
中国水稻科学 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (2): 103-111.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.0905
• 研究报告 • 下一篇
路凯, 陈涛, 姚姝, 梁文化, 魏晓东, 张亚东*( ), 王才林*(
), 王才林*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-09-05
修回日期:2020-09-18
出版日期:2021-03-10
发布日期:2021-03-10
通讯作者:
张亚东,王才林
基金资助:
Kai LU, Tao CHEN, Shu YAO, Wenhua LIANG, Xiaodong WEI, Yadong ZHANG*( ), Cailin WANG*(
), Cailin WANG*( )
)
Received:2020-09-05
Revised:2020-09-18
Online:2021-03-10
Published:2021-03-10
Contact:
Yadong ZHANG, Cailin WANG
摘要:
【目的】盐胁迫是制约水稻生长和产量主要逆境之一,研究盐胁迫响应基因对于了解植物耐盐机理和培育耐盐水稻品种具有重要意义。类受体蛋白激酶RLK(receptor-like protein kinases)广泛参与调控植物细胞信号转导和对逆境胁迫的响应过程。本研究的目的是分析盐胁迫下四个RLK基因的表达模式和生物学功能。【方法】通过荧光定量PCR检测4个RLK基因在NaCl处理下的表达变化以及在不同组织器官中的表达情况,同时利用CRISPR/Cas9对4个RLK基因分别进行编辑。【结果】4个RLK基因的转录均受NaCl诱导或抑制,其中Os04g0275100基因和Os07g0541900基因主要在根中表达;Os09g0353200基因主要在叶片中表达;Os01g0852100基因在根、茎、叶、叶鞘中均有表达。通过测序分别筛选到4个基因的功能缺失突变体,耐盐性实验结果表明四个基因的突变体对NaCl的敏感程度与野生型一致。【结论】鉴定的4个RLK基因的转录受NaCl调控且表达具有组织特异性,突变单个RLK基因不影响水稻的耐盐性。为进一步揭示盐胁迫下RLK基因的功能和作用机制奠定了基础。
路凯, 陈涛, 姚姝, 梁文化, 魏晓东, 张亚东, 王才林. 盐胁迫下四个水稻类受体蛋白激酶的功能分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(2): 103-111.
Kai LU, Tao CHEN, Shu YAO, Wenhua LIANG, Xiaodong WEI, Yadong ZHANG, Cailin WANG. Functional Analysis on Four Receptor-like Protein Kinases Under Salt Stress in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(2): 103-111.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| Os04g0275100-Target-1F Os04g0275100-Target-1R Os04g0275100-Target-2F Os04g0275100-Target-2R Os09g0353200-Target-1F Os09g0353200-Target-1R Os09g0353200-Target-2F Os09g0353200-Target-2R Os07g0541900-Target-1F Os07g0541900-Target-1R Os07g0541900-Target-2F Os07g0541900-Target-2R Os01g0852100-Target-1F Os01g0852100-Target-1R Os01g0852100-Target-2F Os01g0852100-Target-2R | GGCACGGCTCTGCTATGCCTCCT AAACAGGAGGCATAGCAGAGCCG GCCGCTACATCGGCGGCGACAACG AAACCGTTGTCGCCGCCGATGTAG GGCAGCCTCACTATCCGAAGCAG AAACCTGCTTCGGATAGTGAGGC GCCGCTGCGGTTCGATCTGCATCT AAACAGATGCAGATCGAACCGCAG GGCACCTCATCAGCGCCCTCCAG AAACCTGGAGGGCGCTGATGAGG GCCGCCTCCTGAACGCCACCGTG AAACCACGGTGGCGTTCAGGAGG GCCGTATAAGGGGAAGCTCAGGGA AAACTCCCTGAGCTTCCCCTTATA GCCGTGGCCGATTTCGGCTTCGCA AAACTGCGAAGCCGAAATCGGCCA |
| Os04g0275100-T1T2-F Os04g0275100-T1T2-R Os09g0353200-T1T2-F Os09g0353200-T1T2-R Os07g0541900-T1T2-F Os07g0541900-T1T2-R Os01g0852100-T1-F Os01g0852100-T1-R Os01g0852100-T2-F Os01g0852100-T2-R U-F | GTGGGACGGATGAAGTAGTATATCTTCG AATCAAGCAGCAAGGGGACCT ACGTGCAAGGATCTATTCAAAACT GGAGAGAACACATACCGGGTAAG ACATCCAAAATGATACGCATTCCA AGCTCCGACCTCAGGTTACACC GGTACTCGCACCAGGAATTTAGAG CATCATGCTTAGGGGTTCAACA TTGTCCTGAATAAACCAACAGTAGCACT CAACAACTTGGGAAACGTTAAACG CTCCGTTTTACCTGTGGAATCG |
