
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 557-564.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.8034
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhanghua HU1, Xiuyan LIU2, Yufeng WANG3, Yu PENG3, Xiaoliang SHI3, Sheng TENG3,*( )
)
Received:2018-03-23
Revised:2018-06-04
Online:2018-11-27
Published:2018-11-10
Contact:
Sheng TENG
胡张华1, 刘秀艳2, 王玉锋3, 彭瑜3, 史晓亮3, 滕胜3,*( )
)
通讯作者:
滕胜
基金资助:CLC Number:
Zhanghua HU, Xiuyan LIU, Yufeng WANG, Yu PENG, Xiaoliang SHI, Sheng TENG. Agronomic Traits of Marker-free Transgenic japonica Rice with Overexpression of OsPHF1 Under Low Phosphorus Environment[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(6): 557-564.
胡张华, 刘秀艳, 王玉锋, 彭瑜, 史晓亮, 滕胜. 低磷条件下过表达OsPHF1基因对粳稻农艺性状的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 557-564.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.8034
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence(5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| PHF1-full-S | GCTCTAGAATGGCAGGCGGCGGAGGTGGCGAG(XbaⅠ) |
| PHF1-full-A | GCGTCGACTCACCAGGGGTTCTGGTCCTCAGG(SalⅠ) |
| HYB-3S | TGAAAAAGCCTGAACTCACCG |
| HYB-4A | TATTTCTTTGCCCTCGGACG |
| PHF1-7S | GATGGGAAGTATCTGGCTTTGGG |
| PHF1-10A | AACAGGATGGCTGACACTAGGAA |
| PHF-418S | CTCAGAATATTTCATTGGCCGAGC |
| PHF-633A | CCTAGAAAAGCGGCAACATTCAATCTTC |
| Ubi-S | GACGGACGCACCCTGGCTGACTAC |
| Ubi-A | TGCTGCCAATTACCATATACCACGAC |
Table 1 Primers used in the study.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence(5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| PHF1-full-S | GCTCTAGAATGGCAGGCGGCGGAGGTGGCGAG(XbaⅠ) |
| PHF1-full-A | GCGTCGACTCACCAGGGGTTCTGGTCCTCAGG(SalⅠ) |
| HYB-3S | TGAAAAAGCCTGAACTCACCG |
| HYB-4A | TATTTCTTTGCCCTCGGACG |
| PHF1-7S | GATGGGAAGTATCTGGCTTTGGG |
| PHF1-10A | AACAGGATGGCTGACACTAGGAA |
| PHF-418S | CTCAGAATATTTCATTGGCCGAGC |
| PHF-633A | CCTAGAAAAGCGGCAACATTCAATCTTC |
| Ubi-S | GACGGACGCACCCTGGCTGACTAC |
| Ubi-A | TGCTGCCAATTACCATATACCACGAC |
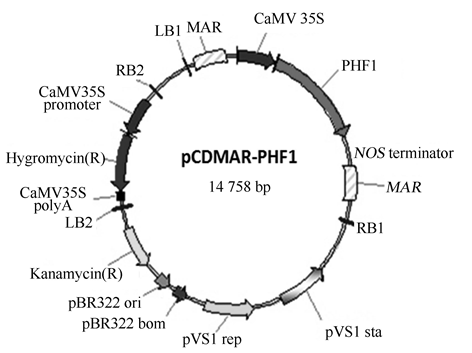
Fig. 1. Construction of overexpression vector of pCDMAR- OsPHF1.^ LB1 and LB2, Left border of T-DNA; RB1 and RB2, Right border of T-DNA; Hygromycin(R), Hygromycin phosphotransferase (HPT), resistant to hygromycin B; MAR, Matrix attachment regions; CaMV 35S, 35S promoter of CaMV.
