
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2016, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 603-610.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.6033
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yong-feng SHI1, Yan HE1, Dan GUO1, Xiang-guang LV1,2, Qi-na HUANG1, Jian-li WU1,*( )
)
Received:2015-12-29
Revised:2016-03-12
Online:2016-11-10
Published:2016-11-10
Contact:
Jian-li WU
施勇烽1, 贺彦1, 郭丹1, 吕向光1,2, 黄奇娜1, 吴建利1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
吴建利
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yong-feng SHI, Yan HE, Dan GUO, Xiang-guang LV, Qi-na HUANG, Jian-li WU. Genetic Analysis and Gene Mapping of a Pale Green Leaf Mutant HM133 in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(6): 603-610.
施勇烽, 贺彦, 郭丹, 吕向光, 黄奇娜, 吴建利. 水稻淡绿叶突变体HM133的遗传分析与基因定位[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(6): 603-610.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.6033
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物(5'-3') Forward primer(5'-3') | 反向引物(5'-3') Reverse primer(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| OsChlD | GGAAAGAGAGGGCATTAG | CAATACGATCAAGTAAGTGTT |
| OsChlI | AGTAACCTTGGTGCTGTG | AATCCATCAACATTCAACTCTG |
| OsChlH | CTATACATTCGCCACACT | TATCACACAACTCCCAAG |
| HEMA1 | CGCTATTTCTGATGCTATGGGT | TCTTGGGTGATGATTGTTTGG |
| PORA | TGTACTGGAGCTGGAACAACAA | GAGCACAGCAAAATCCTAGACG |
| CAO1 | GATCCATACCCGATCGACAT | CGAGAGACATCCGGTAGAGC |
| Cab1R | AGATGGGTTTAGTGCGACGAG | TTTGGGATCGAGGGAGTATTT |
| Cab2R | TGTTCTCCATGTTCGGCTTCT | GCTACGGTCCCCACTTCACT |
| psaA | GCGAGCAAATAAAACACCTTTC | GTACCAGCTTAACGTGGGGAG |
| psbA | CCCTCATTAGCAGATTCGTTTT | ATGATTGTATTCCAGGCAGAGC |
| rbcL | CTTGGCAGCATTCCGAGTAA | ACAACGGGCTCGATGTGATA |
| rbcS | TCCGCTGAGTTTTGGCTATTT | GGACTTGAGCCCTGGAAGG |
| YGL1 | CAGTCTCCAATGGCCACCT | TGCTTTCATCAGTGGCTGG |
| SPP | CGGAGAGGAAACATAATGAC | ATAGGCATTTGTCTTTGTCTC |
| PPR1 | CTAAGACCGAATGACAAATGC | GCACTGCCAACAAGAATACC |
| DVR | CGAGCCCAGGTTCATCAAGGTGC | CCTCCCGATCTTGCCGAACTCC |
| Ubiquitin | GCTCCGTGGCGGTATCAT | CGGCAGTTGACAGCCCTAG |
Table 1 Primers used in real-time PCR.
