
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 209-219.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240204
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
YAN Ying1,#, WANG Kai1,#, ZHANG Lixia1, HU Zejun1, YE Junhua1, YANG Hang1, GU Chunjun2,*( ), WU Shujun1,*(
), WU Shujun1,*( )
)
Received:2024-02-04
Revised:2024-04-26
Online:2025-03-10
Published:2025-03-19
Contact:
GU Chunjun, WU Shujun
About author:#These authors contributed equally to this work
闫影1,#, 王凯1,#, 张丽霞1, 胡泽军1, 叶俊华1, 杨航1, 顾春军2,*( ), 吴书俊1,*(
), 吴书俊1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
顾春军,吴书俊
作者简介:#共同第一作者
基金资助:YAN Ying, WANG Kai, ZHANG Lixia, HU Zejun, YE Junhua, YANG Hang, GU Chunjun, WU Shujun. Development of a New High-Quality and Multi-Resistant japonica Rice Variety, Huxianggeng 216, Through Molecular Pyramiding Breeding[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 209-219.
闫影, 王凯, 张丽霞, 胡泽军, 叶俊华, 杨航, 顾春军, 吴书俊. 利用分子聚合育种培育优质多抗粳稻新品种沪香粳216[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 209-219.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240204
| 性状 Trait | 等位基因 Allele | 分子标记 Molecular marker | 引物序列(5’-3’) Primer sequence(5’-3’) | 多态性 Polymorphism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 香味Fragrance | badh2-E2 | InDel-E2 | F:GGGAGGCGCTGAAGAGGA | 100 bp/107 bp |
| R:GGGTAGTCACCACCCTACCTTG | ||||
| 低直链淀粉含量 Low amylose content | Wxmp | Wx-mp-o | F:ATGTTGTGTTCTTGTGTTCTTTGCAGGC | A/G |
| R:GTAGATCTTCTCACCGGTCTTTCCCCAA | ||||
| KASP-WXMP | F1:GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTGATGAA CACACGGTCGACTCCAT | A/G | ||
| F2:GAAGGTCGGAGTCAACGGATTATGAAC ACACGGTCGACTCCAC | ||||
| R:GAGAGGGTGAGGTTTTTCCATTGCTA | ||||
| 抗稻瘟病 Resistance to rice blast | Pita | YL155/YL87 | F:AGCAGGTTATAAGCTAGGCC | 1042 bp/- |
| R:CTACCAACAAGTTCATCAAA | ||||
| 感稻瘟病 Blast susceptibility | pita | YL183/YL87 | F:AGCAGGTTATAAGCTAGCTAT | -/1042 bp |
| R:CTACCAACAAGTTCATCAAA | ||||
| 抗稻瘟病 Resistance to rice blast | Pikm | Pikm-1 | 1F:TGAGCTCAAGGCAAGAGTTGAGGA | 174 bp / 213 bp |
| 1R:TGTTCCAGCAACTCGATGAG | ||||
| Pikm-2 | 2F:CAGTAGCTGTGTCTCAGAACTATG | 290 bp / 332 bp | ||
| 2R:AAGGTACCTCTTTTCGGCCAG |
Table 1. Genes and molecular markers
| 性状 Trait | 等位基因 Allele | 分子标记 Molecular marker | 引物序列(5’-3’) Primer sequence(5’-3’) | 多态性 Polymorphism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 香味Fragrance | badh2-E2 | InDel-E2 | F:GGGAGGCGCTGAAGAGGA | 100 bp/107 bp |
| R:GGGTAGTCACCACCCTACCTTG | ||||
| 低直链淀粉含量 Low amylose content | Wxmp | Wx-mp-o | F:ATGTTGTGTTCTTGTGTTCTTTGCAGGC | A/G |
| R:GTAGATCTTCTCACCGGTCTTTCCCCAA | ||||
| KASP-WXMP | F1:GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTGATGAA CACACGGTCGACTCCAT | A/G | ||
| F2:GAAGGTCGGAGTCAACGGATTATGAAC ACACGGTCGACTCCAC | ||||
| R:GAGAGGGTGAGGTTTTTCCATTGCTA | ||||
| 抗稻瘟病 Resistance to rice blast | Pita | YL155/YL87 | F:AGCAGGTTATAAGCTAGGCC | 1042 bp/- |
| R:CTACCAACAAGTTCATCAAA | ||||
| 感稻瘟病 Blast susceptibility | pita | YL183/YL87 | F:AGCAGGTTATAAGCTAGCTAT | -/1042 bp |
| R:CTACCAACAAGTTCATCAAA | ||||
| 抗稻瘟病 Resistance to rice blast | Pikm | Pikm-1 | 1F:TGAGCTCAAGGCAAGAGTTGAGGA | 174 bp / 213 bp |
| 1R:TGTTCCAGCAACTCGATGAG | ||||
| Pikm-2 | 2F:CAGTAGCTGTGTCTCAGAACTATG | 290 bp / 332 bp | ||
| 2R:AAGGTACCTCTTTTCGGCCAG |
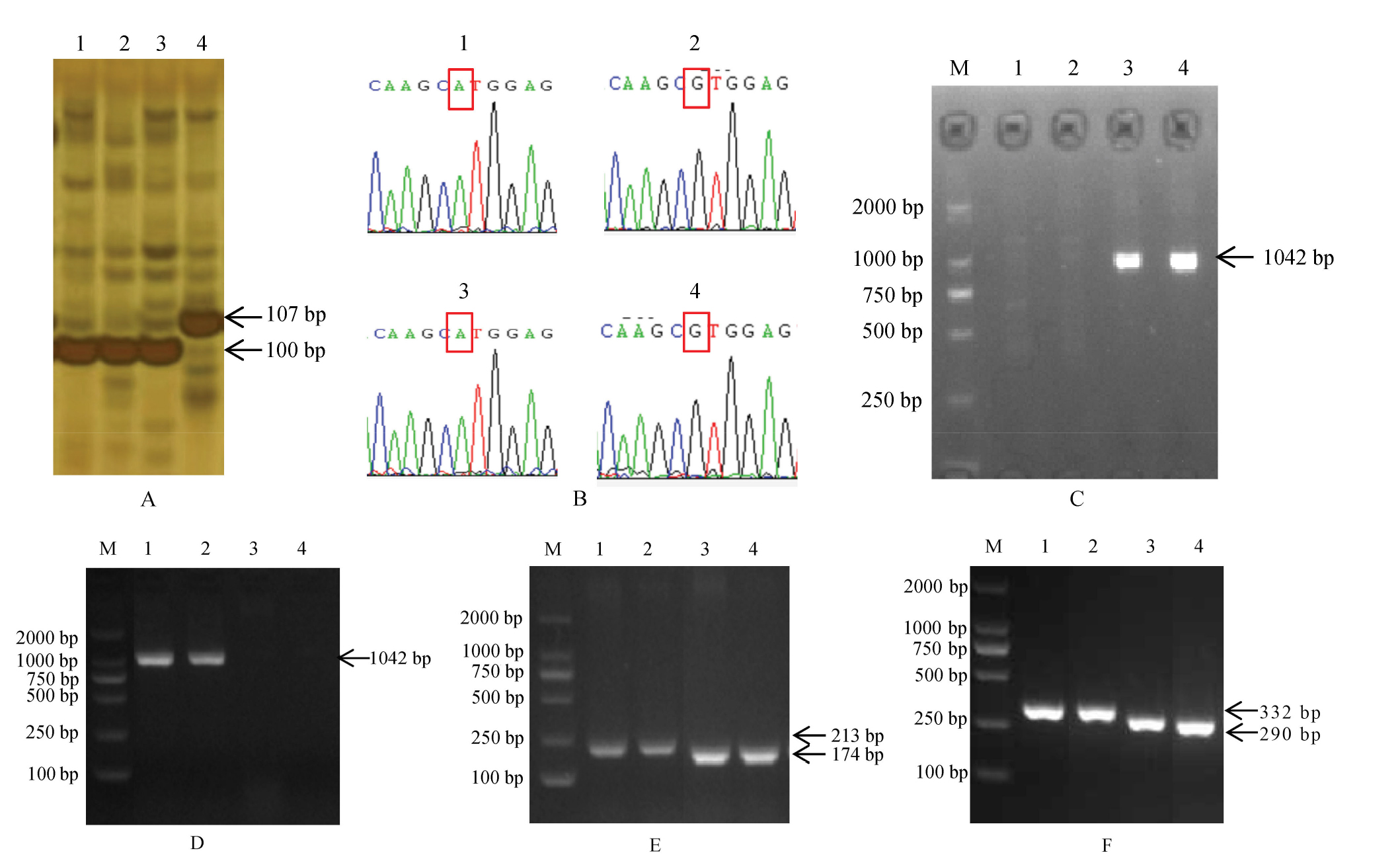
Fig. 1. Molecular marker-powered genotyping of badh2-E2(A), Wxmp(B), Pita(C), pita(D) and Pikm(E, F) for Huxianggeng 216 and its parents M, DL2000 Marker; 1, Nangeng 46; 2, Wuxianggeng 1; 3, Huxianggeng 216; 4, Xiushui 114.
