
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 552-562.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240713
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Jiale1,5, YU Qingtao2, ZHENG Chenfan1,5, WANG Qing3, TAN Yuanyuan4, CHEN Baicui2, LI Chengxin2, JIANG Meng1,5, SHU Qingyao1,5,*( )
)
Received:2024-07-17
Revised:2024-08-17
Online:2025-07-10
Published:2025-07-21
Contact:
SHU Qingyao
陈嘉乐1,5, 于清涛2, 郑琛凡1,5, 汪庆3, 谭瑗瑗4, 陈百翠2, 李承欣2, 蒋萌1,5, 舒庆尧1,5,*( )
)
通讯作者:
舒庆尧
基金资助:CHEN Jiale, YU Qingtao, ZHENG Chenfan, WANG Qing, TAN Yuanyuan, CHEN Baicui, LI Chengxin, JIANG Meng, SHU Qingyao. Natural Variation of OsNF-YC10 and Its Correlation with Grain Width in Rice[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(4): 552-562.
陈嘉乐, 于清涛, 郑琛凡, 汪庆, 谭瑗瑗, 陈百翠, 李承欣, 蒋萌, 舒庆尧. 水稻OsNF-YC10自然变异及其与谷粒宽度的相关性[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(4): 552-562.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240713
| 引物类型 Type of primer | 引物序列(5’ to 3’) Primer sequence (5’ to 3’) | 等位基因 Allele | 产物长度 Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 扩增OsNF-YC10全长部分 | |||
| Forward primer | CTGTGGGACTGTAAGATCATCTATG | 1466 | |
| Reverse primer | CTTGTTGCCATTACTGGTGCTTGG | ||
| Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR | |||
| Forward outer primer | TAGCCCTGCGGTTCTTGCAAGTATGA | ||
| Reverse outer primer | AATCCTGGTGTCCGAAACATCATCCT | ||
| Forward inner primer | TGCTGCTACAAAGGTTTTcAGTGcCt | T | 241 |
| Reverse inner primer | GTTTCTTTCTCATGTTGTTCTTCaTg | C | 361 |
