
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (6): 565-574.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.9016
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles
Hui FENG2, Yalei FAN2, Jinfeng ZHANG2, Hongli ZHU1, Lihui WEI1,2,*( )
)
Received:2019-01-28
Revised:2019-05-07
Online:2019-11-10
Published:2019-11-10
Contact:
Lihui WEI
冯辉2, 范亚磊2, 张金凤2, 朱红利1, 魏利辉1,2,*( )
)
通讯作者:
魏利辉
基金资助:CLC Number:
Hui FENG, Yalei FAN, Jinfeng ZHANG, Hongli ZHU, Lihui WEI. Protective Effect of Glutaredoxin (AbGrx-1) on Aphelenchoides besseyi Under Oxidative Stress[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(6): 565-574.
冯辉, 范亚磊, 张金凤, 朱红利, 魏利辉. 谷氧还蛋白(AbGrx-1)对水稻干尖线虫在氧化胁迫下的保护作用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 565-574.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.9016
| 引物名 Primer name | 序列 Sequences (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| degGrx-F | TGTCCYTACTGCRASAARGCSAAG |
| degGrx-R | GTGTCGTCGTCGTCRCCTCCRCCKAWGAA |
| AbGrx-F1 | ATCCTTCAATCTAAAGCCCGGAG |
| AbGrx-R1 | TGGCACCAACGTCTTTCAACT |
| AbGrx-R2 | TATCATCACCTCCTCCTAAGAA |
| AbGrx-fullF | GGGAAAGTAAACACCGAAATCG |
| AbGrx-fullR | TCCCAACACTGATTATTTGCC |
| UPM | CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGT (long);CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGC (short) |
| NUP | AAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGT |
| Ab-18S-F | TGCGGTAATTCTGGAGCCAA |
| Ab-18S-R | CCCGTTAGAACCATGGCAGT |
| AbGrx-28aF | CATGCATATGTCCGTCAAGAGTTTTGTCGA |
| AbGrx-28aR | CATGCTCGAGTTAGATGGCACCAACGTCTTTCAA |
Table 1 Primers used in this study.
| 引物名 Primer name | 序列 Sequences (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| degGrx-F | TGTCCYTACTGCRASAARGCSAAG |
| degGrx-R | GTGTCGTCGTCGTCRCCTCCRCCKAWGAA |
| AbGrx-F1 | ATCCTTCAATCTAAAGCCCGGAG |
| AbGrx-R1 | TGGCACCAACGTCTTTCAACT |
| AbGrx-R2 | TATCATCACCTCCTCCTAAGAA |
| AbGrx-fullF | GGGAAAGTAAACACCGAAATCG |
| AbGrx-fullR | TCCCAACACTGATTATTTGCC |
| UPM | CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGT (long);CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGC (short) |
| NUP | AAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGT |
| Ab-18S-F | TGCGGTAATTCTGGAGCCAA |
| Ab-18S-R | CCCGTTAGAACCATGGCAGT |
| AbGrx-28aF | CATGCATATGTCCGTCAAGAGTTTTGTCGA |
| AbGrx-28aR | CATGCTCGAGTTAGATGGCACCAACGTCTTTCAA |

Fig. 1. Complete nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the AbGrx-1 cDNA (GenBank Accession No. KP190142). The 5'- and 3'-UTR are shown in lowercase letters and the open reading frame (ORF) is shown in uppercase letters. The predicted catalytic residues of glutaredoxin is boxed, and the gene-specific primers used for full sequence amplification of AbGrx-1 are underlined. The stop codon (TAA) is marked with an asterisk.