| 品种 Variety | 香味 Fragrance | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content(%) | 穗颈瘟抗性评价 Evaluation of resistance to neck blast |
|---|---|---|---|
| 南粳46 Nangeng 46 | 有 Yes | 10.1±0.44 c | 高感Highly susceptible(HS) |
| 武香粳1号Wuxianggeng 1 | 有 Yes | 16.0±0.17 b | 高感Highly susceptible(HS) |
| 秀水114 Xiushui 114 | 无 No | 17.6±0.20 a | 抗病 Resistant(R) |
Table 2. Evaluation of fragrance, amylose content and blast resistance for cross parents of Huxianggeng216
| 品种 Variety | 香味 Fragrance | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content(%) | 穗颈瘟抗性评价 Evaluation of resistance to neck blast |
|---|---|---|---|
| 南粳46 Nangeng 46 | 有 Yes | 10.1±0.44 c | 高感Highly susceptible(HS) |
| 武香粳1号Wuxianggeng 1 | 有 Yes | 16.0±0.17 b | 高感Highly susceptible(HS) |
| 秀水114 Xiushui 114 | 无 No | 17.6±0.20 a | 抗病 Resistant(R) |
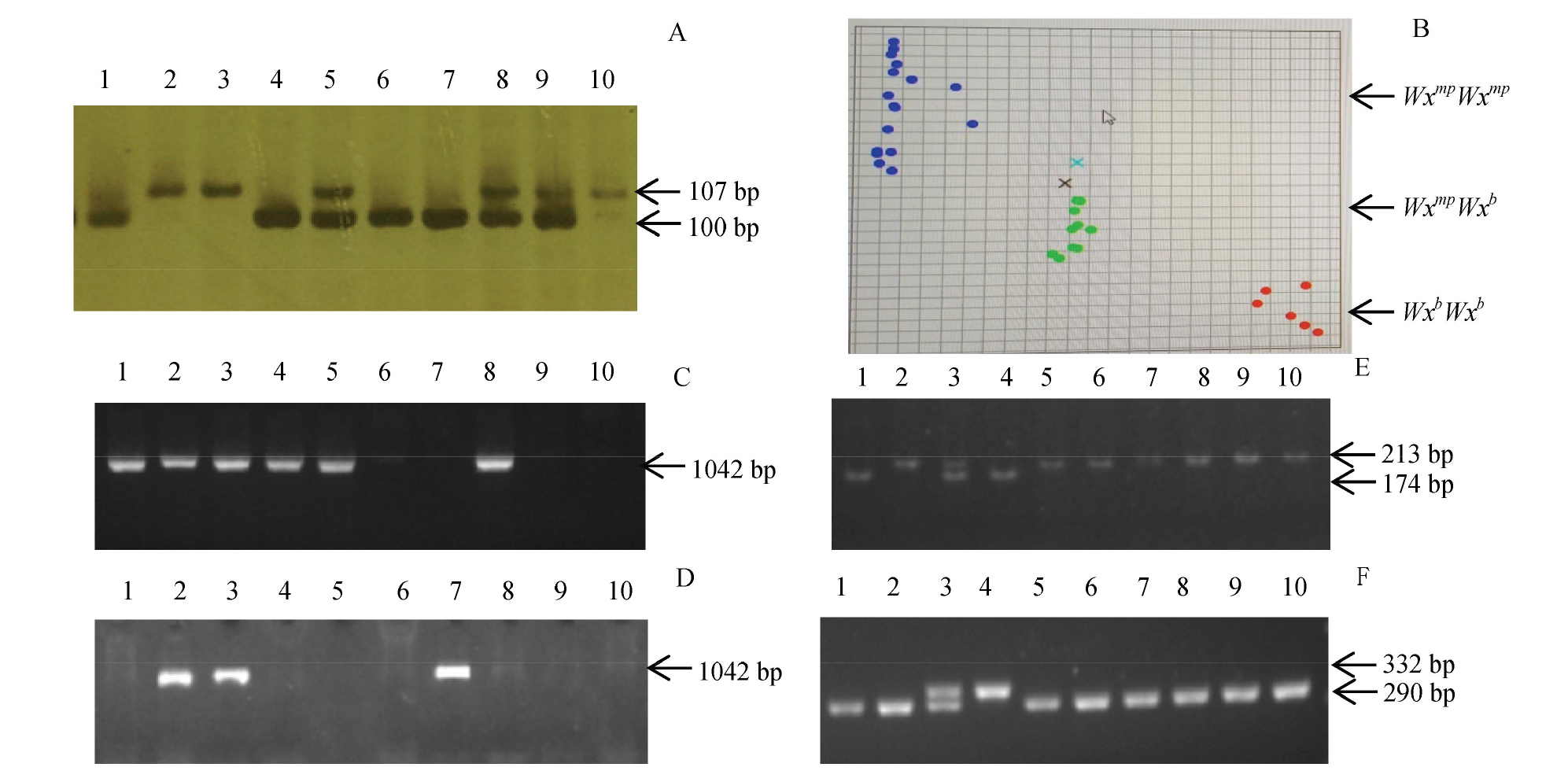
Fig. 3. Molecular marker detection of badh2-E2(A)、Wxmp(B)、Pita(C)、pita(D) and Pikm(E, F) for F3 individuals from the cross Xiushui 114//Xiushui 114/Hu 12-30 1-10, Ten randomly selected F3 individuals from the cross Xiushui 114// Xiushui 114/Hu 12-30. In Fig B, each dot represents a randomly selected F3 individual from the cross Xiushui 114// Xiushui 114/Hu 12-30.
| 品系 Line | 直链淀粉 Amylose content(%) | 胶稠度 Gel consistency (m) | 食味值 Taste value | 峰值黏度 Peak viscosity (RVU) | 热浆黏度Hot paste viscosity (RVU) | 崩解值 Breakdown (RVU) | 终值黏度 Final viscosity (RVU) | 消减值Setback (RVU) | 糊化温度 Gelatinization temperature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZX1 | 8.7±0.3 e | 80.3±1.5 cd | 74.5±1.0 d | 315.6±6.4 ab | 209.4±12.3 a | 106.2±6.0 b | 310.3±6.8 a | −5.3±0.4 b | 73.1±1.2 a |
| ZX2 | 9.2±0.3 d | 82.7±2.1 bc | 81.8±0.8 c | 235.3±7.2 c | 135.1±6.3 b | 100.1±0.8 b | 238.7±7.4 c | 3.4±0.3 a | 70.5±1.1 ab |
| ZX3 | 11.6±0.2 ab | 77.3±2.3 de | 82.3±0.5 c | 285.6±7.7 b | 170.8±22.7 ab | 114.8±15.0 b | 263.7±13.2 bc | −22.0±5.5 c | 71.1±0.5 ab |
| ZX4 | 11.2±0.3 b | 79.3±1.2 d | 84.8±0.4 b | 290.4±7.1 ab | 179.3±5.7 ab | 111.1±12.8 b | 245.6±5.5 c | −44.7±1.7 d | 73.2±1.3 a |
| ZX5 | 9.8±0.4 c | 79.7±1.5 d | 84.3±0.5 b | 303.0±41.9 ab | 161.9±40.4 ab | 141.1±1.6 a | 219.8±41.9 c | −83.1±0.1 e | 70.3±0.6 ab |
| ZX6 | 9.3±0.1 cd | 85.3±0.6 ab | 86.0±0.0 a | 336.7±38.8 a | 182.8±27.7 ab | 153.9±11.2 a | 236.7±38.1 c | −100.0±0.8 e | 70.7±1.1 ab |
| ZX7 | 12.0±0.4 a | 75.3±1.5 de | 81.8±1.2 c | 303.5±12.9 ab | 199.9±15.2 a | 103.5±2.3 b | 305.7±13.1 ab | 2.2±0.2 a | 71.9±1.7 ab |
| ZX8 | 8.5±0.2 e | 86.7±1.5 a | 85.0±0.0 b | 307.4±2.3 ab | 168.2±6.5 ab | 139.2±4.2 a | 228.6±0.1 c | −78.8±2.4 e | 70.0±0.0 b |
Table 3. Comparative analysis of eating and cooking quality among Huxianggeng 216(ZX6) and its seven sister lines
| 品系 Line | 直链淀粉 Amylose content(%) | 胶稠度 Gel consistency (m) | 食味值 Taste value | 峰值黏度 Peak viscosity (RVU) | 热浆黏度Hot paste viscosity (RVU) | 崩解值 Breakdown (RVU) | 终值黏度 Final viscosity (RVU) | 消减值Setback (RVU) | 糊化温度 Gelatinization temperature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZX1 | 8.7±0.3 e | 80.3±1.5 cd | 74.5±1.0 d | 315.6±6.4 ab | 209.4±12.3 a | 106.2±6.0 b | 310.3±6.8 a | −5.3±0.4 b | 73.1±1.2 a |
| ZX2 | 9.2±0.3 d | 82.7±2.1 bc | 81.8±0.8 c | 235.3±7.2 c | 135.1±6.3 b | 100.1±0.8 b | 238.7±7.4 c | 3.4±0.3 a | 70.5±1.1 ab |
| ZX3 | 11.6±0.2 ab | 77.3±2.3 de | 82.3±0.5 c | 285.6±7.7 b | 170.8±22.7 ab | 114.8±15.0 b | 263.7±13.2 bc | −22.0±5.5 c | 71.1±0.5 ab |