| U-R | CGGAGGAAAATTCCATCCAC |
| Uctcg-B1’ | TTCAGAGGTCTCTCTCGCACTGGAATCGGCAGCAAAGG |
| gRctga-B2 | AGCGTGGGTCTCGTCAGGGTCCATCCACTCCAAGCTC |
| Uctga-B2’ | TTCAGAGGTCTCTCTGACACTGGAATCGGCAGCAAAGG |
| gRcggt-BL | AGCGTGGGTCTCGACCGGGTCCATCCACTCCAAGCTC |
| Cas9-F | GATCCTTACTTTCCGTATTCCTTACTACG |
| Cas9-R OsActin1-qPCR-F OsActin1-qPCR-R | ATACCCTCCTCAATCCTCTTCATG GATGACCCAGATCATGTTTG GGGCGATGTAGGAAAGC |
表1 本研究所用引物序列
Table 1 Primers used in this study.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| Os04g0275100-Target-1F Os04g0275100-Target-1R Os04g0275100-Target-2F Os04g0275100-Target-2R Os09g0353200-Target-1F Os09g0353200-Target-1R Os09g0353200-Target-2F Os09g0353200-Target-2R Os07g0541900-Target-1F Os07g0541900-Target-1R Os07g0541900-Target-2F Os07g0541900-Target-2R Os01g0852100-Target-1F Os01g0852100-Target-1R Os01g0852100-Target-2F Os01g0852100-Target-2R | GGCACGGCTCTGCTATGCCTCCT AAACAGGAGGCATAGCAGAGCCG GCCGCTACATCGGCGGCGACAACG AAACCGTTGTCGCCGCCGATGTAG GGCAGCCTCACTATCCGAAGCAG AAACCTGCTTCGGATAGTGAGGC GCCGCTGCGGTTCGATCTGCATCT AAACAGATGCAGATCGAACCGCAG GGCACCTCATCAGCGCCCTCCAG AAACCTGGAGGGCGCTGATGAGG GCCGCCTCCTGAACGCCACCGTG AAACCACGGTGGCGTTCAGGAGG GCCGTATAAGGGGAAGCTCAGGGA AAACTCCCTGAGCTTCCCCTTATA GCCGTGGCCGATTTCGGCTTCGCA AAACTGCGAAGCCGAAATCGGCCA |
| Os04g0275100-T1T2-F Os04g0275100-T1T2-R Os09g0353200-T1T2-F Os09g0353200-T1T2-R Os07g0541900-T1T2-F Os07g0541900-T1T2-R Os01g0852100-T1-F Os01g0852100-T1-R Os01g0852100-T2-F Os01g0852100-T2-R U-F | GTGGGACGGATGAAGTAGTATATCTTCG AATCAAGCAGCAAGGGGACCT ACGTGCAAGGATCTATTCAAAACT GGAGAGAACACATACCGGGTAAG ACATCCAAAATGATACGCATTCCA AGCTCCGACCTCAGGTTACACC GGTACTCGCACCAGGAATTTAGAG CATCATGCTTAGGGGTTCAACA TTGTCCTGAATAAACCAACAGTAGCACT CAACAACTTGGGAAACGTTAAACG CTCCGTTTTACCTGTGGAATCG |
| U-R | CGGAGGAAAATTCCATCCAC |
| Uctcg-B1’ | TTCAGAGGTCTCTCTCGCACTGGAATCGGCAGCAAAGG |
| gRctga-B2 | AGCGTGGGTCTCGTCAGGGTCCATCCACTCCAAGCTC |
| Uctga-B2’ | TTCAGAGGTCTCTCTGACACTGGAATCGGCAGCAAAGG |
| gRcggt-BL | AGCGTGGGTCTCGACCGGGTCCATCCACTCCAAGCTC |
| Cas9-F | GATCCTTACTTTCCGTATTCCTTACTACG |
| Cas9-R OsActin1-qPCR-F OsActin1-qPCR-R | ATACCCTCCTCAATCCTCTTCATG GATGACCCAGATCATGTTTG GGGCGATGTAGGAAAGC |

图1 NaCl、ABA、甘露醇对RLK基因表达的影响荧光定量检测RLK基因的相对表达水平。**代表处理间差异达显著水平(P<0.01)。
Fig. 1. Relative expression level of RLKs under NaCl, ABA and mannitol treatment. qPCR was conducted to detect the relative expression of RLK. ** represent significant difference at P<0.01.
