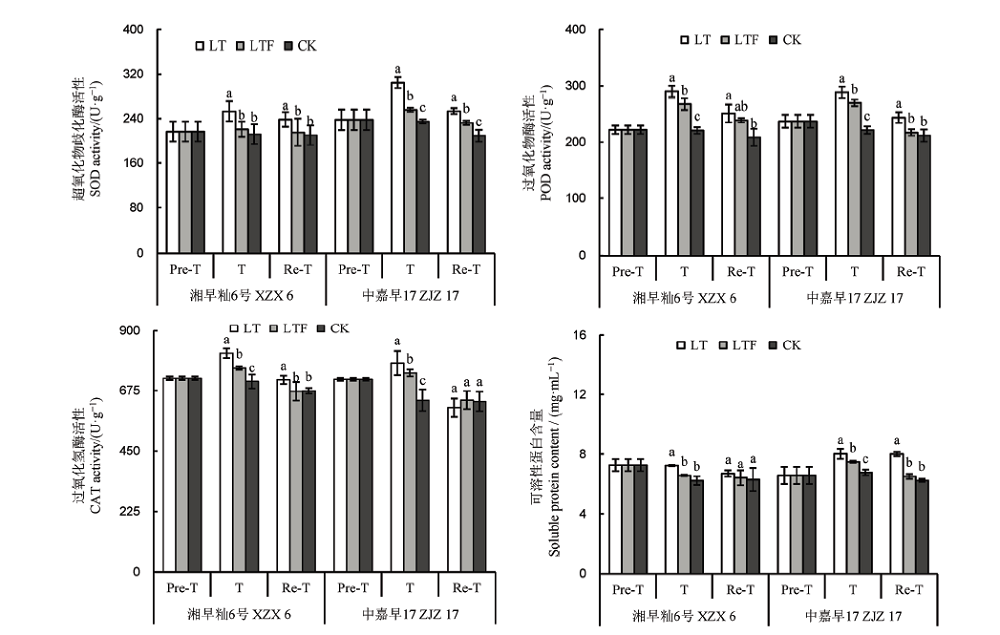
Fig. 1. Effects of flooding on antioxidant enzyme activities and soluble protein contents in direct seeded early indica rice exposed to chilling at the seedling stage. Pre-T, Before treatment; T, After 3 d of treatment; Re-T, After 3 d of recovery; LT, Low temperature; LTF, Low temperature and flooding; CK, Control. Various lowercase letters above the bars mean significant difference at 0.05 probability level. The same as figures below.
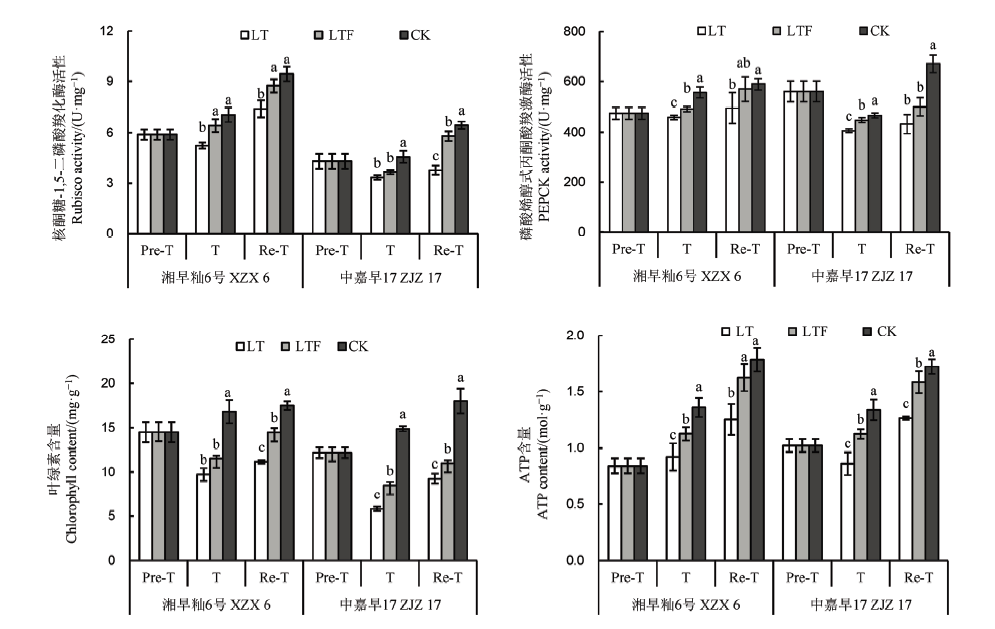
Fig. 3. Effects of flooding on photosynthetic enzyme activity and ATP content of direct seeded early indica rice subjected to chilling at the seedling stage.