| ZX4 | 11.2±0.3 b | 79.3±1.2 d | 84.8±0.4 b | 290.4±7.1 ab | 179.3±5.7 ab | 111.1±12.8 b | 245.6±5.5 c | −44.7±1.7 d | 73.2±1.3 a |
| ZX5 | 9.8±0.4 c | 79.7±1.5 d | 84.3±0.5 b | 303.0±41.9 ab | 161.9±40.4 ab | 141.1±1.6 a | 219.8±41.9 c | −83.1±0.1 e | 70.3±0.6 ab |
| ZX6 | 9.3±0.1 cd | 85.3±0.6 ab | 86.0±0.0 a | 336.7±38.8 a | 182.8±27.7 ab | 153.9±11.2 a | 236.7±38.1 c | −100.0±0.8 e | 70.7±1.1 ab |
| ZX7 | 12.0±0.4 a | 75.3±1.5 de | 81.8±1.2 c | 303.5±12.9 ab | 199.9±15.2 a | 103.5±2.3 b | 305.7±13.1 ab | 2.2±0.2 a | 71.9±1.7 ab |
| ZX8 | 8.5±0.2 e | 86.7±1.5 a | 85.0±0.0 b | 307.4±2.3 ab | 168.2±6.5 ab | 139.2±4.2 a | 228.6±0.1 c | −78.8±2.4 e | 70.0±0.0 b |
| 品系 Line | 穗瘟损失指数 Panicle blast loss index(%) | 病级 Disease grade | 抗性评价 Evaluation of resistance to panicle blast |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZX1 | 0.5 | 1 | 抗病Resistant(R) |
| ZX2 | 16.0 | 5 | 中感Moderately susceptible(MS) |
| ZX3 | 31.6 | 7 | 感Susceptible(S) |
| ZX4 | 30.0 | 5 | 中感Moderately susceptible(MS) |
| ZX5 | 10.1 | 3 | 中抗Moderately resistant(MR) |
| ZX6 | 0.5 | 1 | 抗病Resistant(R) |
| ZX7 | 22.1 | 5 | 中感Moderately susceptible(MS) |
| ZX8 | 46.5 | 7 | 感Susceptible(S) |
Table 4. Comparison of panicle blast resistance among Huxianggeng 216(ZX6) and its seven sister lines
| 品系 Line | 穗瘟损失指数 Panicle blast loss index(%) | 病级 Disease grade | 抗性评价 Evaluation of resistance to panicle blast |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZX1 | 0.5 | 1 | 抗病Resistant(R) |
| ZX2 | 16.0 | 5 | 中感Moderately susceptible(MS) |
| ZX3 | 31.6 | 7 | 感Susceptible(S) |
| ZX4 | 30.0 | 5 | 中感Moderately susceptible(MS) |
| ZX5 | 10.1 | 3 | 中抗Moderately resistant(MR) |
| ZX6 | 0.5 | 1 | 抗病Resistant(R) |
| ZX7 | 22.1 | 5 | 中感Moderately susceptible(MS) |
| ZX8 | 46.5 | 7 | 感Susceptible(S) |
| 品种 Variety | 直播成苗能力 Direct seedling ability | 低氧芽鞘 长度 Hypoxic coleoptile length(cm) | 缺氧反 应指数 Anoxic response index(%) | 中胚轴 长度 Mesocotyl length(cm) | 株高 Plant height(cm) | 抗倒力 Lodging resistance | 发芽率 Germination rate(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苗高 Seedling height/cm | 成苗指数 Seedling index | 低氧Hypoxia | 正常 Normal | ||||||
| 南粳46 Nangeng 46 | 6.6±0.2 d | 2.0±0.8 | 0.8±0.0 d | 42.3±0.2 d | 0.16±0.01 c | 108.7±0.3 a | 4.5±0.2 d | 40.0±1.7 c | 86.7±0.7 b |
| 武香粳1号 | 7.7±0.1 c | 2.0±0.7 | 1.1±0.1 c | 43.3±0.3 c | 0.15±0.01 c | 101.7±0.8 b | 4.9±0.2 c | 66.7±0.6 b | 100.0±0.0 a |
| Wuxianggeng 1 | |||||||||
| 秀水114 Xiushui 114 | 10.5±0.1 a | 2.4±0.5 | 1.8±0.1 a | 50.8±0.3 a | 0.26±0.01 a | 98.5±1.0 c | 6.6±0.1 b | 80.0±0.1 a | 100.0±0.0 a |
| 沪香粳216 | 8.2±0.1 b | 2.0±0.0 | 1.2±0.0 b | 44.9±0.0 b | 0.21±0.03 b | 87.0±0.8 c | 7.5±0.2 a | 80.0±0.2 a | 100.0±0.0 a |
| Huxianggeng 216 | |||||||||
Table 5. Performance of direct seedling related traits among varieties
| 品种 Variety | 直播成苗能力 Direct seedling ability | 低氧芽鞘 长度 Hypoxic coleoptile length(cm) | 缺氧反 应指数 Anoxic response index(%) | 中胚轴 长度 Mesocotyl length(cm) | 株高 Plant height(cm) | 抗倒力 Lodging resistance | 发芽率 Germination rate(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苗高 Seedling height/cm | 成苗指数 Seedling index | 低氧Hypoxia | 正常 Normal | ||||||
| 南粳46 Nangeng 46 | 6.6±0.2 d | 2.0±0.8 | 0.8±0.0 d | 42.3±0.2 d | 0.16±0.01 c | 108.7±0.3 a | 4.5±0.2 d | 40.0±1.7 c | 86.7±0.7 b |
| 武香粳1号 | 7.7±0.1 c | 2.0±0.7 | 1.1±0.1 c | 43.3±0.3 c | 0.15±0.01 c | 101.7±0.8 b | 4.9±0.2 c | 66.7±0.6 b | 100.0±0.0 a |
| Wuxianggeng 1 | |||||||||
| 秀水114 Xiushui 114 | 10.5±0.1 a | 2.4±0.5 | 1.8±0.1 a | 50.8±0.3 a | 0.26±0.01 a | 98.5±1.0 c | 6.6±0.1 b | 80.0±0.1 a | 100.0±0.0 a |
