
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (5): 690-702.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240720
尤赛雅1, 王新雅1, 秦碧蓉2, 蔡汶延1,3, 朱练峰1, 孔亚丽1, 朱春权1, 田文昊1, 张均华1, 金千瑜1, 曹小闯1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-29
修回日期:2024-12-18
出版日期:2025-09-10
发布日期:2025-09-10
通讯作者:
*email: caoxiaochuang@126.com基金资助:
YOU Saiya1, WANG Xinya1, QIN Birong2, CAI Wenyan1,3, ZHU Lianfeng1, KONG Yali1, ZHU Chunquan1, TIAN Wenhao1, ZHANG Junhua1, JIN Qianyu1, CAO Xiaochuang1,*( )
)
Received:2024-07-29
Revised:2024-12-18
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2025-09-10
Contact:
*email: caoxiaochuang@126.com摘要:
【目的】通过评价不同外源有机物料在新复垦丘陵红壤和黄泥田上的培肥效果,构建基于土壤质量指数的最小数据集,以期为新复垦耕地地力培育提供理论与技术支撑。【方法】试验设7个处理:不施肥(No fertilizer,CK),常规施肥(Chemical fertilizers,NPK),常规施肥+2250 kg/hm2秸秆(NPK+2250 kg/hm2 秸秆,NPKS1),常规施肥+4500 kg/hm2秸秆(NPK+4500 kg/hm2 秸秆,NPKS2),常规施肥+3000 kg/hm2腐熟秸秆-畜禽粪便(NPK+3000 kg/hm2 腐熟秸秆-畜禽粪便,NPKSM),常规施肥+1773 kg/hm2木本泥炭(NPK+1773 kg/hm2 木本泥炭,NPKW1),常规施肥+3546 kg/hm2木本泥炭(NPK+3546 kg/hm2 木本泥炭,NPKW2),研究了不同培肥处理下的水稻产量、土壤团聚体结构、各形态碳氮含量、微生物生物量碳氮含量和土壤酶活性等指标,筛选土壤质量评价最小数据集,并对评价指标进行优化验证。【结果】1)与NPK处理相比,丘陵红壤中NPKSM处理显著提高了土壤大团聚体、平均重量直径、有机质含量、碳氮比以及土壤酶活性(如β-1,4-葡萄糖苷酶、β-1,4-N-乙酰基氨基葡萄糖苷酶)等指标;黄泥田中NPKS2处理显著提高了土壤易氧化有机碳、矿物结合态有机碳及微生物生物量碳氮含量,而NPKW2处理显著提高了土壤有机质、颗粒态有机碳、矿物结合态有机碳和可溶性有机碳含量。2)主成分分析结果表明,平均重量直径、铵态氮和矿物结合态有机碳可作为丘陵红壤土壤质量评价的最小数据集,而黄泥田则为土壤碳氮比、矿物结合态有机碳和β-1,4-N-乙酰基氨基葡萄糖苷酶活性。3)基于全量数据集和最小数据集的土壤质量指数评价结果表明,丘陵红壤中NPKSM以及黄泥田NPKS2、NPKW2处理土壤质量指数显著高于其他处理。4)回归分析结果表明,基于全量数据集和最小数据集构建的土壤质量指数在丘陵红壤和黄泥田中均呈极显著正相关,验证了最小数据集可作为有机培肥效果的评价指标。【结论】不同培肥模式对新复垦丘陵红壤和黄泥田培肥效果及其评价指标差异显著,腐熟秸秆-畜禽粪便可通过显著提高丘陵红壤有机质含量、易氧化有机碳含量、酶活性((BG、NAG))和团聚体稳定性性提高其土壤质量指数,而木本泥炭主要通过提高黄泥田有机质含量和矿物结合态有机碳含量提高其土壤质量。综合考虑,建议配施3000 kg/hm2腐熟秸秆-畜禽粪便、3546 kg/hm2木本泥炭作为区域新复垦丘陵红壤和黄泥田的适宜有机培肥模式。
尤赛雅, 王新雅, 秦碧蓉, 蔡汶延, 朱练峰, 孔亚丽, 朱春权, 田文昊, 张均华, 金千瑜, 曹小闯. 新复垦耕地不同有机物料培肥效果及其评价指标优化[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(5): 690-702.
YOU Saiya, WANG Xinya, QIN Birong, CAI Wenyan, ZHU Lianfeng, KONG Yali, ZHU Chunquan, TIAN Wenhao, ZHANG Junhua, JIN Qianyu, CAO Xiaochuang. Fertilization Effects of Different Exogenous Organic Materials in Newly Reclaimed Cultivated Land and Its Optimization of Evaluation Indicators[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(5): 690-702.
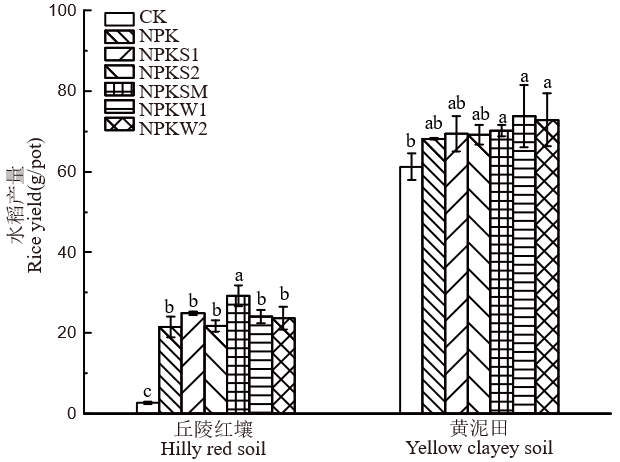
图1 不同有机培肥模式下水稻产量 CK: 不施肥; NPK: 常规施肥; NPKS1: 常规施肥+2250 kg/hm2秸秆; NPKS2: 常规施肥+4500 kg/hm2秸秆; NPKSM: 常规施肥+3000 kg/hm2腐熟秸秆-畜禽粪便; NPKW1: 常规施肥+1773 kg/hm2木本泥炭; NPKW2: 常规施肥+3546 kg/hm2木本泥炭。图中数值均为平均值±标准偏差(n=3); 柱上标以不同小写字母表示在0.05水平差异显著。下同。
Fig. 1. Rice yield in different organic fertilization regimes CK, No fertilizer; NPK, Chemical fertilizers; NPKS1, NPK+2250 kg/hm2 straw; NPKS2, NPK+4500 kg/hm2 straw; NPKSM, NPK+3000 kg/hm2 decomposed straw-livestock manure; NPKW1, NPK+1773 kg/hm2 woody peat; NPKW2, NPK+3546 kg/hm2 woody peat. Values are mean ± standard deviation (n=3). Different letters indicateindicate significant difference at 0.05 level. The same below.
