
中国水稻科学 ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 365-373.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7130
韩瑞才1, 苏如奇1, 万建林2, 龙启樟2, 曾勇军1, 潘晓华1, 石庆华1, 吴自明1,*( )
)
出版日期:2018-07-10
发布日期:2018-07-10
通讯作者:
吴自明
基金资助:
Ruicai HAN1, Ruqi SU1, Jianlin WAN2, Qizhang LONG2, Yongjun ZENG1, Xiaohua PAN1, Qinghua SHI1, Ziming WU1,*( )
)
Online:2018-07-10
Published:2018-07-10
Contact:
Ziming WU
摘要: 【目的】黄嘌呤脱氢酶(xanthine dehydrogenase, XDH)是嘌呤代谢的关键酶。通过分析高温胁迫对OsXDH超表达转基因水稻株系幼苗叶片生理指标的影响,探究XDH缓解水稻高温胁迫的生理机制。【方法】以OsXDH超表达转基因株系(xdh1和xdh5)及受体品种日本晴(WT)为材料,研究了高温胁迫对水稻幼苗叶片叶绿素含量、相对含水量、可溶性蛋白含量、活性氧代谢、抗氧化酶活性、XDH活性及嘌呤代谢产物尿囊素(allantoin)和尿囊酸(allantoate)含量等生理指标的影响。【结果】高温胁迫处理前,超表达株系的叶绿素含量、相对含水量、可溶性蛋白含量、活性氧代谢及抗氧化酶活性等生理指标均与野生型无显著差异;高温胁迫5 d,超表达株系的叶绿素、相对含水量、可溶性蛋白含量及抗氧化酶活性均高于野生型,而过氧化氢(H2O2)及丙二醛(MDA)的含量显著低于野生型;适温恢复生长5 d,野生型和超表达株系的叶绿素含量、相对含水量及可溶性蛋白含量均有所提高,超表达株系均高于野生型,H2O2 和MDA的含量降低,超表达株系均低于野生型;受高温诱导超表达株系与野生型中XDH酶活性及尿囊素和尿囊酸的含量均提高,且在整个处理过程中超表达转基因株系均高于野生型。【结论】XDH通过调控酰脲类物质的合成,补偿自身的抗氧化能力并增强抗氧化酶系统的活性,从而有效提高水稻幼苗对高温胁迫的耐受能力。
中图分类号:
韩瑞才, 苏如奇, 万建林, 龙启樟, 曾勇军, 潘晓华, 石庆华, 吴自明. 高温胁迫下黄嘌呤脱氢酶基因超表达对水稻幼苗的保护作用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(4): 365-373.
Ruicai HAN, Ruqi SU, Jianlin WAN, Qizhang LONG, Yongjun ZENG, Xiaohua PAN, Qinghua SHI, Ziming WU. Protective Roles of Over-expression of OsXDH in Rice Seedlings Under High Temperature Stress[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(4): 365-373.
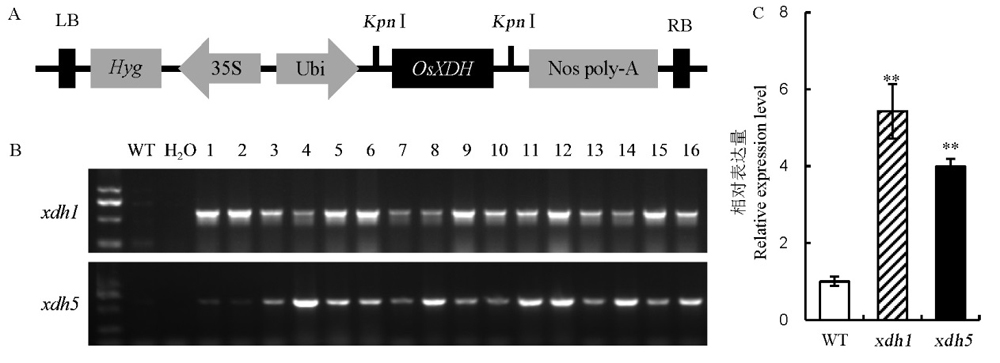
图1 OsXDH超表达载体的构建、转基因植株的鉴定和目的基因表达量检测 A–超表达载体结构。LB为T-DNA左边界,Hyg为潮霉素抗性筛选基因,35S为花椰菜花叶病毒启动子,Ubi为ubiqutin基因启动子,Kpn I为酶切位点,RB为T-DNA右边界。B–T2代转基因植株PCR阳性鉴定。WT为野生型,1~16为16个随机选取的T2代转基因植株。C–转基因植株OsXDH基因的表达量。xdh1为OsXDH超表达株系1,xdh5为OsXDH超表达株系5。数据用平均数±标准差表示(n=3)。**表示在0.01水平上差异极显著(LSD)。
Fig. 1. Construction of OsXDH over-expression vector, PCR analysis of OsXDH gene in T2 transgenic plants and expression analysis of OsXDH in over-expressed lines. A, Structure of OsXDH over-expression vector. LB, Left border of T-DNA; Hyg, Hygromycin gene; 35S, 35S promoter of CaMV; Ubi, Promoter of ubiqutin; Kpn I, Restriction enzyme cutting site; RB, Right border of T-DNA. B, PCR identification of the T2 transgenic plants. WT, Wild type; 1–16, 16 randomly selected T2 transgenic plants. C, Relative expression level of OsXDH in transgenic plants. xdh1, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 1; xdh5, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 5. Values are shown as mean±SD (n=3). **, Significant difference at P<0.01 level by LSD.
