
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 55-66.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.231112
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
HU Fengyue, WANG Jian, WANG Chun, WANG Kejian*( ), LIU Chaolei*(
), LIU Chaolei*( )
)
Received:2023-11-15
Revised:2023-12-12
Online:2025-01-10
Published:2025-01-14
Contact:
WANG Kejian, LIU Chaolei
通讯作者:
王克剑,刘朝雷
基金资助:HU Fengyue, WANG Jian, WANG Chun, WANG Kejian, LIU Chaolei. Generation of Rice DMP1, DMP2 and DMP3 Mutants and Identification of Their Haploid Induction Ability[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(1): 55-66.
胡风越, 王健, 王春, 王克剑, 刘朝雷. 水稻DMP1、DMP2、DMP3基因突变体的创制及其单倍体诱导能力鉴定[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(1): 55-66.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.231112
| 重命名Rename | 基因登录号Accession number | 描述 Description | 长度Length/aa | 相似性Identity | E值 E value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsDMP1 | LOC_Os05g48840 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 239 | 137 | 3e−33 |
| OsDMP2 | LOC_Os08g01530 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 225 | 132 | 1e−31 |
| OsDMP3 | LOC_Os01g29240 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 226 | 120 | 4e−28 |
| OsDMP4 | LOC_Os07g22510 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 263 | 119 | 9e−28 |
| OsDMP5 | LOC_Os03g25440 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 194 | 112 | 2e−25 |
| OsDMP6 | LOC_Os06g24490 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 254 | 110 | 5e−25 |
| OsDMP7 | LOC_Os01g65992 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 domain containing protein | 240 | 107 | 4e−24 |
| OsDMP8 | LOC_Os01g27100 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 domain containing protein | 319 | 107 | 7e−24 |
| OsDMP9 | LOC_Os01g29330 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 241 | 100 | 8e−22 |
| OsDMP10 | LOC_Os01g29280 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 265 | 96.3 | 1e−20 |
| OsDMP11 | LOC_Os07g45080 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 189 | 90.9 | 5e−19 |
| OsDMP12 | LOC_Os01g27120 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 domain containing protein | 226 | 83.2 | 9e−17 |
| OsDMP13 | LOC_Os12g23310 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 domain containing protein | 111 | 53.1 | 1e−7 |
Table 1. The DMP homologous genes in rice
| 重命名Rename | 基因登录号Accession number | 描述 Description | 长度Length/aa | 相似性Identity | E值 E value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsDMP1 | LOC_Os05g48840 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 239 | 137 | 3e−33 |
| OsDMP2 | LOC_Os08g01530 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 225 | 132 | 1e−31 |
| OsDMP3 | LOC_Os01g29240 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 226 | 120 | 4e−28 |
| OsDMP4 | LOC_Os07g22510 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 263 | 119 | 9e−28 |
| OsDMP5 | LOC_Os03g25440 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 194 | 112 | 2e−25 |
| OsDMP6 | LOC_Os06g24490 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 254 | 110 | 5e−25 |
| OsDMP7 | LOC_Os01g65992 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 domain containing protein | 240 | 107 | 4e−24 |
| OsDMP8 | LOC_Os01g27100 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 domain containing protein | 319 | 107 | 7e−24 |
| OsDMP9 | LOC_Os01g29330 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 241 | 100 | 8e−22 |
| OsDMP10 | LOC_Os01g29280 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 265 | 96.3 | 1e−20 |
| OsDMP11 | LOC_Os07g45080 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 family protein | 189 | 90.9 | 5e−19 |
| OsDMP12 | LOC_Os01g27120 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 domain containing protein | 226 | 83.2 | 9e−17 |
| OsDMP13 | LOC_Os12g23310 | Protein of unknown function DUF679 domain containing protein | 111 | 53.1 | 1e−7 |
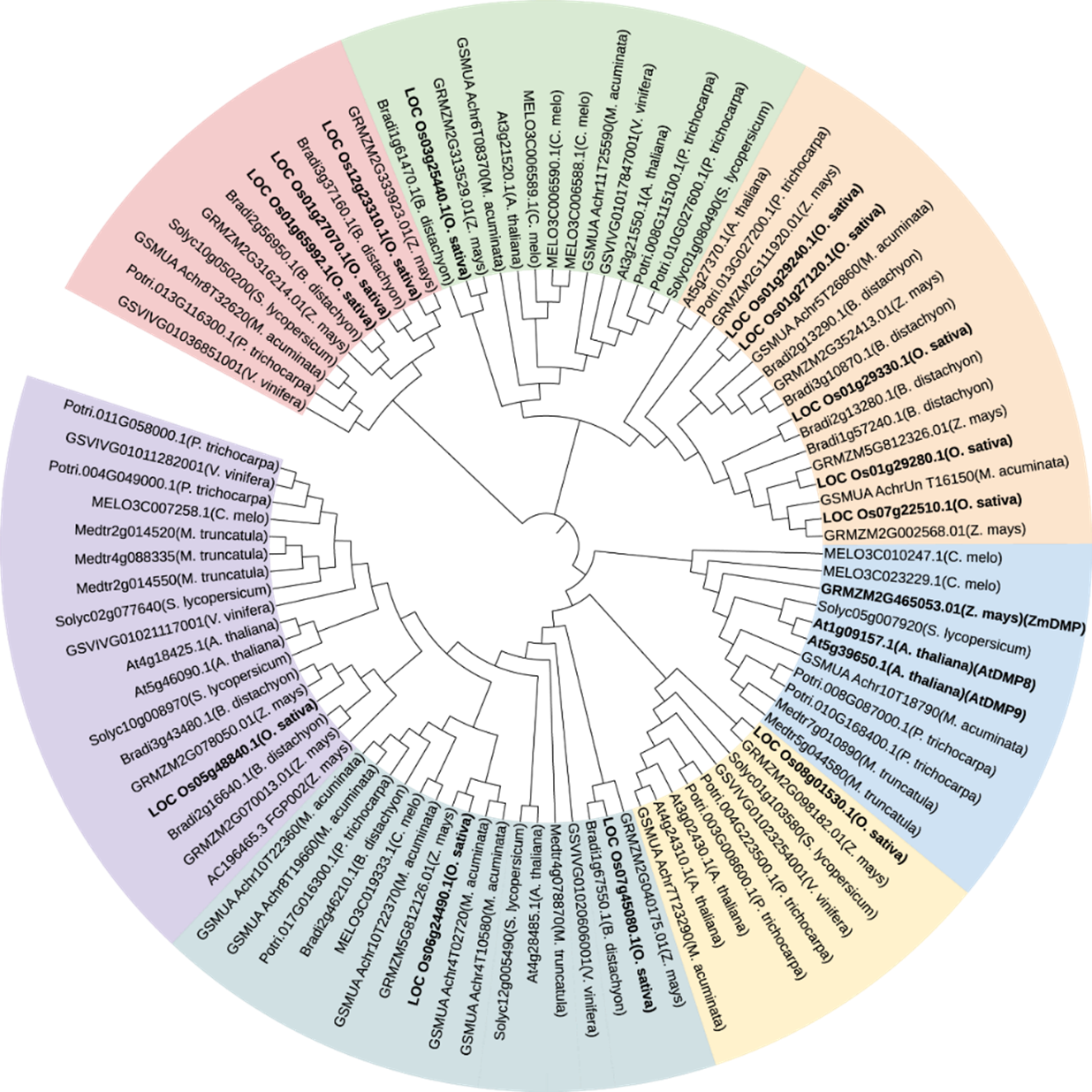
Fig. 1. Phylogenetic analysis of DMP proteins in various species A. thaliana, Arabidopsis thaliana; B. distachyon, Brachypodium distachyon; C. melo, Cucumis melo; M. acuminate, Musa acuminata; M. truncatula, Medicago truncatul; P. trichocarpa, Populus trichocarpa; S. lycopersicum, Solanum lycopersicum; V. vinifera, Vitis vinifera; Z. mays, Zea mays. The maximum likelihood method in MEGA7 software was adopted. Bootstrap = 1000. ZmDMP, AtDMP8, AtDMP and rice DMP homologous proteins are shown in bold.