| [1] | 李刚华. 特高产水稻产量形成机理及定量栽培技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2010. |
| Li G H.Study on yield formation mechanism and quantitative cultivation technology of special high-yield rice[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Ohno H, Banayo N P M C, Bueno C, Kashiwagi J I, Nakashima T, Lwama K, Corales A M, Garcia R, Kato Y. On-farm assessment of a new early-maturing drought-tolerant rice cultivar for dry direct seeding in rainfed lowlands[J]. Field Crops Research, 2018, 219: 222-228. |
| [3] | 吴杏春, 王茵, 林文雄. 水稻苗期耐冷性状的QTL分析[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2008, 16(4): 1067-1069. |
| Wu X C, Wang Y, Lin W X.QTL mapping in controlling seedling cold tolerance in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2008, 16(4): 1067-1069. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 王慰亲. 种子引发促进直播早稻低温胁迫下萌发出苗的机理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2019. |
| Wang W Q.Mechanisms underlying the effects of seed priming on the establishment of direct-seeded early season rice under chilling stress[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 王亚男, 范思静. 低温胁迫对水稻幼苗叶片生理生化特性的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2017, 45(5): 8-9. |
| Wang Y N, Fang S J.Effects of low-temperature stress on the physiological and biochemical characteristics of rice seedling leaves[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(5): 8-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 易子豪. 水分亏缺对水稻秧苗生长的影响及调控[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2020. |
| Yi Z H.Effect of water deficit on rice seedling growth and its regulation[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 唐双勤. 芽期低温、淹水胁迫对早籼稻生长特性与产量的影响[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2019. |
| Tang S Q.Effects of low temperature and water-logging stress at bud stage on growth characteristics and yield of early indica rice[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Singh A, Septiningsih E M, Balyan H S, Singh N K, Rai V.Genetics, physiological mechanisms and breeding of flood-tolerant rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2017, 58(2): 185-197. |
| [9] | 张耗, 余超, 陈可伟, 孔祥胜, 刘海浪, 陈俊义, 顾骏飞, 刘立军, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 直播方式对水稻生理性状和产量的影响及其成本分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(13): 58-64. |
| Zhang H, Yu C, Chen K W, Kong X S,Liu H L, Chen J Y, Gu J F, Liu L J, Wang Z Q, Yang J C.Effect of direct-seeding methods on physiological characteristics and grain yield of rice and its cost analysis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(13): 58-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 宣守丽, 石春林, 张建华, 魏秀芳, 曹宏鑫, 薛昌颖. 分蘖期淹水胁迫对水稻地上部物质分配及产量构成的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2013, 29(6): 1199-1204. |
| Xuan S L, Shi C L, Zhang J H, Wei X F, Cao H X, Xue C Y.Effects of submergence stress on aboveground matter distribution and yield components of rice at tillering stage[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 29(6): 1199-1204. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 向镜, 陈惠哲, 张玉屏, 张义凯, 朱德峰. 淹涝条件下水温对水稻幼苗形态和生理的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(5): 525-531. |
| Xiang J, Chen H Z, Zhang Y P, Zhang Y K, Zhu D F.Effects of on morphological and physiological response of rice seedlings to water temperature under complete submergence[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2016, 30(5): 525-531. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 杨知建, 成诗瑜. 低温下土壤水分对籼稻及粳稻根系生长的影响[J]. 湖南农业大学学报, 2002, 28(5): 369-372. |
| Yang Z J, Cheng S Y.Effects of the soil moisture at low temperature on the growth roots[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University, 2002, 28(5): 369-372. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 杜彦修, 孙红正, 张静, 李俊周, 彭廷, 赵全志. 不同生育时期淹水对水稻Sub1A耐淹基因导入系产量的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2016, 22(4): 28-34. |
| Du Y X, Sui H Z, Zhang J, Li J Z, Peng T, Zhao Q Z.Effects of waterflooding on yield of rice submergence tolerance gene Sub1A introgression line at different growth stage[J]. China Rice, 2016, 22(4): 28-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. |
| Li H S. Principle and Technology of plant physiology and biochemistry experiment[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 张志良. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1990. |
