
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 440-450.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.250317
李慧捷1, 袁浩宇1, 解臣硕1, 肖茂华1,*( ), 黄伟星1, 曹瑜轩1, 唐存干2
), 黄伟星1, 曹瑜轩1, 唐存干2
收稿日期:2025-03-21
修回日期:2025-04-20
出版日期:2025-07-10
发布日期:2025-07-21
通讯作者:
*email: xiaomaohua@njau.edu.cn基金资助:
LI Huijie1, YUAN Haoyu1, XIE Chenshuo1, XIAO Maohua1,*( ), HUANG Weixing1, CAO Yuxuan1, TANG Cungan2
), HUANG Weixing1, CAO Yuxuan1, TANG Cungan2
Received:2025-03-21
Revised:2025-04-20
Online:2025-07-10
Published:2025-07-21
Contact:
*email:xiaomaohua@njau.edu.cn
摘要:
【目的】针对当前农业生产中传统耕作机具容易受到地形和工作负载变化的影响,适应性较差和调平控制精度不高等问题,【方法】提出了一种基于模糊PID算法的智能耕深自适应调平控制方法,设计了一种四杆式电控液压后悬挂调平装置,实现了耕深的自适应调控与均匀性保障。通过三维建模软件对四杆式液压后悬挂调平装置进行设计建模,并对该自适应耕深调节的电控液压后悬挂调平装置进行仿真分析,验证其能够安全稳定运行的载荷条件。【结果】实际田间作业试验验证,当拖拉机以低速、中速和高速三种不同行驶速度在田间作业时,采用模糊PID算法的液压后悬挂调平装置在10°和20°的坡上平均调平响应时间分别为2.2 s和5.3 s,调平误差均小于0.5°,且无超调现象。【结论】该系统能较好保证耕深的合格率和均匀度,实现了旋耕机在耕作过程中对耕深的实时自适应调控。
李慧捷, 袁浩宇, 解臣硕, 肖茂华, 黄伟星, 曹瑜轩, 唐存干. 基于自适应耕深调节的后悬挂调平系统方法研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 440-450.
LI Huijie, YUAN Haoyu, XIE Chenshuo, XIAO Maohua, HUANG Weixing, CAO Yuxuan, TANG Cungan. Design and Testing of an Adaptive Rear-hitch Leveling Control System for Tillage Depth Using Fuzzy PID Algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(4): 440-450.
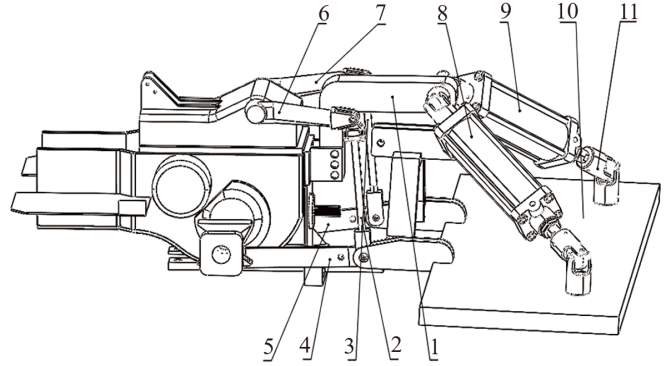
图1 四杆式液压后悬挂调平机构 1: 左旋转臂; 2: 右旋转臂; 3: 上支撑横梁; 4: 左长液压杆; 5: 右长液压杆; 6: 万向节; 7: 调平平台; 8: 左支撑杆; 9: 右支撑杆; 10: 左下支撑横梁; 11: 右下支撑横梁.