Table 1. PCR primers used in the present study
| 引物类型 Type of primer | 引物序列(5’ to 3’) Primer sequence (5’ to 3’) | 等位基因 Allele | 产物长度 Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 扩增OsNF-YC10全长部分 | |||
| Forward primer | CTGTGGGACTGTAAGATCATCTATG | 1466 | |
| Reverse primer | CTTGTTGCCATTACTGGTGCTTGG | ||
| Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR | |||
| Forward outer primer | TAGCCCTGCGGTTCTTGCAAGTATGA | ||
| Reverse outer primer | AATCCTGGTGTCCGAAACATCATCCT | ||
| Forward inner primer | TGCTGCTACAAAGGTTTTcAGTGcCt | T | 241 |
| Reverse inner primer | GTTTCTTTCTCATGTTGTTCTTCaTg | C | 361 |
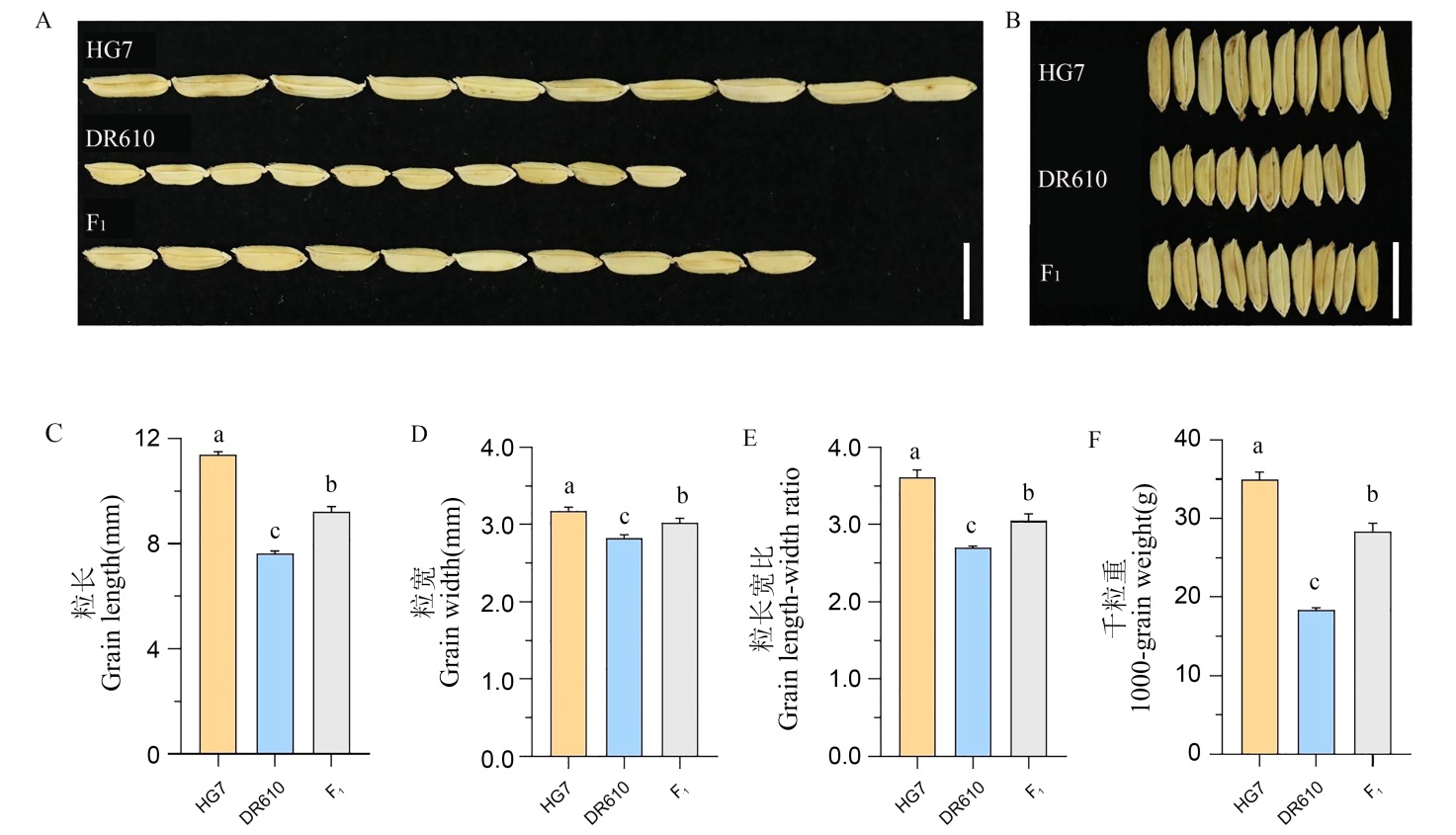
Fig. 1. Grain traits of HG7, DR610 and their F1 A and B, Grain phenotype, bar = 1 cm; C-F, Grain length, grain width, grain length-to-width ratio, and 1000-grain weight. Values are mean ± SD (n = 3). Different letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05(analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test).
| 样品名称 Sample | 总读序数 Total reads | 比对率 Alignment (%) | 基因组覆盖率 Genome coverage (%) | 测序深度 Average depth (×) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HG7 | 85 448 290 | 90.70 | 97.47 | 30 |
| DR610 | 113 535 356 | 98.54 | 92.73 | 43 |
| LGMP | 99 534 914 | 96.99 | 99.00 | 37 |
Table 2. Statistics of whole-genome sequencing results of DR610, HG7 and their F2 large grain mixing pool (LGMP)
