
中国水稻科学 ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 108-117.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2019.9001
收稿日期:2019-01-01
修回日期:2019-01-15
出版日期:2019-03-10
发布日期:2019-03-10
通讯作者:
陈忱
基金资助:
Hui DENG1, Zhiguo E2, Baixiao NIU1, Lei WANG2, Chen CHEN1,*( )
)
Received:2019-01-01
Revised:2019-01-15
Online:2019-03-10
Published:2019-03-10
Contact:
Chen CHEN
摘要:
【目的】DNA甲基化是高等植物中普遍存在的一种表观修饰形式,其在调节基因表达、维持基因组稳定以及调控植物生长发育等方面发挥重要作用。本研究拟对基因组甲基化如何影响水稻发育进行解析。【方法】利用DNA甲基化抑制剂5-氮脱氧胞苷(AZA, 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine)处理水稻幼苗,研究DNA甲基化抑制剂对水稻幼苗生长发育及相关基因表达的影响。【结果】AZA处理后水稻基因组甲基化水平下降、植株发育迟缓,但种子萌发并不受AZA处理的影响;DNA和组蛋白表观修饰相关基因的表达受到AZA处理抑制。此外,防卫反应和光合通路相关基因表达也受到AZA处理的影响,暗示DNA甲基化在这些基因的表达调控中可能发挥作用。【结论】这些结果表明AZA是一种有效的DNA甲基化抑制剂,AZA处理可以破坏水稻基因组甲基化水平的正常状态,从而影响水稻的正常发育。
中图分类号:
邓卉, 鄂志国, 牛百晓, 王磊, 陈忱. DNA甲基化抑制剂5-氮脱氧胞苷对水稻基因组甲基化及幼苗生长发育的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(2): 108-117.
Hui DENG, Zhiguo E, Baixiao NIU, Lei WANG, Chen CHEN. Influence of DNA Methylation Inhibitor 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine on DNA Methylation and Seedling Development of Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(2): 108-117.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'-3') Primer sequence(5'-3') | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'-3') Primer sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|---|
| MET1-1-qrt-f | GCATGTGCTTCCATCCTGAG | Lsi6-qrt-f | TTCCCTCCTAACCTCCTCAA |
| MET1-1-qrt-r | ATCTGCCTGTGCTTGTTCTG | Lsi6-qrt-r | CCTGCGAAGATCGACGTAAT |
| MET1-2-qrt-f | GCGCCAGTAAACTCCTACTT | LOC_Os07g05360-qrt-f | GTTGATGGGTACAGCCCAATA |
| MET1-2-qrt-r | CCCAATCCAGCCTACCATAAA | LOC_Os07g05360-qrt-r | GAGTGATTGCCCAGAGAAGTAA |
| CMT3-qrt-f | ATCTGCCTGTGCTTGTTCTG | LOC_Os07g05365-qrt-f | GCCAGCAAGTATGGAGCTAAT |
| CMT3-qrt-r | ATCTGCCTGTGCTTGTTCTG | LOC_Os07g05365-qrt-r | AGAGCAACAACCCTGTCTTTC |
| CMT2-qrt-f | TCAGGTTGTGGTGGCTTTAC | LOC_Os08g40160-qrt-f | CATTCCACAAGACTGGCTGAT |
