
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 451-464.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.250209
林逸1, 孙良1,3,*( ), 陈东顺1, 朱广飞4, 孔子阳1, 俞高红1,2
), 陈东顺1, 朱广飞4, 孔子阳1, 俞高红1,2
收稿日期:2025-02-25
修回日期:2025-04-22
出版日期:2025-07-10
发布日期:2025-07-21
通讯作者:
*email: liangsun@zstu.edu.cn基金资助:
LIN Yi1, SUN Liang1,3,*( ), CHEN Dongshun1, ZHU Guangfei4, KONG Ziyang1, YU Gaohong1,2
), CHEN Dongshun1, ZHU Guangfei4, KONG Ziyang1, YU Gaohong1,2
Received:2025-02-25
Revised:2025-04-22
Online:2025-07-10
Published:2025-07-21
Contact:
*email:liangsun@zstu.edu.cn
摘要:
【目的】解决水稻侧深施肥装置在施肥过程中施肥管末端落肥速度慢且易堵肥的问题。【方法】基于通用颗粒复合肥物理参数提出一种末端分流式加速装置,根据气固两相流理论的研究方法,将气流和肥料分流,使引出气流经变径管加速后引入出肥口,提升出肥口风速,加速肥料下落并预防堵塞。【结果】通过建立流体动力学与离散元耦合仿真模型,选取气肥分流器混合管倾角、弯径比以及导气口倾角作为影响因素,以导气口的肥料误入率和气流速度作为响应值,采用Box-Behnken三因素三水平的中心组合设计法设计正交仿真实验,组合出最佳的气肥分流装置的结构参数。结果表明,气肥分流装置的最佳结构参数组合为混合管倾角10°,导气管倾角16°,弯径比2。在此条件下进行台架实验,测量得到的加速后气流平均速度为19.74 m/s,肥料误入率为7.74%,肥料下落平均速度为2.14 m/s,【结论】该装置能有效提高施肥管末端风速及落肥速度,可为气送式水田施肥技术研究提供参考。
林逸, 孙良, 陈东顺, 朱广飞, 孔子阳, 俞高红. 水田侧深施肥末端分流式加速装置的设计与优化[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 451-464.
LIN Yi, SUN Liang, CHEN Dongshun, ZHU Guangfei, KONG Ziyang, YU Gaohong. Design and Optimization of a Terminal Shunting Acceleration Device for Rice Side Deep Fertilization[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(4): 451-464.
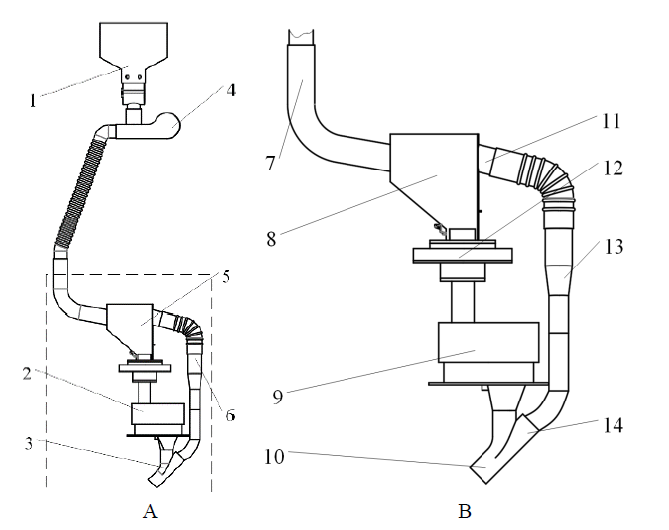
图1 气送式防堵施肥机结构 A: 整体结构; B: 加速装置结构。1: 落肥机; 2: 预存肥装置; 3: 三通管; 4: 风机; 5: 气肥分流器; 6: 变径管; 7: 混合进口; 8: 分流器内腔; 9: 存肥仓; 10: 三通管口Ⅰ; 11: 导气口; 12: 叶片阀; 13: 变径管; 14: 三通管管口Ⅱ。
Fig. 1. Structure of pneumatic clog-resistant fertilizer applicator A, Overall structure; B, Acceleration device structure. 1, Electric fertilizer feeder; 2, Pre-storage fertilizer device; 3, Y-tube; 4, Fan; 5, Air fertilizer divider; 6, Reducing pipe; 7, Mixing inlet; 8, Divider inner cavity; 9, Feeding port; 10, Y-tube port Ⅰ; 11, Air inlet; 12, Vane valve; 13, Reducer; 14, Y-tube nozzle II.