| 样品名称 Sample | 总读序数 Total reads | 比对率 Alignment (%) | 基因组覆盖率 Genome coverage (%) | 测序深度 Average depth (×) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HG7 | 85 448 290 | 90.70 | 97.47 | 30 |
| DR610 | 113 535 356 | 98.54 | 92.73 | 43 |
| LGMP | 99 534 914 | 96.99 | 99.00 | 37 |
| 染色体 Chr | 开始 Start | 结束 End | 大小 Size (Mb) | 基因数目 Number of genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12 931 694 | 13 481 021 | 0.55 | 28 |
| 1 | 13 645 077 | 13 688 772 | 0.04 | 0 |
| 1 | 13 705 131 | 13 820 507 | 0.12 | 8 |
| 3 | 23 567 245 | 24 695 746 | 1.13 | 86 |
| Total | - | - | 1.84 | 122 |
Table 3. Genomic regions and number of annotated genes, in which four QTLs of grain weight were mapped using QTL-seq of large grain F2 plants of DR610×HG7
| 染色体 Chr | 开始 Start | 结束 End | 大小 Size (Mb) | 基因数目 Number of genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12 931 694 | 13 481 021 | 0.55 | 28 |
| 1 | 13 645 077 | 13 688 772 | 0.04 | 0 |
| 1 | 13 705 131 | 13 820 507 | 0.12 | 8 |
| 3 | 23 567 245 | 24 695 746 | 1.13 | 86 |
| Total | - | - | 1.84 | 122 |
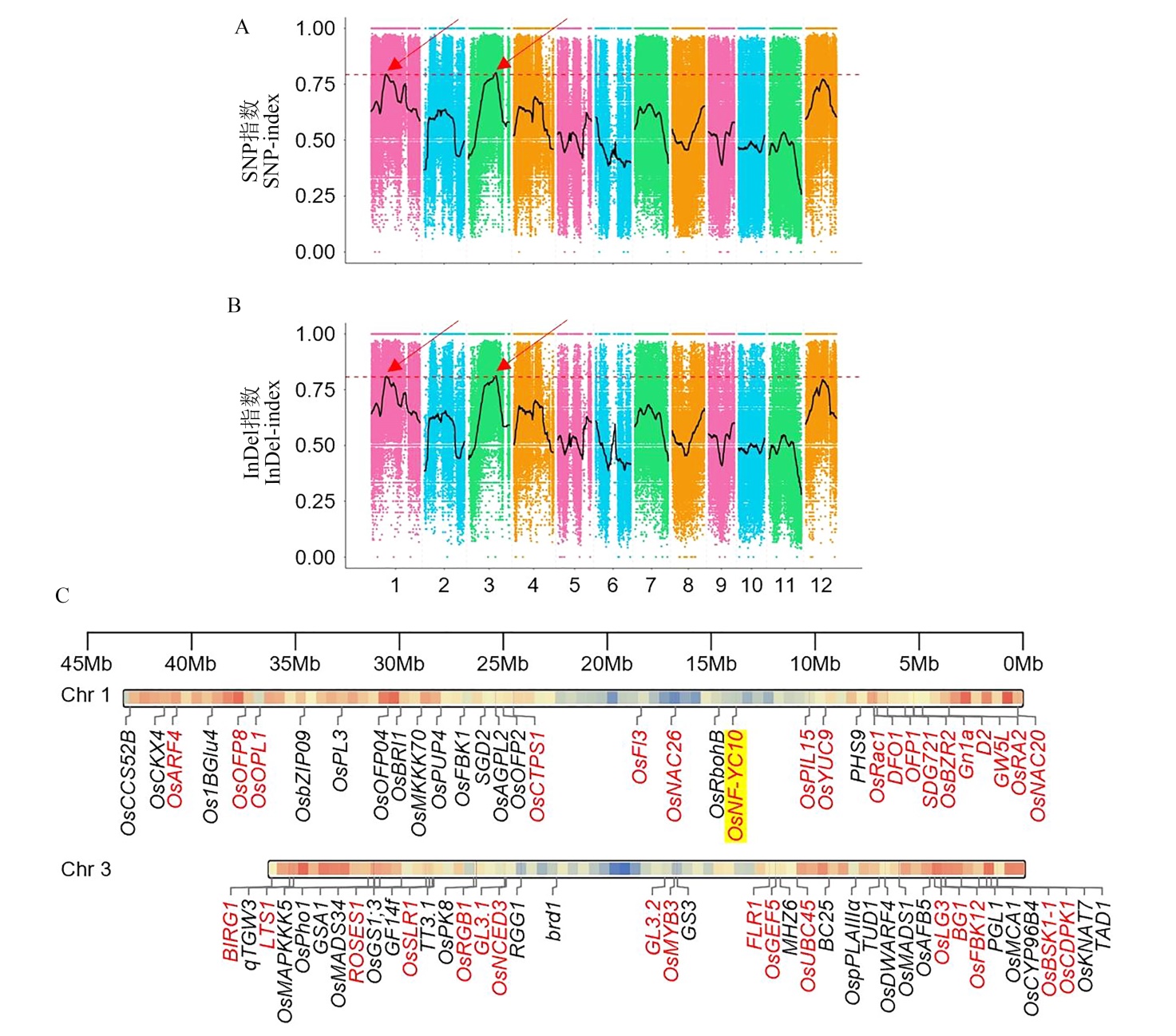
Fig. 3. QTL-seq for rice grain QTL mapping and candidate gene identification The SNP-index plot (A) and InDel-index plot (B) revealed by QTL-seq, the red arrows indicate the candidate regions of grain QTLs. (C) The reported grain shape genes located on chromosomes 1 and 3. Genes highlighted in red indicated coding sequence(CDS) variation between DR610 and HG7. The gene (OsNF-YC10) marked with yellow background coincided with the QTL regions on panels A and B.
