
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 66-77.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220402
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Taotao1, ZOU Jixiang1, WU Longmei1, BAO Xiaozhe1, JIANG Yu2, ZHANG Nan2, ZHANG Bin1( )
)
Received:2022-04-06
Revised:2022-06-17
Online:2023-01-10
Published:2023-01-10
Contact:
ZHANG Bin
杨陶陶1, 邹积祥1, 伍龙梅1, 包晓哲1, 江瑜2, 张楠2, 张彬1( )
)
通讯作者:
张彬
基金资助:YANG Taotao, ZOU Jixiang, WU Longmei, BAO Xiaozhe, JIANG Yu, ZHANG Nan, ZHANG Bin. Effect of Free Air Temperature Increase on Grain Quality of Double-cropping Rice in South China[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 66-77.
杨陶陶, 邹积祥, 伍龙梅, 包晓哲, 江瑜, 张楠, 张彬. 开放式增温对华南双季稻稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 66-77.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.220402

Fig. 2. Trends of daily mean temperature in rice canopy under FATI conditions in 2020 and 2021. CK, Ambient temperature; W, Warming during the whole growth period.
| 季别 Season | 年份 Year | 品种 Cultivar | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | 移栽至成熟 Transplanting to maturity | 抽穗至成熟 Heading to maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻 | 2020 | 合丰丝苗Hefengsimiao | 不增温CK | 29.3±0.1 | 31.1±0.2 |
| Early rice | 全生育期增温W | 30.8±0.1 | 32.4±0.3 | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 27.7±0.1 | 28.8±0.2 | |
| 全生育期增温W | 29.5±0.4 | 31.0±0.3 | |||
| 晚稻 | 2020 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 27.6±0.1 | 24.4±0.1 |
| Late rice | 全生育期增温W | 29.5±0.5 | 25.9±0.2 | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 27.2±0.1 | 24.0±0.3 | |
| 全生育期增温W | 29.2±0.1 | 25.3±0.2 |
Table 1. Effect of FATI on average temperature of early and late rice canopy. ℃
| 季别 Season | 年份 Year | 品种 Cultivar | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | 移栽至成熟 Transplanting to maturity | 抽穗至成熟 Heading to maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻 | 2020 | 合丰丝苗Hefengsimiao | 不增温CK | 29.3±0.1 | 31.1±0.2 |
| Early rice | 全生育期增温W | 30.8±0.1 | 32.4±0.3 | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 27.7±0.1 | 28.8±0.2 | |
| 全生育期增温W | 29.5±0.4 | 31.0±0.3 | |||
| 晚稻 | 2020 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 27.6±0.1 | 24.4±0.1 |
| Late rice | 全生育期增温W | 29.5±0.5 | 25.9±0.2 | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 27.2±0.1 | 24.0±0.3 | |
| 全生育期增温W | 29.2±0.1 | 25.3±0.2 |
| 季别 Season | 年份 Year | 品种 Cultivar | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | 播种期 Sowing | 移栽期 Transplanting | 抽穗期 Heading | 成熟期 Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻 | 2020 | 合丰丝苗Hefengsimiao | 不增温CK | 03-16 | 04-09 | 06-14 | 07-12 |
| Early rice | 全生育期增温W | 03-16 | 04-09 | 06-12 | 07-09 | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 03-16 | 04-06 | 05-29 | 06-29 | |
| 全生育期增温W | 03-16 | 04-06 | 05-28 | 06-27 | |||
| 晚稻 | 2020 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 07-21 | 08-05 | 10-03 | 11-10 |
| Late rice | 全生育期增温W | 07-21 | 08-05 | 10-06 | 11-12 | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 07-19 | 08-05 | 09-29 | 11-07 | |
| 全生育期增温W | 07-19 | 08-05 | 10-01 | 11-09 |
Table 2. Effects of FATI on phenophase of early and late rice
| 季别 Season | 年份 Year | 品种 Cultivar | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | 播种期 Sowing | 移栽期 Transplanting | 抽穗期 Heading | 成熟期 Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻 | 2020 | 合丰丝苗Hefengsimiao | 不增温CK | 03-16 | 04-09 | 06-14 | 07-12 |