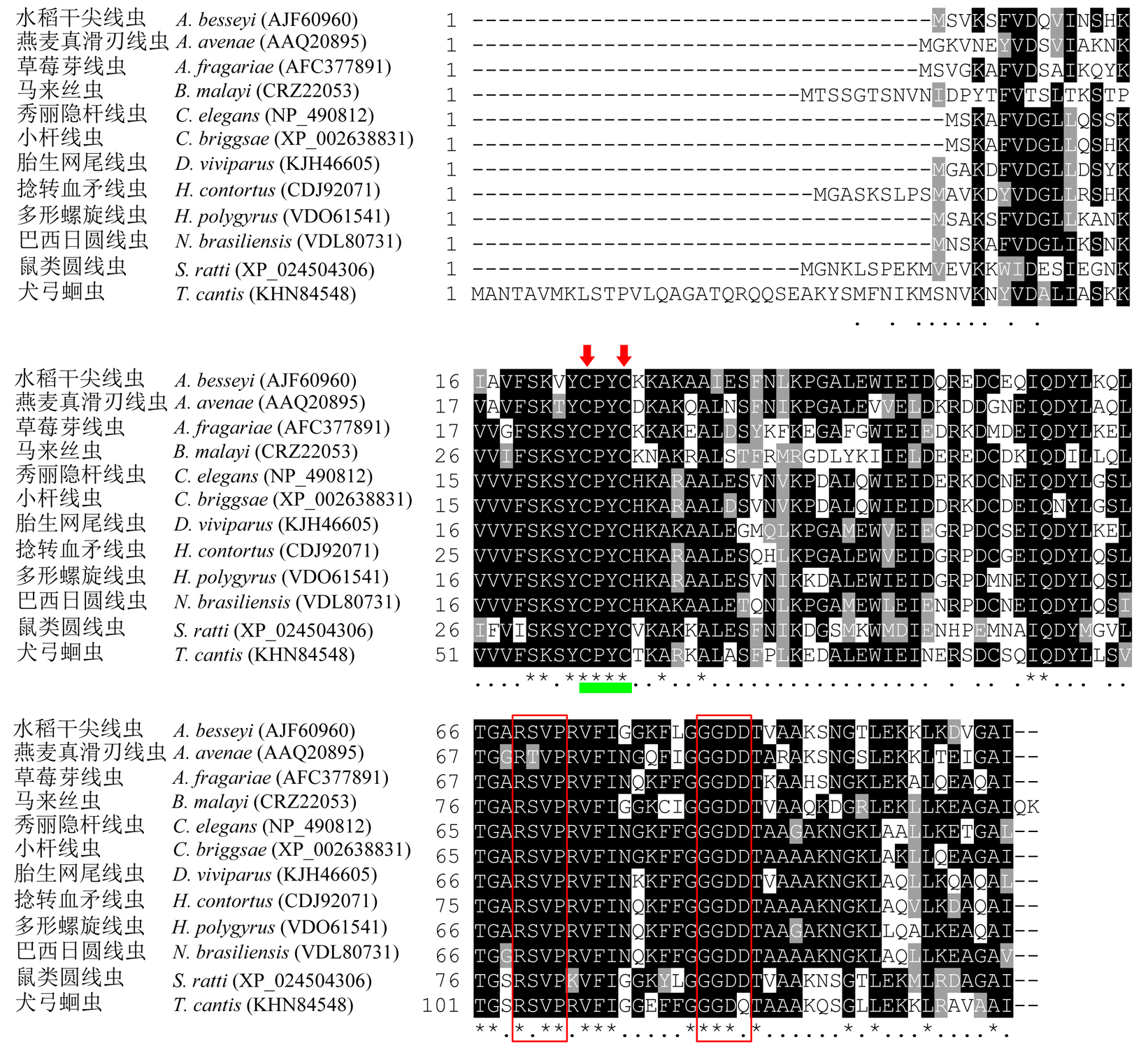
Fig. 2. Sequences alignment of A. besseyi and other nematode glutaredoxin proteins. Boxed amino acids are glutathione (GSH) binding sites, and arrows indicate catalytic residues of glutaredoxin. Consensus and similar sequences similarity are separately shaded with dark (asterisks) and gray (dots) shadows.
