
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2018, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 387-397.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.8004
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chang TIAN1,2, Xuan ZHOU3, Guixian XIE1,2,*( ), Qiang LIU1,2,*(
), Qiang LIU1,2,*( ), Xiangmin RONG1,2, Yuping ZHANG1,2, Lizhang TAN1, Jianwei PENG1,2
), Xiangmin RONG1,2, Yuping ZHANG1,2, Lizhang TAN1, Jianwei PENG1,2
Online:2018-07-10
Published:2018-07-10
Contact:
Guixian XIE, Qiang LIU
About author:#共同第一作者
田昌1,2, 周旋3, 谢桂先1,2,*( ), 刘强1,2,*(
), 刘强1,2,*( ), 荣湘民1,2, 张玉平1,2, 谭力彰1, 彭建伟1,2
), 荣湘民1,2, 张玉平1,2, 谭力彰1, 彭建伟1,2
通讯作者:
谢桂先,刘强
作者简介:#These authors contributed equally to this work
基金资助:CLC Number:
Chang TIAN, Xuan ZHOU, Guixian XIE, Qiang LIU, Xiangmin RONG, Yuping ZHANG, Lizhang TAN, Jianwei PENG. Ammonia Volatilization Loss and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Double-cropping Rice Field as Affected by Decreasing Controlled-release Urea Application Level[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(4): 387-397.
田昌, 周旋, 谢桂先, 刘强, 荣湘民, 张玉平, 谭力彰, 彭建伟. 控释尿素减施对双季稻田氨挥发损失和氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 32(4): 387-397.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.8004
| 稻季 Season | 肥料类型 Fertilizer type | 施肥时期 Application date | 施肥量Fertilizer application rate / (kg·hm-2) | 施肥方式 Application method | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | U | CRU1 | CRU2 | CRU3 | CRU4 | ||||
| 早稻 Early rice | 尿素 Urea | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 0.0 | 90.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 土层混施 Incorporated |
| 追肥 Topdressing | 0.0 | 60.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 表层撒施 Broadcated | ||
| 控释尿素 Controlled-release urea | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 0.0 | 0.0 | 90.0 | 81.0 | 72.0 | 63.0 | 土层混施 Incorporated | |
| 追肥 Topdressing | 0.0 | 0.0 | 60.0 | 54.0 | 48.0 | 42.0 | 表层撒施 Broadcated | ||
| 过磷酸钙 Calcium superphosphate | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 72.0 | 72.0 | 72.0 | 72.0 | 72.0 | 72.0 | 土层混施 Incorporated | |
| 氯化钾 Potassium chloride | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 54.0 | 54.0 | 54.0 | 54.0 | 54.0 | 54.0 | 土层混施 Incorporated | |
| 追肥 Topdressing | 36.0 | 36.0 | 36.0 | 36.0 | 36.0 | 36.0 | 表层撒施 Broadcated | ||
| 晚稻 Late rice | 尿素 Urea | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 0.0 | 108.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 土层混施 Incorporated |
| 追肥 Topdressing | 0.0 | 72.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 表层撒施 Broadcated | ||
| 控释尿素 Controlled-release urea | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 0.0 | 0.0 | 108.0 | 97.2 | 86.4 | 75.6 | 土层混施 Incorporated | |
| 追肥 Topdressing | 0.0 | 0.0 | 72.0 | 64.8 | 57.6 | 50.4 | 表层撒施 Broadcated | ||
| 过磷酸钙 Calcium superphosphate | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 60.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 土层混施 Incorporated | |
| 氯化钾 Potassium chloride | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 63.0 | 63.0 | 63.0 | 63.0 | 63.0 | 63.0 | 土层混施 Incorporated | |
| 追肥 Topdressing | 42.0 | 42.0 | 42.0 | 42.0 | 42.0 | 42.0 | 表层撒施 Broadcated | ||
Table 1 Fertilizer application rate and method in the early and late cropping seasons.
