
中国水稻科学 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (5): 413-424.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2020.0208
王小秋1, 杜海波1, 陈夕军2, 李明友1, 王嘉楠1, 许志文2, 冯志明1,2, 陈宗祥1,2, 左示敏1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-02-20
修回日期:2020-03-30
出版日期:2020-09-10
发布日期:2020-09-10
通讯作者:
左示敏
基金资助:
Xiaoqiu WANG1, Haibo DU1, Xijun CHEN2, Mingyou LI1, Jianan WANG1, Zhiwen XU2, Zhiming FENG1,2, Zongxiang CHEN1,2, Shimin ZUO1,2,*( )
)
Received:2020-02-20
Revised:2020-03-30
Online:2020-09-10
Published:2020-09-10
Contact:
Shimin ZUO
摘要:
【目的】明确水稻品种携带的抗稻瘟病基育种应用价值,是利用抗病基因培育抗病品种控制病害流行的重要前期工作。【方法】利用功能标记分析了14个抗稻瘟病基因在江苏近年育成的195个粳稻新品种/系中的分布情况,并对其中158个品种和17份携带抗稻瘟病基因Pigm的高世代回交株系进行穗颈瘟接种鉴定。【结果】大多数品种携带2~5个抗病基因,但所有品种均不含有Pigm基因;Pib、Pita和Pikh基因在供试品种中的分布频率较高,均在45%以上,其余基因均在30%以内;Pid3、Pid2、Pia、Pb1在新育成品种中的出现频率明显高于审定品种。测试品种对穗颈瘟的抗性主要与3个基因显著相关,贡献率由高至低依次为Pia、Pi3/5/i和Pita;其中,Pia或Pi3/5/i与Pita间的聚合效应均显著高于各基因单独存在时的抗病效应,且以Pia和Pita间的聚合效应最强,携带该基因组合的所有品种对穗颈瘟均表现抗至高抗水平抗性。回交导入Pigm基因的所有17份株系对穗颈瘟的抗性均显著高于各自轮回亲本,且均达到了抗病以上水平。【结论】抗病基因Pigm及基因组合“Pia+Pita”在江苏粳稻抗穗颈瘟育种中具有重要的育种应用价值。
中图分类号:
王小秋, 杜海波, 陈夕军, 李明友, 王嘉楠, 许志文, 冯志明, 陈宗祥, 左示敏. 江苏近年育成粳稻新品种/系的稻瘟病抗性基因及穗颈瘟抗性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(5): 413-424.
Xiaoqiu WANG, Haibo DU, Xijun CHEN, Mingyou LI, Jianan WANG, Zhiwen XU, Zhiming FENG, Zongxiang CHEN, Shimin ZUO. Analysis of Blast Resistance Genes and Neck Blast Resistance of japonica Rice Varieties/Lines Recently Developed in Jiangsu Province[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(5): 413-424.
| 基因 | 染色体 | 阳性对照 | 阴性对照 | 基因 | 染色体 | 阳性对照 | 阴性对照 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | Chr. | Control 1 | Control 2 | Gene | Chr. | Control 1 | Control 2 |
| Pit | 1 | IRBLt-K59 | 丽江新团黑谷LTH | Pia | 11 | IRBLa-A | 丽江新团黑谷LTH |
| Pib | 2 | IRBLb-B | 丽江新团黑谷LTH | Pik | 11 | IRBLk-Ka | 丽江新团黑谷LTH |
| Pigm | 6 | 谷梅4号Gumei 4 | 丽江新团黑谷LTH | Pikm | 11 | IRBLkm-Ts | 日本晴Nipponbare |
| Pid3 | 6 | 地谷Digu | 丽江新团黑谷LTH | Pikh | 11 | IRBLkh-K3 | 丽江新团黑谷LTH |
| Pi25 | 6 | 地谷Digu | 丽江新团黑谷LTH | Pi1 | 11 | IRBL1-CL | 日本晴Nipponbare |
| Pid2 | 6 | 地谷Digu | 丽江新团黑谷LTH | Pb1 | 11 | 镇稻18 Zhendao 18 | 日本晴Nipponbare |
| Pid2 | 6 | 地谷Digu | 丽江新团黑谷LTH | Pita | 12 | IRBLta-K1 | 丽江新团黑谷LTH |
| Pi3/5/i | 9 | IRBL5-M | 丽江新团黑谷LTH |
表1 本研究用于各抗病基因检测的阴阳性对照
Table 1 Information of controls used in detection of resistance genes to blast disease in present study.