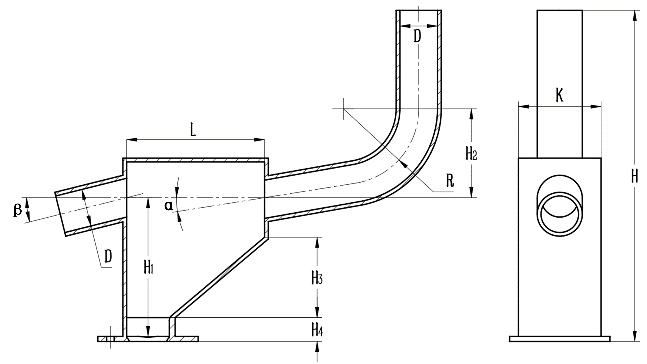
图2 气肥分流器内腔结构 L为内腔水平距离(mm);D为混合管与导气管管径(mm);H为总高(mm);H1为落肥口到混合管轴线的高度(mm);H2为混合管轴线到弯曲段圆心的垂直距离(mm);H3为倾斜段的高度(mm);H4为底部到倾斜段的高度(mm); θ为混合管与水平线的夹角(°);β为导气管与水平线的夹角(°);K为总宽(mm)。
Fig. 2. Internal structure of gas and fertilizer shunt L is the horizontal distance of the inner cavity(mm); D is the diameter of mixing tube and airway tube(mm); H is the total height(mm); H1 is the height from the fertilizer opening to the axis of the mixing tube(mm); H2 is the vertical distance from the axis of the mixing tube to the center of the circle of the bending section(mm); H3 is the height of the inclined section(mm); H4 is the height from the bottom to the inclined section(mm); α is the Angle between the mixing tube and the horizontal line(°); β is the angle between the airway and the horizontal line(°); K is the total width(mm).
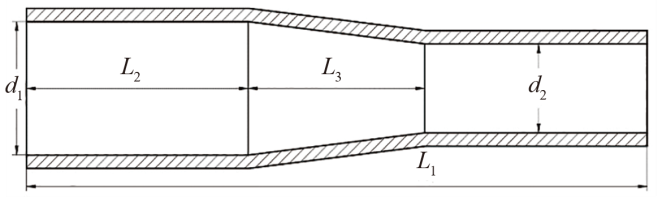
图4 变径加速管结构参数 L1为总长(mm);L2为进气段长度(mm);L3为变径段长度(mm);d1为进气段管径(mm);d2为出气段管径。
Fig. 4. Structural parameters of reducer accelerator L1 is the total length(mm); L2 is the length of the intake section(mm); L3 is the length of the reducing section(mm); d1 is the inlet section pipe diameter(mm); d2 is the outlet pipe diameter.