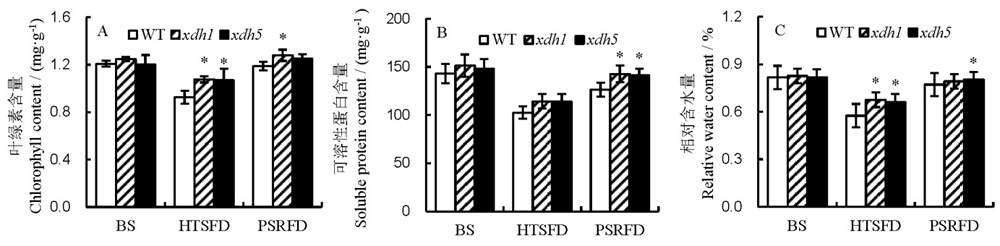
图2 高温胁迫对水稻叶片叶绿素含量、可溶性蛋白含量和相对含水量的影响 A–叶绿素含量; B–可溶性蛋白含量; C–相对含水量。BS为高温处理前,HTSFD为高温处理5 d,PSRFD为高温处理后适温恢复生长5 d。WT为野生型,xdh1为OsXDH超表达株系1,xdh5为OsXDH超表达株系5。数据用平均数±标准差表示(n=3),*表示在0.05水平上差异显著(LSD)。
Fig. 2. Effects of high temperature stress on chlorophyll content, soluble protein content and relative water content in rice leaves. A, Chlorophyll content; B, Soluble protein content; C, Relative water content. BS, Before high temperature stress; HTSFD, High temperature stress for 5 days; PSRFD, Post-stress recovery for 5 days. WT, Wild type; xdh1, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 1; xdh5, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 5. Values are shown as mean±SD (n=3). *, Significant difference at P<0.05 level by LSD.
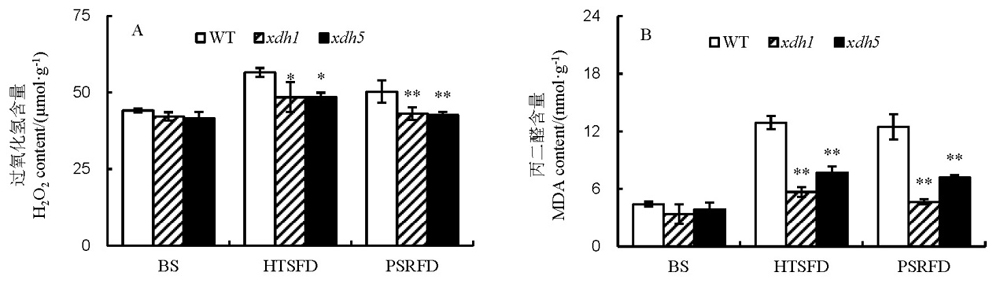
图3 高温胁迫对水稻叶片过氧化氢含量和丙二醛含量的影响 A–过氧化氢含量; B–丙二醛含量。BS为高温处理前; HTSFD为高温处理5 d; PSRFD为适温恢复生长5 d。WT为野生型; xdh1为OsXDH超表达株系1; xdh5为OsXDH超表达株系5。数据用平均数±标准差表示(n=3)。 *和**分别表示在0.05和0.01水平上显著差异(LSD)。
Fig. 3. Effects of high temperature stress on H2O2 and Malondialdehyde(MDA) content in rice leaves. A, H2O2 content; B, MDA content. BS, Before high temperature stress; HTSFD, High temperature stress for 5 days; PSRFD, Post-stress recovery for 5 days. WT, Wild type; xdh1, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 1; xdh5, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 5. Values are shown as mean±SD (n=3). * and **, Significant difference at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels by LSD, respectively.