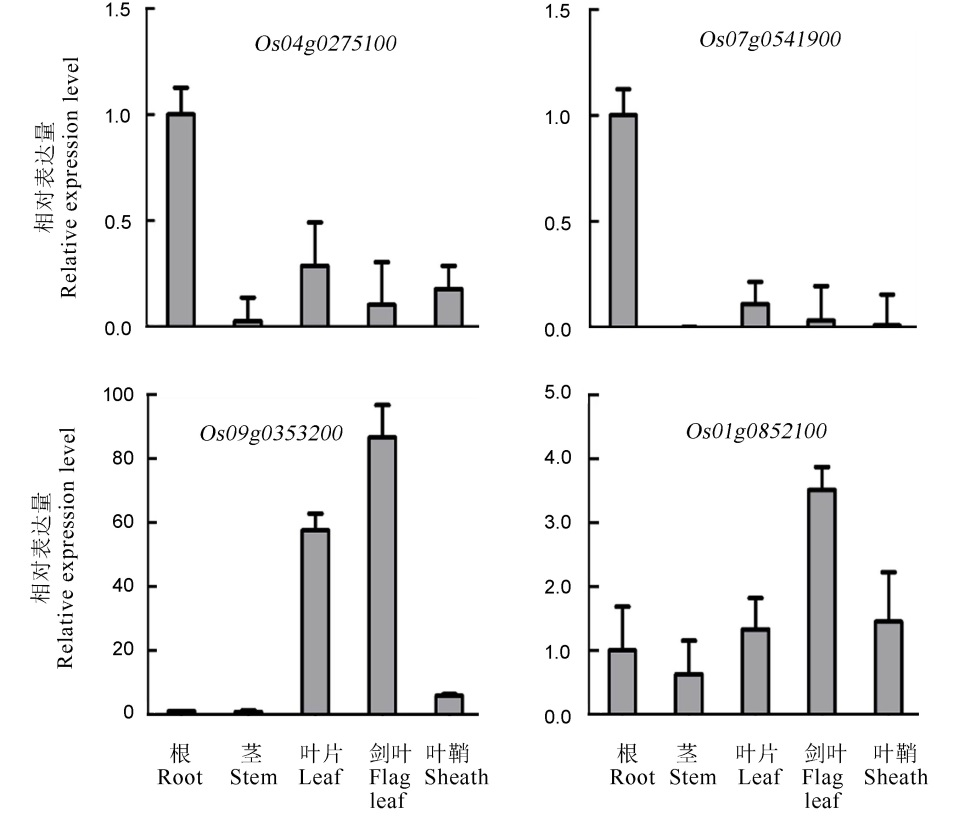
图2 RLK基因在不同组织器官中的相对表达水平 qPCR检测RLK基因在灌浆期水稻的根、茎、叶、剑叶、叶鞘中的相对表达水平。
Fig. 2. Relative expression level of RLKs in different tissues and organs. qPCR was conducted to detect the relative RLK expression in root, shoot, leaf, flag leaf and sheath at the filling stage.