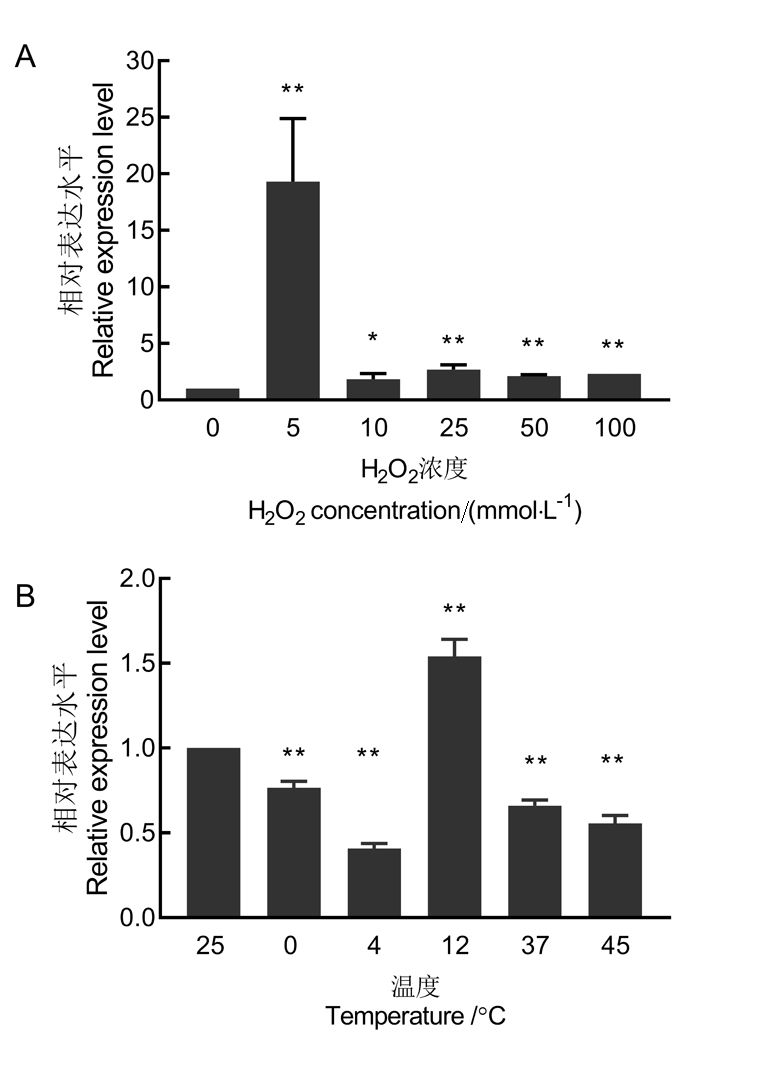
Fig. 5. Relative expression level of AbGrx-1 in A. besseyi exposed to H2O2 and temperature stress for 12 hours. Bars are stardand error. *, ** indicate significant difference between the treatment and the CK(0mml/L or 25℃)at 0.05 and 0.01 levels. The same as in figures below.
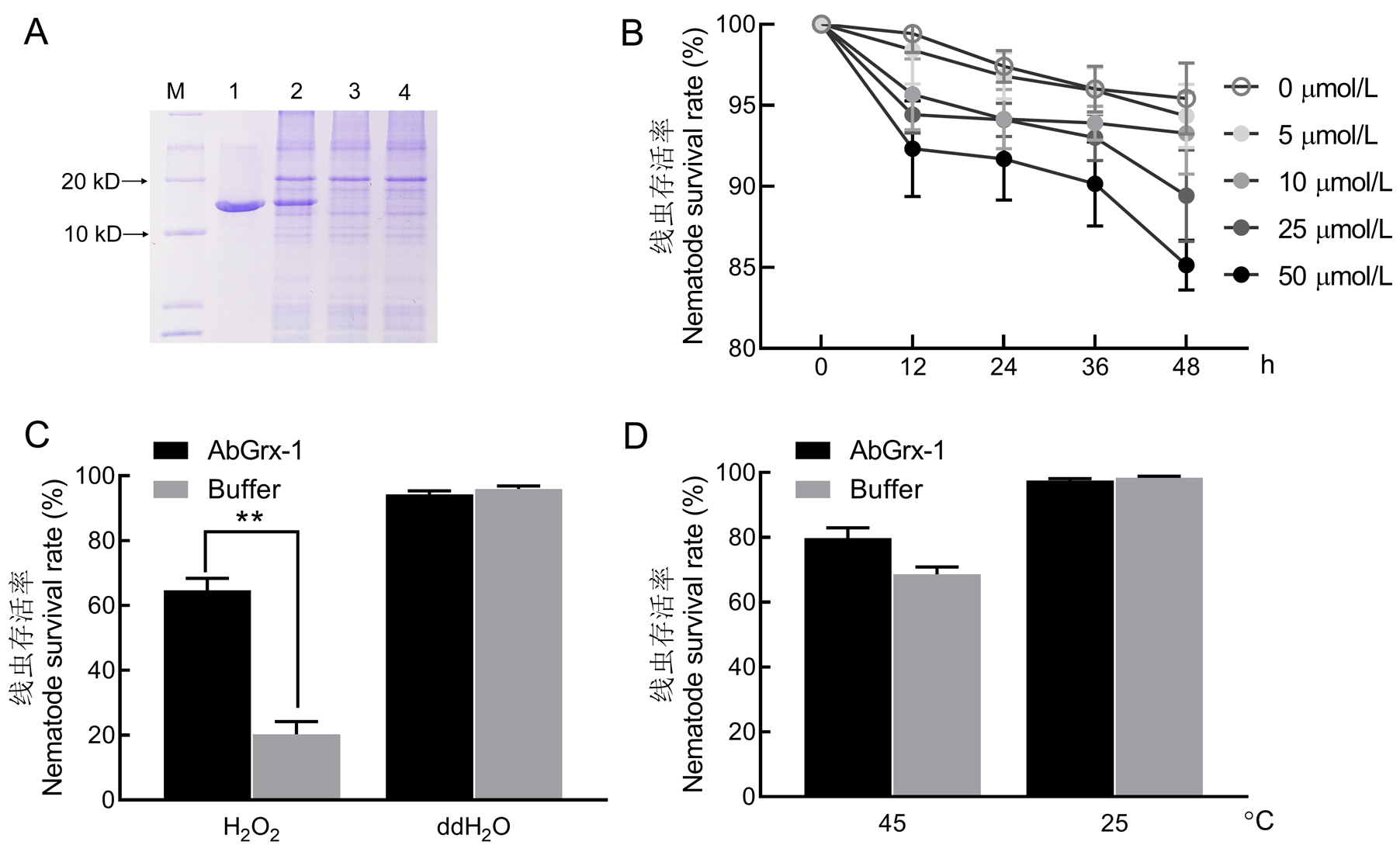
Fig. 6. Role of AbGrx-1 protein in the response of A. besseyi to oxidization and temperature stresses. A, Prokaryotic expression and purification of AbGrx1 protein; M, Marker; Lanes 1 to 5, Purified protein, induced protein with IPTG, non-induced protein and empty vector; B, Cumulative survival rate of A. besseyi soaked in AbGrx-1 solution; C-D, Cumulative survival rate of A. besseyi presoaked in AbGrx-1 solution and then exposed to H2O2 (C) and high temperature stresses (D). **, Significant difference between the treatment and the CK at 0.01 level.
