
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 27-37.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.0507
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Danping HOU, Jinsong TAN, Qingyu BI, Anning ZHANG, Yi LIU, Feiming WANG, Guolan LIU, Xinqiao YU, BIJunguo*( ), Lijun LUO*(
), Lijun LUO*( )
)
Received:2020-05-07
Revised:2020-09-10
Online:2021-01-10
Published:2021-01-10
Contact:
BIJunguo, Lijun LUO
侯丹平, 谭金松, 毕庆宇, 张安宁, 刘毅, 王飞名, 刘国兰, 余新桥, 毕俊国*( ), 罗利军*(
), 罗利军*( )
)
通讯作者:
毕俊国,罗利军
基金资助:Danping HOU, Jinsong TAN, Qingyu BI, Anning ZHANG, Yi LIU, Feiming WANG, Guolan LIU, Xinqiao YU, BIJunguo, Lijun LUO. Effects of Water Stress on Yield Formation and Root Morphological and Physiological Characteristics of Water-saving and Drought-resistantRice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(1): 27-37.
侯丹平, 谭金松, 毕庆宇, 张安宁, 刘毅, 王飞名, 刘国兰, 余新桥, 毕俊国, 罗利军. 水分胁迫对节水抗旱稻产量形成和根系形态生理特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 27-37.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2021.0507
| 年份Year | 处理 Treatment | 组合 Combination | 生育期 Growth duration/d | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number per plant | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number perpanicle | 结实率 Filled-grain percentage/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 单株产量 Yield per plant/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 113 | 11.4 c | 151.5 a | 81.2 a | 26.5 a | 37.2 a |
| H优518 H You 518 | 115 | 16.2 a | 115.2 c | 79.9 b | 24.2 b | 36.1 a | ||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 115 | 11.1 c | 148.9 ab | 81.4 a | 25.9 a | 34.8 a | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 117 | 15.6 ab | 103.4 d | 71.8 c | 22.9 cd | 26.5 b | ||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 118 | 10.2 d | 139.9 b | 79.0 b | 23.4 bc | 26.4 b | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 121 | 14.2 b | 104.3 d | 62.0 d | 22.1 d | 20.3 c | ||
| 2019 | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 114 | 10.3 c | 156.5 a | 82.5 a | 27.2 a | 36.2 a |
| H优518 H You 518 | 115 | 14.8a | 120.1 c | 78.5 b | 24.7 b | 34.5 a | ||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 116 | 10.1 c | 148.7 ab | 81.6 a | 27.0 a | 33.1 a | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 118 | 14.5ab | 107.2 d | 71.3 c | 23.5 cd | 26.0 b | ||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 119 | 9.6 d | 140.9 b | 79.7 b | 24.0 bc | 25.9 b | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 122 | 12.3 b | 103.2 d | 60.9 d | 23.0 d | 17.8 c |
Table 1 Effect of water stress on yield and its components of two varieties.
| 年份Year | 处理 Treatment | 组合 Combination | 生育期 Growth duration/d | 有效穗数 Effective panicle number per plant | 每穗粒数 Spikelet number perpanicle | 结实率 Filled-grain percentage/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g | 单株产量 Yield per plant/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 113 | 11.4 c | 151.5 a | 81.2 a | 26.5 a | 37.2 a |
| H优518 H You 518 | 115 | 16.2 a | 115.2 c | 79.9 b | 24.2 b | 36.1 a | ||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 115 | 11.1 c | 148.9 ab | 81.4 a | 25.9 a | 34.8 a | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 117 | 15.6 ab | 103.4 d | 71.8 c | 22.9 cd | 26.5 b | ||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 118 | 10.2 d | 139.9 b | 79.0 b | 23.4 bc | 26.4 b | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 121 | 14.2 b | 104.3 d | 62.0 d | 22.1 d | 20.3 c | ||
| 2019 | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 114 | 10.3 c | 156.5 a | 82.5 a | 27.2 a | 36.2 a |
