
中国水稻科学 ›› 2016, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 567-576.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.6017
• • 下一篇
胡训霞1, 史春阳1, 丁艳1, 张萍1, 葛永胜1, 刘玉金2,*( ), 王泽港1, 葛才林1,*(
), 王泽港1, 葛才林1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2016-02-02
修回日期:2016-04-28
出版日期:2016-11-10
发布日期:2016-11-10
通讯作者:
刘玉金,葛才林
基金资助:
Xun-xia HU1, Chun-yang SHI1, Yan DING1, Ping ZHANG1, Yong-sheng GE1, Yu-jin LIU2,*( ), Ze-gang WANG1, Cai-lin GE1,*(
), Ze-gang WANG1, Cai-lin GE1,*( )
)
Received:2016-02-02
Revised:2016-04-28
Online:2016-11-10
Published:2016-11-10
Contact:
Yu-jin LIU, Cai-lin GE
摘要:
研究水稻耐低磷机制,对高效利用土壤磷的水稻品种改良具有重要意义。应用基因芯片和qRT-PCR技术,分析了耐低磷水稻品种仪2434和低磷敏感品种通粳981根系中磷高效吸收和利用相关基因表达对低磷胁迫的应答。水稻叶片磷含量的测定结果表明,低磷胁迫下仪2434的叶片磷含量较对照降幅小,这表明仪2434较通粳981具有更强的磷素吸收利用能力。基因芯片检测结果表明,在低磷胁迫下的仪2434根系中,PHR1、osa-miR399s和SPXs基因的表达诱导、激活磷饥饿信号途径;APA、PAPs、MPE、PA、PEPC和VDAC1、C4-DT/MAT 等基因的表达诱导,增强有机磷水解酶和有机酸的合成和分泌,促进介质中难溶性磷的活化;OsPT2、OsPT6基因的表达诱导,促进仪2434根系对磷的高效吸收。qRT-PCR检测结果表明,仪2434根系中与磷饥饿信号转导、磷活化、磷高效吸收相关的8个代表性基因(PHR1、SPX、PAP、APA、PEPC、MFS、OsPT2、OsPT6)的表达水平均随低磷处理时间的延长呈逐步增高的趋势;经低磷处理后,所检测的8个基因在仪2434根系中的转录水平均显著高于其在通粳981根系中的转录水平,PHR1、APA、OsPT2在通粳981根系中的表达诱导作用不明显,且仪2434根系组织和根系分泌的酸性磷酸酶活性较通粳981增强更显著,这可能是仪2434较通粳981对低磷胁迫有较高耐性的主要机制之一。
中图分类号:
胡训霞, 史春阳, 丁艳, 张萍, 葛永胜, 刘玉金, 王泽港, 葛才林. 水稻根系中磷高效吸收和利用相关基因表达对低磷胁迫的应答[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(6): 567-576.
Xun-xia HU, Chun-yang SHI, Yan DING, Ping ZHANG, Yong-sheng GE, Yu-jin LIU, Ze-gang WANG, Cai-lin GE. Response of Gene Expression Related to Efficient Phosphorus Absorption and Utilization to Low-P Stress in Rice Roots[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(6): 567-576.
