
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 277-286.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240804
• Research Papers • Previous Articles
JIA Yifan, WANG Xinfeng, WANG Yaxuan, LIU Fang, XIAO Jing, WEI Qi, FU Qiang, WAN Pinjun*( )
)
Received:2024-08-06
Revised:2024-09-12
Online:2025-03-10
Published:2025-03-19
Contact:
WAN Pinjun
贾毅帆, 王新峰, 王雅宣, 刘芳, 肖晶, 魏琪, 傅强, 万品俊*( )
)
通讯作者:
万品俊
基金资助:JIA Yifan, WANG Xinfeng, WANG Yaxuan, LIU Fang, XIAO Jing, WEI Qi, FU Qiang, WAN Pinjun. Molecular Characterization and Biological Function of Serine/Arginine-rich Alternative Splicing Factors in Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera:Delphacidae)[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2025, 39(2): 277-286.
贾毅帆, 王新峰, 王雅宣, 刘芳, 肖晶, 魏琪, 傅强, 万品俊. 褐飞虱中富含丝氨酸/精氨酸的可变剪接因子特性和生物学功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2025, 39(2): 277-286.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2025.240804
| 引物名称 Primer | 上游引物序列(5′-3′) Upstream primer sequences (5′-3′) | 下游引物序列(5′-3′) Downstream primer sequences (5′-3′) | Use 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| cNlSRSF1 | AAGACGACGCCTTGCCT | AGCTGTGTGTTGCTCCTTAATT | 克隆 Clone |
| cNlSRSF2.1 | TCCACAACTTCACATAAGTTCG | TTAGGCTTGGTAGCCAGCA | |
| cNlSRSF2.2 | GCATCTGTTTCTTGGCGG | TGAGCAGTATTGGTCGCCT | |
| cNlSRSF7.1 | TCGGTAGTAGCCTAAGCAGTCA | ACGTGGGTATCAAATAATTAACAAA | |
| cNlSRSF7.2 | CATGTAATTTCTGCTGGTGTTG | GACTTTGTTGTGTGATGTGAGG | |
| qNlSRSF1 | GATATCGCGACAGCGAGGAC | CACCGGAGAGTAAACCGGAC | qPCR |
| qNlSRSF2.1 | GCGGTCAGACAGCAAGAGTT | GAGTGCGACCTTGACTTGGA | |
| qNlSRSF2.2 | GAGCTGAAAGTTCAGATGGC | TGATGCGAGTGATGGCGAC | |
| qNlSRSF7.1 | CGCGGTCACTACGCAAGGAAC | GGACGACCTTGACCGTGAC | |
| qNlSRSF7.2 | AGGTCACGCGATAGACGTTC | CGTTGCCATTTCTCTCGGGT | |
| qNlRPS15 | TAAAAATGGCAGACGAAGAGCCCAA | TTCCACGGTTGAAACGTCTGCG | |
| dsNlSRSF1 | T7-TTGAAGAACCGAAGAGGCCC | T7-TAAATCCTGCCAGCTTCCCG | RNAi |
| dsNlSRSF2.1 | T7-GTCCGTCTAAAAGGCGTCCA | T7-ATGAGTTACGGACGCCCACC | |
