
中国水稻科学 ›› 2015, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (4): 305-310.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001G7216.2015.03.010
• 研究报告 • 下一篇
华丽霞1,2, 汪文娟1,2, 陈深1,2, 汪聪颖1,2, 曾烈先1, 杨健源1, 朱小源1, 苏菁1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2014-05-20
修回日期:2014-07-15
出版日期:2015-07-10
发布日期:2015-07-10
通讯作者:
苏菁
基金资助:
Li-xia HUA1,2, Wen-juan WANG1,2, Shen CHEN1,2, Cong-ying WANG1,2, Lie-xian ZENG1, Jian-yuan YANG1, Xiao-yuan ZHU1, Jing SU1,2,*( )
)
Received:2014-05-20
Revised:2014-07-15
Online:2015-07-10
Published:2015-07-10
Contact:
Jing SU
摘要:
通过对已克隆的抗稻瘟病基因Pi2、Pi9以及Piz-t 进行序列比对,寻找各自特异的核苷酸差异,成功开发了基于PCR技术以及电泳检测技术的 Pi2/Pi9/Piz-t 以及Piz-t 的基因特异性分子标记,能有效地将 Pi2/Pi9/Piz-t 与该位点上的其他抗性等位基因及感病等位基因区分开,这为分子标记辅助育种及抗病基因聚合提供有效的分子标记。用 Pi2/Pi9/Piz-t 基因特异性分子标记对来自全国各稻区的共101份水稻品种和育种亲本进行分子检测,结果发现,除2个品种检测到Piz-t带型之外,大部分水稻品种不携带这3个抗性基因,这为有目的地开展品种的抗性改良提供了重要的参考信息。
中图分类号:
华丽霞, 汪文娟, 陈深, 汪聪颖, 曾烈先, 杨健源, 朱小源, 苏菁. 抗稻瘟病Pi2/9/z-t基因特异性分子标记的开发[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(4): 305-310.
Li-xia HUA, Wen-juan WANG, Shen CHEN, Cong-ying WANG, Lie-xian ZENG, Jian-yuan YANG, Xiao-yuan ZHU, Jing SU. Development of Specific DNA Markers for Detecting the Rice Blast Resistance Gene Alleles Pi2/9/z-t[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2015, 29(4): 305-310.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'-3') Sequences (5'-3') | 退火温度 Annealing temperature /℃ | 预期片段大小 Expected size /bp | 标记类型 Marker type | 内切酶 Cutting enzyme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pi9SNP | F:CGCCGGTTGATAAGTAAAAGCT | 60 | 126 | dCAPS | Hind Ⅲ |
| R:CAAGAACTAATATCTACCCATGG | |||||
| Pi2SNP | F:TACTCTTCGTTGTATAGGAC | 58 | 462 | CAPS | Hinf Ⅰ |
| R:GGAGGAGGAGATGAAATAGAATC | |||||
| Pizt PA | F:ATGTGGATGCTGTGTTAT | 62 | 176 | Presence/ | — |
| R:TAGTTTGCTGCTCAATAAGTA | Absence |
表1 Pi2/Pi9/Piz-t 基因特异性分子标记相关信息
Table 1 Information of specific markers for Pi2/Pi9/Piz-t.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'-3') Sequences (5'-3') | 退火温度 Annealing temperature /℃ | 预期片段大小 Expected size /bp | 标记类型 Marker type | 内切酶 Cutting enzyme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pi9SNP | F:CGCCGGTTGATAAGTAAAAGCT | 60 | 126 | dCAPS | Hind Ⅲ |
| R:CAAGAACTAATATCTACCCATGG | |||||
| Pi2SNP | F:TACTCTTCGTTGTATAGGAC | 58 | 462 | CAPS | Hinf Ⅰ |
| R:GGAGGAGGAGATGAAATAGAATC | |||||
| Pizt PA | F:ATGTGGATGCTGTGTTAT | 62 | 176 | Presence/ | — |
| R:TAGTTTGCTGCTCAATAAGTA | Absence |
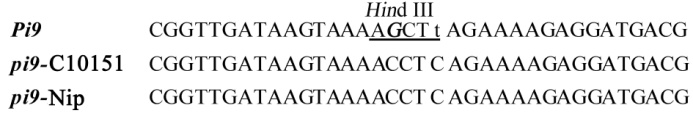
图1 Pi9 部分序列比对结果(小写字母“t”代表Pi9特异SNP,斜体字母“G”代表在正向引物3'端引入的错配碱基,下划线表示的位点是限制性内切酶 Hind Ⅲ识别位点。)
Fig. 1. Sequence alignment of Pi9 and its orthlogs. (The Pi9-specific SNP is indicated in lowercase. A forward primer with a mismatch base (in italic and bold) is designed adjacent to Pi9-specific SNP, creating a Hind Ⅲ recognition site that is dependent on this specific SNP.)