| Gene ID 基因ID | 功能注释 Function annotation | 上游引物 Forward primer | 下游引物 Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Os01g0239000 | PHR1 | 5'-CGCAAGGTGAAGGTGGACT-3' | 5'-CGATGTTGTGGCGAGTGAG-3' |
| Os07g0614700 | SPX | 5'-CCCATCCAATGACCACC-3' | 5'-TTGAAAGCCAAAACACG-3' |
| Os10g0116800 | PAP | 5'-ATCACTATGACTGGAGGGG-3' | 5'-TGTTTCTGCTGCTGATGTG-3' |
| Os05g0192100 | APA | 5'-AGTAGCACAAAGCAGCAATA-3' | 5'-CGTTCAGCATCTCCGTC-3' |
| Os01g0758300 | PEPC | 5'-TCCAAGCCGCCTTTAGAA-3' | 5'-ATCACGGTCTCCACCCATC-3' |
| Os06g0324800 | MFS | 5'-CCCTACGATGGATACTGGC-3' | 5'-AGGATGAAGGTGGTGGTGTT-3' |
| Os03g0150800 | QsPT2 | 5'-AGCAAGGTCGGGTGGAT-3' | 5'-GAAGGTGAGTGCGTAGAGC-3' |
| Os08g0564000 | OsPT6 | 5'-GCCTGCTCTTCACCTTCC-3' | 5'-CCGACGACAACGACAAAA-3' |
表1 用于实时荧光定量PCR的特异性引物序列
Table 1 The primer sequences used for qRT-PCR verification.
| Gene ID 基因ID | 功能注释 Function annotation | 上游引物 Forward primer | 下游引物 Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Os01g0239000 | PHR1 | 5'-CGCAAGGTGAAGGTGGACT-3' | 5'-CGATGTTGTGGCGAGTGAG-3' |
| Os07g0614700 | SPX | 5'-CCCATCCAATGACCACC-3' | 5'-TTGAAAGCCAAAACACG-3' |
| Os10g0116800 | PAP | 5'-ATCACTATGACTGGAGGGG-3' | 5'-TGTTTCTGCTGCTGATGTG-3' |
| Os05g0192100 | APA | 5'-AGTAGCACAAAGCAGCAATA-3' | 5'-CGTTCAGCATCTCCGTC-3' |
| Os01g0758300 | PEPC | 5'-TCCAAGCCGCCTTTAGAA-3' | 5'-ATCACGGTCTCCACCCATC-3' |
| Os06g0324800 | MFS | 5'-CCCTACGATGGATACTGGC-3' | 5'-AGGATGAAGGTGGTGGTGTT-3' |
| Os03g0150800 | QsPT2 | 5'-AGCAAGGTCGGGTGGAT-3' | 5'-GAAGGTGAGTGCGTAGAGC-3' |
| Os08g0564000 | OsPT6 | 5'-GCCTGCTCTTCACCTTCC-3' | 5'-CCGACGACAACGACAAAA-3' |
| 功能注释 Function annotation | 基因ID Gene ID | Log2倍数 Log2FC | P值 P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR399 | osa-miR399d | 3.398±0.307 | 1.133×10-4 |
| osa-miR399i | 2.572±0.173 | 8.032×10-5 | |
| osa-miR399j | 3.184±0.115 | 1.027×10-6 | |
| 磷饥饿调控蛋白 Similar to phosphate starvation regulator protein (PHR1) | Os01g0239000 | 1.953±0.799 | 0.048 |
| 磷饥饿调控蛋白 Similar to phosphate starvation response regulator-like protein | Os02g0325600 | 2.144±0.080 | 4.665×10-4 |