| 材料 Material | 参数 Parameter | 数值 Value |
|---|---|---|
| 史丹利复合肥 Stanley compound fertilizer | 泊松比 Poisson’s ratio | 0.21 |
| 剪切模量 Shear modulus(Pa) | 3.2×107 | |
| 密度 Density(kg/m3) | 2143 | |
| 等效粒径 Equivalent particle size(mm) | 3.67 | |
| 碰撞恢复系数(对颗粒) Coefficient of restitution (for particles) | 0.3 | |
| 静摩擦因素(对装置) Coefficient of static friction (for the device) | 0.26 | |
| 滚动摩擦因素(对装置) Coefficient of rolling friction (for the device) | 0.08 | |
| 气流加速装置 Airflow acceleration device | 泊松比 Poisson’s ratio | 0.29 |
| 剪切模量 Shear modulus(Pa) | 2.2 | |
| 密度 Density(kg/m3) | 1530 | |
| 等效粒径 Equivalent particle size(mm) | 0.42 | |
| 碰撞恢复系数(对颗粒) Coefficient of restitution (for particles) | 0.26 | |
| 静摩擦因素(对装置) Coefficient of static friction (for the device) | 0.06 |
表1 材料基本参数
Table 1. Basic parameters of materials
| 材料 Material | 参数 Parameter | 数值 Value |
|---|---|---|
| 史丹利复合肥 Stanley compound fertilizer | 泊松比 Poisson’s ratio | 0.21 |
| 剪切模量 Shear modulus(Pa) | 3.2×107 | |
| 密度 Density(kg/m3) | 2143 | |
| 等效粒径 Equivalent particle size(mm) | 3.67 | |
| 碰撞恢复系数(对颗粒) Coefficient of restitution (for particles) | 0.3 | |
| 静摩擦因素(对装置) Coefficient of static friction (for the device) | 0.26 | |
| 滚动摩擦因素(对装置) Coefficient of rolling friction (for the device) | 0.08 | |
| 气流加速装置 Airflow acceleration device | 泊松比 Poisson’s ratio | 0.29 |
| 剪切模量 Shear modulus(Pa) | 2.2 | |
| 密度 Density(kg/m3) | 1530 | |
| 等效粒径 Equivalent particle size(mm) | 0.42 | |
| 碰撞恢复系数(对颗粒) Coefficient of restitution (for particles) | 0.26 | |
| 静摩擦因素(对装置) Coefficient of static friction (for the device) | 0.06 |
| 编码水平 Coding level | 混合管倾角 Mixing angle(°) | 导气管倾角 Air deflector angle(°) | 弯径比 Ratio of cornering radius |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | 30 | 4 |
| 0 | 20 | 20 | 3 |
| −1 | 10 | 10 | 2 |
表2 实验因素编码表
Table 2. Coding table of experimental factors
| 编码水平 Coding level | 混合管倾角 Mixing angle(°) | 导气管倾角 Air deflector angle(°) | 弯径比 Ratio of cornering radius |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | 30 | 4 |
| 0 | 20 | 20 | 3 |
| −1 | 10 | 10 | 2 |
| 序号 Number | A | B | C | 气流均速 Airflow velocity(m/s) | 肥料误入率 Fertilizer fall rate(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 11.3288 | 12.10 |
| 2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 13.6998 | 18.31 |
| 3 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 9.7277 | 6.79 |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 9.0358 | 10.85 |
| 5 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 16.5551 | 8.29 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.6226 | 9.51 |
| 7 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 12.3705 | 6.37 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.8202 | 2.75 |
| 9 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 14.8379 | 20.95 |
| 10 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 10.9157 | 3.58 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.2228 | 10.91 |
| 12 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 11.1226 | 5.72 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.5015 | 4.3 |
| 14 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 9.0739 | 13.75 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.8224 | 8.06 |
| 16 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 10.3928 | 2.56 |
| 17 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 9.8274 | 8.93 |
表3 试验设计及其结果
Table 3. Experimental design and results
| 序号 Number | A | B | C | 气流均速 Airflow velocity(m/s) | 肥料误入率 Fertilizer fall rate(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 11.3288 | 12.10 |