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物(5'-3') Forward primer(5'-3') | 反向引物(5'-3') Reverse primer(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| OsChlD | GGAAAGAGAGGGCATTAG | CAATACGATCAAGTAAGTGTT |
| OsChlI | AGTAACCTTGGTGCTGTG | AATCCATCAACATTCAACTCTG |
| OsChlH | CTATACATTCGCCACACT | TATCACACAACTCCCAAG |
| HEMA1 | CGCTATTTCTGATGCTATGGGT | TCTTGGGTGATGATTGTTTGG |
| PORA | TGTACTGGAGCTGGAACAACAA | GAGCACAGCAAAATCCTAGACG |
| CAO1 | GATCCATACCCGATCGACAT | CGAGAGACATCCGGTAGAGC |
| Cab1R | AGATGGGTTTAGTGCGACGAG | TTTGGGATCGAGGGAGTATTT |
| Cab2R | TGTTCTCCATGTTCGGCTTCT | GCTACGGTCCCCACTTCACT |
| psaA | GCGAGCAAATAAAACACCTTTC | GTACCAGCTTAACGTGGGGAG |
| psbA | CCCTCATTAGCAGATTCGTTTT | ATGATTGTATTCCAGGCAGAGC |
| rbcL | CTTGGCAGCATTCCGAGTAA | ACAACGGGCTCGATGTGATA |
| rbcS | TCCGCTGAGTTTTGGCTATTT | GGACTTGAGCCCTGGAAGG |
| YGL1 | CAGTCTCCAATGGCCACCT | TGCTTTCATCAGTGGCTGG |
| SPP | CGGAGAGGAAACATAATGAC | ATAGGCATTTGTCTTTGTCTC |
| PPR1 | CTAAGACCGAATGACAAATGC | GCACTGCCAACAAGAATACC |
| DVR | CGAGCCCAGGTTCATCAAGGTGC | CCTCCCGATCTTGCCGAACTCC |
| Ubiquitin | GCTCCGTGGCGGTATCAT | CGGCAGTTGACAGCCCTAG |

Fig. 1. Phenotype of the wide-type IR64 and the mutant HM133 at different growth stages. A, Phenotype of the wide type IR64 and the mutant HM133 at the seedling stage; B, Phenotype of the wide type IR64 and the mutant HM133 at the tillering stage.
| 材料 Material | 株高 Plant height /cm | 有效穗数 No. of productive panicles | 穗长 Panicle length /cm | 每穗实粒数 Number of filled grains per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IR64 | 113.0±1.7 | 14.0±1.0 | 25.0±1.4 | 81.2±7.1 | 74.6±1.6 | 27.52±0.38 |
| HM133 | 108.7±0.6* | 12.7±2.1 | 24.9±0.3 | 62.9±7.3* | 68.8±2.1* | 28.35±0.35 |
Table 2 Agronomic traits of the wild-type IR64 and mutant HM133.
| 材料 Material | 株高 Plant height /cm | 有效穗数 No. of productive panicles | 穗长 Panicle length /cm | 每穗实粒数 Number of filled grains per panicle | 结实率 Seed-setting rate/% | 千粒重 1000-grain weight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IR64 | 113.0±1.7 | 14.0±1.0 | 25.0±1.4 | 81.2±7.1 | 74.6±1.6 | 27.52±0.38 |
| HM133 | 108.7±0.6* | 12.7±2.1 | 24.9±0.3 | 62.9±7.3* | 68.8±2.1* | 28.35±0.35 |
| 取样时间 Sampling time | 材料 Material | 叶绿素a Chlorophyll a content | 叶绿素b Chlorophyll b content | 总叶绿素 Total chlorophyll content | 类胡萝卜素 Carotenoid content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 播种后6周 6 weeks after sowing | IR64 | 3.76±0.57 | 1.00±0.14 | 4.78±0.67 | 0.85±0.19 |
| HM133 | 2.11±0.06** | 0.46±0.04** | 2.58±0.03** | 0.52±0.10* | |
| 播种后15周 15 weeks after sowing | IR64 | 2.86±0.29 | 0.88±0.13 | 3.77±0.42 | 0.63±0.04 |
| HM133 | 1.54±0.08** | 0.42±0.03** | 1.97±0.12** | 0.33±0.01** |
Table 3 Comparison of photosynthetic pigment contents between HM133 and IR64 at different growth stages. mg/g
| 取样时间 Sampling time | 材料 Material | 叶绿素a Chlorophyll a content | 叶绿素b Chlorophyll b content | 总叶绿素 Total chlorophyll content | 类胡萝卜素 Carotenoid content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 播种后6周 6 weeks after sowing | IR64 | 3.76±0.57 | 1.00±0.14 | 4.78±0.67 | 0.85±0.19 |
| HM133 | 2.11±0.06** | 0.46±0.04** | 2.58±0.03** | 0.52±0.10* | |
| 播种后15周 15 weeks after sowing | IR64 | 2.86±0.29 | 0.88±0.13 | 3.77±0.42 | 0.63±0.04 |
| HM133 | 1.54±0.08** | 0.42±0.03** | 1.97±0.12** | 0.33±0.01** |
| 材料 Material | 净光合速率 Pn/(μmol·m-2 s-1) | 气孔导度 GS/(mol·m-2 s-1) | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci/(μmol·mol-1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr/(mmol·m-2s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IR64 | 14.45±1.78 | 0.57±0.13 | 309.13±7.30 | 4.12±0.64 |
| HM133 | 12.74±1.38* | 0.73±0.09* | 313.75±6.41 | 4.26±0.25 |
Table 4 Photosynthetic parameters of flag leaf of IR64 and HM133 at the heading stage.