| SPX结构域 Oryza sativa SYG/PHO8/XPR1 (SPX) domain gene | Os06g0603600 | 1.412±0.271 | 9.934×10-4 |
| SPX结构域 SPX N-terminal domain containing protein | Os07g0614700 | 4.475±0.241 | 2.628×10-4 |
| Os10g0392600 | 2.218±0.263 | 4.952×10-5 | |
| Os02g0202200 | 2.374±0.204 | 1.624×10-4 | |
| 磷酸盐1 Similar to PHO1-like protein | Os06g0493600 | 3.119±0.047 | 2.594×10-4 |
| 高亲和力磷载体2 High affinity phosphate transporter 2 (OsPht2) | Os03g0150800 | 1.395±0.426 | 1.964×10-3 |
| 磷载体6 Oryza sativa phosphate transporter 6 (OsPht6) | Os08g0564000 | 6.488±0.525 | 5.095×10-5 |
| 磷载体6 Similar to phosphate transporter 6(OsPht6-like) | Os04g0186400 | 1.297±0.119 | 0.040 |
| 紫色酸性磷酸酶 Purple acid phosphatase (PAP) | Os12g0576600 | 4.514±0.490 | 7.743×10-5 |
| 紫色酸性磷酸酶 Similar to purple acid phosphatase (PAP) | Os12g0637100 | 2.559±0.342 | 6.757×10-3 |
| Os10g0116800 | 5.107±0.219 | 6.184×10-5 | |
| Os11g0151700 | 3.024±0.376 | 3.155×10-3 | |
| Os01g0776600 | 2.573±0.077 | 9.358×10-5 | |
| 紫色酸性磷酸酶 Purple acid phosphatase-like (PAP-like) | Os01g0941800 | 5.442±0.449 | 1.612×10-5 |
| 金属磷酸酯酶 Metallophosphoesterase domain protein (MPE) | Os07g0106000 | 3.055±0.603 | 2.646×10-4 |
| 植酸酶 Similar to Phytase (PA) | Os08g0280100 | 3.372±0.025 | 1.659×10-5 |
| Os03g0848200 | 1.926±0.124 | 1.610×10-5 | |
| 酸性磷酸酶 Acid phosphatase (Class B) (APA) | Os05g0192100 | 1.353±0.075 | 1.420×10-3 |
| 磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸羧化酶 Similar toPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) | |||
| Os01g0758300 | 1.791±0.860 | 0.017 | |
| Os01g0110700 | 2.147±0.677 | 2.508×10-3 | |
| C4-二羧酸转运/苹果酸转运蛋白 C4-dicarboxylate transporter/malic acid transport protein (C4-DT/MAT) | Os01g0226600 | 2.537±1.118 | 7.562×10-3 |
| 电压依赖阴离子通道1 Voltage-dependent anion channe1 (VDAC1) | Os01g0588200 | 1.276±0.240 | 4.216×10-4 |
| 协助转运超家族Major facilitator superfamily protein (MFS) | Os06g0324800 | 4.217±1.267 | 1.278×10-3 |
| Os08g0409900 | 4.113±0.415 | 2.175×10-5 | |
| Os08g0156600 | 3.465±0.131 | 4.637×10-5 |
表2 低磷胁迫对仪2434根系中与磷饥饿信号、磷活化和高效吸收相关基因表达的影响
Table 2 Effect of low-P stress on the expression of genes related to phosphorus starvation signals, phosphorus activation and high efficiency absorption.
