
中国水稻科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (3): 306-321.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240812
王雅宣, 王新峰, 杨后红, 刘芳, 肖晶, 蔡玉彪, 魏琪, 傅强, 万品俊*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-08-26
修回日期:2024-10-12
出版日期:2025-05-10
发布日期:2025-05-21
通讯作者:
*email:wanpinjun@caas.cn基金资助:
WANG Yaxuan, WANG Xinfeng, YANG Houhong, LIU Fang, XIAO Jing, CAI Yubiao, WEI Qi, FU Qiang, WAN Pinjun*( )
)
Received:2024-08-26
Revised:2024-10-12
Online:2025-05-10
Published:2025-05-21
Contact:
*email:wanpinjun@caas.cn
摘要:
稻飞虱包括褐飞虱、白背飞虱和灰飞虱,是全球水稻生产的主要威胁之一。为了抵抗这些害虫,水稻进化出了一系列防御机制,包括抗生性、趋避性或不选择性、耐害性。与此同时,稻飞虱也进化出多种适应机制,如复杂的化学感受系统识别各类化学物质,分泌的唾液蛋白精细调控植物防御反应,肠道内的解毒酶代谢各类有毒物质,体内的共生菌提高对生态系统的适应性,翅型分化使其根据寄主营养状况进行生长发育等。本文依据稻飞虱适应水稻抗性机制的最新发现,总结了水稻抗稻飞虱基因和稻飞虱致害性机理,重点就稻飞虱与水稻的化学通讯、唾液成分、解毒酶、共生菌和翅型分化方面进行综述。稻飞虱的生物型进化和抗虫品种的推广后易失去抗性问题是当前稻飞虱防控面临的主要挑战。未来研究需要进一步探索稻飞虱适应性变化的分子机制,并开发新型的、更有效的管理策略,以实现稻飞虱防控的长远目标和可持续性。此外,本文还探讨了如何通过基因组学、转录组学、代谢组学和表观遗传学等现代生物技术,深化对稻飞虱与水稻互作网络的理解,以及如何利用这些知识制定更有效的害虫管理策略。
王雅宣, 王新峰, 杨后红, 刘芳, 肖晶, 蔡玉彪, 魏琪, 傅强, 万品俊. 稻飞虱适应水稻抗性机制的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(3): 306-321.
WANG Yaxuan, WANG Xinfeng, YANG Houhong, LIU Fang, XIAO Jing, CAI Yubiao, WEI Qi, FU Qiang, WAN Pinjun. Recent Advances in Mechanisms of Adaptation of Planthoppers to Rice Resistance[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(3): 306-321.
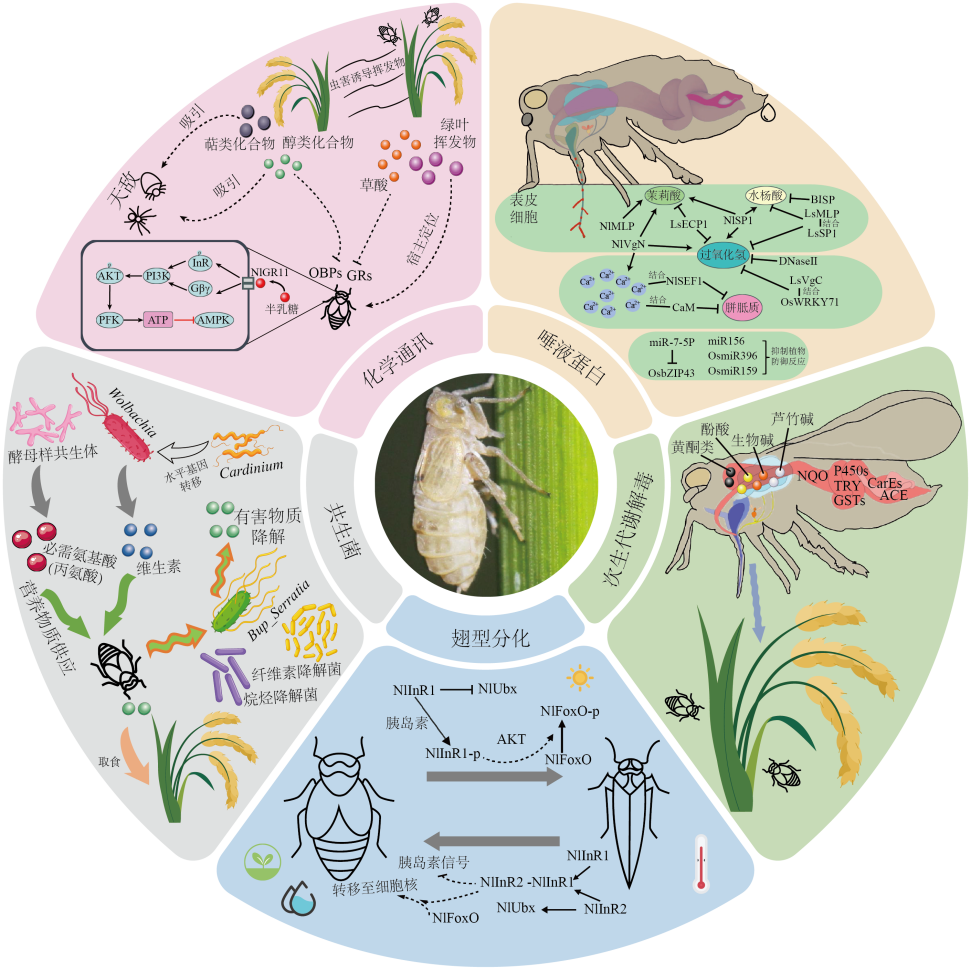
图1 稻飞虱与水稻互作的多维适应机制 化学通讯:OBP,气味结合蛋白;GR,味觉受体;NlGr11,褐飞虱味觉受体11;InR,胰岛素受体;Gβγ,G蛋白;PI3K,磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶;AKT,蛋白激酶B;PFK,磷酸果糖激酶;AMPK,依赖AMP的蛋白激酶。唾液蛋白:NlMLP,褐飞虱黏样蛋白;LsECP1,灰飞虱EF-hand钙结合蛋白1;NlSP1,褐飞虱唾液蛋白1;LsMLP,灰飞虱黏样蛋白;LsSP1,灰飞虱唾液鞘蛋白1;BISP:与BPH14互作的唾液蛋白;DNaseⅡ,核酸内切酶Ⅱ;NlSEF1,褐飞虱EF-hand唾液蛋白1;CaM,钙调素蛋白;NlVgN,褐飞虱卵黄蛋白的N末端;LsVgC,灰飞虱卵黄蛋白的C末端;OsbZIP43,水稻bZIP转录因子43。次生代谢解毒:P450,细胞色素P450单加氧酶;GST,谷胱甘肽S-转移酶;CarE,羧酸酯酶;ACE,乙酰胆碱酯酶;NQO,NADH-醌氧化还原酶;TRY,胰蛋白酶。翅型分化:NlInR1,褐飞虱胰岛素受体1;NlInR2,褐飞虱胰岛素受体2;NlInR1-p,磷酸化的褐飞虱胰岛素受体1;NlFoxO:褐飞虱叉头转录因子;NlFoxO-p:磷酸化的褐飞虱叉头转录因子;NlUbx,褐飞虱Ultrabithorax蛋白。
Fig. 1. Multidimensional adaptation mechanism behind rice planthopper-rice interaction Chemical Communications: OBPs, Odorant binding proteins; GRs, Gustatory receptors; NlGr11, Nilaparvata lugens gustatory receptor 11; InR, Insulin receptor; Gβγ, G-protein; PI3K, Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT, Protein kinase B; PFK, Phosphofructokinase; AMPK, Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase. Salivary Protein: NlMLP, Nilaparvata lugens mucin-like protein; LsECP1, Laodelphax striatellus EF-hand Ca2+-binding protein 1; NlSP1, Nilaparvata lugens salivary protein 1; LsMLP, Laodelphax striatellus mucin-like protein; LsSP1, Laodelphax striatellus sheath protein 1; BISP: BPH14-Interacting salivary protein; DNaseⅡ, Deoxyribonuclease II; NlSEF1, Nilaparvata lugens salivary EF-hand 1; CaM, Calmodulin protein; NlVgN, Nilaparvata lugens N-terminal subunit of vitellogenin; LsVgC, Laodelphax striatellus C-terminal subunit of vitellogenin; OsbZIP43, Oryza sativa bZIP transcription factor 43. Secondary metabolic detoxification: P450, Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenases; GST, Glutathione S-transferases; CarE, Carboxylesterases; ACE, Acetylcholinesterase; NQO, NADH-Quinone oxidoreductase; TRY, Trypsin. Ultrabithorax Differentiation: NlInR1, Nilaparvata lugens insulin receptor 1; NlInR2, Nilaparvata lugens insulin receptor 2; NlInR1-p, Phosphorylating Nilaparvata lugens insulin receptor 1; NlFoxO, Nilaparvata lugens forkhead transcription factor; NlFoxO-p, Phosphorylating Nilaparvata lugens forkhead transcription factor; NlUbx, Nilaparvata lugens ultrabithorax.
| [1] | 刘万才, 刘振东, 黄冲, 陆明红, 刘杰, 杨清坡. 近10年农作物主要病虫害发生危害情况的统计和分析[J]. 植物保护, 2016, 42(5): 1-9, 46. |
| Liu W C, Liu Z D, Huang C, Lu M H, Liu J, Yang Q P. Statistics and analysis of crop yield losses caused by main diseases and insect pests in recent 10 years[J]. Plant Protection, 2016, 42(5): 1-9, 46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Bottrell D G, Schoenly K G. Resurrecting the ghost of green revolutions past: The brown planthopper as a recurring threat to high-yielding rice production in tropical Asia[J]. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 2012, 15(1): 122-140. |
| [3] | Smith C M, Clement S L. Molecular bases of plant resistance to arthropods[J]. Annual Review of Entomology, 2012, 57(1): 309-328. |
| [4] | Yan L H, Luo T P, Huang D H, Wei M Y, Ma Z F, Liu C, Qin Y Y, Zhou X L, Lu Y P, Li R B, Qin G, Zhang Y X. Recent advances in molecular mechanism and breeding utilization of brown planthopper resistance genes in rice: An integrated review[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(15): 12061. |
| [5] | Zheng X H, Zhu L L, He G C. Genetic and molecular understanding of host rice resistance and Nilaparvata lugens adaptation[J]. Current Opinion in Insect Science, 2021, 45: 14-20. |
| [6] | 杨明, 李丹婷, 范德佳, 谭嵩娟, 程遐年, 刘裕强, 万建民. 广西野生稻Y11抗白背飞虱QTL定位[J]. 作物学报, 2022, 48(11): 2715-23. |
