
中国水稻科学 ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 238-246.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.6156 238
吕育松1,#, 谢耘丰1,2,#, 圣忠华1, 邬亚文1, 唐绍清1, 胡培松1, 魏祥进1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2016-11-24
修回日期:2017-02-06
出版日期:2017-05-10
发布日期:2017-05-10
通讯作者:
魏祥进
基金资助:
Yusong LÜ1,#, Yunfeng XIE1,2,#, Zhonghua SHENG1, Yawen WU1, Shaoqing TANG1, Peisong HU1, Xiangjin WEI1,*( )
)
Received:2016-11-24
Revised:2017-02-06
Online:2017-05-10
Published:2017-05-10
Contact:
Xiangjin WEI
摘要:
【目的】研究揭示潇湘矮矮秆小粒的遗传机制,为潇湘矮的育种利用提供理论基础。【方法】利用水稻育种过程中自然突变而得到的稳定遗传的矮秆小粒水稻材料潇湘矮,对其进行农艺性状考查、赤霉素(GA3)和油菜素内酯(BR)敏感性分析、遗传学分析,并利用潇湘矮与其近等基因系NIL(NIP)衍生的F2群体对控制矮秆小粒的基因xxa进行图位克隆,最终利用转基因互补试验验证候选基因。【结果】潇湘矮除表现为矮秆小粒外,其穗长变短,穗型紧凑,千粒重极显著下降。不同浓度梯度的赤霉素(GA3)和油菜素内酯(BR)处理,发现潇湘矮对GA3部分敏感,而对BR不敏感。遗传分析发现其符合孟德尔3:1分离规律。图位克隆将xxa基因定位于第5染色体InDel标记F81和F82之间约70 kb区间的物理距离内。该区间包含8个开放阅读框(ORF)。其中,第5个ORF(LOC_Os05g26890)被注释为水稻株高基因D1。序列分析发现,潇湘矮的D1基因在第5和12外显子分别有1个碱基的无义替换和3个碱基的缺失,其中第12外显子3个碱基的缺失导致1个赖氨酸的缺失。转基因互补显示D1可以恢复潇湘矮的表型。【结论】潇湘矮控制株高的途径可能与GA3代谢有关;潇湘矮矮秆小粒表型符合单隐性核基因控制的遗传规律;潇湘矮矮秆小粒性状是由D1基因突变所致。
中图分类号:
吕育松, 谢耘丰, 圣忠华, 邬亚文, 唐绍清, 胡培松, 魏祥进. 矮秆小粒水稻潇湘矮的形态学与分子遗传学分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(3): 238-246.
Yusong LÜ, Yunfeng XIE, Zhonghua SHENG, Yawen WU, Shaoqing TANG, Peisong HU, Xiangjin WEI. Morphological and Molecular Genetic Analysis of a Dwarf and Small Grain Rice Variety Xiaoxiang’ai[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(3): 238-246.
| 引物 Marker name | 前引物序列 Forward(5′-3′) | 后引物序列 Reverse(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| RM18408 | GGCACTCTGGTTCCTCAATGG | TCTGTATCATCAACGGCAACTCC |
| RM5140 | GGCACTCGTATTTCTCAACTTCTCC | GGGTGTATCAGGAGTACAGGTTGC |
| RM18457 | ATCCTCCACCGCTCAAGAACACG | CGAGGCCATTCATCGAACAAAGC |
| RM18402 | TTATGAGGCAGCCCGTAATGTTGC | GCAGCGGTGTCAACAGCTTCC |
| RM18450 | AAGGCTCCATGGTTGGTTGC | CGATGGACAGACAGTGTGTAGTGG |
| F78 | GGGACGAATTCTTTTCGATTAC | CGTGGACCAATTTTGGTAACTG |
| F79 | AATTATTCCACTATGCACATGT | ATTTTCTTCCATCGCCTCTTGC |
| F81 | GTAAACTATCGACTTGCTATGT | ACTAGTGCAGACTGTTTTCCTG |
| F82 | AGATGATTGGATGAGAATTTAA | ACCCAGAAACCATCTAGTAATT |
| F84 | GGGTGGCTCCTTACGACATTAC | TTTCATATTTTAGCGGTGCTCT |
| F85 | CCTCGACCCACTGCATCATCAG | TGGTCGGTCTCCTCCCTCTTCA |
| F86 | CAGTATTCGAGTAAGTTCACAA | CCTCGCCCCTATTCATCCTCTT |
表1 本研究中基因定位所用引物
Table 1 Primers for mapping in the study.