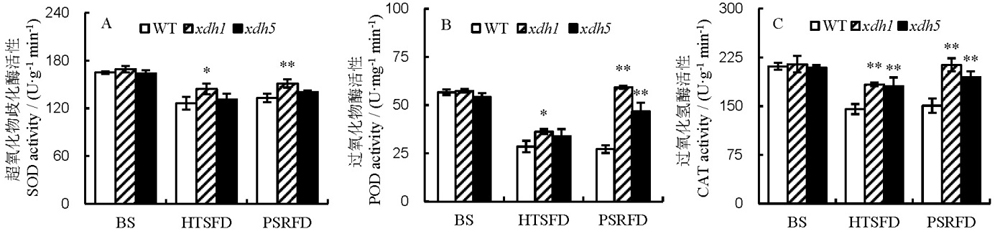
图4 高温胁迫对水稻叶片超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化物酶和过氧化氢酶活性的影响 A–超氧化物歧化酶活性; B–过氧化物酶活性; C–过氧化氢酶活性。BS为高温处理前; HTSFD为高温处理5 d; PSRFD为适温恢复生长5 d。WT为野生型; xdh1为OsXDH超表达株系1; xdh5为OsXDH超表达株系5。数据用平均数±标准差表示(n=3)。 *,**分别表示在0.05和0.01水平上显著差异(LSD)。
Fig. 4. Effects of high temperature stress on activities of superoxide dismutase(SOD), peroxidase(POD) and catalase(CAT) in rice leaves. A, SOD activity; B, POD activity; C, CAT activity. BS, Before high temperature stress; HTSFD, High temperature stress for 5 days; PSRFD, Post-stress recovery for 5 days. WT, Wild type; xdh1, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 1; xdh5, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 5. Values are shown as mean±SD (n=3). * and **, Significant difference at P<0.05 and P<0.01 level by LSD, respectively.
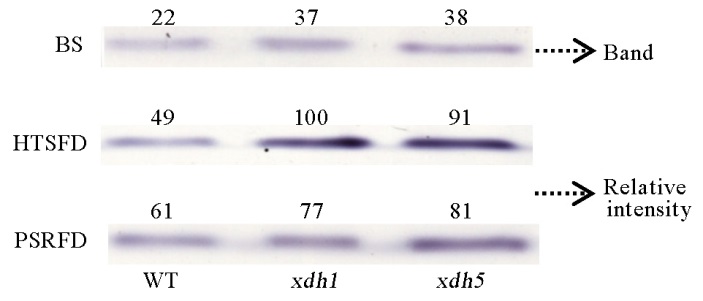
图5 高温胁迫对水稻叶片黄嘌呤脱氢酶活性的影响 BS为高温处理前; HTSFD为高温处理5 d; PSRFD为适温恢复生长5 d。WT为野生型; xdh1为OsXDH超表达株系1; xdh5为OsXDH超表达株系5。每条通道可溶性蛋白的上样量均为50μg。以次黄嘌呤作为底物,条带亮度为XDH酶相对活性。用软件ImageJ2x分析条带亮度,显示酶活相对值。
Fig. 5. Effects of high temperature stress on xanthine dehydrogenase(XDH) activity in rice leaves. BS, Before high temperature stress; HTSFD, High temperature stress for 5 days; PSRFD, Post-stress recovery for 5 days. WT, Wild type; xdh1, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 1; xdh5, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 5. Each lane in the gel was loaded with equal content soluble protein. XDH activity was detected in gel with hypoxanthine as substrate. Numbers above the lanes indicate relative intensity obtained by scanning the formazan bands with a computing laser densitometer using ImageJ2x software.