| Yang M, Li D T, Fan D J, Tan S J, Cheng X N, Liu Y Q, Wan J M. Mapping of QTLs for resistance to white-backed planthopper in Guangxi wild rice Y11[J]. The Crop Journal, 2022, 48(11): 2715-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | Zhao Y, Huang J, Wang Z Z, Jing S L, Wang Y, Ouyang Y D, Cai B D, Xin X F, Liu X, Zhang C X, Pan Y F, Ma R, Li Q F, Jiang W H, Zeng Y, Shangguan X X, Wang H Y, Du B, Zhu L L, Xu X, Feng Y Q, He S Y, Chen R Z, Zhang Q F, He G C. Allelic diversity in an NLR gene BPH9 enables rice to combat planthopper variation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(45): 12850-12855. |
| [8] | Du B, Zhang W L, Liu B F, Hu J, Wei Z, Shi Z Y, He R F, Zhu L L, Chen R Z, Han B, He G C. Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(52): 22163-22168. |
| [9] | Qiu Y F, Guo J P, Jing S L, Zhu L L, He G C. High-resolution mapping of the brown planthopper resistance gene Bph6 in rice and characterizing its resistance in the 9311 and Nipponbare near isogenic backgrounds[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2010, 121(8): 1601-1611. |
| [10] | Li J, Chen Q H, Wang L Q, Liu J, Shang K K, Hua H X. Biological effects of rice harbouring Bph14 and Bph15 on brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens[J]. Pest Management Science, 2011, 67(5): 528-534. |
| [11] | Ji H, Kim S R, Kim Y H, Suh J P, Park H M, Sreenivasulu N, Misra G, Kim S M, Hechanova S L, Kim H, Lee G S, Yoon U H, Kim T H, Lim H, Suh S C, Yang J, An G, Jena K K. Map-based cloning and characterization of the BPH18 Gene from wild rice conferring resistance to brown planthopper (BPH) insect pest[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 34376. |
| [12] | Jing S L, Zhang L, Ma Y H, Liu B F, Zhao Y, Yu H J, Zhou X, Qin R, Zhu L, He G C. Genome-wide mapping of virulence in brown planthopper identifies loci that break down host plant resistance[J]. PLoS ONE, 2014, 9(6): e98911. |
| [13] | Jena K K, Kim S M. Current status of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance and genetics[J]. Rice, 2010, 3(2): 161-171. |
| [14] | 陈建明, 俞晓平, 程家安, 吕仲贤, 郑许松, 徐红星. 水稻新品种(系)对褐飞虱抗性的筛选及评价[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2005, 29(6): 573-576. |
| Chen J M, Yu X P, Chen J A, Lü Z X, Zheng X S, Xu H X. Resistance screening and evaluation of newly-bred rice varieties (lines) to the rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2005, 29(6): 573-576. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | Zhou C, Zhang Q, Chen Y, Huang J, Guo Q, Li Y, Wang W S, Qiu Y F, Guan W, Zhang J, Guo J P, Shi S J, Wu D, Zheng X H, Nie L Y, Tan J Y, Huang C M, Ma Y H, Yang F, Fu X Q, Du B, Zhu L L, Chen R Z, Li Z K, Yuan L P, He G C. Balancing selection and wild gene pool contribute to resistance in global rice germplasm against planthopper[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(10): 1695-1711. |
| [16] | Ishwarya Lakshmi V G, Sreedhar M, Jhansilakshmi V, Gireesh C, Rathod S, Bohar R, Deshpande S, Laavanya R, Kiranmayee K N S U, Siddi S, Vanisri S. Development and validation of diagnostic KASP markers for brown planthopper resistance in rice[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2022, 13: 914131. |
| [17] | Satturu V, Vattikuti J L, Durga Sai J, Kumar A, Singh R K, Srinivas Prasad M, Zaw H, Jubay M L, Satish L, Rathore A, Mulinti S, Lakshmi V I, Chakraborty A, Thirunavukkarasu N. Multiple genome wide association mapping models identify quantitative trait nucleotides for brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) resistance in MAGIC indica population of rice[J]. Vaccines, 2020, 8(4): 608. |
| [18] | Heinrichs E A, Medrano F G. Leersia hexandra, a weed host of the rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)[J]. Crop Protection, 1984, 3(1): 77-85. |
| [19] | 任西明, 向聪, 雷东阳, 管利凤. 水稻抗褐飞虱育种研究进展与展望[J]. 作物研究, 2017, 31(4): 453-458. |
| Ren X M, Xiang C, Lei D Y, Guan L F. Present status and prospect of resistance breeding of brown planthopper in rice[J]. Crop Research, 2017, 31(4): 453-458. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 肖汉祥, 李燕芳, 张扬, 黄炳超. 水稻抗褐飞虱遗传和育种研究进展[J]. 广东农业科学, 2009(7): 124-127. |
| Xiao H X, Li Y F, Zhang Y, Huang B C. Research progress on the genetics and breeding of rice resistance to brown planthopper[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2009(7): 124-127. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 陶林勇, 俞晓平, 巫国瑞. 我国褐飞虱生物型监测初报[J]. 中国农业科学, 1992(3): 9-13. |
| Tao L Y, Yu X P, Wu G R. Preliminary report on the monitoring of brown planthopper biotypes in China. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 1992(3): 9-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 黄所生, 黄凤宽, 吴碧球, 张雪丽, 农春莲, 凌炎, 龙丽萍. 广西白背飞虱生物型测定[J]. 南方农业学报, 2011, 42(1): 46-49. |
| Huang S S, Huang F K, Wu B Q, Zhang X L, Nong C L, Ling Y, Long L P. Identification of whitebacked plant- hopper biotype in Guangxi[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2011, 42(1): 46-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 蔡祥承, 张陈伟, 姜张. 稻褐飞虱致害性的转化(同翅目:飞虱科)[J]. 昆虫学报, 1997, 40(1): 110-115. |
| Cai X C, Zhang C W, Jiang Z. Transformation of the damage potential of the brown planthopper (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) in rice[J]. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 1997, 40(1): 110-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 陈建明, 俞晓平, 吕仲贤, 郑许松, 徐红星, 程家安, 刘光杰. 水稻品种对白背飞虱的耐虫性反应及稻株营养成分的变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 2003, 14(12): 2246-2250. |
