
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2018, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (1): 111-118.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7094
• Research Papers • Next Articles
Shaofeng JIANG, Chenjiaozi WANG, Canwei SHU, Erxun ZHOU*( )
)
Received:2017-08-10
Online:2018-01-10
Published:2018-03-10
Contact:
Erxun ZHOU
通讯作者:
周而勋
基金资助:CLC Number:
Shaofeng JIANG, Chenjiaozi WANG, Canwei SHU, Erxun ZHOU. Cloning and Expression Analysis of RsPhmGene inRhizoctoniasolani AG-1ⅠA of Rice Sheath Blight Pathogen[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 1(1): 111-118.
江绍锋, 王陈骄子, 舒灿伟, 周而勋. 水稻纹枯病菌RsPhm基因的克隆及其表达分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 1(1): 111-118.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2018.7094
| 引物 Primer | 序列 Sequence(5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| DF01905 | ATGCCCGCTGTTGAATCTAA |
| DR01905 | TCACGCGGAAGCCATAAACC |
| F01905 | CCTGATATCCGAAACCGTACC |
| R01905 | TCATCTTGCTCCTGTCCATTC |
| GAPDHF | TACTCCGCAATGCTATCG |
| GAPDHR | TACTCGGTCCCAGTGGT |
Table 1 Sequences of oligonucleotide primers used in this study.