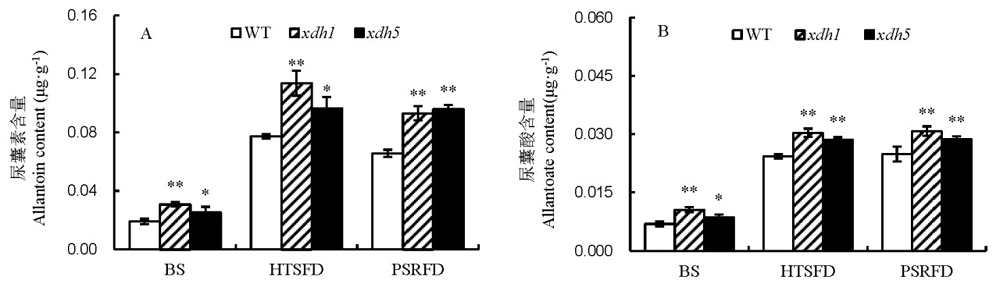
图6 高温胁迫对水稻叶片尿囊素和尿囊酸含量的影响 A–尿囊素含量; B–尿囊酸含量。BS为高温处理前,HTSFD为高温处理5 d,PSRFD为适温恢复生长5 d。WT为野生型,xdh1为OsXDH超表达株系1,xdh5为OsXDH超表达株系5。数据用平均数±标准差表示(n=3)。*,**分别表示在0.05和0.01水平上差异显著(LSD)。
Fig. 6. Effects of high temperature stress on allantoin and allantoate contents in rice leaves. A, Allantoin content. B, Allantoate content. BS, Before high temperature stress; HTSFD, High temperature stress for 5 days; PSRFD, Post-stress recovery for 5 days. WT, Wild type; xdh1, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 1; xdh5, OsXDH over-expressed transgenic line 5. Values are shown as mean±SD (n=3). *, and **, Significant difference at P<0.05 and P<0.01 levels by LSD, respectively.
| [1] | Challinor A J, Ewert F, Arnold S, Simelton E, Fraser E.Crops and climate change: Progress, trends, and challenges in simulating impacts and informing adaptation.J Exp Bot, 2009, 60(10): 2775-2789. |
| [2] | Maestri E, Klueva N, Perrotta C, Gulli M, Nguyen H T, Marmiroli N.Molecular genetics of heat tolerance and heat shock proteins in cereals.Plant Mol Biol, 2002, 48(5-6): 667-681. |
| [3] | 段骅, 杨建昌. 高温对水稻的影响及其机制的研究进展. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(4): 393-400. |
| Duan Y, Yang J C.Research advances in the effect of high temperature on rice and its mechanism. Chin J Rice Sci, 2012, 26(4): 393-400.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 曹云英, 赵华. 高温胁迫下油菜素内酯对水稻幼苗的保护作用. 中国水稻科学, 2007, 21(5):525-529. |
| Cao Y Y, Zhao H.Protective Roles of brassinolide in rice seedlings under heat stress. Chin J Rice Sci, 2007, 21(5): 525-529. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 周伟辉, 薛大伟, 张国平. 高温胁迫下水稻叶片的蛋白响应及其基因型和生育期差异. 作物学报, 2011, 37(5): 820-831. |
| Zhou W Hui, Xue D W, Zhang G P.Protein response of rice leaves to high temperature stress and its difference of genotypes at different growth stage.Acta Agron Sin, 2011, 37(5): 820-831.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 曹云英, 段骅, 杨立年, 王志琴, 周少川, 杨建昌. 减数分裂期高温胁迫对耐热性不同水稻品种产量的影响及其生理原因. 作物学报, 2008, 34(12): 2134-2142. |
| Cao Y Y, Duan H, Yang L N, Wang Z Q, Zhou S C, Yang J C.Effect of heat-stress during meiosis on grain yield of rice cultivars differing in heat-tolerance and its physiological mechanism.Acta Agron Sin, 2008, 34(12): 2134-2142. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 张桂莲, 张顺堂, 王力, 肖应辉, 唐文帮, 陈光辉, 陈立云. 抽穗结实期不同时段高温对稻米品质的影响. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46(14): 2869-2879. |
| Zhang G L, Zhang S T, Wang L, Xiao Y H, Tang W B, Chen G H, Chen L Y.Effects of high temperature at different times during the heading and filling periods on rice quality.Sci Agric Sin, 2013, 46(14): 2869-2879.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Werner A K, Witte C P.The biochemistry of nitrogen mobilization: purine ring catabolism.Trends Plant Sci, 2011, 16(7): 381-387. |
| [9] | Yesbergenova Z, Yang G H, Oron E, Soffer D, Fluhr R, Sagi M.The plant Mo-hydroxylases aldehyde oxidase and xanthine dehydrogenase have distinct reactive oxygen species signatures and are induced by drought and abscisic acid. Plant J, 2005, 42(6): 862-876. |
| [10] | Zdunek-Zastocka E, Lips H S.Is xanthine dehydrogenase involved in response of pea plants (Pisum sativum L.) to salinity or ammonium treatment? Acta Physiol Plant, 2003, 25(4): 395-401. |
| [11] | Barabás N K, Omarov R T, Erdei L, Lips S H.Distribution of the Mo-enzymes aldehyde oxidase, xanthine dehydrogenase and nitrate reductase in maize (Zea mays L.) nodal roots as affected by nitrogen and salinity. Plant Sci, 2000, 155(1): 49-58. |