| Chen J M, Yu X P, Lv Z X, Zheng X S, Cheng J A, Liu G J. Tolerance of rice varieties to whitebacked planthopper Sogatella furcifera and variation of nutrient components in rice plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2003, 14(12): 2246-2250. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 沈君辉, 王燕, 寒川一成, 服部诚, 刘光杰. 抗虫水稻品种上饲养的白背飞虱种群的致害性变化[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2003, 17(S1): 84-88. |
| Shen J H, Wang Y, Sogawa K, Hattori M, Liu G J. Monitoring the changes in virulence of different populations of the whitebacked planthopper, Sogatella furcifera rearing on resistant rice varieties[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2003, 17(S1): 84-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 王桂荣, 赖凤香, 傅强, 张志涛, 郭兰芳. 稻褐飞虱致害性变异的研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 1999, 13(4): 229-232. |
| Wang G R, Lai F X, Fu Q, Zhang Z T, Guo L F. Virulent shift in populations of Nilaparvata lugens (Homptera: Delphacidae)[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 1999, (4): 229-232. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 吕仲贤, 俞晓平, 陈建明, 郑许松, 徐红星, 陶林勇. 共生菌在褐飞虱致害性变化中的作用[J]. 昆虫学报, 2001, 44(2): 197-204. |
| Lu Z X, Yu X P, Chen J M, Zheng X S, Xu H X, Tao L Y. Role of endosymbiote in virulence change of the brown planthopper to rice resistant varieties[J]. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 2001, 44(2): 197-204. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 吕仲贤, 俞晓平, 陈建明, 郑许松, 徐红星. 不同虫源和致害性的褐飞虱体内共生菌的种群动态[J]. 华东昆虫学报, 2001(1): 44-49. |
| Lu Z X, Yu X P, Chen J M, Zheng X S, Xu H X. The population dynamics of symbiote in body of brown planthopper from different geographic fields and adapted to different resistant rice varieties[J]. Entomological Journal of East China, 2001(1): 44-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 袁龙宇, 李燕芳, 肖汉祥, 齐国君, 张振飞. 褐飞虱致害性变异机制研究进展[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2022, 44(2): 297-304. |
| Yuan L Y, Li Y F, Xiao H X, Qi G J, Zhang Z F. Research progress on mechanism of virulence of the brown planthopper (Hemiptera: Delphacidae)[J]. Journal of Environmental Entomology, 2022, 44(2): 297-304. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 孙虹霞, 胡新军, 舒迎花, 张古忍. 白背飞虱触角感器的扫描电镜观察[J]. 昆虫学报, 2006(2): 349-354. |
| Sun H X, Hu X J, Shu Y H, Zhang G R. Observation on the antennal sensilla of Sogatella furcifera (Horváth) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) with scanning electron microscope[J]. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 2006(2): 349-354. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | Yang Z F, Zhang F T, He Q, He G C. Molecular dynamics of detoxification and toxin-tolerance genes in brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens (Stål), Homoptera: Delphacidae) feeding on resistant rice plants[J]. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 2005, 59(2): 59-66. |
| [32] | Xue J, Zhou X, Zhang C X, Yu L L, Fan H W, Wang Z, Xu H J, Xi Y, Zhu Z R, Zhou W W, Pan P L, Li B L, Colbourne J K, Noda H, Suetsugu Y, Kobayashi T, Zheng Y, Liu S L, Zhang R, Liu Y, Luo Y D, Fang D M, Chen Y, Zhan D L, Lü X D, Cai Y, Wang Z B, Huang H J, Cheng R L, Zhang X C, Lou Y H, Yu B, Zhuo J C, Ye Y X, Zhang W Q, Shen Z C, Yang H M, Wang J, Wang J, Bao Y Y, Cheng J A. Genomes of the rice pest brown planthopper and its endosymbionts reveal complex complementary contributions for host adaptation[J]. Genome Biology, 2014, 15(12). |
| [33] | Kusakabe S. Dispersal of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål): (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) in relation to its population growth[J]. Applied Entomology and Zoology, 1979, 14(2): 224-225. |
| [34] | Hu D B, Luo B Q, Li J, Han Y, Jiang T R, Liu J, Wu G, Hua H X, Xiong Y F, Li J S. Genome-wide analysis of Nilaparvata lugens nymphal responses to high-density and low-quality rice hosts[J]. Insect Science, 2013, 20(6): 703-716. |
| [35] | Tong X H, Qi J F, Zhu X D, Mao B Z, Zeng L J, Wang B H, Li Q, Zhou G X, Xu X J, Lou Y G, He Z H. The rice hydroperoxide lyase OsHPL3 functions in defense responses by modulating the oxylipin pathway[J]. The Plant Journal, 2012, 71(5): 763-775. |
| [36] | Han S J, Shen Z F, Gao Q, Jin N, Lou Y G. Knocking out OsRLK7-1 impairs rice growth and development but enhances its resistance to planthoppers[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(19): 14569. |
| [37] | Cheng X Y, Zhu L L, He G C. Towards understanding of molecular interactions between rice and the brown planthopper[J]. Molecular Plant, 2013, 6(3): 621-634. |
| [38] | Xiao Y, Wang Q, Erb M, Turlings T C J, Ge L, Hu L, Li J, Han X, Zhang T, Lu J, Zhang G, Lou Y. Specific herbivore-induced volatiles defend plants and determine insect community composition in the field[J]. Ecology Letters, 2012, 15(10): 1130-1139. |
| [39] | Yuan J S, Köllner T G, Wiggins G, Grant J, Degenhardt J, Chen F. Molecular and genomic basis of volatile-mediated indirect defense against insects in rice[J]. The Plant Journal, 2008, 55(3): 491-503. |
| [40] | Lou Y G, Du M H, Turlings T C J, Cheng J A, Shan W F. Exogenous application of jasmonic acid induces volatile emissions in rice and enhances parasitism of Nilaparvata lugens eggs by the parasitoid Anagrus nilaparvatae[J]. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 2005, 31(9): 1985-2002. |