Fig. 1. Four-bar hydraulic rear suspension leveling mechanism 1, Left rotating arm; 2, Right rotating arm; 3, Upper support beam; 4, Left long hydraulic cylinder; 5, Right long hydraulic cylinder; 6, Universal joint; 7, Leveling platform; 8, Left support rod; 9, Right support rod; 10, Lower left support beam; 11, Lower right support beam.
| 部件名称 Component name | 尺寸参数 Dimensional parameters | 材质 Material |
|---|---|---|
| 上支撑横梁 Upper support beam | 长:1.5 m,宽:200 mm,厚:50 mm Length: 1.5 m, Width: 200 mm, Thickness: 50 mm | Q460D钢 Q460D Steel |
| 左/右支撑杆 Left/Right support rod | 长:1.2 m,直径:50 mm Length: 1.2 m, Diameter: 50 mm | Q345B钢 Q345B Steel |
| 左下/右下支撑横梁 Lower support beam | 长:1.2 m,宽:150 mm,厚:40 mm Length: 1.2 m, Width: 150 mm, Thickness: 40 mm | Q345B钢 Q345B Steel |
| 左/右旋转臂 Left/Right rotation arm | 长:0.8 m,直径:40 mm Length: 0.8 m, Diameter: 40 mm | 40Cr合金钢 40Cr Alloy steel |
| 左/右长液压杆 Left/Right hydraulic rod | 行程:1.5 m,直径:60 mm Stroke: 1.5 m, Diameter: 60 mm | 20CrMo合金钢 20CrMo Alloy steel |
| 调平平台 Leveling platform | 长:1.5 m,宽:0.8 m,厚:50 mm Length: 1.5 m, Width: 0.8 m, Thickness: 50 mm | Q345钢 Q345 Steel |
| 万向节 Universal joint | 外径:100 mm,高:150 mm Outer Diameter: 100 mm, Height: 150 mm | 42CrMo合金钢 42CrMo Alloy steel |
| 液压缸 Hydraulic cylinder | 缸径:80 mm,杆径:40 mm,行程:500 mm Bore: 80 mm, Rod Diameter: 40 mm, Stroke: 500 mm | 铸铁 Cast Iron |
| 液压泵 Hydraulic pump | 额定流量:20 L/min,输出压力:20 MPa Rated Flow: 20 L/min, Output Pressure: 20 MPa | 铸铁 Cast Iron |
| 比例阀 Proportional valve | 响应时间:≤50 ms,控制精度:±0.1% Response Time: ≤50 ms, Control Accuracy: ±0.1% | 铝合金 Aluminum alloy |
| 连接件 Fasteners | M16,长度:100 mm,抗拉强度≥800 MPa M16, Length: 100 mm, Tensile Strength ≥800 MPa | 10.9级高强度螺栓 Grade 10.9 High-strength bolt |
表1 调平平台的结构参数
Table 1. Structural parameters of leveling platform
| 部件名称 Component name | 尺寸参数 Dimensional parameters | 材质 Material |
|---|---|---|
| 上支撑横梁 Upper support beam | 长:1.5 m,宽:200 mm,厚:50 mm Length: 1.5 m, Width: 200 mm, Thickness: 50 mm | Q460D钢 Q460D Steel |
| 左/右支撑杆 Left/Right support rod | 长:1.2 m,直径:50 mm Length: 1.2 m, Diameter: 50 mm | Q345B钢 Q345B Steel |
| 左下/右下支撑横梁 Lower support beam | 长:1.2 m,宽:150 mm,厚:40 mm Length: 1.2 m, Width: 150 mm, Thickness: 40 mm | Q345B钢 Q345B Steel |
| 左/右旋转臂 Left/Right rotation arm | 长:0.8 m,直径:40 mm Length: 0.8 m, Diameter: 40 mm | 40Cr合金钢 40Cr Alloy steel |
| 左/右长液压杆 Left/Right hydraulic rod | 行程:1.5 m,直径:60 mm Stroke: 1.5 m, Diameter: 60 mm | 20CrMo合金钢 20CrMo Alloy steel |
| 调平平台 Leveling platform | 长:1.5 m,宽:0.8 m,厚:50 mm Length: 1.5 m, Width: 0.8 m, Thickness: 50 mm | Q345钢 Q345 Steel |
| 万向节 Universal joint | 外径:100 mm,高:150 mm Outer Diameter: 100 mm, Height: 150 mm | 42CrMo合金钢 42CrMo Alloy steel |
| 液压缸 Hydraulic cylinder | 缸径:80 mm,杆径:40 mm,行程:500 mm Bore: 80 mm, Rod Diameter: 40 mm, Stroke: 500 mm | 铸铁 Cast Iron |
| 液压泵 Hydraulic pump | 额定流量:20 L/min,输出压力:20 MPa Rated Flow: 20 L/min, Output Pressure: 20 MPa | 铸铁 Cast Iron |
| 比例阀 Proportional valve | 响应时间:≤50 ms,控制精度:±0.1% Response Time: ≤50 ms, Control Accuracy: ±0.1% | 铝合金 Aluminum alloy |
| 连接件 Fasteners | M16,长度:100 mm,抗拉强度≥800 MPa M16, Length: 100 mm, Tensile Strength ≥800 MPa | 10.9级高强度螺栓 Grade 10.9 High-strength bolt |
| 变量 | 基本论域 | 量化论域 | 量化因子 |
|---|---|---|---|
| r* | [-2.8, 2.8] | [-6, 6] | 0.05 |
| e(c) | [-0.02, 0.02] | [-6, 6] | 0.12 |
| ∆kp | [-0.9, 0.9] | [-3, 3] | 0.30 |
| ∆ki | [-0.05, 0.05] | [-3, 3] | 0.02 |
| ∆kd | [-1.6, 1.6] | [-3, 3] | 0.50 |