| 稻季 Season | 肥料类型 Fertilizer type | 施肥时期 Application date | 施肥量Fertilizer application rate / (kg·hm-2) | 施肥方式 Application method | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | U | CRU1 | CRU2 | CRU3 | CRU4 | ||||
| 早稻 Early rice | 尿素 Urea | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 0.0 | 90.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 土层混施 Incorporated |
| 追肥 Topdressing | 0.0 | 60.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 表层撒施 Broadcated | ||
| 控释尿素 Controlled-release urea | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 0.0 | 0.0 | 90.0 | 81.0 | 72.0 | 63.0 | 土层混施 Incorporated | |
| 追肥 Topdressing | 0.0 | 0.0 | 60.0 | 54.0 | 48.0 | 42.0 | 表层撒施 Broadcated | ||
| 过磷酸钙 Calcium superphosphate | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 72.0 | 72.0 | 72.0 | 72.0 | 72.0 | 72.0 | 土层混施 Incorporated | |
| 氯化钾 Potassium chloride | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 54.0 | 54.0 | 54.0 | 54.0 | 54.0 | 54.0 | 土层混施 Incorporated | |
| 追肥 Topdressing | 36.0 | 36.0 | 36.0 | 36.0 | 36.0 | 36.0 | 表层撒施 Broadcated | ||
| 晚稻 Late rice | 尿素 Urea | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 0.0 | 108.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 土层混施 Incorporated |
| 追肥 Topdressing | 0.0 | 72.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 表层撒施 Broadcated | ||
| 控释尿素 Controlled-release urea | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 0.0 | 0.0 | 108.0 | 97.2 | 86.4 | 75.6 | 土层混施 Incorporated | |
| 追肥 Topdressing | 0.0 | 0.0 | 72.0 | 64.8 | 57.6 | 50.4 | 表层撒施 Broadcated | ||
| 过磷酸钙 Calcium superphosphate | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 60.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 土层混施 Incorporated | |
| 氯化钾 Potassium chloride | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 63.0 | 63.0 | 63.0 | 63.0 | 63.0 | 63.0 | 土层混施 Incorporated | |
| 追肥 Topdressing | 42.0 | 42.0 | 42.0 | 42.0 | 42.0 | 42.0 | 表层撒施 Broadcated | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 分蘖肥Topdressing for tillering | 总计Total | N肥利用率 Nitrogen use efficiency/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 损失量 Cumulative loss /(kg·hm-2) | 损失率 Loss rate/% | 损失量 Cumulative loss /(kg·hm-2) | 损失率 Loss rate/% | 损失量 Cumulative loss /(kg·hm-2) | 损失率 Loss rate/% | ||||
| CK | 3.3±1.3 d | 4.2±0.5 e | 7.6±1.2 e | ||||||
| U | 22.9±0.4 a | 21.7 | 24.3±2.0 a | 33.5 | 47.2±2.2 a | 26.4 | 23.0 b | ||
| CRU1 | 14.5±0.1 b | 12.4 | 17.7±0.8 b | 22.5 | 32.3±0.9 b | 16.5 | 34.3 a | ||
| CRU2 | 12.8±0.7 bc | 11.7 | 15.1±0.6 bc | 20.1 | 27.9±0.8 c | 15.1 | 40.5 a | ||
| CRU3 | 12.2±1.1 bc | 12.3 | 13.4±1.4 cd | 19.1 | 25.6±0.6 cd | 15.0 | 38.8 a | ||
| CRU4 | 12.0±0.5 c | 13.7 | 10.9±1.3 d | 15.8 | 22.8±0.9 d | 14.6 | 37.8 a | ||
| 拟合方程Equation (y=ax+b) | |||||||||
| a | 0.1221 | - | 0.2110 | 0.1402 | 0.1577 | 0.0388 | - | ||
| b | 3.4778 | - | 3.6720 | 1.5286 | 7.1498 | 10.3300 | - | ||
| R2 | 0.9872 | - | 0.9512 | 0.9626 | 0.9899 | 0.8210 | - | ||
| r | 0.994** | - | 0.975** | 0.981* | 0.995** | 0.904 | - | ||
Table 2 Cumulative NH3 volatilization loss and loss ratio after fertilization and their fitted equations with N application rate for early rice season.