| [41] | Khetnon P, Busarakam K, Sukhaket W, Niwaspragrit C, Kamolsukyeunyong W, Kamata N, Sanguansub S. Mechanisms of trichomes and terpene compounds in indigenous and commercial Thai rice varieties against brown planthopper[J]. Insects, 2022, 13(5): 427. |
| [42] | Leal W S. Odorant reception in insects: Roles of receptors, binding proteins, and degrading enzymes[J]. Annual Review of Entomology, 2013, 58(1): 373-391. |
| [43] | Cruse C, Moural T W, Zhu F. Dynamic roles of insect carboxyl/cholinesterases in chemical adaptation[J]. Insects, 2023, 14(2): 194. |
| [44] | Zhu J J, Jiang F, Wang X H, Yang P C, Bao Y Y, Zhao W, Wang W, Lu H, Wang Q S, Cui N, Li J, Chen X F, Luo L, Yu J T, Kang L, Cui F. Genome sequence of the small brown planthopper, Laodelphax striatellus[J]. GigaScience, 2017, 6(12): 1-12. |
| [45] | He P, Chen G L, Li S, Wang J, Ma Y F, Pan Y F, He M. Evolution and functional analysis of odorant-binding proteins in three rice planthoppers: Nilaparvata lugens, Sogatella furcifera, and Laodelphax Striatellus[J]. Pest Management Science, 2019, 75(6): 1606-1620. |
| [46] | Xue J, Zhou X, Zhang C X, Yu L L, Fan H W, Wang Z, Xu H J, Xi Y, Zhu Z R, Zhou W W, Pan P L, Li B L, Colbourne J K, Noda H, Suetsugu Y, Kobayashi T, Zheng Y, Liu S L, Zhang R, Liu Y, Luo Y D, Fang D M, Chen Y, Zhan D L, Lü X D, Cai Y, Wang Z B, Huang H J, Cheng R L, Zhang X C, Lou Y H, Yu B, Zhuo J C, Ye Y X, Zhang W Q, Shen Z C, Yang H M, Wang J, Wang J, Bao Y Y, Cheng J A. Genomes of the rice pest brown planthopper and its endosymbionts reveal complex complementary contributions for host adaptation[J]. Genome Biology, 2014, 15(12): 521. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [47] | Kang K, Yang P, Chen L E, Pang R, Yu L J, Zhou W W, Zhu Z R, Zhang W Q. Identification of putative fecundity-related gustatory receptor genes in the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens[J]. BMC Genomics, 2018, 19(1): 970. |
| [48] | Zhou W W, Yuan X, Qian P, Cheng J A, Zhang C X, Gurr G, Zhu Z R. Identification and expression profiling of putative chemosensory protein genes in two rice planthoppers, Laodelphax striatellus (Fallén) and Sogatella furcifera (Horváth)[J]. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 2015, 18(4): 771-778. |
| [49] | He P, Wang M M, Wang H, Ma Y F, Yang S, Li S B, Li X G, Li S, Zhang F, Wang Q, Ran H N, Yang G Q, Dewer Y, He M. Genome-wide identification of chemosensory receptor genes in the small brown planthopper, Laodelphax striatellus[J]. Genomics, 2020, 112(2): 2034-2040. |
| [50] | He P, Engsontia P, Chen G L, Yin Q, Wang J, Lu X, Zhang Y N, Li Z Q, He M. Molecular characterization and evolution of a chemosensory receptor gene family in three notorious rice planthoppers, Nilaparvata lugens, Sogatella furcifera and Laodelphax striatellus, based on genome and transcriptome analyses[J]. Pest Management Science, 2018, 74(9): 2156-2167. |
| [51] | Duan S G, Lü C L, Liu J H, Yi S C, Yang R N, Liu A, Wang M Q. NlugOBP8 in Nilaparvata lugens involved in the perception of two terpenoid compounds from rice plant[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2022, 70(51): 16323-16334. |
| [52] | Liu H, Wang C, Qiu C L, Shi J H, Sun Z, Hu X J, Liu L, Wang M Q. A salivary odorant-binding protein mediates Nilaparvata lugens feeding and host plant phytohormone suppression[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(9): 4988. |
| [53] | He P, Zhang J, Liu N Y, Zhang Y N, Yang K, Dong S L. Distinct expression profiles and different functions of odorant binding proteins in Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)[J]. PLOS ONE, 2011, 6(12): e28921. |
| [54] | Zhang J J, Mao K K, Ren Z J, Jin R H, Zhang Y H, Cai T W, He S, Li J H, Wan H. Odorant binding protein 3 is associated with nitenpyram and sulfoxaflor resistance in Nilaparvata lugens[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2022, 209: 1352-1358. |
| [55] | Waris M I, Younas A, Adeel M M, Duan S G, Quershi S R, Ullah R M K, Wang M Q. The role of chemosensory protein 10 in the detection of behaviorally active compounds in brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens[J]. Insect Science, 2020, 27(3): 531-544. |
| [56] | Foster S, Goodman L J, Duckett J G. Sensory receptors associated with the stylets and cibarium of the rice brown planthopper, Nilapavarta lugens[J]. Cell and Tissue Research, 1983, 232(1): 111-119. |
| [57] | Chen W W, Kang K, Yang P, Zhang W Q. Identification of a sugar gustatory receptor and its effect on fecundity of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens[J]. Insect Science, 2019, 26(3): 441-452. |
| [58] | Chen W W, Kang K, Lü J, Yue L, Zhang W Q. Galactose-NlGr11 inhibits AMPK phosphorylation by activating the PI3K-AKT-PKF-ATP signaling cascade via insulin receptor and Gβγ[J]. Insect Science, 2021, 28(3): 735-745. |
| [59] | Ojha A, Zhang W Q. Characterization of gustatory receptor 7 in the brown planthopper reveals functional versatility[J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2021, 132: 103567. |
| [60] | Kang K, Zhang M Y, Yue L, Chen W W, Dai Y S, Lin K, Liu K, Lv J, Guan Z W, Xiao S, Zhang W Q. Oxalic acid inhibits feeding behavior of the brown planthopper via binding to gustatory receptor Gr23a[J]. Cells, 2023, 12(5): 771. |