| 基因 | 染色体 | 阳性对照 | 阴性对照 | 基因 | 染色体 | 阳性对照 | 阴性对照 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | Chr. | Control 1 | Control 2 | Gene | Chr. | Control 1 | Control 2 |
| Pit | 1 | IRBLt-K59 | 丽江新团黑谷LTH | Pia | 11 | IRBLa-A | 丽江新团黑谷LTH |
| Pib | 2 | IRBLb-B | 丽江新团黑谷LTH | Pik | 11 | IRBLk-Ka | 丽江新团黑谷LTH |
| Pigm | 6 | 谷梅4号Gumei 4 | 丽江新团黑谷LTH | Pikm | 11 | IRBLkm-Ts | 日本晴Nipponbare |
| Pid3 | 6 | 地谷Digu | 丽江新团黑谷LTH | Pikh | 11 | IRBLkh-K3 | 丽江新团黑谷LTH |
| Pi25 | 6 | 地谷Digu | 丽江新团黑谷LTH | Pi1 | 11 | IRBL1-CL | 日本晴Nipponbare |
| Pid2 | 6 | 地谷Digu | 丽江新团黑谷LTH | Pb1 | 11 | 镇稻18 Zhendao 18 | 日本晴Nipponbare |
| Pid2 | 6 | 地谷Digu | 丽江新团黑谷LTH | Pita | 12 | IRBLta-K1 | 丽江新团黑谷LTH |
| Pi3/5/i | 9 | IRBL5-M | 丽江新团黑谷LTH |
| 基因 Gene | 染色体 Chr. | 标记 Marker | 引物序列(5'-3') Primer sequences(5'-3') | 片段大小 Fragment size / bp | 抗/感病功能 Function | 限制性内切酶 Enzyme | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pit | 1 | tRn1 | F: GTTGGAGCTACGGTTGTTCAG | 733 | 抗 R | [20] | |
| tRn2 | F: CCAAGGGATTAGGTCCTAGTG | ||||||
| tN11 | R: CAGCGATGGTATGAGCACAA | 530 | 感 S | ||||
| Pib | 2 | Pibdom | F: GAACAATGCCCAAACTTGAGA | 365 | 抗 R | [21] | |
| R: GGGTCCACATGTCAGTGAGC | |||||||
| Lys145 | F: TCGGTGCCTCGGTAGTCAGT | 803 | 感 S | ||||
| R: GGGAAGCGGATCCTAGGTCT | |||||||
| Pigm | 6 | GMR-3 | F: AGTTCTACTTACGGAGGAGC | 146+98 | 抗 R | [22] | |
| R: AGAATTATGATAAAGAGAAAGGAA | |||||||
| Actin1-1 | F: ACAAAGTTTTCAACCGGCCTA | 146 | 感 S | ||||
| R: CTGGTACCCTCATCAGGCATC | |||||||
| Pid3 | 6 | Pid3-dCAPS | F: TACTACTCATGGAAGCTAGTTCTC | 751 | 抗 R | BamH I | [23] |
| R: ACGTCACAAATCATTCGCTC | |||||||
| Pi25 | 6 | CAP3 | F: CCTCACGTTTCTACGTCTTG | 490 | 抗 R | Nde I | [24] |
| R: CACACCATTTCTGATGAACC | |||||||
| Pid2 | 6 | D2 | F: TTGGCTATCATAGGCGTCC | 1057 | 抗 R | MIu I | [25] |
| R: ATTTGAAGGCGTTTGCGTAGA | |||||||
| Pi3/5/i | 9 | M-Pi5 | F: ATAGATCATGCGCCCTCTTG | 206 | 抗 R | [26] | |
| R: ATAGATCATGCGCCCTCTTG | 307 | 感 S | |||||
| Pia | 11 | Pia | F: CTTTTGAGCTTGATTGGTCTGC | 116 | 抗 R | [27] | |
| R: CTATTGCACCAGAGGGACCAG | 125 | 感 S | |||||
| Pik | 11 | RGA4 | F: GGAAAGCTGATATGTTGTCG | 1650 - | 抗 R | ||
| R:ACTCGGAGTCGGAGAGTCAG | 感 S | ||||||
| Pikh | 11 | FM143 | F: CCCAACATTGGTAGTAGTGC | 285 | 抗 R | [28] | |
| R: TCCTTCATACGCAAVCCAATCT | 401 | 感 S | |||||
| Pikm | 11 | DKm1 | F: TGAGCTCAAGGCAAGAGTTGAGGA | 174 | 抗 R | [29] | |
| R: TGTTCCAGCAACTCGATGAG | 213 | 感 S | |||||
| DKm2 | F: CAGTAGCTGTGTCTCAGAACTATG | 290 | 抗 R | ||||
| R: AAGGTACCTCTTTTCGGCCAG | 332 | 感 S | |||||
| Pi1 | 11 | M-Pi1 | F: GTGCTGCTGTGGCTAGTTTG | 460 - | 抗 R | [30] | |
| R: AGTCCCCGCTCAATTTTTCT | 感 S | ||||||
| Pb1 | 11 | Pb1 | F: ATCAACGCTACCTTCCC | 159 - | 抗 R | [31] | |
| R: GTGCCATCACAATTTCTTC | 感 S | ||||||
| Pita | 12 | Pita-R | F: AGCAGGTTATAAGCTAGGCC | 1042 | 抗 R | [32] | |
| R: CTACCAACAAGTTCATCAAA | |||||||
| Pita-S | F: AGCAGGTTATAAGCTAGCTAT | 1042 | 感 S | ||||
| R: CTACCAACAAGTTCATCAAA |
表2 本研究用于各抗病基因检测的功能标记引物信息
Table 2 Information of molecular markers used in detection of resistant genes to blast disease in present study.
