
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (5): 635-642.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.241114
徐群1,#, 王珊1,#, 袁筱萍1, 金石桥2, 晋芳2, 郝万军3, 吴小碧3, 冯跃1, 余汉勇1, 孙燕飞1, 杨窑龙1,*( ), 魏兴华1,*(
), 魏兴华1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-21
修回日期:2025-02-24
出版日期:2025-09-10
发布日期:2025-09-10
通讯作者:
*email: yangyaolong@caas.cn,email: weixinghua@caas.cn
作者简介:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
XU Qun1,#, WANG Shan1,#, YUAN Xiaoping1, JIN Shiqiao2, JIN Fang2, HAO Wanjun3, WU Xiaobi3, FENG Yue1, YU Hanyong1, SUN Yanfei1, YANG Yaolong1,*( ), WEI Xinghua1,*(
), WEI Xinghua1,*( )
)
Received:2024-11-21
Revised:2025-02-24
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2025-09-10
Contact:
*email: yangyaolong@caas.cn,email: weixinghua@caas.cn
About author:#These authors contributed equally to the work
摘要:
【目的】高鉴别力的SNP位点组合对建立高效、精准、低成本的水稻品种验证技术至关重要,可广泛应用于种子监管和品种创新等领域。【方法】利用农业行业标准推荐的96个SNP标记(RGIsnp96),构建1383个常规种和2702个杂交种水稻品种的SNP指纹图谱。【结果】发现在常规种中,杂合基因型比率、平均多态性信息成分(PIC)、平均次要等位基因频率(MAF)分别为0.03、0.30和0.27;在杂交种中,相关指标分别为0.39、0.30和0.29。RGIsnp96对常规稻、杂交稻的品种识别率分别为99.94%、99.99%。基于品种间异同基因型位点的比例,对RGIsnp96与农业行业标准推荐的48个SSR标记(RGIssr48)的鉴定结果进行比较,结果显示,不论是对于常规种、还是杂交种,这两套标记均具有良好的等效性。同时,还发现对部分常规品种的鉴别,组合不同类型的标记,比单一类型的标记能取得更好的效果,并推荐了相应的策略。【结论】RGIsnp96展现出卓越的水稻品种鉴别能力,为提升水稻种子质量、规范种子市场秩序以及保障农民权益提供了坚实的技术支持。
徐群, 王珊, 袁筱萍, 金石桥, 晋芳, 郝万军, 吴小碧, 冯跃, 余汉勇, 孙燕飞, 杨窑龙, 魏兴华. 用于水稻品种真实性验证的SNP位点评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 635-642.
XU Qun, WANG Shan, YUAN Xiaoping, JIN Shiqiao, JIN Fang, HAO Wanjun, WU Xiaobi, FENG Yue, YU Hanyong, SUN Yanfei, YANG Yaolong, WEI Xinghua. Evaluation of SNP Loci for Rice Variety Authenticity Verification[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(5): 635-642.
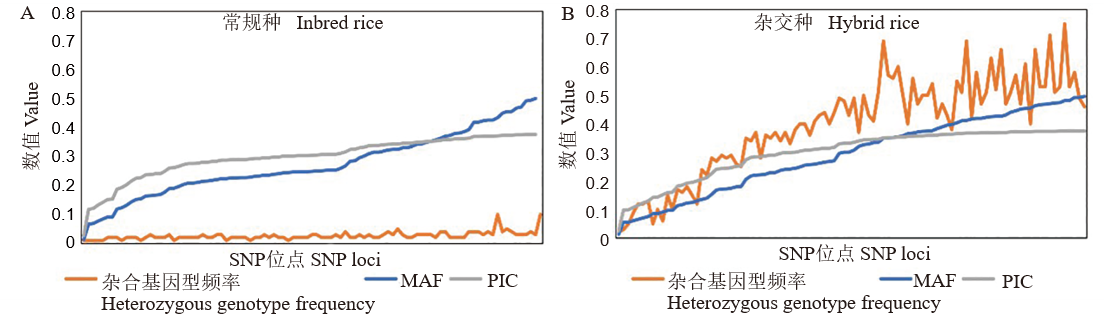
图2 RGIsnp96在1383个常规种品种、2702个杂交种品种中的PIC、MAF和杂合基因型频率分布
Fig. 2. Distribution of PIC, MAF, heterozygous genotype rates of RGIsnp96 in 2702 hybrid rice and 1383 inbred rice varieties
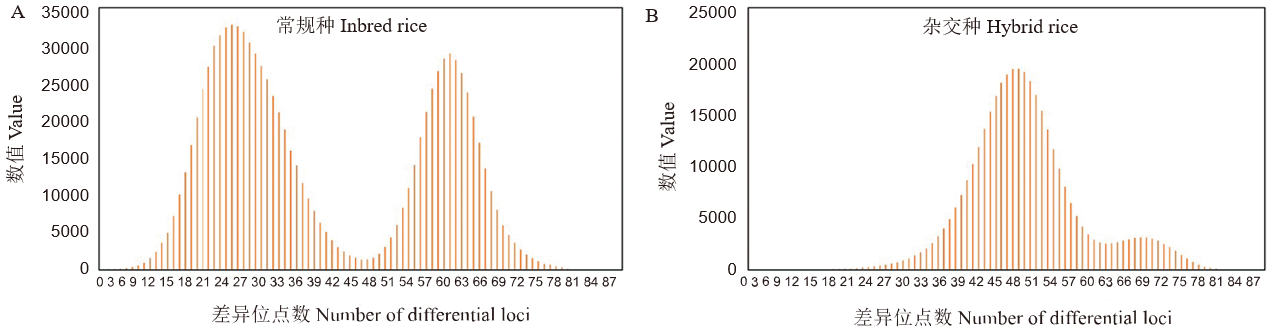
图4 1383个常规种、2702个杂交种各群体内分别成对比较差异SNP位点数目分布
Fig. 4. Distribution of the number of different SNPs obtained by pairwise analysis of hybrid rice and inbred rice varieties, respectively
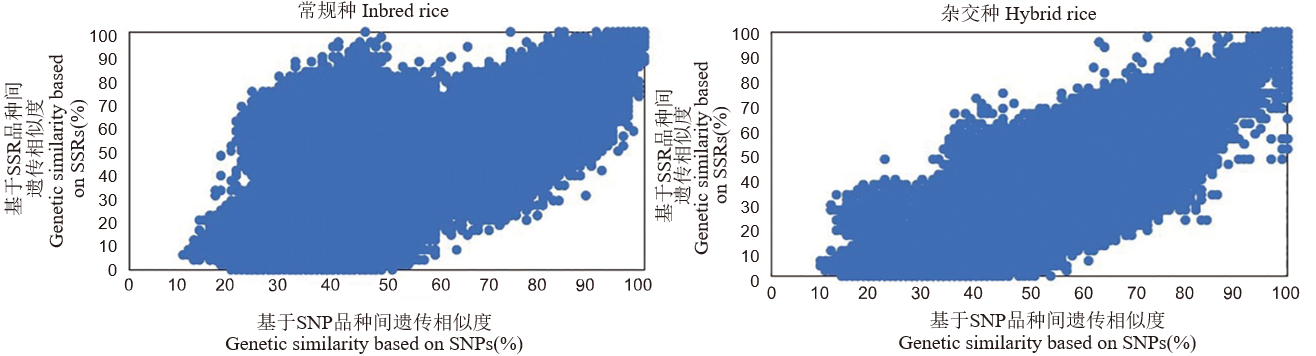
图5 基于RGIsnp96和RGIssr48指纹数据的水稻1383个常规种、2702个杂交种群体品种对位点相似度分布
Fig. 5. Distribution of pairwise similarity of 1383 inbred rice and 2702 hybrid rice varieties based on RGIsnp96 and RGIssr48
| [1] | Singh R K, Sharma R K, Singh A K, Singh V P, Singh N K, Tiwari S P, Mohapatra T. Suitability of mapped sequence tagged microsatellite site markers for establishing distinctness, uniformity and stability in aromatic rice[J]. Euphytica, 2004, 135(2): 135-143. |
| [2] | Sato H, Endo T, Shiokai S, Nishio T, Yamaguchi M. Identification of 205 current rice cultivars in Japan by dot-blot-SNP analysis[J]. Breeding Science, 2010, 60(4): 447-453. |