| [61] | Tjallingii W F. Salivary secretions by aphids interacting with proteins of phloem wound responses[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2006, 57(4): 739-745. |
| [62] | Seo B Y, Kwon Y H, Jung J K, Kim G H. Electrical penetration graphic waveforms in relation to the actual positions of the stylet tips of Nilaparvata lugens in rice tissue[J]. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 2009, 12(2): 89-95. |
| [63] | Will T, Furch A C U, Zimmermann M R. How phloem-feeding insects face the challenge of phloem-located defenses[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2013, 4: 336. |
| [64] | Wang Y C, Tang M, Hao P Y, Yang Z F, Zhu L L, He G C. Penetration into rice tissues by brown planthopper and fine structure of the salivary sheaths[J]. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 2008, 129(3): 295-307. |
| [65] | Rao W W, Zheng X H, Liu B F, Guo Q, Guo J P, Wu Y, Shangguan X X, Wang H Y, Wu D, Wang Z Z, Hu L, Xu C X, Jiang W H, Huang J, Shi S J, He G C. Secretome analysis and in planta expression of salivary proteins identify candidate effectors from the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2019, 32(2): 227-239. |
| [66] | Huang H J, Liu C W, Xu H J, Bao Y Y, Zhang C X. Mucin-like protein, a saliva component involved in brown planthopper virulence and host adaptation[J]. Journal of Insect Physiology, 2017, 98: 223-230. |
| [67] | Shangguan X X, Zhang J, Liu B F, Zhao Y, Wang H Y, Wang Z Z, Guo J P, Rao W W, Jing S L, Guan W, Ma Y H, Wu Y, Hu L, Chen R Z, Du B, Zhu L L, Yu D Z, He G C. A mucin-Like protein of planthopper is required for feeding and induces immunity response in plants[J]. Plant Physiology, 2018, 176(1): 552-565. |
| [68] | Huang H J, Wang Y Z, Li L L, Lu H B, Lu J B, Wang X, Ye Z X, Zhang Z L, He Y J, Lu G, Zhuo J C, Mao Q Z, Sun Z T, Chen J P, Li J M, Zhang C X. Planthopper salivary sheath protein LsSP1 contributes to manipulation of rice plant defenses[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 737. |
| [69] | Huang J, Zhang N, Shan J H, Peng Y X, Guo J P, Zhou C, Shi S J, Zheng X H, Wu D, Guan W, Yang K, Du B, Zhu L, Yuan L P, He G C, Chen R Z. Salivary protein 1 of brown planthopper is required for survival and induces immunity response in plants[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 571280. |
| [70] | Gao H L, Zou J Z, Lin X M, Zhang H H, Yu N, Liu Z W. Nilaparvata lugens salivary protein NlG14 triggers defense response in plants[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2022, 73(22): 7477-7487. |
| [71] | Huang H J, Liu C W, Cai Y F, Zhang M Z, Bao Y Y, Zhang C X. A salivary sheath protein essential for the interaction of the brown planthopper with rice plants[J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2015, 66: 77-87. |
| [72] | Liu X Q, Zhou H Y, Zhao J, Hua H X, He Y P. Identification of the secreted watery saliva proteins of the rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) by transcriptome and Shotgun LC-MS/MS approach[J]. Journal of Insect Physiology, 2016, 89: 60-69. |
| [73] | Sōgawa K. The rice brown planthopper: feeding physiology and host plant interactions[J]. Annual Review of Entomology, 1982, 27(1): 49-73. |
| [74] | Ji R, Ye W F, Chen H D, Zeng J M, Li H, Yu H X, Li J C, Lou Y G. A salivary endo-β-1,4-glucanase acts as an effector that enables the brown planthopper to feed on rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2017, 173(3): 1920-1932. |
| [75] | Guo J P, Wang H Y, Guan W, Guo Q, Wang J, Yang J, Peng Y X, Shan J H, Gao M Y, Shi S J, Shangguan X X, Liu B F, Jing S L, Zhang J, Xu C X, Huang J, Rao W W, Zheng X H, Wu D, Zhou C, Du B, Chen R Z, Zhu L L, Zhu Y X, Walling L L, Zhang Q F, He G C. A tripartite rheostat controls self-regulated host plant resistance to insects[J]. Nature, 2023, 618(7966): 799-807. |
| [76] | Konishi H, Noda H, Tamura Y, Hattori M. Proteomic analysis of the salivary glands of the rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Homoptera: Delphacidae)[J]. Applied Entomology and Zoology, 2009, 44(4): 525-534. |
| [77] | Ye W F, Yu H X, Jian Y K, Zeng J M, Ji R, Chen H D, Lou Y G. A salivary EF-hand calcium-binding protein of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens functions as an effector for defense responses in rice[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 40498. |
| [78] | Fu J M, Shi Y, Wang L H, Tian T, Li J, Gong L, Zheng Z T, Jing M F, Fang J C, Ji R. Planthopper-secreted salivary calmodulin acts as an effector for defense responses in rice[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 841378. |
| [79] | Tian T, Ji R, Fu J M, Li J, Wang L, Zhang H, Yang S Y, Ye W F, Fang J C, Zhu-Salzman K. A salivary calcium‐binding protein from Laodelphax striatellus acts as an effector that suppresses defense in rice[J]. Pest Management Science, 2021, 77(5): 2272-2281. |
| [80] | Huang H J, Cui J R, Xia X, Chen J, Ye Y X, Zhang C X, Hong X Y. Salivary DNase II from Laodelphax striatellus acts as an effector that suppresses plant defence[J]. New Phytologist, 2019, 224(2): 860-874. |