| [1] | Kalinina E V, Chernov N N, Novichkova M D.Role of glutathione, glutathione transferase, and glutaredoxin in regulation of redox-dependent processes.Biochemistry (Moscow), 2014, 79(13): 1562-1583. |
| [2] | Lillig C H, Berndt C, Holmgren A.Glutaredoxin systems.BBA-Gen Subjects, 2008, 1780(11): 1304-1317. |
| [3] | Morita S, Yamashita Y, Fujiki M, Todaka R, Nishikawa Y, Hosoki A, Yabe C, Nakamura J I, Kawamura K, Suwastika I N, Sato M H, Masumura T, Ogihara Y, Tanaka K, Satoh S.Expression of a rice glutaredoxin in aleurone layers of developing and mature seeds: Subcellular localization and possible functions in antioxidant defense.Planta, 2015, 242(5): 1195-1206. |
| [4] | Morgan K L, Estevez A O, Mueller C L, Cacho-Valadez B, Miranda-Vizuete A, Szewczyk N J, Estevez M.The glutaredoxin GLRX-21 functions to prevent selenium- induced oxidative stress inCaenorhabditis elegans. Toxicol Sci, 2010, 118(2): 530-543. |
| [5] | Vanina E. Marquez, Diego G. Arias, Claudia V. Piattoni, Carlos Robello, Alberto A. Iglesias, Guerrero A S A. Cloning, expression, and characterization of a dithiol glutaredoxin fromTrypanosoma cruzi. Antioxid Redox Sign, 2010, 12(6): 787-791. |
| [6] | Fu Z, Agudelo P, Wells C E.Induction of glutaredoxin expression in response to desiccation stress in the foliar nematodeAphelenchoides fragariae. J Nematol, 2012, 44(4): 370-367. |
| [7] | Shigeru H, Katsumi T.Effect of water-soaking and air-drying on survival of Aphelenchoides besseyi in Oryza sativa seeds. J Nematol, 2000, 32(3): 303-308 |
| [8] | Tenente R V V, Wetzel M M V S, Manso E S B G, Marques A S A. Survival of Aphelenchoides besseyi in infested rice seeds stored under controlled conditions. Nematol Bras, 1994, 18: 85-92. |
| [9] | Feng H, Wei L, Chen H, Zhou Y.Calreticulin is required for responding to stress, foraging, and fertility in the white-tip nematode,Aphelenchoides besseyi. Exp Parasitol, 2015, 155: 58-67. |
| [10] | 冯辉, 陈曦, 束兆林, 姚克兵, 魏利辉. 水稻干尖线虫Hsp90基因克隆及在不同逆境、侵染早期和取食过程的表达差异. 农业生物技术学报, 2016, 24(11): 1741-1753. |
| Feng H, Chen X, Shu Z L, Yao K B, Wei L H.Characterization of the Hsp90 Gene in the white tip nematode (Aphelenchoides besseyi) and its expression in response to environmental stresses, early infection and feeding. Chin J Agric Biotechol, 2016, 24(11): 1741-1753. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 陈曦, 冯辉, 束兆林, 姚克兵, 魏利辉. 水稻干尖线虫海藻糖酶Ab-tre-1基因克隆与逆境条件下的表达分析. 核农学报, 2016, 30(12): 2304-2311. |
| Chen X, Feng H, Shu Z L,Yao K B, Wei L H.Isolation and expression analysis of a trehalase gene from white tip nematode.J Nucl Agric Sci, 2016, 30(12): 2304-2311. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 陈俏丽, 王峰, 李丹蕾, 零雅茗, 张瑞芝. 水稻干尖线虫Ab-lea 基因在高渗透压下的表达. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(6): 652-657. |
| Chen Q L, Wang F, Li D L, Ling Y M, Zhang R Z.Expression under hypertonic osmotic stress of Ab-lea from Aphelenchoides besseyi. Chin J Rice Sci, 2017, 31(6): 652-657. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Staheli J P, Boyce R, Kovarik D, Rose T M.CODEHOP PCR and CODEHOP PCR Primer Design. In: PARK D J, PCR Protocols. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press 2011: 57-73. |
| [14] | Schmittgen T D, Livak K J.Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method.Nat Protoc, 2008, 3(6): 1101-1108. |
| [15] | An S, Zhang Y, Wang T, Luo M, Li C.Molecular characterization of glutaredoxin 2 from Ostrinia furnacalis. Integr Zool, 2013, 8(Suppl 1): 30-38. |
| [16] | Yao P, Chen X, Yan Y, Liu F, Zhang Y, Guo X, Xu B.Glutaredoxin 1, glutaredoxin 2, thioredoxin 1, and thioredoxin peroxidase 3 play important roles in antioxidant defense in Apis cerana cerana.Free Radical Bio Med, 2014, 68: 335-346. |