| [3] | Ni J J, Colowit P M, MacKill D J. Evaluation of genetic diversity in rice subspecies using microsatellite markers[J]. Crop Science, 2002, 42(2): 601-607. |
| [4] | 施勇烽, 应杰政, 王磊, 朱智伟, 庄杰云. 鉴定水稻品种的微卫星标记筛选[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 19(3): 195-201. |
| Shi Y F, Ying J Z, Wang L, Zhu Z W, Zhuang J Y. Screening SSR markers for rice variety identification[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2005, 19(3): 195-201. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | McCouch S R, Zhao K Y, Wright M, Tung C W, Ebana K, Thomson M, Reynolds A, Wang D, DeClerck G, Ali M L, McClung A, Eizenga G, Bustamante C. Development of genome-wide SNP assays for rice[J]. Breeding Science, 2010, 60(5): 524-535. |
| [6] | Xu X, Zhang M C, Xu Q, Feng Y, Yuan X P, Yu H Y, Wang Y P, Wei X H, Yang Y L. Quantitative trait loci identification and genetic diversity analysis of panicle structure and grain shape in rice[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2020, 90(1): 89-100. |
| [7] | Huang X H, Wei X H, Sang T, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhao Y, Li C Y, Zhu C R, Lu T T, Zhang Z W, Li M, Fan D L, Guo Y L, Wang A H, Wang L, Deng L W, Li W J, Lu Y Q, Weng Q J, Liu K Y, Huang T, Zhou T Y, Jing Y F, Li W, Lin Z, Buckler E S, Qian Q, Zhang Q F, Li J Y, Han B. Genome-wide association studies of 14 agronomic traits in rice landraces[J]. Nature Genetics, 2010, 42(11): 961-967. |
| [8] | Huang X H, Kurata N, Wei X H, Wang Z X, Wang A H, Zhao Q, Zhao Y, Liu K Y, Lu H Y, Li W J, Guo Y L, Lu Y Q, Zhou C C, Fan D L, Weng Q J, Zhu C R, Huang T, Zhang L, Wang Y C, Feng L, Furuumi H, Kubo T, Miyabayashi T, Yuan X P, Xu Q, Dong G J, Zhan Q L, Li C Y, Fujiyama A, Toyoda A, Lu T T, Feng Q, Qian Q, Li J Y, Han B. A map of rice genome variation reveals the origin of cultivated rice[J]. Nature, 2012, 490(7421): 497-501. |
| [9] | Xu X, Liu X, Ge S, Jensen J D, Hu F, Li X, Dong Y, Gutenkunst R N, Fang L, Huang L, Li J X, He W M, Zhang G J, Zheng X M, Zhang F M, Li Y R, Yu C, Kristiansen K, Zhang X Q, Wang J, Wright M, McCouch S, Nielsen R, Wang J, Wang W. Resequencing 50 accessions of cultivated and wild rice yields markers for identifying agronomically important genes[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2011, 30(1): 105-111. |
| [10] | Lu Q, Zhang M C, Niu X J, Wang C H, Xu Q, Feng Y, Wang S, Yuan X P, Yu H Y, Wang Y P, Wei X H. Uncovering novel loci for mesocotyl elongation and shoot length in indica rice through genome-wide association mapping[J]. Planta, 2016, 243(3): 645-657. |
| [11] | Xu Q, Yuan X P, Wang S, Feng Y, Yu H Y, Wang Y P, Yang Y L, Wei X H, Li X M. The genetic diversity and structure of indica rice in China as detected by single nucleotide polymorphism analysis[J]. BMC Genetics, 2016, 17: 53. |