| dsNlSRSF2.2 | T7-GTTTTGGAAGACCACCCCCT | T7-TCGGCATCACGCTTGTCATA | |
| dsNlSRSF7.1 | T7-TGCGTAGTGACCGCGTTTAT | T7-AATCAGGAACGTGTGGGTGG | |
| dsNlSRSF7.2 | T7-ATACAGGGACTCAGGCAACC | T7-GCTACGCCCATCTAGACCAC | |
| dsGFP | T7-CCTGAAGTTCATCTGCACCAC | T7-TGATGCCGTTCTTCTGCTTGT |
Table 1. Primers for amplification, mRNA expression and dsRNA synthesis in this study
| 引物名称 Primer | 上游引物序列(5′-3′) Upstream primer sequences (5′-3′) | 下游引物序列(5′-3′) Downstream primer sequences (5′-3′) | Use 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| cNlSRSF1 | AAGACGACGCCTTGCCT | AGCTGTGTGTTGCTCCTTAATT | 克隆 Clone |
| cNlSRSF2.1 | TCCACAACTTCACATAAGTTCG | TTAGGCTTGGTAGCCAGCA | |
| cNlSRSF2.2 | GCATCTGTTTCTTGGCGG | TGAGCAGTATTGGTCGCCT | |
| cNlSRSF7.1 | TCGGTAGTAGCCTAAGCAGTCA | ACGTGGGTATCAAATAATTAACAAA | |
| cNlSRSF7.2 | CATGTAATTTCTGCTGGTGTTG | GACTTTGTTGTGTGATGTGAGG | |
| qNlSRSF1 | GATATCGCGACAGCGAGGAC | CACCGGAGAGTAAACCGGAC | qPCR |
| qNlSRSF2.1 | GCGGTCAGACAGCAAGAGTT | GAGTGCGACCTTGACTTGGA | |
| qNlSRSF2.2 | GAGCTGAAAGTTCAGATGGC | TGATGCGAGTGATGGCGAC | |
| qNlSRSF7.1 | CGCGGTCACTACGCAAGGAAC | GGACGACCTTGACCGTGAC | |
| qNlSRSF7.2 | AGGTCACGCGATAGACGTTC | CGTTGCCATTTCTCTCGGGT | |
| qNlRPS15 | TAAAAATGGCAGACGAAGAGCCCAA | TTCCACGGTTGAAACGTCTGCG | |
| dsNlSRSF1 | T7-TTGAAGAACCGAAGAGGCCC | T7-TAAATCCTGCCAGCTTCCCG | RNAi |
| dsNlSRSF2.1 | T7-GTCCGTCTAAAAGGCGTCCA | T7-ATGAGTTACGGACGCCCACC | |
| dsNlSRSF2.2 | T7-GTTTTGGAAGACCACCCCCT | T7-TCGGCATCACGCTTGTCATA | |
| dsNlSRSF7.1 | T7-TGCGTAGTGACCGCGTTTAT | T7-AATCAGGAACGTGTGGGTGG | |
| dsNlSRSF7.2 | T7-ATACAGGGACTCAGGCAACC | T7-GCTACGCCCATCTAGACCAC | |
| dsGFP | T7-CCTGAAGTTCATCTGCACCAC | T7-TGATGCCGTTCTTCTGCTTGT |
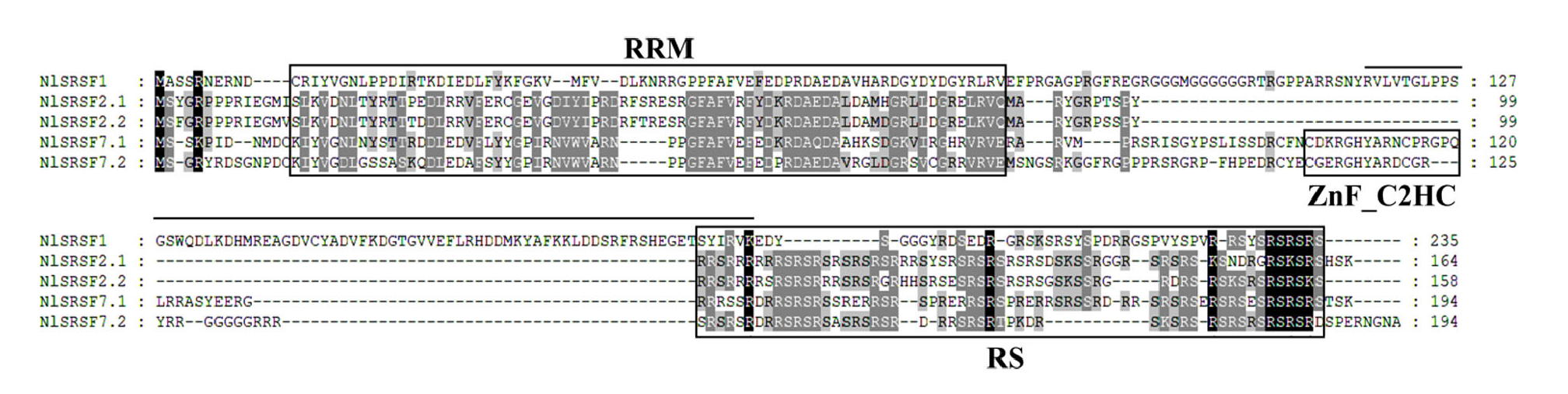
Fig. 1. Alignment of amino acid residues of SRs in Nilaparavata lugens Amino acid positions are indicated on the right. The predicted RRM domain, RS domain, and ZnF_C2HC domain are highlighted with boxes, respectively.