| H优518 H You 518 | 115 | 14.8a | 120.1 c | 78.5 b | 24.7 b | 34.5 a | ||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 116 | 10.1 c | 148.7 ab | 81.6 a | 27.0 a | 33.1 a | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 118 | 14.5ab | 107.2 d | 71.3 c | 23.5 cd | 26.0 b | ||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 119 | 9.6 d | 140.9 b | 79.7 b | 24.0 bc | 25.9 b | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 122 | 12.3 b | 103.2 d | 60.9 d | 23.0 d | 17.8 c |
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 分蘖期 Mid-tillering | 穗分化始期 Panicleinitiation | 抽穗期 Heading | 成熟期 Maturity | 茎蘖成穗率 Percentageof productive tillers/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 8.9 c | 14.8 d | 14.0 c | 11.4 c | 77.0 f |
| H优518 H You 518 | 13.0 a | 19.6 a | 17.0 a | 16.2 a | 82.7 c | ||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 8.7 c | 14.1 d | 13.9 c | 11.1 c | 78.7 e | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 12.7 a | 18.7 b | 15.1 b | 15.6 ab | 83.4 b | ||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 7.8 d | 12.7 e | 11.5 d | 10.2 d | 80.3 d | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 11.4 b | 16.8 c | 14.6 b | 14.2 b | 84.5 a | ||
| 2019 | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 8.2 c | 14.3 c | 13.8 c | 10.3 c | 72.0 f |
| H优518 H You 518 | 11.9 a | 18.5 a | 16.9 a | 14.8 a | 80.0 c | ||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 8.1 c | 13.8 d | 12.9 d | 10.1 c | 73.2 e | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 11.7 a | 17.6 b | 15.1 b | 14.5 a | 82.4 b | ||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 7.8 d | 12.9 e | 10.7 e | 9.6 d | 74.4 d | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 11.2 b | 14.8 c | 13.8 c | 12.3 b | 83.1 a |
Table 2 Effects of water stress on the number of tillers and the percentage of productive tillers in main growth stages of the two varieties.
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 分蘖期 Mid-tillering | 穗分化始期 Panicleinitiation | 抽穗期 Heading | 成熟期 Maturity | 茎蘖成穗率 Percentageof productive tillers/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 8.9 c | 14.8 d | 14.0 c | 11.4 c | 77.0 f |
| H优518 H You 518 | 13.0 a | 19.6 a | 17.0 a | 16.2 a | 82.7 c | ||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 8.7 c | 14.1 d | 13.9 c | 11.1 c | 78.7 e | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 12.7 a | 18.7 b | 15.1 b | 15.6 ab | 83.4 b | ||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 7.8 d | 12.7 e | 11.5 d | 10.2 d | 80.3 d | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 11.4 b | 16.8 c | 14.6 b | 14.2 b | 84.5 a | ||
| 2019 | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 8.2 c | 14.3 c | 13.8 c | 10.3 c | 72.0 f |
| H优518 H You 518 | 11.9 a | 18.5 a | 16.9 a | 14.8 a | 80.0 c | ||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 8.1 c | 13.8 d | 12.9 d | 10.1 c | 73.2 e | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 11.7 a | 17.6 b | 15.1 b | 14.5 a | 82.4 b | ||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 7.8 d | 12.9 e | 10.7 e | 9.6 d | 74.4 d | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 11.2 b | 14.8 c | 13.8 c | 12.3 b | 83.1 a |
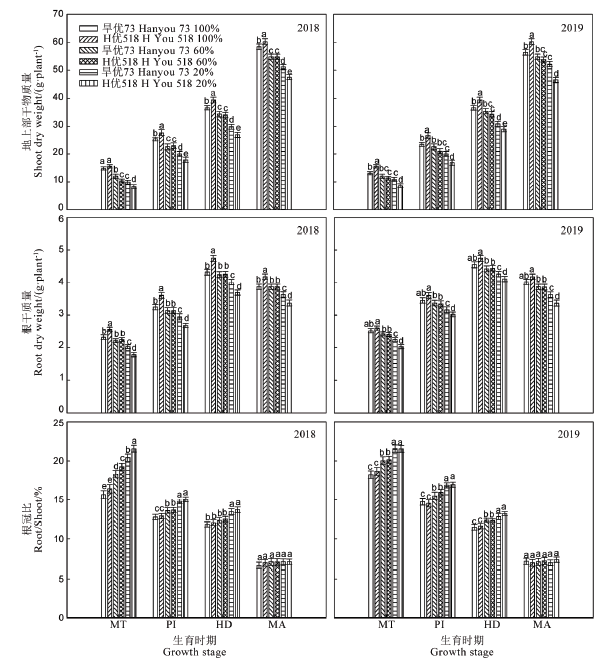
Fig. 2. Effect of water stress on shoot dry matter weight, root dry weight and root/shoot ratio of the two varieties in main growth stages. MT, Mid-tillering; PI, Panicle initiation; HD, Heading; MA, Maturity. Different letters indicate significant difference in the same stage at the level of 0.05.