| 处理 Treatment | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 分蘖肥Topdressing for tillering | 总计Total | N肥利用率 Nitrogen use efficiency/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 损失量 Cumulative loss /(kg·hm-2) | 损失率 Loss rate/% | 损失量 Cumulative loss /(kg·hm-2) | 损失率 Loss rate/% | 损失量 Cumulative loss /(kg·hm-2) | 损失率 Loss rate/% | ||||
| CK | 3.3±1.3 d | 4.2±0.5 e | 7.6±1.2 e | ||||||
| U | 22.9±0.4 a | 21.7 | 24.3±2.0 a | 33.5 | 47.2±2.2 a | 26.4 | 23.0 b | ||
| CRU1 | 14.5±0.1 b | 12.4 | 17.7±0.8 b | 22.5 | 32.3±0.9 b | 16.5 | 34.3 a | ||
| CRU2 | 12.8±0.7 bc | 11.7 | 15.1±0.6 bc | 20.1 | 27.9±0.8 c | 15.1 | 40.5 a | ||
| CRU3 | 12.2±1.1 bc | 12.3 | 13.4±1.4 cd | 19.1 | 25.6±0.6 cd | 15.0 | 38.8 a | ||
| CRU4 | 12.0±0.5 c | 13.7 | 10.9±1.3 d | 15.8 | 22.8±0.9 d | 14.6 | 37.8 a | ||
| 拟合方程Equation (y=ax+b) | |||||||||
| a | 0.1221 | - | 0.2110 | 0.1402 | 0.1577 | 0.0388 | - | ||
| b | 3.4778 | - | 3.6720 | 1.5286 | 7.1498 | 10.3300 | - | ||
| R2 | 0.9872 | - | 0.9512 | 0.9626 | 0.9899 | 0.8210 | - | ||
| r | 0.994** | - | 0.975** | 0.981* | 0.995** | 0.904 | - | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 分蘖肥 Tillering topdressing | 总计 Total | N肥利用率 Nitrogen use efficiency/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 损失量 Cumulative loss /(kg·hm-2) | 损失率 Loss rate/% | 损失量 Cumulative loss /(kg·hm-2) | 损失率 Loss rate/% | 损失量 Cumulative loss /(kg·hm-2) | 损失率 Loss rate/% | ||||
| CK | 5.2±0.7 c | 5.1±0.2 d | 10.3±0.7 d | ||||||
| U | 27.4±2.6 a | 20.6 | 34.4±2.3 a | 40.7 | 61.9±4.2 a | 28.7 | 20.0 c | ||
| CRU1 | 19.9±2.1 b | 13.7 | 22.1±1.8 b | 23.6 | 42.1±1.3 b | 17.6 | 33.8 b | ||
| CRU2 | 20.6±2.4 b | 15.9 | 17.6±2.4 bc | 19.2 | 38.2±4.6 bc | 17.2 | 39.2 a | ||
| CRU3 | 17.5±1.8 b | 14.3 | 17.2±1.5 bc | 21.0 | 34.8±3.3 bc | 17.0 | 38.1 a | ||
| CRU4 | 15.7±1.8 b | 14.0 | 14.6±0.4 c | 18.8 | 30.4±2.2 c | 15.9 | 38.0 a | ||
| 拟合方程Equation (y=ax+b) | |||||||||
| a | 0.1447 | - | 0.2172 | 0.1736 | 0.1737 | 0.0300 | - | ||
| b | 5.1775 | - | 4.7117 | 10.0430 | 9.8891 | 12.3450 | - | ||
| R2 | 0.9823 | - | 0.9637 | 0.5538 | 0.9951 | 0.9021 | - | ||
| r | 0.991** | - | 0.982** | 0.744 | 0.998** | 0.941 | - | ||
Table 3 Cumulative NH3 volatilization loss and loss ratio after fertilization and their fitted equations with N application rate for late rice season
| 处理 Treatment | 基肥 Basal fertilizer | 分蘖肥 Tillering topdressing | 总计 Total | N肥利用率 Nitrogen use efficiency/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 损失量 Cumulative loss /(kg·hm-2) | 损失率 Loss rate/% | 损失量 Cumulative loss /(kg·hm-2) | 损失率 Loss rate/% | 损失量 Cumulative loss /(kg·hm-2) | 损失率 Loss rate/% | ||||
| CK | 5.2±0.7 c | 5.1±0.2 d | 10.3±0.7 d | ||||||
| U | 27.4±2.6 a | 20.6 | 34.4±2.3 a | 40.7 | 61.9±4.2 a | 28.7 | 20.0 c | ||
| CRU1 | 19.9±2.1 b | 13.7 | 22.1±1.8 b | 23.6 | 42.1±1.3 b | 17.6 | 33.8 b | ||
| CRU2 | 20.6±2.4 b | 15.9 | 17.6±2.4 bc | 19.2 | 38.2±4.6 bc | 17.2 | 39.2 a | ||
| CRU3 | 17.5±1.8 b | 14.3 | 17.2±1.5 bc | 21.0 | 34.8±3.3 bc | 17.0 | 38.1 a | ||
| CRU4 | 15.7±1.8 b | 14.0 | 14.6±0.4 c | 18.8 | 30.4±2.2 c | 15.9 | 38.0 a | ||
| 拟合方程Equation (y=ax+b) | |||||||||
| a | 0.1447 | - | 0.2172 | 0.1736 | 0.1737 | 0.0300 | - | ||
| b | 5.1775 | - | 4.7117 | 10.0430 | 9.8891 | 12.3450 | - | ||
| R2 | 0.9823 | - | 0.9637 | 0.5538 | 0.9951 | 0.9021 | - | ||
| r | 0.991** | - | 0.982** | 0.744 | 0.998** | 0.941 | - | ||
| 处理 Treatment | 损失量 Total loss /(kg·hm-2) | 损失率 Loss rate /% | 籽粒产量 Grain yield/(t·hm-2) | 增产率 Increasing rate/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻 Early rice | 晚稻 Late rice | 双季稻 Double season rice | 早稻 Early rice | 晚稻 Late rice | 双季稻 Double season rice | ||||
| CK | 17.9±1.8 e | 4.5±0.1 c | 5.2±0.1 e | 9.6±0.2 e | |||||
| U | 109.1±3.4 a | 27.6 | 5.5±0.3 b | 6.2±0.1 d | 11.7±0.1 d | 23.2 | 19.9 | 21.4 | |
| CRU1 | 74.3±2.0 b | 17.1 | 6.0±0.2 a | 7.1±0.2 ab | 13.1±0.1 b | 34.7 | 38.1 | 36.5 | |
| CRU2 | 66.1±5.4 bc | 16.2 | 6.3±0.1 a | 7.5±0.2 a | 13.8±0.1 a | 41.5 | 44.9 | 43.4 | |
| CRU3 | 60.3±3.7 cd | 16.1 | 5.9±0.1 ab | 6.9±0.1 bc | 12.9±0.1 bc | 33.6 | 34.0 | 33.8 | |
| CRU4 | 53.2±2.8 d | 15.3 | 5.8±0.2 ab | 6.6±0.1 c | 12.5±0.1 c | 31.1 | 27.8 | 29.4 | |
Table 4 NH3 volatilization loss during double-cropping rice season and grain yield.