| 引物 Marker name | 前引物序列 Forward(5′-3′) | 后引物序列 Reverse(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| RM18408 | GGCACTCTGGTTCCTCAATGG | TCTGTATCATCAACGGCAACTCC |
| RM5140 | GGCACTCGTATTTCTCAACTTCTCC | GGGTGTATCAGGAGTACAGGTTGC |
| RM18457 | ATCCTCCACCGCTCAAGAACACG | CGAGGCCATTCATCGAACAAAGC |
| RM18402 | TTATGAGGCAGCCCGTAATGTTGC | GCAGCGGTGTCAACAGCTTCC |
| RM18450 | AAGGCTCCATGGTTGGTTGC | CGATGGACAGACAGTGTGTAGTGG |
| F78 | GGGACGAATTCTTTTCGATTAC | CGTGGACCAATTTTGGTAACTG |
| F79 | AATTATTCCACTATGCACATGT | ATTTTCTTCCATCGCCTCTTGC |
| F81 | GTAAACTATCGACTTGCTATGT | ACTAGTGCAGACTGTTTTCCTG |
| F82 | AGATGATTGGATGAGAATTTAA | ACCCAGAAACCATCTAGTAATT |
| F84 | GGGTGGCTCCTTACGACATTAC | TTTCATATTTTAGCGGTGCTCT |
| F85 | CCTCGACCCACTGCATCATCAG | TGGTCGGTCTCCTCCCTCTTCA |
| F86 | CAGTATTCGAGTAAGTTCACAA | CCTCGCCCCTATTCATCCTCTT |
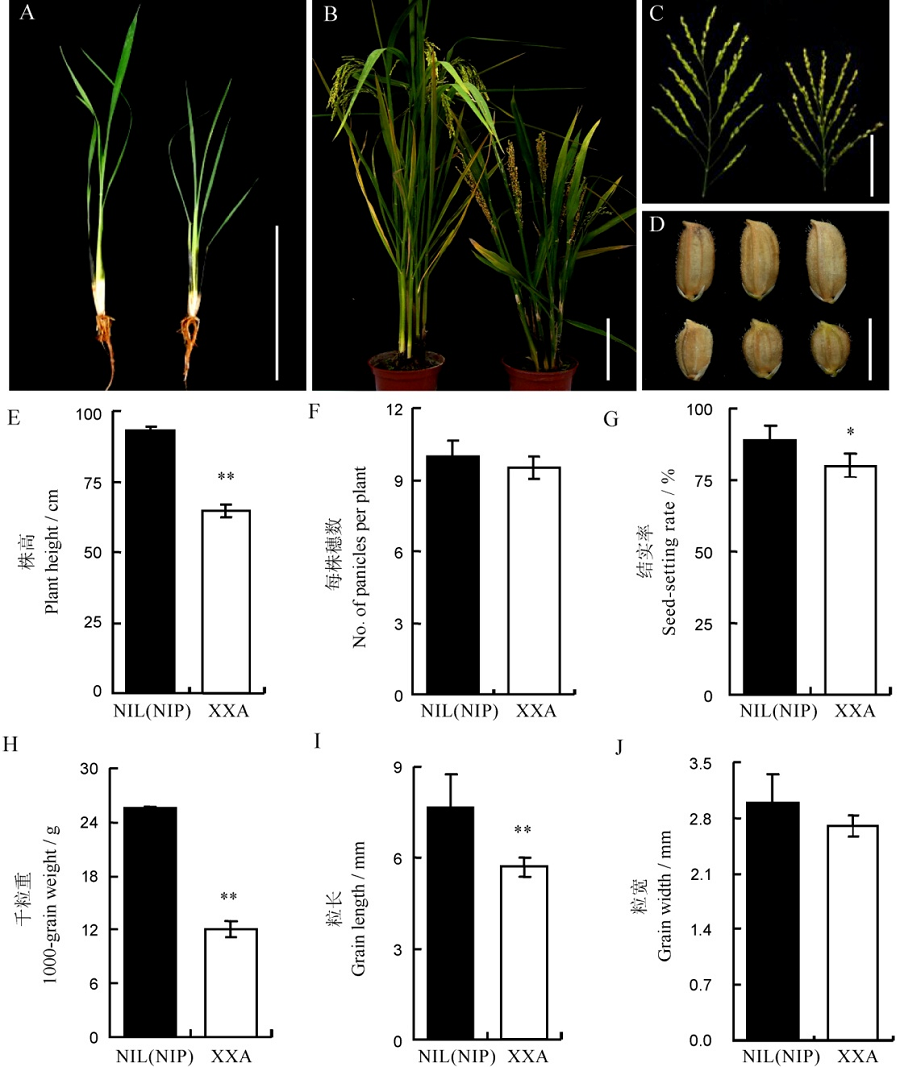