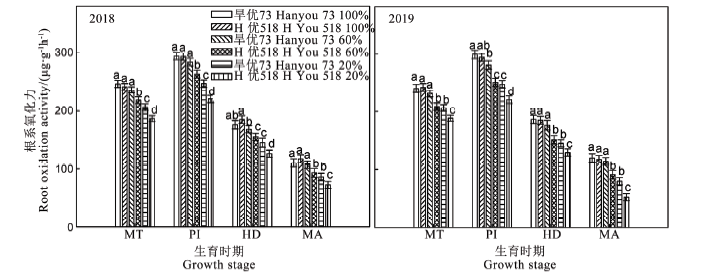
Fig. 3. Effect of water treatments on the root oxidation activity of the two varieties in main growth stages. MT, Mi-illering PI, Panicle initiation; HD, Heading; MA. Matunity. Different ltters indicate signifcant difference at the level of 0.05 in the same stage.

Fig. 4. Effect of water treatment on total absorption area, active absorption area and active absorption area / total absorption area of roots in main growth stages of two varieties. MT, Mid-tillering; PI, Panicle initiation; HD, Heading; MA, Maturity. Different letters indicate significant difference in the same stage at the level of 0.05.
| 年份 Year | 生育期 Growth stage | 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 根系形态 Root morphology | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根体积 Root volume /(cm3·plant-1) | 根长 Root length /m | 根直径 Root diameter /mm | 根尖数 Number of root tips /(×104·plant-1) | ||||
| 2018 | MT | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 13.16 ab | 11.2 ab | 0.37 a | 11.56 b |
| H优518 H You 518 | 14.32 a | 12.3 a | 0.37 a | 13.1 a | |||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 12.91 b | 12.5 a | 0.35 b | 11.45 b | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 12.88 b | 12.2 a | 0.35 b | 11.02 c | |||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 11.02 c | 10.5 b | 0.35 b | 10.35 d | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 9.54 d | 9.2 c | 0.34 b | 9.34 e | |||
| PI | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 31.04 b | 27.8 b | 0.41 a | 30.48 b | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 34.61 a | 30.2 a | 0.41 a | 32.37 a | |||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 30.69 b | 29.7 ab | 0.39 b | 31.54 ab | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 30.71 b | 28.9 ab | 0.39 b | 28.61 c | |||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 27.43 c | 24.3 c | 0.36 c | 26.12 d | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 25.12 d | 21.9 d | 0.36 c | 22.04 e | |||
| HD | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 51.82 b | 40.2 b | 0.4 a | 42.11 b | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 56.73 a | 42.9 a | 0.4 a | 43.54 a | |||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 52.09 b | 42.1 ab | 0.38 b | 42.63 ab | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 52.61 b | 41.9 ab | 0.38 b | 38.13 c | |||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 46.02 c | 36.2 c | 0.36 c | 37.93 c | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 42.81 d | 32.8 d | 0.35 c | 30.19 d | |||
| MA | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 51.63 b | 40.1 ab | 0.4 a | 34.55 b | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 53.21 a | 41.3 a | 0.4 a | 36.21 a | |||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 52.79 ab | 40.4 ab | 0.38 b | 34.43 b | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 51.23 b | 40.2 ab | 0.37 b | 32.18 c | |||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 43.42 c | 36.35 b | 0.35 c | 28.65 d | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 38.72 d | 33.2 c | 0.35 c | 24.13 e | |||
| 2019 | MT | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 15.38 ab | 12.3 ab | 0.38 a | 13.28 bc |
| H优518 H You 518 | 16.59 a | 13.1 a | 0.38 a | 14.05 a | |||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 14.31 b | 12.5 a | 0.37 b | 13.54 b | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 14.72 b | 12.8 a | 0.36 b | 13.19 c | |||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 12.49 c | 11.0 b | 0.35 c | 12.73 d | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 10.95 d | 9.8 c | 0.34 c | 10.79 e | |||
| PI | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 33.15 b | 29.5 b | 0.42 a | 32.48 b | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 36.32 a | 32.9 a | 0.42 a | 34.37 a | |||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 33.69 b | 31.4 ab | 0.4 b | 33.54 ab | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 33.71 b | 31.2 ab | 0.39 b | 30.61 c | |||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 29.43 c | 25.1 c | 0.36 c | 25.32 d | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 26.12 d | 22.1 d | 0.35 c | 21.73 e | |||