| 沪香粳216 | 8.2±0.1 b | 2.0±0.0 | 1.2±0.0 b | 44.9±0.0 b | 0.21±0.03 b | 87.0±0.8 c | 7.5±0.2 a | 80.0±0.2 a | 100.0±0.0 a |
| Huxianggeng 216 | |||||||||
| 年份 Year | 糙米率 Brown rice rate (%) | 整精米率 Head rice rate (%) | 垩白度 Chalkiness (%) | 透明度 Transparency (Grade) | 碱消值 Alkali digestion value(Grade) | 胶稠度 Gel consistency (mm) | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 83.4 | 69.3 | 1.5 | 2 | 6.5 | 80 | 10.4 |
| 2022 | 83.9 | 71.8 | 2.8 | 2 | 7.0 | 74 | 9.2 |
Table 6. Results of rice quality testing for Huxianggeng 216 in 2021−2022
| 年份 Year | 糙米率 Brown rice rate (%) | 整精米率 Head rice rate (%) | 垩白度 Chalkiness (%) | 透明度 Transparency (Grade) | 碱消值 Alkali digestion value(Grade) | 胶稠度 Gel consistency (mm) | 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 83.4 | 69.3 | 1.5 | 2 | 6.5 | 80 | 10.4 |
| 2022 | 83.9 | 71.8 | 2.8 | 2 | 7.0 | 74 | 9.2 |
| 品种 Variety | 苗瘟病级 Grade of seedling blast | 叶瘟病级 Grade of leaf blast | 穗发病率(病级) Incidence of panicle disease(Disease grade) | 穗瘟损失指数(病级) Rice panicle blast loss index(Disease grade) | 综合指数(病级) Composite index (Disease grade) | 抗性评价 Evaluation of resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沪香粳216 Huxianggeng 216 | 0 | 3 | 20%(5) | 2.0%(1) | 2.5(3) | 中抗MR |
Table 7. Identification of resistance to rice blast in Huxianggeng 216
| 品种 Variety | 苗瘟病级 Grade of seedling blast | 叶瘟病级 Grade of leaf blast | 穗发病率(病级) Incidence of panicle disease(Disease grade) | 穗瘟损失指数(病级) Rice panicle blast loss index(Disease grade) | 综合指数(病级) Composite index (Disease grade) | 抗性评价 Evaluation of resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沪香粳216 Huxianggeng 216 | 0 | 3 | 20%(5) | 2.0%(1) | 2.5(3) | 中抗MR |
| 品种 Variety | 发病率 Incidence rate of rice blast (%) | 抗病等级 Disease resistance grade(Grade) |
|---|---|---|
| 沪香粳216 Huxianggeng 216 | 12.90 | 3 |
| 镇稻88(抗病对照)Zhendao 88 (Disease-resistant control) | 5.71 | 3 |
| 武育粳3号(感病对照)Wuyugeng 3(Susceptible control) | 71.43 | 9 |
Table 8. Identification of resistance to rice stripe disease in Huxianggeng 216
| 品种 Variety | 发病率 Incidence rate of rice blast (%) | 抗病等级 Disease resistance grade(Grade) |
|---|---|---|
| 沪香粳216 Huxianggeng 216 | 12.90 | 3 |
| 镇稻88(抗病对照)Zhendao 88 (Disease-resistant control) | 5.71 | 3 |
| 武育粳3号(感病对照)Wuyugeng 3(Susceptible control) | 71.43 | 9 |
| [1] | 国家统计局. 关于2021年粮食产量数据的公告[EB/OL]. (2021-12-06) [2023-12-16]. http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/zxfb/202112/t20211206_1825053.html. |
| National Bureau of Statistics. Announcement on grain production data for 2021[EB/OL]. (2021-12-06) [2023-12-16]. http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/zxfb/202112/t20211206_1825053.html. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | Qiao W H, Chen Y T, Wang R S, Wei X, Cao L R, Zhang W X, Yang Q W. Nucleotide diversity in waxy gene and validation of single nucleotide polymorphism in relation to amylose content in Chinese microcore rice germplasm[J]. Crop Science, 2012, 52(4): 1689-1697. |
| [3] | 张昌泉, 冯琳皓, 顾铭洪, 刘巧泉. 江苏省水稻品质性状遗传和重要基因克隆研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2021, 43(5): 425-441. |
| Zhang C Q, Feng L H, Gu M H, Liu Q Q. Progress on inheritance and gene cloning for rice grain quality in Jiangsu Province[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(5): 425-441. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Verma D K, Srivastav P P. Introduction to rice aroma, flavor, and fragrance//Verma D K, Srivastav P P. Science and Technology of Aroma, Flavour and Fragrance in Rice[M]. USA: Apple Academic Press, 2019: 3-34. |