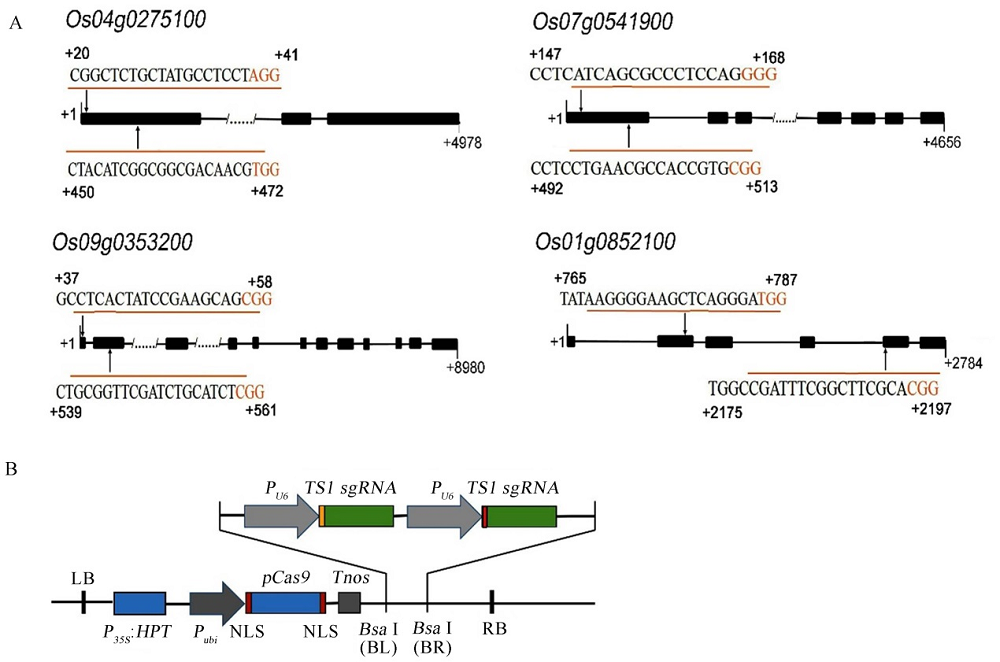
图3 RLK基因靶位点的选择和pYLCRISPR/Cas9PUbi-RLKs-sgRNA载体 A-RLK基因靶位点; B-pYLCRISPR/Cas9PUbi-RLKs-sgRNA载体。
Fig. 3. Target site of RLKs and diagram of pYLCRISPR/Cas9PUbi-RLKs-sgRNA vector. A, Target site of RLKs; B, Diagram of pYLCRISPR/Cas9PUbi-RLKs-sgRNA vector.
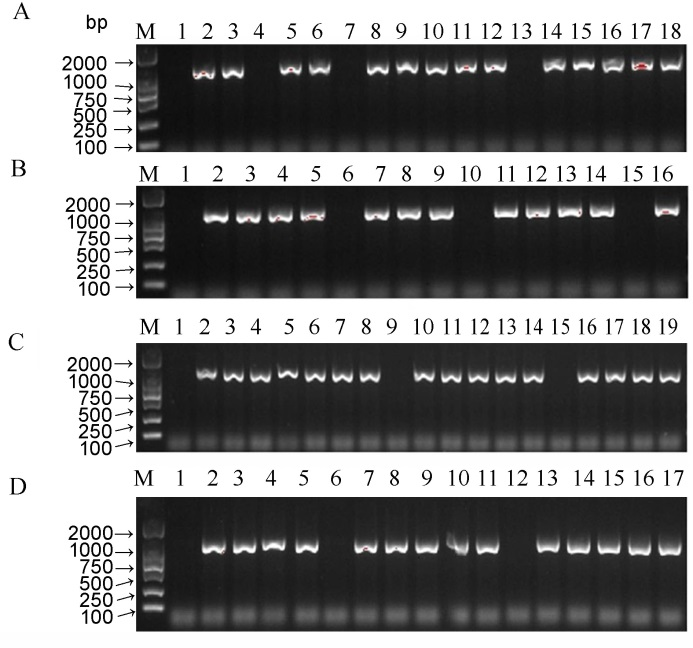
图4 PCR扩增Cas9基因以鉴定转基因植株 A–鉴定Os04g0275100基因编辑植株; B–鉴定Os07g0541900基因编辑植株; C–鉴定Os09g0353200基因编辑植株; D–鉴定Os01g0852100基因编辑植株。
Fig. 4. Identification of the transgenic plants by amplification of Cas9. A, Identification of the Os04g0275100-edited plant; B, Identification of the Os07g0541900-edited plant; C, Identification of the Os09g0353200-edited plant; D, Identification of the Os01g0852100- edited plant.