| 引物 Primer | 序列 Sequence(5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| DF01905 | ATGCCCGCTGTTGAATCTAA |
| DR01905 | TCACGCGGAAGCCATAAACC |
| F01905 | CCTGATATCCGAAACCGTACC |
| R01905 | TCATCTTGCTCCTGTCCATTC |
| GAPDHF | TACTCCGCAATGCTATCG |
| GAPDHR | TACTCGGTCCCAGTGGT |
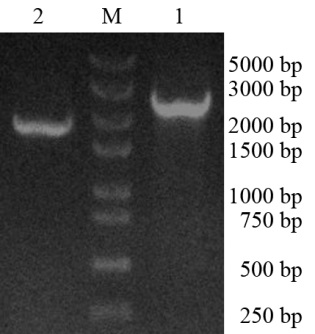
Fig.1. PCR products of RsPhm gene in Rhizoctoniasolani. M, 250 bp DNA marker; 1, The PCR product of RsPhmusing DNA as template; 2, The PCR product of RsPhmusing cDNA as template.
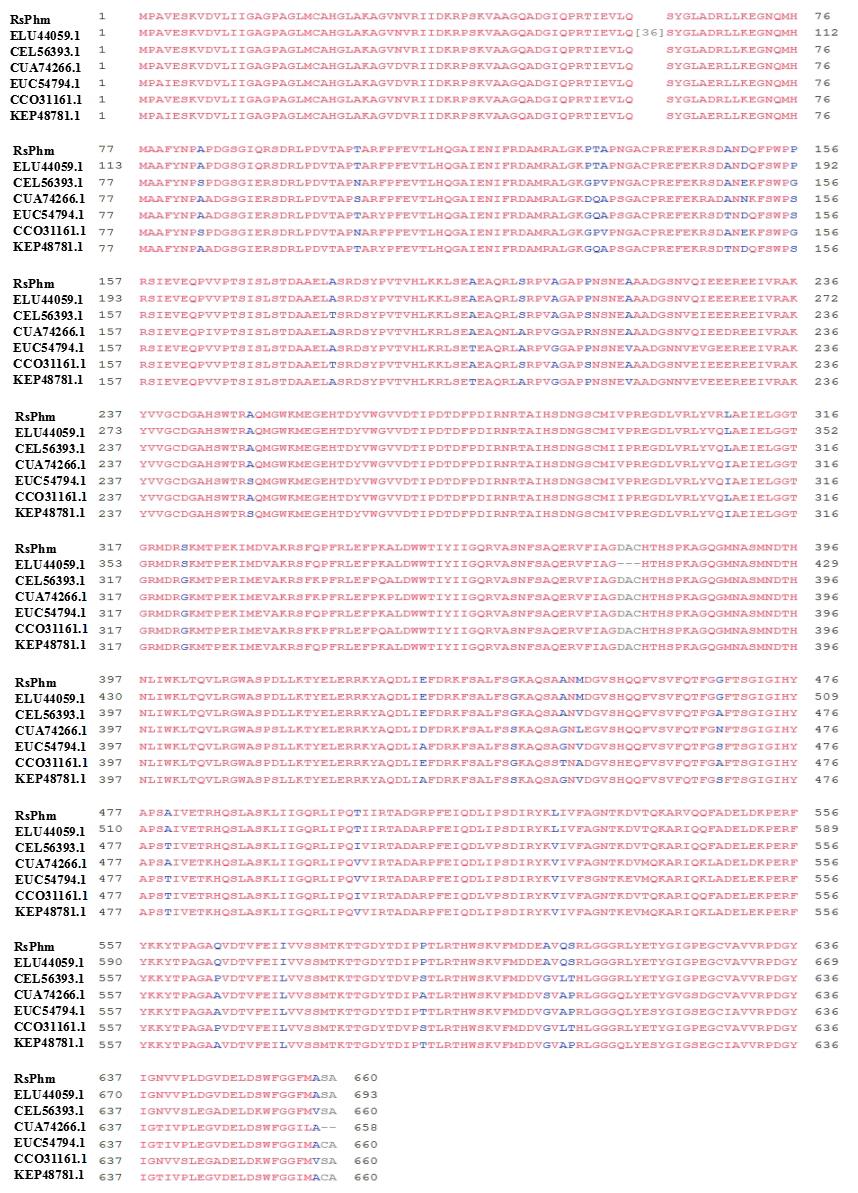
Fig. 2. Comparison of amino acid sequences ofRsPhm proteins in different anastomosis groups ofRhizoctoniasolani. RsPhm is the result of this study, the NCBI GenBank accession numbers of R. solani AG-1ⅠA, R. solani AG-1ⅠB, R. solani AG22ⅢB, R. solani AG-3, R. solani AG-1ⅠB and R. solani 123EareELU44059.1, CEL56393.1, CUA74266.1, EUC54794.1, CCO31161.1 and KEP48781.1, respectively.
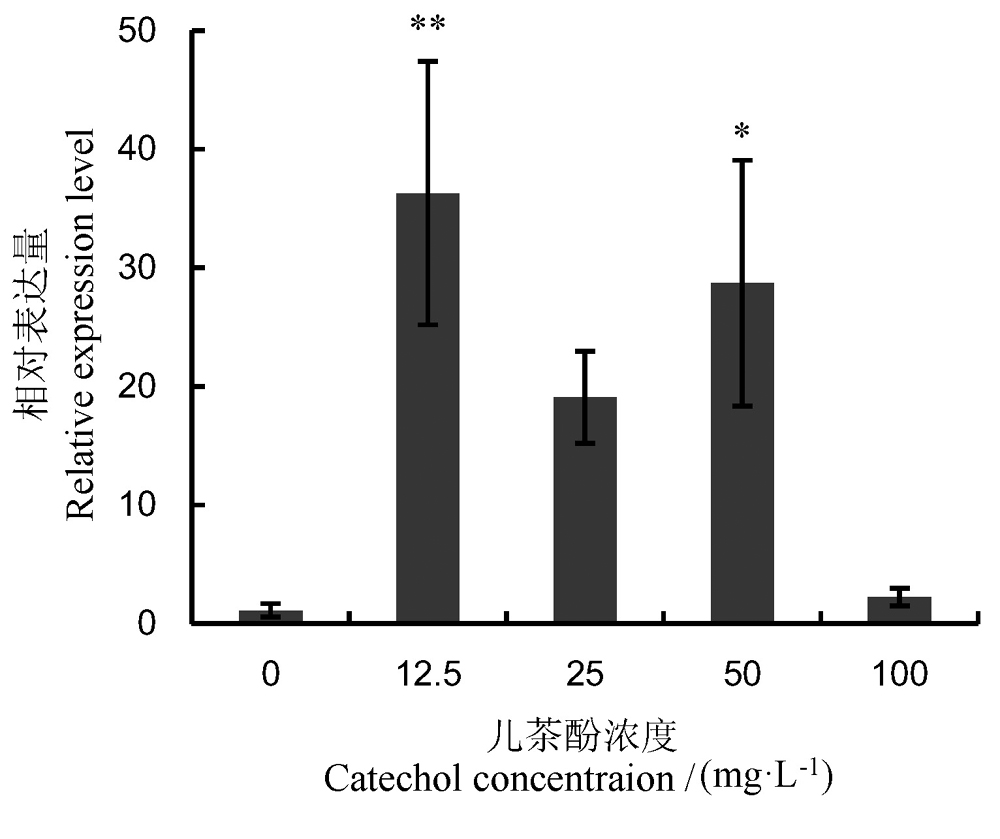
Fig. 5. Expression levelof RsPhm geneinRhizoctoniasolani AG-1 IA at different concentrations of catechol. Values areMean±SE of three replicates. *and**, Significantly different at 5% or 1% levelscompared to the control, respectively.