| 2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 13.6998 | 18.31 |
| 3 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 9.7277 | 6.79 |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 9.0358 | 10.85 |
| 5 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 16.5551 | 8.29 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.6226 | 9.51 |
| 7 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 12.3705 | 6.37 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.8202 | 2.75 |
| 9 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 14.8379 | 20.95 |
| 10 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 10.9157 | 3.58 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.2228 | 10.91 |
| 12 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 11.1226 | 5.72 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.5015 | 4.3 |
| 14 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 9.0739 | 13.75 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.8224 | 8.06 |
| 16 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 10.3928 | 2.56 |
| 17 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 9.8274 | 8.93 |
| 方差来源 Source | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方 Mean square | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型 Model | 65.88 | 9 | 7.32 | 48.09 | <0.0001 |
| A | 42.51 | 1 | 42.51 | 279.28 | <0.0001 |
| B | 2.34 | 1 | 2.34 | 15.38 | 0.0057 |
| C | 5.10 | 1 | 5.10 | 33.50 | 0.0007 |
| AB | 0.82 | 1 | 0.82 | 5.40 | 0.00531 |
| AC | 1.31 | 1 | 1.31 | 8.61 | 0.0219 |
| BC | 0.16 | 1 | 0.16 | 1.03 | 0.3433 |
| A2 | 11.09 | 1 | 11.09 | 72.86 | <0.0001 |
| B2 | 2.17 | 1 | 2.17 | 14.27 | 0.0069 |
| C2 | 0.67 | 1 | 0.67 | 4.38 | 0.0747 |
| 残差 Residual | 1.01 | 7 | 0.15 | ||
| 失拟项 Lack of fit | 0.82 | 3 | 0.27 | 4.34 | 0.0951 |
| 纯误差 Pure error | 0.25 | 4 | 0.063 | ||
| 总和 Total | 66.94 | 16 |
表4 出口气流速度的方差分析
Table 4. Analysis of variance of air velocity at air outlet
| 方差来源 Source | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方 Mean square | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型 Model | 65.88 | 9 | 7.32 | 48.09 | <0.0001 |
| A | 42.51 | 1 | 42.51 | 279.28 | <0.0001 |
| B | 2.34 | 1 | 2.34 | 15.38 | 0.0057 |
| C | 5.10 | 1 | 5.10 | 33.50 | 0.0007 |
| AB | 0.82 | 1 | 0.82 | 5.40 | 0.00531 |
| AC | 1.31 | 1 | 1.31 | 8.61 | 0.0219 |
| BC | 0.16 | 1 | 0.16 | 1.03 | 0.3433 |
| A2 | 11.09 | 1 | 11.09 | 72.86 | <0.0001 |
| B2 | 2.17 | 1 | 2.17 | 14.27 | 0.0069 |
| C2 | 0.67 | 1 | 0.67 | 4.38 | 0.0747 |
| 残差 Residual | 1.01 | 7 | 0.15 | ||
| 失拟项 Lack of fit | 0.82 | 3 | 0.27 | 4.34 | 0.0951 |
| 纯误差 Pure error | 0.25 | 4 | 0.063 | ||
| 总和 Total | 66.94 | 16 |
| 方差来源 Source | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方 Mean square | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型 Model | 365.05 | 9 | 40.56 | 4.74 | 0.261 |
| A | 59.90 | 1 | 59.90 | 7.00 | 0.0331 |
| B | 15.15 | 1 | 15.15 | 1.77 | 0.2248 |
| C | 112.80 | 1 | 112.80 | 13.19 | 0.0084 |
| AB | 115.99 | 1 | 115.99 | 13.56 | 0.0078 |
| AC | 3.33 | 1 | 3.33 | 0.39 | 0.5523 |
| BC | 0.20 | 1 | 0.20 | 0.023 | 0.8833 |
| A2 | 42.03 | 1 | 42.03 | 4.92 | 0.0621 |
| B2 | 12.16 | 1 | 12.16 | 1.42 | 0.2719 |
| C2 | 2.32 | 1 | 2.32 | 0.27 | 0.6182 |
| 残差 Residual | 59.86 | 7 | 8.55 | ||
| 失拟项 Lack of fit | 11.85 | 3 | 3.95 | 0.33 | 0.8060 |
| 纯误差 Pure error | 48.01 | 4 | 12.00 | ||
| 总和 Total | 424.90 | 16 |
表5 肥料误入率方差分析结果
Table 5. Analysis of variance of fatting rate of air inlet
| 方差来源 Source | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方 Mean square | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型 Model | 365.05 | 9 | 40.56 | 4.74 | 0.261 |