| HD | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 53.28 b | 42.2 b | 0.41 a | 43.16 b | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 58.86 a | 44.1 a | 0.41 a | 44.14 a | |||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 55.94 b | 43.5 ab | 0.38 b | 43.81 ab | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 55.76 b | 43.8 ab | 0.39 b | 39.53 c | |||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 47.11 c | 35.6 c | 0.36 c | 38.55 c | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 41.82 d | 31.3 d | 0.35 c | 31.82 d | |||
| MA | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 52.19 b | 41.4 ab | 0.39 a | 36.92 b | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 55.47 a | 42.3 a | 0.4 a | 38.43 a | |||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 53.82 ab | 41.8 ab | 0.36 b | 36.67 b | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 52.51 b | 41.4 ab | 0.37 b | 33.09 c | |||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 42.33 c | 38.1 b | 0.33 c | 29.02 d | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 36.79 d | 32.5 c | 0.34 c | 25.03 e | |||
Table 3 Effect of water treatments on root morphology of the two varieties in main growth stages
| 年份 Year | 生育期 Growth stage | 处理 Treatment | 品种 Variety | 根系形态 Root morphology | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根体积 Root volume /(cm3·plant-1) | 根长 Root length /m | 根直径 Root diameter /mm | 根尖数 Number of root tips /(×104·plant-1) | ||||
| 2018 | MT | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 13.16 ab | 11.2 ab | 0.37 a | 11.56 b |
| H优518 H You 518 | 14.32 a | 12.3 a | 0.37 a | 13.1 a | |||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 12.91 b | 12.5 a | 0.35 b | 11.45 b | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 12.88 b | 12.2 a | 0.35 b | 11.02 c | |||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 11.02 c | 10.5 b | 0.35 b | 10.35 d | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 9.54 d | 9.2 c | 0.34 b | 9.34 e | |||
| PI | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 31.04 b | 27.8 b | 0.41 a | 30.48 b | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 34.61 a | 30.2 a | 0.41 a | 32.37 a | |||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 30.69 b | 29.7 ab | 0.39 b | 31.54 ab | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 30.71 b | 28.9 ab | 0.39 b | 28.61 c | |||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 27.43 c | 24.3 c | 0.36 c | 26.12 d | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 25.12 d | 21.9 d | 0.36 c | 22.04 e | |||
| HD | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 51.82 b | 40.2 b | 0.4 a | 42.11 b | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 56.73 a | 42.9 a | 0.4 a | 43.54 a | |||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 52.09 b | 42.1 ab | 0.38 b | 42.63 ab | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 52.61 b | 41.9 ab | 0.38 b | 38.13 c | |||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 46.02 c | 36.2 c | 0.36 c | 37.93 c | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 42.81 d | 32.8 d | 0.35 c | 30.19 d | |||
| MA | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 51.63 b | 40.1 ab | 0.4 a | 34.55 b | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 53.21 a | 41.3 a | 0.4 a | 36.21 a | |||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 52.79 ab | 40.4 ab | 0.38 b | 34.43 b | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 51.23 b | 40.2 ab | 0.37 b | 32.18 c | |||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 43.42 c | 36.35 b | 0.35 c | 28.65 d | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 38.72 d | 33.2 c | 0.35 c | 24.13 e | |||
| 2019 | MT | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 15.38 ab | 12.3 ab | 0.38 a | 13.28 bc |
| H优518 H You 518 | 16.59 a | 13.1 a | 0.38 a | 14.05 a | |||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 14.31 b | 12.5 a | 0.37 b | 13.54 b | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 14.72 b | 12.8 a | 0.36 b | 13.19 c | |||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 12.49 c | 11.0 b | 0.35 c | 12.73 d | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 10.95 d | 9.8 c | 0.34 c | 10.79 e | |||