| [12] | You S H, Zhu B, Wang F B, Han H J, Sun M, Zhu H W, Peng R H, Yao Q H.A Vitis vinifera xanthine dehydrogenase gene, VvXDH, enhances salinity tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnol Rep, 2017, 11(4): 247. |
| [13] | Hofmann N R.Opposing functions for plant xanthine dehydrogenase in response to powdery mildew infection: production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species.Plant Cell, 2016, 28(5): 1001. |
| [14] | 孙学成, 胡承孝. 高等植物含钼酶与钼营养. 植物生理学通讯, 2005, 6(3): 395-399. |
| Sun X C, Hu C X.Molybdoenzymes and Molybdenum Nutrition in Higher Plants.Plant Physiol Commun, 2005, 6(3): 395-399. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | Taylor N J, Cowan A K.Xanthine dehydrogenase and aldehyde oxidase impact plant hormone homeostasis and affect fruit size in ‘Hass’ avocado.J Plant Res, 2004, 117(2): 121-130. |
| [16] | Lichtenthaler H K, Wellbuen A R.Determinations of total caroten oids and chlorophylls a and b leaf extracts in different solvents.Biochem Soc Trans, 1983, 11(5): 591-592. |
| [17] | 张志良. 植物生理学实验指导. 2版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1991: 183-184. |
| Zhang Z L.Experimental Guidance on Plant Physiology. 2nd ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1991: 183-184. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 李合生, 孙群, 赵世杰, 章文华. 植物生理生化实验原理与技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. |
| Li H S, Sun Q, Zhao S J, Zhang W H.The Experiment Principle and Technique on Plant Physiology and Biochemistry. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | Lin C C, Kao C H.Abscisic acid induced changes in cell wall peroxidase activity and hydrogen peroxide level in roots of rice seedlings.Plant Sci, 2001, 160: 323-329. |
| [20] | Sagi M, Omarov R T, Lips S H.The Mo-hydroxylases xanthine dehydrogenase and aldehyde oxidase in ryegrass as affected by nitrogen and salinity.Plant Sci, 1998, 135(2): 125-135. |
| [21] | 张桂莲, 陈立云, 雷东阳, 张顺堂. 水稻耐热性研究进展. 杂交水稻, 2005, 20(1): 1-5. |
| Zhang G L, Chen L Y, Lei D Y, Zhang S T.Research progress on heat resistance of rice. Hybrid Rice, 2005, 20(1): 1-5.(in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 李轶冰, 杨顺强, 任广鑫, 冯永忠, 张强, 李鹏. 低温处理下不同禾本科牧草的生理变化及其抗寒性比较. 生态学报, 2009, 29(3): 1341-1347. |
| Li T B, Yang S Q, Ren G X, Feng Y Z, Zhang Q, Li P.Changes analysis in physiological properties of several gram ineous grass species and cold-resistance comparison on under cold stress.Acta Ecol Sin, 2009, 29(3): 1341-1347. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 张顺堂, 张桂莲, 陈立云, 肖应辉. 高温胁迫对水稻剑叶净光合速率和叶绿素荧光参数的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(3): 335-338. |
| Zhang S T, Zhang G L, Chen L Y, Xiao Y H.Effects of high temperature stress on net photosynthetic rate and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of flag leaf in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2011, 25(3): 335-338. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Rang Z W, Jagadish S V K, Zhou Q M, Craufurd P Q, Heuer S. Effect of high temperature and water stress on pollen germination and spikelet fertility in rice.Environ Exp Bot, 2011, 70(1): 60-65. |
| [25] | Mehdy M C.Active oxygen species in plant defense against pathogens.Plant Physiol, 1994, 105(2): 467-472. |
| [26] | Gill S S, Tuteja N.Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants.Plant Physiol Bioch, 2010, 48(12): 909-930. |
| [27] | 王贺正, 马均, 李旭毅, 李艳, 张荣萍, 汪仁全. 水分胁迫对水稻结实期活性氧产生和保护系统的影响. 中国农业科学, 2007, 40(7): 1379-1387. |