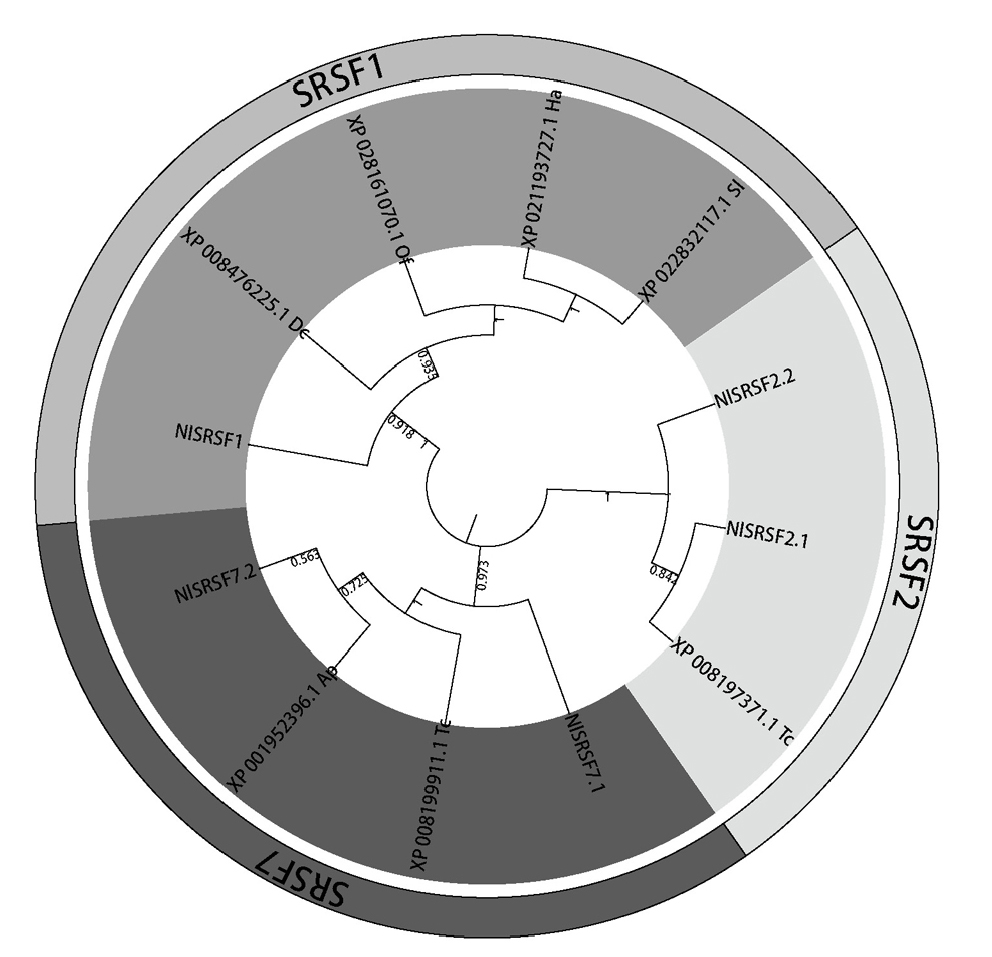
Fig. 2. Phylogenetic tree of NlSRs in Nilaparvata lugens and homologs from other insects Tc, Tribolium castaneum;Ap, Acyrthosiphon pisum;Dc, Diaphorina citri;Ha, Helicoverpa armigera;Sl, Spodoptera litura;Of, Ostrinia furnacalis. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method, and different groups are represented by shaded areas.