| PI | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 33.15 b | 29.5 b | 0.42 a | 32.48 b | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 36.32 a | 32.9 a | 0.42 a | 34.37 a | |||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 33.69 b | 31.4 ab | 0.4 b | 33.54 ab | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 33.71 b | 31.2 ab | 0.39 b | 30.61 c | |||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 29.43 c | 25.1 c | 0.36 c | 25.32 d | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 26.12 d | 22.1 d | 0.35 c | 21.73 e | |||
| HD | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 53.28 b | 42.2 b | 0.41 a | 43.16 b | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 58.86 a | 44.1 a | 0.41 a | 44.14 a | |||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 55.94 b | 43.5 ab | 0.38 b | 43.81 ab | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 55.76 b | 43.8 ab | 0.39 b | 39.53 c | |||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 47.11 c | 35.6 c | 0.36 c | 38.55 c | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 41.82 d | 31.3 d | 0.35 c | 31.82 d | |||
| MA | 100% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 52.19 b | 41.4 ab | 0.39 a | 36.92 b | |
| H优518 H You 518 | 55.47 a | 42.3 a | 0.4 a | 38.43 a | |||
| 60% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 53.82 ab | 41.8 ab | 0.36 b | 36.67 b | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 52.51 b | 41.4 ab | 0.37 b | 33.09 c | |||
| 20% | 旱优73 Hanyou 73 | 42.33 c | 38.1 b | 0.33 c | 29.02 d | ||
| H优518 H You 518 | 36.79 d | 32.5 c | 0.34 c | 25.03 e | |||
| 性状 Trait | 分蘖期MT | 穗分化始期PI | 抽穗期HD | 成熟期MA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部干物质量Shoot dry weight | 0.875* | 0.909* | 0.922** | 0.890* |
| 根干物质量Root dry weight | 0.921** | 0.897* | 0.857* | 0.907* |
| 根冠比Root/Shoot | -0.877* | -0.915* | -0.906* | -0.597 |
| 根系氧化力Root oxidation activity | 0.992** | 0.995** | 0.991** | 0.988** |
| 根系总吸收表面积Root total absorption area | 0.896* | 0.850* | 0.923** | 0.946** |
| 根系活跃吸收表面积Root active absorption area | 0.961** | 0.947** | 0.977** | 0.986** |
| 活跃吸收表面积/总吸收表面积 Active/total ratio | -0.008 | -0.320 | -0.356 | 0.980** |
| 过氧化物酶活性POD | 0.987** | 0.966** | 0.961** | 0.936** |
| 超氧化物歧化酶活性SOD | 0.962** | 0.951** | 0.950** | 0.964** |
| 过氧化氢酶活性CAT | 0.933** | 0.944** | 0.921** | 0.901* |
| 丙二醛含量MAD | -0.932** | -0.957** | -0.921** | -0.924** |
| 根体积Root volume | 0.869* | 0.839* | 0.804 | 0.857* |
| 根长Root length | 0.796 | 0.798 | 0.808 | 0.849* |
| 根直径Root diameter | 0.972** | 0.935** | 0.856* | 0.767 |
| 根尖数Number of root tips | 0.871* | 0.917* | 0.962** | 0.957** |
Table 4 Correlation between root physiological characteristics and yield of the two varieties.
| 性状 Trait | 分蘖期MT | 穗分化始期PI | 抽穗期HD | 成熟期MA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部干物质量Shoot dry weight | 0.875* | 0.909* | 0.922** | 0.890* |
| 根干物质量Root dry weight | 0.921** | 0.897* | 0.857* | 0.907* |
| 根冠比Root/Shoot | -0.877* | -0.915* | -0.906* | -0.597 |
| 根系氧化力Root oxidation activity | 0.992** | 0.995** | 0.991** | 0.988** |
| 根系总吸收表面积Root total absorption area | 0.896* | 0.850* | 0.923** | 0.946** |
| 根系活跃吸收表面积Root active absorption area | 0.961** | 0.947** | 0.977** | 0.986** |
| 活跃吸收表面积/总吸收表面积 Active/total ratio | -0.008 | -0.320 | -0.356 | 0.980** |
| 过氧化物酶活性POD | 0.987** | 0.966** | 0.961** | 0.936** |
| 超氧化物歧化酶活性SOD | 0.962** | 0.951** | 0.950** | 0.964** |
| 过氧化氢酶活性CAT | 0.933** | 0.944** | 0.921** | 0.901* |
| 丙二醛含量MAD | -0.932** | -0.957** | -0.921** | -0.924** |
| 根体积Root volume | 0.869* | 0.839* | 0.804 | 0.857* |
| 根长Root length | 0.796 | 0.798 | 0.808 | 0.849* |
| 根直径Root diameter | 0.972** | 0.935** | 0.856* | 0.767 |
| 根尖数Number of root tips | 0.871* | 0.917* | 0.962** | 0.957** |
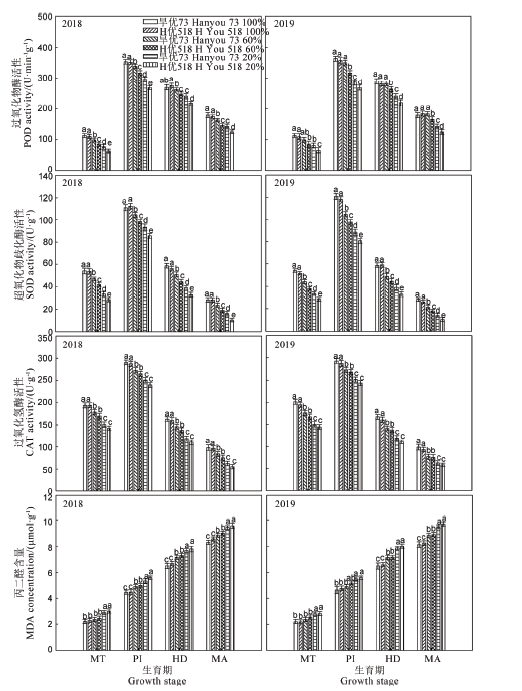
Fig. 5. Effect of water treatment on antioxidant enzyme activities and malondialdehyde content in roots of two varieties in main growth stages. MT, Mid-tillering; PI, Panicle initiation; HD, Heading; MA, Maturity. Different letters indicate that the value of each treatment in the same stage is significantly different at the level of 0.05.