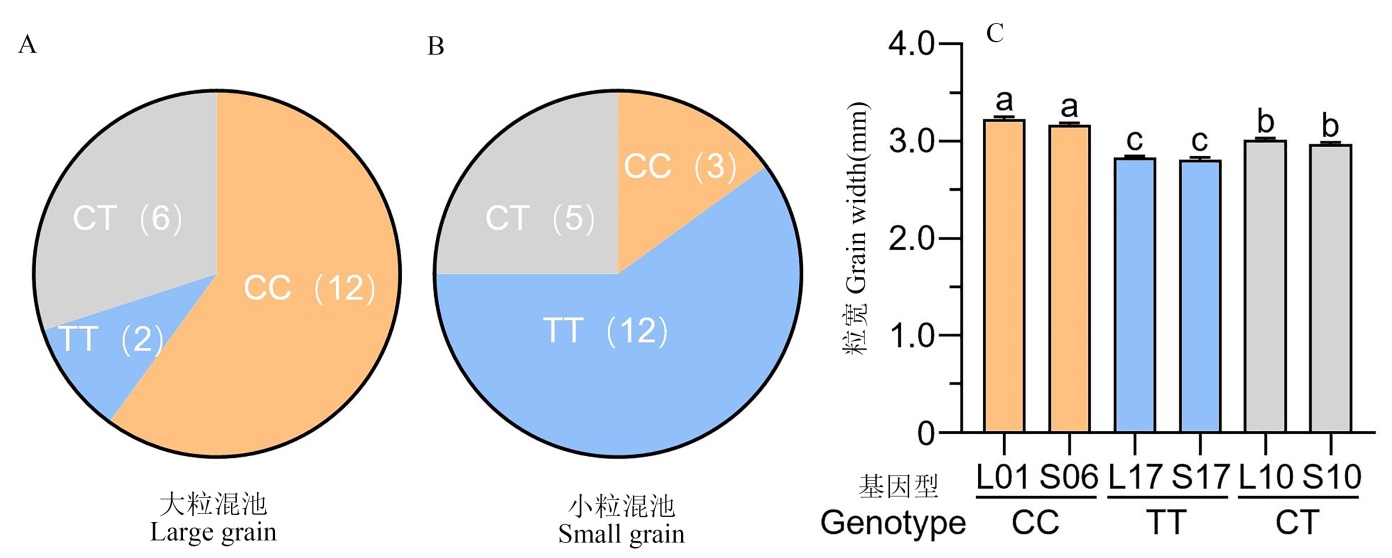
Fig. 4. Number of plants with different OsNF-YC10 genotypes (based on the 13789514 SNP) having extreme large (A) and extreme small grains (B) in the DR610×HG7 F2 population, and grain width of F2 plants with different OsNF-YC10 genotypes (C)
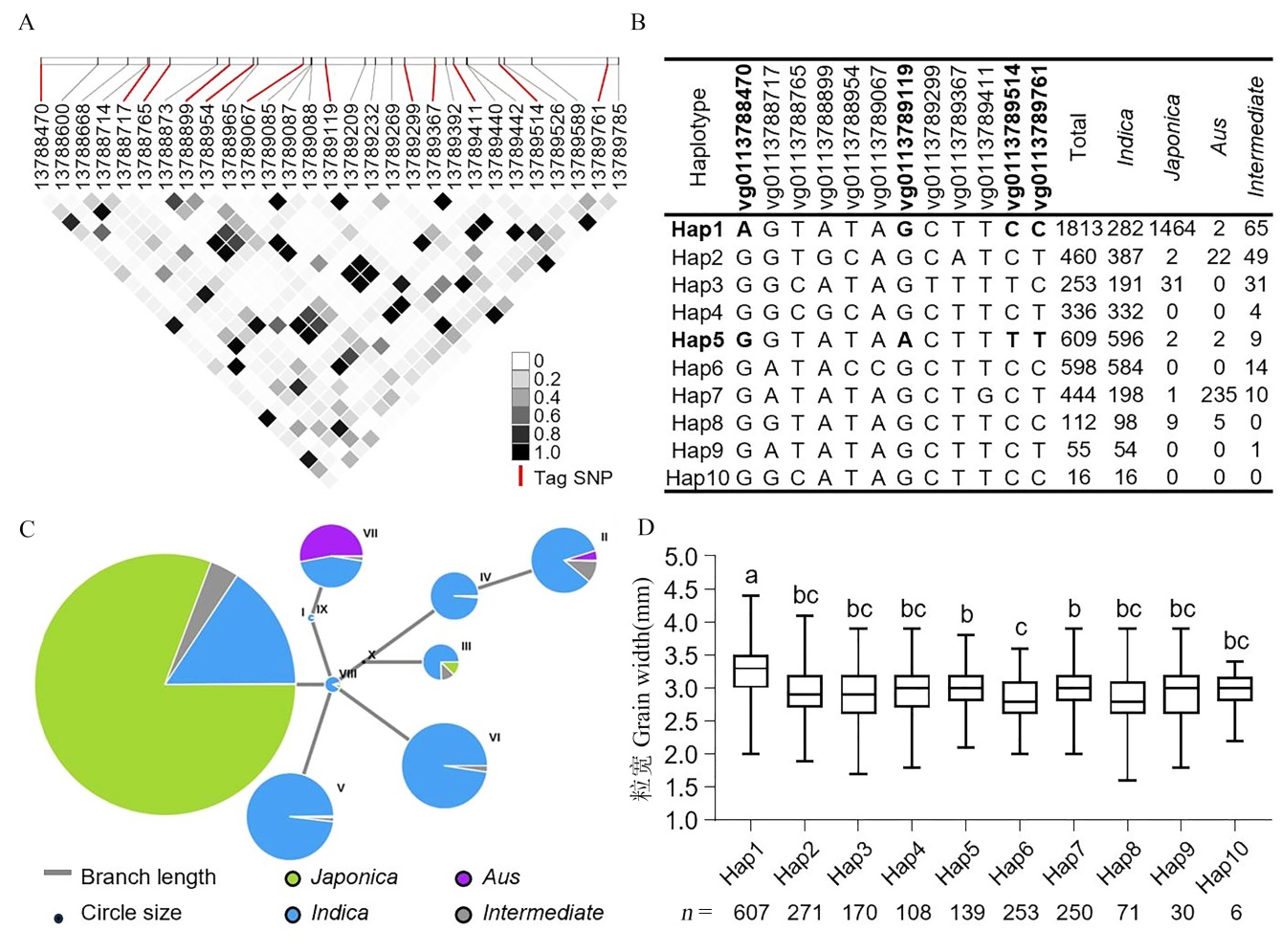
Fig. 5. Haplotype analysis of OsNF-YC10 in rice germplasm collections A, Pairwise r2 values (a measure of linkage disequilibrium) among all polymorphic sites in OsNF-YC10 coding sequence (CDS). The darkness of the color of each box corresponds to the r2 value, as shown in the legend. B, Haplotypes (Hap) of the OsNF-YC10 CDS region among 4726 rice accessions. C, Haplotype network analysis of OsNF-YC10. D, Grain width comparison of different OsNF-YC10 haplotypes from about 2000 rice germplasm accessions. Different letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05(analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test).
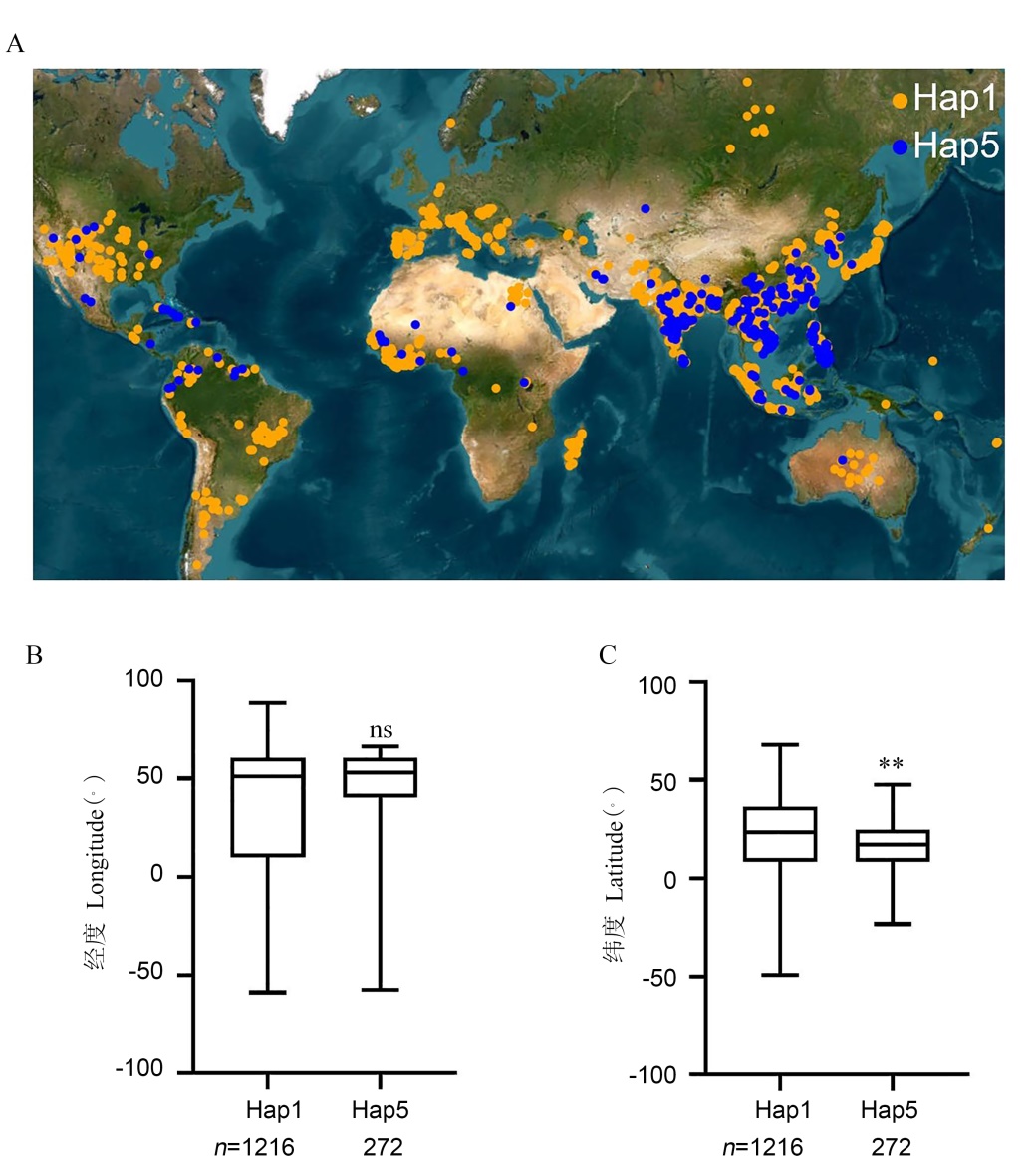
Fig. 6. Global distribution of rice accessions of two major OsNF-YC10 haplotypes A, Geographical distribution of rice accessions with different OsNF-YC10 haplotypes. B and C, Box plot showing the distribution of rice accessions according to longitude (B) and latitude (C), respectively. ** indicates significant differences at P < 0.01(by Mann-Whitney U test).
| [1] | Xing Y Z, Zhang Q. Genetic and molecular bases of rice yield[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2010, 61(1): 421-442. |
| [2] | Yang W F, Zhan P L, Lin S J, Gou Y J, Zhang G Q, Wang S K. Research progress of grain shape genetics in rice[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2019, 40(5): 203-210. |
| [3] | Li G M, Tang J Y, Zheng J K, Chu C C. Exploration of rice yield potential: Decoding agronomic and physiological traits[J]. The Crop Journal, 2021, 9(3): 577-589. |
| [4] | 李堂, 曹华盛, 熊亮, 王福军, 李曙光, 顾海永, 罗文永, 何高, 梁世胡. 水稻粒型调控基因功能研究进展[J]. 广东农业科学, 2023, 50(12): 12-28. |
| Li T, Cao H S, Xiong L, Wang F J, Li S G, Gu H Y, Luo W Y, He G, Liang S H. Research progress on the function of rice grain type genes[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 50(12): 12-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | Zuo J R, Li J Y. Molecular genetic dissection of quantitative trait loci regulating rice grain size[J]. Annual Review of Genetics, 2014, 48: 99-118. |
| [6] | Li N, Xu R, Li Y H. Molecular networks of seed size control in plants[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2019, 70: 435-463. |