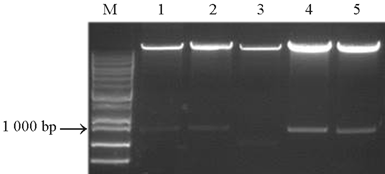
Fig. 2. Confirmation of recombinant plasmid pCDMAR- OsPHF1 by double enzyme digestion.^ Confirmation of recombinant plasmid pCDMAR-OsPHF1 by double enzyme digestion. Lanes 1-5, Five independent clones of recombinant plasmid. M represents DNA marker; A band about 1 kb appears at lanes 1, 2, 4 and 5, indicating that they are positive cloneion.
| 株系名称 Line name | 检测的总株数 Total number of detected plants | 含有插入的OsPHF1株数 Plant number containing inserted OsPHF1 | 不含插入的OsPHF1株数 Plant number without inserted OsPHF1 | χ2 (3:1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F18 | 57 | 39 | 18 | 1.32 |
| F22 | 56 | 45 | 11 | 0.86 |
| F25 | 56 | 40 | 16 | 0.38 |
| F32 | 60 | 43 | 17 | 0.36 |
Table 2 Identification of separation ratio for the inserted gene OsPHF1 in T1 generation transgenic rice.
| 株系名称 Line name | 检测的总株数 Total number of detected plants | 含有插入的OsPHF1株数 Plant number containing inserted OsPHF1 | 不含插入的OsPHF1株数 Plant number without inserted OsPHF1 | χ2 (3:1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F18 | 57 | 39 | 18 | 1.32 |
| F22 | 56 | 45 | 11 | 0.86 |
| F25 | 56 | 40 | 16 | 0.38 |
| F32 | 60 | 43 | 17 | 0.36 |
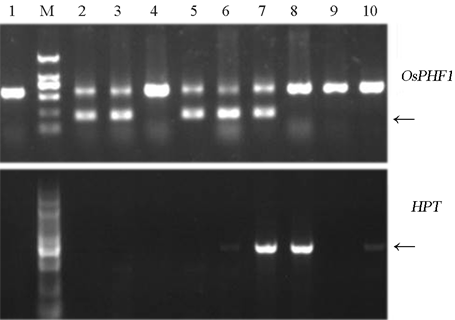
Fig. 3. PCR analysis of OsPHF1 gene and selective marker HPT in T1 transgenic plants.^ M, DNA marker. Lane 1, Kongyu 131(control); 2-10, PCR results for different OsPHF1 transgenic T1 lines’ genomic DNA. Upper row is the amplification of OsPHF1 gene, and the amplified product of the inserted OsPHF1 is 215 bp, while the endogenous OsPHF1 in the genome is 600 bp. The bottom row represents the amplification of HPT gene, and the product is 1000 bp. Lanes 2, 3, 5 and 6 represent transgenic lines of F18, F22, F25 and F32, respectively.
| 株系名称 Line name | OsPHF1相对表达量(叶) Relative expression of OsPHF1 (Leaf) | OsPHF1相对表达量(根) Relative expression of OsPHF1 (Root) |
|---|---|---|
| F18-18 | 0.38±0.03 b | 0.05±0.00 a |
| F22-32 | 16.17±4.57 d | 1.42±0.94 b |
| F25-6 | 12.92±1.11 c | 1.28±0.89 b |
| 空育131 Kongyu 131 | 0.20±0.03 a | 0.07±0.01 a |
Table 3 The total relative expression of OsPHF1 in three independent overexpression transgenic plants by real-time PCR.