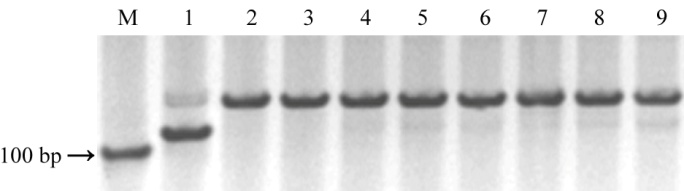
图2 Pi9特异性分子标记Pi9SNP的多态性检测(M-D600;泳道1-IRBL9-W (Pi9+);泳道2-C101A51 (Pi2);泳道3-IRBLz-Fu (Piz );泳道4-IRBLzt-T (Piz-t);泳道5-谷梅2号(Pi26);泳道6-谷梅4号 (Pigm);泳道7-EBZ (Pi50);泳道8-日本晴;泳道9-LTH。)
Fig. 2. Polymorphism validation of Pi9-specific marker. (M, D600; Line 1, IRBL9-W (Pi9+); Line 2, C101A51 (Pi2); Line 3, IRBLz-Fu (Piz ); Line 4, IRBLzt-T (Piz-t); Line 5, Gumei 2 (Pi26); Line 6, Gumei 4 (Pigm); Line 7, EBZ (Pi50); Line 8, Nipponbare; Line 9, LTH.)
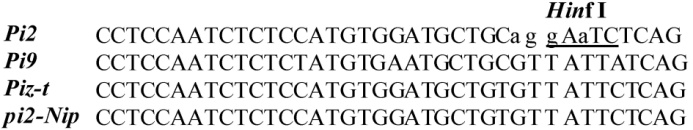
图3 Pi2与等位基因之间的序列比对(小写字母代表Pi2特异SNP,下划线所表示的位点是限制性内切酶 Hinf I识别位点。)
Fig. 3. Sequence alignment of Pi2 and its orthlogs. (The Pi2-specific SNP is indicated in lowercase. Underlined bases refer to a Hinf I recognition site that is dependent on the Pi2-specific SNP.)
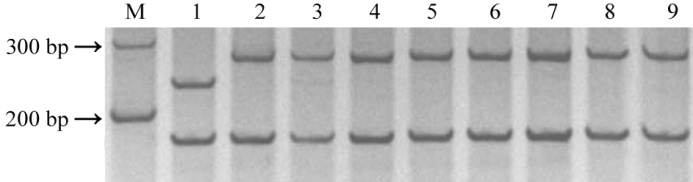
图4 Pi2特异性分子标记Pi2SNP的多态性检测(M-D600; 泳道1-C101A51 (Pi2+); 泳道2-IRBL9-W (Pi9); 泳道3- IRBLz-Fu ( Piz ); 泳道4-IRBLzt-T (Piz-t ); 泳道5-Gumei 2 (Pi26 );泳道6-Gumei 4 (Pigm); 泳道7-EBZ (Pi50); 泳道8- Nipponbare; 泳道9- LTH。)
Fig. 4. Polymorphism validation of Pi2-specific marker. (D600; Line 1, C101A51 (Pi2+); Line 2, IRBL9-W (Pi9); Line 3, IRBLz-Fu ( Piz ); Line 4, IRBLzt-T (Piz-t); Line 5, Gumei 2 (Pi26 ); Line 6, Gumei 4 (Pigm); Line 7, EBZ (Pi50); Line 8, Nipponbare; Line 9, LTH.)