| Zhang Z L. Experimental Guidance on Plant Physiology[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1990. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | Chen G, Zhang Y, Ruan B P, Guo L B, Zeng D L, Gao Z Y, Zhu L, Hu J, Ren D Y, Yu L, Xu G H, Qian Q.OsHAK1 controls the vegetative growth and panicle fertility of rice by its effect on potassium-mediated sugar metabolism[J]. Plant Science, 2018, 274: 261-270. |
| [17] | Wu K, Li J X, Luo J P, Liu Y K, Song Y C, Liu N L, Rafiq M T, Li T Q.Effects of elevated CO2 and endophytic bacterium on photosynthetic characteristics and cadmium accumulation in Sedum alfredii[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 643: 357-366. |
| [18] | Teng Y B, Cui H Q, Wang M Y, Liu X Y.Nitrate reductase is regulated by circadian clock-associated1 in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Plant and Soil, 2017, 416(1): 1-9. |
| [19] | 周伟江, 吴旺嫔, 唐才宝, 肖志芳, 陈光辉, 王悦. 外源油菜素内酯对低温胁迫下水稻幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2020, 29(9): 1-7. |
| Zhou W J, Wu W P, Tang C B, Xiao Z F, Chen G H, Wang Y.Effects of exogenous 2,4-epibrassinolide on germination and physiological characteristics of rice seedlings under chilling stress[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2020, 29(9): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 李响珍. 水稻发芽期亚干旱对苗期、孕穗期与开花期耐冷性的影响[D]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学, 2019. |
| Li X Z.Effects of subdrought at germination stage on cold tolerance at seedling stage, booting stage and flowering stage in rice[D]. Changsha: Hunan Normal University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 胡涛. 低温对水稻根系生理特性及其基因表达的影响[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2019. |
| Hu T.Effects of low temperature on physiological characteristics and gene expression of rice roots[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 吴立群, 蔡志欢, 张桂莲, 刘逸童, 赵瑞. 低温对不同耐冷性水稻品种秧苗生理特性及根尖解剖结构的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 2018, 39(12): 805-813. |
| Wu L Q, Cai Z H, Zhang G L, Liu Y T, Zhao R.Effects of low temperature on physiological characteristics of rice seedlings with different cold tolerance and anatomical structure of root tip[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2018, 39(12): 805-813. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 向丹. 水稻苗期低温耐性差异及其调控研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2013. |
| Xiang D.The difference in low temperature tolerance of Rice Seedlings and its regulation[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Farrell T C, Fox K M, Williams R L, Fukai S.Genotypic variation for cold tolerance during reproductive develop ment in rice: screening with cold air and cold water[J]. Field Crops Research, 2006, 98(2): 178-194. |
| [25] | Gunawardena T A, Fukai B.The interaction of nitrogen application and temperature during reproductive stage on spikelet sterility infield-grown rice[J]. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 2005, 56: 625-636. |
| [26] | 于艳梅, 李芳花, 姜丽霞, 孟岩. 不同淹水处理对寒地水稻生长规律及产量影响的研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2018, 29(3): 249-253. |
| Yu Y M, Li F H, Jiang L X, Meng Y.Effects of different flooding treatments on growth law and yield of rice in cold region[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2018, 29(3): 249-253. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 杨生龙, 贾志英. 不同水分处理对水稻和旱稻产量及产量构成因子的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(31): 17410-17412. |
| Yang S L, Jia Z Y.Effect of different water treatments on yield and yield components of lowland rice and aerobic rice[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science, 2010, 38(31): 17410-17412. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Sanghera S G, Wani S H, Hussain W, Singh N B.Engineering cold stress tolerance in crop plants[J]. Current Genomics, 2011, 12(1): 30-43. |
| [29] | 许培磊. 低温对不同基因型黄瓜叶片抗氧化酶与蛋白质组的影响[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2009. |
| Xu P L.Effects of low temperature on antioxidant enzymes and leaf proteome from Cucumis sativus of different genotypes[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 喻方圆, 徐锡增. 植物逆境生理研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2003, 16(5): 6-11. |