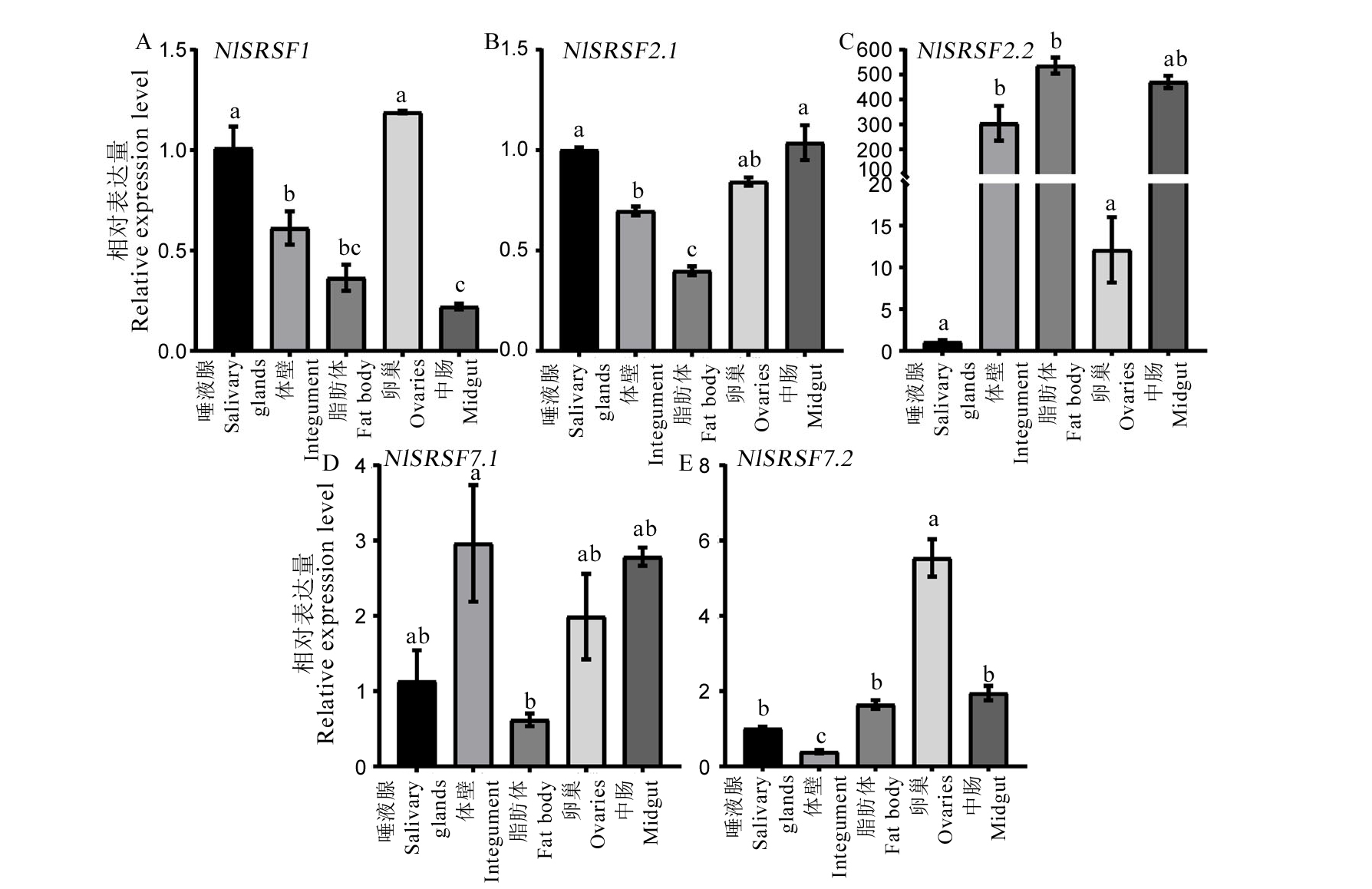
Fig. 3. Relative expression levels of NlSRs in various tissues of Nilaparavata lugens The expression levels of NlSR genes in various tissues of Nilaparvata lugens were determined by qPCR, using the NlRPS15 gene as an internal reference. The bars represent 2−△△CT values (± SE), normalized to the geometric mean of housekeeping gene expression. Different letters indicate significant differences at P value < 0.05, as analyzed by ANOVA and Turkey’s test.