| [1] | Webb K M, Freeman C, Broeckling C D.Metabolome profiling to understand the defense response of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) to Rhizoctoniasolani AG 2-2 IIIB. PhysiolMol Plant Pathol, 2016, 94: 108-117. |
| [2] | HannukkalaA O, Rastas M, Laitinen P, Latvala S.Rhizoctoniasolani injuries in oilseed crops in Finland and impacts of different crop management practices on disease incidence and severity. Ann ApplBiol, 2016, 169(2): 257-273. |
| [3] | 邹成佳, 唐芳, 杨媚, 贺晓霞, 李献军, 周而勋. 华南3省(区)水稻纹枯病菌的生物学性状与致病力分化研究. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(2): 206-212. |
| Zou C J, Tang F, Yang M, He X X, Li X J, Zhou E X.Studies on biological characteristics and pathogenicity differentiation of rice sheath blight pathogen from three provinces in South China.Chin J Rice Sci,2011, 25(2): 206-212. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Feng S J, Shu C W, Wang C J Z, Jiang S H, Zhou E X. Survival of Rhizoctoniasolani AG-1 IA, the causal agent of rice sheath blight, under different environmental conditions. J Phytopathol, 2017, 165(1): 44-52. |
| [5] | 刘卫东. Pseudomonas putid DLL-E4 1,2,4 -苯三酚1,2-双加氧酶的晶体结构及两种农药降解相关酶的蛋白质晶体学研究. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2010. |
| Liu W D.Structural analysis of hydroxyquinol 1, 2-dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida DLL-E4 and crystallographic study on two pesticide degradation related enzymes. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University,2010. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | Neujahr H Y, Gaal A.Phenol hydroxylase from yeast. Sulfhydryl groups in phenol hydroxylase from Trichosporoncutaneum. Eur J Biochem,1975, 58(2): 351-357. |
| [7] | Yotinov I, Todorova Y, Schneider I, Daskalova E, Topalova Y.The effect of nanodiamonds on phenol biodegradation by Pseudomonassp. strain isolated from polluted sediments. J NanosciNanotechnol, 2016, 16(7): 7696-7706. |
| [8] | Nakagawa H, Takeda Y.Phenol hydroxylase.BiochimBiophysActa, 1962, 62(2): 423-426. |
| [9] | Yang R D, Humphrey A E.Dynamic and steady state studies of phenol degradation in pure and mixed cultures.BiotechnolBioeng, 1975, 17(8): 1211-1235. |
| [10] | Hamada T, Asanagi M, Satozawa T, Araki N, Banba S, Higashimura N, Akase T, Hirase K.Action mechanism of the novel rice blast fungicide tolprocarb distinct from that of conventional melanin biosynthesis inhibitors.J PesticSci, 2014, 39(3): 152-158. |
| [11] | Chai L Y A, Netea M G, Sugui J, Vonk A G, van de Sande W W J, Warris A, Kwon-Chung K J, Jan Kullberg B.Aspergillus fumigatus conidial melanin modulates host cytokine response. Immunobiology, 2010, 215(11): 915-920. |
| [12] | Soares A R, de Lourdes Lucio Ferrarese M, de CássiaSiqueira-Soares R, Marchiosi R, Finger-Teixeira A, Ferrarese-Filho O. The allelochemical1-dopa increases melanin production and reduces reactive oxygen species in soybean roots.J Chem Ecol, 2011, 37(8): 891-898. |
| [13] | Piattelli M, Fattorusso E, Magno S, Nicolaus RA.Ustilago melanin, a naturally occurring catechol melanin. Tetrahedron Lett, 1963, 4(15): 997-998. |
| [14] | Chen J Y, Wang C J Z, Shu C W, Zhu M H, Zhou E X. Isolation and characterization of a melanin from Rhizoctoniasolani, the causal agent of rice sheath blight. Eur J Plant Pathol, 2015, 142(2): 281-290. |