| [5] | He Q, Park Y J. Discovery of a novel fragrant allele and development of functional markers for fragrance in rice[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2015, 35(11): 217. |
| [6] | Bradbury L M T, Fitzgerald T L, Henry R J, Jin Q S, Waters D L E. The gene for fragrance in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2005, 3(3): 363-370. |
| [7] | 闫影, 诸光明, 张丽霞, 万常照, 曹黎明, 赵志鹏, 吴书俊. 水稻香味基因分子标记的开发及应用[J]. 西北植物学报, 2015, 35(2): 269-274. |
| Yan Y, Zhu G M, Zhang L X, Wan C Z, Cao L M, Zhao Z P, Wu S J. Development of molecular markers for fragrant gene and its application[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2015, 35(2): 269-274. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Dean R, van Kan J A L, Pretorius Z A, Hammond- Kosack K E, Di Pietro A, Spanu P D, Rudd J J, Dickman M, Kahmann R, Ellis J, Foster G D. The top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology[J]. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2012, 13(4): 414-430. |
| [9] | Zhou B, Qu S H, Liu G F, Dolan M, Sakai H, Lu G D, Bellizzi M, Wang G L. The eight amino-acid differences within three leucine-rich repeats between Pi2 and Piz-t resistance proteins determine the resistance specificity to Magnaporthe grisea[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2006, 19: 1216-1228. |
| [10] | Deng Y W, Zhai K R, Xie Z, Yang D Y, Zhu X D, Liu J Z, Wang X, Qin P, Yang Y Z, Zhang G M, Li Q, Zhang J F, Wu S Q, Milazzo J, Mao B Z, Wang E T, Xie H A, Tharreau D, He Z H. Epigenetic regulation of antagonistic receptors confers rice blast resistance with yield balance[J]. Science, 2017, 355: 962-965. |
| [11] | Lee S K, Song M Y, Seo Y S, Kim H K, Ko S, Cao P J, Suh J P, Yi G, Roh J H, Lee S, An G, Hahn T R, Wang G L, Ronald P, Jeon J S. Rice Pi5-mediated resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae requires the presence of two coiled- coil-nucleotide-binding-leucine-rich repeat genes[J]. Genetics, 2009, 181: 1627-1638. |
| [12] | Ashikawa I, Hayashi N, Yamane H, Kanamori H, Wu J Z, Matsumoto T, Ono K, Yano M. Two adjacent nucleotide- binding site-leucine-rich repeat class genes are required to confer Pikm-specific rice blast resistance[J]. Genetics, 2008, 180: 2267-2276. |
| [13] | Bryan G T, Wu K S, Farrall L, Jia Y, Hershey H P, McAdams S A, Faulk K N, Donaldson G K, Tarchini R, Valent B. A single amino acid difference distinguishes resistant and susceptible alleles of the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta[J]. The Plant Cell, 2000, 12: 2033-2046. |
| [14] | 李莹. 抗稻瘟病早粳稻空育131(Pid2/Pid3)的培育[D]. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江大学, 2015. |
| Li Y. Cultivation of blast resistant early japonica rice Kongyu 131 (Pid2/Pid3)[D]. Harbin: Heilongjiang University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 国家水稻数据中心. 中国水稻品种及其系谱数据库[DB/OL]. http://www.ricedata.cn/variety/. |
| National Rice Data Center. China Rice Varieties and Pedigree Database[DB/OL]. http://www.ricedata.cn/gene/. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 陈涛, 骆名瑞, 张亚东, 朱镇, 赵凌, 赵庆勇, 周丽慧, 姚姝, 于新, 王才林. 利用四引物扩增受阻突变体系PCR技术检测水稻低直链淀粉含量基因Wx-mq[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(5): 529-534. |