| 处理 Treatment | 损失量 Total loss /(kg·hm-2) | 损失率 Loss rate /% | 籽粒产量 Grain yield/(t·hm-2) | 增产率 Increasing rate/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早稻 Early rice | 晚稻 Late rice | 双季稻 Double season rice | 早稻 Early rice | 晚稻 Late rice | 双季稻 Double season rice | ||||
| CK | 17.9±1.8 e | 4.5±0.1 c | 5.2±0.1 e | 9.6±0.2 e | |||||
| U | 109.1±3.4 a | 27.6 | 5.5±0.3 b | 6.2±0.1 d | 11.7±0.1 d | 23.2 | 19.9 | 21.4 | |
| CRU1 | 74.3±2.0 b | 17.1 | 6.0±0.2 a | 7.1±0.2 ab | 13.1±0.1 b | 34.7 | 38.1 | 36.5 | |
| CRU2 | 66.1±5.4 bc | 16.2 | 6.3±0.1 a | 7.5±0.2 a | 13.8±0.1 a | 41.5 | 44.9 | 43.4 | |
| CRU3 | 60.3±3.7 cd | 16.1 | 5.9±0.1 ab | 6.9±0.1 bc | 12.9±0.1 bc | 33.6 | 34.0 | 33.8 | |
| CRU4 | 53.2±2.8 d | 15.3 | 5.8±0.2 ab | 6.6±0.1 c | 12.5±0.1 c | 31.1 | 27.8 | 29.4 | |
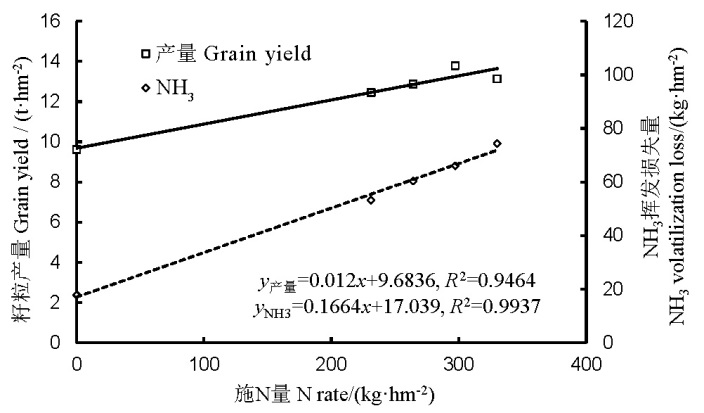
Fig. 5. Relationship of controlled-release urea N application rate with grain yield and total NH3 volatilization loss in early- and late-rice seasons.