| [15] | Yang Y Q, Yang M, Li M H, Zhou E X.Cloning and functional analysis of an endo-PG-encoding gene Rrspg1 of Rhizoctoniasolani, the causal agent of rice sheath blight. Eur J Plant Pathol, 2012, 34(3): 1-12. |
| [16] | Zheng A P, Lin R M, Zhang D H, Qin P G, Xu L Z, Ai P, Ding L, Wang Y R, Chen Y, Liu Y, Sun Z G, Feng H T, Liang X X, Fu R G, Tang C Q, Li Q, Zhang J, Xie Z L, Deng Q M, Li S C, Wang S Q, Zhu J, Wang L X, Liu H N, Li P.The evolution and pathogenic mechanisms of the rice sheath blight pathogen.Nat Commun, 2013, 4: 1424. |
| [17] | Wojcieszynska D, Gren I, Labuzek S, Respondek M.Substrate specificity and sensitiveness of phenol monooxygenase from Stenotrophomonasmaltophilia strain KB2 versus their potential application to bioremediation of the environment. Biotechnologia, 2007, 2: 181-191. |
| [18] | 李朦. 嗜酸硫化芽孢杆菌苯酚羟化酶还原酶组分的重组表达与性质研究. 厦门: 国家海洋局第三海洋研究所, 2016. |
| Li M.Expression and characterization of the phenol hydroxylase reductase from Sulfobacillus acidophilus TPY. Xiamen: The Third Institute of Oceanography,StateOceanicAdministration, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 沈文静, 张静, 曹慧, 崔中利. 恶臭假单胞菌DLL-E4对硝基苯酚降解途径关键基因pnpC的突变分析. 生态与农村环境学报, 2008, 24(4): 77-82. |
| Shen W J, Zhang J, Cao H,Cui Z L.p-nitrophenol degradation characteristics of hydroxyquinol1, 2-D ioxygenase gene (pnpC) knock-out mutant of Pseudomonas putida DLL-E4. J Ecol Rural Environ, 2008, 24(4): 77-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | Kasak L, Hôrak R, Nurk A, Talvik K, Kivisaar M.Regulation of the catechol 1,2-dioxygenase- and phenol monooxygenase-encodingpheBA operon in Pseudomonas putida PaW85. J Bacteriol, 1993, 175(24): 8038-8042. |
| [21] | Tuan N N, Hsieh H C, Lin Y W, Huang S L.Analysis of bacterial degradation pathways for long-chain alkylphenols involving phenol hydroxylase, alkylphenol monooxygenase and catechol dioxygenase genes.BioresourceTechnol, 2011, 102(5): 4232-4240. |
| [22] | Lu L, Shu C W, Liu C J Z, Zhou E X. The impacts of natural antioxidants on sclerotial differentiation and development in RhizoctoniasolaniAG-1 IA. Eur J Plant Pathol, 2016, 146(4): 729-740. |
| [23] | Weijn A, Bastiaan-Net S, Wichers H J, Mes J J.Melanin biosynthesis pathway in Agaricusbisporus mushrooms. Fungal Genet Biol, 2013, 55(6): 42-53. |
| [24] | Butler M J, Gardiner R B, Day A W.Melanin synthesis by Sclerotiniasclerotiorum.Mycologia, 2009, 101(3): 296. |
| [25] | Butler M J, Day A W.Destruction of fungal melanins by ligninases of Phanerochaetechrysosporiumand other white rot fungi.Int J Plant Sci, 1998, 159(6): 989-995. |
| [26] | Casadevall A, Rosas A L, Nosanchuk J D.Melanin and virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans. CurrOpinMicrobiol, 2000, 3(4): 354-358. |
| [27] | Eisenman H C, Chow S, Tsé K K, McClelland E, Casadevall A. The effect of L-DOPA on Cryptococcus neoformans growth and gene expression. Virulence, 2014, 2(4): 329-336. |
| [28] | Hyakumachi M, Yokoyama K, Ui T.Role of melanin in susceptibility and resistance of Rhizoctoniasolani to microbial lysis. T BritMycolSoc, 1987, 89(1): 27-33. |
| [29] | Kim H T, Chung Y R, Cho K Y.Mycelial melanization of RhizoctoniasolaniAG1 affecting pathogenicity in rice. Plant Pathol J, 2001, 17: 210-215. |