| Wang H Z, Ma J, Li X Y, Li Y, Zhang R P, Wang R Q.Effects of Water Stress on Active Oxygen Generation and Protection System in Rice During Grain Filling Stage.Sci Agric Sin, 2007, 40(7): 1379-1387. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 杨淑慎, 高俊凤. 活性氧、自由基与植物的衰老. 西北植物学报, 2001, 21(2): 215-220. |
| Yang S S, Gao J F.Influence of active oxygen and free radicals on plant senescence.Acta Bot Boreal, 2001, 21(2): 215-220. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | Hung K T, Kao C H.Nitric oxide counteracts the senescence of rice leaves induced by abscisic acid.J Plant Physiol, 2003, 160(8): 871-879. |
| [30] | Nakagawa A, Sakamoto S, Takahashi M, Morikawa H, Sakamoto A.The RNAi-mediated silencing of xanthine dehydrogenase impairs growth and fertility and accelerates leaf senescence in transgenic Arabidopsis Plants. Plant Cell Physiol, 2007, 48(10): 1484-1495. |
| [31] | Brychkova G, Alikulov Z, Fluhr R, Sagi M.A critical role for ureides in dark and senescence-induced purine remobilization is unmasked in the Atxdh1 Arabidopsis mutant. Plant J, 2008, 54(3): 496-509. |
| [32] | Watanabe S, Nakagawa A, Izumi S, Shimada H, Sakamoto A.RNA interference-mediated suppression of xanthine dehydrogenase reveals the role of purine metabolism in drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. FEBS Lett, 2010, 584(6): 1181-1186. |
| [33] | Pastori G M, del Rio L A. Natural senescence of pea leaves: an activated oxygen-mediated function for peroxisomes.Plant Physiol, 1997, 113(2): 411-418. |
| [34] | Yobi A, Wone B W, Xu W X, Alexander D C, Guo L N, Ryals J A, Oliver M J, Cushman J C.Metabolomic profling in Selaginella lepidophylla at various hydration states provides new insights into the mechanistic basis of desiccation tolerance. Mol Plant, 2013, 6(2): 369-385. |
| [35] | Brychkova G, Fluhr R, Sagi M.Formation of xanthine and the use of purine metabolites as a nitrogen source in Arabidopsis plants. Plant Signal & Behav, 2008, 3(11): 999-1001. |
| [36] | 郭培国, 李荣华. 夜间高温胁迫对水稻叶片光合机构的影响. 植物学报, 2000, 42(7): 673-678. |
| Guo P G, Li R H.Effects of high nocturnal temperature on photosynthetic organization in rice leaves.Acta Bot Sin, 2000, 42(7): 673-678. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | Ma X F, Wang W M, Bittner F, Schmidt N, Berkey R, Zhang L L, King H, Zhang Y, Feng J Y, Wen Y Q, Tan L Q, Li Y, Zhang Q, Deng Z N, Xiong X Y, Xiao S Y.Dual and opposing roles of xanthine dehydrogenase in defense-associated reactive oxygen species metabolism in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 2016, 28(5): 1108-1126. |
| [38] | Smith P M C, Atkins C A. Purine biosynthesis, big in cell division, even bigger in nitrogen assimilation.Plant Physiol, 2004, 128(3): 793-802. |
| [39] | Bittner F, Oreb M, Mendel R R.ABA3 is a molybdenum cofactor sulfurase required for activation of aldehyde oxidase and xanthine dehydrogenase in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276(44): 40381-40384. |
| [40] | Watanabe S, Kounosu Y, Shimada H, Sakamoto A.Arabidopsis xanthine dehydrogenase mutants defective in purine degradation show a compromised protective response to drought and oxidative stress. Plant Biotechnol,2014, 31(2): 173-178. |
| [41] | Leydecker M T, Moureaux T, Kraepiel Y, Caboche M.Molybdenum cofactor mutants, specifically impaired in xanthine dehydrogenase activity and abscisic acid biosynthesis, simultaneously overexpress nitrate reductase. Plant Physiol, 1995, 107(4): 1427-1431. |
| [42] | Taylor N, Cowan K.Plant hormone homeostasis and the control of avocado fruit size.Plant Grow Regul, 2001, 35(3): 247-255. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||