| CMT2-qrt-r | CTCTGTGTCTTTGGAGGTTGAG | LOC_Os08g40160-qrt-r | GTGATGGCTACGCTGACATT |
| DNMT2-qrt-f | GACACCTACATTCCTAACATTGG | LOC_Os10g21192-qrt-f | GATAGCCAAGGTCGCGTTATTA |
| DNMT2-qrt-r | TCAGCGACATTCAGACTTATTG | LOC_Os10g21192-qrt-r | AGAGGGAAGTTGTGAGCATTAC |
| DRM2-qrt-f | CGTGCGGCATCTTACTACTGA | LOC_Os10g39880-qrt-f | GAGAGAGAACGCGAAAGTACAA |
| DRM2-qrt-r | ATCTCGGTGATGGCGGTTG | LOC_Os10g39880-qrt-r | ACCGAACCATCCGATGTAAAG |
| JIOsPR10-qrt-f | CCTCAGCCATGCCATTCA | LOC_Os07g37030-qrt-f | GCTCGCAGTACAACAACCA |
| JIOsPR10-qrt-r | CTTGGTGATCTCGTCCTTCAC | LOC_Os07g37030-qrt-r | CCACGGCACGAAGAGAAC |
| RSOsPR10-qrt-f | GCACTGTCACCACCATGAA | LOC_Os01g64120-qrt-f | CCACGCCGATCACCAATTA |
| RSOsPR10-qrt-r | CGAGCTCATACTCCACGTTTATC | LOC_Os01g64120-qrt-r | CTGAACCTGCCGGAGAAC |
| OsPR10a-qrt-f | GCCGCAAGTCATGTCCTAAA | LOC_Os07g30670-qrt-f | CGACAACTACATCGACCTCTAC |
| OsPR10a-qrt-r | CGAGGTAGTCCTCGATCATCTT | LOC_Os07g30670-qrt-r | AGTTCACCGCCTTCAACTAC |
| Lsi2-qrt-f | CTGGAGATGTCGGAGAACATAAC | Actin-f | CCAGGTATCGCTGACCGTAT |
| Lsi2-qrt-r | CCACCTCATCACCCATAAGAAG | Actin-r | GGAAAGTGCTGAGTGAGGCT |
| Lsi3-qrt-f | CGTTCGGTGTGTTCTGGAT | Tos17methy-f | GTTGATTATAGGGGATGATTTGGAGTATATTGTTT |
| Lsi3-qrt-r | GCCGAGGAGGAAGGAAATAAA | Tos17methy-r | CATAAAACACAAAACAAATAACCATAATAAACTA |
表1 本研究所用PCR引物
Table 1 Primers used in the study.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'-3') Primer sequence(5'-3') | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'-3') Primer sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|---|
| MET1-1-qrt-f | GCATGTGCTTCCATCCTGAG | Lsi6-qrt-f | TTCCCTCCTAACCTCCTCAA |
| MET1-1-qrt-r | ATCTGCCTGTGCTTGTTCTG | Lsi6-qrt-r | CCTGCGAAGATCGACGTAAT |
| MET1-2-qrt-f | GCGCCAGTAAACTCCTACTT | LOC_Os07g05360-qrt-f | GTTGATGGGTACAGCCCAATA |
| MET1-2-qrt-r | CCCAATCCAGCCTACCATAAA | LOC_Os07g05360-qrt-r | GAGTGATTGCCCAGAGAAGTAA |
| CMT3-qrt-f | ATCTGCCTGTGCTTGTTCTG | LOC_Os07g05365-qrt-f | GCCAGCAAGTATGGAGCTAAT |
| CMT3-qrt-r | ATCTGCCTGTGCTTGTTCTG | LOC_Os07g05365-qrt-r | AGAGCAACAACCCTGTCTTTC |