图1 潇湘矮(XXA)及其近等基因系NIL(NIP)的表型分析 A—NIL(NIP)(左)与潇湘矮(右)5周大小苗期表型;B—成熟期NIL(NIP)(左)和潇湘矮(右)植株表型;C—成熟期NIL(NIP)(左)和潇湘矮(右)主穗表型;D—NIL(NIP)(上)和潇湘矮(下)粒型比较;E-J—NIL(NIP)与潇湘矮株高、每株穗数、结实率、千粒重、粒长以及粒宽比较。A~C图中标尺为10 cm,D图中标尺为5 mm;E~J中数据为10次重复实验的平均值,利用t测验检测数据差异显著性(*P< 0.05, **P< 0.01)。
Fig. 1. Phenotype analysis of XXA and NIL(NIP). A, 5-weeks-old seedlings of NIL(NIP)(left) and XXA(right); B, Phenotypes of NIL(NIP) and XXA plants at the mature stage in paddy field; C, Comparison of main panicles between NIL(NIP) and XXA at the mature stage; D, Grain size of NIL(NIP) and XXA at the mature stage; E-J, Plant height(E), number of panicles per plant(F), seed setting rate(G), 1,000-grain weight(H), grain length(I) and grain width(J) between NIL(NIP) and XXA. Bar=10 cm in Figures A, B and C; Bar=5 mm in Figure D. Data in E-J are shown as Mean±SD from 10 individual replicates. The asterisks indicate statistical significance, as determined by the Student’s t-test(*P<0.05, **P<0.01).