| 功能注释 Function annotation | 基因ID Gene ID | Log2倍数 Log2FC | P值 P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR399 | osa-miR399d | 3.398±0.307 | 1.133×10-4 |
| osa-miR399i | 2.572±0.173 | 8.032×10-5 | |
| osa-miR399j | 3.184±0.115 | 1.027×10-6 | |
| 磷饥饿调控蛋白 Similar to phosphate starvation regulator protein (PHR1) | Os01g0239000 | 1.953±0.799 | 0.048 |
| 磷饥饿调控蛋白 Similar to phosphate starvation response regulator-like protein | Os02g0325600 | 2.144±0.080 | 4.665×10-4 |
| SPX结构域 Oryza sativa SYG/PHO8/XPR1 (SPX) domain gene | Os06g0603600 | 1.412±0.271 | 9.934×10-4 |
| SPX结构域 SPX N-terminal domain containing protein | Os07g0614700 | 4.475±0.241 | 2.628×10-4 |
| Os10g0392600 | 2.218±0.263 | 4.952×10-5 | |
| Os02g0202200 | 2.374±0.204 | 1.624×10-4 | |
| 磷酸盐1 Similar to PHO1-like protein | Os06g0493600 | 3.119±0.047 | 2.594×10-4 |
| 高亲和力磷载体2 High affinity phosphate transporter 2 (OsPht2) | Os03g0150800 | 1.395±0.426 | 1.964×10-3 |
| 磷载体6 Oryza sativa phosphate transporter 6 (OsPht6) | Os08g0564000 | 6.488±0.525 | 5.095×10-5 |
| 磷载体6 Similar to phosphate transporter 6(OsPht6-like) | Os04g0186400 | 1.297±0.119 | 0.040 |
| 紫色酸性磷酸酶 Purple acid phosphatase (PAP) | Os12g0576600 | 4.514±0.490 | 7.743×10-5 |
| 紫色酸性磷酸酶 Similar to purple acid phosphatase (PAP) | Os12g0637100 | 2.559±0.342 | 6.757×10-3 |
| Os10g0116800 | 5.107±0.219 | 6.184×10-5 | |
| Os11g0151700 | 3.024±0.376 | 3.155×10-3 | |
| Os01g0776600 | 2.573±0.077 | 9.358×10-5 | |
| 紫色酸性磷酸酶 Purple acid phosphatase-like (PAP-like) | Os01g0941800 | 5.442±0.449 | 1.612×10-5 |
| 金属磷酸酯酶 Metallophosphoesterase domain protein (MPE) | Os07g0106000 | 3.055±0.603 | 2.646×10-4 |
| 植酸酶 Similar to Phytase (PA) | Os08g0280100 | 3.372±0.025 | 1.659×10-5 |
| Os03g0848200 | 1.926±0.124 | 1.610×10-5 | |
| 酸性磷酸酶 Acid phosphatase (Class B) (APA) | Os05g0192100 | 1.353±0.075 | 1.420×10-3 |
| 磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸羧化酶 Similar toPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) | |||
| Os01g0758300 | 1.791±0.860 | 0.017 | |