| [1] | 彭少兵, 黄见良, 钟旭华, 杨建昌, 王光火, 邹应斌, 张福锁, 朱庆森, Roland Buresh, Christian Witt.提高中国稻田氮肥利用率的研究策略. 中国农业科学, 2002, 35(9): 1095-1103. |
| Peng S B, Huang J L, Zhong X H, Yang J C, Zou Y B, Zhang F S, Zhu Q S, Roland B, Christian W.Research strategy in improving fertilizer-nitrogen use efficiency of irrigated rice in China.Sci Agric Sin, 2002, 35(9): 1095-1103. (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 杨梢娜, 俞巧钢, 叶静, 姜丽娜, 马军伟, 王强, 汪建妹, 孙万春, 符建荣. 施氮水平对杂交晚粳“浙优12”产量及氮素利用效率的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(5): 1120-1125. |
| Yang S N, Yu Q G, Ye J, Jiang L N, Ma J W, Wang Q, Wang J M, Sun W C, Fu J R.Effects of nitrogen fertilization on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of hybrid rice.Plant Nutr & Fert Sci, 2010, 16(5): 1120-1125. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 朱德峰, 陈惠哲, 徐一成, 张玉屏. 我国双季稻生产机械化制约因子与发展对策. 中国稻米, 2013, 19(4):1-4. |
| Zhu D F, Chen H Z, Xu Y C, Zhang Y P.Constraints and countermeasures of the mechanization of double rice production in China.China Rice, 2013, 19(4): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 刘立军, 杨立年, 孙小淋, 王志琴, 杨建昌. 水稻实地氮肥管理的氮肥利用效率及其生理原因. 作物学报, 2009, 35(9): 1672-1680. |
| Liu L J, Yang L N, Sun X L, Wang Z Q, Yang J C.Fertilizer-nitrogen use efficiency and its physiological mechanism under site-specific nitrogen management in rice.Acta Agron Sin, 2009, 35(9): 1672-1680. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 蔡贵信. 稻田中化肥氮的气态损失. 土壤学报, 1995, 32(2): 128-135. |
| Cai G X.Evaluation of gaseous nitrogen losses from fertilizers applied to flooded rice fields.Acta Pedol Sin, 1995, 32(2): 128-135. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Ghosh B C, Bhat R.Environmental hazards of nitrogen loading in wetland rice fields.Environ Poll, 1998, 102(1): 123-126. |
| [7] | Gao X J, Hu X F, Wang S P, He B G, Xu S Y.Nitrogen losses from flooded rice field.Pedosphere, 2002, 12(2): 151-156. |
| [8] | 赵冬, 颜廷梅, 乔俊, 杨林章, 吕寒. 太湖地区稻田氮素损失特征及环境效应分析. 生态环境学报, 2012, 21(6): 1149-1154. |
| Zhao D, Yan TM, Qiao J, Yang L Z, Lv H.Characteristics of N loss and environmental effect of paddy field in Taihu area.Ecol & Environ Sci, 2012, 21(6): 1149-1154. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 邓美华, 尹斌, 张绍林, 朱兆良, 石孝均. 不同施氮量和施氮方式对稻田氨挥发损失的影响. 土壤, 2006, 38(3): 263-269. |
| Deng M H, Yin B, Zhang S L, Zhu Z L, Shi X J.Effects of rate and method of N application on ammonia volatilization in paddy fields.Soils, 2006, 38(3): 263-269. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | Yang F, Tan J, Zhao Q, Du Z, He K, Ma Y, Duan F, Chen G, Zhao Q,.Characteristics of PM2.5 speciation in representative megacities and across China.Atmos Chem & Physiol, 2011, 11(11): 1025-1051. |
| [11] | Feng L, Liao W.Legislation, plans, and policies for prevention and control of air pollution in China: Achievements, challenges, and improvements.J Clean Prod, 2016, 112: 1549-1558. |
| [12] | Ho K F, Ho S S H, Huang R J, Chuang H C, Cao J J, Han Y M, Lui K H, Ning Z, Chuang K J, Cheng T J, Lee S C, Hu D, Wang B, Zhang R J. Chemical composition and bioreactivity of PM 2.5, during 2013 haze events in China.Atmos Environ, 2016, 126: 162-170. |
| [13] | Vlek P L, Byrnes B H.The efficiency and loss of fertilizer N in lowland rice.Fert Res, 1986, 9(1-2): 131-147. |
| [14] | 朱兆良, 孙波, 杨林章, 张林秀. 我国农业面源污染的控制政策和措施. 科技导报, 2005, 23(4): 47-51. |
| Zhu Z L, Sun B, Yang L Z, Zhang L X.Policy and countermeasures to control non-point pollution of agriculture in China.Sci Technol Rev, 2005, 23(4): 47-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | Lin DX, Fan XH, Hu F, Zhao H T, Luo J F.Ammonia volatilization and nitrogen utilization efficiency in response to urea application in rice fields of the Taihu Lake region, China.Pedosphere, 2007, 17(5): 639-645. |