| CMT2-qrt-f | TCAGGTTGTGGTGGCTTTAC | LOC_Os08g40160-qrt-f | CATTCCACAAGACTGGCTGAT |
| CMT2-qrt-r | CTCTGTGTCTTTGGAGGTTGAG | LOC_Os08g40160-qrt-r | GTGATGGCTACGCTGACATT |
| DNMT2-qrt-f | GACACCTACATTCCTAACATTGG | LOC_Os10g21192-qrt-f | GATAGCCAAGGTCGCGTTATTA |
| DNMT2-qrt-r | TCAGCGACATTCAGACTTATTG | LOC_Os10g21192-qrt-r | AGAGGGAAGTTGTGAGCATTAC |
| DRM2-qrt-f | CGTGCGGCATCTTACTACTGA | LOC_Os10g39880-qrt-f | GAGAGAGAACGCGAAAGTACAA |
| DRM2-qrt-r | ATCTCGGTGATGGCGGTTG | LOC_Os10g39880-qrt-r | ACCGAACCATCCGATGTAAAG |
| JIOsPR10-qrt-f | CCTCAGCCATGCCATTCA | LOC_Os07g37030-qrt-f | GCTCGCAGTACAACAACCA |
| JIOsPR10-qrt-r | CTTGGTGATCTCGTCCTTCAC | LOC_Os07g37030-qrt-r | CCACGGCACGAAGAGAAC |
| RSOsPR10-qrt-f | GCACTGTCACCACCATGAA | LOC_Os01g64120-qrt-f | CCACGCCGATCACCAATTA |
| RSOsPR10-qrt-r | CGAGCTCATACTCCACGTTTATC | LOC_Os01g64120-qrt-r | CTGAACCTGCCGGAGAAC |
| OsPR10a-qrt-f | GCCGCAAGTCATGTCCTAAA | LOC_Os07g30670-qrt-f | CGACAACTACATCGACCTCTAC |
| OsPR10a-qrt-r | CGAGGTAGTCCTCGATCATCTT | LOC_Os07g30670-qrt-r | AGTTCACCGCCTTCAACTAC |
| Lsi2-qrt-f | CTGGAGATGTCGGAGAACATAAC | Actin-f | CCAGGTATCGCTGACCGTAT |
| Lsi2-qrt-r | CCACCTCATCACCCATAAGAAG | Actin-r | GGAAAGTGCTGAGTGAGGCT |
| Lsi3-qrt-f | CGTTCGGTGTGTTCTGGAT | Tos17methy-f | GTTGATTATAGGGGATGATTTGGAGTATATTGTTT |
| Lsi3-qrt-r | GCCGAGGAGGAAGGAAATAAA | Tos17methy-r | CATAAAACACAAAACAAATAACCATAATAAACTA |
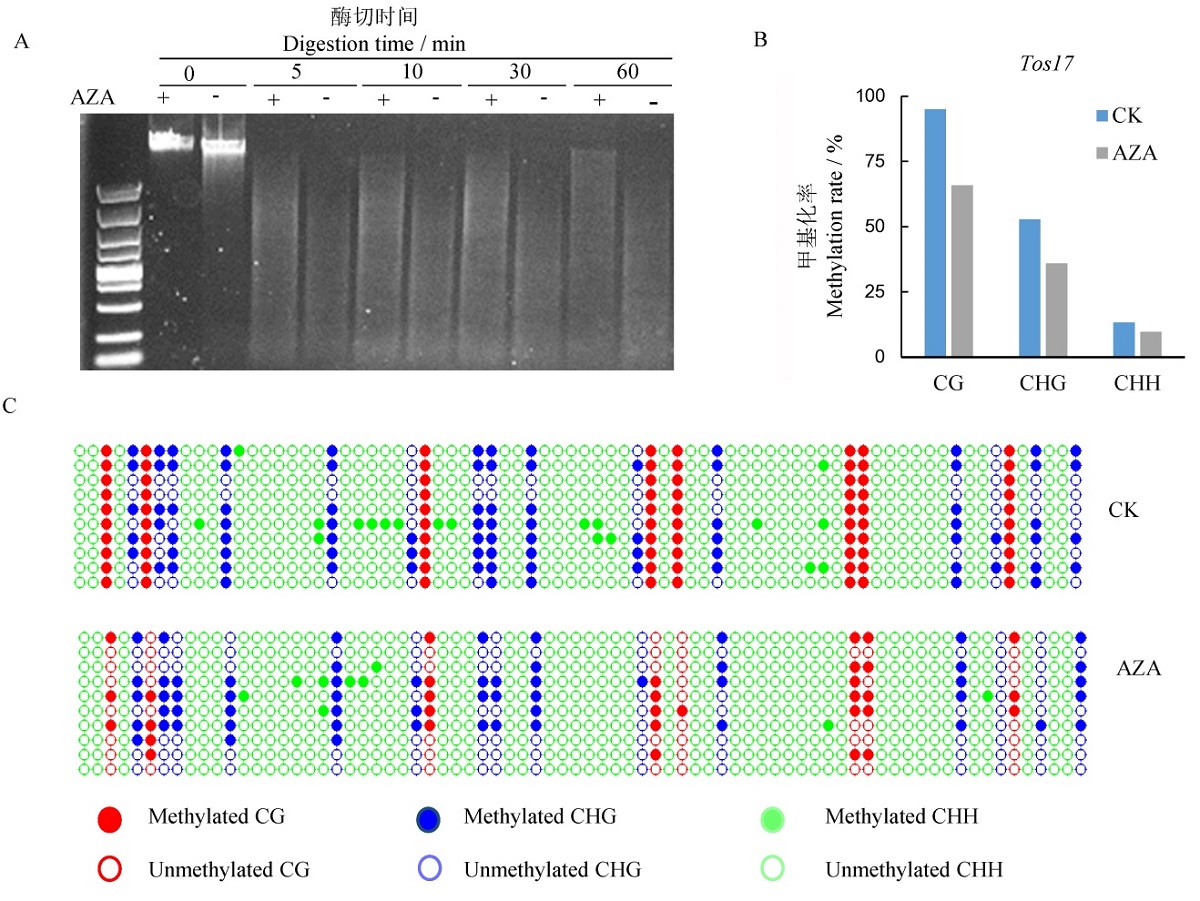
图1 AZA处理对基因组和转座子Tos17chr7的DNA甲基化的影响 A-基因组DNA甲基化;B-转座子Tos17chr7的甲基化水平;C-转座子Tos17chr7的甲基化模式。
Fig. 1. Effects of AZA treatment on genomic methylation. A, Digestion of the genomic DNA by methylation-sensitive MspⅠ; B, Methylation level of transposons Tos17chr7; C, Methylation pattern of transposons Tos17chr7 detected by bisulfate sequencing.
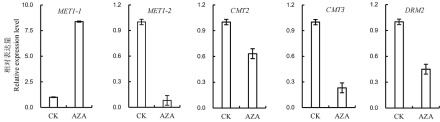
图2 DNA甲基化酶编码基因在对照和AZA处理的水稻幼苗中的表达情况图中所显示数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。
Fig. 2. Relative expression level of DNA methylation related genes in AZA-untreated and -treated rice seedlings. Values are Mean±SD(n=3).