| Early rice | 全生育期增温W | 03-16 | 04-09 | 06-12 | 07-09 | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 03-16 | 04-06 | 05-29 | 06-29 | |
| 全生育期增温W | 03-16 | 04-06 | 05-28 | 06-27 | |||
| 晚稻 | 2020 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 07-21 | 08-05 | 10-03 | 11-10 |
| Late rice | 全生育期增温W | 07-21 | 08-05 | 10-06 | 11-12 | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗Yuehesimiao | 不增温CK | 07-19 | 08-05 | 09-29 | 11-07 | |
| 全生育期增温W | 07-19 | 08-05 | 10-01 | 11-09 |
| 季别 Season | 年份 Year | 品种 Cultivar | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | 加工品质Milling quality/% | 外观品质Appearance quality/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 糙米率 Brown rice rate | 精米率 Milled rice rate | 整精米率 Head rice rate | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate | 垩白度 Chalkiness | |||||
| 早稻 | 2020 | 合丰丝苗 | 不增温CK | 79.4 ab | 71.1 a | 50.4 c | 37.1 b | 14.1 b | |
| Early rice | Hefengsimiao | 全生育期增温W | 79.8 ab | 69.3 ab | 45.1 d | 50.5 a | 21.8 a | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗 | 不增温CK | 80.9 a | 69.0 b | 65.6 a | 6.7 d | 6.1 d | ||
| Yuehesimiao | 全生育期增温W | 78.8 b | 67.1 c | 61.4 b | 12.7 c | 11.6 c | |||
| 晚稻 | 2020 | 粤禾丝苗 | 不增温CK | 81.3 b | 72.5 a | 66.7 a | 1.8 c | 0.5 b | |
| Late rice | Yuehesimiao | 全生育期增温W | 82.0 ab | 72.9 a | 67.3 a | 1.9 c | 0.4 b | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗 | 不增温CK | 81.9 ab | 72.8 a | 65.7 a | 7.0 a | 2.1 a | ||
| Yuehesimiao | 全生育期增温W | 82.2 a | 73.1 a | 66.0 a | 5.7 b | 1.9 a | |||
| 方差分析 | 早稻Early rice | 年份Year(Y) | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| ANOVA | 温度Temperature (T) | ns | * | ** | ** | ** | |||
| Y*T | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ||||
| 晚稻Late rice | 年份Year (Y) | ns | ns | ns | ** | * | |||
| 温度Temperature (T) | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ||||
| YsT | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ||||
Table 3. Effects of FATI on grain milling and appearance qualities of early and late rice.
| 季别 Season | 年份 Year | 品种 Cultivar | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | 加工品质Milling quality/% | 外观品质Appearance quality/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 糙米率 Brown rice rate | 精米率 Milled rice rate | 整精米率 Head rice rate | 垩白粒率 Chalky grain rate | 垩白度 Chalkiness | |||||
| 早稻 | 2020 | 合丰丝苗 | 不增温CK | 79.4 ab | 71.1 a | 50.4 c | 37.1 b | 14.1 b | |
| Early rice | Hefengsimiao | 全生育期增温W | 79.8 ab | 69.3 ab | 45.1 d | 50.5 a | 21.8 a | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗 | 不增温CK | 80.9 a | 69.0 b | 65.6 a | 6.7 d | 6.1 d | ||
| Yuehesimiao | 全生育期增温W | 78.8 b | 67.1 c | 61.4 b | 12.7 c | 11.6 c | |||
| 晚稻 | 2020 | 粤禾丝苗 | 不增温CK | 81.3 b | 72.5 a | 66.7 a | 1.8 c | 0.5 b | |
| Late rice | Yuehesimiao | 全生育期增温W | 82.0 ab | 72.9 a | 67.3 a | 1.9 c | 0.4 b | ||
| 2021 | 粤禾丝苗 | 不增温CK | 81.9 ab | 72.8 a | 65.7 a | 7.0 a | 2.1 a | ||
| Yuehesimiao | 全生育期增温W | 82.2 a | 73.1 a | 66.0 a | 5.7 b | 1.9 a | |||
| 方差分析 | 早稻Early rice | 年份Year(Y) | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| ANOVA | 温度Temperature (T) | ns | * | ** | ** | ** | |||
| Y*T | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ||||
| 晚稻Late rice | 年份Year (Y) | ns | ns | ns | ** | * | |||
| 温度Temperature (T) | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ||||
| YsT | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ||||

Fig. 3. Correlations of milled rice rate and head rice rate with chalky grain rate and chalkiness. ** indicate significant correlation at P < 0.01 (n=24).