| [16] | 叶世超, 林忠成, 戴其根, 贾玉书, 顾海燕, 陈京都, 许露生, 吴福观, 张洪程, 霍中洋, 许轲, 魏海燕. 施氮量对稻季氨挥发特点与氮素利用的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(1): 71-78. |
| Ye S C, Lin Z C, Dai Q G, Jia Y S, Gu H Y, Chen J D, Xu L S, Wu F G, Zhang H C, He Z Y, Xu K, Wei H Y.Effects of nitrogen application rate on ammonia volatilization and nitrogen utilization in rice growing season.Chin J Rice Sci, 2011, 25(1): 71-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 高翠民, 梅新兰, 商庆银, 杨秀霞, 沈其荣, 郭世伟. 长期不同施肥红壤性稻田水稻产量和氨挥发的变化. 南京农业大学学报, 2012, 35(1): 63-68. |
| Gao C M, Mei X L, Shang Q Y, Yang X X, Shen Q R, Guo S W.Dynamic change of ammonia volatilization and rice yield during double-rice growing seasons in red paddy soil under different long-term fertilizing systems.J Nanjing Agric Univ, 2012, 35(1): 63-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 曹金留, 田光明, 任立涛, 蔡祖聪, 何任红. 江苏南部地区稻麦两熟土壤中尿素的氨挥发损失. 南京农业大学学报, 2000, 23(4): 51-54. |
| Cao J L, Tian G M, Ren LT Cai Z C, He R H. Ammonia volatilization from urea applied to the field of wheat and rice in southern Jiangsu Province T.Nanjing Agric Univ, 2000, 23(4): 51-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 张惠, 杨正礼, 罗良国, 张晴雯, 易军, 王永生, 陈媛媛, 王明. 黄河上游灌区稻田氨挥发损失研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(5): 1131-1139. |
| Zhang H, Yang Z L, Luo L G, Zhang Q W, Yi J, Wang Y S, Chen Y Y, Wang M.Study on the ammonia volatilization from paddy field in irrigation area of the Yellow River.Plant Nutr & Fert Sci, 2011, 17(5): 1131-1139. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 田光明, 蔡祖聪, 曹金留, 李小平. 镇江丘陵区稻田化肥氮的氨挥发及其影响因素. 土壤学报, 2001, 38(3): 324-332. |
| Tian G M, Cai Z C, Cao J L, Li X P.Ammonia volatilization from paddy field and its affecting factors in Zhenjiang hilly region.Acta Pedol Sin, 2001, 38(3): 324-332. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 郑圣先, 刘德林, 聂军, 戴平安, 肖剑. 控释氮肥在淹水稻田土壤上的去向及利用率. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2004, 10(2): 137-142. |
| Zheng S X, Liu D L, Nie J, Dai P A, Xiao J.Fate and recovery efficiency of controlled release nitrogen fertilizer in flooding paddy soil.Plant Nutr & Fert Sci, 2004, 10(2): 137-142. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 鲁艳红, 聂军, 廖育林, 周兴, 谢坚, 汤文光, 杨曾平. 不同控释氮肥减量施用对双季水稻产量和氮素利用的影响. 水土保持学报, 2016, 30(2): 155-161. |
| Lu Y H, Nie J, Liao Y L, Zhou X, Xie J, Tang W G, Yang Z P.Effects of Application Reduction of Controlled Release Nitrogen Fertilizer on Yield of Double Cropping Rice and Nitrogen Nutrient Uptake.J Soil Water Con, 2016, 30(2): 155-161. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 叶玉适, 梁新强, 金熠, 赵越, 傅朝栋. 节水灌溉与控释肥施用对稻田田面水氮素变化及径流流失的影响. 水土保持学报, 2014, 28(5): 105-112. |
| Ye Y S, Liang X Q, Jin Y, Zhao Y, Fu C D.Dynamic Variation and runoff loss of nitrogen in surface water of paddy affected by saving irrigation and controlled-release fertilizer application.J Soil & Water Cons, 2014, 28(5): 105-112. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 孙祥鑫, 李东坡, 武志杰, 崔亚兰, 韩梅, 李永华, 杨德福, 崔永坤. 持续施用缓/控释尿素条件下水田土壤NH3挥发与N2O排放特征. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(6): 1901-1909. |
| Sun X X, Li D P, Wu Z J, Cui Y L, Han M, Li Y H, Yang D F, Cui Y K.Characteristics of ammonia volatilization and nitrous oxide emission from a paddy soil under continuous application of different slow/controlled release urea.Chin J Appl Ecol, 2016, 27(6): 1901-1909. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 郭晨, 徐正伟, 王斌, 任涛, 万运帆, 邹家龙, 鲁剑巍, 李小坤. 缓/控释尿素对稻田周年CH4和N2O排放的影响. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(5): 1489-1495. |
| Guo C, Xu Z W, Wang B, Ren T, Wan Y F, Zou J L, Lu J W, Li X K.Effects of slow/controlled release urea on annual CH4 and N2O emissions in paddy field.Chin J Appl Ecol, 2016, 27(5): 1489-1495. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 朱坚, 石丽红, 田发祥, 霍莲杰, 纪雄辉. 湖南典型双季稻田氨挥发对施氮量的响应研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(5): 1129-1138. |