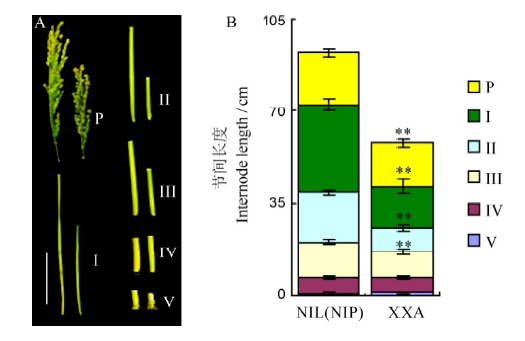
图2 潇湘矮与近等基因系NIL(NIP)主茎穗长、节间长度 A–近等基因系NIL(NIP)(左)与潇湘矮(右)主茎不同节间及穗长比较,标尺为15 cm;B–近等基因系NIL(NIP) 与潇湘矮主茎不同节间长度及穗长差异统计分析(Mean±SD, **P<0.01, n=10,t测验)。
Fig. 2. The internode and panicle length comparison in XXA and NIL(NIP). A, Differences in panicles and internode length for NIL(NIP)(left) and XXA(right) plants. P, Panicle. Those from I to V indicate the corresponding internodes from the top to bottom, bar = 15 cm; B, Internode and young panicle length analysis of NIL(NIP) and XXA at the heading stage. Data in B are shown as Mean±SD from 10 individual replicates. The asterisks indicate statistical significance, as determined by the t-test(**P<0.01).
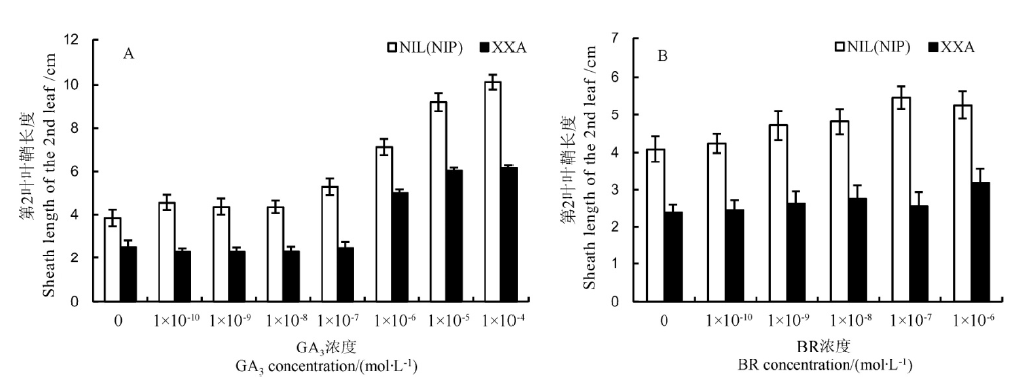
图3 潇湘矮与NIL(NIP) 幼苗期第2叶叶鞘对外源赤霉素(A)和油菜素内酯(B)的响应 A, B中数据为10次重复实验的平均值±标准差。
Fig. 3. Elongation of the second leaf sheath in response to gibberellin(A) and brassinolide(B) in NIL(NIP) and XXA plants. Data in A, B are shown as Mean±SD from 10 individual replicates.
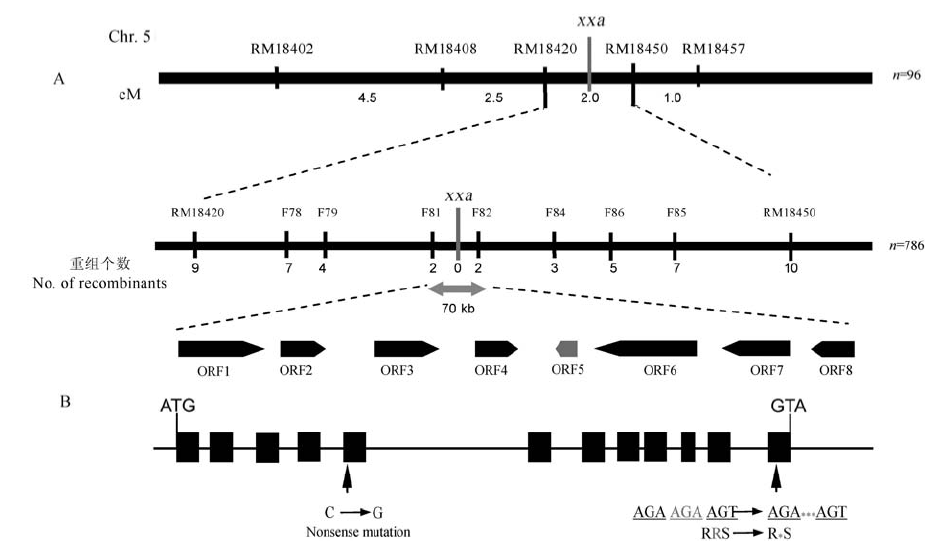
图4 矮秆小粒基因的精细定位与候选基因分析 A–潇湘矮矮秆小粒基因的精细定位;B–候选基因 LOC_Os05g26890的结构及其在潇湘矮中的突变位点。箭头指示位置分别为1个碱基突变和3个碱基缺失,前者为无义突变,后者造成1个赖氨酸缺失。
Fig. 4. Fine mapping and positional cloning of the candidate gene. A, Fine mapping of the xxa gene; B, The structure of candidate gene LOC_Os05g26890 and the mutation sites in XXA. Black arrows show 1-bp nonsense mutation in the 5th exon and a 3-bp deletion that resulted in a lysine deletion in the 12th exon of D1.
