
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (1): 35-42.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022. 210504
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
DONG Zheng1,2,#, WANG Yamei3,#, LI Yongchao1,2, XIONG Haibo1,2, XUE Canhui1, PAN Xiaowu1,2, LIU Wenqiang1,2, WEI Xiucai1,2, LI Xiaoxiang1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-05-24
Revised:2021-08-16
Online:2022-01-10
Published:2022-01-10
Contact:
LI Xiaoxiang
About author:First author contact:#These authors contributed equally to the work;
董铮1,2,#, 王雅美3,#, 黎用朝1,2, 熊海波1,2, 薛灿辉1, 潘孝武1,2, 刘文强1,2, 魏秀彩1,2, 李小湘1,2,*( )
)
通讯作者:
李小湘
作者简介:第一联系人:#共同第一作者;
基金资助:DONG Zheng, WANG Yamei, LI Yongchao, XIONG Haibo, XUE Canhui, PAN Xiaowu, LIU Wenqiang, WEI Xiucai, LI Xiaoxiang. Genome-wide Association Analysis of Cadmium Content in Rice Based on MAGIC Population[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(1): 35-42.
董铮, 王雅美, 黎用朝, 熊海波, 薛灿辉, 潘孝武, 刘文强, 魏秀彩, 李小湘. 基于MAGIC群体的水稻镉含量全基因组关联分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(1): 35-42.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2022. 210504
| 年份 Year | 亲本 Parent | 多亲本高世代互交群体MAGIC population | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | 平均值±标准差 Mean±SD | 变幅 Range | 变异系数 CV/% | |
| 2017 | 0.889 | 0.528 | 1.070 | 1.338 | 0.542 | 1.412 | 0.527 | 0.514 | 0.651±0.184 a | 0.148~1.336 | 28.26 |
| 2018 | 1.239 | 0.579 | 1.667 | 1.254 | 0.949 | 1.140 | 0.841 | 0.845 | 0.672±0.226 ab | 0.068~1.516 | 33.63 |
| 2019 | 0.605 | 0.291 | 0.627 | 0.823 | 0.491 | 0.443 | 0.459 | 0.509 | 0.327±0.154 c | 0.070~1.188 | 47.10 |
| 2020 | 0.944 | 0.509 | 0.903 | 0.739 | 0.288 | 0.554 | 0.380 | 0.532 | 0.534±0.160 b | 0.192~1.125 | 29.96 |
| 年份 Year | 亲本 Parent | 多亲本高世代互交群体MAGIC population | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | 平均值±标准差 Mean±SD | 变幅 Range | 变异系数 CV/% | |
| 2017 | 0.889 | 0.528 | 1.070 | 1.338 | 0.542 | 1.412 | 0.527 | 0.514 | 0.651±0.184 a | 0.148~1.336 | 28.26 |
| 2018 | 1.239 | 0.579 | 1.667 | 1.254 | 0.949 | 1.140 | 0.841 | 0.845 | 0.672±0.226 ab | 0.068~1.516 | 33.63 |
| 2019 | 0.605 | 0.291 | 0.627 | 0.823 | 0.491 | 0.443 | 0.459 | 0.509 | 0.327±0.154 c | 0.070~1.188 | 47.10 |
| 2020 | 0.944 | 0.509 | 0.903 | 0.739 | 0.288 | 0.554 | 0.380 | 0.532 | 0.534±0.160 b | 0.192~1.125 | 29.96 |
| QTL 名称 | 环境 Environment | 染色体Chromosome | 优异等位基因 Allele | 位置 Position/Mb | 峰值SNP Peak SNP | P值 P-value | 贡献率 R2/% | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qCd1.1 | E1/E2/E4 | 1 | G | 20.9-22.0 | rs1_21942515 | 5.3×10-4 | 8.26 | [20] |
| qCd2.1 | E4 | 2 | G | 23.8-24.3 | S2_23819612 | 1.7×10-4 | 8.53 | |