| [7] | Ren D Y, Ding C Q, Qian Q. Molecular bases of rice grain size and quality for optimized productivity[J]. Science Bulletin, 2023, 68(3): 314-350. |
| [8] | Jia S Z, Xiong Y F, Xiao P P, Wang X, Yao J L. OsNF-YC10, a seed preferentially expressed gene regulates grain width by affecting cell proliferation in rice[J]. Plant Science, 2019, 280: 219-227. |
| [9] | Si L Z, Chen J Y, Huang X H, Gong H, Luo J H, Hou Q Q, Zhou T Y, Lu T Q, Zhu J J, Shangguan Y Y, Chen E W, Gong C X, Zhao Q, Jing Y F, Zhao Y, Li Y, Cui L L, Fan D L, Lu Y Q, Weng Q J, Wang Y C, Zhan Q L, Liu K Y, Wei X H, An K, An G, Han B. OsSPL13 controls grain size in cultivated rice[J]. Nature Genetics, 2016, 48(4): 447-456. |
| [10] | Yuan H, Qin P, Hu L, Zhan S J, Wang S F, Gao P, Li J, Jin M Y, Xu Z Y, Gao Q, Du A P, Tu B, Chen W L, Ma B T, Wang Y P, Li S G. OsSPL18 controls grain weight and grain number in rice[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2019, 46(1): 41-51. |
| [11] | Huang J P, Chen Z M, Lin J J, Chen J W, Wei M H, Liu L, Yu F, Zhang Z S, Chen F Y, Jiang L R, Zheng J S, Wang T S, Chen H Y, Xie W Y, Huang S H, Wang H C, Huang Y M, Huang R Y. Natural variation of the BRD2 allele affects plant height and grain size in rice[J]. Planta, 2022, 256(2): 27. |
| [12] | Yan Y, Wei M X, Li Y, Tao H, Wu H Y, Chen Z F, Li C, Xu J H. MiR529a controls plant height, tiller number, panicle architecture and grain size by regulating SPL target genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Science, 2021, 302: 110728. |
| [13] | Li R S, Li Z, Ye J, Yang Y Y, Ye J H, Xu S L, Liu J R, Yuan X P, Wang Y P, Zhang M C, Yu H Y, Xu Q, Wang S, Yang Y L, Wang S, Wei X H, Feng Y. Identification of SMG3, a QTL coordinately controls grain size, grain number per panicle, and grain weight in rice[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 880919. |
| [14] | Takagi H, Abe A, Yoshida K, Kosugi S, Natsume S, Mitsuoka C, Uemura A, Utsushi H, Tamiru M, Takuno S, Innan H, Cano L M, Kamoun S, Terauchi R. QTL-seq: Rapid mapping of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole genome resequencing of DNA from two bulked populations[J]. The Plant Journal, 2013, 74(1): 174-183. |
| [15] | Bommisetty R, Chakravartty N, Bodanapu R, Naik J B, Panda S K, Lekkala S P, Lalam K, Thomas G, Mallikarjuna S J, Eswar G R, Kadambari G M, Bollineni S N, Issa K, Akkareddy S, Srilakshmi C, Hariprasadreddy K, Rameshbabu P, Sudhakar P, Gupta S, Lachagari V B R, Vemireddy L R. Discovery of genomic regions and candidate genes for grain weight employing next generation sequencing based QTL-seq approach in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2020, 47(11): 8615-8627. |