| F1组合 Combination of F1 | 总植株数 Total No. of plants | 正常植株数 No. of half-dwarfing plants | 矮秆小粒植株数 No. of dwarfing plants | 理论比 Expressed ratio | χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日本晴/潇湘矮 Nipponbare/XXA | 3223 | 2341 | 782 | 3:1 | 0.078 |
| 热研1号/潇湘矮 Reyan 1/XXA | 2964 | 2249 | 725 | 3:1 | 0.420 |
| 0248/潇湘矮 0248/XXA | 3744 | 2812 | 932 | 3:1 | 0.937 |
| Y01/潇湘矮 Y01/XXA | 3416 | 2560 | 856 | 3:1 | 0.937 |
表2 日本晴、热研1号、0248、Y01和潇湘矮杂交组合F2株高的分离情况
Table 2 Segregation of combination Nipponbare/XXA , Reyan 1/XXA, 0248/XXA and Y01/XXA.
| F1组合 Combination of F1 | 总植株数 Total No. of plants | 正常植株数 No. of half-dwarfing plants | 矮秆小粒植株数 No. of dwarfing plants | 理论比 Expressed ratio | χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日本晴/潇湘矮 Nipponbare/XXA | 3223 | 2341 | 782 | 3:1 | 0.078 |
| 热研1号/潇湘矮 Reyan 1/XXA | 2964 | 2249 | 725 | 3:1 | 0.420 |
| 0248/潇湘矮 0248/XXA | 3744 | 2812 | 932 | 3:1 | 0.937 |
| Y01/潇湘矮 Y01/XXA | 3416 | 2560 | 856 | 3:1 | 0.937 |