图5 Piz-t与等位基因之间的序列比对(Piz-t 特异SNP用小写字母表示,下划线表示Piz-t 特异引物对序列(左侧为正向引物,右侧为反向引物),Piz-t 的特异性SNP均位于引物的3'末端。虚线代表引物之间的序列。)
Fig. 5. Sequence alignment for Piz-t and its orthlogs. (The Pizt-specific SNPs are noted in lowercase. The designed Pizt-specific primers are underlined (left, forward primer; right, reverse), harbouring the Pizt-specific SNPs at the end of the 3'primer. Dash lines indicate the elliptical base pairs between the primer pair.)
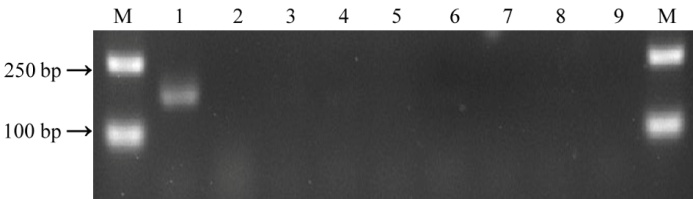
图6 Piz-t 特异性分子标记Pizt-PA的多态性检测(M, DL2000; 泳道1-IRBLzt-T (Piz-t+); 泳道2-IRBL9-W (Pi9); 泳道3-IRBLz-Fu ( Piz ); 泳道4-C101A51 (Pi2); 泳道5-Gumei 2 ( Pi26 ); 泳道6-Gumei 4 ( Pigm ); 泳道7-EBZ (Pi50); 泳道8-Nipponbare; 泳道9-LTH。)
Fig. 6. Specific SNP diagnosis for Piz-t and its polymorphism validation. (M, DL2000; Line 1, IRBLzt-T (Piz-t+); Line 2, IRBL9-W (Pi9); Line 3, IRBLz-Fu ( Piz ); Line 4, C101A51 (Pi2); Line 5, Gumei 2 ( Pi26) ; Line 6, Gumei 4 ( Pigm ); Line 7, EBZ (Pi50); Line 8, Nipponbare; Line 9, LTH.)
| [1] | Liu J, Wang X, Mitchell T, et al.Recent progress and understanding of the molecular mechanisms of the rice-Magnaporthe oryzae interaction.Mol Plant Pathol, 2010, 11(3): 419-427. |
| [2] | Kiyosawa S.Breakdown of blast resistance in rice in relation to general strategies of resistance gene deployment to prolong effectiveness of disease resistance in plants//Leonard K J, Fry W E. Plant Disease Epidemiology. New York:McGraw-Hill, 1989: 251-283. |
| [3] | 殷得所, 夏明元, 李进波, 等. 抗稻瘟病基因Pi9的STS连锁标记开发及在分子标记辅助育种中的应用. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(1): 25-30. |
| [4] | 柳武革, 王丰, 金素娟, 等.利用分子标记辅助选择聚合Pi1和Pi2基因改良两系不育系稻瘟病抗性.作物学报, 2008, 34(7): 1128-1136. |
| [5] | Hittalmani S, Parco A, Mew T V, et al.Fine mapping and DNA marker-assisted pyramiding of the three major genes for blast resistance in rice.Theor Appl Genet, 2000, 100(7): 1121-1128. |
| [6] | Jena K K, Mackill D J.Molecular markers and their use in marker-assisted selection in rice.Crop Sci, 2008, 48(4): 1266-1276. |
| [7] | Fu C, Wu T, Liu W, et al.Genetic improvement of resistance to blast and bacterial blight of the elite maintainer line Rongfeng B in hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.) by using marker-assisted selection.Afric J Biotechnol, 2012, 11(67): 13104-13124. |
| [8] | Hayashi K, Yoshida H, Ashikawa I.Development of PCR-based allele-specific and InDel marker sets for nine rice blast resistance genes.Theor Appl Genet, 2006, 113(2): 251-260. |
| [9] | Ingvardsen C R, Schejbel B, Lübberstedt T. Functional markers in resistance breeding. Prog Bot, 2008, 69: part 2, 61-87. |
| [10] | Zhou B, Qu S, Liu G, et al.The eight amino-acid differences within three leucine-rich repeats between Pi2 and Piz-t resistance proteins determine the resistance specificity to Magnaporthe grisea.Mol Plant Microb Interact, 2006, 19(11): 1216-1228. |
| [11] | Ashikawa I, Hayashi N, Yamane H, et al.Two adjacent nucleotide-binding site-leucine rich repeat class genes are required to confer Pikm-specific rice blast resistance.Genetics, 2008, 180(4): 2267-2276. |