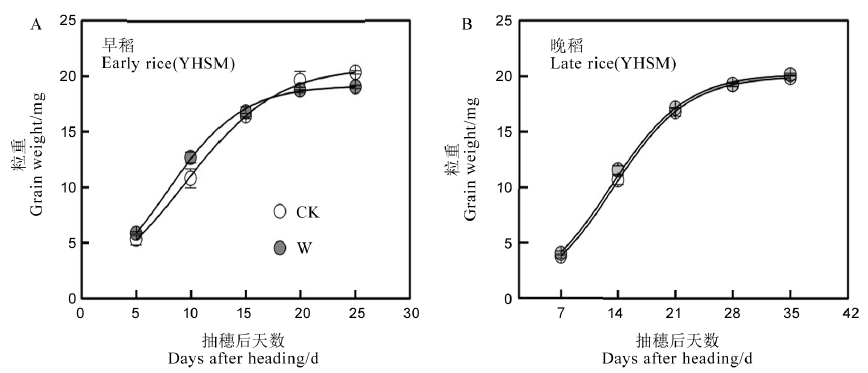
Fig. 4. Effects of FATI on grain-filling patterns of early and late rice in 2021. CK, Ambient temperature; W, Whole growth period warming. YHSM, Yuehesimiao.
| 季别 (品种) Season (Cultivar) | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | R2 | GR0 /(mg·grain−1d−1) | GRmax /(mg·grain−1d−1) | GRmean /(mg·grain−1d−1) | Tmax/d | D/d | K/mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻(粤禾丝苗) | CK | 0.996 | 0.42 b | 1.26 b | 0.73 b | 9.7 a | 22.1 a | 21.12 a |
| Early rice (YHSM) | W | 0.999 | 0.48 a | 1.39 a | 0.81 a | 7.8 b | 18.0 b | 19.23 b |
| 晚稻(粤禾丝苗) | CK | 0.999 | 0.20 a | 1.11 a | 0.59 a | 13.5 a | 26.7 a | 19.99 a |
| Late rice (YHSM) | W | 0.998 | 0.22 a | 1.11 a | 0.59 a | 13.2 a | 26.6 a | 20.21 a |
Table 5. Effects of FATI on grain-filling parameters of early and late rice in 2021.
| 季别 (品种) Season (Cultivar) | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | R2 | GR0 /(mg·grain−1d−1) | GRmax /(mg·grain−1d−1) | GRmean /(mg·grain−1d−1) | Tmax/d | D/d | K/mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻(粤禾丝苗) | CK | 0.996 | 0.42 b | 1.26 b | 0.73 b | 9.7 a | 22.1 a | 21.12 a |
| Early rice (YHSM) | W | 0.999 | 0.48 a | 1.39 a | 0.81 a | 7.8 b | 18.0 b | 19.23 b |
| 晚稻(粤禾丝苗) | CK | 0.999 | 0.20 a | 1.11 a | 0.59 a | 13.5 a | 26.7 a | 19.99 a |
| Late rice (YHSM) | W | 0.998 | 0.22 a | 1.11 a | 0.59 a | 13.2 a | 26.6 a | 20.21 a |
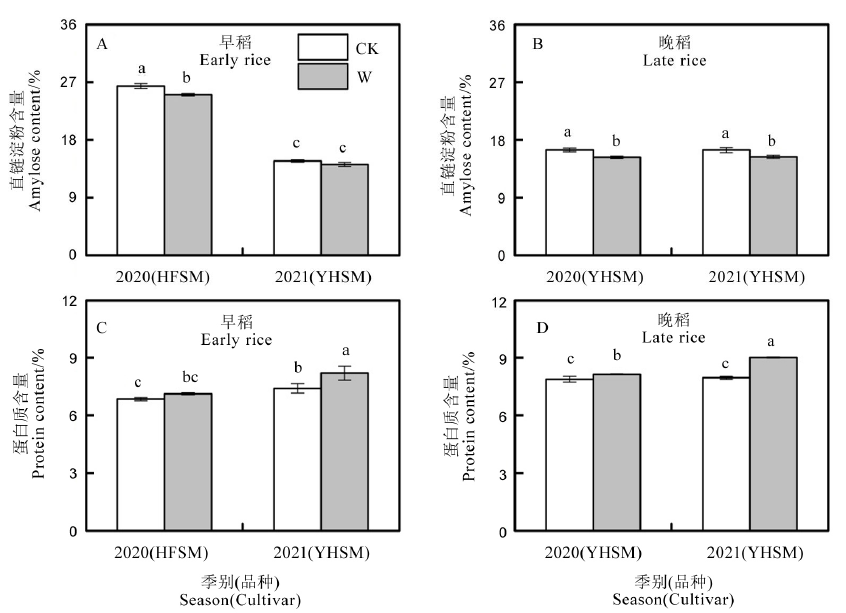
Fig. 5. Effects of FATI on amylose and protein contents of early and late rice. CK, Ambient temperature; W, Whole growth period warming. HFSM, Hefengsimiao; YHSM, Yuehesimiao. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference in the same season (P < 0.05, LSD test, n=3).