| [17] | Zhang S D, Shen Z J, Liu X M, Li Z, Zhang Q W, Liu X X.Molecular identification of three novel glutaredoxin genes that play important roles in antioxidant defense in Helicoverpa armigera. Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 2016, 75: 107-116. |
| [18] | Olahova M, Taylor S R, Khazaipoul S, Wang J, Morgan B A, Matsumoto K, Blackwell T K, Veal E A.A redox-sensitive peroxiredoxin that is important for longevity has tissue- and stress-specific roles in stress resistance.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2008, 105(50): 19839-19844. |
| [19] | Isermann K, Liebau E, Roeder T, Bruchhaus I.A peroxiredoxin specifically expressed in two types of pharyngeal neurons is required for normal growth and egg production in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol, 2004, 338(4): 745-755. |
| [20] | Dubreuil G, Deleury E, Magliano M, Jaouannet M, Abad P, Rosso M N.Peroxiredoxins from the plant parasitic root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita, are required for successful development within the host. Int J Parasitol, 2011, 41(3-4): 385-396. |
| [21] | Zhou T, Gao C, Du L, Feng H, Wang L, Lan Y, Sun F, Wei L, Fan Y, Shen W, Zhou Y.Genetic analysis and QTL detection for resistance to white tip disease in rice.PLoS One, 2014, 9(8): e106099. |
| [22] | Sun M J, Liu W H, Lin M S.Effects of temperature, humidity and different rice growth stages on vertical migration of Aphelenchoides besseyi. Rice Sci, 2009, 16(4): 301-306. |
| [23] | Kung S-P, Gaugler R, Kaya H K.Effects of soil temperature, moisture, and relative humidity on entomopathogenic nematode persistence. J Invertebr Pathol, 1991, 57(2): 242-249. |
| [24] | Heald C M, Inserra R N.Effect of Temperature on Infection and Survival of Rotylenchulus reniformis.J Nematol, 1988, 20(3): 356-361. |
| [25] | Browne J A, Dolan K M, Tyson T, Goyal K, Tunnacliffe A, Burnell A M.Dehydration-specific induction of hydrophilic protein genes in the anhydrobiotic nematode Aphelenchus avenae. Eukaryot Cell, 2004, 3(4): 966-975. |
| [26] | Stringham E G, Candido E P M. Transgenic hsp 16-Lacz strains of the soil nematode caenorhabditis elegans as biological monitors of environmental stress.Environ Toxicol Chem, 1994, 13(8): 1211-1220. |
| [27] | Li F, Ma X, Cui X, Li J, Wang Z.Recombinant buckwheat glutaredoxin intake increases lifespan and stress resistance via hsf-1 upregulation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Exp Gerontol, 2018, 104: 86-97. |
| [28] | Henkle-Duhrsen K, Kampkotter A.Antioxidant enzyme families in parasitic nematodes.Mol Biochem Parasitol, 2001, 114: 129-142. |
| [29] | Zhen L, Xiaoxia L, Yanna C, Yan W, Qingwen Z, Xuguo Z.Cloning and characterization of a 2-Cys peroxiredoxin in the pine wood nematode,Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, a putative genetic factor facilitating the infestation. Int J Biol Sci, 2011, 7(6): 823-836. |
| [30] | Lin B, Zhuo K, Chen S, Hu L, Sun L, Wang X, Zhang L H, Liao J.A novel nematode effector suppresses plant immunity by activating host reactive oxygen species-scavenging system.New Phytol, 2016, 209(3): 1159-1173. |
| [1] | ZHOU Zhenling, LIN Bing, ZHOU Qun, YANG Bo, LIU Yan, ZHOU Tianyang, WANG Baoxiang, GU Junfei, XU Dayong, YANG Jianchang. Responses of Rice Varieties Differing in Salt Tolerance to Salt Stress and Their Physiological Mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(2): 153-165. |
| [2] | QIU Linlin, LIU Qiao, FU Yaping, LIU Wenzhen, HU Guocheng, ZHAI Yufeng, PANG Bo, WANG Dekai. Identification and Gene Cloning of DSP2 in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(2): 150-158. |