| Chen T, Luo M R, Zhang Y D, Zhu Z, Zhao L, Zhao Q Y, Zhou L H, Yao S, Yu X, Wang C L. Detection of Wx-mq gene for low-amylose content tetra-primer amplification refractory mutation system PCR in rice[J]. Chinese Journal Rice Science, 2013, 27(5): 529-534. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 姚姝, 张亚东, 刘燕清, 赵春芳, 周丽慧, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, Pillay B, 王才林. Wxmp基因背景下可溶性淀粉合成酶基因SSⅡa和去分支酶基因PUL对水稻蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2020, 34(3): 217-227. |
| Yao S, Zhang Y D, Liu Y Q, Zhao C F, Zhou L H, Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Zhu Z, Pillay B, Wang C L. Allelic effects on eating and cooking quality of SSⅡa and PUL genes under Wxmp background in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2020, 34(3): 217-227. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 王军, 杨杰, 陈志德, 仲维功. 水稻香米基因标记的开发与应用[J]. 分子植物育种, 2008, 6(6): 1209-1212. |
| Wang J, Yang J, Chen Z D, Zhong W G. Development and application of fragrance gene markers in rice[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2008, 6(6): 1209-1212. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 王忠华. 水稻抗稻瘟病基因Pi-ta分子标记的建立及其应用[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2003. |
| Wang Z H. Development of molecular markers of the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta and its application[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2003. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 范方军, 王芳权, 刘永峰, 王军, 朱金燕, 李文奇, 仲维功, 杨杰. Pi-b、Pi-ta、Pikm和Pi54对水稻穗颈瘟的抗性评价[J]. 华北农学报, 2014, 29(3): 221-226. |
| Fan F J, Wang F Q, Liu Y F, Wang J, Zhu J Y, Li W Q, Zhong W G, Yang J. Evaluation of resistance to rice panicle blast with resistant genes Pi-b, Pi-ta, Pikm and Pi54[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-sinica, 2014, 29(3): 221-226. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 吴书俊, 闫影, 张丽霞, 万常照, 龚凯, 顾永平. 分子标记辅助选择培育抗条纹叶枯病香粳品种沪香粳106[J]. 上海农业学报, 2017, 33(3): 25-30. |
| Wu S J, Yan Y, Zhang L X, Wan C Z, Gong K, Gu Y P. Breeding of RSD-resistant and fragrant japonica variety ‘Huxiangjing106’ by marker assisted selection in rice(Oryza sativa)[J]. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai, 2017, 33(3): 25-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 陈桂华, 邓化冰, 张桂莲, 唐文帮, 黄璜. 水稻茎秆性状与抗倒性的关系及配合力分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(3): 407-417. |
| Chen G H, Deng H B, Zhang G L, Tang W B, Huang H. The correlation of stem characters and lodging resistance and combining ability analysis in rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(3): 407-417. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 朱镇, 赵凌, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 赵春芳, 张亚东, 王才林. 利用分子标记辅助选择培育优良食味、低谷蛋白香粳稻新品系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(1): 55-65. |
| Chen T, Zhao Q Y, Zhu Z, Zhao L, Yao S, Zhou L H, Zhao C F, Zhang Y D, Wang C L. Development of new low glutelin content japonica rice lines with good eating quality and fragrance by molecular marker-assisted selection[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 55-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 降好宇, 曾盖, 郝明, 黄湘桂, 肖应辉. 广谱抗稻瘟病种质75-1-127的褐飞虱抗性基因鉴定及分子标记辅助选择育种[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(2): 227-234. |
| Jiang H Y, Zeng G, Hao M, Huang X G, Xiao Y H. Identification of brown planthopper resistance genes in broad-spectrum blast resistant rice germplasm 75-1-127 and its molecular marker-assisted selection breeding[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(2): 227-234. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 马作斌, 全东兴, 时羽, 王昌华, 周广春, 郑文静. 分子标记辅助选育聚合抗稻瘟病基因Pi5及Pita的水稻新品系[J]. 分子植物育种, 2021(1): 173-179. |