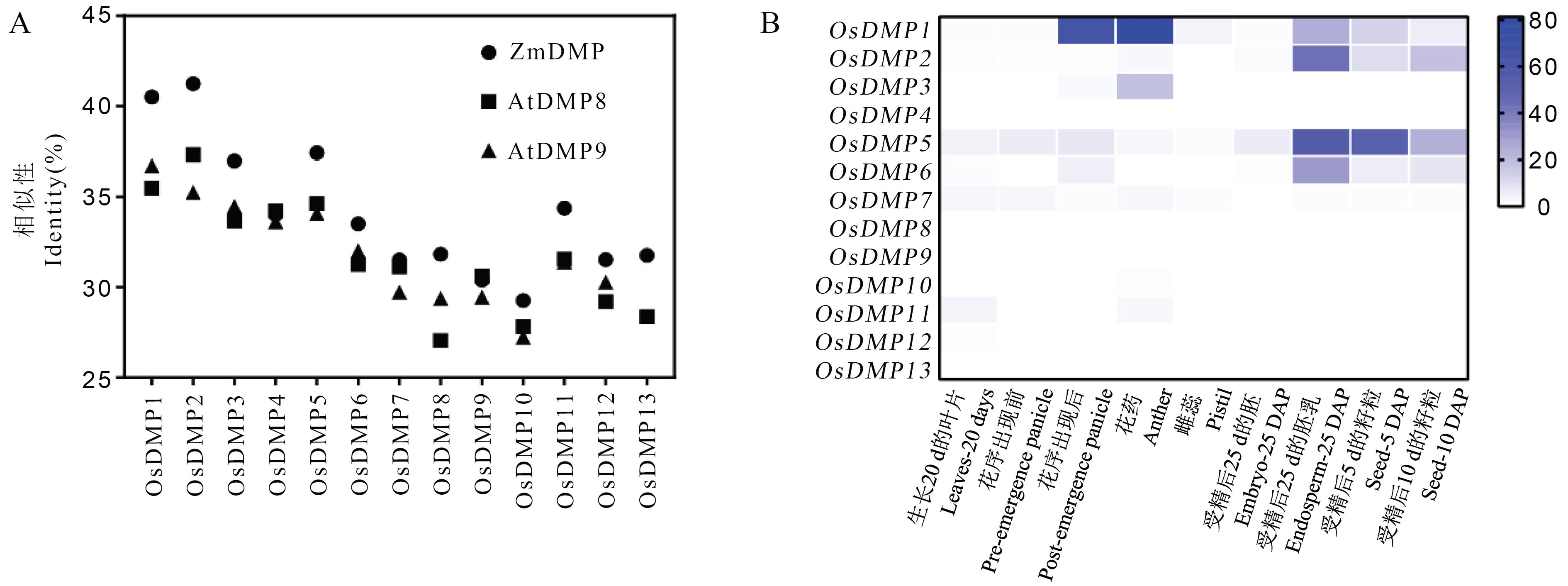
Fig. 2. Candidate genes of rice DMP family by homologous comparison and expression profile analysis A, Similarity analysis of OsDMP family proteins with ZmDMP, AtDMP8 and AtDMP9 proteins; B, Online expression analysis of OsDMP family genes.