| 季别 (品种) Season (Cultivar) | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | 糊化特性Pasting property | 米饭质构Cooked rice texture | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 峰值黏度 Peak viscosity /cP | 崩解值 Breakdown /cP | 消减值 Setback /cP | 糊化温度 Pasting temperature/℃ | 硬度 Hardness /g | 黏度 Stickiness /(g·s) | |||
| 早稻(粤禾丝苗) | CK | 3405.0 b | 1240.3 a | −225.7 a | 78.0 a | 1403.4 a | 288.8 b | |
| Early rice (YHSM) | W | 3573.7 a | 1268.3 a | −368.3 b | 77.9 a | 1359.3 a | 329.1 a | |
| 晚稻(粤禾丝苗) | CK | 3032.0 b | 1008.7 a | 85.7 a | 88.5 a | 2364.9 a | 267.7 b | |
| Late rice (YHSM) | W | 3117.0 a | 979.7 a | 22.7 b | 87.5 b | 2155.4 b | 319.7 a | |
Table 5. Effects of FATI on rice pasting property and cooked rice texture of early and late rice in 2021.
| 季别 (品种) Season (Cultivar) | 温度处理 Temperature treatment | 糊化特性Pasting property | 米饭质构Cooked rice texture | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 峰值黏度 Peak viscosity /cP | 崩解值 Breakdown /cP | 消减值 Setback /cP | 糊化温度 Pasting temperature/℃ | 硬度 Hardness /g | 黏度 Stickiness /(g·s) | |||
| 早稻(粤禾丝苗) | CK | 3405.0 b | 1240.3 a | −225.7 a | 78.0 a | 1403.4 a | 288.8 b | |
| Early rice (YHSM) | W | 3573.7 a | 1268.3 a | −368.3 b | 77.9 a | 1359.3 a | 329.1 a | |
| 晚稻(粤禾丝苗) | CK | 3032.0 b | 1008.7 a | 85.7 a | 88.5 a | 2364.9 a | 267.7 b | |
| Late rice (YHSM) | W | 3117.0 a | 979.7 a | 22.7 b | 87.5 b | 2155.4 b | 319.7 a | |
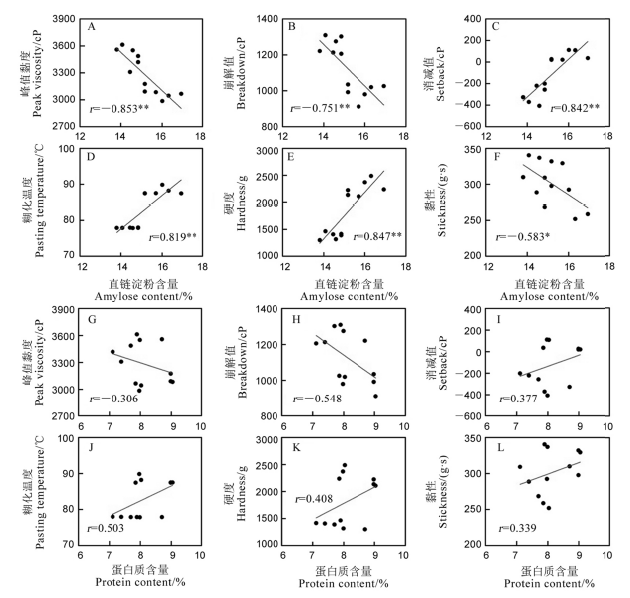
Fig. 6. Correlations of rice pasting property and cooked rice texture with amylose and protein content(2021). * and ** indicate significant correlation at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively (n=12).