| Ma Z B, Quan D X, Shi Y, Wang C H, Zhou G C, Zheng W J. Molecular markers-assisted selection of new rice lines with blast resistance gene Pi5 and Pita[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021(1): 173-179. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 上海市农业农村委员会. 关于2021年水稻机械化种植情况的通报[EB/OL]. (2021-08-25) [2023-12-25]. http://nyncw.sh.gov.cn/xxgk/20210825/1234567890abcdef.html. |
| Shanghai Agriculture and Rural Affairs Committee. Bulletin on Mechanized Rice Planting in 2021[EB/OL]. (2021-08-25) [2023-12-25]. http://nyncw.sh.gov.cn/xxgk/20210825/1234567890abcdef.html. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 熊怀阳, 李阳生. 水稻的耐淹性状及其Sub1基因[J]. 遗传, 2010, 32(9): 886-892. |
| Xiong H Y, Li Y S. Submergence tolerance and Sub1 locus in rice[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2010, 32(9): 886-892. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Kretzschmar T, Pelayo M A F, Trijatmiko K R, Gabunada L F M, Alam R, Jimenez R, Mendioro M S, Slamet-Loedin I H, Sreenivasulu N, Bailey-Serres J, Ismail A M, Mackill D J. A trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase enhances anaerobic germination tolerance in rice[J]. Nature Plants, 2015, 1(9): 15124. |
| [29] | Ye N H, Wang F Z, Shi L, Chen M X, Cao Y Y, Zhu F Y, Wu Y Z, Xie L J, Liu T Y, Su Z Z, Xiao S, Zhang H, Yang J, Gu H Y, Hou X X, Hu Q J, Yi H J, Zhu C X, Zhang J, Liu Y G. Natural variation in the promoter of rice calcineurin B-like protein 10(OsCBL10) affects flooding tolerance during seed germination among rice subspecies[J]. The Plant Journal, 2018, 94(4): 612-625. |
| [30] | Sun J, Zhang G C, Cui Z B, Kong X M, Yu X Y, Gui R, Han Y Q, Li Z, Lang H, Hua Y C, Zhang X M, Xu Q, Tang L, Xu Z J, Ma D R, Chen W F. Regain flood adaptation in rice through a 14-3-3 protein OsGF14h[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 5664. |
| [31] | He Y Q, Sun S, Zhao J, Huang Z B, Peng L L, Huang C W, Tang Z B, Huang Q Q, Wang Z F. UDP- glucosyltransferase OsUGT75A promotes submergence tolerance during rice seed germination[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 2296. |
| [32] | Lü Y S, Shao G N, Jiao G A, Sheng Z H, Xie L H, Hu S K, Tang S Q, Wei X J, Hu P S. Targeted mutagenesis of POLYAMINE OXIDASE 5 that negatively regulates mesocotyl elongation enables the generation of direct-seeding rice with improved grain yield[J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(2): 344-351. |
| [33] | Xiong Q, Ma B, Lu X, Huang Y H, He S J, Yang C, Yin C C, Zhao H, Zhou Y, Zhang W K, Wang W S, Li Z K, Chen S Y, Zhang J S. Ethylene-inhibited jasmonic acid biosynthesis promotes mesocotyl/coleoptile elongation of etiolated rice seedlings[J]. The Plant Cell, 2017, 29: 1053-1072. |
| [34] | Sun S Y, Wang T, Wang L L, Li X M, Jia Y C, Liu C, Huang X H, Xie W B, Wang X L. Natural selection of a GSK3 determines rice mesocotyl domestication by coordinating strigolactone and brassinosteroid signaling[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 2523. |
| [35] | 李先锋. 水稻热精胺合成酶基因OsACL5的功能研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2022. |
| Li X F. Functional analysis of OsACL5, a gene putatively encoding thermospermine synthase[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] |
LU Yezi, QIU Jiehua, JIANG Nan, KOU Yanjun, SHI Huanbin.