| [12] | Zhang M C, Lu Q, Wu W, Niu X J, Wang C H, Feng Y, Xu Q, Wang S, Yuan X P, Yu H Y, Wang Y P, Wei X H. Association mapping reveals novel genetic loci contributing to flooding tolerance during germination in indica rice[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 678. |
| [13] | Zhao Q, Feng Q, Lu H Y, Li Y, Wang A H, Tian Q L, Zhan Q L, Lu Y Q, Zhang L, Huang T, Wang Y C, Fan D L, Zhao Y, Wang Z Q, Zhou C C, Chen J Y, Zhu C R, Li W J, Weng Q J, Xu Q, Wang Z X, Wei X H, Han B, Huang X H. Pan-genome analysis highlights the extent of genomic variation in cultivated and wild rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2018, 50(2): 278-284. |
| [14] | Shirasawa K, Shiokai S, Yamaguchi M, Kishitani S, Nishio T. Dot-blot-SNP analysis for practical plant breeding and cultivar identification in rice[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2006, 113(1): 147-155. |
| [15] | 马小定, 崔迪, 韩冰, 焦成智, 韩龙植. 水稻种质资源全基因组DNA指纹鉴定方法研究[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2023, 24(4): 1106-1113. |
| Ma X D, Cui D, Han B, Jiao C Z, Han L Z. Identification and evaluation method for genomic-wide DNA fingerprinting of rice germplasm[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2023, 24(4): 1106-1113. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 田红丽, 杨扬, 范亚明, 易红梅, 王蕊, 金石桥, 晋芳, 张云龙, 刘亚维, 王凤格, 赵久然. 用于玉米品种真实性鉴定的最优核心SNP 位点集的研发[J]. 作物学报, 2024, 50(5): 1115-1123. |
| Tian H L, Yang Y, Fan Y M, Yi H M, Wang R, Jin S Q, Jin F, Zhang Y L, Liu Y W, Wang F G, Zhao J R. Development of an optimal core SNP loci set for maize variety genuineness identification[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2024, 50(5): 1115-1123. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 中华人民共和国农业部. 水稻品种鉴定 DNA指纹方法: NY/T 1433—2007[S] 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2007. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. Identification of rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties using microsatellite markers: NY/T 1433—2007[S]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2007. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 中华人民共和国农业部. 水稻品种鉴定技术规程 SSR标记法: NY/T 1433—2014[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2014. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. Protocol for identification of rice varieties—SSR marker method: NY/T 1433—2014[S]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2014. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 主要农作物品种真实性和纯度SSR分子标记检测稻: GB/T 39917—2021[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021. |
| State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Variety genuineness and purity testing of main crops with SSR markers—Rice: GB/T 39917—2021[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 中华人民共和国农业部. 水稻品种鉴定SNP标记法: NY/T 2745—2015[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2015. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. Protocol for identification of rice varieties.SNP marker method: NY/T 2745—2015[S]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2015. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 中华人民共和国农业农村部. 水稻品种真实性鉴定 SNP标记法: NY/T 2745—2021[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2021. |
| Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Rice (Oryza sativa L.) variety genuineness identification-SNP based method: NY/T 2745—2021[S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | Xu Q, Chen H, Wang C H, Yu H Y, Yuan X P, Wang Y P, Feng Y, Tang S X, Wei X H. Genetic diversity and structure of new inbred rice cultivars in China[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture. 2012, 11(10): 1567-1573. |
| [23] | Muhamad K, Ebana K, Fukuoka S, Okuno K. Genetic relationships among improved varieties of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Indonesia over the last 60 years as revealed by morphological traits and DNA markers[J]. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 2017, 64(4): 701-715. |
| [24] | Yang G L, Chen S P, Chen L K, Sun K, Huang C H, Zhou D H, Huang Y T, Wang J F, Liu Y Z, Wang H, Chen Z Q, Guo T. Development of a core SNP arrays based on the KASP method for molecular breeding of rice[J]. Rice, 2019, 12(1): 21. |
| [25] | Zhang D L, Zhang H L, Wang M X, Sun J L, Qi Y W, Wang F M, Wei X H, Han L Z, Wang X K, Li Z C. Genetic structure and differentiation of Oryza sativa L. in China revealed by microsatellites[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2009, 119(6): 1105-1117. |
| [26] | Kuang M, Wei S J, Wang Y Q, Zhou D Y, Ma L, Fang D, Yang W H, Ma Z Y. Development of a core set of SNP markers for the identification of upland cotton cultivars in China[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2016, 15(5): 954-962. |
| [27] | 刘丽华, 庞斌双, 刘阳娜, 李宏博, 王娜, 王拯, 赵昌平. 基于SNP标记的小麦高通量身份鉴定模式[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2018, 38(5): 529-534. |
| Liu L H, Pang B S, Liu Y N, Li H B, Wang N, Wang Z, Zhao C P. High-throughput identification mode for wheat varieties based on SNP markers[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2018, 38(5): 529-534. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Li P R, Su T B, Yu S C, Wang H P, Wang W H, Yu Y J, Zhang D S, Zhao X Y, Wen C L, Zhang F L. Identification and development of a core set of informative genic SNP markers for assaying genetic diversity in Chinese cabbage[J]. Horticulture, Environment and Biotechnology, 2019, 60: 411-425. |
| [29] | Liu Z X, Li J, Fan X H, Htwe N M P S, Wang S M, Huang W, Yang J Y, Xing L L, Chen L J, Li Y H, Guan R X, Chang R Z, Wang D C, Qiu L J. Assessing the numbers of SNPs needed to establish molecular IDs and characterize the genetic diversity of soybean cultivars derived from Tokachi nagaha[J]. The Crop Journal, 2017, 5(4): 326-336. |
| [30] | 徐群, 魏兴华, 杨窑龙, 王珊, 冯跃, 章孟臣, 袁筱萍, 余汉勇, 王一平. 用于水稻品种鉴定的组合SNP核心位点及应用: CN112662796A[P]. 2021-04-16. |