| [16] | Bommisetty R, Chakravartty N, Hariprasad K R, Rameshbabu P, Sudhakar P, Bodanapu R, Naik J B, Bhaskar Reddy B V, Lekkala S P, Gupta S, Tanti B, Lachagari V B R, Vemireddy L R. Identification of a novel QTL for grain number per panicle employing NGS-based QTL-seq approach in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Biotechnology Reports, 2023, 17(2): 191-201. |
| [17] | 王豪, 张健, 王加峰, 杨瑰丽, 郭涛, 陈志强, 王慧. 基于QTL-seq的水稻粒质量QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 华北农学报, 2020, 35(2): 18-28. |
| Wang H, Zhang J, Wang J F, Yang G L, Guo T, Chen Z Q, Wang H. QTL Mapping and candidate gene analysis of rice grain weight based on QTL-seq. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2020, 35(2): 18-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | Sun H Z, Yuan Z K, Li F H, Zhang Q Q, Peng T, Li J Z, Du Y X. Mapping of qChalk1 controlling grain chalkiness in japonica rice[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2023, 50(7): 5879-5887. |
| [19] | Yuan H, Xu Z Y, Tan X Q, Gao P, Jin M Y, Song W C, Wang S G, Kang Y H, Liu P X, Tu B, Wang Y P, Qin P, Li S G, Ma B T, Chen W L. A natural allele of TAW1 contributes to high grain number and grain yield in rice[J]. The Crop Journal, 2021, 9(5): 1060-1069. |
| [20] | Alexandrov N, Tai S, Wang W, Mansueto L, Palis K, Fuentes R R, Ulat V J, Chebotarov D, Zhang G, Li Z, Mauleon R, Hamilton R S, McNally K L. SNP-Seek database of SNPs derived from 3000 rice genomes[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, 43(D1): D1023-D1027. |
| [21] | Zhao H, Yao W, Ouyang Y D, Yang W N, Wang G W, Lian X M, Xing Y Z, Chen L L, Xie W B. RiceVarMap: A comprehensive database of rice genomic variations[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, 43(D1): D1018-D1022. |
| [22] | Chen S, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Gu J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor[J]. Bioinformatics, 2018, 34(17): i884-i890. |
| [23] | Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform[J]. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(14): 1754-1760. |
| [24] | Danecek P, Bonfield J K, Liddle J, Marshall J, Ohan V, Pollard M O, Whitwham A, Keane T, McCarthy S A, Davies R M, Li H. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools[J]. GigaScience, 2021, 10(2): giab008. |