Research Progress in Effectors of Magnaporthe oryzae [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 287-294. |
| [2] |
WANG Chaorui, ZHOU Yukun, WEN Ya, ZHANG Ying, FA Xiaotong, XIAO Zhilin, ZHANG Hao.
Effects of Straw Returning Methods on Soil Characteristics and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Paddy Fields and Their Regulation Through Water-fertilizer Interactions [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 295-305. |
| [3] |
WANG Yaxuan, WANG Xinfeng, YANG Houhong, LIU Fang, XIAO Jing, CAI Yubiao, WEI Qi, FU Qiang, WAN Pinjun.
Recent Advances in Mechanisms of Adaptation of Planthoppers to Rice Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 306-321. |
| [4] |
HUANG Tao, WEI Zhaogen, CHENG Qi, CHENG Ze, LIU Xin, WANG Guangda, HU Keming, XIE Wenya, CHEN Zongxiang, FENG Zhiming, ZUO Shimin.
Gene |
| [5] |
MA Shunting, HU Yungao, GAO Fangyuan, LIU Liping, MOU Changling, LÜ Jianqun, SU Xiangwen, LIU Song, LIANG Yuyu, REN Guangjun, GUO Hongming.
Functional Study of Rice Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor OseIF6.2 in Grain Size Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 331-342. |
| [6] |
ZHANG Bintao, LIU Congcong, GUO Mingliang, YANG Shaohua, WU Shiqiang, GUO Longbiao, ZHU Yiwang.
Evaluation of Blast Resistance and Identification of Superior Haplotype of OsDR8 in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 343-351. |
| [7] |
WEI Xinyu, ZENG Yuehui, XIAO Changchun, HUANG Jianhong, RUAN Hongchun, YANG Wangxing, ZOU Wenguang, XU Xuming.
Cloning and Functional Verification of Rice-Blast Resistance Gene Pi-kf2(t) in Kangfeng B [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 352-364. |
| [8] |
LI Wenqi, XU Yang, WANG Fangquan ZHU Jianping, TAO Yajun, LI Xia, FAN Fangjun, JIANG Yanjie, CHEN Zhihui, YANG Jie.
Development and Application of KASP Marker for Broad-Spectrum Resistance Gene PigmR to Rice Blast [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 365-372. |
| [9] |
WEI Huanhe, WANG Lulu, MA Weiyi, ZHANG Xiang, ZUO Boyuan, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHU Wang, ZHU Jizou, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, DAI Qigen.
Grain-filling Characteristics and Its Relationship with Grain Yield Formation of japonica Rice Nanjing 9108 Under Combined Salinity-drought Stress [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 373-386. |
| [10] |
ZHANG Haiwei, GU Xinyi, CHEN Mingshuai, LI Fukang, SHI Yuecheng, YANG Ting, JIANG Shuochen.
Effects of Nitrogen Type of Basal Fertilizer on Growth, Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Ratooning Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 387-398. |
| [11] |
SHEN Zhida, YU Qiuhua, ZHANG Bin, CAO Yudong, WANG Shaohua, WANG Hongfei, WU Yongqing, DAI Zhigang, LI Xiaokun.
Effects of Phosphorus Fertilizer Application Rate on Grain Yield, Phosphorus Accumulation and Utilization of Direct-seeded Rice in Hubei Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 399-411. |
| [12] |
HE Yong, ZHANG Shiqian, WANG Zhicheng, ZHAN Xiaokang, DING Yike, LIU Xiaorui, MA Susu, TIAN Zhihong.
Synergistic Impact of Piriformospora indica and Compound Fertilizer on Rice Seedling Quality for Mechanical Transplanting [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 412-422. |
| [13] | WU Jinshui, TANG Jiangying, TAN Li, GUO Zhiqiang, YANG Juan, ZHANG Xinzhen, CHEN Guifang, WANG Jianlong, SHI Wanju. Mechanisms of Arsenic Uptake and Transport in Rice and Agronomic Mitigation Strategies [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 143-155. |
| [14] | MA Weiyi, ZHU Jizou, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, DIAO Liuyun, WANG Lulu, MENG Tianyao, GAO Pinglei, CHEN Yinglong, DAI Qigen, WEI Huanhe. Research Progress in Effects of Salt and Drought Stresses on Rice Quality Formation and Associated Physiological Mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 156-170. |
| [15] | ZHANG Laitong, YANG Le, LIU Hong, ZHAO Xueming, CHENG Tao, XU Zhenjiang. Research Advances of Fragrance Substances in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 171-186. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||