Fig. 4. Relative expression levels of NlSRs in different developmental stages of Nilaparavata lugens The expression levels of NlSR genes in different development stages of Nilaparavata lugens were determined by qPCR, using the NlRPS15 gene as an internal reference. The bars represent 2-△△CT values ( ± SE) normalized to the geometric mean of housekeeping gene expression. Different letters indicate a significant difference at P value < 0.05, as analyzed by ANOVA and Turkey’s test.
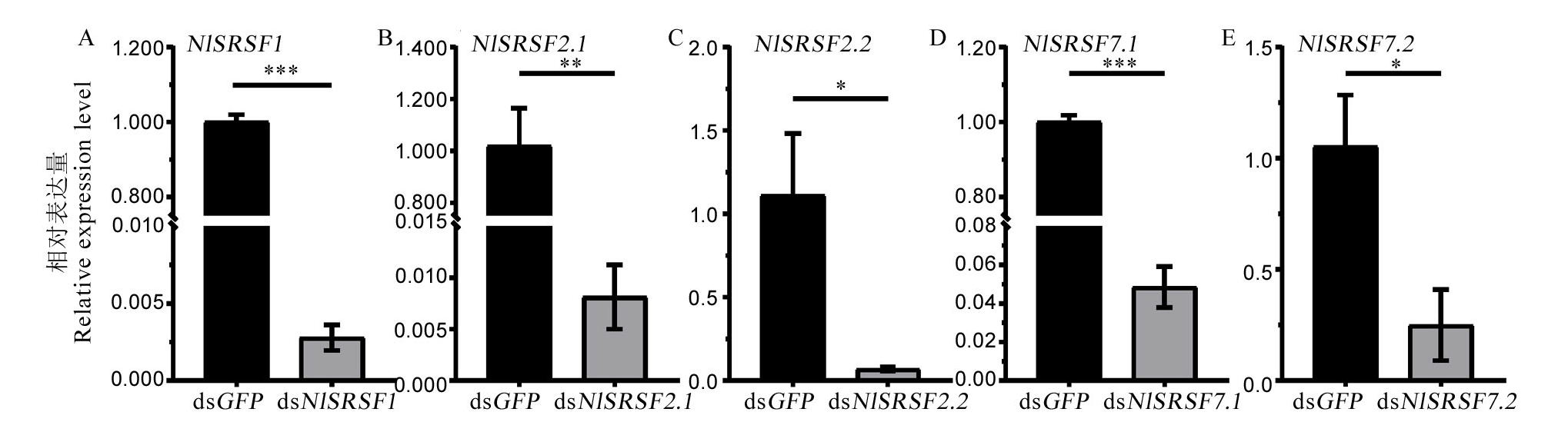
Fig. 5. Relative expression level of NlSRs on the 3rd day after injection with dsRNA in Nilaparavata lugens Utilizing the brown planthopper RPS15 gene as an internal reference for normalization, the relative expression levels of NlSR were determined in each treatment. Different symbols indicate significant differences, as analyzed by the Student’s t test. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001.