| 土壤 Soil | 处理 Treatment | 土壤团聚体构成 Composition of soil aggregates(%) | MWD(mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >2.000 mm | 0.250~2.000 mm | 大团聚体R0.25 | 0.053~0.250 mm | <0.053 mm | |||
| 丘陵红壤 Hilly red soil | CK | 7.80±1.56 b | 27.78±0.64 bc | 36.38±1.81 bc | 11.02±0.66 c | 47.84±2.01 ab | 0.50±0.04 c |
| NPK | 7.51±0.97 b | 27.17±0.50 c | 34.68±0.79 c | 10.58±0.56 c | 50.91±1.32 a | 0.50±0.02 c | |
| NPKS1 | 9.29±0.47 ab | 29.78±1.70 ab | 41.21±2.64 a | 18.14±2.08 a | 35.57±1.48 d | 0.56±0.03 b | |
| NPKS2 | 11.55±2.53 a | 26.73±1.07 c | 37.92±0.90 b | 17.88±2.22 a | 39.17±0.65 c | 0.58±0.01 ab | |
| NPKSM | 10.49±0.55 a | 31.65±2.84 a | 42.15±2.36 a | 17.35±1.62 a | 37.71±0.76 cd | 0.61±0.03 a | |
| NPKW1 | 10.36±0.23 a | 26.85±1.07 c | 36.90±0.80 bc | 13.39±0.10 b | 39.76±0.23 c | 0.55±0.01 b | |
| NPKW2 | 10.44±1.91 a | 26.60±0.88 c | 36.86±1.37 bc | 9.83±0.59 c | 45.42±2.71 b | 0.57±0.03 ab | |
| 黄泥田 Yellow clayey soil | CK | 4.98±2.41 a | 43.99±2.34 a | 49.62±0.36 a | 22.49±2.59 a | 26.84±2.59 a | 0.65±0.02 ab |
| NPK | 5.40±2.16 a | 44.78±2.74 a | 50.71±0.61 a | 20.78±0.75 a | 24.17±2.92 ab | 0.65±0.01 ab | |
| NPKS1 | 6.08±1.39 a | 41.96±1.74 a | 48.41±3.18 a | 23.49±2.41 a | 24.50±2.51 ab | 0.65±0.05 ab | |
| NPKS2 | 6.18±1.87 a | 45.43±3.78 a | 49.76±1.90 a | 21.98±2.59 a | 22.82±1.65 b | 0.70±0.04 a | |
| NPKSM | 4.67±1.50 a | 43.34±2.39 a | 49.14±3.07 a | 23.73±5.28 a | 24.26±2.50 ab | 0.61±0.01 b | |
| NPKW1 | 5.11±1.38 a | 45.40±2.42 a | 51.56±0.86 a | 22.67±1.65 a | 23.39±1.80 ab | 0.67±0.02 a | |
| NPKW2 | 6.98±2.42 a | 44.89±2.00 a | 51.23±0.88 a | 22.94±1.11 a | 22.63±1.36 b | 0.70±0.04 a | |
表1 不同有机培肥模式下土壤团聚体结构
Table 1. Soil aggregate structure in the different organic fertilization regimes
| 土壤 Soil | 处理 Treatment | 土壤团聚体构成 Composition of soil aggregates(%) | MWD(mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >2.000 mm | 0.250~2.000 mm | 大团聚体R0.25 | 0.053~0.250 mm | <0.053 mm | |||
| 丘陵红壤 Hilly red soil | CK | 7.80±1.56 b | 27.78±0.64 bc | 36.38±1.81 bc | 11.02±0.66 c | 47.84±2.01 ab | 0.50±0.04 c |
| NPK | 7.51±0.97 b | 27.17±0.50 c | 34.68±0.79 c | 10.58±0.56 c | 50.91±1.32 a | 0.50±0.02 c | |
| NPKS1 | 9.29±0.47 ab | 29.78±1.70 ab | 41.21±2.64 a | 18.14±2.08 a | 35.57±1.48 d | 0.56±0.03 b | |
| NPKS2 | 11.55±2.53 a | 26.73±1.07 c | 37.92±0.90 b | 17.88±2.22 a | 39.17±0.65 c | 0.58±0.01 ab | |
| NPKSM | 10.49±0.55 a | 31.65±2.84 a | 42.15±2.36 a | 17.35±1.62 a | 37.71±0.76 cd | 0.61±0.03 a | |
| NPKW1 | 10.36±0.23 a | 26.85±1.07 c | 36.90±0.80 bc | 13.39±0.10 b | 39.76±0.23 c | 0.55±0.01 b | |
| NPKW2 | 10.44±1.91 a | 26.60±0.88 c | 36.86±1.37 bc | 9.83±0.59 c | 45.42±2.71 b | 0.57±0.03 ab | |
| 黄泥田 Yellow clayey soil | CK | 4.98±2.41 a | 43.99±2.34 a | 49.62±0.36 a | 22.49±2.59 a | 26.84±2.59 a | 0.65±0.02 ab |
| NPK | 5.40±2.16 a | 44.78±2.74 a | 50.71±0.61 a | 20.78±0.75 a | 24.17±2.92 ab | 0.65±0.01 ab | |
| NPKS1 | 6.08±1.39 a | 41.96±1.74 a | 48.41±3.18 a | 23.49±2.41 a | 24.50±2.51 ab | 0.65±0.05 ab | |
| NPKS2 | 6.18±1.87 a | 45.43±3.78 a | 49.76±1.90 a | 21.98±2.59 a | 22.82±1.65 b | 0.70±0.04 a | |
| NPKSM | 4.67±1.50 a | 43.34±2.39 a | 49.14±3.07 a | 23.73±5.28 a | 24.26±2.50 ab | 0.61±0.01 b | |
| NPKW1 | 5.11±1.38 a | 45.40±2.42 a | 51.56±0.86 a | 22.67±1.65 a | 23.39±1.80 ab | 0.67±0.02 a | |
| NPKW2 | 6.98±2.42 a | 44.89±2.00 a | 51.23±0.88 a | 22.94±1.11 a | 22.63±1.36 b | 0.70±0.04 a | |
| 土壤 Soil | 处理 Treatment | SOM (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | C/N | NH4+-N (mg/kg) | NO3−-N (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丘陵红壤 Hilly red soil | CK | 4.06±0.39 de | 0.18±0.01 c | 15.06±1.25 bcd | 4.26±0.12 d | 3.55±1.01 a |
| NPK | 3.25±0.52 e | 0.18±0.02 c | 12.04±2.42 d | 5.33±0.19 cd | 1.80±0.18 bc | |
| NPKS1 | 5.06±0.91 cd | 0.18±0.02 c | 19.05±2.71 ab | 4.89±0.24 d | 2.68±0.04 b | |
| NPKS2 | 5.60±0.54 bc | 0.21±0.02 bc | 17.11±1.58 abc | 6.02±0.90 c | 2.12±0.26 bc | |
| NPKSM | 6.46±0.15 ab | 0.18±0.02 c | 20.92±2.95 a | 4.82±0.79 d | 2.36±0.56 b | |
| NPKW1 | 5.12±0.72 cd | 0.22±0.02 b | 13.26±2.54 cd | 11.08±0.79 a | 2.03±0.36 bc | |
| NPKW2 | 6.69±0.53 a | 0.26±0.02 a | 17.04±2.14 abc | 7.65±0.32 b | 1.24±0.14 c | |
| 黄泥田 Yellow clayey soil | CK | 21.36±1.83 c | 1.05±0.06 b | 13.66±0.36 bc | 13.17±0.54 a | 3.46±0.40 a |
| NPK | 23.09±1.25 bc | 0.89±0.08 b | 14.63±1.32 ab | 9.17±0.32 c | 2.41±0.30 b | |
| NPKS1 | 22.29±0.35 bc | 1.05±0.18 b | 12.89±1.40 c | 12.37±2.21 ab | 1.60±0.39 cd | |
| NPKS2 | 23.79±0.92 ab | 1.05±0.02 b | 13.65±0.73 bc | 8.34±1.53 c | 2.45±0.42 b | |
| NPKSM | 22.91±0.75 bc | 1.28±0.04 a | 10.14±0.83 d | 12.96±2.59 a | 2.26±0.25 bc | |