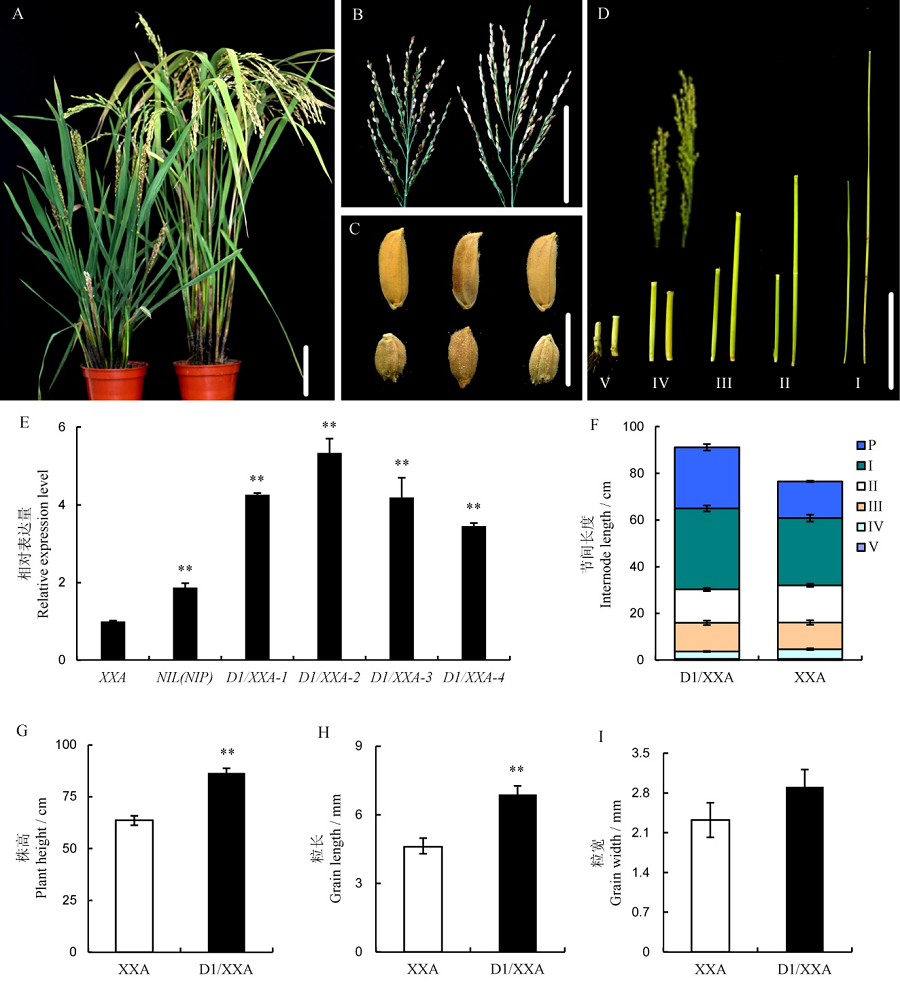
图5 转基因功能互补 A~D–潇湘矮(左)和转基因阳性T0家系(D1/XXA-1, 右) 成熟期表型。包括株型(A)、分枝(B)、粒型(C, 上为D1/XXA-1, 下为XXA)、节间以及穗长(D); E–D1基因在潇湘矮(XXA)以及转基因互补家系中表达水平。F~I–潇湘矮与互补转基因植株在节间长度(F)、株高(G)、粒长(H)以及粒宽(I)比较。A, B, D图中Bar = 10 cm,C图中Bar = 5 mm;E中数据为3次重复实验的平均值,F~I中数据为10次重复实验的平均值,利用t测验检测数据差异显著性(*P <0.05, **P <0.01)。
Fig. 5. Phenotype analysis of complementary plants(D1/XXA). A-D, Phenotypes of the complementary plants of D1/XXA-1(right) and XXA(left) at harvesting time, including plant type(A), panicle(B), grain size(C) and internode(D) of D1/XXA-1 and XXA; E, Relative expression levels of D1 gene in XXA and D1/XXA lines. F-I, Internode length(F), plant height(G), grain length(H) and grain width(I) of D1/XXA-1 and XXA(Bar=10 cm in A, B and D; Bar=5 mm in C). Data in E are shown as Mean±SD from 3 individual replicates. Data in F-I are shown as Mean±SD from 10 individual replicates. The asterisks indicate statistical significance, as determined by the Student’s t-test(*P<0.05; **P<0.01).