| A | 59.90 | 1 | 59.90 | 7.00 | 0.0331 |
| B | 15.15 | 1 | 15.15 | 1.77 | 0.2248 |
| C | 112.80 | 1 | 112.80 | 13.19 | 0.0084 |
| AB | 115.99 | 1 | 115.99 | 13.56 | 0.0078 |
| AC | 3.33 | 1 | 3.33 | 0.39 | 0.5523 |
| BC | 0.20 | 1 | 0.20 | 0.023 | 0.8833 |
| A2 | 42.03 | 1 | 42.03 | 4.92 | 0.0621 |
| B2 | 12.16 | 1 | 12.16 | 1.42 | 0.2719 |
| C2 | 2.32 | 1 | 2.32 | 0.27 | 0.6182 |
| 残差 Residual | 59.86 | 7 | 8.55 | ||
| 失拟项 Lack of fit | 11.85 | 3 | 3.95 | 0.33 | 0.8060 |
| 纯误差 Pure error | 48.01 | 4 | 12.00 | ||
| 总和 Total | 424.90 | 16 |
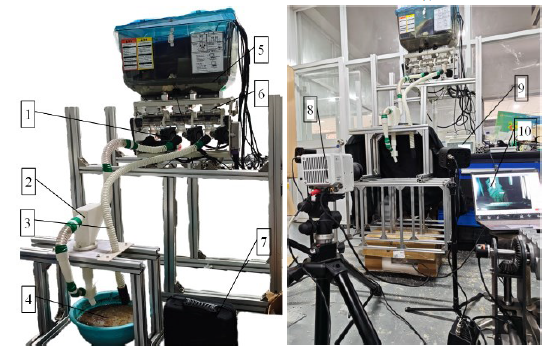
图10 台架试验台 1: 风机; 2: 气流加速装置; 3: 对照管; 4: 水田粉土; 5: 肥箱; 6: 送肥槽轮; 7: 流速检测装置; 8: 高速摄影机; 9: 控制器; 10: 计算机。
Fig. 10. Test bench 1, Fan; 2, Air acceleration device; 3, Control air supply pipe; 4, Paddy field silt; 5, Fertilizer box; 6, Fertilizer feed tank wheel; 7, Flow rate detection device; 8, High-speed camera; 9, Controller; 10, Computer.
| 组别 Group | 序号 Number | 导气口气流速度 Airflow velocity in guide vane(m/s) | 导气口肥料误入率 Air guide port fall rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 Experimental group | 1 | 16.2 | 7.8 |
| 2 | 15.4 | 7.9 | |
| 3 | 16.1 | 7.3 | |
| 4 | 16.3 | 7.7 | |
| 5 | 15.8 | 8.0 | |
| 均值 Mean | 15.96 | 7.74 | |
表6 分流装置台架试验结果
Table 6. Results of bench test of airflow acceleration device
| 组别 Group | 序号 Number | 导气口气流速度 Airflow velocity in guide vane(m/s) | 导气口肥料误入率 Air guide port fall rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 Experimental group | 1 | 16.2 | 7.8 |
| 2 | 15.4 | 7.9 | |
| 3 | 16.1 | 7.3 | |
| 4 | 16.3 | 7.7 | |
| 5 | 15.8 | 8.0 | |
| 均值 Mean | 15.96 | 7.74 | |
| 组别 Group | 序号 Number | 气流速度 Air velocity(m/s) | 落肥速度 Fattening rate (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 实验组 Experimental group | 1 | 19.9 | 2.123 |
| 2 | 19.7 | 2.395 | |
| 3 | 19.8 | 2.061 | |
| 4 | 19.3 | 2.093 | |
| 5 | 20.0 | 2.028 | |
| 均值 Mean | 19.74 | 2.140 | |
| 对照组 Control group | 1 | 14.8 | 1.857 |
| 2 | 14.6 | 1.834 | |
| 3 | 15.0 | 1.646 | |
| 4 | 14.9 | 1.708 | |
| 5 | 15.1 | 1.738 | |
| 均值 Mean | 14.88 | 1.757 | |
表7 对照试验结果
Table 7. Results of the control experiment
| 组别 Group | 序号 Number | 气流速度 Air velocity(m/s) | 落肥速度 Fattening rate (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 实验组 Experimental group | 1 | 19.9 | 2.123 |
| 2 | 19.7 | 2.395 | |
| 3 | 19.8 | 2.061 | |
| 4 | 19.3 | 2.093 | |
| 5 | 20.0 | 2.028 | |
| 均值 Mean | 19.74 | 2.140 | |
| 对照组 Control group | 1 | 14.8 | 1.857 |
| 2 | 14.6 | 1.834 | |
| 3 | 15.0 | 1.646 | |
| 4 | 14.9 | 1.708 | |
| 5 | 15.1 | 1.738 | |
| 均值 Mean | 14.88 | 1.757 | |
| [1] | 徐春春, 纪龙, 陈中督, 方福平. 2022年我国水稻产业发展分析及2023年展望[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(2): 1-4. |
| Xu C C, Ji L, Chen Z D, Fang F P. Analysis of rice industry development in China in 2022 and prospect in 2023[J]. China Rice, 2023, 29(2): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 李文昭, 颜雄, 柳叶红, 冯博, 赵君. 长期不均衡施肥对水稻土土壤肥力及水稻生物量的影响[J]. 农业与技术, 2021, 41(16): 78-80. |
| Li W Z, Yan X, Liu Y H, Fen B, Zhao J. Long-term unbalanced fertilization effects on soil fertility and rice paddy soil biomass[J]. Journal of Agriculture and Technology, 2021, 41(16): 78-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 周奥. 我国缓控释肥的应用研究和发展建议[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2020, 35(12): 16-19. |
| Zhou A. Application research and development suggestions of slow-controlled release fertilizer in China[J]. Phosphorus Fertilizer and Compound Fertilizer, 2019, 35(12): 16-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 韩英, 贾如, 唐汉. 精准变量施肥机械研究现状与发展建议[J]. 农业工程, 2019, 9(5): 1-6. |