| [81] | Zeng J M, Ye W F, Hu W H, Jin X C, Kuai P, Xiao W H, Jian Y K, Turlings T C J, Lou Y G. The N-terminal subunit of vitellogenin in planthopper eggs and saliva acts as a reliable elicitor that induces defenses in rice[J]. New Phytologist, 2023, 238(3): 1230-1244. |
| [82] | Ji R, Fu J M, Shi Y, Li J, Jing M F, Wang L, Yang S Y, Tian T, Wang L H, Ju J F, Guo H F, Liu B, Dou D L, Hoffmann A A, Zhu-Salzman K, Fang J C. Vitellogenin from planthopper oral secretion acts as a novel effector to impair plant defenses[J]. New Phytologist, 2021, 232(2): 802-817. |
| [83] | Zhang Z L, Wang X J, Lu J B, Lu H B, Ye Z X, Xu Z T, Zhang C, Chen J P, Li J M, Zhang C X, Huang H J. Cross-kingdom RNA interference mediated by insect salivary microRNAs may suppress plant immunity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2024, 121(16): e2318783121. |
| [84] | Wu Y, Lü W T, Hu L, Rao W W, Zeng Y, Zhu L L, He Y Q, He G C. Identification and analysis of brown planthopper-responsive microRNAs in resistant and susceptible rice plants[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 8712. |
| [85] | Ge Y F, Han J Y, Zhou G X, Xu Y M, Ding Y, Shi M, Guo C K, Wu G. Silencing of miR156 confers enhanced resistance to brown planthopper in rice[J]. Planta, 2018, 248(4): 813-826. |
| [86] | Dai Z Y, Tan J, Zhou C, Yang X F, Yang F, Zhang S J, Sun S C, Miao X X, Shi Z Y. The OsmiR396-OsGRF8-OsF3H-flavonoid pathway mediates resistance to the brown planthopper in rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 17(8): 1657-1669. |
| [87] | Shen Y J, Yang G Q, Miao X X, Shi Z Y. OsmiR159 modulate BPH resistance through regulating G-protein γ subunit GS3 gene in rice[J]. Rice, 2023, 16(1): 30. |
| [88] | Shen S, Zhan C, Yang C, Fernie A R, Luo J. Metabolomics-centered mining of plant metabolic diversity and function: past decade and future perspectives[J]. Molecular Plant, 2023, 16(1): 43-63. |
| [89] | Chen W, Gao Y Q, Xie W B, Gong L, Lu K, Wang W S, Li Y, Liu X Q, Zhang H Y, Dong H X, Zhang W, Zhang L J, Yu S, Wang G W, Lian X M, Luo J. Genome-wide association analyses provide genetic and biochemical insights into natural variation in rice metabolism[J]. Nature Genetics, 2014, 46(7): 714-721. |
| [90] | Peng L, Zhao Y, Wang H Y, Zhang J J, Song C P, Shangguan X X, Zhu L L, He G C. Comparative metabolomics of the interaction between rice and the brown planthopper[J]. Metabolomics, 2016, 12(8): 132. |
| [91] | Kaushik P, Sarkar D J, Chander S, Rana V S, Shakil N A. Insecticidal activity of phenolic acid amides against brown planthopper (BPH), Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) and their QSAR analysis[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B: Pesticides Food Contaminants and Agricultural Wastes, 2019, 54(6): 489-497. |
| [92] | Sun X Q, Zhang M X, Yu J Y, Jin Y, Ling B, Du J P, Li G H, Qin Q M, Cai Q N. Glutathione S-transferase of brown planthoppers (Nilaparvata lugens) is essential for their adaptation to gramine-containing host plants[J]. PLoS ONE, 2013, 8(5): e64026. |
| [93] | Yang J, Kong X D, Zhu-Salzman K, Qin Q M, Cai Q N. The key glutathione S-transferase family genes involved in the detoxification of rice gramine in brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens[J]. Insects, 2021, 12(12): 1055. |
| [94] | Hao P Y, Feng Y L, Zhou Y S, Song X M, Li H L, Ma Y, Ye C L, Yu X P. Schaftoside interacts with NlCDK1 protein: a mechanism of rice resistance to brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 970. |
| [95] | Liu M Y, Hong G J, Li H J, Bing X L, Chen Y M, Jing X F, Gershenzon J, Lou Y G, Baldwin I T, Li R. Sakuranetin protects rice from brown planthopper attack by depleting its beneficial endosymbionts[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2023, 120(23): e2305007120. |
| [96] | 刘玉坤, 王渭霞, 傅强, 赖凤香, 罗举. 寄主植物对3种稻飞虱解毒酶和保护酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(6): 8. |
| Liu Y K, Wang W X, Fu Q, Lai F X, Luo J. Effects of host plants on activities of detoxification and protective enzymes in three rice planthoppers[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25(6): 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [97] | Rout P, Ravindranath N, Gaikwad D, Nanda S. Unveiling Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) genes defining compatible and incompatible interactions with rice through transcriptome analysis and gene silencing[J]. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 2023, 45(8): 6790-6803. |
| [98] | Zhang J, Guan W, Huang C M, Hu Y X, Chen Y, Guo J P, Zhou C, Chen R Z, Du B, Zhu L L, Huanhan D, He G C. Combining next-generation sequencing and single- molecule sequencing to explore brown plant hopper responses to contrasting genotypes of japonica rice[J]. BMC Genomics, 2019, 20(1): 682. |
| [99] | Liu Y B, Wang W Q, Li Y H, Liu F, Han W J, Li J S. Transcriptomic and proteomic responses to brown plant hopper (Nilaparvata lugens) in cultivated and Bt-transgenic rice (Oryza sativa) and wild rice (O. rufipogon)[J]. Journal of Proteomics, 2021, 232: 104051. |
| [100] | Zhang Y X, Yang Y X, Sun H H, Liu Z W. Metabolic imidacloprid resistance in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, relies on multiple P450 enzymes[J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2016, 79: 50-56. |