| qCd2.2 | E2 | 2 | A | 30.1 | rs2_30102654 | 9.4×10-4 | 6.62 | |
| qCd3.1 | E2/E3 | 3 | A | 5.8-6.9 | S3_5834039 | 3.4×10-4 | 7.40 | [21] |
| qCd4.1 | E2/E3/E4 | 4 | T | 20.2-24.2 | S4_20195543 | 4.4×10-4 | 7.46 | |
| qCd5.1 | E1/E3 | 5 | C | 1.7-2.1 | rs5_1811027 | 2.9×10-4 | 7.27 | OsMTP1[22] |
| qCd6.1 | E1/E2/E4 | 6 | C | 27.0-30.8 | S6_27300620 | 2.6×10-5 | 10.57 | OsHMA2[23] |
| qCd7.1 | E3/E4 | 7 | C | 14.5-17.1 | S7_16945471 | 6.8×10-5 | 9.11 | |
| qCd9.1 | E1/E2 | 9 | C | 8.1-9.8 | rs9_9777578 | 6.9×10-5 | 9.64 | |
| qCd9.2 | E1 | 9 | G | 12.2-12.8 | rs9_12209561 | 3.0×10-4 | 8.00 | |
| qCd9.3 | E4 | 9 | G | 16.6-16.8 | S9_16720741 | 4.1×10-4 | 7.53 | [24] |
| qCd10.1 | E3 | 10 | C | 15.9 | S10_15856776 | 2.7×10-4 | 7.66 | |
| qCd11.1 | E3/E4 | 11 | G | 17.6-18.0 | S11_17883239 | 1.3×10-4 | 8.77 | [25] |
| qCd12.1 | E3 | 12 | G | 8.0-8.2 | S12_8031425 | 9.7×10-5 | 8.73 |
Table 2 Loci for cadmium content by GWAS in MAGIC-Hei.
| QTL 名称 | 环境 Environment | 染色体Chromosome | 优异等位基因 Allele | 位置 Position/Mb | 峰值SNP Peak SNP | P值 P-value | 贡献率 R2/% | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qCd1.1 | E1/E2/E4 | 1 | G | 20.9-22.0 | rs1_21942515 | 5.3×10-4 | 8.26 | [20] |
| qCd2.1 | E4 | 2 | G | 23.8-24.3 | S2_23819612 | 1.7×10-4 | 8.53 | |
| qCd2.2 | E2 | 2 | A | 30.1 | rs2_30102654 | 9.4×10-4 | 6.62 | |
| qCd3.1 | E2/E3 | 3 | A | 5.8-6.9 | S3_5834039 | 3.4×10-4 | 7.40 | [21] |
| qCd4.1 | E2/E3/E4 | 4 | T | 20.2-24.2 | S4_20195543 | 4.4×10-4 | 7.46 | |
| qCd5.1 | E1/E3 | 5 | C | 1.7-2.1 | rs5_1811027 | 2.9×10-4 | 7.27 | OsMTP1[22] |
| qCd6.1 | E1/E2/E4 | 6 | C | 27.0-30.8 | S6_27300620 | 2.6×10-5 | 10.57 | OsHMA2[23] |
| qCd7.1 | E3/E4 | 7 | C | 14.5-17.1 | S7_16945471 | 6.8×10-5 | 9.11 | |
| qCd9.1 | E1/E2 | 9 | C | 8.1-9.8 | rs9_9777578 | 6.9×10-5 | 9.64 | |
| qCd9.2 | E1 | 9 | G | 12.2-12.8 | rs9_12209561 | 3.0×10-4 | 8.00 | |
| qCd9.3 | E4 | 9 | G | 16.6-16.8 | S9_16720741 | 4.1×10-4 | 7.53 | [24] |
| qCd10.1 | E3 | 10 | C | 15.9 | S10_15856776 | 2.7×10-4 | 7.66 | |
| qCd11.1 | E3/E4 | 11 | G | 17.6-18.0 | S11_17883239 | 1.3×10-4 | 8.77 | [25] |
| qCd12.1 | E3 | 12 | G | 8.0-8.2 | S12_8031425 | 9.7×10-5 | 8.73 |
| 候选基因 Candidate gene | 注释信息 Annotation |
|---|---|
| LOC_Os02g37160 | 重金属转运蛋白Heavy metal transport/detoxification protein, putative, expressed |
| LOC_Os02g49560 | bZIP转录因子bZIP transcription factor domain containing protein, expressed |
| LOC_Os04g39010 | 重金属相关结构域蛋白Heavy metal associated domain containing protein, expressed |
| LOC_Os06g46310 | 重金属转运因子Nramp6 Metal transporter Nramp6, putative, expressed |
Table 3 Candidate genes for rice cadmium content.