| Zhu J, Shi L H, Tian F X, He L J, Ji X H.Responses of ammonia volatilization to nitrogen application amount in typical double cropping paddy fields in Hunan Province.J Plant Nut & Fert, 2013, 19(5): 1129-1138. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 田玉华, 贺发云, 尹斌, 朱兆良. 太湖地区氮磷肥施用对稻田氨挥发的影响. 土壤学报, 2007, 44(5): 893-900. |
| Tian Y H, He F Y, Yin B, Zhu Z L.Ammonia Volatilization from Paddy Fields in the Taihu Lake Region as Affected by N and P Combination in Fertilization.Acta Pedol Sin, 2007, 44(5): 893-900. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 周亮, 荣湘民, 谢桂先, 王心星, 谢勇, 宁琪. 不同氮肥施用对双季稻稻田氨挥发及其动力学特性的影响. 水土保持学报, 2014, 28(4): 143-147. |
| Zhou L, Rong X M, Xie G X, Wang X X, Xie Y, Ning Q.Effects of different nitrogen fertilizers on ammonia volatilization and its dynamic characteristics of double cropping rice.J Soil & Water Cons, 2014, 28(4): 143-147. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 李菊梅, 李冬初, 徐明岗, 申华平, 秦道珠. 红壤双季稻田不同施肥下的氨挥发损失及其影响因素. 生态环境学报, 2008, 17(4): 1610-1613. |
| Li J M, Li D C, Xu M G, Shen H P, Qin D Z.Ammonia volatilization and its influence factors under different fertilization in red paddy soil with double rice cropping system.Ecol & Environ, 2008, 17(4): 1610-1613. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 吴萍萍, 刘金剑, 杨秀霞, 商庆银, 周毅, 谢小立, 沈其荣, 郭世伟. 不同施肥制度对红壤地区双季稻田氨挥发的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(1): 85-93. |
| Wu P P, Liu J J, Yang X X, Shang Q Y, Zhou Y, Xie X L, Shen Q R, Guo S W.Effects of different fertilization systems on ammonia volatilization from double-rice cropping field in red soil region.Chin J Rice Sci, 2009, 23(1): 85-93. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 王淳, 周卫, 李祖章, 刘秀梅, 孙刚, 夏文建, 王秀斌, 刘光荣. 不同施氮量下双季稻连作体系土壤氨挥发损失研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(2): 349-358. |
| Wang C, Zhou W, Li Z Z, Liu X M, Sun G, Xia W J, Wang X B, Liu G R.Effects of different nitrogen application rates on ammonia volatilization from paddy fields under double-harvest rice system.Plant Nut & Fert Sci, 2012, 18(2): 349-358. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 胡小凤, 王正银, 孙倩倩, 游媛. 缓释复合肥料在不同pH值紫色土中氨挥发特性. 农业工程学报, 2009, 25(6): 100-103. |
| Hu X F, Wang Z Y, Sun Q Q, You Y.Characteristics of ammonia volatilization of slow release compound fertilizer in different pH values of purple soils.Trans CSAE, 2009, 25(6):100-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 邹洪涛, 高艺伟, 韩艳玉, 曹敏建, 汪景宽, 张玉龙. 包膜尿素对水田土壤排放NH3、NOx、CO2影响的研究. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(12): 1940-1944. |
| Zou H T, Gao Y W, Han Y Y, Cao M J, Wang J K, Zhang Y L.Effect of coated urea on NH3, NO x and CO2 emissions from paddy soil. Ecol & Environ Sci, 2011, 20(12): 1940-1944. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 王霞, 崔键, 周静. 典型红壤区稻田树脂包膜控释氮肥氨挥发研究. 土壤, 2011, 43(1): 56-59. |
| Wang X, Cui J, Zhou J.Ammonia volatilization of controlled-release urea enveloped with colophony from paddy field in typical red soil.Soils, 2011, 43(1): 56-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 黄晶晶, 朱波, 林超文, 庞良玉, 张建华, 罗付香, 朱永群, 易丽霞. 施氮量和田面水含氮量对紫色土丘陵区稻田氨挥发的影响. 土壤, 2014(4): 623-629. |
| Huang J J, Zhu B, Lin C W, Pang L Y, Zhang J H, Luo F X, Zhu Y Q, Yi L X.Effects of nitrogen rate and field water nitrogen content on ammonia volatilization from paddy field in a purple soil hilly district.Soils, 2014(4): 623-629. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | Li J, Li D, Xu M, Shen H.Ammonia volatilization and its influence factors under different fertilization in red paddy soil with double rice cropping system.Ecol & Environ, 2008, 17(4): 1610-1613. |