| NPKW1 | 22.66±1.07 bc | 1.36±0.06 a | 9.64±0.40 d | 9.98±1.22 bc | 1.57±0.46 d | |
| NPKW2 | 25.45±0.40 a | 0.89±0.08 b | 15.48±0.46 a | 8.74±0.47 c | 1.85±0.27 bcd | |
| 土壤 Soil | 处理 Treatment | EOC (mg/g) | POC (mg/kg) | MAOC (mg/kg) | DOC (mg/kg) | DON (mg/kg) |
| 丘陵红壤 Hilly red soil | CK | 0.17±0.02 c | 1.19±0.24 a | 1.04±0.08 c | 60.23±1.97 d | 4.65±0.20 b |
| NPK | 0.11±0.02 d | 0.86±0.14 a | 1.63±0.14 a | 63.57±5.62 cd | 4.94±0.39 b | |
| NPKS1 | 0.22±0.02 c | 1.36±0.36 a | 1.46±0.07 ab | 68.71±1.53 bcd | 5.73±0.24 a | |
| NPKS2 | 0.21±0.04 c | 0.84±0.03 a | 1.62±0.07 a | 77.94±1.38 a | 5.90±0.11 a | |
| NPKSM | 0.71±0.02 a | 0.74±0.15 a | 1.56±0.16 a | 70.16±3.66 abc | 5.84±0.64 a | |
| NPKW1 | 0.48±0.02 b | 1.37±0.22 a | 1.39±0.19 ab | 76.36±9.07 ab | 5.67±0.47 a | |
| NPKW2 | 0.67±0.05 a | 1.21±1.06 a | 1.26±0.27 bc | 60.63±3.36 d | 4.52±0.16 b | |
| 黄泥田 Yellow clayey soil | CK | 1.55±0.25 d | 1.31±0.13 b | 4.29±0.11 c | 173.13±41.38 ab | 21.00±3.24 ab |
| NPK | 2.07±0.43 cd | 1.26±0.08 b | 4.58±0.27 c | 158.43±16.13 b | 20.53±1.14 abc | |
| NPKS1 | 2.79±0.25 ab | 1.58±0.13 ab | 4.50±0.14 c | 146.22±8.43 b | 18.20±1.77 bc | |
| NPKS2 | 2.72±0.10 ab | 1.44±0.18 ab | 5.44±0.25 ab | 146.81±9.15 b | 17.19±1.14 c | |
| NPKSM | 3.04±0.32 a | 1.35±0.20 ab | 5.61±0.22 a | 180.83±20.55 ab | 21.01±2.64 ab | |
| NPKW1 | 2.15±0.25 c | 1.51±0.18 ab | 5.33±0.16 ab | 178.95±2.53 ab | 20.32±0.79 abc | |
| NPKW2 | 2.37±0.39 bc | 1.75±0.41 a | 5.16±0.13 b | 205.23±6.69 a | 22.57±1.09 a |
表2 不同有机培肥模式下土壤各形态碳氮含量
Table 2. Contents of different types of soil carbon and nitrogen in the different organic fertilization regimes
| 土壤 Soil | 处理 Treatment | SOM (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | C/N | NH4+-N (mg/kg) | NO3−-N (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丘陵红壤 Hilly red soil | CK | 4.06±0.39 de | 0.18±0.01 c | 15.06±1.25 bcd | 4.26±0.12 d | 3.55±1.01 a |
| NPK | 3.25±0.52 e | 0.18±0.02 c | 12.04±2.42 d | 5.33±0.19 cd | 1.80±0.18 bc | |
| NPKS1 | 5.06±0.91 cd | 0.18±0.02 c | 19.05±2.71 ab | 4.89±0.24 d | 2.68±0.04 b | |
| NPKS2 | 5.60±0.54 bc | 0.21±0.02 bc | 17.11±1.58 abc | 6.02±0.90 c | 2.12±0.26 bc | |
| NPKSM | 6.46±0.15 ab | 0.18±0.02 c | 20.92±2.95 a | 4.82±0.79 d | 2.36±0.56 b | |
| NPKW1 | 5.12±0.72 cd | 0.22±0.02 b | 13.26±2.54 cd | 11.08±0.79 a | 2.03±0.36 bc | |
| NPKW2 | 6.69±0.53 a | 0.26±0.02 a | 17.04±2.14 abc | 7.65±0.32 b | 1.24±0.14 c | |
| 黄泥田 Yellow clayey soil | CK | 21.36±1.83 c | 1.05±0.06 b | 13.66±0.36 bc | 13.17±0.54 a | 3.46±0.40 a |
| NPK | 23.09±1.25 bc | 0.89±0.08 b | 14.63±1.32 ab | 9.17±0.32 c | 2.41±0.30 b | |
| NPKS1 | 22.29±0.35 bc | 1.05±0.18 b | 12.89±1.40 c | 12.37±2.21 ab | 1.60±0.39 cd | |
| NPKS2 | 23.79±0.92 ab | 1.05±0.02 b | 13.65±0.73 bc | 8.34±1.53 c | 2.45±0.42 b | |
| NPKSM | 22.91±0.75 bc | 1.28±0.04 a | 10.14±0.83 d | 12.96±2.59 a | 2.26±0.25 bc | |
| NPKW1 | 22.66±1.07 bc | 1.36±0.06 a | 9.64±0.40 d | 9.98±1.22 bc | 1.57±0.46 d | |
| NPKW2 | 25.45±0.40 a | 0.89±0.08 b | 15.48±0.46 a | 8.74±0.47 c | 1.85±0.27 bcd | |
| 土壤 Soil | 处理 Treatment | EOC (mg/g) | POC (mg/kg) | MAOC (mg/kg) | DOC (mg/kg) | DON (mg/kg) |
| 丘陵红壤 Hilly red soil | CK | 0.17±0.02 c | 1.19±0.24 a | 1.04±0.08 c | 60.23±1.97 d | 4.65±0.20 b |
| NPK | 0.11±0.02 d | 0.86±0.14 a | 1.63±0.14 a | 63.57±5.62 cd | 4.94±0.39 b | |
| NPKS1 | 0.22±0.02 c | 1.36±0.36 a | 1.46±0.07 ab | 68.71±1.53 bcd | 5.73±0.24 a | |
| NPKS2 | 0.21±0.04 c | 0.84±0.03 a | 1.62±0.07 a | 77.94±1.38 a | 5.90±0.11 a | |
| NPKSM | 0.71±0.02 a | 0.74±0.15 a | 1.56±0.16 a | 70.16±3.66 abc | 5.84±0.64 a | |
| NPKW1 | 0.48±0.02 b | 1.37±0.22 a | 1.39±0.19 ab | 76.36±9.07 ab | 5.67±0.47 a | |
| NPKW2 | 0.67±0.05 a | 1.21±1.06 a | 1.26±0.27 bc | 60.63±3.36 d | 4.52±0.16 b | |
| 黄泥田 Yellow clayey soil | CK | 1.55±0.25 d | 1.31±0.13 b | 4.29±0.11 c | 173.13±41.38 ab | 21.00±3.24 ab |
| NPK | 2.07±0.43 cd | 1.26±0.08 b | 4.58±0.27 c | 158.43±16.13 b | 20.53±1.14 abc | |
| NPKS1 | 2.79±0.25 ab | 1.58±0.13 ab | 4.50±0.14 c | 146.22±8.43 b | 18.20±1.77 bc | |
| NPKS2 | 2.72±0.10 ab | 1.44±0.18 ab | 5.44±0.25 ab | 146.81±9.15 b | 17.19±1.14 c | |
| NPKSM | 3.04±0.32 a | 1.35±0.20 ab | 5.61±0.22 a | 180.83±20.55 ab | 21.01±2.64 ab | |
| NPKW1 | 2.15±0.25 c | 1.51±0.18 ab | 5.33±0.16 ab | 178.95±2.53 ab | 20.32±0.79 abc | |
| NPKW2 | 2.37±0.39 bc | 1.75±0.41 a | 5.16±0.13 b | 205.23±6.69 a | 22.57±1.09 a |
| 土壤 Soil | 处理 Treatment | MBC(mg/kg) | MBN(mg/kg) | BG(nmol·h−1g−1) | LAP( nmol·h−1g−1) | NAG( nmol·h−1g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丘陵红壤 Hilly red soil | CK | 8.52±0.37 c | 0.42±0.20 c | 2.13±0.34 e | 0.24±0.02 a | 0.61±0.04 d |