| 候选基因 Candidate gene | 注释信息 Annotation |
|---|---|
| LOC_Os02g37160 | 重金属转运蛋白Heavy metal transport/detoxification protein, putative, expressed |
| LOC_Os02g49560 | bZIP转录因子bZIP transcription factor domain containing protein, expressed |
| LOC_Os04g39010 | 重金属相关结构域蛋白Heavy metal associated domain containing protein, expressed |
| LOC_Os06g46310 | 重金属转运因子Nramp6 Metal transporter Nramp6, putative, expressed |
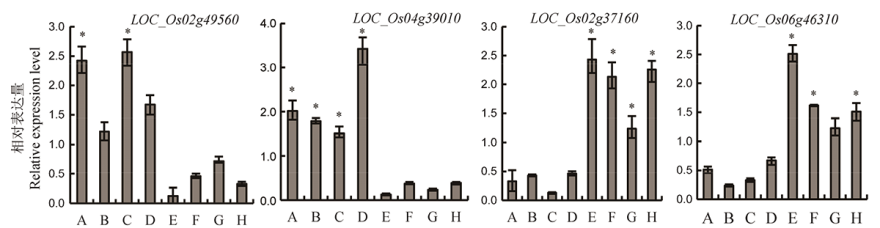
Fig. 4. Expression difference of candidate genes among different parents in MAGIC-Hei. A-D are high Cd content parents, E-F are low Cd content parents. The internal reference gene is β-Actin. *Significant correlation at P<0.05 (n≥3).
| [1] | Canli M, Furness R W. Toxicity of heavy metals dissolved in sea water and influences of sex and size on metal accumulation and tissue distribution in the norway lobster Nephrops norvegicus[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 1993,36(4):217-236. |
| [2] | Grant C A, Clarke J M, Duguid S, Chaney R L. Selection and breeding of plant cultivars to minimize cadmium accumulation[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2008,390(2/3):301-310. |
| [3] | Yao H, Xu J, Huang C. Substrate utilization pattern, biomass and activity of microbial communities in a sequence of heavy metal-polluted paddy soils[J]. Geoderma, 2003,115(1):139-148. |
| [4] | Li Z, Ma Z, der Kuijp T J, Yuan Z, Huang L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 468-469:843-853. |
| [5] | Clemens S, Aarts M G, Thomine S, Verbruggen N. Plantscience: The key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2013,18(2):92-99. |
| [6] | 丁仕林, 刘朝雷, 钱前, 高振宇. 水稻重金属镉吸收和转运的分子遗传机制研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019,33(5):383-390. |
| Ding S L, Liu C L, Qian Q, Gao Z Y. Research advances on molecular genetic mechanism for Cadmium absorption and transportation in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019,33(5):383-390. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Uraguchi S, Fujiwara T. Cadmium transport and tolerance in rice: Perspectives for reducing grain cadmium accumulation[J]. Rice, 2012,5(1):1-8. |
| [8] | Kashiwagi T, Shindoh K, Hirotsu N, Ishimaru K. Evidence for separate translocation pathways in determining cadmium accumulation in grain and aerial plant parts in rice[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2009,9(8):1-10. |
| [9] | Huang D R, Fan Y Y, Hu B L, Xiao Q Y, Chen D Z, Zhuang J Y. Assessment and genetic analysis of heavy metal content in rice grain using an Oryza sativa×O. rufipogon backcross inbred line population[J]. Journal of the Science of Food & Agriculture, 2018,98(4):1339-1345. |
| [10] | Zhao K, Tung C, Eizenga G C, Wright M H, Ali M L, Price A H, Norton G J, Islam M R, Reynolds A, Mezey J, McClung A M, Bustamante C D, McCouch S R. Genome-wide association mapping reveals a rich genetic architecture of complex traits in Oryza sativa L[J]. Nature Communications, 2011,2(1):467. |
| [11] | Liu J D, He Z H, Rasheed A, Wen W E, Yan J, Zhang P Z, Wan Y X, Xie C J, Xia X C. Genome-wide association mapping of black point reaction in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2017,17(1):220-232. |
| [12] | Elshire R J, Glaubitz J C, Sun Q, Poland J A, Kawamoto K, Buckler E S, Mitchell S E. A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species[J]. PloS ONE, 2011,6(5):e19379. |
| [13] | Bandillo N, Raghavan C, Muyco P A, Sevilla M A L, Lobina I T, Dilla-Ermita C J, Tung C W, McCouch S, Thomson M, Mauleon R, Singh R K, Gregorio G, Redoña E, Leung H. Multi-parent advanced generation inter-cross (MAGIC) populations in rice: Progress and potential for genetics research and breeding[J]. Rice, 2013,6(1):1-15. |