| [1] | IPCC. Summary for policymakers. In: Climate Change 2021:The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021: 14. |
| [2] | 秦大河. 气候变化与干旱[J]. 科技导报, 2009, 27(11): 3-9. |
| Qin D H.Climate change and drought[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2009, 27(11): 3-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 国家统计局农村社会经济调查司. 中国农村统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2020: 113-139. |
| Department of Rural Socio-Economic Survey, National Bureau of Statistics. China rural statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2020: 113-139. | |
| [4] | Liu Y J, Tang L, Qiu X L, Liu B, Chang X N, Liu L L, Zhang X H, Cao W X, Zhu Y. Impacts of 1.5 and 2.0 °C global warming on rice production across China[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2020, 284: 107900. |
| [5] | Zhou Y J, Xu L, Xu Y Z, Xi M, Tu D B, Chen J H, Wu W G. A meta‐analysis of the effects of global warming on rice and wheat yields in a rice-wheat rotation system[J]. Food and Energy Security, 2021, 10(4): e316. |
| [6] | Chen C Q, van Groenigen K J, Yang H Y, Hungate B A, Yang B, Tian Y L, Chen J, Dong W J, Huang S, Deng A X, Jiang Y, Zhang W J. Global warming and shifts in cropping systems together reduce China's rice production[J]. Global Food Security, 2020, 24: 100359. |
| [7] | 凌霄霞, 张作林, 翟景秋, 叶树春, 黄见良. 气候变化对中国水稻生产的影响研究进展[J]. 作物学报, 2019, 45(3): 323-334. |
| Ling X X, Zhang Z L, Zhai J Q, Ye S C, Huang J L. A review for impacts of climate change on rice production in China[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 45(3): 323-334. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Chen Y, Wang M, Ouwerkerk P B F. Molecular and environmental factors determining grain quality in rice[J]. Food and Energy Security, 2012, 1(2): 111-132. |
| [9] | Chun A, Lee H J, Hamaker B R, Janaswamy S. Effects of ripening temperature on starch structure and gelatinization, pasting, and cooking properties in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2015, 63(12): 3085-3093. |
| [10] | Tsukaguchi T, Iida Y. Effects of assimilate supply and high temperature during grain-filling period on the occurrence of various types of chalky kernels in rice plants (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Production Science, 2008, 11(2): 203-210. |
| [11] | Ahmed N, Tetlow I J, Nawaz S, Iqbal A, Mubin M, Rehman M S N, Butt A, Lightfoot D A, Maekawa M. Effect of high temperature on grain filling period, yield, amylose content and activity of starch biosynthesis enzymes in endosperm of basmati rice[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2015, 95(11): 2237-2243. |
| [12] | Shi W J, Muthurajan R, Rahman H, Selvam J, Peng S B, Zou Y B, Jagadish K S V. Source-sink dynamics and proteomic reprogramming under elevated night temperature and their impact on rice yield and grain quality[J]. New Phytologist, 2013, 197(3): 825-837. |
| [13] | Rehmani M I A, Zhang J Q, Li G H, Ata-Ul-Karim S T, Wang S H, Kimball B A, Yan C, Liu Z H, Ding Y F. Simulation of future global warming scenarios in rice paddies with an open-field warming facility[J]. Plant Methods, 2011, 7: 41. |
| [14] | 阮俊梅, 张俊, 刘猷红, 董文军, 孟英, 邓艾兴, 杨万深, 宋振伟, 张卫建. 田间开放式增温对东北水稻氮素利用的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2022, 48(1): 193-202. |
| Ruan J M, Zhang J, Liu Y H, Dong W J, Meng Y, Deng A X, Yang W S, Song Z W, Zhang W J. Effects of free air temperature increase on nitrogen utilization of rice in northeastern China[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinia, 2022, 48(1): 193-202. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | Tang S, Chen W Z, Liu W Z, Zhou Q Y, Zhang H X, Wang S H, Ding Y F. Open-field warming regulates the morphological structure, protein synthesis of grain and affects the appearance quality of rice[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2018, 84: 20-29. |