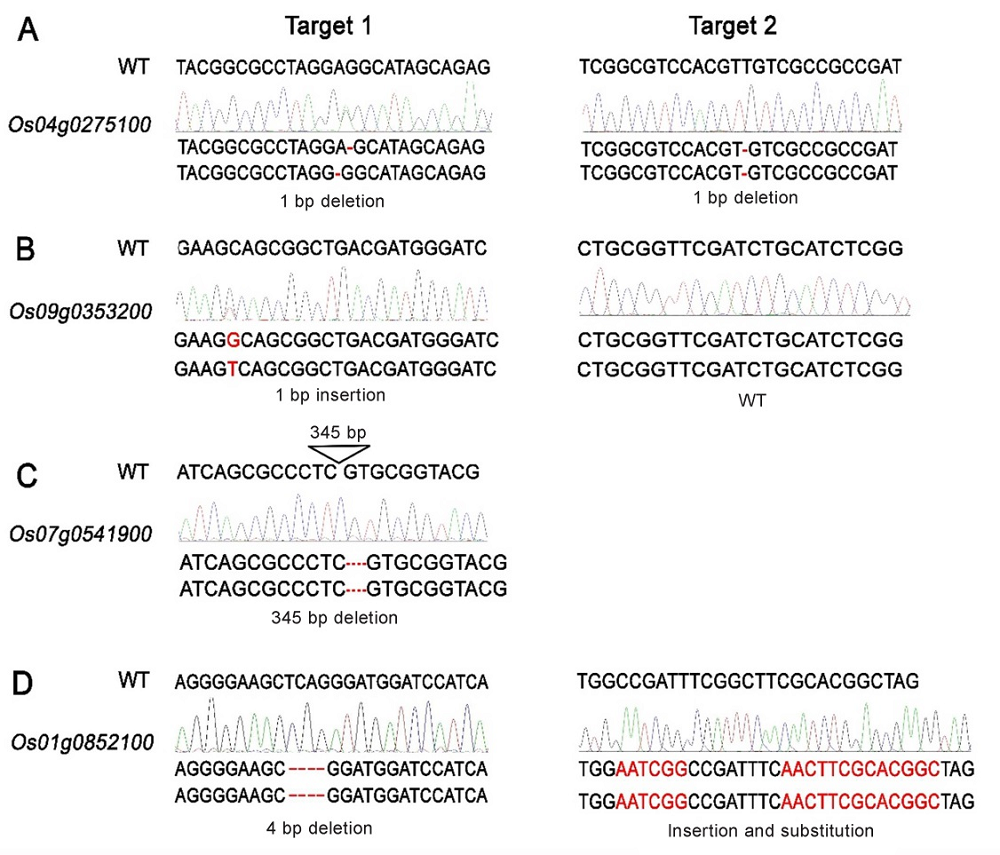
图5 RLK基因功能缺失突变体的鉴定 A-Os04g0275100基因缺失突变体的突变类型;B-Os09g0353200基因缺失突变体的突变类型;C-Os07g0541900基因缺失突变体的突变类型;D-Os01g0852100基因缺失突变体的突变类型。
Fig. 5. Identification of the loss-of-function mutants of RLKs. A, Identification of the mutation type of Os04g0275100; B, Identification of the mutation type of Os09g0353200; C, Identification of the mutation type of Os07g0541900; D, Identification of the mutation type of Os01g0852100.