| Han Y, Jia R, Tang H. Research status and development suggestions of precision variable fertilization machinery[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 9(5): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Bangura K, Wu S L, Tang Z Y, Feng X, Hu R J, Cai Y H, Zhou Y H, Liang Z P, Zeng Z W, Bangura A, Owusu-Sekyere E, Qi L, Gong H. Design and performance evaluation of the six-row side deep fertilizer applicator for paddy fields[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2024, 17(6): 166-175. |
| [6] | Zha X, Zhang G, Zhang S, Hou Q, Wang Y, Zhou Y. Design and experiment of centralized pneumatic deep precision fertilization device for rice transplanter[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2020, 13(6): 109-117. |
| [7] | Bao L, Gang C, Lin W, Guihong Z. Improved design of mechanized side deep fertilization device of Yangma rice transplanter[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology and Equipment, 2018,(05):5-6+9. |
| [8] | Campbell C M, Fulton J P, McDonald T P, Wood C W, Zech W C, Srivastava P. Spinner-disc technology to enhance the application of poultry litter[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2010, 26(5): 759-767. |
| [9] | 王金峰, 刘源峰, 翁武雄, 王金武, 付佐栋, 王震涛. 滑槽回转式水田侧深施肥装置设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2022, 53(10): 76-85. |
| Wang J F, Liu Y F, Weng W X, Wang J W, Fu Z D, Wang Z T. Design and experiment of rotary chute side deep fertilization device for paddy field[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2022, 53(10): 76-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 王金峰, 付佐栋, 翁武雄, 王震涛, 王金武, 杨东泽. 圆锥盘推板式水田侧深施肥双行排肥器设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2023, 54(2): 53-62. |
| Wang J F, Fu Z D, Weng W X, Wang Z T, Wang J W, Yang D Z. Design and experiment of double-row fertilizer applicator for side deep fertilization in paddy field with conical tray pushing plate[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2023, 54(2): 53-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 王金峰, 高观保, 王金武, 闫东伟. 叶片调节式水田侧深施肥装置设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(3): 68-76. |
| Wang J F, Gao G B, Wang J F, Yan D W. Design and experiment of lateral deep fertilization device with leaf regulation in paddy field[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(3): 68-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 熊文江. 2BDF-12机械式强排侧深施肥水稻直播机改进设计[J]. 南方农机, 2020, 51(1): 1. |
| Xiong W J. Improved design of 2BDF-12 mechanical strong row side deep fertilization rice livestreamer[J]. Southern Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(1): 1. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 马旭, 赵旭, 刘赛赛, 王宇唯, 王羲成, 李泽华. 水稻高速插秧机固体颗粒肥料变量施肥装置设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2023, 54(9): 99-110. |
| Ma X, Zhao X, Liu S S, Wang Y W, Wang X C, Li Z H. Design and experiment of variable fertilizer device for solid particle fertilizer in high-speed rice transplanter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2023, 54(9): 99-110. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 左兴健, 武广伟, 付卫强, 李立伟, 魏学礼, 赵春江. 风送式水稻侧深精准施肥装置的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(3): 14-21. |
| Zuo X J, Wu G W, Fu W Q, Li L W, Wei X L, Zhao C J. Design and experiment of wind-driven side deep precision fertilization device for rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(3): 14-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 辛明金, 张曼, 朱仰昆, 姜志文, 宋玉秋, 孔爱菊, 崔红光. 超大颗粒肥水田气力深施加速器设计及参数优化[J]. 农业工程学报, 2024, 40(8): 43-52. |