| Xu Q, Wei X H, Yang Y L, Wang S, Feng Y, Zhang M C, Yuan X P, Yu H Y, Wang Y P. Combination of core SNP loci for rice variety identification and its applications: CN112662796A[P]. 2021-04-16. (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 主要农作物品种真实性和纯度SSR分子标记检测玉米: GB/T 39914—2021[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021. |
| State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Variety genuineness and purity testing of main crops with SSR markers—Maize: GB/T 39914—2021[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2021. (in Chinese) | |
| [32] | 中华人民共和国农业部. 主要农作物品种真实性SSR分子标记检测普通小麦: NY/T 2859—2015[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2015. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. Variety genuineness testing of main crops with SSR markers—Wheat(Triticum aestivum L.): NY/T 2859—2015[S]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2015. (in Chinese) | |
| [33] | 中华人民共和国农业农村部. 向日葵品种真实性鉴定 SSR分子标记法: NY/T 3752—2020[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2020. |
| Sunflower variety authenticity identification SSR molecular marker method: NY/T 3752—2020[S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2020. (in Chinese) | |
| [34] | 中华人民共和国农业农村部. 黄瓜品种真实性鉴定 SSR分子标记法: NY/T 4200—2022[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2022. |
| Ministry of Agriculture and Rural affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Cucumber(Cucumis sativus L.)variety genuineness identification-SSR based me thods: NY/T 4200—2022[S]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2022. (in Chinese) | |
| [35] | 徐婷婷, 孟珊, 朱小品, 邹淑琼, 狄佳春, 杨欣, 朱银, 郭春滨, 颜伟. 基于高通量芯片的大麦高效KASP标记的开发和应用[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2024, 25(9): 1504-1515. |
| Xu T T, Meng S, Zhu X P, Zou S Q, Di J C, Yang X, Zhu Y, Guo C B, Yan W. Development and application of high efficiency KASP markers in barley based on high throughput chip[J]. Jounal of Plant Genetic Resouces, 2024, 25(9): 1504-1515. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 刘欣, 程瑞, 徐兵划, 白甜, 徐文钊, 张朝阳, 罗德旭, 赵建锋, 张兴平, 孙玉东. 基于KASP技术的SNP标记用于西瓜品种指纹图谱构建和种子纯度检测[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2022, 38(5): 1348-1356. |
| Liu X, Cheng R, Xu B H, Bai T, Xu W Z, Zhang C Y, Luo D X, Zhao J F, Zhang X P, Sun Y D. Application of SNP markers based on KASP technology in fingerprint construction and seed purity detection of watermelon varieties[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 38(5): 1348-1356. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | De la Vega F M, Lazaruk K D, Rhodes M D, Wenz M H. Assessment of two flexible and compatible SNP genotyping platforms: TaqMan SNP genotyping assays and the SNPlex genotyping system[J]. Mutation Research, 2005, 573(1/2): 111-135. |