| Yu F Y, Xu X Z.A review on plant stress physiology[J]. World Forestry Research, 2003, 16(5): 6-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | Li Y S, Ou S L, Yang C Y.The seedlings of different japonica rice varieties exhibit differ physiological properties to modulate plant survival rates under submergence stress[J]. Plants, 2020, 9(8): 982. |
| [32] | Minami A, Yano K, Gamuyao R, Nagai K, Kuroha T, Ayano M, Nakamori M, Koike M, Kondo Y, Niimi Y, Kuwata K, Suzuki T, Higashiyama T, Takebayashi Y, Kojima M, Sakakibara H, Toyoda A, Fujiyama A, Kurata N, Ashikari M, Reuscher S.Time-course transcriptomics analysis reveals key responses of submerged deepwater rice to flooding[J]. Plant Physiology, 2018, 176(4): 3081-3102. |
| [33] | 何云, 李贤伟, 李西, 龚伟. 2 种野生岩生植物叶片可溶性蛋白含量对低温胁迫的响应[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2008, 36(18): 7552-7553. |
| He Y, Li X W, Li X, Gong W.Response of two kinds of wild rock plant leaf soluble protein content to low temperature stress[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2008, 36(18): 7552-7553. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 齐光, 佟伟霜, 杨雨华, 陈明辉, 吴秀菊. ABA 对低温胁迫下水稻幼苗抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2016, 55(23): 6079-6082. |
| Qi G, Tong W S, Yang L H, Chen M H, Wu Z J.Effects of aba on antioxidase activity in rice seedlings under low temperature stress[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 55(23): 6079-6082. (in Chinese) | |
| [35] | Bilska A, Sowinski P.Closure of plasmodesmata in maize (Zea mays) at low temperature: A new mechanism for inhibition of photosynthesis[J]. Annals of Botany, 2010, 106(5): 675-686. |
| [36] | 何亚飞, 李霞, 谢寅峰. 核酮糖-1,5-二磷酸羧化酶/加氧酶(Rubisco)与Rubisco活化酶的分子机理研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2017, 15(8): 399-405. |
| He Y F, Li X, Xie Y F.Advances in molecular mechanism of Rrubisco activase[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2017, 15(8): 399-405. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | Sperotto R A, Cruz R P D, Cargnelutti D, Adamski J M, Fett J P. Avoiding damage and achieving cold tolerance in rice plants[J]. Food and Energy Security, 2013, 2(2): 96-119. |
| [38] | 姜籽竹, 朱恒光, 张倩, 宋北光, 孟丽君, 杨德光. 低温胁迫下植物光合作用的研究进展[J]. 作物杂志, 2015(3): 23-28. |
| Jiang Z Z, Zhu H G, Zhang Q, Song B G, Meng L J, Yang D G.Progress of influence of low temperature on plant photosynthesis[J]. Crops, 2015(3): 23-28. (in Chinese) | |
| [39] | Kato Y,Collard B C Y, Septiningsih E M, Ismail A M, Increasing flooding tolerance in rice: combining tolerance of submergence and of stagnant flooding[J]. Annals of Botany, 124(7): 1199-1210. |
| [40] | 柏斌, 吴俊, 盛文涛, 庄文, 李莺歌, 邓启云. 育性敏感期低温胁迫对水稻光温敏不育系叶片内源激素的影响[J].杂交水稻, 2016, 31(1): 57-61. |
| Bai B, Wu J, Sheng W T, Zhuang W, Li Y G, Deng Q Y.Effects of cold stress at fertility sensitive stage on endogenous hormones of rice ptgms lines[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2016, 31(1): 57-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 曾研华, 张玉屏, 潘晓华, 朱德峰, 向镜, 陈惠哲, 张义凯. 花后低温对水稻籽粒灌浆与内源激素含量的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(10): 1551-1559. |
| Zeng Y H, Zhang Y P, Pan X H, Zhu D F, Xiang J, Chen H Z, Zhang Y K.Effect of low temperature after flowering on grain filling and plant hormones contents in rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(10): 1551-1559. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 刘春风. 淹水对15个树种苗木生长和形态特征的影响[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2009. |
| Liu C F.Effects of artificial flooding on the growth and morphological characteristics of 15 tree species seedlings[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | 潘向艳, 季孔庶, 方彦. 淹水胁迫下杂交鹅掌楸无性系叶片内源激素含量的变化[J]. 南京林业大学学报, 2008, 32(1): 29-32. |
| Pan X Y, Ji K S, Fang Y.Changes in contents of endogenous hormones in different clones of Liriodendron chinense ×L. tulipifera under flooding stress[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University, 2008, 32(1): 29-32. (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [44] | Zhou Y J, Li X X, Cao J, Li Y, Huang J L, Peng S B.High nitrogen input reduces yield loss from low temperature during the seedling stage in early-season rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2018, 228: 68-75. |