| Xin M J, Zhang M, Zhu Y K, Jiang Z W, Song Y Q, Kong A J, Cui H G. Design and parameter optimization of pneumatic deep application accelerator for super large particle fertilizer field[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2024, 40(8): 43-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 王嘉骏, 顾雪萍, 杨富军, 冯连芳. 双流体模型中曳力及恢复系数对气固流动的影响[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2006(2): 164-168. |
| Wang J J, Gu X P, Yang F J, Feng L F. Effects of drag force and restitution coefficient in the two-fluid model on gas-solid flow[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2006(2): 164-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 马飞, 宋志辉. 水射流动力特性及破土机理[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2006(5): 413-416. |
| Ma F, Song Z H. Dynamic characteristics of water jet and its soil penetration mechanism[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2006(5): 413-416. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 杨庆璐, 李子涵, 李洪文, 何进, 王庆杰, 卢彩云. 基于CFD-DEM的集排式分肥装置颗粒运动数值分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(8): 81-89. |
| Yang Q L, Li Z, Li H W, He J, Wang Q J, Lu C Y. Numerical analysis of particle movement in a compost fertilizer distribution device based on CFD-DEM[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(8): 81-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 陈钰佩, 孔海民, 朱伟锋, 陆若辉. 浙江省化肥定额制示范推广成效与经验[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2021, 62(11): 2188-2190. |
| Chen Y P, Kong H M, Zhu W F, Lu R H. Fertilizer quota system in Zhejiang Province demonstrated and results and experience[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Science, 2021, 62(11): 2188-2190. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 华晴赉, 韦光超, 但家云, 汪小毅, 崔佳鑫, 鄂殿玉. 高炉风口回旋区多形貌颗粒混合流动特性数值模拟[J]. 中国粉体技术, 2024, 30(6): 130-139. |
| Hua Q L, Wei G C, Dan J Y, Wang X Y, Cui J X, E D Y. Blast furnace tuyere raceway hybrid flow characteristics of the morphology of particles numerical simulation[J]. China Powder Technology, 2024, 30(6): 130-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 侯艳君, 王庆辉, 周甲伟, 闫翔宇, 郑泽冰, 刘晓辉. 基于CFD-DEM的气力输送变径管中颗粒流动特性分析[J]. 矿冶工程, 2023, 43(6): 6-10. |
| Hou Y J, Wang Q H, Zhou J W, Yan X, Zhen Z, Liu X H. Analysis of particle flow characteristics in pneumatic conveying reducer based on CFD-DEM[J]. Mining and Metallurgy Engineering, 2023, 43(6): 6-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Wu W X, Liu Z M, Duan G B. Numerical simulation of dense phase pneumatic conveying gypsum in stepped pipeline[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 306/307: 1387-1392. |
| [23] | McGlinchey D, Cowell A, Crowe R. CFD investigation of dense phase pneumatic conveying at a pipeline enlargement[J]. Particuology, 2012, 10(2): 176-183. |
| [24] | 宋金华, 舒梦, 帖金鑫, 杨洋, 吴育洁, 洪晨, 李瑞龙, 何逸波. 90°弯管中球柱状颗粒气力输送特性研究[J]. 力学与实践, 2025, 47(2): 315-322. |
| Song J H, Shu M, Tian J X, Yang Y, Wu Y J, Hong C, Li R L, He Y B. Study on Pneumatic conveying Characteristics of spheroid-column particles in 90° bending pipe[J]. Mechanics and Practice, 2025, 47(2): 315-322. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 王明旭, 秦超, 李永祥, 曹宪周. 气力输送过程中粮食颗粒的输送特性研究[J]. 农机化研究, 2014, 36(9): 18-22. |
| Wang M X, Qin C, Li Y X, Cao X Z. Food particles in the process of pneumatic conveying transportation research[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2014, 36(9): 18-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 魏海, 谢焕雄, 胡志超, 颜建春, 刘敏基, 徐弘博. 花生荚果气力输送设备参数优化与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(2): 6-12. |