| 基因 Gene | 染色体 Chr. | 标记 Marker | 引物序列(5'-3') Primer sequences(5'-3') | 片段大小 Fragment size / bp | 抗/感病功能 Function | 限制性内切酶 Enzyme | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pit | 1 | tRn1 | F: GTTGGAGCTACGGTTGTTCAG | 733 | 抗 R | [20] | |
| tRn2 | F: CCAAGGGATTAGGTCCTAGTG | ||||||
| tN11 | R: CAGCGATGGTATGAGCACAA | 530 | 感 S | ||||
| Pib | 2 | Pibdom | F: GAACAATGCCCAAACTTGAGA | 365 | 抗 R | [21] | |
| R: GGGTCCACATGTCAGTGAGC | |||||||
| Lys145 | F: TCGGTGCCTCGGTAGTCAGT | 803 | 感 S | ||||
| R: GGGAAGCGGATCCTAGGTCT | |||||||
| Pigm | 6 | GMR-3 | F: AGTTCTACTTACGGAGGAGC | 146+98 | 抗 R | [22] | |
| R: AGAATTATGATAAAGAGAAAGGAA | |||||||
| Actin1-1 | F: ACAAAGTTTTCAACCGGCCTA | 146 | 感 S | ||||
| R: CTGGTACCCTCATCAGGCATC | |||||||
| Pid3 | 6 | Pid3-dCAPS | F: TACTACTCATGGAAGCTAGTTCTC | 751 | 抗 R | BamH I | [23] |
| R: ACGTCACAAATCATTCGCTC | |||||||
| Pi25 | 6 | CAP3 | F: CCTCACGTTTCTACGTCTTG | 490 | 抗 R | Nde I | [24] |
| R: CACACCATTTCTGATGAACC | |||||||
| Pid2 | 6 | D2 | F: TTGGCTATCATAGGCGTCC | 1057 | 抗 R | MIu I | [25] |
| R: ATTTGAAGGCGTTTGCGTAGA | |||||||
| Pi3/5/i | 9 | M-Pi5 | F: ATAGATCATGCGCCCTCTTG | 206 | 抗 R | [26] | |
| R: ATAGATCATGCGCCCTCTTG | 307 | 感 S | |||||
| Pia | 11 | Pia | F: CTTTTGAGCTTGATTGGTCTGC | 116 | 抗 R | [27] | |
| R: CTATTGCACCAGAGGGACCAG | 125 | 感 S | |||||
| Pik | 11 | RGA4 | F: GGAAAGCTGATATGTTGTCG | 1650 - | 抗 R | ||
| R:ACTCGGAGTCGGAGAGTCAG | 感 S | ||||||
| Pikh | 11 | FM143 | F: CCCAACATTGGTAGTAGTGC | 285 | 抗 R | [28] | |
| R: TCCTTCATACGCAAVCCAATCT | 401 | 感 S | |||||
| Pikm | 11 | DKm1 | F: TGAGCTCAAGGCAAGAGTTGAGGA | 174 | 抗 R | [29] | |
| R: TGTTCCAGCAACTCGATGAG | 213 | 感 S | |||||
| DKm2 | F: CAGTAGCTGTGTCTCAGAACTATG | 290 | 抗 R | ||||
| R: AAGGTACCTCTTTTCGGCCAG | 332 | 感 S | |||||
| Pi1 | 11 | M-Pi1 | F: GTGCTGCTGTGGCTAGTTTG | 460 - | 抗 R | [30] | |
| R: AGTCCCCGCTCAATTTTTCT | 感 S | ||||||
| Pb1 | 11 | Pb1 | F: ATCAACGCTACCTTCCC | 159 - | 抗 R | [31] | |
| R: GTGCCATCACAATTTCTTC | 感 S | ||||||
| Pita | 12 | Pita-R | F: AGCAGGTTATAAGCTAGGCC | 1042 | 抗 R | [32] | |
| R: CTACCAACAAGTTCATCAAA | |||||||
| Pita-S | F: AGCAGGTTATAAGCTAGCTAT | 1042 | 感 S | ||||
| R: CTACCAACAAGTTCATCAAA |
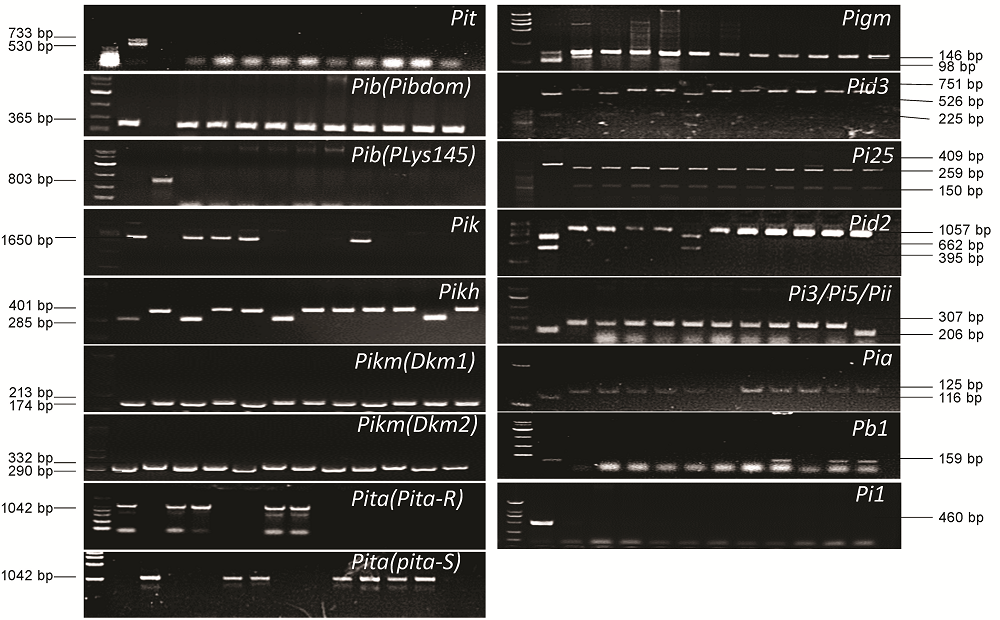
图1 各抗病基因功能标记在阳性、阴性等品种/系上的扩增验证图中各基因标记检测图谱中,泳道从左至右依次为分子量标记、阳性对照、阴性对照及随机选择的10个江苏粳稻品种;在分子量标记上,除了Pid2和Pia检测时使用DL2000、Pit检测时使用的20 bp DNA ladder外,其余基因检测中采用的标记均是DL10000;各基因采用的阳性和阴性对照具体名称见表1。
Fig. 1. Validation of the molecular markers in determining the corresponding resistance gene using known positive and negative varieties or lines as well as 10 japonica varieties randomly selected from Jiangsu Province. In the picture, the lanes from left to right are DNA Markers, positive control, negative control and 10 random japonica varieties from Jiangsu Province; About the DNA markers, expect Pid2 and Pia were DL2000, Pit was 20 bp DNA ladder, others was DL10000; The information of positive and negative control is listed in Table 1.