| NPK | 31.97±0.49 a | 1.35±0.29 b | 1.35±0.11 e | 0.27±0.03 a | 0.70±0.02 d | |
| NPKS1 | 28.73±3.03 a | 2.15±0.58 a | 1.28±0.12 e | 0.17±0.01 b | 0.81±0.10 d | |
| NPKS2 | 14.97±6.04 bc | 0.93±0.34 bc | 34.35±2.13 b | 0.14±0.02 bc | 7.15±0.25 b | |
| NPKSM | 24.23±5.79 ab | 0.80±0.09 bc | 45.60±1.75 a | 0.07±0.01 d | 8.74±1.44 a | |
| NPKW1 | 20.16±3.69 ab | 2.25±0.80 a | 11.86±1.96 c | 0.08±0.02 d | 3.08±0.66 c | |
| NPKW2 | 30.45±13.25 a | 1.22±0.43 bc | 7.22±1.18 d | 0.13±0.03 c | 1.35±0.07 d | |
| 黄泥田 Yellow clayey soil | CK | 101.01±5.36 c | 3.96±0.83 b | 64.76±6.90 b | 2.17±0.08 a | 110.77±3.34 b |
| NPK | 80.83±4.35 d | 3.20±0.47 b | 58.58±8.07 bc | 1.92±0.22 a | 123.18±5.44 b | |
| NPKS1 | 126.10±2.46 a | 6.80±0.17 a | 110.33±22.32 a | 2.07±0.32 a | 162.00±24.44 a | |
| NPKS2 | 115.18±13.85 ab | 6.03±0.72 a | 67.45±1.20 b | 2.21±0.39 a | 105.03±0.89 b | |
| NPKSM | 108.98±2.87 bc | 7.11±0.32 a | 53.36±2.33 bc | 1.98±0.32 a | 109.02±10.56 b | |
| NPKW1 | 80.36±5.93 d | 4.59±0.37 b | 57.53±3.31 bc | 2.19±0.59 a | 125.58±5.87 b | |
| NPKW2 | 68.28±8.71 d | 3.95±1.54 b | 45.90±2.62 c | 2.34±0.56 a | 124.31±4.45 b |
表3 不同有机培肥模式下土壤微生物生物量碳氮及酶活性
Table 3. Soil microbial biomassbiomass carbon and nitrogen, and enzyme activities in the different organic fertilization regimes
| 土壤 Soil | 处理 Treatment | MBC(mg/kg) | MBN(mg/kg) | BG(nmol·h−1g−1) | LAP( nmol·h−1g−1) | NAG( nmol·h−1g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丘陵红壤 Hilly red soil | CK | 8.52±0.37 c | 0.42±0.20 c | 2.13±0.34 e | 0.24±0.02 a | 0.61±0.04 d |
| NPK | 31.97±0.49 a | 1.35±0.29 b | 1.35±0.11 e | 0.27±0.03 a | 0.70±0.02 d | |
| NPKS1 | 28.73±3.03 a | 2.15±0.58 a | 1.28±0.12 e | 0.17±0.01 b | 0.81±0.10 d | |
| NPKS2 | 14.97±6.04 bc | 0.93±0.34 bc | 34.35±2.13 b | 0.14±0.02 bc | 7.15±0.25 b | |
| NPKSM | 24.23±5.79 ab | 0.80±0.09 bc | 45.60±1.75 a | 0.07±0.01 d | 8.74±1.44 a | |
| NPKW1 | 20.16±3.69 ab | 2.25±0.80 a | 11.86±1.96 c | 0.08±0.02 d | 3.08±0.66 c | |
| NPKW2 | 30.45±13.25 a | 1.22±0.43 bc | 7.22±1.18 d | 0.13±0.03 c | 1.35±0.07 d | |
| 黄泥田 Yellow clayey soil | CK | 101.01±5.36 c | 3.96±0.83 b | 64.76±6.90 b | 2.17±0.08 a | 110.77±3.34 b |
| NPK | 80.83±4.35 d | 3.20±0.47 b | 58.58±8.07 bc | 1.92±0.22 a | 123.18±5.44 b | |
| NPKS1 | 126.10±2.46 a | 6.80±0.17 a | 110.33±22.32 a | 2.07±0.32 a | 162.00±24.44 a | |
| NPKS2 | 115.18±13.85 ab | 6.03±0.72 a | 67.45±1.20 b | 2.21±0.39 a | 105.03±0.89 b | |
| NPKSM | 108.98±2.87 bc | 7.11±0.32 a | 53.36±2.33 bc | 1.98±0.32 a | 109.02±10.56 b | |
| NPKW1 | 80.36±5.93 d | 4.59±0.37 b | 57.53±3.31 bc | 2.19±0.59 a | 125.58±5.87 b | |
| NPKW2 | 68.28±8.71 d | 3.95±1.54 b | 45.90±2.62 c | 2.34±0.56 a | 124.31±4.45 b |
| 因子 Factor | 主成分Principal component | 分组 Grouping | Norm值 Norm value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 5.911 | 2.566 | 2.010 | 1.594 | 1.188 | ||
| 方差贡献率Variance contribution rate(%) | 39.410 | 17.104 | 13.397 | 10.629 | 7.920 | ||
| 累积贡献率Cumulative contribution rate(%) | 39.410 | 56.514 | 69.911 | 80.540 | 88.459 | ||
| 因子载荷Factor loading | |||||||
| R0.25 | 0.678 | −0.343 | −0.165 | 0.345 | 0.430 | 1 | 1.866 |
| MWD | 0.927 | 0.071 | −0.172 | 0.065 | 0.007 | 1 | 2.271 |
| SOM | 0.767 | 0.216 | −0.440 | −0.128 | 0.017 | 1 | 2.003 |
| C/N | 0.625 | −0.408 | −0.402 | 0.296 | 0.158 | 1 | 1.798 |
| NH4+-N | 0.189 | 0.761 | 0.244 | −0.420 | 0.139 | 2 | 1.457 |
| NO3--N | −0.262 | -0.689 | 0.117 | −0.101 | 0.560 | 2 | 1.428 |
| EOC | 0.701 | 0.333 | −0.498 | −0.205 | 0.020 | 1 | 1.937 |
| MAOC | 0.400 | 0.031 | 0.415 | 0.626 | −0.381 | 3 | 1.447 |
| DOC | 0.513 | 0.027 | 0.743 | −0.248 | 0.020 | 1 | 1.663 |
| DON | 0.621 | −0.149 | 0.622 | 0.187 | 0.210 | 1 | 1.794 |
| MBC | 0.088 | 0.565 | −0.151 | 0.654 | −0.077 | 3 | 1.265 |
| MBN | 0.043 | 0.657 | 0.300 | 0.316 | 0.490 | 2 | 1.321 |
| BG | 0.844 | −0.337 | 0.121 | −0.155 | −0.291 | 1 | 2.162 |
| LAP | −0.879 | −0.275 | 0.007 | 0.283 | −0.205 | 1 | 2.223 |
| NAG | 0.845 | −0.320 | 0.195 | −0.137 | −0.285 | 1 | 2.165 |
表4 丘陵红壤肥力指标主成分分析
Table 4. Principal component analysis of fertility index in the hilly red soil
| 因子 Factor | 主成分Principal component | 分组 Grouping | Norm值 Norm value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 5.911 | 2.566 | 2.010 | 1.594 | 1.188 | ||
| 方差贡献率Variance contribution rate(%) | 39.410 | 17.104 | 13.397 | 10.629 | 7.920 | ||
| 累积贡献率Cumulative contribution rate(%) | 39.410 | 56.514 | 69.911 | 80.540 | 88.459 | ||
| 因子载荷Factor loading | |||||||
| R0.25 | 0.678 | −0.343 | −0.165 | 0.345 | 0.430 | 1 | 1.866 |
| MWD | 0.927 | 0.071 | −0.172 | 0.065 | 0.007 | 1 | 2.271 |