Fig. 6. Survival rate (A) of the 4th instar nymphs and the honeydew amount (B) and body weight gain (C) of Nilaparvata lugens after dsRNA injection The brown planthopper injected with dsGFP were used as controls. Data in Figs. B and C are mean ± SE. Different letters above bars indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) in the gene expression levels, as analyzed by ANOVA and the Tukey’s HSD test. Data in Fig. A were calculated by the Kaplan-Meier method and compared by the log-rank test.
| [1] | Sahebi M, Hanafi M M, van Wijnen A J, Azizi P, Abiri R, Ashkani S, Taheri S. Towards understanding pre-mRNA splicing mechanisms and the role of SR proteins[J]. Gene, 2016, 587(2): 107-119. |
| [2] | Wahl M C, Will C L, Lührmann R. The spliceosome: Design principles of a dynamic RNP machine[J]. Cell, 2009, 136(4): 701-718. |
| [3] | Fu X D, Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus[J]. Nature, 1990, 343(6257): 437-441. |
| [4] | Chen S, Li J, Liu Y, Li H. Genome-wide analysis of serine/arginine-rich protein family in wheat and Brachypodium distachyon[J]. Plants, 2019, 8(7): 188. |
| [5] | Shepard P J, Hertel K J. The SR protein family[J]. Genome Biology, 2009, 10(10): 242. |
| [6] | Bennick R A, Nagengast A A, DiAngelo J R. The SR proteins SF2 and RBP1 regulate triglyceride storage in the fat body of Drosophila[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2019, 516(3): 928-933. |
| [7] | Heinrichs V, Baker B S. The Drosophila SR protein RBP1 contributes to the regulation of doublesex alternative splicing by recognizing RBP1 RNA target sequences[J]. The EMBO Journal, 1995, 14(16): 3987-4000. |
| [8] | Wan P J, Zhou R N, Nanda S, He J C, Yuan S Y, Wang W X, Lai F X, Fu Q. Phenotypic and transcriptomic responses of two Nilaparvata lugens populations to the Mudgo rice containing Bph1[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 14049. |
| [9] | 娄永根, 程家安. 稻飞虱灾变机理及可持续治理的基础研究[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2011, 48(2): 231-238. |
| Lou Y G, Cheng J A. Basic research on the outbreak mechanism and sustainable management of rice planthoppers[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2011, 48(2): 231-238. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 芮明方, 谭宏, 沈卫新, 马善林. 稻褐飞虱发生规律及防治研究进展[J]. 上海农业科技, 2011(3): 115-117. |
| Rui M F, Tan H, Shen W X, Ma S L. Research progress on the occurrence pattern and control of rice brown planthopper[J] Shanghai Agricultural Science and Technology, 2011(3): 115-117. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 程家安, 祝增荣. 中国水稻病虫草害治理60年: 问题与对策[J]. 植物保护学报, 2017, 44(6): 885-895. |
| Cheng J A, Zhu Z R. Development of rice pest management in the past 60 years in China: Problems and strategies[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2017, 44(6): 885-895. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | Wan P J, Tang Y H, Yuan S Y, He J C, Wang W X, Lai F X, Fu Q. Reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR analysis in symbiont Entomomyces delphacidicola of Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 42206. |
| [13] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method[J]. Methods, 2001, 9(3): 299-308. |
| [14] | Wang W X, Li K L, Chen Y, Lai F X, Fu Q. Identification and function analysis of enolase gene NlEno1 from Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae)[J]. Journal of Insect Science, 2015, 15(1): 66. |
| [15] | Li K L, Wan P J, Wang W X, Lai F X, Fu Q. Ran involved in the development and reproduction is a potential target for RNA-interference-based pest management in Nilaparvata lugens[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(11): e0142142. |