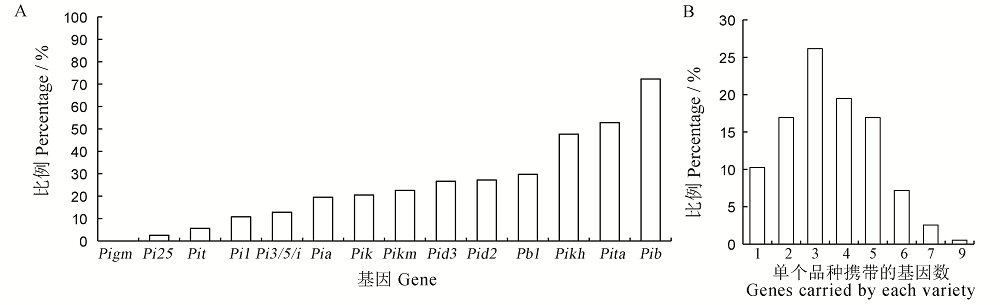
图2 各抗病基因在江苏粳稻品种中的分布频率(A)及品种携带不同抗病基因数分布(B)
Fig. 2. Distribution frequency of resistance genes in japonica rice from Jiangsu Province(A) and the distribution of gene number carried by varieties(B).
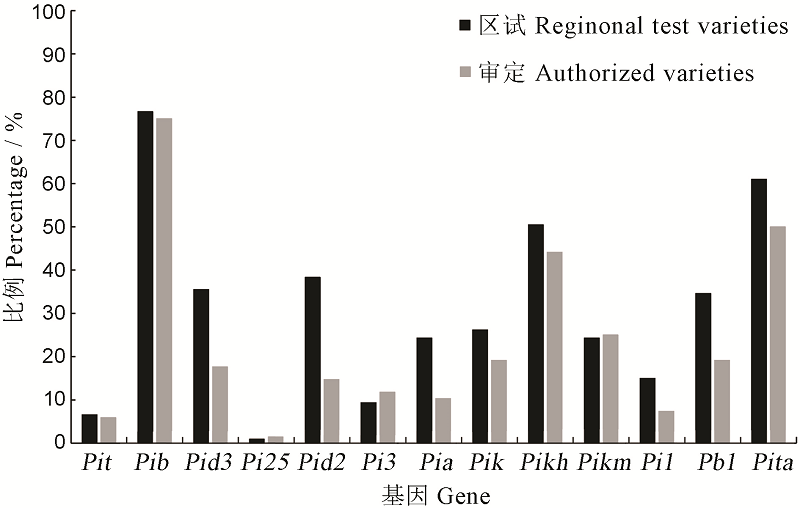
图4 各抗病基因在2019年前审定及2019年区试品种/系间的频率分布比较
Fig. 4. Comparison of resistance gene distribution frequency between varieties authorized before 2019 and regional test varieties in 2019.
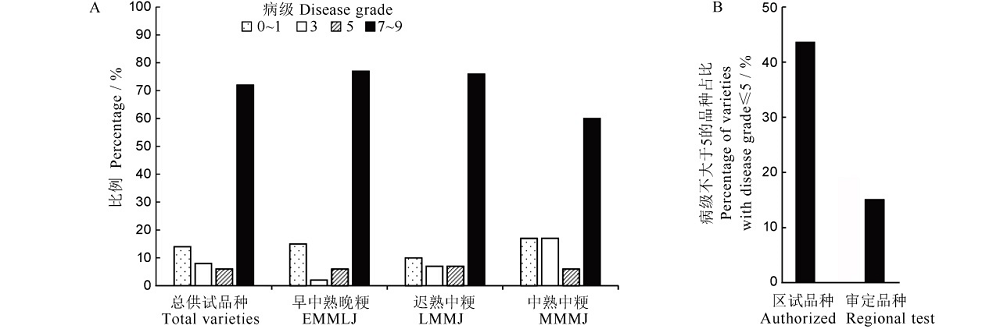
图5 供试品种稻瘟病病级分布
Fig. 5. Distribution of disease grade in varieties tested. EMMLJ, Early- and medium-maturity late japonica rice; LMMJ, Late-maturity medium japonica rice; MMMJ, Medium-maturity medium japonica rice.
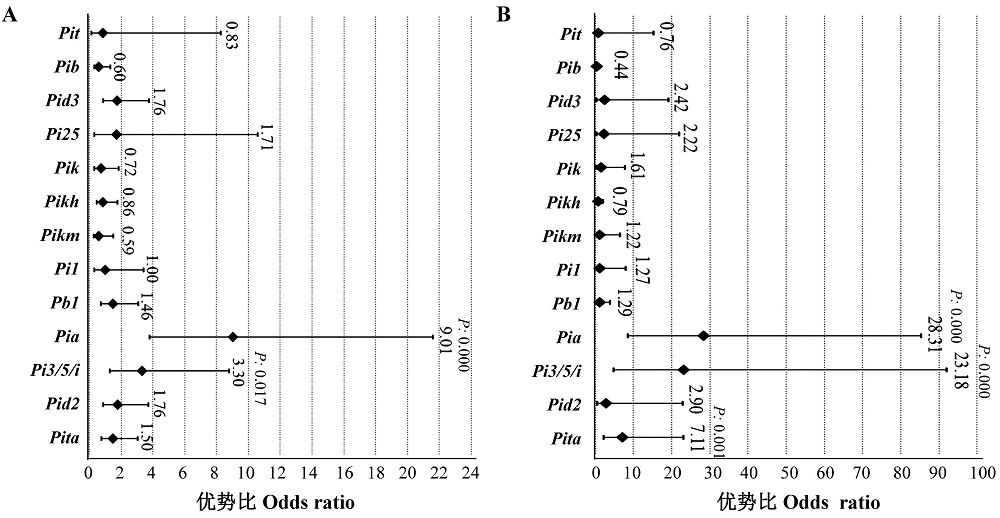
图7 各抗病基因对穗颈瘟抗性的贡献逻辑回归统计参数 A、B图分别为单基因逐一逻辑回归和多基因逻辑回归的统计参数;回归分析中的基因回归系数达到统计分析中的显著或极显著水平的,其P值分别以蓝色字体标注在相应的基因位置;图中黑点为优势比值,黑点左右黑线分别为各优势比的95%置信区间。
Fig. 7. Logistic regression statistical analysis about the contribution of each resistance genes to neck blast resistance. A and B mean single gene one by one logistic regression statistical parameter chart and multigene logistic regression statistical parameter chart, respectively; In regressive analysis, if the regression coefficient reached significant or extremely significant level, then there will be a P value around the specific gene; The dark dots mean dominance ration, the dark lines mean 95% confidence interval of each dominance ration.