| [1] | Khush G S.Green revolution: the way forward.Nat Rev Genet, 2001, 2(10): 815-822. |
| [2] | Hu C H.Evaluation of breeding semidwarf rice by induced mutation and hybridization.Euphytica, 1973, 22: 562-574. |
| [3] | Sasaki A, Ashikari M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Itoh H, Nishimura A, Swapan D, Ishiyama K, Saito T, Kobayashi M, Khush G S, Kitano H, Matsuoka M.Green revolution: A mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice.Nature, 2002, 416: 701-702. |
| [4] | Peng J, Richards D E, Hartley N M, Murphy G P, Devos K M, Flintham J E, Beales J, Fish L J, Worland A J, Pelica F, Sudhakar D, Christou P, Snape J W, Gale M D, Harberd N P.“Green revolution” genes encode mutant gibberellin response modulators.Nature, 1999, 400: 256-261. |
| [5] | 张云辉, 张所兵, 林静, 汪迎节, 方先文. 水稻株高基因克隆及功能分析的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2014, 30: 1-7. |
| Zhang Y H, Zhang S B, Fang X W, Lin J, Wang Y J, Fang X W.Research progress on cloning and functional analysis of plant height genes in rice(Oryza sativa L.).Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2014, 30: 1-7.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Fujioka S, Yokota T.Biosynthesis and metabolism of brassinosteroids.Annu Rev Plant Biol, 2003, 54: 137-164. |
| [7] | Itoh H, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Sato Y, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M.The gibberellin signaling pathway is regulated by the appearance and disappearance of SLENDER RICE1 in nuclei.Plant Cell, 2002, 14: 57-70. |
| [8] | Hirano K1, Asano K, Tsuji H, Kawamura M, Mori H, Kitano H, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Matsuoka M. Characterization of the molecular mechanism underlying gibberellin perception complex formation in rice.Plant Cell, 2010, 22: 2680-2696. |
| [9] | Smith S M, Waters M T.Strigolactones: Destruction- dependent perception?Curr Biol, 2012, 22: 924-927. |
| [10] | Monna L1, Kitazawa N, Yoshino R, Suzuki J, Masuda H, Maehara Y, Tanji M, Sato M, Nasu S, Minobe Y. Positional cloning of rice semidwarfing gene, sd-1: Rice “green revolution gene” encodes a mutant enzyme involved in gibberellin synthesis.DNA Res, 2002, 9: 11-17. |
| [11] | Spielmeyer W, Ellis M H, Chandler P M.Semidwarf(sd-1), “green revolution” rice, contains a defective gibberellin 20-oxidase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2002, 99: 9043-9048. |
| [12] | Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Ashikari M, Nakajima M, Itoh H, Katoh E, Kobayashi M, Chow T Y, Hsing Y I, Kitano H, Yamaguchi I, Matsuoka M.GIBBERELLIN INSENSITIVE DWARF1 encodes a soluble receptor for gibberellin. Nature, 2005, 437: 693-698. |
| [13] | Izawa Y, Takayanagi Y, Inaba N, Abe Y, Minami M, Fujisawa Y, Kato H, Ohki S, Kitano H, Iwasaki Y.Function and expression pattern of the alpha subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein in rice.Plant Cell Physiol, 2010, 51: 271-281. |
| [14] | Kamei T, Matozaki T, Sakisaka T.Coendocytosis of cadherin and c-Met coupled to disruption of cell-cell adhesion in MDCK cells-regulation by Rho, Rac and Rab small G proteins.Oncogene, 1999, 18: 6776-6784. |
| [15] | Wu Y, Fu Y, Zhao S, Gu P, Zhu Z, Sun C, Tan L.CLUSTERED PRIMARY BRANCH 1, a new allele of DWARF11, controls panicle architecture and seed size in rice.Plant Biotechnol J, 2016, 14: 377-386. |
| [16] | Tong H, Liu L, Jin Y, Du L, Yin Y, Qian Q, Zhu L, Chu C.DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING acts as a direct downstream target of a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase to mediate brassinosteroid responses in rice.Plant Cell, 2012, 24: 2562-2577. |