| SOM | 0.767 | 0.216 | −0.440 | −0.128 | 0.017 | 1 | 2.003 |
| C/N | 0.625 | −0.408 | −0.402 | 0.296 | 0.158 | 1 | 1.798 |
| NH4+-N | 0.189 | 0.761 | 0.244 | −0.420 | 0.139 | 2 | 1.457 |
| NO3--N | −0.262 | -0.689 | 0.117 | −0.101 | 0.560 | 2 | 1.428 |
| EOC | 0.701 | 0.333 | −0.498 | −0.205 | 0.020 | 1 | 1.937 |
| MAOC | 0.400 | 0.031 | 0.415 | 0.626 | −0.381 | 3 | 1.447 |
| DOC | 0.513 | 0.027 | 0.743 | −0.248 | 0.020 | 1 | 1.663 |
| DON | 0.621 | −0.149 | 0.622 | 0.187 | 0.210 | 1 | 1.794 |
| MBC | 0.088 | 0.565 | −0.151 | 0.654 | −0.077 | 3 | 1.265 |
| MBN | 0.043 | 0.657 | 0.300 | 0.316 | 0.490 | 2 | 1.321 |
| BG | 0.844 | −0.337 | 0.121 | −0.155 | −0.291 | 1 | 2.162 |
| LAP | −0.879 | −0.275 | 0.007 | 0.283 | −0.205 | 1 | 2.223 |
| NAG | 0.845 | −0.320 | 0.195 | −0.137 | −0.285 | 1 | 2.165 |
| 因子 Factor | 主成分Principal component | 分组 Grouping | Norm值 Norm value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 2.720 | 2.013 | 1.741 | 1.212 | ||
| 方差贡献率Variance contribution rate(%) | 30.221 | 22.364 | 19.340 | 13.465 | ||
| 累积贡献率Cumulative contribution rate(%) | 30.221 | 52.585 | 71.925 | 85.390 | ||
| 因子载荷Factor loading | ||||||
| SOM | −0.013 | 0.696 | 0.563 | 0.209 | 2 | 1.257 |
| TN | 0.804 | 0.003 | −0.476 | −0.227 | 1 | 1.488 |
| C/N | −0.830 | −0.013 | 0.457 | 0.201 | 1 | 1.512 |
| NO3--N | −0.520 | −0.176 | −0.571 | 0.467 | 1 | 1.277 |
| EOC | 0.678 | 0.056 | 0.518 | 0.349 | 1 | 1.367 |
| MAOC | 0.643 | 0.594 | −0.078 | 0.289 | 2 | 1.395 |
| DON | −0.278 | 0.645 | −0.279 | −0.376 | 2 | 1.164 |
| MBC | 0.379 | −0.710 | 0.037 | 0.403 | 2 | 1.267 |
| NAG | 0.144 | −0.470 | 0.556 | −0.591 | 3 | 1.209 |
表5 黄泥田肥力指标主成分分析
Table 5. Principal component analysis of fertility index in the yellow clayey soil
| 因子 Factor | 主成分Principal component | 分组 Grouping | Norm值 Norm value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 2.720 | 2.013 | 1.741 | 1.212 | ||
| 方差贡献率Variance contribution rate(%) | 30.221 | 22.364 | 19.340 | 13.465 | ||
| 累积贡献率Cumulative contribution rate(%) | 30.221 | 52.585 | 71.925 | 85.390 | ||
| 因子载荷Factor loading | ||||||
| SOM | −0.013 | 0.696 | 0.563 | 0.209 | 2 | 1.257 |
| TN | 0.804 | 0.003 | −0.476 | −0.227 | 1 | 1.488 |
| C/N | −0.830 | −0.013 | 0.457 | 0.201 | 1 | 1.512 |
| NO3--N | −0.520 | −0.176 | −0.571 | 0.467 | 1 | 1.277 |
| EOC | 0.678 | 0.056 | 0.518 | 0.349 | 1 | 1.367 |
| MAOC | 0.643 | 0.594 | −0.078 | 0.289 | 2 | 1.395 |
| DON | −0.278 | 0.645 | −0.279 | −0.376 | 2 | 1.164 |
| MBC | 0.379 | −0.710 | 0.037 | 0.403 | 2 | 1.267 |
| NAG | 0.144 | −0.470 | 0.556 | −0.591 | 3 | 1.209 |
| [1] | 陈硕桐, 夏鑫, 丁元君, 冯潇, 刘晓雨, Marios Drosos, 李恋卿, 潘根兴. 不同形态秸秆还田下乌栅土耕层土壤有机质含量与组成变化[J]. 中国农业科学, 2023, 56(13): 2518-2529. |
| Chen S T, Xia X, Ding Y J, Feng X, Liu X Y, Drosos M, Li L Q, Pan G X. Changes in topsoil organic matter content and composition of a gleyic stagnic anthrosol amended with maize residue in different forms from the Tai Lake Plain, China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2023, 56(13): 2518-2529. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Wang J, Zhai B, Shi D, Chen A, Liu C. How does bio-organic fertilizer combined with biochar affect Chinese small cabbage’s growth and quality on newly reclaimed land?[J]. Plants, 2024, 13(5): 598. |
| [3] | 王艺霖, 梁尧, 蔡红光, 徐康宁, 张水梅, 张畅, 范围, 袁静超, 刘剑钊, 任军. 基于最小数据集的不同有机物料还田黑土土壤质量评价[J]. 土壤通报, 2024, 55(1): 68-75. |
| Wang Y L, Liang Y, Cai H G, Xu K N, Zhang S M, Zhang C, Fan W, Yuan J C, Liu J Z, Ren J. Soil quality evaluation of black soil under different returning treatments of organic materials based on minimum data set[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2024, 55(1): 68-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 徐秋桐, 孔樟良, 章明奎. 不同有机废弃物改良新复垦耕地的综合效果评价[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(2): 567-576. |
| Xu Q T, Kong Z L, Zhang M K. Comprehensive evaluation of improving effects of different organic wastes on a newly reclaimed cultivated land[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(2): 567-576. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Liu B, Xia H, Jiang C, Riaz M, Yang L, Chen Y, Fan X, Xia X. 14 year applications of chemical fertilizers and crop straw effects on soil labile organic carbon fractions, enzyme activities and microbial community in rice-wheat rotation of middle China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 841: 156608. |
| [6] | 陈美淇, 马垒, 赵炳梓, 范树印, 谭钧, 鞠振山, 朱锦尉, 徐国华, 王淑媛, 徐基胜, 张佳宝. 木本泥炭对红黄壤性水田土壤有机质提升和细菌群落组成的影响[J]. 土壤, 2020, 52(2): 279-286. |