| [16] | Yang T T, Yang H F, Zhang B, Wu L M, Huang Q, Zou J X, Jiang Y, Zhang N. Effects of warming on starch structure, rice flour pasting property, and cooked rice texture in a double rice cropping system[J]. Cereal Chemistry, 2022, 99(3): 680-691. |
| [17] | 邓艾兴, 刘猷红, 孟英, 陈长青, 董文军, 李歌星, 张俊, 张卫建. 田间增温 1.5 °C对高纬度粳稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(1): 51-60. |
| Deng A X, Liu Y H, Meng Y, Chen C Q, Dong W J, Li G X, Zhang J, Zhang W J. Effects of 1.5 °C field warming on rice yield and quality in high latitude planting area[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(1): 51-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Rehmani M I A, Wei G B, Hussain N, Ding C Q, Li G H, Liu Z H, Wang S H, Ding Y F. Yield and quality responses of two indica rice hybrids to post-anthesis asymmetric day and night open-field warming in lower reaches of Yangtze River delta[J]. Field Crops Research, 2014, 156: 231-241. |
| [19] | Dou Z, Tang S, Li G H, Liu Z H, Ding C Q, Chen L, Wang S H, Ding Y F. Application of nitrogen fertilizer at heading stage improves rice quality under elevated temperature during grain-filling stage[J]. Crop Science, 2017, 57(4): 2183-2192. |
| [20] | Dou Z, Tang S, Chen W Z, Zhang H X, Li G H, Liu Z H, Ding C Q, Chen L, Wang S H, Zhang H C, Ding Y F. Effects of open-field warming during grain-filling stage on grain quality of two japonica rice cultivars in lower reaches of Yangtze River delta[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2018, 81: 118-126. |
| [21] | Tang S, Zhang H X, Liu W Z, Dou Z, Zhou Q Y, Chen W Z, Wang S H, Ding Y F. Nitrogen fertilizer at heading stage effectively compensates for the deterioration of rice quality by affecting the starch-related properties under elevated temperatures[J]. Food Chemistry, 2019, 277: 455-462. |
| [22] | 杨陶陶, 胡启星, 黄山, 曾研华, 谭雪明, 曾勇军, 潘晓华, 石庆华, 张俊. 双季优质稻产量和品质形成对开放式主动增温的响应[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(6): 572-580. |
| Yang T T, Hu Q X, Huang S, Zeng Y H, Tan X M, Zeng Y J, Pan X H, Shi Q H, Zhang J. Response of yield and quality of double-cropping high quality rice cultivars under free-air temperature increasing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(6): 572-580. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 杨陶陶, 孙艳妮, 曾研华, 黄山, 张俊, 谭雪明, 曾勇军, 潘晓华. 花后增温对双季优质稻产量和品质的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2019, 33(3): 583-591. |
| Yang T T, Sun Y N, Zeng Y H, Huang S, Zhang J, Tan X M, Zeng Y J, Pan X H. Effect of post-anthesis warming on the grain yield and quality of double-cropped high-quality rice cultivars[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 33(3): 583-591. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Chen H, Chen D, He L H, Wang T, Lu H, Yang F, Deng F, Chen Y, Tao Y F, Li M, Li G Y, Ren W J. Correlation of taste values with chemical compositions and Rapid Visco Analyser profiles of 36 indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties[J]. Food Chemistry, 2021, 349: 129176. |
| [25] | Li H Y, Gilbert R G. Starch molecular structure: The basis for an improved understanding of cooked rice texture[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2018, 195: 9-17. |
| [26] | Jing L Q, Wang J, Shen S B, Wang Y X, Zhu J G, Wang Y L, Yang L X. The impact of elevated CO2 and temperature on grain quality of rice grown under open-air field conditions[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2016, 96(11): 3658-3667. |
| [27] | Xiong D L, Ling X X, Huang J L, Peng S B. Meta-analysis and dose-response analysis of high temperature effects on rice yield and quality[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2017, 141: 1-9. |
| [28] | Lyman N B, Jagadish K S V, Nalley L L, Dixon B L, Siebenmorgen T. Neglecting rice milling yield and quality underestimates economic losses from high-temperature stress[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(8): e72157. |