| [3] | ZHANG Taohui, WANG Haiyu, WAN Hua, ZHANG Liping, XIE Zhenwei, CHEN Keyi, HE Xiaodong, ZHAO Zhigang, WAN Jianmin. Cytological Observation of a Female and Male Sterile Osfma2 Mutant in Rice and Its Map-based Cloning [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(1): 13-26. |
| [4] | Xianmei WU, Sanfeng LI, Ping HU, Rui HE, Ran JIAO, Yijian MAO, Caolin LU, Juan HU, Han LIN, Rongliang WU, Xudong ZHU, Yuchun RAO, Yuexing WANG. Cloning and Functional Analysis of Rice Tillering Regulatory Gene HTD3 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(6): 535-542. |
| [5] | DU Yimo, PAN Tian, TIAN Yunlu, LIU Shijia, LIU Xi, JIANG Ling, ZHANG Wenwei, WANG Yihua*,WAN Jianmin . Phenotypic Analysis and Gene Cloning of Rice Floury Endosperm Mutant fse4 [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(6): 499-512. |
| [6] | Qiaoli CHEN, Feng WANG, Danlei LI, Yaming LING, Ruizhi ZHANG. Expression Under Hypertonic Osmotic Stress of Ab-lea from Aphelenchoides besseyi [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(6): 652-657. |
| [7] | Zongshi BAI, Meng QIN, Lirong ZHAO, Yuchun HAN, Dongwei WANG, Chunling XU, Hui XIE. Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Rapid Diagnosis of Aphelenchoides besseyi [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(4): 432-440. |
| [8] | Chenxing ZHAO, Yewei YU, Yipeng XU, Xiaoping YU. Gene Cloning, Polyclonal Antibody Preparation and Expression Localization of Two dynamin-1-like Genes from Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(4): 345-354. |
| [9] | Wen JING, Wenhua ZHANG. Research Progress on Gene Mapping and Cloning for Salt Tolerance and Variety Improvement for Salt Tolerance by Molecular Marker-Assisted Selection in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(2): 111-123. |
| [10] | Peng WANG, Yue CAI, Wei-wei CHEN, Jing MA, Xin-gang CHEN, Xiao-jie TANG, Xiao-man YOU, Fei KONG, Jie ZHANG, Hai-gang YAN, Guo-xiang WANG, Ling JIANG, Wen-wei ZHANG, Jian-min WAN. Phenotyping and Gene Cloning of a Small-grain Dwarf Mutant sgd1(t) in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(1): 1-9. |
| [11] | Feng WANG, Qiao-li CHEN, Dan-lei LI, Ya-ming LING, Bo-wen WANG, Rui-zhi ZHANG, Yan-yan JIA, Yong-hang LI, Yu-ying PEI, Xin-ming LU. Cloning and Expression of the Gene OC-XII Conferring Resistance to Aphelenchoides besseyi in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2015, 29(6): 658-664. |
| [12] | YANG Hailian#, LIU Min#, GUO Min, LI Rongde, ZHANG Honggen, YAN Changjie*. Genetic Analysis and Position Cloning of a yellowgreen leaf 10 (ygl10) Gene, Responsible for Leaf Color in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2014, 28(1): 41-48. |
| [13] | FENG Gongneng1,2, ZHANG Changquan1, ZHAO Dongsheng1, ZHU Kongzhi1, TU Huaizhou1, XU Chenwu1, LIU Qiaoquan1,*. Identification and Gene Cloning of the Leafy Head Mutant pla15 in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2013, 27(2): 111-116. |
| [14] | ZHANG Yafang, YU Yongqi, ZUO Shimin, LOU Lijuan, CHEN Zongxiang, PAN Xuebiao*. Cloning of an Inorganic Pyrophosphatase Gene OsIP1 in Rice Based on Bioinformatics Analysis and its Genetic Transformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2013, 27(1): 17-25. |
| [15] | MA Liang yong ,BAO Jin song ,LI Xi ming ,ZHU Xu dong ,JI Zhi juan ,XIA Ying wu ,YANG Chang deng . Progress on Cloning and Functional Analysis of Dwarfism Related Genes in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2009, 23(1): 1-1~11 . |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||