| Chen M Q, Ma L, Zhao B Z, Fan S Y, Tan J, Ju Z S, Zhu J W, Xu G H, Wang S Y, Xu J S, Zhang J B. Effects of woody peat on quick improvement of soil organic matter and bacterial community composition in newly reclaimed red-yellow paddy soils[J]. Soils, 2020, 52(2): 279-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 宓文海. 中低产黄泥田培肥模式与氮素高效利用研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017. |
| Mi W H. Reaearch on the fertilization pattern and nitrogen use efficiency for middle and low productive yellow clayey paddy soil[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Shi C, Zhang Q, Yu B. Higher improvement in soil health by animal-sourced than plant-sourced organic materials through optimized substitution[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2024, 363: 108875. |
| [9] | Ding F, Sun W, Huang Y, Hu X. Larger Q10 of carbon decomposition in finer soil particles does not bring long-lasting dependence of Q10 on soil texture[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2018, 69(2): 336-347. |
| [10] | Poirier V, Angers D A, Whalen J K. Formation of millimetric-scale aggregates and associated retention of 13C-15N-labelled residues are greater in subsoil than topsoil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2014, 75: 45-53. |
| [11] | Lehmann J, Bossio D A, Kögel-Knabner I, Rillig M C. The concept and future prospects of soil health[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2020, 1(10): 544-553. |
| [12] | 范庆锋, 张玉龙, 张玉玲, 虞娜. 不同灌溉方式对设施土壤交换性盐基组成及比例的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(1): 264-268. |
| Fan Q F, Zhang Y L, Zhang Y L, Yu N. Effects of irrigation mode on composition and ratios of soil exchangeable base in greenhouse[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 32(1): 264-268. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Zhou L, Ding M. Soil microbial characteristics as bioindicators of soil health[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2007, 15(2): 162. |
| [14] | 郑铭洁, 姜铭北, 章明奎, 严建立, 王道泽. 浙江省新垦耕地土壤熟化指标研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2020, 32(10): 1834-1840. |
| Zheng M J, Jiang M B, Zhang M K, Yan J L, Wang D Z. Study on soil maturity index of newly cultivated land in Zhejiang Province[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2020, 32(10): 1834-1840. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 张江周, 李奕赞, 李颖, 张俊伶, 张福锁. 土壤健康指标体系与评价方法研究进展[J]. 土壤学报, 2022, 59(3): 603-616. |
| Zhang J Z, Li Y Z, Li Y, Zhang J L, Zhang F S. Advances in the indicators system and evaluation approaches of soil health[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2022, 59(3): 603-616. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | Bünemann E K, Bongiorno G, Bai Z, Creamer R E, de Deyn G, de Goede R, Fleskens L, Geissen V, Kuyper T W, Mäder P, Pulleman M, Sukkel W, van Groenigen J W, Brussaard L. Soil quality: A critical review[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2018, 120: 105-125. |
| [17] | 金慧芳, 史东梅, 陈正发, 刘益军, 娄义宝, 杨旭. 基于聚类及PCA分析的红壤坡耕地耕层土壤质量评价指标[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(7): 155-164. |
| Jin H F, Shi D M, Chen Z F, Liu Y J, Lou Y B, Yang X. Evaluation indicators of cultivated layer soil quality for red soil slope farmland based on cluster and PCA analysis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(7): 155-164. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Hyun J, Kim Y J, Kim A, Plante A F, Yoo G. Ecosystem services-based soil quality index tailored to the metropolitan environment for soil assessment and management[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 820: 153301. |
| [19] | van Leeuwen J P, Creamer R E, Cluzeau D, Debeljak M, Gatti F, Henriksen C B, Kuzmanovski V, Menta C, Pérès G, Picaud C, Saby N P A, Trajanov A, Trinsoutrot-Gattin I, Visioli G, Rutgers M. Modeling of soil functions for assessing soil quality: Soil biodiversity and habitat provisioning[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2019, 7: 113. |
| [20] | Six J, Paustian K. Aggregate-associated soil organic matter as an ecosystem property and a measurement tool[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2014, 68: A4-A9. |
| [21] | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析: 第3版[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. |
| Bao S D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis: 3rd edn[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 毛兵, 曾悦, 赖彩婷, 杨艳, 周春宏, 李卓亭, 徐强胜, 李廷化. 减氮施肥对甘蔗生物量及土壤硝态氮和铵态氮的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2023, 42(11): 2604-2612. |