| [29] | Wang X Q, Wang K L, Yin T Y, Zhao Y F, Liu W Z, Shen Y Y, Ding Y F, Tang S. Nitrogen fertilizer regulated grain storage protein synthesis and reduced chalkiness of rice under actual field warming[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 715436. |
| [30] | Sanchez B, Rasmussen A, Porter J R. Temperatures and the growth and development of maize and rice: a review[J]. Global Change Biology, 2014, 20: 408-417. |
| [31] | Chen C, Huang J L, Zhu L Y, Shah F, Nie L X, Cui K H, Peng S B. Varietal difference in the response of rice chalkiness to temperature during ripening phase across different sowing dates[J]. Field Crops Research, 2013, 151: 85-91. |
| [32] | Dong W J, Chen J, Wang L L, Tian Y L, Zhang B, Lai Y C, Meng Y, Qian C R, Guo J. Impacts of nighttime post-anthesis warming on rice productivity and grain quality in East China[J]. The Crop Journal, 2014, 2(1): 63-69. |
| [33] | Yamakawa H, Hakata M. Atlas of rice grain filling-related metabolism under high temperature: Joint analysis of metabolome and transcriptome demonstrated inhibition of starch accumulation and induction of amino acid accumulation[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2010, 51(5): 795-809. |
| [34] | Jing L Q, Chen C, Hu S W, Dong S P, Pan Y, Wang Y X, Lai S K, Wang Y L, Yang L X. Effects of elevated atmosphere CO2 and temperature on the morphology, structure and thermal properties of starch granules and their relationship to cooked rice quality[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2021, 112: 106360. |
| [35] | Huang L C, Tan H Y, Zhang C Q, Li Q F, Liu Q Q. Starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperms: An updated review over the last decade[J]. Plant Communications, 2021, 2(5): 100237. |
| [36] | Cao Z Z, Pan G, Wang F B, Wei K S, Li Z W, Shi C H, Geng W, Cheng F M. Effect of high temperature on the expressions of genes encoding starch synthesis enzymes in developing rice endosperms[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2015, 14(4): 642-659. |
| [37] | Zhong Y Y, Qu J G, Li Z H, Tian Y, Zhu F, Blennow A, Liu X X. Rice starch multi-level structure and functional relationships[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2022, 275: 118777. |
| [38] | Chung H J, Liu Q, Lee L, Wei D Z. Relationship between the structure, physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of rice starches with different amylose contents[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2011, 25(5): 968-975. |
| [39] | Li C, Luo J X, Zhang C Q, Yu W W. Causal relations among starch chain-length distributions, short-term retrogradation and cooked rice texture[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2020, 108: 106064. |
| [40] | Zhang C Q, Zhou L H, Zhu Z B, Lu H W, Zhou X H, Qian Y T, Li Q F, Lu Y, Gu M H, Liu Q Q. Characterization of grain quality and starch fine structure of two japonica rice (Oryza Sativa) cultivars with good sensory properties at different temperatures during the filling stage[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2016, 64(20): 4048-4057. |
| [41] | Li H Y, Prakash S, Nicholson T M, Fitzgerald M A, Gilbert R G. The importance of amylose and amylopectin fine structure for textural properties of cooked rice grains[J]. Food Chemistry, 2016, 196: 702-711. |
| [42] | Yang T T, Xiong R Y, Tan X M, Huang S, Pan X H, Guo L, Zeng Y J, Zhang J, Zeng Y H. The impacts of post-anthesis warming on grain yield and quality of double-cropping high-quality indica rice in Jiangxi Province, China[J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 2022, 139: 126551. |
| [1] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [2] | TANG Zhiwei, ZHU Xiangcheng, ZHANG Jun, DENG Aixing, ZHANG Weijian. Effects of Green Manure Planting and Lime Application on Cadmium Content in Double-cropping Rice Under Controlled Irrigation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(2): 211-222. |