| [14] | Raghavan C, Mauleon R, Lacorte V, Jubay M, Zaw H, Bonifacio J, Singh R K, Huang B E, Leung H. Approaches in characterizing genetic structure and mapping in a rice multiparental population[J]. Genes Genome Genetics, 2017,7(6):1721-1730. |
| [15] | Miyadate H, Adachi S, Hiraizumi A, Tezuka K, Nakazawa N, Kawamoto T, Katou K, Kodama I, Sakurai K, Takahashi H. OsHMA3, a P1B-type of ATPase affects root-to-shoot cadmium translocation in rice by mediating efflux into vacuoles[J]. New Phytologist, 2011,189(1):190-199. |
| [16] | Luo J, Huang J, Zeng D, Peng J S, Zhang G B, Ma H L, Guan Y, Yi H Y, Fu Y L, Lin H X, Qian Q, Gong J M. A defensin-like protein drives cadmium efflux and allocation in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2018,9(1):645. |
| [17] | Yan H, Xu W, Xie J, Gao Y W, Wu L L, Sun L, Feng L, Chen X, Zhang T, Dai C H, Li T, Lin X N, Zhang Z Y, Wang X Q, Li F M, Zhu X Y, Li J J, Li Z C, Chen C Y, Ma M, Zhang H L, He Z Y. Variation of a major facilitator superfamily gene contributes to differential cadmium accumulation between rice subspecies[J]. Nature Communications, 2019,10(1):1-12. |
| [18] | Chen J, Huang X, Salt D E, Zhao F J. Mutation in OsCADT1 enhances cadmium tolerance and enriches selenium in rice grain[J]. New Phytologist, 2020,226(3):838-850. |
| [19] | Tang Y, Liu X, Wang J, Li M, Wang Q, Tian F, Su Z, Pan Y, Liu D, Lipka A E, Buckler E S, Zhang Z. GAPIT Version 2: An enhanced integrated tool for genomic association and prediction[J]. Plant Genome, 2016 9(2):1-9. |
| [20] | Xu Q, Zheng T Q, Hu X, Cheng L R, Xu J L, Shi Y M, Li Z K. Examining two sets of introgression lines in rice (Oryza sativa L.) reveals favorable alleles that improve grain Zn and Fe concentrations[J]. PloS ONE, 2015,10(7):e0131846 |
| [21] | Zhang M, Pinson S R M, Tarpley L, Huang X Y, Lahner B, Yakubova E, Baxter I, Guerinot M L, Salt D E. Mapping and validation of quantitative trait loci associated with concentrations of 16 elements in unmilled rice grain[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2014,127(1):137-165. |
| [22] | Yuan L, Yang S, Liu B, Zhang M, Wu K. Molecular characterization of a rice metal tolerance protein, OsMTP1[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2012,31(1):67-79 |
| [23] | Takahashi R, Ishimaru Y, Shimo H, Ogo Y, Senoura T, Nishizawa N K, Nakanishi H. The OsHMA2 transporter is involved in root-to-shoot translocation of Zn and Cd in rice[J]. Plant Cell and Environment, 2012,35(11):1948-1957. |
| [24] | Yan Y F, Lesta I P, Lee K J, Kim M Y, Lee S H, Lee B W. Identification of quantitative trait loci for cadmium accumulation and distribution in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Genome, 2013,56(4):227-232. |
| [25] | 陈志德. 水稻不同品种耐镉性鉴定及耐镉胁迫相关性状的QTL定位[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2010 |
| Chen Z D. Screening of rice varieties with cadmium tolerance and mapping of QTLs related to cadmium stress in rice[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2010 | |
| [26] | 陈艳彩, 唐文帮. 筛选和培育镉低积累水稻品种的进展和问题探讨[J]. 农业现代化研究, 2018,39(6):1044-1051 |
| Chen C Y, Tang W B. A perspective on the selection and breeding of low-Cd rice[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 2018,39(6):1044-1051. | |
| [27] | Lan H, Wang Z, Wang Q H, Wang M M, Bao Y M, Huang J, Zhang H S. Characterization of a vacuolar zinc transporter OsZT1 in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2013,40(2):1201-1210. |
| [28] | 鄂志国, 张玉屏, 王磊. 水稻镉胁迫应答分子机制研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013,27(5):539-544. |
| E Z G, Zhang Y P, Wang L. Molecular mechanism of rice responses to cadmium stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2013,27(5):539-544. (in Chinese with English abstract). |