| [45] | Si L L, Xie Y N, Ma Q X, Wu L H.The short-term effects of rice straw biochar, nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer on rice yield and soil properties in a cold waterlogged paddy field[J]. Sustainability, 2018, 10(2): 537. |
| [1] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [2] | ZHENG Guangjie, YE Chang, ZHU Junlin, TAO Yi, XIAO Deshun, XU Yanan, CHU Guang, XU Chunmei, WANG Danying. Relationship Between Embryo Survival and Glucose Supply of Rice Seed and Embryo Under Flooding Stress [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(2): 172-184. |
| [3] | ZOU Yuao, WU Qixia, ZHOU Qianshun, ZHU Jianqiang, YAN Jun. Response of Middle-season Hybrid Rice to Flooding Stress at the Booting Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(6): 642-656. |
| [4] | DONG Liqiang, YANG Tiexin, LI Rui, SHANG Wenqi, MA Liang, LI Yuedong, SUI Guomin. Effect of Plant-row Spacing on Rice Yield and Root Morphological and Physiological Characteristics in Super High Yield Field [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(4): 392-404. |
| [5] | CHEN Hongyang, JIA Yan, ZHAO Hongwei, QU Zhaojun, WANG Xinpeng, DUAN Yuyang, YANG Rui, BAI Xu, WANG Changcheng. Effects of Low Temperature Stress During Grain Filling on Starch Formation and Accumulation of Superior and Inferior Grains in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(5): 487-504. |
| [6] | HUANG Qina, JIANG Su, WANG Limin, ZHANG Yan, YU Linfei, LI Chunfu, DING Liqun, SHAO Guosheng. Effects of Moisture Content on Root Vigor and the Expression of Aquaporin-related Genes in Rice Seedlings Under Low Temperature Stress [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(4): 367-376. |
| [7] | XU Qingshan, HUANG Jing, SUN Aijun, HONG Xiaozhi, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, KONG Yali, JIN Qianyu, ZHU Chunquan, ZHANG Junhua. Effects of Low Temperature on the Growth and Development of Rice Plants and the Advance of Regulation Pathways: A Review [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(2): 118-130. |
| [8] | Shengfeng QIAO, Yaping DENG, Hanbing QU, Weiyang ZHANG, Junfei GU, Hao ZHANG, Lijun LIU, Zhiqin WANG, Jianchang YANG. Differences in Response to Low Phosphorus Stress Among indica Rice Varieties and Their Agronomic and Physiological Characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(4): 396-406. |
| [9] | Danping HOU, Jinsong TAN, Qingyu BI, Anning ZHANG, Yi LIU, Feiming WANG, Guolan LIU, Xinqiao YU, BIJunguo, Lijun LUO. Effects of Water Stress on Yield Formation and Root Morphological and Physiological Characteristics of Water-saving and Drought-resistantRice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(1): 27-37. |
| [10] | Xiaolong YANG, Jianping CHENG, Benfu WANG, Yang LI, Zhisheng ZHANG, Jinlan LI, Ping LI. Effects of Drought Stressat Grain Filling Stage on Rice Physiological Characteristics and Yield [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(1): 38-46. |
| [11] | Ke LI, Qing YU, Yunji XU, Jianchang YANG. Research Progress in Agronomic and Physiological Traits of Early Leaf Senescence Mutants in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(2): 104-114. |
| [12] | Su CHEN, Jiankun XIE, Wenxin HUANG, Dengyun CHEN, Xiaojian PENG, Xueqin FU. Effects of Plant Growth-promoting Rhizobacteria(PGPR) on Physiological Characteristics of Rice Under Drought Stress [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(5): 485-492. |
| [13] | Yanhua ZENG, Yuping ZHANG, Xiaohua PAN, Defeng ZHU, Jing XIANG, Huizhe CHEN, Yikai ZHANG, Yongjun ZENG. Effect of Low Temperature After Flowering on Grain Quality of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(2): 166-174. |
| [14] | Bao-wei GUO, Ke XU, Hong-cheng ZHANG, Qi-gen DAI, Zhong-yang HUO, Hai-yan WEI, Hou-cun CHEN. Effect of Ordered Transplanting and Optimized Broadcasting on Rice Root System Morphological and Physiological Characteristics Under Super High-yielding Cultivation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(6): 611-625. |
| [15] | Ying-hong LI, Hai-yue WANG, Feng-jun YAN, Na LI, Yong-jian SUN, Zou DAI, Hua-ying XIE, Jun MA. Effects of Root-cutting Treatment on Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Hybrid Rice at Different Seedling-ages [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(6): 626-636. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||