| [3] | CHEN Liming, YANG Taotao, XIONG Ruoyu, TAN Xueming, HUANG Shang, ZENG Yongjun, PAN Xiaohua, SHI Qinghua, ZHANG Jun, ZENG Yanhua. Effect of Free-air Temperature Increasing on Activities of Enzymes Involved in Starch Synthesis and Accumulation of Double-cropping indica Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(2): 166-177. |
| [4] | PEI Feng, WANG Guangda, GAO Peng, FENG Zhiming, HU Keming, CHEN Zongxiang, CHEN Hongqi, CUI Ao, ZUO Shimin. Evaluation of New japonica Rice Lines with Low Cadmium Accumulation and Good Quality Generated by Knocking Out OsNramp5 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 16-28. |
| [5] | WANG Yingheng, CHEN Lijuan, CUI Lili, ZHAN Shengwei, SONG Yu, CHEN Shian, XIE Zhenxing, JIANG Zhaowei, WU Fangxi, ZHUO Chuanying, CAI Qiuhua, XIE Huaan, ZHANG Jianfu. Effects of Nitrogen Rate on Photosynthesis, Yield and Grain Quality of Superior Quality Rice “Fuxiangzhan” [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 89-101. |
| [6] | JING Wenjiang, GU Hanzhu, ZHANG Xiaoxiang, WU Hao, ZHANG Weiyang, GU Junfei, LIU Lijun, WANG Zhiqin, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Hao. Response of Grain Quality and Root Characteristics to Irrigation Methods During Mid-season indica Rice Varieties Improvement [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(5): 505-519. |
| [7] | Haoliang YAN, Song WANG, Xueyan WANG, Chengcheng DANG, Meng ZHOU, Rongrong HAO, Xiaohai TIAN. Performance of Different Rice Varieties Under High Temperature and Its Relationship with Field Meteorological Factors [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(6): 617-628. |
| [8] | Zhuanzhuan CHEN, Yong YANG, Linhao FENG, Ye SUN, Changquan ZHANG, Xiaolei FAN, Qianfeng LI, Qiaoquan LIU. Effects of Different Combinations of Wx and ALK Main Alleles on Rice Grain Quality [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(3): 228-236. |
| [9] | Zhuanzhuan CHEN, Xianfeng LI, Min ZHONG, Jiaqi GE, Xiaolei FAN, Changquan ZHANG, Qiaoquan LIU. Grain Quality as Affected by Down-regulation of Expression of Different ALK Alleles in indica Rice (Oryza sativa L.) [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(6): 513-522. |
| [10] | Chanchan ZHOU, Yuancai HUANG, Baoyan JIA, Yan WANG, Ruifeng LI, Shu WANG, Yue FENG, DOU Fugen. Effect of Interaction Between Nitrogen Rate and Irrigation Regime on Grain Quality of japonica Rice in Northeast China [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(4): 357-367. |
| [11] | Zhongdu CHEN, Chunchun XU, Long JI, Fuping FANG. Carbon Footprint Analysis of Double Cropping Rice Production in the Middle Yangtze River Valley Based on Household Surveys [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(6): 601-609. |
| [12] | Taotao YANG, Qixing HU, Shan HUANG, Yanhua ZENG, Xueming TAN, Yongjun ZENG, Xiaohua PAN, Qinghua SHI, Jun ZHANG. Response of Yield and Quality of Double-cropping High Quality Rice Cultivars Under Free-air Temperature Increasing [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(6): 572-580. |
| [13] | CHEN Zhongdu, XU Chunchun, JI Long, FANG Fuping*. Carbon Footprint Analysis of Double Cropping Rice Production in the Middle Yangtze River Valley Based on Household Surveys [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2018, 32(6): 601-609. |
| [14] | Lang ZHANG, Linghong ZHOU, Jiabin WEI, Xiaolin CHENG, Huaqin XU, Zhixiang XIAO, Qiyuan TANG, Jianwu TANG. Effects ofRicePlanting Combined with ChickenRaisingin Winter on Double-cropping Rice Growth and Soil Fertility [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(3): 226-236. |
| [15] | Chengxin JU, Yaojie CHEN, Buhong ZHAO, Lijun LIU, Zhiqin WANG, Jianchang YANG. Effect of Site-Specific Nitrogen Management on Grain Yield and Quality of japonicaRice Varieties Differed in Response to Nitrogen [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(3): 237-246. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||