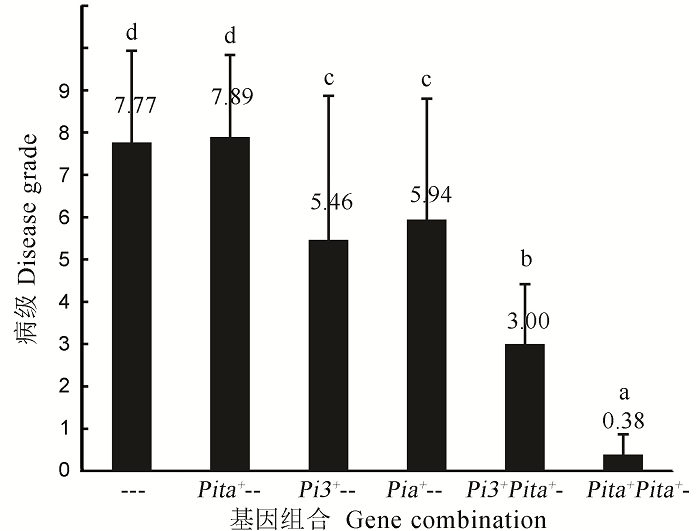
图8 三个对穗颈瘟抗性有显著贡献的基因及组合间的品种病级差异比较-表示不带有相应的抗病等位基因;柱状图上的数值表示携带相应基因或组合的品种平均病级;不同的小写字母表示彼此间的病级差异达到5%水平上的统计显著性差异。
Fig. 8. Contribute significantly of three genes to the resistance of neck blast resistance and the comparison of disease grade differences among them and their combinations. - means the absence of the specific resistance gene; The value above each bar means the average disease grade of each gene or gene combination; The lowercase letter means significance difference at 5% level between two disease grades.
| [1] | Ziegler R S, Leong S, Teng P S.Rice Blast Disease[M]. Wallingford: CAB International, 1994: 267-292. |
| [2] | 王军, 杨杰, 杨金欢, 范方军, 朱金燕, 陈志德, 仲维功. Pi-ta、Pi-b基因在江苏粳稻穗颈瘟抗性育种中的价值分析[J]. 华北农学报, 2012, 27(6): 141-145. |
| Wang J, Yang J, Yang J H, Fan F J, Zhu J Y, Chen Z D, Zhong W G.Analysis on breeding value of Pi-ta, Pi-b genes in japonica rice breeding with neck resistance in Jiangsu[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2012, 27(6): 141-145. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 常彭阳, 朱建生. 关于稻穗颈瘟的早期侵染过程[J]. 江西植保, 1995, 3(18): 15-16. |
| Chang P Y, Zhu J S.On the early infection process of rice neck blast[J]. Jiangxi Plant Protection, 1995, 3(18): 15-16. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 王小军, 王丽锋. 水稻穗颈瘟发病特征、原因及其对策浅析[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2010, 16(2): 90-91. |
| Wang X J, Wang L F.A brief analysis of the characteristics, causes and countermeasures of neck blast in rice[J]. Anhui Agriculture Science, 2010, 16(2): 90-91. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 宋益民, 丛国. 9种杀菌剂防治水稻穗颈瘟田间药效比较[J]. 现代农药, 2016, 2(15): 48-50. |
| Song Y M, Cong G.Field efficacy comparison of nine fungicides on rice neck blast[J]. Modern Agrochemicals, 2010, 16(2): 90-91. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 余玲, 李爱宏, 潘存红, 周长海, 刘广青, 李育红, 肖宁, 张小祥, 黄年生, 吴云雨, 戴正元.分子标记辅助选择培育抗病优质晚粳稻品种扬粳806[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2014, 42(8): 75-77. |
| Yu L, Li A H, Pan C H, Zhou C H, Liu G Q, Li Y H, Xiao N, Zhang X X, Huang N S, Wu Y Y, Dai Z Y.Molecular marker-assisted selection of a high quality late japonica rice variety Yangjing 806 for disease resistance[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 2014, 42(8): 75-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Li W T, Chen M S, Yu J J, Wang J, Chen X W.Recent advances in broad-spectrum resistance to the rice blast disease[J]. Plant Biology, 2019, 50: 114-120. |
| [8] | Yadav M K, Aravindan S, Ngangkham U, Prabhukarthikeyan S R, Keerthana U, Raghu S, Pramesh D, Banerjee A, Roy S, Sanghamitra P, Adak T, Priyadarshinee P, Jena M, Kar M K, Rath P C.Candidate screening of blast resistance donors for rice breeding[J]. Journal of Geneties, 2019, 98(3): 1-13. |
| [9] | Wu Y Y, Yu L, Xiao N, Dai Z Y, Li Y H, Pan C H, Zhang X X, Liu G Q, Li A H.Characterization and evaluation of rice blast resistance of Chinese indica hybrid rice parental lines[J]. Crop Journal, 2017, 5(6): 509-517. |
| [10] | 杨豪. 江苏省稻瘟病菌遗传多样性及水稻抗瘟基因鉴定[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2010. |
| Yang H.Genetic diversity of Magnaporthe grisea from rice in Jiangsu and identification of resistance rice blast gene[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 刘辉, 孟德龙, 査日扬, 徐大勇. 江苏水稻品种稻瘟病主效抗性基因鉴定及应用评价[J]. 福建农业学报, 2015, 30(5): 452-458. |
| Liu H, Meng D L, Zha R Y, Xu D Y.Identification and evaluation on blast resistance of rice varieties in Jiangsu[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Science, 2015, 30(5): 452-458. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 李刚, 袁彩勇, 曹奎荣, 孙祥良, 李军, 王健, 程保山, 罗伯祥, 徐卫军, 唐九友, 储成才. 544份水稻种质稻瘟病抗性鉴定及抗性基因的分布研究[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2018, 23(5): 22-28. |
| Li G, Yuan C Y, Cao K R, Sun X L, Li J, Wang J, Cheng B S, Luo B X, Xu W J, Tang J Y, Chu C C.Evaluation and distribution of the blast resistance genes of 544 rice materials[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2018, 23(5): 22-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 朱勇良, 范方军, 谢裕林, 伍英保, 乔中英, 张建栋. 江苏省迟熟中粳新品系稻瘟病抗病基因检测与抗性评价[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2018, 46(19): 106-109. |
| Zhu Y L, Fan F J, Xie Y L, Wu Y B, Qiao Z Y, Zhang J D.Detection and evaluation of resistance genes of rice blast in late ripening middle japonica strain in Jiangsu Province[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 2018, 46(19): 106-109. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 王军, 宫丹妮, 杨杰, 朱金燕, 范方军, 李文奇, 王芳权, 仲维功. 江苏省粳稻品种抗稻瘟病基因型与穗颈瘟抗性分析[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2016, 32(2): 250-256. |