| [25] | McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly M, DePristo M A. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data[J]. Genome Research, 2010, 20(9): 1297-1303. |
| [26] | Abe A, Kosugi S, Yoshida K, Natsume S, Takagi H, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Yoshida K, Mitsuoka C, Tamiru M, Innan H, Cano L, Kamoun S, Terauchi R. Genome sequencing reveals agronomically important loci in rice using MutMap[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2012, 30(2): 174-178. |
| [27] | Altschul S F, Madden T L, Schäffer A A, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman D J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1997, 25(17): 3389-3402. |
| [28] | Medrano R F V, de Oliveira C A. Guidelines for the Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR technique development[J]. Molecular Biotechnology, 2014, 56(7): 599-608. |
| [29] | Zhang K, Calabrese P, Nordborg M, Sun F Z. Haplotype block structure and its applications to association studies: power and study designs[J]. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 2002, 71(6): 1386-1394. |
| [1] | DU Yanxiu, SUN Wenyu, YUAN Zeke, ZHANG Qianqian, LI Fuhao, LI Junzhou, SUN Hongzheng. Mapping of qChalk8 Controlling Chalky Rice Rate in japonica Rice by Combining QTL-Seq with Molecular Markers [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(6): 665-671. |
| [2] | HE Yong, LIU Yaowei, XIONG Xiang, ZHU Danchen, WANG Aiqun, MA Lana, WANG Tingbao, ZHANG Jian, LI Jianxiong, TIAN Zhihong. Creation of Rice Grain Size Mutants by Editing OsOFP30 via CRISPR/Cas9 System [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(5): 507-515. |
| [3] | WEI Minyi, MA Zengfeng, HUANG Dahui, QIN Yuanyuan, LIU Chi, LU Yingping, LUO Tongping, LI Zhenjing, ZHANG Yuexiong, QIN Gang. QTL-Seq Analysis for Identification of Resistance Locus to Bacterial Leaf Streak in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(2): 133-141. |
| [4] | Haoliang YAN, Song WANG, Xueyan WANG, Chengcheng DANG, Meng ZHOU, Rongrong HAO, Xiaohai TIAN. Performance of Different Rice Varieties Under High Temperature and Its Relationship with Field Meteorological Factors [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(6): 617-628. |
| [5] | Ke GONG, Pao XUE, Xiaoxia WEN, Feifei LIAO, Bin SUN, Zequn PENG, Shihua CHENG, Liyong CAO, Yingxin ZHANG, Weixun WU, Lianping SUN, Xiaodeng ZHAN. Distribution of Grain Shape Related Genes in Rice Big Grain Germplasm BG1 and Elite Restorer Line Huazhan and Development of Relevant Functional Markers [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(6): 543-553. |