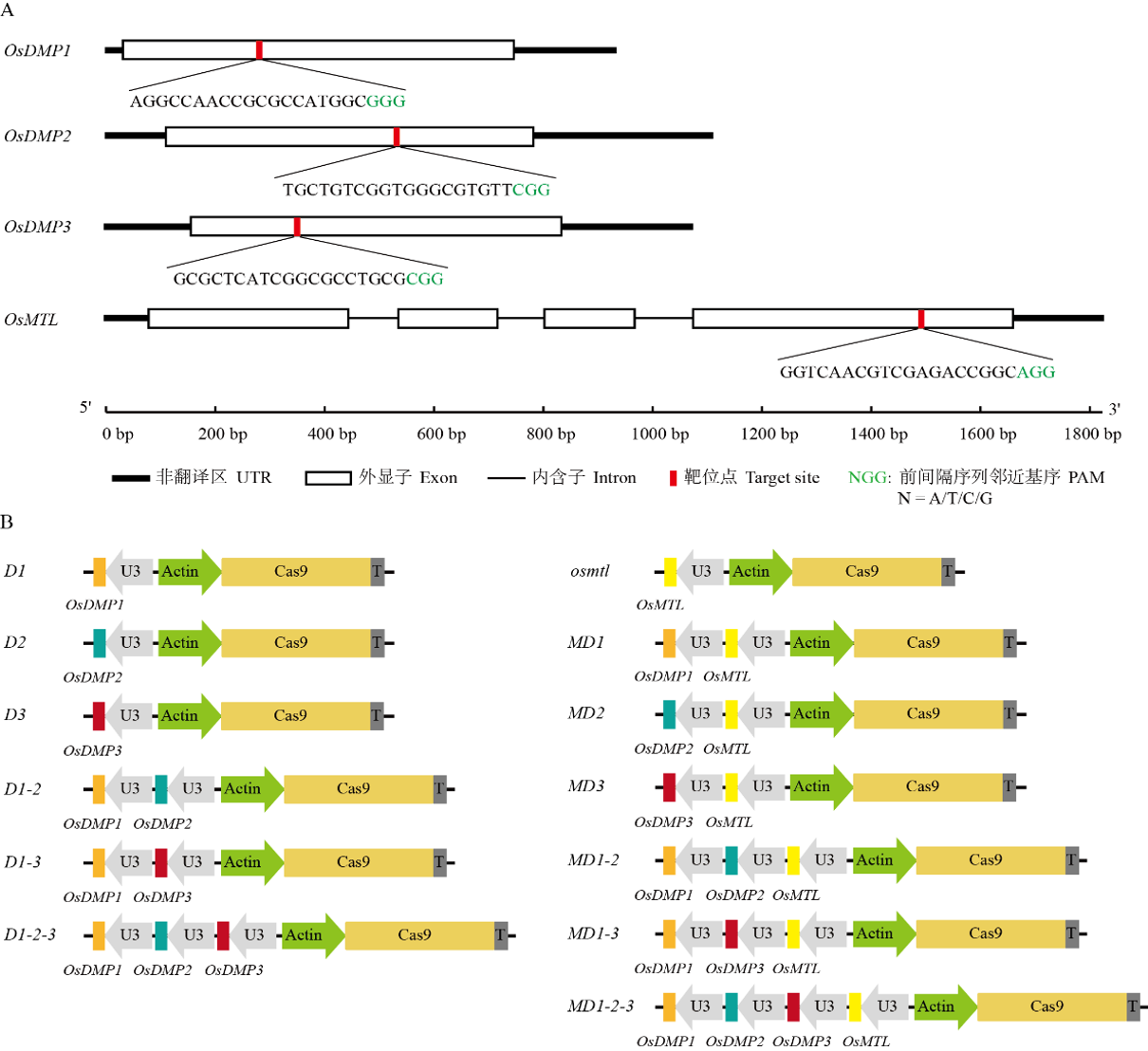
Fig. 3. Structure schematic diagram of CRISPR/Cas9 multi-gene knockout vectors for OsDMP1, OsDMP2, OsDMP3 and OsMTL genes The promoter of the target gene gRNA is U3, and the promoter of Cas9 protein is Actin.
| 编号 Code | 转化株数 No. of transgenic lines | 突变株数 No. of mutant lines | 突变株占比 (突变株数/转化株数) Proportion of mutant lines (No. of mutant lines / No. of transgenic lines) (%) | 双等位突变株数 No. of biallelic mutant lines | 双等位突变株占比 (双等位突变株数/转化株数) Proportion of biallelic mutant plants (No. of biallelic mutant lines/No. of transgenic lines) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 24 | 21 | 87.5 | 18 | 75.0 |
| D2 | 21 | 17 | 81.0 | 14 | 66.7 |
| D3 | 39 | 38 | 97.4 | 36 | 92.3 |
| D1-2 | 24 | 24 | 100.0 | 19 | 79.2 |
| D1-3 | 24 | 23 | 95.8 | 11 | 45.8 |
| D1-2-3 | 37 | 35 | 94.6 | 24 | 64.9 |
| osmtl | 22 | 15 | 68.2 | 12 | 54.5 |
| MD1 | 23 | 21 | 91.3 | 15 | 65.2 |
| MD2 | 21 | 13 | 61.9 | 12 | 57.1 |
| MD3 | 24 | 19 | 79.2 | 12 | 50.0 |
| MD1-2 | 24 | 15 | 62.5 | 9 | 37.5 |
| MD1-3 | 24 | 19 | 79.2 | 14 | 58.3 |
| MD1-2-3 | 40 | 33 | 82.5 | 14 | 35.0 |
Table 2. Proportion of mutations in T0 transgenic plants
| 编号 Code | 转化株数 No. of transgenic lines | 突变株数 No. of mutant lines | 突变株占比 (突变株数/转化株数) Proportion of mutant lines (No. of mutant lines / No. of transgenic lines) (%) | 双等位突变株数 No. of biallelic mutant lines | 双等位突变株占比 (双等位突变株数/转化株数) Proportion of biallelic mutant plants (No. of biallelic mutant lines/No. of transgenic lines) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 24 | 21 | 87.5 | 18 | 75.0 |