| [101] | Yang Z, Zhang Y, Liu X, Wang X. Two novel cytochrome P450 genes CYP6CS1 and CYP6CW1 from Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae): cDNA cloning and induction by host resistant rice[J]. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 2011, 101(1): 73-80. |
| [102] | Wang X Q, Guo J S, Li D T, Yu Y, Hagoort J, Moussian B, Zhang C X. Three-dimensional reconstruction of a whole insect reveals its phloem sap-sucking mechanism at nano-resolution[J]. eLife, 2021, 10: e62875. |
| [103] | Zhang X F, Zhao D X, Hong X Y. Cardinium-the leading factor of cytoplasmic incompatibility in the planthopper Sogatella furcifera doubly infected with Wolbachia and Cardinium[J]. Environmental Entomology, 2012, 41(4): 833-840. |
| [104] | 李迁, 范佳, 孙京瑞, 王满囷, FRANCIS F, 陈巨莲. 昆虫内共生菌-昆虫-植物互作关系研究进展. 植物保护学报, 2016, 43(6): 11. |
| Li Q, Fan J, Sun J R, Wang M Q, Francis F, Chen J L. Research progress in the interactions among the plants, insects and endosymbionts[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2016, 43(6): 11. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [105] | Yan Z C, Qi L D, Ji H L, Wang X X, Hong X Y, Li Y X. Frequent intertrophic transmission of Wolbachia by parasitism but not predation[J]. eLife, 2024, 13: RP97872. |
| [106] | Ju J F, Bing X L, Zhao D S, Guo Y, Xi Z Y, Hoffmann A A, Zhang K J, Huang H J, Gong J T, Zhang X, Hong X Y. Wolbachia supplement biotin and riboflavin to enhance reproduction in planthoppers[J]. The International Society for Microbial Ecology Journal, 2020, 14(3): 676-687. |
| [107] | Wan P J, Yang L, Wang W X, Fan J M, Fu Q, Li G Q. Constructing the major biosynthesis pathways for amino acids in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae), based on the transcriptome data[J]. Insect Molecular Biology, 2014, 23(2): 152-164. |
| [108] | Wan P J, Yuan S Y, Tang Y H, Li K L, Yang L, Fu Q, Li G Q. Pathways of amino acid degradation in Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) with special reference to lysine- ketoglutarate reductase/saccharopine dehydrogenase (LKR/SDH)[J]. PLoS ONE, 2015, 10(5): e0127789. |
| [109] | Lin K, Yue L, Yuan L Y, Kang K, Zhang Y B, Pang R, Zhang W Q. Alanine metabolism mediates energy allocation of the brown planthopper to adapt to resistant rice[J]. Journal of Advanced Research, 2024, 67: 25-41. |
| [110] | 孙佳音, 傅强, 赖凤香, 王渭霞. 不同褐飞虱寄主种群类酵母共生菌形态和数量的比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(5): 546-550. |
| Sun J Y, Fu Q, Lai F X, Wang W X. Comparison on morphology and number of yeast like symbionts in different host-associated populations of Nilaparvata lugens[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2009, 23(5): 546-550. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [111] | 陈法军, 张珏锋, 陈建明, 郑许松, 陈列忠, 俞晓平. 水稻与褐飞虱互作过程中虫体内类酵母共生菌的个体大小及数量变化[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2006, 18(5): 294-8. |
| Chen F J, Zhang Y F, Chen J M, Zheng X S, Chen L Z, Yu X P. Change in size and abundance of the yeast-like endosymbiote during the interaction between brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) and resistant-variety rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2006, 18(5): 294-298. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [112] | 王国超, 傅强, 赖凤香, 陈铭学, 牟仁祥, 张志涛. 褐飞虱体内类酵母共生菌与氨基酸营养的关系[J]. 昆虫学报, 2005, 48(4): 8. |
| Wang G Q, Fu Q, Lai F X, Chen M X, Mou R X, Zhang Z T. Relationship between yeast-like symbiotes and amino acid requirements in the ricebrown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Homoptera: Delphacidae)[J]. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 2005, 48(4): 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [113] | Jia D S, Mao Q Z, Chen Y, Liu Y Y, Chen Q, Wu W, Zhang X F, Chen H Y, Li Y, Wei T Y. Insect symbiotic bacteria harbour viral pathogens for transovarial transmission[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2017, 2(5): 17025. |
| [114] | Ingwell L L, Eigenbrode S D, Bosque-Pérez N A. Plant viruses alter insect behavior to enhance their spread[J]. Scientific Reports, 2012, 2(1): 578. |
| [115] | Gildow F E. Increased production of alatae by Aphids1 reared on oats infected with barley yellow dwarf virus[J]. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 1980, 73(3): 343-347. |
| [116] | Wang Z L, Pan H B, Wu W, Li M Y, Yu X P. The gut bacterial flora associated with brown planthopper is affected by host rice varieties[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2021, 203(1): 325-333. |
| [117] | Hong Xing X, Xu Song Z, Ya Jun Y, Jun Ce T, Qiang F, Gong Yin Y, Zhong Xian L. Changes in endosymbiotic bacteria of brown planthoppers during the process of adaptation to different resistant rice varieties[J]. Environmental Entomology, 2015, 44(3): 582-587. |
| [118] | Tang M, Lü L, Jing S L, Zhu L L, He G C. Bacterial symbionts of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Homoptera: Delphacidae)[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76(6): 1740-1745. |
| [119] | Wang Y Y, Wang X L, Yuan H Y, Chen R Z, Zhu L L, He R F, He G C. Responses of two contrasting genotypes of rice to brown planthopper[J]. Molecular Plant- Microbe Interactions, 2008, 21(1): 122-132. |