| [16] | Manley J L, Krainer A R. A rational nomenclature for serine/arginine-rich protein splicing factors (SR proteins)[J]. Genes & Development, 2010, 24(11): 1073-1074. |
| [17] | Brown R S. Zinc finger proteins: Getting a grip on RNA[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2005, 15(1): 94-98. |
| [18] | Gamsjaeger R, Liew C K, Loughlin F E, Crossley M, MacKay J P. Sticky fingers: Zinc-fingers as protein-recognition motifs[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2007, 32(2): 63-70. |
| [19] | Hall T M T. Multiple modes of RNA recognition by zinc finger proteins[J]. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2005, 15(3): 367-373. |
| [20] | Klug A. Zinc finger peptides for the regulation of gene expression[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1999, 293(2): 215-218. |
| [21] | Matthews J M, Sunde M. Zinc fingers: Folds for many occasions[J]. IUBMB Life, 2002, 54(6): 351-355. |
| [22] | 邵伟, 樊玉杰, 徐永镇. SR蛋白家族在RNA剪接中的调控作用[J]. 生命科学, 2010, 22(7): 710-716. |
| Shao W, Fan Y J, Xu Y Z. Function of SR protein family in pre-mRNA splicing[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2010, 22(7): 710-716. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | Arrese E L, Soulages J L. Insect fat body: Energy, metabolism, and regulation[J]. Annual Review of Entomology, 2010, 55: 207-225. |
| [24] | Barta A, Kalyna M, Reddy A S N. Implementing a rational and consistent nomenclature for serine/arginine-rich protein splicing factors (SR proteins) in plants[J]. The Plant Cell, 2010, 22(9): 2926-2929. |
| [25] | Duque P. A role for SR proteins in plant stress responses[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2011, 6(1): 49-54. |
| [26] | Christiaens O, Smagghe G. The challenge of RNAi-mediated control of hemipterans[J]. Current Opinion in Insect Science, 2014, 6: 15-21. |
| [27] | Ma X, Yin Z, Li H, Guo J. Roles of herbivorous insects salivary proteins[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(7): e29201. |
| [28] | Huang H J, Wang Y Z, Li L L, Lu H B, Lu J B, Wang X, Ye Z X, Zhang Z L, He Y J, Lu G, Zhuo J C, Mao Q Z, Sun Z T, Chen J P, Li J M, Zhang C X. Planthopper salivary sheath protein LsSP1 contributes to manipulation of rice plant defenses[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 737. |
| [29] | Tang C, Xu Q, Zhao J, Yue M, Wang J, Wang X, Kang Z, Wang X. A rust fungus effector directly binds plant pre-mRNA splice site to reprogram alternative splicing and suppress host immunity[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2022, 20(6): 1167-1181. |
| [30] | Gao X, Yin C, Liu X, Peng J, Chen D, He D, Wei S, Zhao W S, Yang Jun, Peng Y L. A glycine-rich protein MoGrp1 functions as a novel splicing factor to regulate fungal virulence and growth in Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Phytopathology Research, 2019, 1(1): 2. |
| [31] | Rao W, Zheng X, Liu B, Guo Q, Guo J, Wu Y, Shangguan X, Wang H, Wu D, Wang Z, Hu L, Xu C, Jiang W, Huang J, Shi S, He G. Secretome analysis and in planta expression of salivary proteins identify candidate effectors from the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2019, 32(2): 227-239. |
| [1] | REN Zhiqi, XUE Kexin, DONG Zheng, LI Xiaoxiang, LI Yongzhao, GUO Yujing, LIU Wenqiang, GUO Liang, SHENG Xinnian, LIU Zhixi, PAN Xiaowu. Identification and Gene Mapping of Outcurved Leaf Mutant ocl1 in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(4): 337-346. |
| [2] | LUO Ju, YANG Suwen, BEI Wenyong, YU Junwei, TANG Jian, LIU Shuhua. Direct Multiplex TaqMan qPCR Assay for Rapid Detection of Three Sibling Species from Nilaparvata Distant [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(3): 329-336. |