| D2 | 21 | 17 | 81.0 | 14 | 66.7 |
| D3 | 39 | 38 | 97.4 | 36 | 92.3 |
| D1-2 | 24 | 24 | 100.0 | 19 | 79.2 |
| D1-3 | 24 | 23 | 95.8 | 11 | 45.8 |
| D1-2-3 | 37 | 35 | 94.6 | 24 | 64.9 |
| osmtl | 22 | 15 | 68.2 | 12 | 54.5 |
| MD1 | 23 | 21 | 91.3 | 15 | 65.2 |
| MD2 | 21 | 13 | 61.9 | 12 | 57.1 |
| MD3 | 24 | 19 | 79.2 | 12 | 50.0 |
| MD1-2 | 24 | 15 | 62.5 | 9 | 37.5 |
| MD1-3 | 24 | 19 | 79.2 | 14 | 58.3 |
| MD1-2-3 | 40 | 33 | 82.5 | 14 | 35.0 |
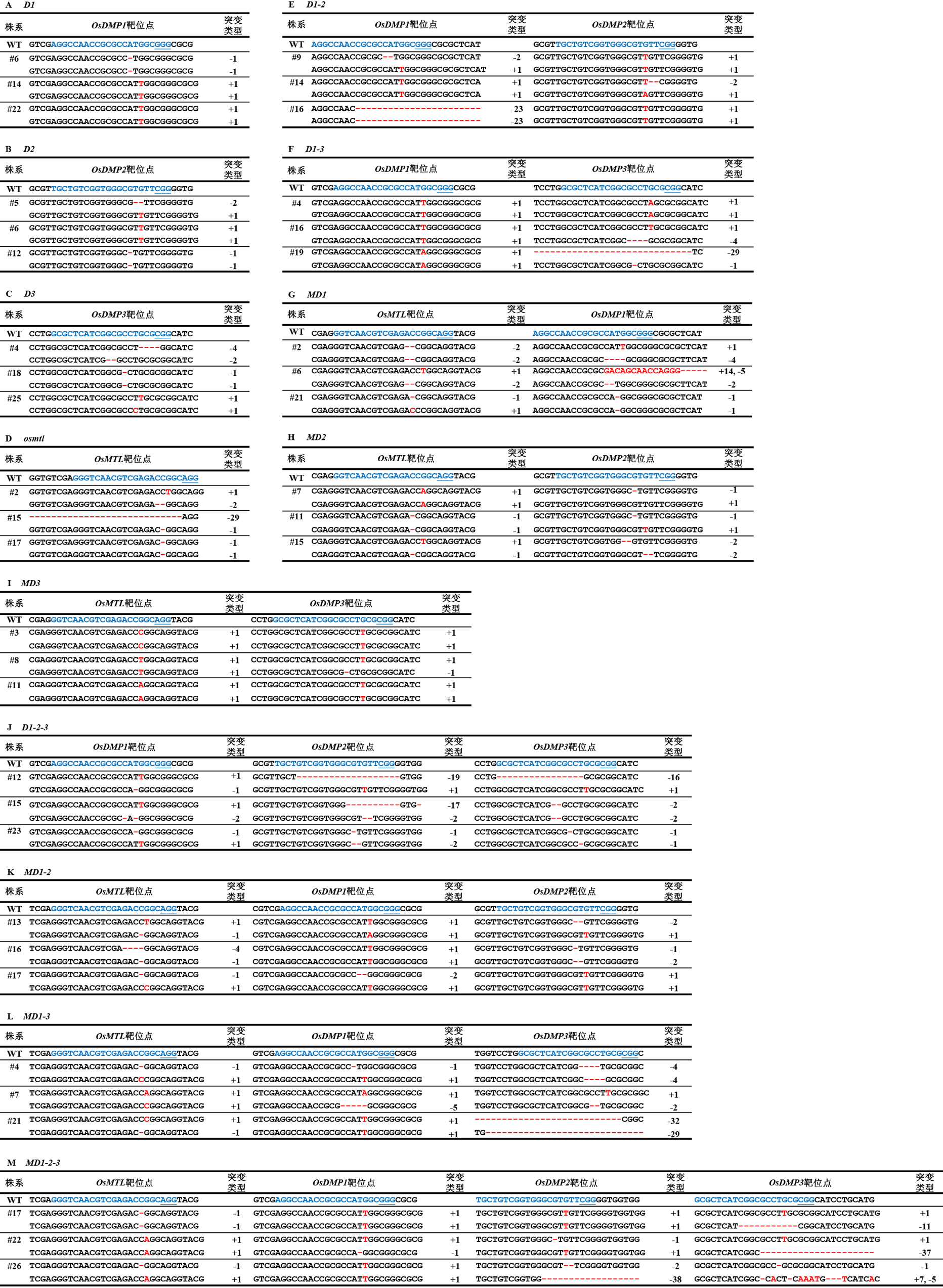
Fig. 4. Mutations of transgenic T0 plants Blue letters indicate the target site sequences; blue underscores indicate the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM); red letters indicate ‘insertion’ mutant bases; and red hyphens indicate ‘deletion’ mutations.
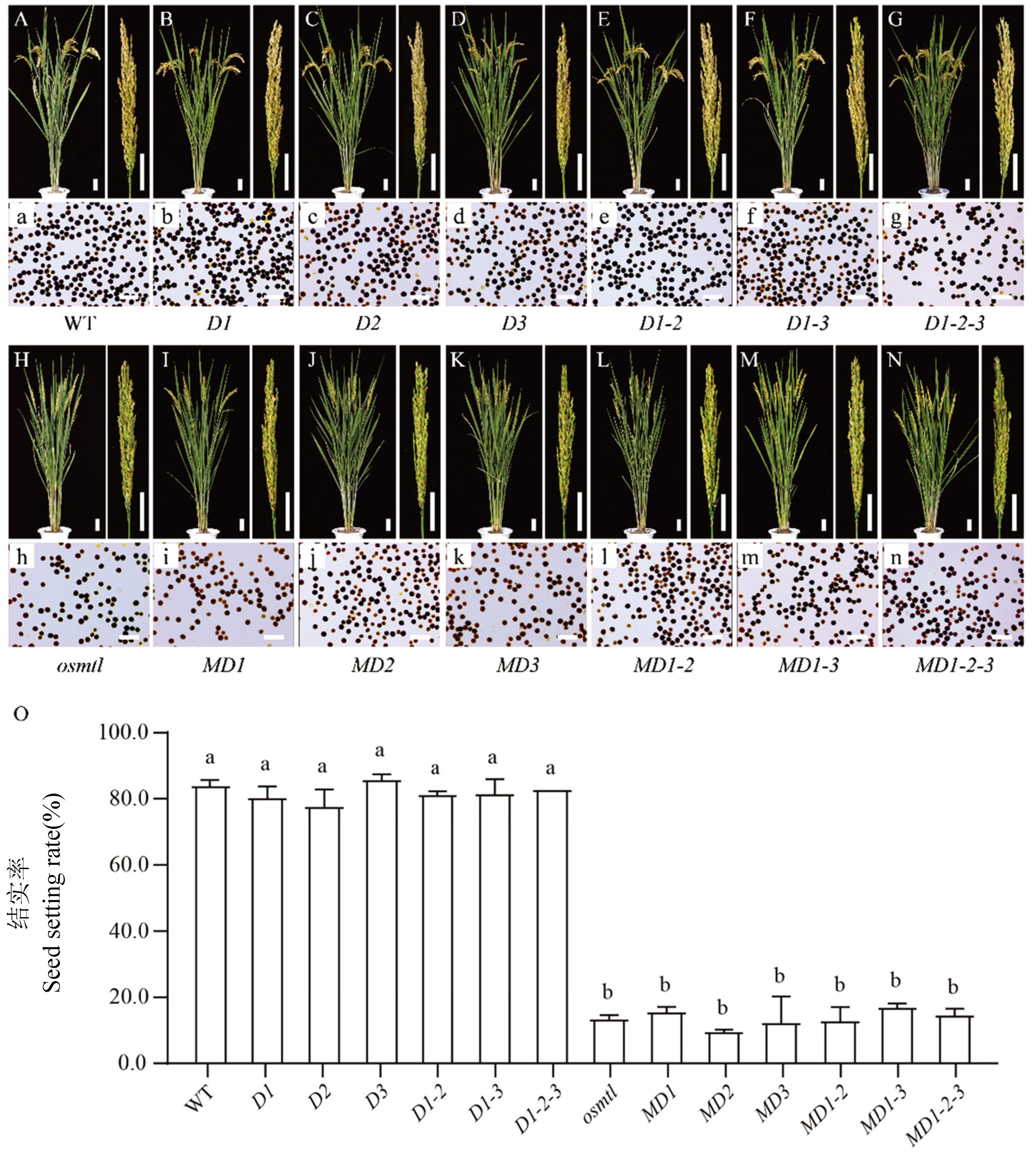
Fig. 5. Morphologic observation, pollen fertility analysis and seed setting rate of wild-type and mutants A-N, The morphology of mature plant and panicle, bar = 5 cm; a-n, Results of pollen iodine staining, bar = 100 μm; O, Comparison and analysis of seed setting rate in wild-type and mutants. Duncan's Multiple Range test was used to analyze the significance of mean difference, and letters a and b indicate significant difference at α = 0.05 level.