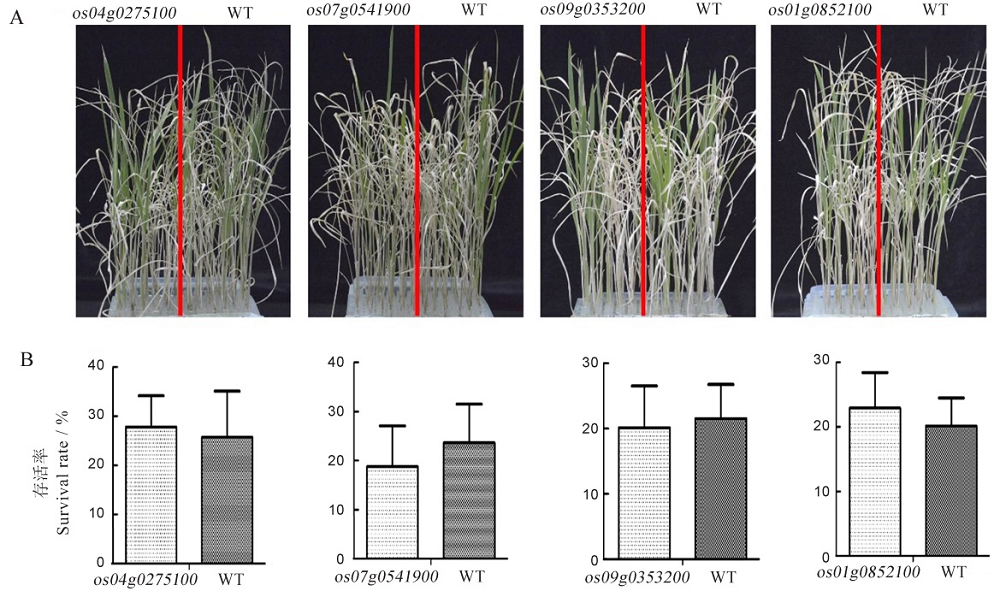
图6 RLK基因功能缺失突变体的耐盐性分析 A-突变体和野生型的耐盐表型分析;B-突变体和野生型的存活率比较。
Fig. 6. Salt tolerance analysis of the loss-of-function mutants of RLKs. A, Phenotypic analysis on salt tolerance of mutants and WT; B, Comparison of survival rate between mutants and WT.
| [1] | Gong Z, Xiong L M, Shi H Z, Yang S H, Herrera-Estrella L R, Xu G H, Chao D Y, Li J R, Wang P Y, Qin F, Li J, Ding Y L, Shi Y T, Wang Y, Yang Y Q, Guo Y, Zhu J K. Plant abiotic stress response and nutrient use efficiency.Science China: Life Sciences, 2020, 63(5): 635-674. |
| [2] | Zhu J K.Plant salt tolerance.Trends in Plant Science, 2001, 6(2): 66-71. |
| [3] | Flowers T J.Improving crop salt tolerance.Journal of Experimental Botany, 2004, 55(396): 307-319. |
| [4] | Sahi C, Singh A, Kumar K, Blumwald E, Grover A.Salt stress response in rice: Genetics, molecular biology, and comparative genomics.Functional & Integrative Genomics, 2006, 6(4): 263-284. |
| [5] | Zelm E V, Zhang Y X, Testerink C.Salt tolerance mechanisms of plants.Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2020, 71(1): 403-433. |
| [6] | Hanin M, Ebel C, Ngom M, Laplaze L, Masmoudi K.New insights on plant salt tolerance mechanisms and their potential use for breeding.Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7(11): 1787. |
| [7] | Sivakumar P, Sharmila P, Saradhi P P.Proline suppresses rubisco activity in higher plants.Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 1998, 252(2): 428-432. |
| [8] | Lemmon M A, Schlessinger J.Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases.Cell, 2010, 141(7): 1117-1134. |
| [9] | Morillo S A, Tax F E.Functional analysis of receptor-like kinases in monocots and dicots.Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2006, 9(5): 460-469. |
| [10] | Ouyang S Q, Liu Y F, Liu P, Lei G, He S J, Ma B, Zhang W K, Zhang J S, Chen S Y.Receptor-like kinase OsSIK1 improves drought and salt stress tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa) plants. Plant Journal, 2010, 62(2): 316-329. |
| [11] | Li C H, Wang G, Zhao J L, Zhang L Q, Ai L F, Han Y F, Sun D Y, Zhang S W, Sun Y.The receptor-like kinase SIT1 mediates salt sensitivity by activating MAPK3/6 and regulating ethylene homeostasis in rice.Plant Cell, 2014, 26(6): 2538-2553. |
| [12] | Shi C C, Feng C C, Yang M M, Li J L, Li X X, Zhao B C, Huang Z J, Ge R C. Overexpression of the receptor-like protein kinase genes AtRPK1 and OsRPK1 reduces the salt tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Science, 2014, 217-218: 63-70. |
| [13] | Osakabe Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K, Tran L S.Sensing the environment: Key roles of membrane-localized kinases in plant perception and response to abiotic stress.Journal of Experimental Botany, 2013, 64(2): 445-458. |