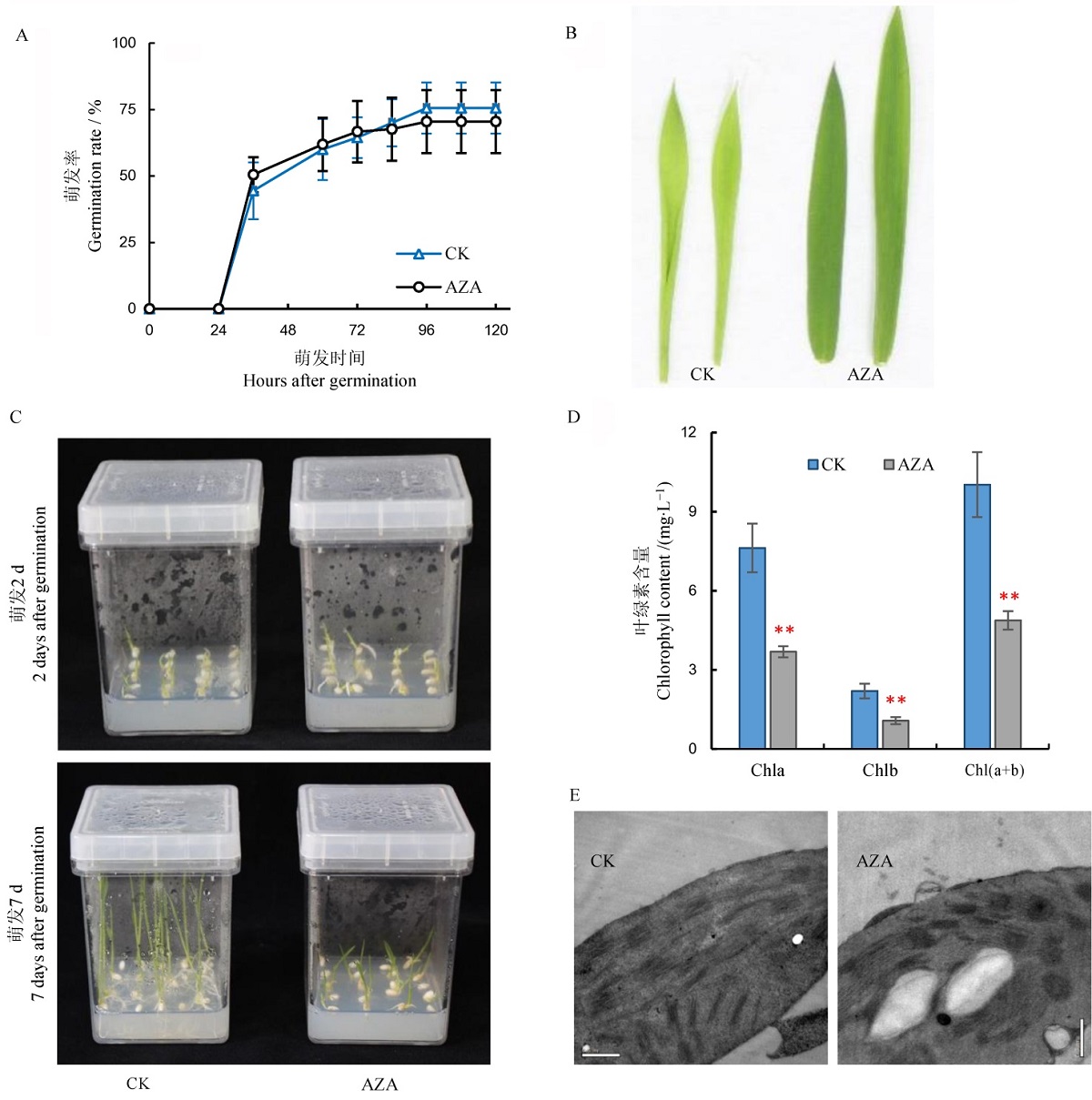
图3 AZA处理水稻幼苗的表型分析 A-萌发率动态曲线,图中所显示数据为平均值±标准差(n=50);B-生长2 d后及7 d后植株表型;C-叶片表型;D-叶绿素含量测定,图中所显示数据为平均值±标准差(n=3),**表示差异达0.01显著水平;E-叶绿体结构观察,标尺为0.5 μm。
Fig. 3. Phenotypic analysis of the AZA-treated rice seedlings. A, Germination rate, values are mean±SD(n=50); B, Morphology of AZA treated and untreated plants at 2 days after germination(DAI) and 7DAI; C, Leaves of AZA treated and untreated plants; D, Chlorophyll contents, values are Mean±SD(n=3), **indicates significant difference at 0.01 level; E, Chloroplast structure, bar=0.5 μm.