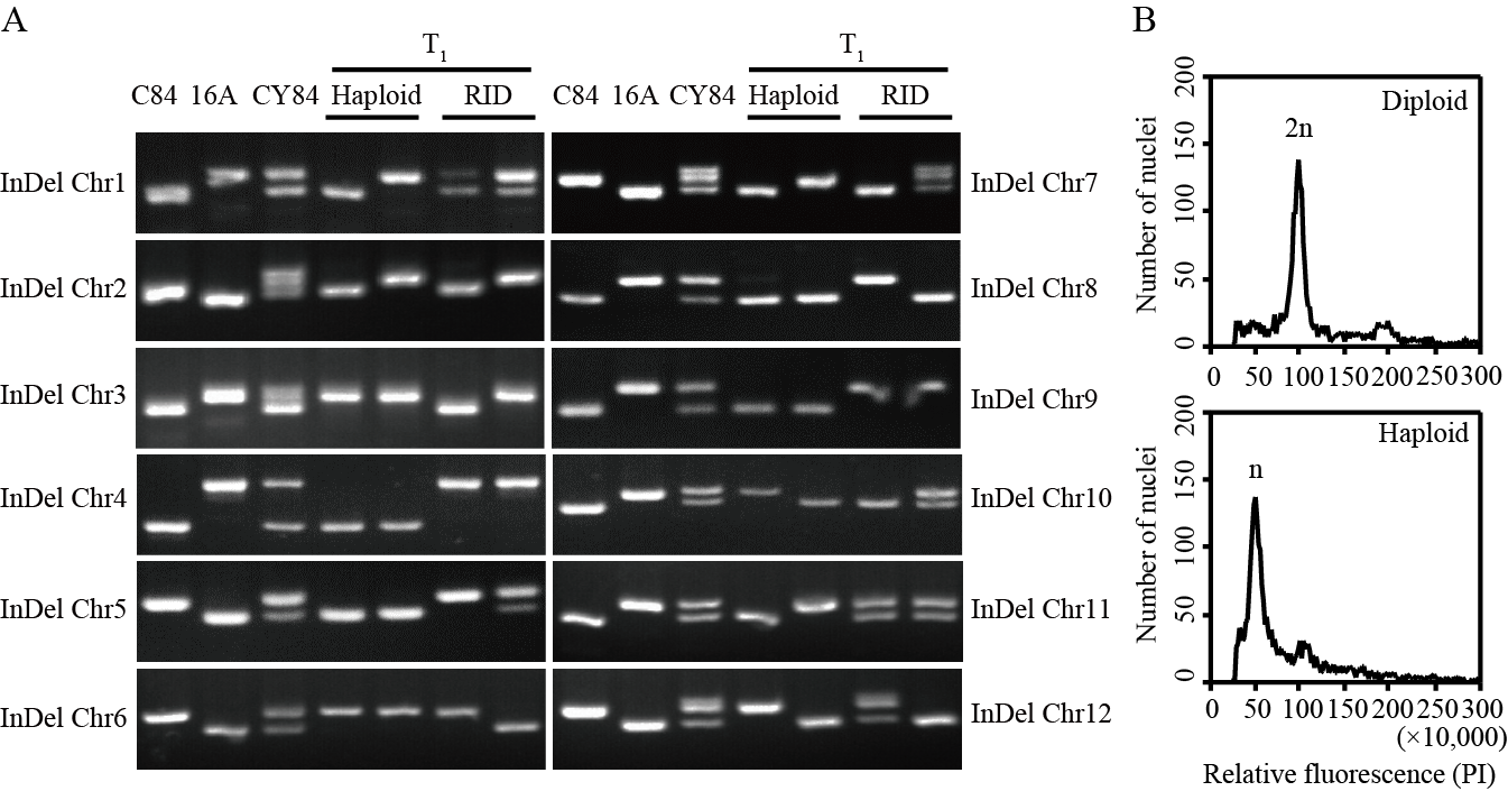
Fig. 6. Ploidy identification with InDel markers and flow cytometry A, Gel electrophoresis band pattern of InDel markers on 12 chromosomes of rice in different materials; chr, Abbreviation of chromosome; C84, Male parent of CY84; 16A, Female parent of CY84; RID, Recombinant inbred diploid. B, Ploidy analysis of diploid and haploid by flow cytometry; PI, Propidium iodide.