| 材料 Material | 净光合速率 Pn/(μmol·m-2 s-1) | 气孔导度 GS/(mol·m-2 s-1) | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci/(μmol·mol-1) | 蒸腾速率 Tr/(mmol·m-2s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IR64 | 14.45±1.78 | 0.57±0.13 | 309.13±7.30 | 4.12±0.64 |
| HM133 | 12.74±1.38* | 0.73±0.09* | 313.75±6.41 | 4.26±0.25 |
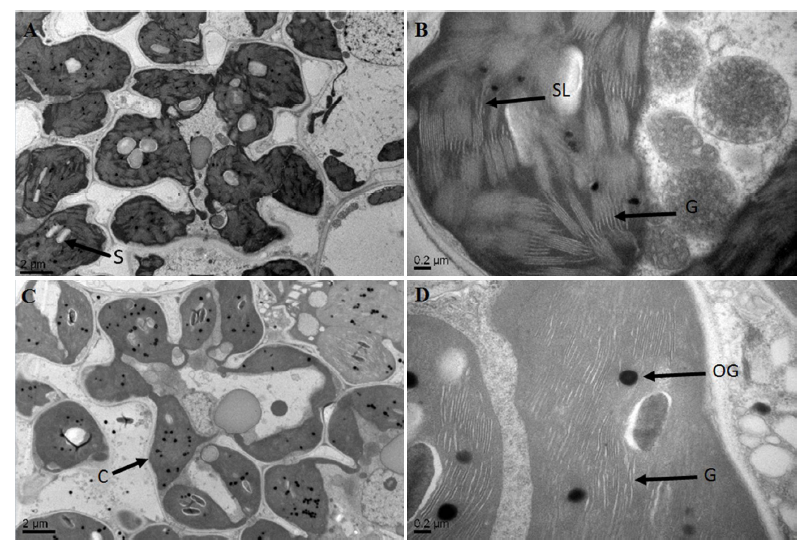
Fig. 2. Chloroplast ultrastructure of IR64 and HM133. A and B, IR64; C and D, HM133. S, Starch granule; C, Chloroplast; G, Granum; SL, Stroma lamella; OG, Osmiophilic granule.
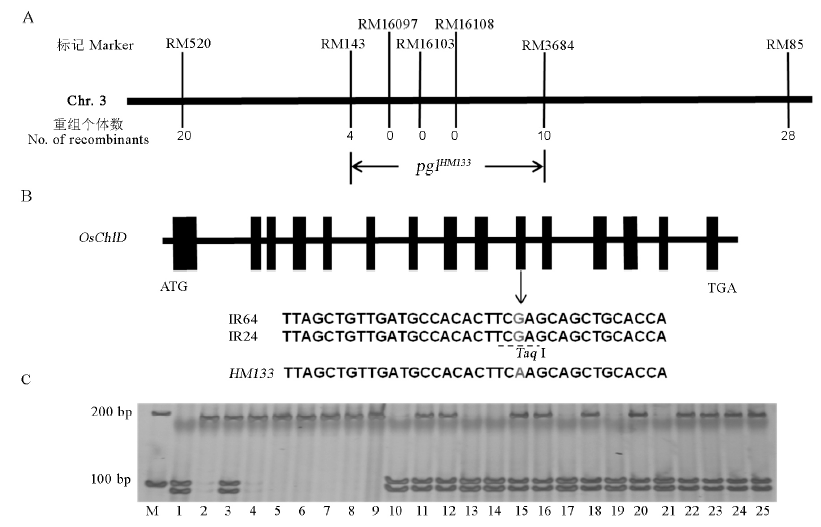
Fig. 3. Location of pglHM133 and candidate gene prediction. A,Primary mapping of yglHM133 on chromosome 3; B, Sequence analysis of the candidate gene OsChlD. The gray letters indicate single base substitution from G to A at position 1541; C, Mutation base of OsChlD confirmed with Taq I restriction enzyme digestion. M, Molecular marker; 1, IR24; 2, HM133; 3, F1; 4-9, Pale green plant of F2; 10-25, Normal plant of F2.