| [3] | HE Jiachun, HE Yuting, WAN Pinjun, WEI Qi, LAI Fengxiang, CHEN Xiangsheng, FU Qiang. Effects of Temperature on Biological Traits of the Pincer Wasp [Gonatopus flavifemur (Esaki & Hashimoto)], a Natural Enemy of the Brown Planthopper(Nilaparvata lugens) [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 318-326. |
| [4] | LUO Ju, TANG Jian, WANG Aiying, YANG Baojun, LIU Shuhua. A Rapid Detection Assay of Nilaparvata lugens Based on Recombinase Aided Amplification-lateral Flow Dipstick Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(1): 96-104. |
| [5] | Lei PAN, Lihua WANG, Feng ZHU, Yangchun HAN, Pei WANG, Jichao FANG. Expression Profiles and Functions of Small Heat Shock Proteins in Nilaparvata lugens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(1): 37-45. |
| [6] | Jiachun HE, Bo LI, Maocheng XIE, Fengxiang LAI, Guowen HU, Qiang FU. Laboratory Bioactivity Study on Neonicotinoid and Other Rice Paddy Used Insecticides Against the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens(Stål) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(5): 467-478. |
| [7] | Juefeng ZHANG, Fang LI, Haiying ZHONG, Jianming CHEN. Effects of Nystatin Treatment on Detoxification Enzymes and Uricase Content in Nymphs of the Brown Planthopper [Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)] [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(2): 186-190. |
| [8] | Qiaoli CHEN, Feng WANG, Danlei LI, Yaming LING, Ruizhi ZHANG. Expression Under Hypertonic Osmotic Stress of Ab-lea from Aphelenchoides besseyi [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(6): 652-657. |
| [9] | Huanhuan ZHU, Yang CHEN, Pinjun WAN, Weixia WANG, Fengxiang LAI, Qiang FU. Influence of Symbiotic Bacteria Arsenophonus, Rice Variety and Temperature on the Incidence Rate of Nilaparvata lugens to Metarhizium flavoviride [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(6): 643-651. |
| [10] | Dan SHAN, Lihua WANG, Yueliang ZHANG, Yangchun HAN, Hongtao NIU, Lei PAN, Jichao FANG. Induced Expression Profiles of Hsp70s in Brown Planthoppers, Nilaparvata lugens, Under Different Temperatures [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(5): 533-541. |
| [11] | Chenxing ZHAO, Yewei YU, Yipeng XU, Xiaoping YU. Gene Cloning, Polyclonal Antibody Preparation and Expression Localization of Two dynamin-1-like Genes from Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(4): 345-354. |
| [12] | Long-fei CHEN, Pin-jun WAN, Wei-xia WANG, Qiang FU, Ting-heng ZHU. Molecular Cloning and Functional Analysis of NlTgo in the Rice Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(6): 653-660. |
| [13] | Yu ZHENG, Jia-chun HE, Pin-jun WAN, Feng-xiang LAI, Yan-qun SUN, Jing-jing LIN, Qiang FU. Virulence Characteristics of Nilaparvata lugens(Stål) Reared on Resistant Rice Variety IR56 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(5): 552-558. |
| [14] | TANG Yaohua1,2, WAN Pinjun2, HAO Peiying1, FU Qiang2, *, YU Xiaoping1, *. Roles of Two Genes Involved in Histidine Biosynthetic Pathway in YeastLike Symbiont in Development of Nilaparvata lugens (Stl) [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2016, 30(4): 406-416. |
| [15] | Kai LIU, Ya-jun YANG, Jun-ce TIAN, Yan-hui LU, Hong-xing XU, Xu-song ZHENG, Zhong-xian LV. Effects of Bt Rice with cry1C and cry2A on the Ecological Generation Fitness of Rice Brown Planthoppers(Nilaparvata lugens) and Whitebacked Planthoppers (Sogatella furcifera) at Various Nitrogen Rates [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(2): 200-209. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||