| 编号 Number | 基因型 Genotype | 单倍体诱导效率%(单倍体数/检测数) Haploid induction rate % (Haploid/Tested number) | 均值±标准差Mean±SD(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株系1 Line 1 | 株系2 Line 2 | 株系3 Line 3 | |||
| WT | WT | 0.0%(0/92) | 0.0%(0/93) | 0.0%(0/93) | 0.0 |
| D1 | osdmp1 | 0.0%(0/179) | 0.0%(0/186) | 0.0%(0/172) | 0.0 |
| D2 | osdmp2 | 0.0%(0/182) | 0.0%(0/179) | 0.0%(0/186) | 0.0 |
| D3 | osdmp3 | 0.0%(0/186) | 0.0%(0/183) | 0.0%(0/185) | 0.0 |
| D1-2 | osdmp1-osdmp2 | 0.0%(0/978) | 0.0%(0/165) | 0.0%(0/172) | 0.0 |
| D1-3 | osdmp1-osdmp3 | 0.0%(0/1662) | 0.0%(0/176) | 0.0%(0/175) | 0.0 |
| D1-2-3 | osdmp1-osdmp2-osdmp3 | 0.0%(0/1393) | 0.0%(0/181) | 0.0%(0/169) | 0.0 |
| osmtl | osmtl | 1.1%(1/93) | 1.3%(1/78) | 2.2%(2/93) | 1.5±0.5 |
| MD1 | osmtl-osdmp1 | 0.0%(0/102) | 0.0%(0/104) | 1.2%(1/86) | 0.4±0.6 ns |
| MD2 | osmtl-osdmp2 | 1.3%(1/77) | 6.5%(4/62) | 0.0%(0/58) | 2.6±2.8 ns |
| MD3 | osmtl-osdmp3 | 2.2%(2/90) | 0.9%(1/107) | 1.2%(1/82) | 1.4±0.6 ns |
| MD1-2 | osmtl-osdmp1-osdmp2 | 3.2%(3/94) | 0.0%(0/84) | 1.4%(1/72) | 1.5±1.3 ns |
| MD1-3 | osmtl-osdmp1-osdmp3 | 5.4%(5/93) | 0.9%(0/108) | 0.0%(0/64) | 2.1±2.4 ns |
| MD1-2-3 | osmtl-osdmp1-osdmp2-osdmp3 | 1.6%(2/129) | 1.9%(2/108) | 3.1%(3/96) | 2.2±0.6 ns |
Table 3. Haploid induction rate of different type mutants
| 编号 Number | 基因型 Genotype | 单倍体诱导效率%(单倍体数/检测数) Haploid induction rate % (Haploid/Tested number) | 均值±标准差Mean±SD(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株系1 Line 1 | 株系2 Line 2 | 株系3 Line 3 | |||
| WT | WT | 0.0%(0/92) | 0.0%(0/93) | 0.0%(0/93) | 0.0 |
| D1 | osdmp1 | 0.0%(0/179) | 0.0%(0/186) | 0.0%(0/172) | 0.0 |
| D2 | osdmp2 | 0.0%(0/182) | 0.0%(0/179) | 0.0%(0/186) | 0.0 |
| D3 | osdmp3 | 0.0%(0/186) | 0.0%(0/183) | 0.0%(0/185) | 0.0 |
| D1-2 | osdmp1-osdmp2 | 0.0%(0/978) | 0.0%(0/165) | 0.0%(0/172) | 0.0 |
| D1-3 | osdmp1-osdmp3 | 0.0%(0/1662) | 0.0%(0/176) | 0.0%(0/175) | 0.0 |
| D1-2-3 | osdmp1-osdmp2-osdmp3 | 0.0%(0/1393) | 0.0%(0/181) | 0.0%(0/169) | 0.0 |
| osmtl | osmtl | 1.1%(1/93) | 1.3%(1/78) | 2.2%(2/93) | 1.5±0.5 |
| MD1 | osmtl-osdmp1 | 0.0%(0/102) | 0.0%(0/104) | 1.2%(1/86) | 0.4±0.6 ns |
| MD2 | osmtl-osdmp2 | 1.3%(1/77) | 6.5%(4/62) | 0.0%(0/58) | 2.6±2.8 ns |
| MD3 | osmtl-osdmp3 | 2.2%(2/90) | 0.9%(1/107) | 1.2%(1/82) | 1.4±0.6 ns |
| MD1-2 | osmtl-osdmp1-osdmp2 | 3.2%(3/94) | 0.0%(0/84) | 1.4%(1/72) | 1.5±1.3 ns |
| MD1-3 | osmtl-osdmp1-osdmp3 | 5.4%(5/93) | 0.9%(0/108) | 0.0%(0/64) | 2.1±2.4 ns |
| MD1-2-3 | osmtl-osdmp1-osdmp2-osdmp3 | 1.6%(2/129) | 1.9%(2/108) | 3.1%(3/96) | 2.2±0.6 ns |
| [1] | 陈海强, 刘会云, 王轲, 张双喜, 叶兴国. 植物单倍体诱导技术发展与创新[J]. 遗传, 2020, 42(5): 466-482. |
| Chen H Q, Liu H Y, Wang K, Zhang S X, Ye X G. Development and innovation of haploid induction technologies in plants[J]. Hereditas (Beijing), 2020, 42(5): 466-482. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | Dunwell J M. Haploids in flowering plants: origins and exploitation[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2010, 8(4): 377-424. |
| [3] | 相志国, 海燕, 康明辉, 赵永英. 单倍体的产生途径及其在作物遗传育种中的应用[J]. 河南农业科学, 2011, 40(11): 17-21. |
| Xiang Z G, Hai Y, Kang M H, Zhao Y Y. Generation ways of haploid and its application in crop genetics and breeding[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 40(11): 17-21. | |
| [4] | Coe E H. A line of maize with high haploid frequency[J]. American Naturalist, 1959, 93(873): 381-382. |
| [5] | Prigge V, Xu X W, Li L, Babu R, Chen S J, Atlin G N, Melchinger A E. New insights into the genetics of in vivo induction of maternal haploids, the backbone of doubled haploid technology in maize[J]. Genetics, 2012, 190(2): 781-793. |
| [6] | Kelliher T, Starr D, Richbourg L, Chintamanani S, Delzer B, Nuccio M L, Green J, Chen Z, McCuiston J, Wang W, Liebler T, Bullock P, Martin B. MATRILINEAL, a sperm-specific phospholipase, triggers maize haploid induction[J]. Nature, 2017, 542(7639): 105-109. |
| [7] | Gilles L M, Khaled A, Laffaire J B, Chaignon S, Gendrot G, Laplaige J, Bergès H, Beydon G, Bayle V, Barret P, Comadran J, Martinant J P, Rogowsky P M, Widiez T. Loss of pollen-specific phospholipase NOT LIKE DAD triggers gynogenesis in maize[J]. The EMBO Journal, 2017, 36(6): 707-717. |
| [8] | Liu C X, Li X, Meng D X, Zhong Y, Chen C, Dong X, Xu X W, Chen B J, Li W, Li L, Tian X L, Zhao H M, Song W B, Luo H S, Zhang Q H, Lai J S, Jin W W, Yan J B, Chen S J. A 4-bp insertion at ZmPLA1 encoding a putative phospholipase a generates haploid induction in maize[J]. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10(3): 520-522. |
| [9] | Yao L, Zhang Y, Liu C, Liu Y, Wang Y, Liang D, Liu J, Sahoo G, Kelliher T. OsMATL mutation induces haploid seed formation in indica rice[J]. Nature Plants, 2018, 4(8): 530-533. |
| [10] | Liu C X, Zhong Y, Oi X L, Chen M, Liu Z K, Chen C, Tian X L, Li I L, Jiao Y Y, Wang D, Wang Y W, Li M R, Xin M M, Liu W X, Jin W W, Chen S J. Extension of the in vivo haploid induction system from diploid maize to hexaploid wheat[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18(2): 316-318. |
| [11] | Cheng Z X, Sun Y, Yang S H, Zhi H, Yin T, Ma X J, Zhang H S, Diao X M, Guo Y, Li X H, Wu C Y, Sui Y. Establishing in planta haploid inducer line by edited SiMTL in foxtail millet (Setaria italica)[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2021, 19(6): 1089-1091. |
| [12] | Zhong Y, Liu C X, Qi X L, Jiao Y Y, Wang D, Wang Y W, Liu Z K, Chen C, Chen B J, Tian X L, Li J L, Chen M, Dong X, Xu X W, Li L, Li W, Liu W X, Jin W W, Lai J S, Chen S J. Mutation of ZmDMP enhances haploid induction in maize[J]. Nature Plants, 2019, 5(6): 575-580. |
| [13] | Zhong Y, Chen B J, Li M R, Wang D, Jiao Y Y, Qi X L, Wang M, Liu Z K, Chen C, Wang Y W, Chen M, Li J L, Xiao Z J, Cheng D H, Liu W X, Boutilier K, Liu C X, Chen S J. A DMP-triggered in vivo maternal haploid induction system in the dicotyledonous Arabidopsis[J]. Nature Plants, 2020, 6(5): 466-472. |