| [6] | Yujun ZHU, Ziwei ZUO, Zhenhua ZHANG, Yeyang FAN. A New Approach for Fine-mapping and Map-based Cloning of Minor-Effect QTL in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(4): 407-414. |
| [7] | Xuemei DENG, Peng HU, Yueying WANG, Yi WEN, Yiqing TAN, Hao WU, Kaixiong WU, Junge WANG, Linlin HOU, Lixin ZHU, Li ZHU, Guang CHEN, Dali ZENG, Guangheng ZHANG, Longbiao GUO, Zhenyu GAO, Deyong REN, Qian QIAN, Jiang HU. Identification and Fine Mapping of a Grain Width Mutant gw4 in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2021, 35(3): 259-268. |
| [8] | Yiwei KANG, Yuyu CHEN, Yingxin ZHANG. Research Progress and Breeding Prospects of Grain Size Associated Genes in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(6): 479-490. |
| [9] | Tao CHEN, Xuchao SUN, Shanlei ZHANG, Wenhua LIANG, Lihui ZHOU, Qingyong ZHAO, Shu YAO, Ling ZHAO, Chunfang ZHAO, Zhen ZHU, Yadong ZHANG, Cailin WANG. Development and Verification of Specific Molecular Markers for Pigm Gene Associated with Broad-spectrum Resistance to Rice Blast [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(1): 28-36. |
| [10] | Andong ZHU, Zhichao SUN, Yujun ZHU, Hui ZHANG, Xiaojun NIU, Yeyang FAN, Zhenhua ZHANG, Jieyun ZHUANG. Identification of QTL for Grain Weight and Grain Shape Using Populations Derived from Residual Heterozygous Lines of indica Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(2): 144-151. |
| [11] | Xue-qin YANG, Ting-ting CHEN, Xia ZHAO, Cai-xia ZHANG, Yong-jie YANG, Guan-fu FU, Long-xing TAO. Mechanism Behind the Effects of GA3 and PP333 on Grain Yield Formation of Super Rice Yongyou 12 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(1): 53-61. |
| [12] | Lin-lin WANG, Yu-yu CHEN, Liang GUO, Hong-wei ZHANG, Ye-yang FAN, Jie-yun ZHUANG. Dissection of Quantitative Trait Loci for Grain Weight and Its Component Traits in the qTGW1.2 Region on Chromosome 1 of Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2015, 29(3): 232-240. |
| [13] | WU Jia-sheng ,ZHOU Hong-kai ,CHEN Guo-bo ,LIU Gui-fu. Mapping and Dissection of QTLs for Grain Weight per Panicle and 1000-Grain Weight in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2008, 22(2): 143-147 . |
| [14] | Zhong Xuhua,Li Taigui. The Correlation between Amylose Content and Grain Weight under Different Ripening Temperature [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 1994, 8(2): 126-128 . |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||