| [1] | 李婷婷,冯钰枫,朱安,黄健,汪浩,李思宇,刘昆,彭如梦,张宏路,刘立军.主要节水灌溉方式对水稻根系形态生理的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(4): 293-302. |
| Li T T, Feng Y F, Zhu A,Huang J, Wang H, Li S Y, Liu K, Peng R M, Zhang H L, Liu L J.Effects of main water-saving irrigation methods on morphological and physiological traits of rice roots[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(4): 293-302. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 杨志远,李娜,马鹏,严田蓉,何艳,蒋明金,吕腾飞,李郁,郭翔,胡蓉,郭长春,孙永健,马均.水肥“三匀”技术对水稻水、氮利用效率的影响[J].作物学报, 2020, 46(3): 408-422. |
| Yang Z Y, Li N, Ma P, Yan T R, He Y, Jiang M J, Lv T F, Li Y, Guo X, Hu R, Guo C C, Sun Y J, Ma J.Effects of methodical nitrogen-water distribution management on water and nitrogen use efficiency of rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(3): 408-422. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 郑雨,李玉影,韩晓日,刘双全,姬景红. 不同水肥管理措施对寒地水稻产量及水肥利用效率的影响[J].黑龙江农业科学, 2019(11): 52-57. |
| Zheng Y, Li Y Y, Han X R, Liu S Q, Ji J H.Effects of different measures of water and fertilizer management on rice yield and water and fertilizer utilization efficiency in cold region[J].Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019(11): 52-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 李思林. 水稻节水灌溉栽培技术措施的运用[J]. 农业与技术, 2019, 39(15): 105-106. |
| Li S L.Application of water-saving irrigation and cultivation techniques for rice[J].Agriculture and Technology, 2019, 39(15): 105-106. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 罗利军, 梅捍卫, 余新桥, 刘鸿艳, 冯芳君. 节水抗旱稻及其发展策略. 科学通报, 2011, 56(11): 804-811. |
| Luo L J, Mei H W, Yu X Q, Liu H Y, Feng F J.Water-saving and drought-resistance rice and its development strategy.Scientific Bulletin, 2011, 56(11): 804-811. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Luo LJ.Breeding for water-saving and drought-resistance rice (WDR) in China[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2010, 61(13): 3509-3517. |
| [7] | 朱宽宇,展明飞,陈静,王志琴,杨建昌,赵步洪. 不同氮肥水平下结实期灌溉方式对水稻弱势粒灌浆及产量的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(2): 155-168. |
| Zhu K Y, Zhan M F, Chen J, Wang Z Q, Yang J C, Zhao B H J. Effects of irrigation regimes during grain filling under different nitrogen rates on inferior spikeles grain-filling and grain yield of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018,32(2): 155-168.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 卞金龙,蒋玉兰,刘艳阳,冯咏芳,刘贺,夏仕明,刘立军. 干湿交替灌溉对抗旱性不同水稻品种产量的影响及其生理原因分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(4): 379-390. |
| Bian J L, Jiang Y L, Liu Y Y, Feng Y F, Liu H, Xia S M, Liu L J.Effects of alternate wetting and drying irrigation on grain yield in rice cultivars with different drought resistance and its physiological mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(4): 379-390. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 刘建华,李铭亮,李进,刘迪牛,曹慧,陈丽群. 节水抗旱稻旱优73在沅江市的种植表现与推广前景[J]. 基层农技推广, 2018, 6(7): 23-24. |
| Liu J H, Li M L, Li J, Liu D N, Cao H, Chen L Q.Planting performance and extension prospect of water saving and drought resistant rice Hanyou 73 in Yuanjiang City[J].Primary Agricultural Technology Extension, 2018, 6(7): 23-24. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 赵洪阳,聂元元,朱敬乐,刘毅,罗利军. 节水抗旱稻新品种旱优73在江西的种植表现[J]. 中国稻米, 2018, 24(1): 103-104. |
| Zhao H Y, Nie Y Y, Zhu J L, Liu Y, Luo L J.Planting performance of a new water-saving and drought-resistance rice Hanyou 73 in Jiangxi Provine[J]. China Rice, 2018, 24(1): 103-104. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | Ramasamy S,ten Berge HFM, Purushothaman S. Yield formation in rice in response to drainage and nitrogen application[J]. Elsevier B.V., 1997, 51(1). |
| [12] | 杨建昌,王志琴,朱庆森.不同土壤水分状况下氮素营养对水稻产量的影响及其生理机制的研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 1996, 29: 58-66. |