| [12] | Yuan B,Zhai C, Wang W, et al.The Pik-p resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae in rice is mediated by a pair of closely linked CC-NBS-LRR genes.Theor Appl Genet 2011, 122(5): 1017-1028. |
| [13] | Zhai C, Lin F, Dong Z, et al.The isolation and characterization of Pik, a rice blast resistance gene which emerged after rice domestication.New Phytol, 2011, 189(1): 321-334. |
| [14] | Hua L, Wu J, Chen C, et al.The isolation of Pi1, an allele at the Pik locus which confers broad spectrum resistance to rice blast.Theor Appl Genet, 2012, 125(5): 1047-1055. |
| [15] | Jiang N, Li Z, Wu J, et al.Molecular mapping of the Pi2/9 allelic gene Pi2-2 conferring broad-spectrum resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae in the rice cultivar Jefferson.Rice, 2012, 5: 29. |
| [16] | Qu S, Liu G, Zhou B, et al.The broad-spectrum blast resistance gene Pi9 encodes a nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat protein and is a member of a multigene family in rice.Genetics, 2006, 172(3): 1901-1914. |
| [17] | Neff MM, Turk E, Kalishman M.Web-based primer design for single nucleotide polymorphism analysis.Trends Genet, 2002, 18(12): 613-615. |
| [18] | Koide Y, Kobayashi N, Xu D, et al.Resistance genes and selection DNA markers for blast disease in rice (Oryza sativa L.).JARQ, 2009, 43(4): 255-280. |
| [19] | Wen S, Gao B.Introgressing blast resistant gene Pi9 (t) into elite rice restorer Luhui 17 by marker-assisted selection.Rice Genom Genet, 2011, 2(4): 31-36. |
| [20] | Jiang H, Feng Y,Bao L, et al.Improve blast resistance of Jin 23B and its hybrid rice by marker-assisted gene pyramiding.Mol Breeding, 2012, 30(4): 1679-1688. |
| [21] | Lei C,Hao K, Yang Y, et al.Identification and fine mapping of two blast resistance genes in rice cultivars 93-11.Crop J, 2013, 1(1): 2-14. |
| [22] | Takagi H,Uemura A, Yaegashi H, et al.MutMap-Gap: Whole-genome resequencing of mutant F2 progeny bulk combined with de novo assembly of gap regions identifies the rice blast resistance gene Pii.New Phytol, 2013, 200(1): 276-283. |
| [23] | Hayashi K, Yasuda N, Fujita Y, et al.Identification of the blast resistance genePit in rice cultivars using functional markers.Theor Appl Genet, 2010, 121(7): 1357-1367. |
| [24] | Wang H M, Chen J, Shi Y F, et al.Development and validation of CAPS markers for marker-assisted selection of rice blast resistance gene Pi25.Acta Agron Sin, 2012, 38(11):1960-1968. |
| [25] | Huang B, Xu J Y,Hou M S, et al.Introgression of bacterial blight resistance genes Xa7, Xa21, Xa22 and Xa23 into hybrid rice restorer lines by molecular marker-assisted selection.Euphytica, 2012, 187(3): 449-459. |
| [26] | Chen J, Shi Y, Liu W, et al.A Pid3 allele from rice cultivar Gumei 2 confers resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae.J Gen Genom, 2011, 38(5): 209-216. |
| [27] | Zhu X, Chen S, Yang J, et al.The identification of Pi50 (t), a new member of the rice blast resistance Pi2/9 multigene family.Theor Appl Genet, 2012, 124(7): 1295-1304. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||