| [1] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [2] | LIU Zhongqi, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai, GUI Jinxin. Genome-wide Association Analysis of Rice Seed Dehydration Rate at Maturity Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(2): 150-159. |
| [3] | HOU Benfu, YANG Chuanming, ZHANG Xijuan, YANG Xianli, WANG Lizhi, WANG Jiayu, LI Hongyu, JIANG Shukun. Mapping of Grain Shape QTLs Using RIL Population from Longdao 5/Zhongyouzao 8 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(1): 13-24. |
| [4] | HU Jiaxiao, LIU Jin, CUI Di, LE Si, ZHOU Huiying, HAN Bing, MENG Bingxin, YU Liqin, HAN Longzhi, MA Xiaoding, LI Maomao. Mapping Major QTLs for Panicle Traits Using CSSLs of Dongxiang Wild Rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(6): 597-608. |
| [5] | XIE Kaizhen, ZHANG Jianming, CHENG Can, ZHOU Jihua, NIU Fuan, SUN Bin, ZHANG Anpeng, WEN Weijun, DAI Yuting, HU Qiyan, QIU Yue, CAO Liming, CHU Huangwei. Identification and QTL Mapping of Rice Germplasm Resources with Low Amylose Content [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(6): 609-616. |
| [6] | YAO Xiaoyun, CHEN Chunlian, XIONG Yunhua, HUANG Yongping, PENG Zhiqing, LIU Jin, YIN Jianhua. Identification of QTL for Milling and Appearance Quality Traits in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(5): 507-517. |
| [7] | WEI Minyi, MA Zengfeng, HUANG Dahui, QIN Yuanyuan, LIU Chi, LU Yingping, LUO Tongping, LI Zhenjing, ZHANG Yuexiong, QIN Gang. QTL-Seq Analysis for Identification of Resistance Locus to Bacterial Leaf Streak in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(2): 133-141. |
| [8] | LIU Jin, CUI Di, YU Liqin, ZHANG Lina, ZHOU Huiying, MA Xiaoding, HU Jiaxiao, HAN Bing, HAN Longzhi, LI Maomao. Screening and QTL Mapping of Heat-tolerant Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Germplasm Resources at Seedling Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 259-268. |
| [9] | HUANG Tao, WANG Yanning, ZHONG Qi, CHENG Qin, YANG Mengmeng, WANG Peng, WU Guangliang, HUANG Shiying, LI Caijing, YU Jianfeng, HE Haohua, BIAN Jianmin. Mapping and Analysis of QTLs for Rice Grain Weight and Grain Shape Using Chromosome Segment Substitution Line Population [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(2): 159-170. |
| [10] | Jie LI, Rongrong TIAN, Tianliang BAI, Chunyan ZHU, Jiawei SONG, Lei TIAN, Shuaiguo MA, Jiandong LÜ, Hui HU, Zhenyu WANG, Chengke LUO, Yinxia ZHANG, Peifu LI. Comprehensive Evaluation and QTL Analysis for Flag Leaf Traits Using a Backcross Population in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(6): 573-585. |
| [11] | Xina CHEN, Zeke YUAN, Zhenzhen HU, Quanzhi ZHAO, Hongzheng SUN. QTL-Seq Mapping of Head Rice Rate QTLs in japonica Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(5): 449-454. |
| [12] | Chengxing DU, Huali ZHANG, Dongqing DAI, Mingyue WU, Minmin LIANG, Junyu CHEN, Liangyong MA. QTL Analysis for Grain Weight and Shape and Validation of qTGW1.2/qGL1.2 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(4): 359-372. |
| [13] | Yujun ZHU, Ziwei ZUO, Zhenhua ZHANG, Yeyang FAN. A New Approach for Fine-mapping and Map-based Cloning of Minor-Effect QTL in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(4): 407-414. |
| [14] | Wei LIU, Zhanhua LU, Dongbai LU, Xiaofei WANG, Shiguang WANG, Jia XUE, Xiuying HE. Location and Candidate Gene Analysis of Rice Clustered Spikelets Gene OsCL6 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(3): 238-248. |
| [15] | Zhijuan JI, Yuxiang ZENG, Yan LIANG, YANGChangdeng. Research and Progress of Bakanae Disease Resistance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(1): 1-10. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||