| Yang J C, Wang Z Q, Zhu Q S.Effect of nitrogen nutrition on rice yield and its physiological mechanism under different status of soil moisture[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 1996, 29: 58-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Yang J C,Zhang J H,Wang Z Q,Xu G W,Zhu Q S.Activities of key enzymes in sucrose-to-starch conversion in wheat grains subjected to water deficit during grain filling[J]. Plant Physiology, 2004, 135(3): 1621-1629. |
| [14] | Yang J C, Liu K, Wang Z Q, Du Y, Zhang J H.Water-saving and high-yielding irrigation for lowland rice by controlling limiting values of soil water potential.Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2007, 49: 1445-1454. |
| [15] | 李俊峰,杨建昌.水分与氮素及其互作对水稻产量和水肥利用效率的影响研究进展[J].中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(3): 327-334. |
| Li J F, Yang J C.Research advances in the effects of water, nitrogen and their interaction on the yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2017, 31(3): 327-334. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Cabangon R J, Tuong T P,Castillo E G, Bao L X,Lu G A,Wang G H,Cui Y L,Bouman B A M,LiY H, Chen C D,Wang J Z. Effect of irrigation method and N-fertilizer management on rice yield, water productivity and nutrient-use efficiencies in typical lowland rice conditions in China[J]. Paddy and Water Environment, 2004, 2(4): 195-206. |
| [17] | Won J G,Choi J S,Lee S P,Son S H,Chung S O.Water saving by shallow intermittent irrigation and growth of rice.Plant Production Science, 2005, 8: 487-492. |
| [18] | Belder P,Bouman B A M,Cabangon R,Guoan L,Quilang E J P,Li Y,Spiertz J H J,Tuong T P. Effect of water-saving irrigation on rice yield and water use in typical lowland conditions in Asia.Agricultural Water Management, 2004, 65(3): 193-210. |
| [19] | 徐芬芬,曾晓春,石庆华,叶利民. 不同灌溉方式对水稻根系生长的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2007, 25(1): 102-104. |
| Xu F F, Ceng X C, Shi Q H, Ye L M.Effects of different irrigation patterns on the growth of rice root[J].Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2007, 25(1): 102-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 邓环,曹凑贵,程建平,蔡明历,汪金平. 不同灌溉方式对水稻生物学特性的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2008, 16(3): 602-606. |
| Deng H, Cao C G, Cheng J P, Cai M L, Wang J P.Impact of different irrigation methods on biological characteristics of rice[J].Chinese Journal of Ecological Agriculture, 2008, 16(3): 602-606. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 徐国伟,吕强,陆大克,王贺正,陈明灿. 干湿交替灌溉耦合施氮对水稻根系性状及籽粒库活性的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2016, 42(10): 1495-1505. |
| Xu G W, Lv Q, Lu D K, Wang H Z, Chen M C.Effect of wetting and drying alternative irrigation coupling with nitrogen application on root characteristic and grain-sink activity[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2016, 42(10): 1495-1505. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 罗利军. 节水抗旱稻的培育与应用[J].生命科学, 2018, 30(10): 1108-1112. |
| Luo L J.Development of water-saving and drought-resistance rice (WDR)[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2018, 30(10): 1108-1112. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 刘长坤,邓洪平,尹灿.土荆芥水浸提液对小麦和水稻的生长及抗氧化酶活性的影响[J].贵州农业科学,2010,38(4):39-42. |
| Liu C K, Deng H P, Yin C.Effects of C.ambrosioidesextract on growth and anti-oxidizing enzyme activity of wheat and rice[J].Guizhou Agricultural Sciences,2010,38(4):39-42. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | XIAO Dakang, HU Ren, HAN Tianfu, ZHANG Weifeng, HOU Jun, REN Keyu. Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer Consumption and Operation on Rice Yield and Its Components in China:A Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(5): 529-542. |
| [2] | Yan JIA, Liang YANG, Detang ZOU, Zhaojun QU, Jingguo WANG, Hualong LIU, Jin WANG, Hongwei ZHAO. Effects of Exogenous Materials on Nitrogen Photosynthetic Efficiency and Yield Formation of japonica Rice in Cold Region Under Cold Water Stress at Booting Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(5): 443-456. |