表2 模糊PID算法参数设置
Table 2. Parameters setting for fuzzy PID algorithm
| 变量 | 基本论域 | 量化论域 | 量化因子 |
|---|---|---|---|
| r* | [-2.8, 2.8] | [-6, 6] | 0.05 |
| e(c) | [-0.02, 0.02] | [-6, 6] | 0.12 |
| ∆kp | [-0.9, 0.9] | [-3, 3] | 0.30 |
| ∆ki | [-0.05, 0.05] | [-3, 3] | 0.02 |
| ∆kd | [-1.6, 1.6] | [-3, 3] | 0.50 |
| 实验指标 Experimental metric | 作业速度Speed | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 低速(1.2 km/h) Low (1.2 km/h) | 中速(3.6 km/h) Medium (3.6 km/h) | 高速(5.2 km/h) High (5.2 km/h) | |
| 耕深平均值Mean depth (mm) | 31.49 | 30.13 | 31.75 |
| 耕深合格率Qualification rate (%) | 92 | 93 | 91 |
| 耕深标准差Depth standard deviation (mm) | 0.26 | 0.18 | 0.21 |
| 耕深变异系数Coefficient of variation (%) | 3.51 | 2.93 | 3.26 |
表3 耕深测量结果
Table 3. Relationship between cultivation depth qualification rate and speed
| 实验指标 Experimental metric | 作业速度Speed | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 低速(1.2 km/h) Low (1.2 km/h) | 中速(3.6 km/h) Medium (3.6 km/h) | 高速(5.2 km/h) High (5.2 km/h) | |
| 耕深平均值Mean depth (mm) | 31.49 | 30.13 | 31.75 |
| 耕深合格率Qualification rate (%) | 92 | 93 | 91 |
| 耕深标准差Depth standard deviation (mm) | 0.26 | 0.18 | 0.21 |
| 耕深变异系数Coefficient of variation (%) | 3.51 | 2.93 | 3.26 |
| 实验指标 Experimental metric | 作业深度Depth | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 浅耕(100 mm) Shallow (100 mm) | 中耕(200 mm) Medium (200 mm) | 深耕(250 mm) Deep (250 mm) | |
| 耕深平均值Mean depth (mm) | 102.5 | 199.1 | 253.4 |
| 耕深合格率Qualification rate (%) | 94.0 | 93.0 | 90.0 |
| 耕深标准差Depth standard deviation (mm) | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
表4 耕深自适应精度与耕作深度关系
Table 4. Relationship between adaptive precision and tillage depth
| 实验指标 Experimental metric | 作业深度Depth | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 浅耕(100 mm) Shallow (100 mm) | 中耕(200 mm) Medium (200 mm) | 深耕(250 mm) Deep (250 mm) | |
| 耕深平均值Mean depth (mm) | 102.5 | 199.1 | 253.4 |
| 耕深合格率Qualification rate (%) | 94.0 | 93.0 | 90.0 |
| 耕深标准差Depth standard deviation (mm) | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| [1] | 梁淑敏, 谢瑞芝, 汤永禄, 李朝苏, 王欣, 何晓莹, 李少昆. 不同耕作措施对成都平原稻麦轮作区土壤蓄水抗蚀性及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(2): 199-205. |
| Liang S M, Xie R Z, Tang Y L, Li C S, Wang X, He X Y, Li S K. Effect of different tillage systems on the corrosion resistance and water storage of soil and crop yield under rice-wheat rotation in Chengdu plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2014, 28(2): 199-205. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 杨通, 吴俊男, 鲍婷, 李凤博, 冯金飞, 周锡跃, 方福平. 耕作方式对双季稻田土壤剖面CH4和N2O分布特征的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 78-88. |
| Yang T, Wu J N, Bao T, Li F B, Feng J F, Zhou X Y, Fang F P. Effects of tillage methods on distribution characteristics of CH4 and N2O in soil profile of double-cropping paddy field[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2021, 35(1): 78-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 孙景彬, 楚国评, 潘冠廷, 孟宠, 刘志杰, 杨福增. 遥控全向调平山地履带拖拉机设计与性能试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2021, 52(5): 358-369. |
| Sun J B, Chu G P, Pan G T, Meng C, Liu Z J, Yang F Z. Design and performance test of remote control omnidirectional leveling hillside crawler tractor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2021, 52(5): 358-369. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 张静, 刘昱, 郑德聪, 李志伟. 丘陵山地拖拉机机身自平衡机构稳定性分析[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2022, 43(9): 102-108. |