| [14] | Shiu S H, Bleecker A B.Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States, 2001, 98(19): 10763-10768. |
| [15] | Tanaka H, Osakabe Y, Katsura S, Mizuno S, Maruyama K, Kusakabe K, Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K.Abiotic stress-inducible receptor-like kinases negatively control ABA signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Journal, 2012, 70(4): 599-613. |
| [16] | Wang X F, Kota U, He K, Blackburn K, Li J, Goshe M B, Huber S C, Clouse S D.Sequential transphosphorylation of the BRI1/BAK1 receptor kinase complex impacts early events in brassinosteroid signaling.Developmental Cell, 2008, 15(2): 220-235. |
| [17] | Shiu S H, Karlowski W M, Pan R, Tzeng Y H, Mayer K F, Li W H.Comparative analysis of the receptor-like kinase family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Cell, 2004, 16(5): 1220-1234. |
| [18] | Ma X L, Zhang Q Y, Zhu Q L, Liu W, Chen Y, Qiu R, Wang B, Yang Z F, Li H Y, Lin Y R, Xie Y Y, Shen R X, Chen S F, Wang Z, Chen Y L, Guo J X, Chen L T, Zhao X C, Dong Z C, Liu Y G.A robust CRISPR/Cas9 system for convenient, high-efficiency multiplex genome editing in monocot and dicot plants.Molecular Plant, 2015, 8(8): 1274-1284. |
| [19] | 王才林, 张亚东, 赵凌, 路凯, 朱镇, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 赵春芳, 梁文化, 孙明法, 严国红. 耐盐碱水稻研究现状、问题与建议. 中国稻米, 2019, 25(1): 1-6. |
| Wang C L, Zhang Y D, Zhao L, Lu K, Zhu Z, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Yao S, Zhou L H, Zhao C F, Liang W H, Shun M F, Yan G H.Research status, questions and suggestions on salt tolerance rice varieties.China Rice, 2019, 25(1): 1-6. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 黄忠明, 周延彪, 唐晓丹, 赵新辉, 周在为, 符星学, 王凯, 史江伟, 李艳锋, 符辰建, 杨远柱. 基于CRISPR/Cas9 技术的水稻温敏不育基因tms5突变体的构建. 作物学报, 2018, 44(6): 844-851. |
| Huang Z M, Zhou Y B, Tang X D, Zhao X H, Zhou Z W, Fu X X, Wang K, Shi J W, Li Y F, Fu C J, Yang Y Z.Construction of tms5 mutants in rice based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2018, 44(6): 844-851. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | Zhao D S, Li Q F, Zhang C Q, Zhang C, Yang Q Q, Pan L X, Ren X Y, Lu J, Gu M H, Liu Q Q.GS9 acts as a transcriptional activator to regulate rice grain shape and appearance quality. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1240. |
| [22] | 王才林, 张亚东, 朱镇, 姚姝, 赵庆勇, 陈涛, 周丽慧, 赵凌. 优良食味粳稻新品种南粳9108的选育与利用. 江苏农业科学, 2013, 41(9): 86-88. |