| 株系名称 Line name | OsPHF1相对表达量(叶) Relative expression of OsPHF1 (Leaf) | OsPHF1相对表达量(根) Relative expression of OsPHF1 (Root) |
|---|---|---|
| F18-18 | 0.38±0.03 b | 0.05±0.00 a |
| F22-32 | 16.17±4.57 d | 1.42±0.94 b |
| F25-6 | 12.92±1.11 c | 1.28±0.89 b |
| 空育131 Kongyu 131 | 0.20±0.03 a | 0.07±0.01 a |
| 施磷肥量 P application /(kg∙hm-2) | 株系名称 Line name | T3植株, 上海基地 T3 at Shanghai base | T4植株, 海南省三亚基地 T4 at Sanya base, Hainan Province | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖数 Tiller number | 单株产量 Yield per plant /g | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 结实率 Seed-setting rate /% | 分蘖数 Tiller number | 单株产量 Yield per plant /g | |||
| 112.5 | F22-32 | 16.44±4.16 a | 13.26±2.71 b | 27.64±2.29 a | 94±4 a | 23.33±2.94 ab | 40.36±6.32 b | |
| F25-6 | 16.20±5.16 a | 12.61±2.50 b | 26.98±2.71 a | 93±6 a | 22.83±3.49 ab | 38.62±8.21 b | ||
| 空育131 Kongyu 131 | 15.20±4.62 a | 10.90±2.75 a | 27.29±2.36 a | 95±4 a | 19.83±1.47 a | 29.70±5.31 a | ||
| 225.0 | F22-32 | 23.60±6.33 a | 19.18±5.13 b | 30.13±2.39 a | 91±8 a | 23.60±2.61 ab | 36.91±4.02 b | |
| F25-6 | 21.50±4.30 a | 17.89±3.43 b | 29.23±2.10 a | 92±6 a | 22.67±4.18 ab | 37.29±7.91 b | ||
| 空育131 Kongyu 131 | 15.15±3.20 b | 14.27±2.00 a | 28.41±2.33 a | 94±5 a | 20.67±3.08 a | 31.74±6.39 a | ||
| 450.0 | F22-32 | 21.75±2.14 a | 20.83±3.76 a | 29.37±2.03 a | 92±6 a | 25.60±4.33 a | 40.91±4.52 a | |
| F25-6 | 21.91±3.44 a | 20.02±3.06 a | 29.97±2.84 a | 93±7 a | 24.67±3.78 a | 39.29±5.31 a | ||
| 空育131 Kongyu 131 | 22.89±3.76 a | 22.28±3.61 a | 30.52±2.54 a | 95±5 a | 29.67±3.28 a | 42.70±6.11 a | ||
Table 4 Agronomic traits of OsPHF1 transgenic plants (T3 generation) at Shanghai base.
| 施磷肥量 P application /(kg∙hm-2) | 株系名称 Line name | T3植株, 上海基地 T3 at Shanghai base | T4植株, 海南省三亚基地 T4 at Sanya base, Hainan Province | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖数 Tiller number | 单株产量 Yield per plant /g | 千粒重 1000-grain weight /g | 结实率 Seed-setting rate /% | 分蘖数 Tiller number | 单株产量 Yield per plant /g | |||
| 112.5 | F22-32 | 16.44±4.16 a | 13.26±2.71 b | 27.64±2.29 a | 94±4 a | 23.33±2.94 ab | 40.36±6.32 b | |
| F25-6 | 16.20±5.16 a | 12.61±2.50 b | 26.98±2.71 a | 93±6 a | 22.83±3.49 ab | 38.62±8.21 b | ||
| 空育131 Kongyu 131 | 15.20±4.62 a | 10.90±2.75 a | 27.29±2.36 a | 95±4 a | 19.83±1.47 a | 29.70±5.31 a | ||
| 225.0 | F22-32 | 23.60±6.33 a | 19.18±5.13 b | 30.13±2.39 a | 91±8 a | 23.60±2.61 ab | 36.91±4.02 b | |
| F25-6 | 21.50±4.30 a | 17.89±3.43 b | 29.23±2.10 a | 92±6 a | 22.67±4.18 ab | 37.29±7.91 b | ||
| 空育131 Kongyu 131 | 15.15±3.20 b | 14.27±2.00 a | 28.41±2.33 a | 94±5 a | 20.67±3.08 a | 31.74±6.39 a | ||
| 450.0 | F22-32 | 21.75±2.14 a | 20.83±3.76 a | 29.37±2.03 a | 92±6 a | 25.60±4.33 a | 40.91±4.52 a | |
| F25-6 | 21.91±3.44 a | 20.02±3.06 a | 29.97±2.84 a | 93±7 a | 24.67±3.78 a | 39.29±5.31 a | ||
| 空育131 Kongyu 131 | 22.89±3.76 a | 22.28±3.61 a | 30.52±2.54 a | 95±5 a | 29.67±3.28 a | 42.70±6.11 a | ||
| [1] | Schachtman D P, Reid R J, Ayling S M.Phosphorus uptake by plants: From soil to cell.Plant Physiol, 1998, 116(2): 447-453. |
| [2] | Wang F, Deng M J, Xu J M, Zhu X L, Mao C Z.Molecular mechanisms of phosphate transport and signaling in higher plants.Sem Cell & Dev Biol, 2018, 74: 114-122. |
| [3] | Muchhal U S, Pardo J M, Raghothama K G.Phosphate transporters from the higher plantArabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1996, 93(19): 10519-10523. |
| [4] | Rae A L, Cybinski D H, Jarmey J M, Smith F W.Characterization of two phosphate transporters from barley: Evidence for diverse function and kinetic properties among members of the Pht1 family.Plant Mol Biol, 2003, 53(1): 27-36. |