| Wei H, Xie H X, Hu Z C, Yan J C, Liu M J, Xu H B. Parameter optimization and experiment of pneumatic conveying equipment for peanut pod[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(2): 6-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 张洋凯, 卢义玉, 汤积仁, 李倩, 凌远非, 龙海洋. 增压式脉冲水射流多脉冲特性试验研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2024, 53(1): 132-140. |
| Zhang Y K, Lu Y Y, Tang J R, Li Q, Ling Y F, Long H Y. Experimental study on multipulse characteristics of pressurized pulsed water jet[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2024, 53(1): 132-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 景建强, 李佳佳. 松软低透气性煤层瓦斯抽采技术研究[J]. 煤炭与化工, 2023, 46(1): 98-102. |
| Jing J Q, Li J J. Soft and low permeability of coal seam gas extraction technology research[J]. Journal of Coal and Chemical Industry, 2023 46(1): 98-102. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Yu C, Ma Y A, Li H B, Deng S C, Hao Y F, Zhu K. Analysis of impact pressure, rock-breaking effect, and ground vibration induced by the disposable CO2fracturing tube[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2024, 16(8):3099-3121. |
| [30] | 潘岩, 马飞, 蔡腾飞, 祝启恒, 孙智祥. 壁面约束作用下的空化射流冲蚀模式[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(S2): 618-625. |
| Pan Y, Ma F, Cai T F, Zhu Q H, Sun Z X. Wall under the action of constraint of cavitation jet erosion model[J]. Journal of Coal, 2023(S2): 618-625. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 李凌峰, 王沁沅, 王俊阳. 基于含水率改变的抗剪强度指标折减方法在膨胀土基坑支护设计计算中的应用[J]. 岩土工程技术, 2024, 38(5): 554-559. |
| Li L F, Wang Q Y, Wang J Y. Application of reduction method of shear strength index based on change of water content in support design calculation of expansive soil foundation pit[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technology, 2024, 38(5): 554-559. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 罗惟惟. 大庆地区粉土渗透性研究//中国石油学会石油工程专业委员会. 石油天然气勘察技术中心站第三十一次技术交流研讨会论文集[C]. 淮安: 大庆油田设计院有限公司, 2024: 66-71. DOI: 10.26914/c.cnkihy.2024.026936. |
| Luo W W. Research on silt permeability in Daqing Area //Petroleum Engineering Committee of China Petroleum Society. Proceedings of the 31st technical Exchange Seminar of Petroleum and Natural Gas Exploration Technology Central Station[C]. Huai’an: Daqing Oilfield Design Institute Co., LTD., 2024, 66-71. DOI: 10.26914/Arthurc.nkihy.2024.026936. | |
| [33] | Blotz L R, Benson C H, Boutwell G P. Estimating optimum water content and maximum dry unit weight for compacted clays[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 1998, 124(9): 907-912. |
| [34] | Pfister A, West A M, Bronner S, Noah J A. Comparative abilities of Microsoft Kinect and Vicon 3D motion capture for gait analysis[J]. Journal of Medical Engineering & Technology, 2014, 38(5): 274-280. |
| [35] | Liu W, Wang J B, Liu Z C. A method of fluid dynamic analysis based on Navier-Stokes equation and conservation equation on fluid mechanical energy[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 109: 393-396. |
| [36] | Mohebujjaman M, Rebholz L G, Xie X P, Iliescu T. Energy balance and mass conservation in reduced order models of fluid flows[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2017, 346: 262-277. |
| [1] | 曹玉东, 吴朋浩, 戴志刚, 王贵兵, 何帅, 巩细民, 李小坤. 侧深施肥对水稻产量、养分吸收及经济效益的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(6): 695-708. |
| [2] | 徐飞, 隋文志, 张拓, 怀宝东, 杨雪. 叶龄调控下水肥耦合对寒地水稻生物学特征及水肥利用效率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(4): 339-347. |
| [3] | 钟雪梅, 黄铁平, 彭建伟, 卢文璐, 康兴蓉, 孙梦飞, 宋思明, 唐启源, 陈裕新, 湛冬至, 周旋. 机插同步一次性精量施肥对双季稻养分累积及利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5): 436-446. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||