| [1] | 李智强, 朱丹, 王志龙, 等. 水稻黄绿叶突变体djyg的遗传分析与基因定位. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29: 601-609. |
| Li Z Q, Zhu D, Wang Z L,et al.Genetic analysis and gene mapping of a yellow-green leaf mutant djyg in rice. Chin J Rice Sci, 2015, 29: 601-609. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Jung K H, Hur J, Ryu C H, et al.Characterization of a rice chlorophyll-deficient mutant using the T-DNA gene-trap system.Plant Cell Physiol, 2003, 44: 463-472. |
| [3] | 韩帅, 王立静, 钟世宜, 等. 一个新的玉米叶色突变体的遗传分析及基因定位. 玉米科学, 2012, 20: 26-28. |
| Han S, Wang L J,Zhong S Y, et al.Genetic analysis and gene mapping of a new leaf color mutant in maize.J Maize Sci, 2012, 20: 26-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | Sawers R J, Viney J, Farmer P R, et al.The maize Oil yellow1 (Oy1) gene encodes the I subunit of magnesium chelatase. Plant Mol Biol, 2006, 60: 95-106. |
| [5] | Axelsson E, Lundqvist J, Sawicki A, et al.Recessiveness and dominance in barley mutants deficient in Mg-chelatase subunit D, an AAA protein involved in chlorophyll biosynthesis.Plant Cell, 2006, 18: 3606-3616. |
| [6] | Mochizuki N,Brusslan J A, Larkin R, et al. Arabidopsis genomes uncoupled 5 (GUN5) mutant reveals the involvement of Mg-chelatase H subunit in plastid-to-nucleus signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2001, 98: 2053-2058. |
| [7] | 肖华贵, 杨焕文, 饶勇, 等. 甘蓝型油菜黄化突变体的叶绿体超微结构、气孔特征参数及光合特性. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46: 715-727. |
| Xiao H G, Yang H W, Rao Y,et al.Analysis of chloroplast ultrastructure, stomatal characteristic parameters and photosynthetic characteristics of chlorophyll-reduced mutant in Brassica napus L. Sci Agric Sin, 2013, 46: 715-727. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | Beale S I.Green genes gleaned.Trends Plant Sci, 2005, 10: 309-312. |
| [9] | Lee S, Kim J H, Yoo E S, et al.Differential regulation of chlorophyll a oxygenase genes in rice.Plant Mol Biol, 2005, 57: 805-818. |
| [10] | Zhang H, Li J, Yoo J H, et al.Rice Chlorina-1 and Chlorina-9 encode ChlD and ChlI subunits of Mg-chelatase, a key enzyme for chlorophyll synthesis and chloroplast development. Plant Mol Biol, 2006, 62: 325-337. |
| [11] | Wu Z, Zhang X, He B, et al.A chlorophyll-deficient rice mutant with impaired chlorophyllide esterification in chlorophyll biosynthesis.Plant Physiol, 2007, 145: 29-40. |
| [12] | Wang P, Gao J, Wan C, et al.Divinyl chlorophyll(ide) a can be converted to monovinyl chlorophyll(ide) a by a divinyl reductase in rice.Plant Physiol, 2010, 153: 994-1003. |
| [13] | Deng X J, Zhang H Q, Wang Y, et al.Mapped clone and functional analysis of leaf-color gene Ygl7 in a rice hybrid(Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica). PLoS One, 2014, 9(6): e99564. |
| [14] | Sakuraba Y, Rahman M L, Cho S H, et al.The rice faded green leaf locus encodes protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase B and is essential for chlorophyll synthesis under high light conditions.Plant J, 2013, 74: 122-133. |
| [15] | Li Q Z, Zhu F Y, Gao X, et al.Young Leaf Chlorosis 2 encodes the stroma-localized heme oxygenase 2 which is required for normal tetrapyrrole biosynthesis in rice.Planta, 2014, 240: 701-712. |