| Wang J, Gong D N, Yang J, Zhu J Y, Fan F J, Li W Q, Wang F Q, Zhong W G.Relationship between rice blast resistance genotypes and neck blast resistance of japonica rice in Jiangsu Province[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 2016, 32(2): 250-256. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 刘士平, 李信, 汪朝阳, 李香花, 何予卿. 基因聚合对水稻稻瘟病的抗性影响[J]. 分子植物育种, 2003, (1): 22-26. |
| Liu S P, Li X, Wang C Y, Li X H, He Y Q.Gene pyramiding to increase the blast resistance in rice[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2003, 1(1): 22-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 陈羽. 扬稻6号背景下不同稻瘟病广谱抗性基因聚合效应研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2016. |
| Chen Y.Polymer effect of different broad-spectrum blast resistance genes under the background of YD6[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 杨光, 雷海霞, 乔利. 稻瘟病室内产孢及人工接种鉴定[J]. 种业导刊, 2018, 12: 23-24. |
| Yang G, Lei H X, Qiao L.Identification of indoor spore production and inoculation of rice blast[J]. Seed Industry Tribune, 2018, 12: 23-24. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 中华人民共和国农业部. 水稻品种试验稻瘟病抗性鉴定与评价技术规程: NY/T2646-2014[S]. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. Technical rules for identification and evaluation of blast resistance in rice variety test: NY/T 2646-2014[S]. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 张莉, 纪铭阳, 胡宗玉, 陈悦, 郭晓东, 陈尚上, 李少鹏. 基于随机森林和逻辑回归分类模型的烟草精选品控指标筛选[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(3): 214-217. |
| Zhang L, Ji M Y, Hu Z Y, Chen Y, Guo X D, Chen S S, Li S P.Based on random forest and logistic regression classification model selection of tobacco leaf quality control indicators[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 2020, 48(3): 214-217. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Hayashi K, Yasuda N, Fujita Y, Koizumi S, Yoshida H.Identification of the blast resistance gene Pit in rice cultivars using functional markers[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2010, 121: 1357-1367. |
| [21] | 刘洋, 徐培洲, 张红宇, 徐建第, 吴发强, 吴先军. 水稻抗稻瘟病Pib 基因的分子标记辅助选择与应用[J]. 中国农业科学, 2008, 41(1): 9-14. |
| Liu Y, Xu P Z, Zhang H Y, Xu J D, Wu F Q, Wu X J.Marker-assisted selection and application of blast resistant gene Pib in rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2008, 41(1): 9-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 王芳权, 陈智慧, 许扬, 王军, 李文奇, 范方军, 陈丽琴, 陶亚军, 仲维功, 杨杰. 水稻广谱抗稻瘟病基因PigmR功能标记的开发及应用[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019,52(6): 955-967. |
| Wang F Q, Chen Z H, Xu Y, Wang J, Li W Q, Fan F J, Chen L Q, Tao Y J, Zhong W G, Yang J.Development and application of the functional marker for the broad-spectrum blast resistance gene PigmR in rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52(6): 955-967. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Shang J J, Tao Y, Chen X W, Zou Y, Lei C L, Wang J, Li X B, Zhao X F, Zhang M J, Lu Z K, Xu J C, Cheng Z K, Wan J M, Zhu L H.Identification of a new rice blast resistance gene, Pid3, by genome wide comparison of paired nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat genes and their pseudogene alleles between the two sequenced rice genomes[J]. Genetics, 2009, 182: 1303-1311. |
| [24] | Wang H M, Chen J, Shi Y F, Pan G, Shen H C, Wu J L.Development and validation of CASP markers for marker-assisted selection of rice blast resistance gene Pi25[J]. Acta Agronomic Sinica, 2012, 38(11): 1960-1968. |
| [25] | 王亚, 陈献功, 尹海庆, 王越涛, 杨瑞芳, 臧之光, 王生轩. 河南主要水稻种质资源中抗稻瘟病基因的分子检测[J]. 分子植物育种, 2018, 16(10): 3203-3212. |
| Wang Y, Chen X G, Yin H Q, Wang Y T, Yang R F, Zang Z G, Wang S X.Molecular detection of rice blast resistance gene in the main rice germplasms in Henan Province[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2018, 16(10): 3203-3212. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 高利军, 高汉亮, 颜群, 周萌, 周维永, 张晋, 邓国富. 4个抗稻瘟病基因分子标记的建立及在水稻亲本中的分布[J]. 杂交水稻, 2010, 25(S1): 294-298. |
| Gao L J, Gao H L, Yan Q, Zhou M, Zhou W Y, Zhang J, Deng G F.Establishment of molecular markers of four rice blast resistance genes and their distribution in rice parents[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2010, 25(S1): 294-298. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 潘庆华. 稻瘟病抗性基因Pia功能特异性分子标记及其方法与应用[P]. 中国广东: CN 102703443A, 2012.10.03. |