| [120] | Foissac X, Edwards M G, Du J P, Gatehouse A M R, Gatehouse J A. Putative protein digestion in a sap-sucking homopteran plant pest (rice brown plant hopper; Nilaparvata Lugens: Delphacidae): Identification of trypsin-like and cathepsin B-like proteases[J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2002, 32(9): 967-978. |
| [121] | Ryan C A. Protease inhibitors in plants: Genes for improving defenses against insects and pathogens[J]. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 1990, 28: 425-449. |
| [122] | Chen Y H, Bernal C C, Tan J, Horgan F G, Fitzgerald M A. Planthopper “adaptation” to resistant rice varieties: Changes in amino acid composition over time[J]. Journal of Insect Physiology, 2011, 57(10): 1375-1384. |
| [123] | Yu H X, Ji R, Ye W F, Chen H D, Lai W X, Fu Q, Lou Y G. Transcriptome analysis of fat bodies from two brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) populations with different virulence levels in rice[J]. PLoS ONE, 2014, 9(2): e88528. |
| [124] | Zeng B, Zhang F, Liu Y T, Wu S F, Bass C, Gao C F. Symbiotic bacteria confer insecticide resistance by metabolizing buprofezin in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)[J]. PLOS Pathogens, 2023, 19(12): e1011828. |
| [125] | Malathi M V, Ravi P M, Anandham R, Gracy R G, Mohan M, Venkatesan T, Sandipan S, Sushil K J. Gut bacterial diversity of insecticide-susceptible and -resistant nymphs of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) and elucidation of their putative functional roles[J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 28(6): 976-986. |
| [126] | Liu W W, Zhang X W, Wu N, Ren Y D, Wang X F. High diversity and functional complementation of alimentary canal microbiota ensure small brown planthopper to adapt different biogeographic environments[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 10: 2953. |
| [127] | Iwanaga K, Tojo S. Comparative studies on the sensitivities to nymphal density, photoperiod and rice plant stage in two strains of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Homoptera: Delphacidae)[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Entomology and Zoology, 1988, 32(1): 68-74. |
| [128] | Xu H J, Xue J, Lu B, Zhang X C, Zhuo J C, He S F, Ma X F, Jiang Y Q, Fan H W, Xu J Y, Ye Y X, Pan P L, Li Q, Bao Y Y, Nijhout H F, Zhang C X. Two insulin receptors determine alternative wing morphs in planthoppers[J]. Nature, 2015, 519(7544): 464-467. |
| [129] | Liu F Z, Li X, Zhao M H, Guo M J, Han K H, Dong X X, Zhao J, Cai W L, Zhang Q F, Hua H X. Ultrabithorax is a key regulator for the dimorphism of wings, a main cause for the outbreak of planthoppers in rice[J]. National Science Review, 2020, 7(7): 1181-1189. |
| [130] | Zhang J L, Chen S J, Liu X Y, Moczek A P, Xu H J. The transcription factor Zfh1 acts as a wing-morph switch in planthoppers[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 5670. |
| [131] | 蒯鹏, 娄永根. 稻飞虱生物学、生态学及其防控技术研究进展. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2022, 48(6): 692-700. |
| Kuai P, Lou Y G. Research advances in biology, ecology and management of rice planthoppers. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agric & Life Sci), 2022, 48(6): 692-700. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [132] | Pan W D, Wan G J, Xu J J, Li X M, Liu Y X, Qi L P, Chen F J. Evidence for the presence of biogenic magnetic particles in the nocturnal migratory brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 18771. |
| [133] | Wan G J, Jiang S L, Zhao Z C, Xu J J, Tao X R, Sword G A, Gao Y B, Pan W D, Chen F J. Bio-effects of near-zero magnetic fields on the growth, development and reproduction of small brown planthopper, Laodelphax striatellus and brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens[J]. Journal of Insect Physiology, 2014, 68: 7-15. |
| [1] | 杨奇欣, 赖凤香, 何佳春, 魏琪, 王渭霞, 万品俊, 傅强. 不同抗感水稻品种对褐飞虱胁迫的高光谱响应特征[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38(1): 81-90. |
| [2] | 张珏锋, 李芳, 钟海英, 陈建明. 制霉菌素对褐飞虱若虫解毒酶、尿酸酶含量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(2): 186-190. |
| [3] | 傅强, 李保平, 孟玲. 土壤施用生物质炭对取食水稻的灰飞虱生活史特征的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2018, 1(1): 200-206. |
| [4] | 唐耀华1,2,万品俊2,郝培应1,傅强2,*,俞晓平1,*. 类酵母共生菌中两个组氨酸合成基因在褐飞虱发育中的作用[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(4): 406-416. |
| [5] | 秦钟,章家恩* ,张锦,骆世明. 稻鸭共作系统中稻飞虱及主要捕食性天敌类群之间的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2012, 26(4): 457-466. |
| [6] | 刘玉坤,王渭霞,傅强*,赖凤香,罗举 . 寄主植物对3种稻飞虱解毒酶和保护酶活性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25(6): 659-666. |
| [7] | 孙佳音,傅 强,赖凤香,王渭霞. 不同褐飞虱寄主种群类酵母共生菌形态和数量的比较 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(5): 546-550 . |
| [8] | 张晓婕,俞晓平,陈建明. 高温对灰飞虱体内类酵母共生菌和耐药性的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2008, 22(4): 416-420 . |
| [9] | 张珏锋,吴鸿,陈建明,郑许松,陈列忠,俞晓平,. 一株褐飞虱内共生菌的分离及分子鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2007, 21(5): 551-554 . |
| [10] | 黄诚华,姚洪渭,叶恭银, 程家安. 氟虫腈亚致死剂量处理对二化螟和大螟幼虫体内解毒酶系活力的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2006, 20(4): 447-450 . |
| [11] | 刘泽文, 韩召军, 张玲春. 褐飞虱对甲胺磷抗性发展与解毒酶系活性的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2003, 17(2): 166-170 . |
| [12] | 吕仲贤 , 俞晓平 , 陈建明 , 郑许松 , 徐红星 , 张志涛 . 田间发生与室内驯化的褐飞虱生物型2的特性比较[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2002, 16(1): 89-92 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||