| [14] | Wang N, Xia X Z, Jiang T, Li L L, Zhang P C, Niu L F, Cheng H M, Wang K J, Lin H. In planta haploid induction by genome editing of DMP in the model legume Medicago truncatula[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2022, 20(1): 22-24. |
| [15] | Li Y F, Li D, Xiao Q, Wang H D, Wen J, Tu J X, Shen J X, Fu T D, Yi B. An in planta haploid induction system in Brassica napus[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2022, 64(6): 1140-1144. |
| [16] | Zhong Y, Wang Y W, Chen B J, Liu J C, Wang D, Li M R, Qi X L, Liu C X, Boutilier K, Chen S J. Establishment of a dmp based maternal haploid induction system for polyploid Brassica napus and Nicotiana tabacum[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2022, 64(6): 1281-1294. |
| [17] | Wang C, Shen L, Fu Y P, Yan C J, Wang K J. A simple CRISPR/Cas9 system for multiplex genome editing in rice[J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2015, 42(12): 703-706. |
| [18] | Wang C, Liu Q, Shen Y, Hua Y F, Wang J J, Lin J R, Wu M G, Sun T T, Cheng Z K, Mercier R, Wang K J. Clonal seeds from hybrid rice by simultaneous genome engineering of meiosis and fertilization genes[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(3): 283-286. |
| [19] | Liu Q, Wang C, Jiao X Z, Zhang H W, Song L L, Li Y X, Gao C X, Wang K J. Hi-TOM: A platform for high-throughput tracking of mutations induced by CRISPR/Cas systems[J]. Science China: Life Sciences, 2019, 62(1): 1-7. |
| [20] | Ma X L, Chen L T, Zhu Q L, Chen Y L, Liu Y G. Rapid decoding of sequence-specific nuclease-induced heterozygous and biallelic mutations by direct sequencing of PCR products[J]. Molecular Plant, 2015, 8(8): 1285-1287. |
| [21] | 曹跃炫, 严绘景, 王克剑, 刘朝雷. 苗期快速分选水稻人工无融合生殖克隆种子[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(6): 656-662. |
| Cao Y X, Yan H J, Wang K J, Liu C L. Rapid identification of rice clonal seeds generated by synthetic apomixis at seedling stage[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2022, 36(6): 656-662. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Liu C L, He Z X, Zhang Y, Hu F Y, Li M Q, Liu Q, Huang Y, Wang J, Zhang W, Wang C, Wang K J. Synthetic apomixis enables stable transgenerational transmission of heterotic phenotypes in hybrid rice[J]. Plant Communications, 2023, 4(2): 100470. |
| [23] | Liu C L, Wang J, Lu H W, Huang Y, Yan H J, Liang H, Wang C, Wang K J. Engineering synthetic apomixis in different hybrid rice varieties using the Fix strategy[J]. New Crops, 2024(1): 100003. |
| [24] | Zhao X, Xu X W, Xie H X, Chen S J, Jin W W. Fertilization and uniparental chromosome elimination during crosses with maize haploid inducers[J]. Plant Physiology, 2013, 163(2): 721-731. |
| [25] | Qiu F Z, Liang Y L, Li Y, Liu Y Z, Wang L M, Zheng Y L. Morphological, cellular and molecular evidences of chromosome random elimination in vivo upon haploid induction in maize[J]. Current Plant Biology, 2014(1): 83-90. |
| [26] | Karimi-Ashtiyani R, Ishii T, Niessen M, Stein N, Heckmann S, Gurushidze M, Banaei-Moghaddam A M, Fuchs J, Schubert V, Koch K, Weiss O, Demidov D, Schmidt K, Kumlehn J, Houben A. Point mutation impairs centromeric CENH3 loading and induces haploid plants[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(36): 11211-11216. |
| [27] | Kelliher T, Starr D, Wang W, Mccuiston J, Zhong H, Nuccio M L, Martin B. Maternal haploids are preferentially induced by CENH3-tailswap transgenic complementation in maize[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 414. |
| [28] | Lü J, Yu K, Wei J, Gui H P, Liu C X, Liang D W, Wang Y L, Zhou H J, Carlin R, Rich R, Lu T C, Que Q D, Wang W C, Zhang X P, Kelliher T. Generation of paternal haploids in wheat by genome editing of the centromeric histone CENH3[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(12): 1397-1401. |
| [29] | Jiang C L, Sun J, Li R, Yan S J, Chen W, Guo L, Qin G C, Wang P C, Luo C, Huang W J, Zhang Q H, Fernie A R, Jackson D, Li X, Yan J B. A reactive oxygen species burst causes haploid induction in maize[J]. Molecular Plant, 2022, 15(6): 943-955. |
| [30] | Sarkar K R, Coe E H. A genetic analysis of the origin of maternal haploids in maize[J]. Genetics, 1966, 54(2): 453-464. |
| [31] | Khanday I, Skinner D, Yang B, Mercier R, Sundaresan V. A male-expressed rice embryogenic trigger redirected for asexual propagation through seeds[J]. Nature, 2019, 565(7737): 91-95. |
| [32] | Conner J A, Podio M, Ozias-Akins P. Haploid embryo production in rice and maize induced by PsASGR-BBML transgenes[J]. Plant Reproduction, 2017, 30(1): 41-52. |
| [33] | Wei X, Liu C L, Chen X, Lu H W, Wang J, Yang S L, Wang K J. Synthetic apomixis with normal hybrid rice seed production[J]. Molecular Plant, 2023, 16(3): 489-492. |
| [34] | Underwood C J, Vijverberg K, Rigola D, Okamoto S, Oplaat C, Camp R, Radoeva T, Schauer S E, Fierens J, Jansen K, Mansveld S, Busscher M, Xiong W, Datema E, Nijbroek K, Blom E J, Bicknell R, Catanach A, Erasmuson S, Winefield C, van Tunen A J, Prins M, Schranz M E, van Dijk P J. A PARTHENOGENESIS allele from apomictic dandelion can induce egg cell division without fertilization in lettuce[J]. Nature Genetics, 2022, 54(1): 84-93. |
| [35] | Zhang X C, Shi C, Li S L, Zhang B, Luo P, Peng X B, Zhao P, Dresselhaus T, Sun M X. A female in vivo haploid-induction system via mutagenesis of egg cell-specific peptidases[J]. Molecular Plant, 2023, 16(2): 471-480. |
| [36] | Cyprys P, Lindemeier M, Sprunck S. Gamete fusion is facilitated by two sperm cell-expressed DUF679 membrane proteins[J]. Nature Plants, 2019, 5(3): 253-257. |
| [1] |
WU Jinshui, TANG Jiangying, TAN Li, GUO Zhiqiang, YANG Juan, ZHANG Xinzhen, CHEN Guifang, WANG Jianlong, SHI Wanju.