| Os01g0110700 | 2.147±0.677 | 2.508×10-3 | |
| C4-二羧酸转运/苹果酸转运蛋白 C4-dicarboxylate transporter/malic acid transport protein (C4-DT/MAT) | Os01g0226600 | 2.537±1.118 | 7.562×10-3 |
| 电压依赖阴离子通道1 Voltage-dependent anion channe1 (VDAC1) | Os01g0588200 | 1.276±0.240 | 4.216×10-4 |
| 协助转运超家族Major facilitator superfamily protein (MFS) | Os06g0324800 | 4.217±1.267 | 1.278×10-3 |
| Os08g0409900 | 4.113±0.415 | 2.175×10-5 | |
| Os08g0156600 | 3.465±0.131 | 4.637×10-5 |
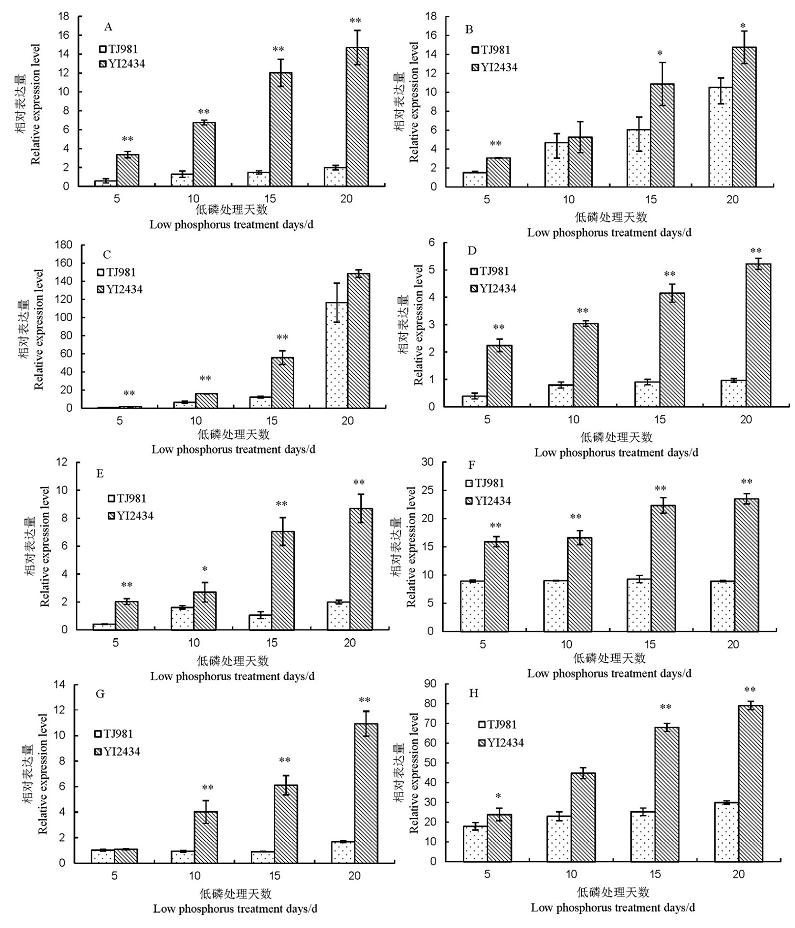
图2 仪2434(YI2434)和通粳981(TJ981)根系中与磷饥饿信号、磷活化和高效吸收相关基因转录水平随时间变化的qRT-PCR验证结果 A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H 分别表示PHR1 (Os01g0239000)、 SPXs (Os07g0614700)、 PAPs (Os10g0116800)、 APA (Os05g0192100)、 PEPC (Os01g0758300)、 MFSs (Os06g0324800)、 OsPT2 (Os03g0150800)、 OsPT6 (Os08g0564000)基因。*、**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平上差异显著。
Fig. 2. Transcription level of phosphorus starvation signals, phosphorus activation and high efficiency absorption related gene changes with low-P treated time in YI2434 and TJ981 roots by qRT-PCR. A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H represent the genes of PHR1 (Os01g0239000), SPXs (Os07g0614700), PAPs (Os10g0116800), APA (Os05g0192100), PEPC (Os01g0758300), MFSs (Os06g0324800), OsPT2 (Os03g0150800), OsPT6 (Os08g0564000), respectively. *, **represent significant difference at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively.
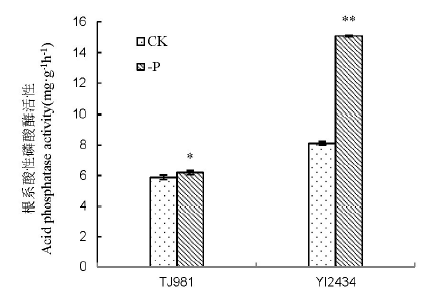
图3 低磷胁迫15 d仪2434和通粳981根系酸性磷酸酶活性。 *、**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平上差异显著。
Fig. 3. The acid phosphatase activity in YI2434 and TJ981 at 15 days after low-P treatment. *, **show significant difference at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively.
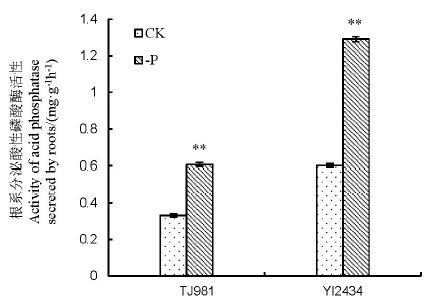
图4 低磷胁迫15 d仪2434和通粳981根系分泌酸性磷酸酶活性 *、**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平上差异显著。
Fig. 4. Acid phosphatase activity secreted by roots in YI2434 and TJ981 at 15 days after low-P treatment. *, **shows significant difference at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01,respectively.