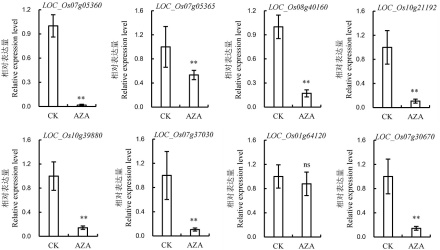
图5 叶片表型鉴定及硅转运蛋白的相对表达量 A-AZA未处理植株叶片半薄切片,*表示维管束,标尺为200 μm;B-AZA处理植株叶片半薄切片,*表示维管束,标尺为200 μm;C-AZA未处理植株叶片放大;D-AZA处理植株叶片放大;E-叶片表皮细胞观察,标尺为25 μm;F-叶片表皮细胞长度和宽度统计,图中所显示数据为平均值±标准差(n=100),0.01<P值<0.05为显著差异;G-硅转运蛋白相对表达量,图中所显示数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。
Fig. 5. Leaf phenotype and relative expression level of silicon transporter. A, Semi-thin section of leaf of AZA-untreated plants, *indicate vascular bundle, bar=200 μm; B, Semi-thin section of leaf of AZA-treated plants, *indicate vascular bundle, bar=200 μm; C, Higher magnification view of leaf of AZA-untreated plant; D, Higher magnification view of leaf of AZA-treated plant; E, Scanning electron microscope (SEM) analysis of the leaf epidermal cells, Bar=25 μm; F, Cell length and width of the leaf epidermal cells, values are mean±SD(n=100); G, Relative expression level of silicon transporter, values are mean±SD(n=3).
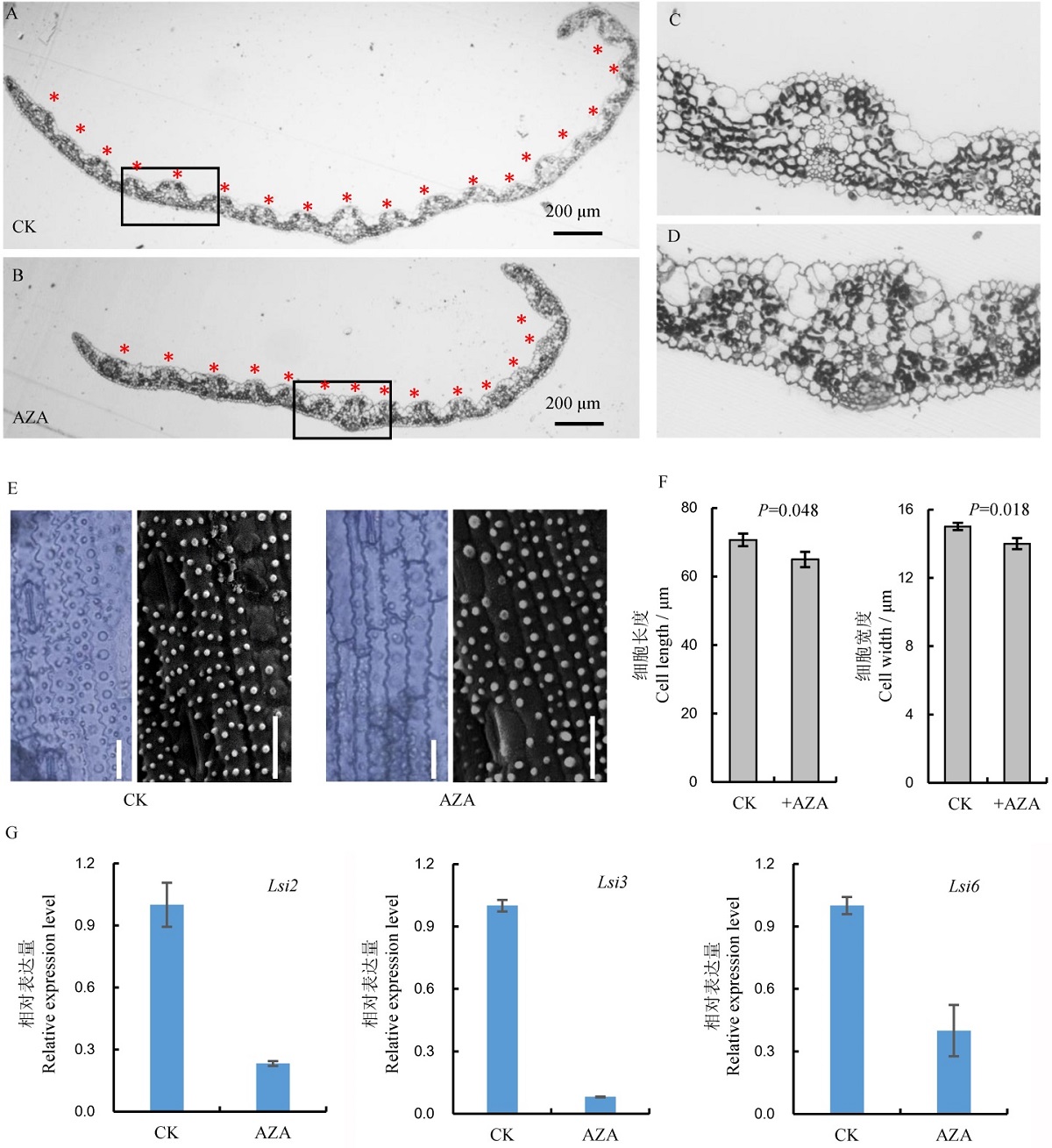
图6 病程相关基因的相对表达量和抗性相关激素的含量差异 A-病程相关基因JIOsPR10、RSOsPR10和OsPR10a的相对表达量, 图中所显示数据为平均值±标准差(n=3);B-AZA处理植株和未处理植株的脱落酸、水杨酸及茉莉酸含量, 图中所显示数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。
Fig. 6. Relative expression level of pathogenesis-related genes and contents of resistance-related hormones. A, Relative expression level of pathogenesis-related genes JIOsPR10, RSOsPR10 and OsPR10a, values are mean±SD(n=3); B, Contents of abscisic acid (ABA), salicylic acid(SA), jasmonic acid(JA) in AZA-untreated and AZA-treated plants, values are mean±SD(n=3).