| Zhang J, Liu Y, Zheng D C, Li Z W. Stability analysis of self-balancing mechanism for the body of hilly tractors[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2022, 43(9): 102-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 彭贺, 马文星, 王忠山, 刘春宝, 黄健, 赵恩鹏. 丘陵山地拖拉机车身调平控制仿真分析与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(1): 157-165. |
| Peng H, Ma W X, Wang Z S, Liu C B, Huang J, Zhao E P. Control system of self-leveling in hilly tractor body through simulation and experiment[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(1): 157-165. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 靳红玲, 朱海军, 张昕杰, 王述杰, 秦名扬, 陈雨, 张硕. 山地茶园模块化全向动态四点调平装置设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2024, 55(9): 205-215. |
| Jin H L, Zhu H J, Zhang X J, Wang S J, Qin M Y, Chen Y, Zhang S. Design and experiment of modular omnidirectional dynamic four-point leveling device for mountain tea plantations[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2024, 55(9): 205-215. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Chen L, Karkee M, He L, Wei Y L, Zhang Q. Evaluation of a leveling system for a weeding robot under field condition[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2018, 51(17): 368-373. |
| [8] | Park Y, Son H I. A sensor fusion-based cutting device attitude control to improve the accuracy of Korean cabbage harvesting[J]. Journal of the ASABE, 2022, 65(6): 1387-1396. |
| [9] | 唐文帮, 张桂莲, 邓化冰. 杂交水稻机械化制种的技术探索与实践[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(2): 95-103. |
| Tang W B, Zhang G L, Deng H B. Technology exploration and practice of hybrid rice mechanized seed production[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(2): 95-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Sunusi I I, Zhou J, Wang Z Z, Sun C Y, Ibrahim I E, Opiyo S, Korohou T, Soomro S A, Sale N A, Olanrewaju T O. Intelligent tractors: Review of online traction control process[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2020, 170: 1-16. |
| [11] | 徐学政, 杨俊茹, 李瑞川, 韩宗冉, 张建. 基于AMESim的丘陵山地拖拉机电液提升系统研究[J]. 农机化研究, 2023, 45(8): 253-258. |
| Xu X Z, Yang J R, Li R C, Han Z R, Zhang J. Research on electro-hydraulic lifting system of hilly tractor based on AMESim[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2023, 45(8): 253-258. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 王沁敏. 拖拉机电子液压悬挂控制器设计与控制技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2008. |
| Wang Q M. The research and deign of the electrohydraulic control technology of hitch control unit for the tractor[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2008. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 赵国栋, 管春松, 肖体琼, 高庆生, 崔志超, 陈永生. 拖拉机电动悬挂机构性能分析及参数优化[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2019, 40(3): 122-127. |
| Zhao G D, Guan C S, Xiao T Q, Gao Q S, Cui Z G, Chen Y S. Performance analysis and parameter optimization of tractor electric suspension mechanism[J]. Journal of Chinese Agriculture Mechanization, 2019, 40(3): 122-127. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 徐煌. 拖拉机电液悬挂系统力位综合控制技术的研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2010. |
| Xu H. Research of force-position combined control technology for tractor electrohydraulic hitch system[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agriculture University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 陈明江, 鲁植雄, 袁越阳, 王沁敏. 拖拉机电子液压悬挂系统位调节控制器设计[J]. 机械与电子, 2008(11): 19-22. |