| [1] | 郭再华, 孟萌, 侯彦琳. 磷、砷双重胁迫对不同耐低磷水稻苗期生长及磷、砷吸收的影响. 应用与环境生物学报, 2009, 15(5): 596-601. |
| Guo Z H, Meng M, Hou Y L.Effect of P and As couple stress on growth, and P and As absorption of different P-tolerant rice seedlings.Chin J Appl Environ Biol, 2009, 15(5): 596-601.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Xiao K, Katagi H, Harrison M, et al.Improved phosphorus acquisition and biomass production in Arabidopsis by transgenic expression of a purple acid phosphatase gene from M.truncatula. Plant Sci, 2006, 170(2): l91-202. |
| [3] | 李俊艳, 胡红青, 李荣纪,等. 改性磷矿粉对油菜幼苗生长和土壤性质的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2009, 15(2): 441-446. |
| Li J Y, Hu Q H, Li R J, et al.Modified phosphate rock by γ-poly glutamic acid and its effects on the growth of rapeseed seedlings and soil properties.Plant Nutr Fert Sci, 2009, 15(2): 441-446.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 叶思诚, 谭晓风, 袁军. 植物低磷适应机制研究进展. 经济林研究, 2012, 30(2): 128-133. |
| Ye S C, Tan X F, Yuan J.Advances in research on mechanism of plant acclimation to low phosphorus.Non For Res, 2012,30(2): 128-133.(in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 胡慧蓉, 郭安, 王海龙. 我国磷资源利用现状与可持续利用的建议. 磷肥与复肥, 2007, 22(2): 1-5. |
| Hu H R,Guo A, Wang H L.Present status of China's phosphorus resource utilization & some suggestions for sustainable development.Phos Com Fert, 2007, 22(2): 1-5.(in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 王森, 朱昌雄, 耿兵. 土壤氮磷流失途径的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(33): 22-25. |
| Wang S, Zhu C X,Geng B.Research advancement in loss pathways of nitrogen and phosphorus in soils.Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2013, 29(33): 22-25.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 付春平, 钟成华, 邓春光. 水体富营养化成因分析. 重庆建筑大学学报, 2005, 27(1): 128-131. |
| Fu C P,Zhong C H, Deng C G.Analysis on cause of the eutrophication of water body.J Chongqing Archit Univ, 2005, 27(1): 128-131.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 李强, 许明祥, 齐治军, 等. 长期施用化肥对黄土丘陵区坡地土壤物理性质的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(1): 103-109. |
| Li Q, Xu M X, Qi Z J, et al.Effects of long-term chemical fertilization on soil physical properties of slope lands in the loess hilly region.Plant Nutr Fert Sci, 2011, 17(1): 103-109.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 李德华, 向春雷, 姜益泉, 等. 低磷胁迫下水稻不同品种根系有机酸分泌的差异. 中国农业通报, 2005, 21(11): 186-188. |
| Li D H, Xiang C L, Jiang Y Q, et al.Difference of organic acid secretion from roots of various rice varieties under the stress of low phosphorus.Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2005, 21(11): 186-188.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Panigrahy M, Rao D N, Sarla N.Molecular mechanisms in response to phosphate starvation in rice.Biotechnol Adv, 2009 27(4): 389-97 |
| [11] | Cai H M, Xie W B, Zhu T, et al.Transcriptome response to phosphorus starvation in rice.Acta Physiol Plant, 2012, 34: 327-341. |
| [12] | Li L, Liu C, Lian X.Gene expression profiles in rice roots under low phosphorus stress.Plant Mol Biol, 2010, 72(4-5): 423-432. |