| [16] | Chen H, Cheng Z, Ma X, et al.A knockdown mutation of YELLOW-GREEN LEAF2 blocks chlorophyll biosynthesis in rice. Plant Cell Rep, 2013, 32: 1855-1867. |
| [17] | Li J, Pandeya D, Nath K, et al. ZEBRA-NECROSIS, a thylakoid-bound protein, is critical for the photoprotection of developing chloroplasts during early leaf development. Plant J, 2010, 62: 713-725. |
| [18] | Su N, Hu M L, Wu D X, et al.Disruption of a rice pentatricopeptide repeat protein causes a seedling-specific albino phenotype and its utilization to enhance seed purity in hybrid rice production.Plant Physiol, 2012, 159: 227-238. |
| [19] | Lv X G, Shi Y F, Xu X, et al. Oryza sativa chloroplast signal recognition particle 43 (OscpSRP43) is required for chloroplast development and photosynthesis. PLoS ONE, 2015, 10(11): e143249. |
| [20] | Zhang F, Luo X, Hu B, et al. YGL138(t), encoding a putative signal recognition particle 54 kDa protein, is involved in chloroplast development of rice. Rice, 2013, 6(1): 7. |
| [21] | Wellburn A R.The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution.J Plant Physiol, 1994, 144: 307-313. |
| [22] | Arnon D I.Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol, 1949, 24: 1-15. |
| [23] | Huang Q N, Shi Y F, Zhang X B, et al.Single base substitution in OsCDC48 is responsible for premature senescence and death phenotype in rice. J Integr Plant Biol, 2016, 58: 12-28. |
| [24] | 卢扬江, 郑康乐. 提取水稻DNA的一种简易方法. 中国水稻科学, 1992, 6(1): 47-48. |
| Lu Y J, Zheng K L.A simple method for isolation of rice DNA.Chin J Rice Sci, 1992, 6(1): 47-48.(in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | Shi Y F, Chen J, Liu W Q, et al.Genetic analysis and gene mapping of a new rolled-leaf mutant in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci China C Life Sci, 2009, 52: 885-890. |
| [26] | Masuda T.Recent overview of the Mg branch of the tetrapyrrole biosynthesis leading to chlorophylls.Photosynth Res, 2008, 96: 121-143. |
| [27] | 孙小秋, 王兵, 肖云华, 等. 水稻ygl98黄绿叶突变基因的精细定位与遗传分析. 作物学报, 2011, 37(6): 991-997. |
| Sun X Q, Wang B, Xiao Y H,et al.Genetic analysis and fine-mapping of ygl98 yellow-green leaf gene in rice. Acta Agron Sin, 2011, 37(6): 991-997. (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [28] | Tian X Q, Ling Y H, Fang L K, et al.Gene cloning and functional analysis of yellow green leaf3 (ygl3) gene during the whole-plant growth stage in rice. Genes & Genom, 2013, 35: 87-93. |
| [29] | Luo T, Luo S, Araujo W L, et al.Virus-induced gene silencing of pea CHLI and CHLD affects tetrapyrrole biosynthesis, chloroplast development and the primary metabolic network.Plant Physiol Biochem, 2013, 65: 17-26. |
| [1] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [2] | XU Huan, ZHOU Tao, SUN Yue, WANG Mumei, YANG Yachun, MA Hui, LI Hao, XU Dawei, ZHOU Hai, YANG Jianbo, NI Jinlong. Characterization and Gene Mapping of a Glume Lesion Mimic Mutant glmm1 in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(5): 497-506. |
| [3] | CHENG Ling, HUANG Fugang, QIU Yipu, WANG Xinyi, SHU Wan, QIU Yongfu, LI Fahuo. Genetic Analysis and Identification of Brown Planthopper Resistance Gene in indica Rice Accession 570011 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(3): 244-252. |