| [1] | Kunneng ZHOU, Jiafa XIA, Tingchen MA, Yuanlei WANG, Zefu LI. Mapping and Mutation Analysis of Stripe Leaf and White Panicle Gene SLWP in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2018, 32(4): 325-334. |
| [2] | Ying-ying LI, Wei XIONG, Ting SONG, Zhen-hua CAO, Wei-jiang LUAN. Overexpressing Analysis of the Flowering Time Gene OsDTH10 in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(2): 121-126. |
| [3] | AI Liping, SHEN Ao, GAO Zhichao, LI Zhenglong, SUN Qionglin, LUAN Weijiang*. Reverse Genetics Analysis of the Transcription Factor OsHox9, a Member of Homeobox Family, in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2014, 28(3): 223-228. |
| [4] | QU Ying, JIN Zhengxun*, LIU Haiying, XU Zhenhua, ZHU Linan, ZHENG Guanlong, ZHU Fangxu, . Analysis of Expression Characters of Soluble Starch Synthase and Isoform Genes Involved in japonica Hybrid Progeny [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2014, 28(1): 23-31. |
| [5] | RAO Yuchun1,2,#, DING Zhengzhong1,3,#, CHEN Xifeng1, ZENG Dali2, MA Bojun1, GU Zhimin1,*. Cloning and Expression Analysis of UvHog1 Gene in Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2014, 28(1): 9-14. |
| [6] | WANG Yanli, REN Yanchun, ZHANG Zhen, WANG Jiaoyu, MAO Xueqin, JIANG Hua, QIU Haiping, CHAI Rongyao, DU Xinfa, SUN Guochang*. Characterization of Glyceraldehyde3phosphate Dehydrogenase Gene Sequences of Different Anastomosis Group Rhizoctonia solani [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2013, 27(6): 639-646. |
| [7] | XU Xing, QIU Jie, XU Yang, XU Chenwu*. Molecular Evolution and Expression Analysis of Subfamily ABCB Transporter Genes in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2012, 26(2): 127-136. |
| [8] | ZHANG Juefeng, HE Yueping, CHEN Jianming*, CHEN Liezhong. Construction of Suppression Subtractive Hybridization cDNA Library of Imidaclopridresistant and Imidaclopridsusceptible Brown Planthopper [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2012, 26(1): 21-26. |
| [9] | GAO Qing-song,ZHANG Dan,XU Liang,XU Chen-wu* . Systematic Identification of Rice ABC1 Genes and Their Expression Analysis under Abiotic Stresses [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(1): 1-10 . |
| [10] | LIANG Weihong*, BI Jiajia,PENG Weifeng,ZHANG Fan,SHI Honghao,LI Li. Cloning and Expression Analysis of a MitogenActivated Protein Kinase Gene OsMPK14 from Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2010, 24(2): 125-130 . |
| [11] | DENG Qi-ming ,WANG Ying-hen ,WANG Shi-quan ,LI Shuang-cheng ,LI Ping. Near Isogonic Lines Establishment and GenomeWide Expression Analysis of a Few Tillering Mutant of Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2008, 22(1): 15-22 . |
| [12] | LI Yu-sheng ,HUANG Ji ,YU Shan-lin ,HOU Fu-yun ,ZHANG Hong-sheng. Cloning and Structure Analysis of a Panicle-Specific Zinc Finger Protein Gene from Rice(Oryza sativa) [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2006, 20(4): 343-347 . |
| [13] | CHEN Xiu-hua ,LIU Qiao-quan ,WU Hsin-gang ,WANG Zong-yang ,GU Ming-hong . cDNA Cloning and Sequence Analysis of Rice Sbe1 and Sbe3 Genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2003, 17(2): 109-112 . |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||