Mechanisms of Arsenic Uptake and Transport in Rice and Agronomic Mitigation Strategies [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 143-155. |
| [2] |
MA Weiyi, ZHU Jizou, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, DIAO Liuyun, WANG Lulu, MENG Tianyao, GAO Pinglei, CHEN Yinglong, DAI Qigen, WEI Huanhe.
Research Progress in Effects of Salt and Drought Stresses on Rice Quality Formation and Associated Physiological Mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 156-170. |
| [3] |
ZHANG Laitong, YANG Le, LIU Hong, ZHAO Xueming, CHENG Tao, XU Zhenjiang.
Research Advances of Fragrance Substances in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 171-186. |
| [4] |
FENG Tao, ZHANG Zhaoyang, HUANG Xinni, WANG Yue, ZHONG Xuzhi, FENG Zhiming, LIU Xin, ZUO Shimin, OUYANG Shouqiang.
Osa-miR166i-3 Positively Regulates Resistance to Sheath Blight Through Mediating the Accumulation of Reactive Oxygen Species [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 187-196. |
| [5] |
GONG Mengmeng, SONG Shufeng, QIU Mudan, DONG Hao, ZHANG Longhui, LI Lei, LI Bin, CHEN Weijun , LI Yixing, WANG Tiankang, LEI Dongyang, LI Li.
Functional Characterization of Rice Leaf Color Gene OsClpP6 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 197-208. |
| [6] |
YAN Ying, WANG Kai, ZHANG Lixia, HU Zejun, YE Junhua, YANG Hang, GU Chunjun, WU Shujun.
Development of a New High-Quality and Multi-Resistant japonica Rice Variety, Huxianggeng 216, Through Molecular Pyramiding Breeding [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 209-219. |
| [7] |
XU Yuemei, PENG Shiyan, SUN Zhiwei, WANG Zhiqin, ZHU Kuanyu, YANG Jianchang.
Differences in Endogenous Hormone Levels and Their Relationship with Yield and Phosphorus Use Efficiency in Rice Varieties With Various Tolerance to Low Phosphorus Stress [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 231-244. |
| [8] |
TANG Chenghan, WANG Jingqing, CHEN Huizhe, ZHANG Yuping, XIANG Jing, ZHANG Yikai, WANG Zhigang, HUAI Yan, CHEN Jiafeng, WANG Yaliang.
Effects of Hybrid Rice Seedling Quality in Drill-seeding Nursery on Grain Yield in Mechanical Transplanting [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 245-254. |
| [9] |
SHU Ao, XIE Jiaxin, CAO Wei, ZHOU Chuanming, LI Beilei, CHEN Jiaxin, LI Li, CAO Fangbo, CHEN Jiana, HUANG Min.
Effect of Nitrogen Management Strategies on Yield and Grain Quality of High-quality Hybrid Mid-season Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 255-263. |
| [10] |
SHAO Yafang, ZHU Dawei, ZHENG Xin, MOU Renxiang, ZHANG Linping, CHEN Mingxue.
Development Status and Regional Differences of japonica Rice Quality in the Yangtze River Delta Region from 2002 to 2022 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 264-276. |
| [11] | SUI Jingjing, ZHAO Guilong, JIN Xin, BU Qingyun, TANG Jiaqi. Advances in Molecular and Physiological Mechanisms of Cold Tolerance Regulation of Rice at the Booting Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(1): 1-10. |
| [12] | REN Ningning, SUN Yongjian, SHEN Congcong, ZHU Shuangbing, LI Huiju, ZHANG Zhiyuan, CHEN Kai. Research Progress in Rice Mesocotyl [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(1): 11-23. |
| [13] | XIAO Wuwei, ZHU Chenguang, WANG Fei, XIONG Dongliang, HUANG Jianliang, PENG Shaobing, CUI Kehui. Research Progress in Rice Quality of Ratoon Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(1): 33-46. |
| [14] | CHEN Zhihui, TAO Yajun, FAN Fangjun, XU Yang, WANG Fangquan, LI Wenqi, GULINAER·Bahetibieke , JIANG Yanjie, ZHU Jianping, LI Xia, YANG Jie. Development and Application of a Functional Marker for Heading Date Gene Hd6 in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(1): 47-54. |
| [15] | YANG Chuanming, WANG Lizhi, ZHANG Xijuan, YANG Xianli, WANG Yangyang, HOU Benfu, CUI Shize, LI Qingchao, LIU Kai, MA Rui, FENG Yanjiang, LAI Yongcai, LI Hongyu, JIANG Shukun. Analysis of QTL Controlling Cold Tolerance at Seedling Stage by Using a High-Density SNP Linkage Map in japonica Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(1): 82-91. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||