| [5] | Raghothama K G.Phosphate transport and signaling.Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2000, 3(3): 182-187. |
| [6] | Mudge S R, Rae A L, Diatloff E, Smith F W.Expression analysis suggests novel roles for members of the Pht1 family of phosphate transporters inArabidopsis. Plant J, 2002, 31(3): 341-353. |
| [7] | Jia H, Zhang S, Wang L, Yang Y, Zhang H, Cui H, Shao H, Xu G.OsPht1;8, a phosphate transporter, is involved in auxin and phosphate star vation response in rice.J Exp Bot, 2017, 68(18): 5057-5068. |
| [8] | Shin H, Shin H S, Dewbre G R, Harrison M J.Phosphate transport in Arabidopsis: Pht1;1 and Pht1;4 play a major role in phosphate acquisition from both low- and high- phosphate environments. Plant J, 2004, 39(4): 629-642. |
| [9] | Wang C, Yue W, Ying Y, Wang S, Secco D, Liu Y, Whelan J, Tyerman S D, Shou H.Rice SPX-Major facility superfamily3, a vacuolar phosphate efflux transporter, is involved in maintaining phosphate homeostasis in rice.Plant Physiol, 2015, 169(4): 2822-2831. |
| [10] | Karthikeyan A S, Varadarajan D K, Mukatira U T,D'Urzo M P,Damsz B, Raghothama K G. Regulated expression of Arabidopsis phosphate transporters. Plant Physiol, 2002, 130(1): 221-233. |
| [11] | Barlowe C, Schekman R.SEC12 encodes a guanine- nucleotide-exchange factor essential for transport vesicle budding from the ER. Nature, 1993, 365(6444): 347-349. |
| [12] | Barlowe C.Signals for COPII-dependent export from the ER: What’s the ticket out?Trends Cell Biol, 2003, 13(6): 295-300. |
| [13] | Gonzalez E, Solano R, Rubio V, Leyva A, Paz-Ares J.PHOSPHATE TRANSPORTER TRAFFIC FACILITATOR1 is a plant-specific SEC12-related protein that enables the endoplasmic reticulum exit of a high-affinity phosphate transporter inArabidopsis. Plant Cell, 2005, 17(12): 3500-3512. |
| [14] | Chen J, Liu Y, Ni J, Wang Y, Bai Y, Shi J, Gan J, Wu Z, Wu P.OsPHF1 regulates the plasma membrane localization of low- and high-affinity inorganic phosphate transporters and determines inorganic phosphate uptake and translocation in rice. Plant Physiol, 2011, 157(1): 269-278. |
| [15] | Wu P, Shou H X, Xu G H, Lian X M.Improvement of phosphorus efficiency in rice on the basis of understanding phosphate signaling and homeostasis.Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2013, 16(2): 205-212. |
| [16] | Gilbert N.Environment: The disappearing nutrient.Nature, 2009, 461(7265): 716-718. |
| [17] | Komari T, Hiei Y, Saito Y, Murai N, Kumashiro T.Vectors carrying two separate T-DNAs for co-transformation of higher plants mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens and segregation of transformants free from selection markers. Plant J, 1996, 10(1): 165-74. |
| [18] | 韩兆雪, 曹墨菊, 朱祯, 荣廷昭. DREB基因双T-DNA植物表达载体的构建及验证. 分子植物育种, 2004, 2(1): 7-12. |
| Han Z X, Cao M J, Zhu Z, Rong T Z.Construction and verification of double T-DNA plant expression vector of the DREB gene. Mol Plant Breed, 2004, 2(1): 7-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 胡张华, 吴关庭, 金卫, 王伏林, 陈锦清. 农杆菌介导的水稻转化及bar基因稳定遗传. 浙江农业学报, 2003, 15(6): 327-331. |
| Hu Z H, Wu G T, Jin W, Wang F L, Chen J Q.Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of rice and stable inheritance of bar gene. Acta Agric Zhejiang, 2003, 15(6): 327-331. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 于恒秀, 陆美芳, 陈秀花, 龚志云, 刘巧泉, 顾铭洪. 不同转化方法培育无抗性选择标记转基因水稻效率的比较. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(2): 120-126. |