| Wang C L, Zhang Y D, Zhu Z, Yao S, Zhao Q Y, Chen T, Zhou L H, Zhao L.Breeding of the japonica rice varieties with good eating quality.Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(9): 86-88. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | Zhou Y, Liu C, Tang D, Yan L, Wang D, Yang Y Z, Liu X M.The receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase STRK1 phosphorylates and activates CatC, thereby regulating H2O2 homeostasis and improving salt tolerance in rice.The Plant Cell, 2018, 30(5): 1100-1118. |
| [24] | Gao L L, Xue H W.Global analysis of expression profiles of rice receptor-like kinase genes.Molecular Plant, 2012, 5(1): 143-153. |
| [1] | 丁正权, 潘月云, 施扬, 黄海祥. 基于基因芯片的嘉禾系列长粒优质食味粳稻综合评价与比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [2] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [3] | 梁楚炎, 巫明明, 黄凤明, 翟荣荣, 叶靖, 朱国富, 俞法明, 张小明, 叶胜海. 基因编辑及全基因组选择技术在水稻育种中的应用展望[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 1-12. |
| [4] | 景秀, 周苗, 王晶, 王岩, 王旺, 王开, 郭保卫, 胡雅杰, 邢志鹏, 许轲, 张洪程. 穗分化末期-灌浆初期干旱胁迫对优质食味粳稻根系形态和叶片光合特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 33-47. |
| [5] | 夏杨, 李传明, 刘琴, 韩光杰, 徐彬, 黄立鑫, 祁建杭, 陆玉荣, 徐健. 印度梨形孢对盐胁迫下水稻幼苗生长及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(5): 543-552. |
| [6] | 李刚, 高清松, 李伟, 张雯霞, 王健, 程保山, 王迪, 高浩, 徐卫军, 陈红旗, 纪剑辉. 定向敲除SD1基因提高水稻的抗倒性和稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 359-367. |
| [7] | 黄亚茹, 徐鹏, 王乐乐, 贺一哲, 王辉, 柯健, 何海兵, 武立权, 尤翠翠. 外源海藻糖对粳稻品系W1844籽粒灌浆特性及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| [8] | 王雨, 孙全翌, 杜海波, 许志文, 吴科霆, 尹力, 冯志明, 胡珂鸣, 陈宗祥, 左示敏. 利用抗稻瘟病基因Pigm和抗纹枯病数量性状基因qSB-9TQ、qSB-11HJX改良南粳9108的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 125-132. |
| [9] | 周振玲, 林兵, 周群, 杨波, 刘艳, 周天阳, 王宝祥, 顾骏飞, 徐大勇, 杨建昌. 耐盐性不同水稻品种对盐胁迫的响应及其生理机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 153-165. |
| [10] | 姚姝, 赵春芳, 陈涛, 路凯, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 梁文化, 赫磊, 王才林, 张亚东. 低谷蛋白半糯型粳稻营养品质与蒸煮食味品质特征分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 178-188. |
| [11] | 刘淑丽, 张瑞, 王洋, 陈英龙, 韦还和, 侯红燕, 戴其根. 外源物质对水稻盐胁迫缓解效应研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 1-15. |
| [12] | 裴峰, 王广达, 高鹏, 冯志明, 胡珂鸣, 陈宗祥, 陈红旗, 崔傲, 左示敏. 敲除OsNramp5基因创制低镉优质粳稻新材料的应用评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 16-28. |
| [13] | 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, 赵凌, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 赵春芳, 张亚东, 王才林. 利用分子标记辅助选择培育优良食味、低谷蛋白香粳稻新品系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 55-65. |
| [14] | 巫明明, 曾维, 翟荣荣, 叶靖, 朱国富, 俞法明, 张小明, 叶胜海. 水稻耐盐分子机制与育种研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 551-561. |
| [15] | 尹丽颖, 张元野, 李荣田, 何明良, 王芳权, 许扬, 刘欣欣, 潘婷婷, 田晓杰, 卜庆云, 李秀峰. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制高效抗除草剂水稻[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(5): 459-466. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||