| [3] | Xiangyu HU, Jiuxin GUO, Guangli TIAN, Limin GAO, Qirong SHEN, Shiwei GUO. Effects of Different Nitrogen Supply Patterns on Root Morphological and Physiological Characteristics of Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(1): 72-80. |
| [4] | Ya-jie HU, Hai-jun QIAN, Wei-wei CAO, Zhi-peng XING, Hong-cheng ZHANG, Qi-gen DAI, Zhong-yang HUO, Ke XU, Hai-yan WEI, Bao-wei GUO. Effect of Different Mechanical Transplantation Methods and Density on Yield and Its Components of Different Panicle-typed Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(5): 493-506. |
| [5] | Shi-qiang WANG, Hai-hong ZHAO, Chang-liang XIAO, Li-ming ZHAO, Chun-mei GU, Yong-guang NA, Bao-sheng XIE, Shi-hua CHENG. Effects of Cold Stress During Booting Stage on Dry Matter Production of Rice in Cold Region [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(3): 313-322. |
| [6] | Nan XIA, Hong-wei ZHAO, Yan-chao LV, Zhen-dong ZHAO, De-tang ZOU, Hua-long LIU, Jing-guo WANG, Yan JIA. Effect of Cold-water Stress at Grain-filling Stage on Starch Accumulation and Related Enzyme Activities in Grains of japonica Rice in Cold-region [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(1): 62-74. |
| [7] | ZHU Qichao, WEI Changzhou*, LI Meining, ZHU Jinlong, WU Cheng, WANG Jia. Effects of Nitrogen Management on Growth and Grain Yield of Rice under Drip Irrigation with Plastic Film Mulching [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2013, 27(4): 440-446. |
| [8] | ZHAO Jianguo2, JIANG Kaifeng1,YANG Li1,YANG Qianhua1 ,WAN Xianqi1,CAO Yingjiang1,YOU Shumei1,LUO Jing1, ZHANG Tao1,*, ZHENG Jiakui1,*. QTL Mapping for Yield Related Components in A RIL Population of Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2013, 27(4): 344-352. |
| [9] | LI Hai-jun,LI Yong,YANG Xiu-xia,SHEN Qi-rong,GUO Shi-wei*. Effects of Different Nitrogen Forms and Water Stress on the Growth and Osmotic Adjustment of Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2010, 24(4): 403-409 . |
| [10] |
XIE Xiaojin,LI Yingxue,LI Bingbai,SHEN Shuanghe,CHENG Gaofeng.
Estimation of Rice Yield under High Temperature Stress by Hyperspectral Remote Sensing [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2010, 24(2): 196-202 . |
| [11] | DONG Gui-chun,LI Jin-qian,DONG Yan-ping,ZHOU Juan,TIAN Hao,YU Xiao-feng,ZHANG Chuan-sheng,ZHANG Yue-fang,WANG Yu-long. Effects of Yield Components and Panicle Traits on Sink Potential in Conventional indica Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2009, 23(5): 523-528 . |
| [12] | LI Ying ,MEI Han-wei ,WU Jin-hong ,ZHANG Hong-jiang ,FENG Fang-jun ,XU Xiao-yan ,LUO Li-jun. QTL Analysis for Amylose Content and Protein Content Predicted by Near Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) in Rice under Normal or Water Stress Conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2007, 21(2): 123-130 . |
| [13] | ZHANG Wen-zhong,HAN Ya-dong,DU Hong-juan,HUANG Rui-dong,CHEN Wen-fu. Relationship Between Canopy Temperature and Soil Water Content, Yield Components at Flowering Stage in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2007, 21(1): 99-102 . |
| [14] |
CHEN Gui ,ZHOU Yi ,GUO Shi-wei ,SHEN Qi-rong.
Effects of Different Nitrogen Forms on Rice Seedlings Growth with Partial Roots Exposed to Water Stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2006, 20(6): 638-644 . |
| [15] | ZHOU Yi ,GUO Shi-wei ,GAO Ying-xu ,CHEN Gui ,SHEN Qi-rong. Effects of Coupling Between Nitrogen Forms and Water Stress on Content and Distribution of Phosphorus in Different Parts of Rice Plants at the Seedling and Tillering Stages [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2006, 20(5): 505-511 . |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||