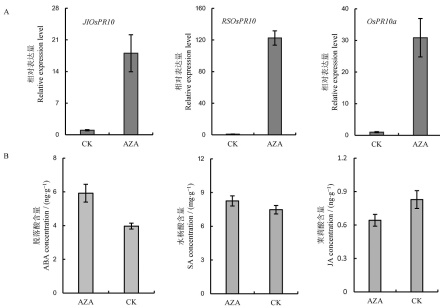
图4 光合通路相关基因在AZA未处理和AZA处理植株的相对表达量图中所显示数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。**表示差异达0.01显著水平, ns表示无差异。
Fig. 4. Relative expression level of photosynthetic genes in AZA-untreated and AZA-treated plants. The error bars indicate standard deviations(n=3). **indicates significant difference at 0.01 level; ns indicates no statistical significance.
| [1] | Springer N M, Schmitz R J.Exploiting induced and natural epigenetic variation for crop improvement.Nat Rev Genet, 2017, 18(9): 563. |
| [2] | Shi J, Dong A, Shen W H.Epigenetic regulation of rice flowering and reproduction.Front Plant Sci, 2015, 5: 803. |
| [3] | 洪苓苓, 马旭东. 组蛋白甲基化修饰的研究进展. 临床血液学杂志, 2010, 23(1): 54-56. |
| Hong L L, Ma X D.Advances in histone methylation modification.J Clin Hematol, 2010, 23(1): 54-56. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 关录飞, 吴笑女, 徐启江. DNA甲基化及其对植物发育的调控. 生物技术通讯, 2008, 19(4): 632-634. |
| Guan L F, Wu X N, Xu Q J.DNA methylation and its regulation effect during plant development.Lett Biotechnol, 2008, 19(4): 632-634. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 郭广平, 袁金玲, 吴晓丽, 顾小平. DNA甲基化在植物研究中的应用现状与前景. 植物遗传资源学报, 2011, 12(3): 425-430. |
| Guo G P, Yuan J L, Wu X L, Gu X P.DNA methylation and its application in plant research.J Plant Genet Resour, 2011, 12(3): 425-430. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Finnegan E J, Kovac K A.Plant DNA methyltransferases.Plant Mol Biol, 2000, 43(2/3): 189-201. |
| [7] | Dowen R H, Pelizzola M, Schmitz R J, Lister R, Dowen J M, Nery J R, Dixon J E, Ecker J R.Widespread dynamic DNA methylation in response to biotic stress.Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2012, 109(32): E2183-91. |
| [8] | Wang W S, Zhao X Q, Pan Y J, Zhu L H, Fu B Y, Li Z K.DNA methylation changes detected by methylation- sensitive amplified polymorphism in two contrasting rice genotypes under salt stress.J Genet Genom, 2011, 38(9): 419-424. |
| [9] | 赵云雷, 叶武威, 王俊娟, 樊保香, 宋丽艳. DNA甲基化与植物抗逆性研究进展. 西北植物学报, 2009, 29(7): 1479-1489. |
| Zhao Y L, Ye W W, Wang J J, Fan B X, Song L Y.Review of DNA methylation and plant stress tolerance.Acta Bot Bor-Occ Sin, 2009, 29(7): 1479-1489. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Ou X F, Zhang Y H, Xu C M, Lin X Y, Zang Q, Zhuang T T, Jiang L L, Wettstein D V, Liu B.Transgenerational inheritance of modified DNA methylation patterns and enhanced tolerance induced by heavy metal stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). PloS One, 2012, 7(9): e41143. |
| [11] | Goll M G, Bestor T H.Eukaryotic cytosine methyltransferases.Annu Rev Biochem, 2005, 74: 481-514. |
| [12] | Kakutani T, Jeddeloh J A, Flowers S K, Munakata K, Richards E J.Developmental abnormalities and epimutations associated with DNA hypomethylation mutations.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1996, 93(22): 12406-12411. |
| [13] | Asao H, Eun S H, Okano Y, Moritoh S, One A, Okano Y, Yamaguchi K, Shimatani Z, Koizumi A, Terada R.Targeted disruption of an orthologue of DOMAINS REARRANGED METHYLASE 2, OsDRM2, impairs the growth of rice plants by abnormal DNA methylation.Plant J & Cell Mol Biol, 2012, 71(1): 85. |
| [14] | Baubec T, Pecinka A, Rozhon W, Scheid O M.Effective, homogeneous and transient interference with cytosine methylation in plant genomic DNA by zebularine.Plant J Cell & Mol Biol, 2010, 57(3): 542-554. |