| [4] | YUAN Yang, AO Hejun, ZHOU Zhonghua, YING Jiezheng, ZHANG Jian, NI Shen. Fine-mapping of SegD8 Loci for Rice Hybrid Segregation Distortion [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 37-44. |
| [5] | TANG Jie, LONG Tuan, WU Chunyu, LI Xinpeng, ZENG Xiang, WU Yongzhong, HUANG Peijin. Identification and Gene Mapping of a New Photo-thermo-sensitive Male Sterile Mutant tms3650 in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 45-54. |
| [6] | WANG Yingheng, CHEN Lijuan, CUI Lili, ZHAN Shengwei, SONG Yu, CHEN Shian, XIE Zhenxing, JIANG Zhaowei, WU Fangxi, ZHUO Chuanying, CAI Qiuhua, XIE Huaan, ZHANG Jianfu. Effects of Nitrogen Rate on Photosynthesis, Yield and Grain Quality of Superior Quality Rice “Fuxiangzhan” [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(1): 89-101. |
| [7] | SUN Zhiguang, DAI Huimin, CHEN Tingmu, LI Jingfang, CHI Ming, ZHOU Zhenling, LIU Yan, LIU Jinbo, XU Bo, XING Yungao, YANG Bo, LI Jian, LU Baiguan, FANG Zhaowei, WANG Baoxiang, XU Dayong. Phenotypic Identification and Gene Mapping of a Lesion Mimic Mutant lmm7 in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(4): 357-366. |
| [8] | YAO Shu, ZHANG Yadong, LU Kai, WANG Cailin. Progress in Functions, Allelic Variations and Interactions of Soluble Starch Synthases Genes SSⅡa and SSⅢa in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 227-236. |
| [9] | WU Longlong, YU Yijun, TIAN Cang, ZHANG Lu, HUANG Jing, ZHU Lianfeng, ZHU Chunquan, KONG Yali, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu. Effects of Different Nitrogen Application Regimes on Translocation of Rice Photosynthetic Products and Nitrogen Under Alternate Wetting and Drying Irrigation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 295-307. |
| [10] | LIANG Cheng, XIANG Xunchao, ZHANG Ouling, YOU Hui, XU Liang, CHEN Yongjun. Analyses on Agronomic Traits and Genetic Characteristics of Two New Plant-architecture Lines in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(2): 171-180. |
| [11] | YANG Jinyu, BAI Chen, DING Xiaohui, SHEN Hongfang, WANG Lei, YING Jiezheng, E Zhiguo. Genetic Analysis and Gene Mapping of a Male Sterile Mutant ms7 in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(1): 27-34. |
| [12] | Yuxiang LI, Hairong LIN, Qian LIANG, Guodong WANG. Effects of Dopamine Priming on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Rice Under Salt Stress [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(5): 487-494. |
| [13] | Yujun ZHU, Ziwei ZUO, Zhenhua ZHANG, Yeyang FAN. A New Approach for Fine-mapping and Map-based Cloning of Minor-Effect QTL in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(4): 407-414. |
| [14] | Bo FANG, Tengwei XIAO, Nana SU, Yan XIA, Zhenguo SHEN, Jin CUI. Research Progress on Cadmium Uptake and Its Transport and Accumulation Among Organs in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(3): 225-237. |
| [15] | Wei LIU, Zhanhua LU, Dongbai LU, Xiaofei WANG, Shiguang WANG, Jia XUE, Xiuying HE. Location and Candidate Gene Analysis of Rice Clustered Spikelets Gene OsCL6 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(3): 238-248. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||