| [17] | Shi Z.Characterization and cloning of SMALL GRAIN 4, a novel DWARF11 allele that affects brassinosteroid biosynthesis in rice.Chin Sci Bull, 2015, 60: 905-915. |
| [18] | Zhou F, Lin Q, Zhu L, Ren Y, Zhou K, Shabek N, Wu F, Mao H, Dong W, Gan L, Ma W, Gao H, Chen J, Yang C, Wang D, Tan J, Zhang X, Guo X, Wang J, Jiang L, Liu X, Chen W, Chu J, Yan C, Ueno K, Ito S, Asami T, Cheng Z, Wang J, Lei C, Zhai H, Wu C, Wang H, Zheng N, Wan J.D14-SCF(D3)-dependent degradation of D53 regulates strigolactone signalling.Nature, 2013, 504(7480): 406-410. |
| [19] | Jiang L, Liu X, Xiong G, Liu H, Chen F, Wang L, Meng X, Liu G, Yu H, Yuan Y, Yi W, Zhao L, Ma H, He Y, Wu Z, Melcher K, Qian Q, Xu H E, Wang Y, Li J.DWARF 53 acts as a repressor of strigolactone signalling in rice.Nature, 2013, 504: 401-405. |
| [20] | Huang N, Courtois B, Khush G S.Association of quantitative trait loci for plant height with major dwarfing genes in rice.Heredity, 1996, 77: 130-137. |
| [21] | Moncada P, Martínez C P, Borrero J.Quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an Oryza sativa × Oryza rufipogon BC2F2 population evaluated in an upland environment.Theor Appl Genet, 2002, 102: 41-52. |
| [22] | 罗炬, 邵高能, 魏祥进, 陈明亮, 唐绍清, 焦桂爱, 谢黎虹, 胡培松. 一个控制水稻株高QTL qPH3的遗传分析. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(4): 417-422. |
| Luo J, Shao G N, Wei X J, Chen M L, Tang S Q, Jiao Q A, Xie L H, Hu P S.Genetic analysis of a QTL qPH3 for plant height in rice.Chin J Rice Sci, 2012, 26(4): 417-422. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 余应弘, 吴云天, 曾翔, 袁隆平. 水稻矮秆小粒突变体潇湘矮的特征特性及其遗传鉴定. 杂交水稻, 2007, 22(6): 67-70. |
| Yu Y H, Wu Y T, Zeng X, Yuan L P.Characterization and genetic studies on dwarf rice mutant Xiaoxiangai with small grains.Hybrid Rice, 2007, 22(6): 67-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 郑贵朝, 胡事君. 提高水稻愈伤组织植株再生能力几种方法的评价. 杂交水稻, 2005, 20(2): 54-57. |
| Zheng C G, Hu S J.Evaluation of some culture methods for enhancing plant regeneration ability of rice callus.Hybrid Rice, 2005, 20(2): 54-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Ashikari M, Wu J, Yano M, Sasaki T, Yoshimura A.Rice gibberellin-insensitive dwarf mutant gene Dwarf 1 encodes the alpha-subunit of GTP-binding protein.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1999, 96: 10284-10289. |
| [26] | Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Fujisawa Y, Kobayashi M.Rice dwarf mutant d1, which is defective in the alpha subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein, affects gibberellin signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2000, 97: 11638-11643. |
| [27] | Hartweck L M, Olszewski N E.Rice GIBBERELLIN INSENSITIVE DWARF1 is a gibberellin receptor that illuminates and raises questions about GA signaling.Plant Cell, 2006, 18: 278-282. |
| [28] | Choe S, Dilkes B P, Gregory B D, Ross A S, Yuan H, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Tanaka A, Yoshida S, Tax F E, Feldmann K A.The Arabidopsis dwarf 1 mutant is defective in the conversion of 24-methylenecholesterol to campesterol in brassinosteroid biosynthesis.Plant Physiol, 1999, 119: 897-907. |
| [29] | Ferrero-Serrano A, Assmann S M.The alpha-subunit of the rice heterotrimeric G protein, RGA1, regulates drought tolerance during the vegetative phase in the dwarf rice mutant d1.J Exp Bot, 2016, 67(11): 3433-3443. |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||