| [15] | 袁建民, 木万福, 麻继仙, 杨龙, 李易蓉, 但忠, 苏银玲. DNA甲基化抑制剂5-azaC对花椰菜生长发育的影响. 江西农业学报, 2018, 30(2): 42-45. |
| Yuan J M, Mu W F, Ma J X, Yang L, Li Y R, Dan Z, Su Y L.The effects of DNA methylation inhibitor 5-azaC on growth and development of cauliflower.Acta Agric Jiangxi, 2018, 30(2): 42-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 汪媛媛. 两种DNA甲基化抑制剂对菊花表型和DNA甲基化的影响. 开封: 河南大学, 2012. |
| Wang Y Y.The effect of two different DNA methylation inhibitors on curcumin phenotype and DNA methylation. Kaifeng: Henan University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 刘秋香. DNA甲基化抑制剂5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine处理后水稻的DNA甲基化研究. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2014. |
| Liu Q X.The research on DNA methylation of rice treated with DNA methylation inhibitor 5-Aza-2′- deoxycytidine. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Sano H, Kamada I, Youssefian S, Katsumi M, Wabiko H.A single treatment of rice seedlings with 5-azacytidine induces heritable dwarfism and undermethylation of genomic DNA.Mol Gene Genet, 1990, 220(3): 441-447. |
| [19] | 段光明. 叶绿素含量测定中Arnon公式的推导. 植物生理学报, 1992(3): 221. |
| Duan G M. Derivation of Arnon formula in determination of chlorophyll content.Plant Physiol Commun, 1992(3): 221. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | Cheng C, Daigen M, Hirochika H.Epigenetic regulation of the rice retrotransposon Tos17.Mol Genet Genom, 2006, 276(4): 378. |
| [21] | 黄菲, 李雪梅, 王文生, 傅彬英. DNA甲基化在植物抗逆反应中的研究进展及其育种应用. 中国农业科技导报, 2013, 15(6): 83-91. |
| Huang F, Li X M, Wang W S, Fu B Y.Research progress of DNA methylation in stress response and breeding in plant.J Agric Sci Technol, 2013, 15(6): 83-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Boyko A, Kovalchuk I.Epigenetic control of plant stress response.Environ Mol Mutag, 2008, 49(1): 61-72. |
| [23] | 彭海, 席婷, 张静, 吴先军. 胁迫条件下植物DNA甲基化的稳定性. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(12): 2431-2438. |
| Peng H, Xi T, Zhang J, Wu X J.Stability of stress-induced DNA methylation in plant.Sci Agric Sin, 2011, 44(12): 2431-2438. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Hu L J, Li N, Xu C M, Zhong S L, Lin X Y, Yang J J, Zhou T Q, Yuliang A, Wu Y, Chen Y R, Cao X F, Zemach A, Rustgi S, Wettstein D V, Liu B.Mutation of a major CG methylase in rice causes genome-wide hypomethylation, dysregulated genome expression, and seedling lethality.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2014, 111(29): 10642-10647. |
| [25] | Kankel M W, Ramsey D E, Stokes T L, Flowers S K, Haag J R, Jeddeloh J A, Riddle N C, Verbsky M L, Rechards E J. Arabidopsis MET1 cytosine methyltransferase mutants. Genetics, 2003, 163(3): 1109. |
| [26] | Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M.RNA-Seq: A revolutionary tool for transcriptomics.Nat Rev Genet, 2010, 10(1): 57-63. |
| [27] | 仪治本, 孙毅, 牛天堂, 梁小红, 刘龙龙, 赵威军, 李炳林. 高粱基因组DNA胞嘧啶甲基化在杂交种和亲本间差异研究. 作物学报, 2005, 31(9): 1138-1143. |