| Pan Q H.Functional specific molecular markers of rice blast resistance gene Pia and their methods and applications[P]. Guangdong, China: CN102703443A, 2012.10.03. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 王军, 杨杰, 朱金燕, 范方军, 李文奇, 王芳权, 黄转运, 仲维功. 稻瘟病抗病基因Pi-kh功能标记的开发及江苏粳稻品种中Pi-kh的变异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(2): 141-147. |
| Wang J, Yang J, Zhu J Y, Fan F J, Li W Q, Wang F Q, Huang Z Y, Zhong W G.Development of a functional marker for rice blast resistance gene Pi-kh and natural variation at Pi-kh locus in japonica rice in Jiangsu Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Sciences, 2014, 28(2): 141-147. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 张羽, 张晓娟, 冯志峰, 王胜宝, 崔明珠. 稻瘟病抗性基因Pi-km的分子标记的选择[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2014, 32(3): 252-259. |
| Zhang Y, Zhang X J, Feng Z F, Wang S B, Cui M Z. Selection of molecular marker of resistance genes Pi-km locus of rice blast[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 32(3): 252-259. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 刘开强, 伍豪, 颜群, 王威豪, 陈小林, 周维永, 李瑞芳, 高利军, 韦善富, 邓国富. 水稻抗稻瘟病基因Pi1的特异性分子标记开发及利用[J]. 西南农业学报, 2016, 29(6): 1241-1244. |
| Liu K Q, Wu H, Yan Q, Wang W H, Chen X L, Zhou W Y, Li R F, Gao L J, Wei S F, Deng G F. Development and application of specific marker of blast resistance gene Pi1 in rice[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 29(6): 1241-1244. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 孙立亭, 林添资, 景德道, 余波, 钱华飞, 曾生元, 李闯, 姚维成, 杜灿灿, 胡庆峰, 周义文, 龚红兵. 江苏省多基因聚合对水稻稻瘟病抗性的效应分析及Pb1基因功能标记开发[J]. 南方农业学报, 2019, 50(5): 913-923. |
| Sun L T, Lin T Z, Jing D D, Yu B, Qian H F, Zeng S Y, Li C, Yao W C, Du C C, Hu Q F, Zhou Y W, Gong H B.Effects of multiple genes polymerization on rice blast resistance in Jiangsu Province and the development of functional markers of Pb1 gene[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2019, 50(5): 913-923. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 王忠华, 贾育林, 吴殿星, 夏英武. 水稻抗稻瘟病基因 Pita 的分子标记辅助选择[J]. 作物学报, 2004, 30(12): 1259-1265. |
| Wang Z H, Jia Y L, Wu D X, Xia Y W.Molecular markers-assisted selection of the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta[J]. Acta Agronomic Sinica, 2004, 30(12): 1259-1265. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 陈涛, 张亚东, 朱镇, 赵春芳, 赵庆勇, 赵凌, 周丽慧, 姚姝, 王才林. Pi-b和Pita基因在江苏省粳稻中的分布以及与穗颈瘟抗性的关系[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2016, 32(1): 1-8. |
| Chen T, Zhang Y D, Zhu Z, Zhao C F, Zhao Q Y, Zhao L, Zhou L H, Yao S, Wang C L.Distribution of Pi-b and Pi-ta genes in japonica rice of Jiangsu Province and their relationship with neck blast resistance[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 32(1): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 张善磊, 孙旭超, 陈涛, 赵春芳, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 姚姝, 王才林. Pi-ta、Pi-5、Pi-km和Pi-b基因在粳稻品种(系)中的分布及对穗颈瘟的抗性[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2018, 34(5): 961-971. |
| Zhang S L, Sun X C, Chen T, Zhao C F, Zhu Z, Zhao Q Y, Zhou L H, Zhao L, Yao S, Wang C L.Distribution of Pi-ta, Pi-5, Pi-km and Pi-b genes in japonica rice varieties (lines) and their relationship with neck blast resistance[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 34(5): 961-971. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 曾晓珊, 杨先锋, 赵正洪, 林菲, 王玲, 潘庆华. 稻瘟病抗病基因Pia 的抗性分析及精细定位[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2011, 41(1): 70-77. |
| Zeng X S, Yang X F, Zhao Z H, Lin F, Wang L, Pan Q H.Characterization and fine mapping of rice blast resistance gene Pia[J]. Science in China: Life Sciences, 2011, 41(1): 70-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | Khallaf A, 唐正合, 王建新, 陈长军, 周明国. 江苏省水稻品种抗稻瘟病基因型的鉴定与分析[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2011, 34(6): 65-70. |
| Khallaf Abdullah, Tang Z H, Wang J X, Chen C J, Zhou M G.Identification and analysis of resistant genotypes of rice varieties to Magnaporthe grisea in Jiangsu Province[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2011, 34(6): 65-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 张柱坚, 陈子强, 顾建强, 田大刚. 稻瘟病抗性基因Pi-d2、Pid-3和Pigm不同敲除突变体的抗性评价[J]. 福建农业学报, 2018, 33(12): 1231-1236. |
| Zhang Z J, Chen Z Q, Gu J Q, Tian D G.Resistance on rice blast of knockout mutants of Pi-d2, Pi-d3 and Pigm[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Science, 2018, 33(12): 65-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | Wang G L, Barbara V.Durable resistance to rice blast: A resistance gene pair balances immunity against crop yield[J]. Science, 2017, 355: 906. |