| [37] | 宋勇生, 范晓晖, 林德喜, 杨林章, 周健民. 太湖地区稻田氨挥发及影响因素的研究. 土壤学报, 2004, 41(2): 265-269. |
| Song Y S, Fan X H, Lin D X, Yang L Z, Zhou J M.Ammonia volatilization from paddy fields in the Taihu Lake region and its influencing factors.Acta Pedol Sin, 2004, 41(2): 265-269. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | Zhang Y M, Hu C S, Dong W X.Ammonia volatilization from wheat-maize rotation field in the piedmont of Taihang.Plant Nut & Fert Sci, 2005, 11(3): 417-419. |
| [39] | Toufiqiqbal M, Tian G M, Liang X Q, FatimaRukshana. Measurement of ammonia emission following surface application of urea fertilizer from irrigated paddy rice fields.J Integ Agric, 2005, 4(4): 288-293. |
| [40] | 纪雄辉, 郑圣先, 鲁艳红, 廖育林. 施用尿素和控释氮肥的双季稻田表层水氮素动态及其径流损失规律. 中国农业科学, 2006, 39(12): 2521-2530. |
| Ji X H, Zheng S X, L, Lu Y H, Liao Y L. Effects of controlled release nitrogen fertilizer on surface water N dynamics and its losses from runoff.Sci Agric Sc, 2006, 39(12): 2521-2530. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 杜建军, 毋永龙, 田吉林, 王益权, 崔英德. 控/缓释肥料减少氨挥发和氮淋溶的效果研究. 水土保持学报, 2007, 21(2): 49-52. |
| Du J J,Wu Y L,Tian J L, Wang Y Q, Cui Y D.Effect of several controlled/slow-release fertilizers on decreasing ammonia volatilization and N leaching.J Soil Water Cons, 2007, 21(2): 49-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 杨越超, 耿毓清, 张民, 陈剑秋, 陈海宁. 膜特性对包膜控释肥养分控释性能的影响. 农业工程学报, 2007, 23(11): 23-30. |
| Yang Y C, Geng Y Q, Zhang M, Chen J Q, Chen H N.Effects of coating properties of controlled-release fertilizers on nutrient release characteristics.Trans Chin Soc Agric Engin(Tran CSAE), 2007, 23(11): 23-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | 张静, 王德建. 太湖地区乌栅土稻田氨挥发损失的研究. 中国生态农业学报, 2007, 15(6): 84-87. |
| Zhang J, Wang D J.Ammonia volatilization in gleyed paddy field soils of Taihu Lake region.Chin J Eco-Agric, 2007, 15(6): 84-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | 俞巧钢, 叶静, 杨梢娜, 符建荣, 马军伟, 孙万春, 姜丽娜, 王强, 汪建妹. 不同施氮量对单季稻养分吸收及氨挥发损失的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(4): 487-494. |
| Yu Q G, Ye J, Yang S N, Fu J R, Ma J W, Sun W C, Jiang L N, Wang Q, Wang J M.Effects of Nitrogen Application Level on Rice Nutrient Uptake and Ammonia Volatilization.Chin J Rice Sci, 2013, 20(2): 139-147. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [45] | Cai G X, Peng G H, Wang X Z, Zhu J W, Zhu Z L.Ammonia volatilization from urea applied to acid paddy soil in Southern China and its control.Pedosphere, 1992, (4): 345-354. |
| [46] | Pfluke P D, Jokela W E, Bosworth S C.Ammonia volatilization from surface-banded and broadcast application of liquid dairy manure on grass forage.J Environ Qual, 2011, 40(2): 374-382. |
| [47] | Xu J G, Heeraman D A, Wang Y.Fertilizer and temperature effects on urea hydrolysis in undisturbed soil.Biol & Fertil Soils, 1993, 16(1): 63-65. |
| [1] | YE Shi-chao,#,LIN Zhong-cheng,#,DAI Qi-gen,JIA Yu-shu,GU Hai-yan,CHEN Jing-dou,XU Lu-sheng,WU Fu-guan,ZHANG Hong-cheng,HUO Zhong-yang,XU Ke,WEI Hai-yan. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate on Ammonia Volatilization and Nitrogen Utilization in Rice Growing Season [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(1): 71-78 . |
| [2] | WU Pingping ,LIU Jinjian,YANG Xiuxia,SHANG Qingyin,ZHOU Yi,XIE Xiaoli,SHEN Qirong,GUO Shiwei. Effects of Different Fertilization Systems on Ammonia Volatilization from DoubleRice Cropping Field in Red Soil Region [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2009, 23(1): 85-85~93 . |
| [3] | WU Xiao-qing ,XU Yang-chun ,SHEN Qi-rong ,GUO Shi-wei. Ammonia Volatilization from Shoots of Different Rice Genotypes with Different Nitrogen Use Efficiency after Flowering [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2006, 20(4): 429-433 . |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||