| Yi Z B, Sun Y, Niu T T, Liang X H, Liu L L, Zhao W J, Li B L.Patterns of DNA cytosine methylation between hybrids and their parents in sorghum genome.Acta Agron Sin, 2005, 31(9): 1138-1143. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Song G S, Zhai H L, Peng Y G, Zhang L, Wei G, Chen X Y, Xiao Y G, Wang L L, Chen Y J, Wu B, Chen B, Zhang Y, Chen H, Feng X J, Gong W K, Liu Y, Yin Z J, Wang F, Liu G Z, Xu H L, Wei X L, Zhao X L, Ouwerkerk P, Hankemeier T, Reijmers T, Heijden R, Lu C M, Wang M, Greef J, Zhu Z.Comparative transcriptional profiling and preliminary study on heterosis mechanism of super- hybrid rice.Mol Plant, 2010, 3(6): 1012-1025. |
| [29] | Dowen R H, Pelizzola M, Schmitz R J, Lister R, Dowen J M, Nery J R, Dixon J E, Ecker J R.Widespread dynamic DNA methylation in response to biotic stress.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2012, 109(32): E2183. |
| [30] | Yu A, Lepere G, Jay F, Wang J Y, Bapaume L, Wang Y, Abraham A L, Penterman J, Fischer R L, Voinnet O, Navarro L.Dynamics and biological relevance of DNA demethylation in Arabidopsis antibacterial defense. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2013, 110(6): 2389-2394. |
| [31] | Akimoto K, Katakami H, Kim H J, Ogawa E, Sano C M, Wada Y, Sano H.Epigenetic inheritance in rice plants.Ann Bot, 2007, 100(2): 205-217. |
| [32] | Deleris A, Halter T, Navarro L.DNA methylation and demethylation in plant immunity.Ann Rev Phytopathol, 2016, 54(1): 579-603. |
| [1] | 任志奇, 薛可欣, 董铮, 李小湘, 黎用朝, 郭玉静, 刘文强, 郭梁, 盛新年, 刘之熙, 潘孝武. 水稻外卷叶突变体ocl1的鉴定及基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 337-346. |
| [2] | 肖乐铨, 李雷, 戴伟民, 强胜, 宋小玲. 转cry2A*/bar基因水稻与杂草稻杂交后代的苗期生长特性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 347-358. |
| [3] | 李刚, 高清松, 李伟, 张雯霞, 王健, 程保山, 王迪, 高浩, 徐卫军, 陈红旗, 纪剑辉. 定向敲除SD1基因提高水稻的抗倒性和稻瘟病抗性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 359-367. |
| [4] | 汪胜勇, 陈宇航, 陈会丽, 黄钰杰, 张啸天, 丁双成, 王宏伟. 水稻减数分裂期高温对苯丙烷类代谢及下游分支代谢途径的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 368-378. |
| [5] | 董立强, 杨铁鑫, 李睿, 商文奇, 马亮, 李跃东, 隋国民. 株行距配置对超高产田水稻产量及根系形态生理特性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 392-404. |
| [6] | 韩聪, 何禹畅, 吴丽娟, 郏丽丽, 王磊, 鄂志国. 水稻碱性亮氨酸拉链(bZIP)蛋白家族功能研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(4): 436-448. |
| [7] | 沈雨民, 陈明亮, 熊焕金, 熊文涛, 吴小燕, 肖叶青. 水稻内外稃异常发育突变体blg1 (beak like grain 1)的表型分析与精细定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 225-232. |
| [8] | 段敏, 谢留杰, 高秀莹, 唐海娟, 黄善军, 潘晓飚. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制广亲和水稻温敏雄性不育系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 233-243. |
| [9] | 程玲, 黄福钢, 邱一埔, 王心怡, 舒宛, 邱永福, 李发活. 籼稻材料570011抗褐飞虱基因的遗传分析及鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 244-252. |
| [10] | 王文婷, 马佳颖, 李光彦, 符卫蒙, 李沪波, 林洁, 陈婷婷, 奉保华, 陶龙兴, 符冠富, 秦叶波. 高温下不同施肥量对水稻产量品质形成的影响及其与能量代谢的关系分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 253-264. |
| [11] | 刘嫒桦, 李小坤. 不同肥料施用与稻米品质关系的整合分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 276-284. |
| [12] | 杨晓龙, 王彪, 汪本福, 张枝盛, 张作林, 杨蓝天, 程建平, 李阳. 不同水分管理方式对旱直播水稻产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 285-294. |
| [13] | 魏晓东, 宋雪梅, 赵凌, 赵庆勇, 陈涛, 路凯, 朱镇, 黄胜东, 王才林, 张亚东. 硅锌肥及其施用方式对南粳46产量和稻米品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 295-306. |
| [14] | 林聃, 江敏, 苗波, 郭萌, 石春林. 水稻高温热害模型研究及其在福建省的应用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 307-320. |
| [15] | 郑承梅, 孙金秋, 刘梦杰, 杨永杰, 陆永良, 郭怡卿, 唐伟. 水稻田糠稷种子萌发和出苗特性及化学防除药剂筛选[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(3): 321-328. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||