| [39] | 向聪, 任西明, 雷东阳, 陈英. 分子标记辅助选择改良C815S的稻瘟病抗性[J]. 湖南农业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 44(1): 62-65. |
| Xiang C, Ren X M, Lei D Y, Chen Y.Improvement of rice blast resistance of C815S through molecular marker-assisted selection[J]. Journal Hunan Agricultural University: Natural Sciences, 2018, 44(1): 62-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | 赖怡帆, 孙君玥, 张旭辉, 梁毅, 李永聪, 廖花, 黄俊, 吴婷婷, 刘雄伦. 分子标记辅助选择Pigm基因改良湘晚籼13号的稻瘟病抗性[J]. 湖南农业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 45(2): 113-117. |
| Lai Y F, Sun J Y, Zhang X H, Liang Y, Li Y C, Liao H, Huang J, Wu T T, Liu X L.Improving the blast resistance of Xiangwanxian 13 by molecular marker-assisted selection of the Pigm gene[J]. Journal Agricultural University: Natural Sciences, 2019, 45(2): 113-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 曾生元, 李闯, 杜灿灿, 孙立亭, 景德道, 林添资, 余波, 钱华飞, 姚维成, 周义文, 龚红兵. Pigm特异性选择标记的开发及其在粳稻穗颈瘟抗性育种中的利用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(5): 453-461. |
| Zeng S Y, Li C, Du C C, Sun L T, Jing D D, Lin T Z, Yu B, Qian H F, Yao W C, Zhou Y W, Gong H B.Development of specific markers for Pigm in marker-assisted breeding of panicle blast resistant japonica rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(5): 453-461. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 李育红, 吴云雨, 戴正元, 肖宁, 刘广青, 张小祥, 潘存红, 周长海, 王闯, 孙业霞, 朱兆兵, 刘晓斌, 李爱宏. 分子标记辅助选择培育抗稻瘟病杂交籼稻新品种扬两优316[J]. 扬州大学学报: 农业与生命科学版, 2018, 39(3): 52-57. |
| Li Y H, Wu Y Y, Dai Z Y, Xiao N, Liu G Q, Zhang X X, Pan C H, Zhou C H, Wang C, Sun Y X, Zhu Z B, Liu X B, Li A H.Development of a new hybrid rice variety Yangliangyou 316 with well resistance to blast disease through molecular maker-assisted selection[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University: Agricultural and Life Science Edition, 2018, 39(3): 52-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 丁正权, 潘月云, 施扬, 黄海祥. 基于基因芯片的嘉禾系列长粒优质食味粳稻综合评价与比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [2] | 景秀, 周苗, 王晶, 王岩, 王旺, 王开, 郭保卫, 胡雅杰, 邢志鹏, 许轲, 张洪程. 穗分化末期-灌浆初期干旱胁迫对优质食味粳稻根系形态和叶片光合特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 33-47. |
| [3] | 黄亚茹, 徐鹏, 王乐乐, 贺一哲, 王辉, 柯健, 何海兵, 武立权, 尤翠翠. 外源海藻糖对粳稻品系W1844籽粒灌浆特性及产量形成的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 379-391. |
| [4] | 王雨, 孙全翌, 杜海波, 许志文, 吴科霆, 尹力, 冯志明, 胡珂鸣, 陈宗祥, 左示敏. 利用抗稻瘟病基因Pigm和抗纹枯病数量性状基因qSB-9TQ、qSB-11HJX改良南粳9108的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 125-132. |
| [5] | 姚姝, 赵春芳, 陈涛, 路凯, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 梁文化, 赫磊, 王才林, 张亚东. 低谷蛋白半糯型粳稻营养品质与蒸煮食味品质特征分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(2): 178-188. |
| [6] | 裴峰, 王广达, 高鹏, 冯志明, 胡珂鸣, 陈宗祥, 陈红旗, 崔傲, 左示敏. 敲除OsNramp5基因创制低镉优质粳稻新材料的应用评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 16-28. |
| [7] | 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, 赵凌, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 赵春芳, 张亚东, 王才林. 利用分子标记辅助选择培育优良食味、低谷蛋白香粳稻新品系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 55-65. |
| [8] | 王才林, 张亚东, 陈涛, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 姚姝, 赵凌, 赵春芳, 周丽慧, 魏晓东, 路凯, 梁文化. 姊妹系间杂交快速培育优良食味半糯粳稻新品种的育种效果[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 455-465. |
| [9] | 王孟佳, 殷敏, 褚光, 刘元辉, 徐春梅, 章秀福, 王丹英, 陈松. 长江中下游双季晚粳稻产量、生育时期及温光资源配置的生态性差异[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(5): 475-486. |
| [10] | 王才林, 张亚东, 陈涛, 朱镇, 赵庆勇, 赵春芳, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 赵凌, 魏晓东, 路凯, 梁文化. 地点和播期对半糯粳稻食味品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(4): 373-382. |
| [11] | 张庆, 胡雅杰, 郭保卫, 张洪程, 徐晓杰, 徐玉峰, 朱邦辉, 徐洁芬, 钮中一, 凃荣文. 太湖地区优良食味高产软米粳稻品种特征研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(3): 279-290. |
| [12] | 路凯, 陈涛, 姚姝, 梁文化, 魏晓东, 张亚东, 王才林. 盐胁迫下四个水稻类受体蛋白激酶的功能分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(2): 103-111. |
| [13] | 杨宇尘, 夏原野, 闫志强, 汪磊, 闫秉春, 王镜博, 王祎玮, 栾金华, 徐海. 抽穗开花期喷施茉莉酸甲酯对不同生态区粳稻花时和株型的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2021, 35(1): 69-77. |
| [14] | 贾琰, 杨亮, 邹德堂, 瞿炤珺, 王敬国, 刘化龙, 王晋, 赵宏伟. 孕穗期冷水胁迫下施用外源物质对寒地粳稻氮光合效率及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(5): 443-456. |
| [15] | 许赵蒙, 李利华, 高晓庆, 袁正杰, 李莘, 田旭丹, 王岚岚, 瞿绍洪. 转Pi9抗稻瘟病基因水稻株系的比较转录组分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(3): 245-255. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||