| Chen M J, Lu Z X, Yuan Y Y., Wang Q M. Design of the position-adjust controller for electro-hydraulic hitch system of tractor[J]. Machinery & Electronics, 2008(11): 19-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Kovačev I G, Košutić S, Jejčič V, Krešimir C, GOSPOdArić Z, PlieSTić S. Impact of electronic-hydraulic hitch control on rational exploitation of tractor in ploughing[J]. Strojarstvo, 2008, 50(5): 287-294. |
| [17] | Pranav P K, Tewari V K, Pandey K P, Jha K R. Automatic wheel slip control system in field operations for 2WD tractors[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2012, 84: 1-6. |
| [18] | Gupta C, Tewari V K, Ashok Kumar A, Shrivastava P. Automatic tractor slip-draft embedded control system[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2019, 165: 104947. |
| [19] | Kumar R, Raheman H. Design and development of a variable hitching system for improving stability of tractor trailer combination[J]. Engineering in Agriculture, Environment and Food, 2015, 8(3): 187-194. |
| [20] | 张峥颖. 拖拉机三点悬挂电-液控制系统的设计与试验[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2022. |
| Zhang Z Y. Design and experiment on the electric-hydraulic control system of tractor’s three-point suspension[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 李国栋. 拖拉机悬挂电液提升控制系统的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017. |
| Li G D. Research on electro-hydraulic hitch control system of tractor[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 高翔, 孙昌旺, 史金钟, 王琪. 拖拉机电控液压悬挂系统的耕深模糊控制策略[J]. 拖拉机与农用运输车, 2008(4): 12-14. |
| Gao X, Sun C W, Shi J Z, Wang Q. Research of fuzzy control method for electronic hydraulic hitch of tractor[J]. Tractor & Farm Transporter, 2008(4): 12-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Xu J K, Li R C, Li Y C, Zhang Y S, Sun H L, Ding X K, Ma Y. Research on variable-universe fuzzy control technology of an electro-hydraulic hitch system[J]. Processes, 2021, 9(11): 1920. |
| [24] | Zhou M K, Xia J F, Zhang S A, Hu M J, Liu Z Y, Liu G Y, Luo C M. Development of a depth control system based on variable-gain single-neuron PID for rotary burying of stubbles[J]. Agriculture, 2022, 12(1): 30. |
| [25] | Torres W L, Araujo I B Q, Menezes Filho J B, Costa A G. Mathematical modeling and PID controller parameter tuning in a didactic thermal plant[J]. IEEE Latin America Transactions, 15(7): 1250-1256. |
| [26] | Anthonis J, Mouazen A M, Saeys W, Ramon H. An automatic depth control system for online measurement of spatial variation in soil compaction: Ⅲ. Design of depth control system[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2004, 89(1): 59-67. |
| [27] | Shafaei S M, Loghavi M, Kamgar S. A practical effort to equip tractor-implement with fuzzy depth and draft control system[J]. Engineering in Agriculture, Environment and Food, 2019, 12(2): 191-203. |
| [28] | Dobrinska R, Jarboe R. The development and application of electro-hydraulic control system for case 4WD Tractors[J]. SAE Technical Paper, 1981(810941): 33-39. |
| [29] | 薛冰, 周利明, 牛康, 郑元坤, 白圣贺, 隗立昂. 基于自适应模糊PID的小麦播深控制系统研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2023, 54(S1): 93-102. |
| Xue B, Zhou L M, Niu K, Zheng Y K, Bai S H, Wei L A. Sowing depth control system of wheat planter based on adaptive fuzzy PID[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2023, 54(S1): 93-102. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||