| [38] | Chen H D, Xie W B, He H, Yu H H, Chen W, Li J, Yu R B, Yao Y, Zhang W H, He Y Q, Tang X Y, Zhou F S, Deng X W, Zhang Q F. A high-density SNP genotyping array for rice biology and molecular breeding[J]. Molecular Plant, 2014, 7(3): 541-553 |
| [39] | Semagn K, Babu R, Hearne S, Olsen M. Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP): Overview of the technology and its application in crop improvement[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2014, 33(1): 1-14. |
| [40] | 王蕊, 施龙建, 田红丽, 易红梅, 杨扬, 葛建镕, 范亚明, 任洁, 王璐, 陆大雷, 赵久然, 王凤格. 玉米杂交种纯度鉴定SNP核心引物的确定及高通量检测方案的建立[J]. 作物学报, 2021, 47(4): 770-779. |
| Wang R, Shi L J, Tian H L, Yi H M, Yang Y, Ge J R, Fan Y M, Ren J, Wang L, Lu D L, Zhao J R, Wang F G. Identification of SNP core primer and establishment of high throughput detection scheme of purity identification in maize hybrids[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2021, 47(4): 770-779. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 周根友, 翟彩娇, 邓先亮, 张蛟, 张振良, 戴其根, 崔士友. 盐逆境对水稻产量、光合特性及品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 1(1): 146-154. |
| [2] | 朱欢欢, 陈洋, 万品俊, 王渭霞, 赖凤香, 傅强. 共生菌Arsenophonus、水稻品种和温度对褐飞虱黄绿绿僵菌发病率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(6): 643-651. |
| [3] | 胡继杰, 朱练峰, 钟楚, 林育炯, 张均华, 曹小闯, 禹盛苗, Allen Bohr JAMES, 金千瑜. 增氧模式对水稻光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(3): 278-287. |
| [4] | 杨奕, 孙一丁, 马继琼, 王炎炎, 许明辉. 云南地方稻种抗稻瘟病基因Pi-d3序列变异分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(1): 17-26. |
| [5] | 苏婷1 ,徐红星2 ,韩海亮1 ,杨亚军2 ,王桂跃1,* ,郑许松2 ,吕仲贤2,*. 褐飞虱胁迫对不同抗性水稻品种根际土壤酶活性和微生物含量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2014, 28(3): 322-326. |
| [6] | 董必琴1,2 ,杨亚军2,* ,徐红星2 ,郑许松2 ,K L HEONG3 ,吕仲贤2,*. 室内不接触农药的褐飞虱种群对农药的敏感性和对水稻品种的适应性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(4): 419-424. |
| [7] | 张羽1 ,张晓娟1 ,杨凤娇2 ,冯志峰3. 水稻稻瘟病抗性基因Pita的SNP检测方法[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(3): 325-328. |
| [8] | 陈夕军1, 2,刘晓维1,左示敏2,童蕴慧1,潘学彪2,*,徐敬友1,*. 水稻抗感纹枯病品种Ospgip1基因的表达特征[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(5): 629-632. |
| [9] | 于颢, 闫旭, 郭卫东, 辛德东*. 水稻microRNA 单核苷酸多态性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(5): 467-474. |
| [10] | 鄂志国1,王磊1,2,*. 中国水稻品种及其系谱数据库[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(5): 565-566. |
| [11] | 应兴华,徐霞,杨仕华,朱智伟,陈铭学,王磊,程本义,夏俊辉. 水稻籽粒农药残留的品种间差异性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(2): 227-230 . |
| [12] | 盛仙俏,张发成,徐红星,郑许松,陈桂华,吕仲贤,. 水稻品种(组合)对褐飞虱抗性的田间表现 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2010, 24(5): 535-538 . |
| [13] | 王保菊徐红星,郑许松,傅强,吕仲贤,. 温度对水稻抗褐飞虱特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2010, 24(4): 443-446 . |
| [14] | 徐红星,张珏锋,郑许松,俞晓平,吕仲贤. 施氮对白背飞虱在水稻上适应性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(2): 219-219~222 . |
| [15] | 陈 峰傅 强罗 举,赖凤香,桂连友,. 苗期抗性不同的水稻品种成株期对褐飞虱的抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(2): 201-201~206 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||