| [13] | Oono Y, Kawahara Y, Yazawa T, et al.Diversity in the complexity of phosphate starvation transcriptomes among rice cultivars based on RNA-Seq profiles.Plant Mol Biol, 2013, 83: 523-537. |
| [14] | 史春阳, 葛永胜, 胡训霞, 等. 不同基因型耐低磷水稻品种的筛选. 扬州大学学报(印刷中). |
| Shi C Y, Ge Y S, Hu X X, et al. Screening of different low phosphorous tolerant genotypes rice varieties.J Yangzhou Univ(in press). | |
| [15] | 汤绍虎, 罗充. 植物生理学实验教程. 第一版. 重庆: 西南师范大学出版社, 2012: 35-38. |
| Tang S H, Luo C.Plant Physiology Experiments Tutorial. 1st edn. Chongqing: Southwest China Normal University Press, 2012: 35-38.(in Chinese) | |
| [16] | Jain M, Nijhawan A, Tyagi A K, et al. Validation of housekeeping genes as internal control for studying gene expression in rice by quantitative real-time PCR.Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2006, 345(2): 646-651. |
| [17] | McLachlan K D, Elliot D E, Marco D G, et al. Leaf acid phosphataseisozymes in the diagnosis of phosphorus status in field-grown wheat.Crop Pas Sci, 1987, 38(1): 1-13. |
| [18] | Ni J J, Wu P, Luo A C, et al.Low phosphorus effects of the metabolism on rice seedlings.Commun Soil Sci Plan Anal, 1996, 27(18): 3073-3084. |
| [19] | Hou Q Z, Yi Y Z, Si Q H, et al.Analysis of phosphorus-deficient responsive miRNAs and cis-elements from soybean (Glycine max L.). J Plant Physiol, 2010, 167(15): 1289-1297. |
| [20] | Doerner P.Phosphate starvation signaling: A threesome controls systemic Pi homeostasis.Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2008, 11: 536-540. |
| [21] | 严宽, 王昌全, 李焕秀,等. 磷水平对杂交水稻及其亲本根系酸性磷酸酶活性的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2010, 24(1): 43-48. |
| Yan K, Wang C Q, Li H X, et al.Effects of phosphorus level on the activity of acid phosphatase in roots of hybrid rice and its parents.Chin J Rice Sci, 2010, 24(1): 43-48.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Schenk G,Miti C N, Hanson G R, et al.Purple acid phosphatase: A journey into the function and mechanism of a colorful enzyme.Coordin Chem Rev, 2013, 257(2): 473-482. |
| [23] | 苏顺宗, 刘丹, 吴玲, 等. 玉米低磷响应基因ZmPAP18 的表达特征与序列变异分析. 分子植物育种, 2013, 11(4): 509-516. |
| Su S Z, Liu D, Wu L, et al.Expression and sequence variation analysis of a low-phosphorus responsive gene ZmPAP18 in maize. Mol Plant Breeding, 2013, 11(4):509-516.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Lung S C, Leung A, Kuang R, et al.Phytase activity in tobacco (Nicotianatabacum) root exudates is exhibited by a purple acid phosphatase. Phytochem, 2008, 69(2): 509-516. |
| [25] | 杨建峰, 贺立源. 缺磷诱导植物分泌低分子量有机酸的研究进展. 安徽农业科学, 2006, 34(20): 5171-5175. |
| Yang J F, He L Y.Research advance in the exudation ofprganic acid in phosphorus-deficient plant.J Anhui Agric Sci ,2006, 34(20): 5171-5175.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 陈声奇, 陈爱珠, 周畅. 植物忍耐低磷胁迫机理的研究进展. 湖南农业科学, 2007(2): 43-46. |
| Chen S Q, Chen A Z, Zhou C. Current Research on adaptation mechanisms of plants to phosphorus deficiency stress. Agri Sci Hunan, 2007(2): 43-46.(in Chinese ) | |