| Mao B, Zeng Y, Lai C T, Yang Y, Zhou C H, Li Z T, Xu S Q, Li T H. Effects of nitrogen reduction fertilization on sugarcane biomass and the concentrations of soil nitrate and ammonium nitrogen[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2023, 42(11): 2604-2612. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Blair G J, Lefroy R D, Lisle L. Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems[J]. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 1995, 46(7): 1459-1466. |
| [24] | Cepáková Š, Tošner Z, Frouz J. The effect of tree species on seasonal fluctuations in water-soluble and hot water-extractable organic matter at post-mining sites[J]. Geoderma, 2016, 275: 19-27. |
| [25] | Cambardella C A, Elliott E T. Particulate soil organic-matter changes across a grassland cultivation sequence[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1992, 56(3): 777-783. |
| [26] | Marx M C, Wood M, Jarvis S C. A microplate fluorimetric assay for the study of enzyme diversity in soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2001, 33(12-13): 1633-1640. |
| [27] | 张文学, 王少先, 刘增兵, 唐先干, 熊丽, 夏文建, 王萍, 袁福生, 孙刚, 李祖章, 刘光荣. 基于土壤肥力质量综合指数评价化肥与有机肥配施对红壤稻田肥力的提升作用[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(5): 777-790. |
| Zhang W X, Wang S X, Liu Z B, Tang X G, Xiong L, Xia W J, Wang P, Yuan F S, Sun G, Li Z Z, Liu G G. Evaluating soil fertility improvement effects of chemical fertilizer combined with organic fertilizers in a red paddy soil using the soil fertility index[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(5): 777-790. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 刘可意, 杨佳, 姜淑娜, 谷会岩. 基于最小数据集的典型黑土区不同林龄小黑杨土壤质量差异[J]. 生态学报, 2024, 44(9): 3623-3635. |
| Liu K Y, Yang J, Jiang S N, Gu H Y. Evaluation of differences in soil quality of Populus simonii×P. nigra (P.xiaohei) of different stand ages in typical black soil areas based on a minimum data set[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(9): 3623-3635. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 张广立, 岑柏霆, 龙新宪, 刘娅, 田政, 廖泽伟. 粪肥施用对土壤团聚体的影响—Meta分析[J]. 土壤, 2024, 56(3): 610-622. |
| Zhang G L, Cen B T, Long X X, Liu Y, Tian Z, Liao Z W. Responses of soil aggregates to mature application: A meta-analysis[J]. Soils, 2024, 56(3): 610-622. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 陈晓东, 吴景贵, 范围, 朱文悦, 李晓航. 有机物料对原生盐碱土微团聚体特征及稳定性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(2): 201-207. |
| Chen X D, Wu J G, Fan W, Zhu W Y, Li X H. Effects of organic materials on the characteristics and stability of micro-aggregates in the native saline-alkali soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 34(2): 201-207. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 荣勤雷, 李若楠, 黄绍文, 周春火, 唐继伟, 王丽荣, 张彦才. 不同施肥模式下设施菜田土壤团聚体养分和微生物量特征[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(7): 1084-1096. |
| Rong Q L, Li R N, Huang S W, Zhou C H, Tang J W, Wang L R, Zhang Y C. Characteristics of nutrients and microbial biomass in soil aggregates under different fertilization modes in greenhouse vegetable production[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2019, 25(7): 1084-1096. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 程琪, 毛霞丽, 孙涛, 王湘洁, 马庆旭, 吴良欢. 长期化肥与不同有机物料配施对土壤微生物生态化学计量特征和群落结构的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2024, 30(2): 209-220. |
| Cheng Q, Mao X L, Sun T, Wang X J, Ma Q X, Wu L H. Effects of long-term combined application of chemical fertilizers with different organic materials on soil microbial ecological stoichiometry and community structure[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2024, 30(2): 209-220. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 刘强, 梁鑫, 董佩丽, 李湘, 史爱玲, 王莉霞, 徐德华. 不同施肥措施对黄土丘陵区农田土壤有机碳组分和碳库管理指数的影响[J]. 土壤, 2023, 55(2): 446-452. |
| Liu Q, Liang X, Dong P L, Li X, Shi A L, Wang L X, Xu D H. Effects of different fertilization methods on farmland soil active organic carbon and carbon pool management indicators in loess hilly area[J]. Soils, 2023, 55(2): 446-452. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | Han L, Sun K, Jin J, Xing B. Some concepts of soil organic carbon characteristics and mineral interaction from a review of literature[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2016, 94: 107-121. |
| [35] | 邓明位, 张思佳, 朱波, 李梦, 蒲玉琳. 猪厩肥和秸秆还田对紫色土有机碳组分及稳定性的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2021, 39(2): 205-211. |
| Deng M W, Zhang S J, Zhu B, Li M, Pu Y L. Effects of pig manure and corn residue on the organic carbon fractions and stability of purple soil[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2021, 39(2): 205-211. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 孙美佳, 周志勇, 王勇强, 沈颖, 夏威. 有机物添加对山西太岳山油松林土壤呼吸及碳组分的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2023, 47(1): 67-75. |