| Yu H X, Lu M F, Che X H, Gong Z Y, Liu Q Q, Gu M H.Comparison on efficiency of generating selectable marker-free transgenic rice by different transformation methods.Chin J Rice Sci, 2009, 23(2): 120-126. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [5] | ZHAO Yiting, XIE Keran, GAO Ti, CUI Kehui. Effects of Drought Priming During Tillering Stage on Panicle Development and Yield Formation Under High Temperature During Panicle Initiation Stage in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 277-289. |
| [6] | ZHOU Tian, WU Shaohua, KANG Jianhong, WU Hongliang, YANG Shenglong, WANG Xingqiang, LI Yu, HUANG Yufeng. Effects of Planting Patterns on Starch Content and Activities of Key Starch Enzymes in Rice Grains [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [7] | LIU Huimin, ZHOU Jieqiang, HU Yuanyi, TIAN Yan, LEI Bin, LI Jianwu, WEI Zhongwei, TANG Wenbang. Super-high Yield Characteristics of Two-line Hybrid Rice Zhuoliangyou 1126 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(2): 160-171. |
| [8] | PENG Xianlong, DONG Qiang, ZHANG Chen, LI Pengfei, LI Bolin, LIU Zhilei, YU Cailian. Effects of Straw Return Rate on Soil Reducing Substances and Rice Growth Under Different Soil Conditions [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(2): 198-210. |
| [9] | ZHU Wang, ZHANG Xiang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Zhe, CHEN Yinglong, WEI Huanhe, DAI Qigen, XU Ke, ZHU Guanglong, ZHOU Guisheng, MENG Tianyao. Morphological and Physiological Characteristics of Rice Roots Under Combined Salinity-Drought Stress and Their Relationships with Yield Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(6): 617-627. |
| [10] | ZOU Yuao, WU Qixia, ZHOU Qianshun, ZHU Jianqiang, YAN Jun. Response of Middle-season Hybrid Rice to Flooding Stress at the Booting Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(6): 642-656. |
| [11] | YUAN Pei, ZHOU Xuan, YANG Wei, YIN Lingjie, JIN Tuo, PENG Jianwei, RONG Xiangmin, TIAN Chang. Effects of Combined Application of Chemical Fertilizers and Nitrogen Reduction on the Yield of Double-cropping Rice and the Risk of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss in Field Water in Dongting Lake Area [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(5): 518-528. |
| [12] | XIAO Dakang, HU Ren, HAN Tianfu, ZHANG Weifeng, HOU Jun, REN Keyu. Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer Consumption and Operation on Rice Yield and Its Components in China:A Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(5): 529-542. |
| [13] | HUANG Yaru, XU Peng, WANG Lele, HE Yizhe, WANG Hui, KE Jian, HE Haibing, WU Liquan, YOU Cuicui. Effects of Exogenous Trehalose on Grain Filling Characteristics and Yield Formation of japonica Rice Cultivar W1844 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| [14] | DONG Liqiang, YANG Tiexin, LI Rui, SHANG Wenqi, MA Liang, LI Yuedong, SUI Guomin. Effect of Plant-row Spacing on Rice Yield and Root Morphological and Physiological Characteristics in Super High Yield Field [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(4): 392-404. |
| [15] | WANG Wenting, MA Jiaying, LI Guangyan, FU Weimeng, LI Hubo, LIN Jie, CHEN Tingting, FENG Baohua, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu, QIN Yebo. Effect of Different Fertilizer Application Rates on Rice Yield and Quality Formation and Its Relationship with Energy Metabolism at High Temperature [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(3): 253-264. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||