| [27] | Liu F, Wang Z Y, Ren H Y, et al. OsSPX1 suppresses the function of OsPHR2 in the regulation ofexpression of OsPT2 and phosphate homeostasis in shoots of rice. Plant J, 2010, 62(3): 508-517. |
| [28] | Ai P, Sun S, Zhao J, et al.Two rice phosphate transporters, OsPht1; 2 and OsPht1; 6, have different functions and kinetic properties in uptake and translocation. Plant J, 2009, 57(5): 798-809. |
| [29] | Wu P,Shou H X, Xu G H, et al.Improvement of phosphorus efficiency in rice on the basis of understanding phosphate signaling and homeostasis.Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2013, 16: 1-8. |
| [30] | Reddy V S, Shlykov M A, Castillo R, et al.The major facilitator superfamily (MFS) revisited.FEBS J, 2012, 279(11): 2022-2035. |
| [31] | 李永夫, 金松恒, 叶正钱,等. 低磷胁迫对山核桃幼苗根系形态和生理特征的影响. 浙江林学院学报, 2010, 27(2):239-245. |
| Li Y F,Jin S H, Ye Z Q, et al.Root morphology and physiological characteristics in Carya cathayensis seedlings with low phosphorus stress.J Zhejiang Coll, 2010, 27(2): 239-245.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 李锋, 李木英, 潘晓华,等. 不同水稻品种幼苗适应低磷胁迫的根系生理生化特性. 中国水稻科学, 2004, 18(1): 48-52. |
| Li F,Li M Y, Pan X X, et al.Biochemical and physiological characteristics in seedlings roots of different rice cultivars under low-phosphorus stress.Chin J Rice Sci, 2004, 18(1): 48-52.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | 韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 汪璐璐, 朱旺, 耿孝宇, 张翔, 孟天瑶, 陈英龙, 高平磊, 许轲, 霍中洋, 戴其根. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东. OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | 候小琴, 王莹, 余贝, 符卫蒙, 奉保华, 沈煜潮, 谢杭军, 王焕然, 许用强, 武志海, 王建军, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 黄腐酸钾提高水稻秧苗耐盐性的作用途径分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [5] | 胡继杰, 胡志华, 张均华, 曹小闯, 金千瑜, 章志远, 朱练峰. 根际饱和溶解氧对水稻分蘖期光合及生长特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [6] | 刘福祥, 甄浩洋, 彭焕, 郑刘春, 彭德良, 文艳华. 广东省水稻孢囊线虫病调查与鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [7] | 陈浩田, 秦缘, 钟笑涵, 林晨语, 秦竞航, 杨建昌, 张伟杨. 水稻根系和土壤性状与稻田甲烷排放关系的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [8] | 缪军, 冉金晖, 徐梦彬, 卜柳冰, 王平, 梁国华, 周勇. 过量表达异三聚体G蛋白γ亚基基因RGG2提高水稻抗旱性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [9] | 尹潇潇, 张芷菡, 颜绣莲, 廖蓉, 杨思葭, 郭岱铭, 樊晶, 赵志学, 王文明. 多个稻曲病菌效应因子的信号肽验证和表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [10] | 朱裕敬, 桂金鑫, 龚成云, 罗新阳, 石居斌, 张海清, 贺记外. 全基因组关联分析定位水稻分蘖角度QTL[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [11] | 魏倩倩, 汪玉磊, 孔海民, 徐青山, 颜玉莲, 潘林, 迟春欣, 孔亚丽, 田文昊, 朱练峰, 曹小闯, 张均华, 朱春权. 信号分子硫化氢参与硫肥缓解铝对水稻生长抑制作用的机制[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| [12] | 周甜, 吴少华, 康建宏, 吴宏亮, 杨生龙, 王星强, 李昱, 黄玉峰. 不同种植模式对水稻籽粒淀粉含量及淀粉关键酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 303-315. |
| [13] | 关雅琪, 鄂志国, 王磊, 申红芳. 影响中国水稻生产环节外包发展因素的实证研究:基于群体效应视角[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(3): 324-334. |
| [14] | 许用强, 姜宁, 奉保华, 肖晶晶, 陶龙兴, 符冠富. 水稻开花期高温热害响应机理及其调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 111-126. |
| [15] | 吕海涛, 李建忠, 鲁艳辉, 徐红星, 郑许松, 吕仲贤. 稻田福寿螺的发生、危害及其防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(2): 127-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||