| Sun M J, Zhou Z Y, Wang Y Q, Shen Y, Xia W. The effect of organic matter addition on soil respiration and carbon component in Pinus tabuliformis forests in Taiyue Mountain, Shanxi Province, China[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University: Natural Sciences Edition, 2023, 47(1): 67-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 汪月, 张名豪, 赵秀兰. 有机物料对紫色土微生物量碳、氮及氮素供应的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(8): 3808-3815. |
| Wang Y, Zhang M H, Zhao X L. Effects of organic amendments on microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen uptake by corn seedlings grown in two purple soils[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(8): 3808-3815. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 彭丹丹, 徐开未, 刘圆圆, 裴丽珍, 周元, 陈远学. 有机物料等氮量还田对紫色土土壤质量的影响[J/OL]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2025, 42(4): 1010-1020. |
| Peng D D, Xu K W, Liu Y Y, Pei L Z, Zhou Y, Chen Y X. Effects of organic material returned on quality of purple soil under equal nitrogen rate[J/OL]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2025, 42(4): 1010-1020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 石丽红, 李超, 唐海明, 程凯凯, 李微艳, 文丽, 肖小平. 长期不同施肥措施对双季稻田土壤活性有机碳组分和水解酶活性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(3): 921-930. |
| Shi L H, Li C, Tang H M, Cheng K K, Li W Y, Wen L, Xiao X P. Effects of long-term fertilizer management on soil labile organic carbon fractions and hydrolytic enzyme activity under a double-cropping rice system of southern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(3): 921-930. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | 付蔷, 秦方锦, 魏亮, 王双, 王萍, 祝贞科, 葛体达, 刘亚龙. 有机肥长期施用对红壤性水稻土磷组分和土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2025, 42(2): 320-328. |
| Fu Q, Qin F J, Wei L, Wang S, Wang P, Zhu Z K, Ge T D, Liu Y L. Effects of long-term fertilization on phosphorus fractions and soil-enzyme activities in red paddy soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2025, 42(2): 320-328. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | Jiang M, Xu L, Chen X, Zhu H, Fan H. Soil quality assessment based on a minimum data set: A case study of a county in the typical river delta wetlands[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12: 9033. |
| [42] | Sasanifar S, Alijanpour A, Banj Shafiei A, Eshaghi Rad J, Molaei M. Forest conservation mediating soil quality relationship with diversity of various plant layers in the biosphere of Arasabran, Iran[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 928: 172475. |
| [43] | 谭智铭, 宁晨, 林先滢, 许煜东, 张正, 刘四黑, 李建安. 油茶低产林转化下土壤质量关键因子的识别与筛选[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 140-147+157. |
| Tan Z M, Ning C, Lin X Y, Xu Y D, Zhang Z, Liu S H, Li J A. Identification and screening for key factors of soil quality under the conversion of low-yield Camellia oleifera forest[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2019, 43(10): 140-147+157. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | Nabiollahi K, Golmohamadi F, Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi R, Kerry R, Davari M. Assessing the effects of slope gradient and land use change on soil quality degradation through digital mapping of soil quality indices and soil loss rate[J]. Geoderma, 2018, 318: 16-28. |
| [45] | 胡伟, 刘文辉, 刘凯强, 吴雨涵. 基于最小数据集土壤质量评价及生物指标的确立[J]. 草地学报, 2024, 32(12): 3855-3867. |
| Hu W, Liu W H, Liu K Q, Wu Y H. Evaluation of soil quality and establishment of bio-indicators based on minimal data set[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(12): 3855-3867. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 田蕾, 陈亚萍, 刘俊, 马晓刚, 王娜, 杨兵, 李莹, 郭海东, 李娟, 胡慧, 张银霞, 李培富. 粳稻种质资源芽期耐盐性综合评价与筛选[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(6): 631-642. |
| [2] | 刘传光1,周汉钦1,冯道基1,周新桥1,陈达刚1,李丽君1,李巨昌1,张桂权2,*,陈友订1,*. 影响华南稻区常规籼稻产量水平的主要农艺性状分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(2): 182-188. |
| [3] | 李淑顺,张连举,强 胜. 江苏中部轻型栽培稻田杂草群落特征及草害综合评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(2): 207-207~214 . |
| [4] | 乔慧刘 芳,罗 举,赖凤香,傅 强王华弟,戴德江. 不同植物上灰飞虱适合度的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(1): 71-71~78 . |
| [5] | 任鄄胜, 汪秀志, 肖培村, 田彦华, 韩赞平, 韩 磊, 汪旭东, . 杂交水稻稻米品质性状的相关及聚类分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2004, 18(2): 130-134 . |
| [6] | 蒋开锋, 郑家奎, 赵甘霖, 杨乾华, 万先齐, 汪旭东,. 四川省新育成的杂交水稻组合的品质分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2004, 18(1): 80-82 . |
| [7] | 陈 能,罗玉坤,朱智伟,张伯平,郑有川,谢黎虹. 优质食用稻米品质的理化指标与食味的相关性研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 1997, 11(2): 70-76 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||