
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (6): 563-576.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.230301
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
TONG Qi, WANG Chunyan, QUE Yawei, XIAO Yu, WANG Zhengyi*( )
)
Received:2023-03-30
Revised:2023-04-20
Online:2023-11-10
Published:2023-11-14
Contact:
*email: zhywang@zju.edu.cn
通讯作者:
*email: zhywang@zju.edu.cn
基金资助:TONG Qi, WANG Chunyan, QUE Yawei, XIAO Yu, WANG Zhengyi. Identification and Functional Characterization of the Heat Shock Protein (HSP) 40 Encoding Gene, MoMHF6, in Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(6): 563-576.
童琪, 王春燕, 阙亚伟, 肖宇, 王政逸. 稻瘟病菌热激蛋白(HSP)40编码基因MoMHF6的鉴定及功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37(6): 563-576.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.230301
| 引物 Primer | 序列 Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| MHF6-up-F | CCCCCGGGCTGCAGGAATTCGAGATAACAAAAGGTAT |
| MHF6-up-R | GCTCCTTCAATATCATCTTCTCTCGCTCAGTTCGAAATGGGAT |
| MHF6-down-F | TAGAGTAGATGCCGACCGAACAAGAATCAATGCCCAGTCTCGTGC |
| MHF6-down-R | TACCGGGCCCCCCCTCGAGCGAATACACTTTGGAGAC |
| HPT-F | GACAGACGTCGCGGTGAGTT |
| HPT-R | GTCCGAGGGCAAAGAAATAG |
| MHF6-YW-F | TCGAGGAGATTGAGTGCGTC |
| MHF6-YW-R | CTTCTTTTGCTTGGCTTTGC |
| MHF6-DX-F | GACTTCAATCAACCCTAACC |
| MHF6-DX-R | AAGCCGGACGGAAAGACTTT |
| HB-MHF6-F | TCCCCCGGGCTGCAGGAATTCTTCTCCAGAAAATCCCTGGA |
| HB-MHF6-R | GATAAGCTTGATATCGAATTCATTCGACCGGCGATCTTCCG |
| Actin-RT-F | ATTTACGAGGGTTTCTCCTTGC |
| Actin-RT-R | TCTCCTGCTCAAAGTCAAGAG |
| HOX2-qRT-F | CGATAATTGCTCCCACACCT |
| HOX2-qRT-R | GAAGGAGTCGGTGGTGACAT |
| COS1-qRT-F | ATGGATTCCCAGCCTCGTA |
| COS1-qRT-R | CGTTGACCAGCAAAGACAA |
| HTF1-qRT-F | GGCGACGATACGAAGAAA |
| HTF1-qRT-R | TGAACCACCTTGGCTTTG |
| CON7-qRT-F | GGCGACGATACGAAGAAA |
| CON7-qRT-R | TGAACCACCTTGGCTTTG |
| COM1-qRT-F | GAAAGAACCTATCAGGGCG |
| COM1-qRT-R | GTTTGCGATTGGCATTAGC |
| STU1-qRT-F | CTACGTTAAGTCCGAGATGG |
| STU1-qRT-R | CGTGATCAGCCTCATCTTCC |
Table 1. Primers used in this study.
| 引物 Primer | 序列 Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| MHF6-up-F | CCCCCGGGCTGCAGGAATTCGAGATAACAAAAGGTAT |
| MHF6-up-R | GCTCCTTCAATATCATCTTCTCTCGCTCAGTTCGAAATGGGAT |
| MHF6-down-F | TAGAGTAGATGCCGACCGAACAAGAATCAATGCCCAGTCTCGTGC |
| MHF6-down-R | TACCGGGCCCCCCCTCGAGCGAATACACTTTGGAGAC |
| HPT-F | GACAGACGTCGCGGTGAGTT |
| HPT-R | GTCCGAGGGCAAAGAAATAG |
| MHF6-YW-F | TCGAGGAGATTGAGTGCGTC |
| MHF6-YW-R | CTTCTTTTGCTTGGCTTTGC |
| MHF6-DX-F | GACTTCAATCAACCCTAACC |
| MHF6-DX-R | AAGCCGGACGGAAAGACTTT |
| HB-MHF6-F | TCCCCCGGGCTGCAGGAATTCTTCTCCAGAAAATCCCTGGA |
| HB-MHF6-R | GATAAGCTTGATATCGAATTCATTCGACCGGCGATCTTCCG |
| Actin-RT-F | ATTTACGAGGGTTTCTCCTTGC |
| Actin-RT-R | TCTCCTGCTCAAAGTCAAGAG |
| HOX2-qRT-F | CGATAATTGCTCCCACACCT |
| HOX2-qRT-R | GAAGGAGTCGGTGGTGACAT |
| COS1-qRT-F | ATGGATTCCCAGCCTCGTA |
| COS1-qRT-R | CGTTGACCAGCAAAGACAA |
| HTF1-qRT-F | GGCGACGATACGAAGAAA |
| HTF1-qRT-R | TGAACCACCTTGGCTTTG |
| CON7-qRT-F | GGCGACGATACGAAGAAA |
| CON7-qRT-R | TGAACCACCTTGGCTTTG |
| COM1-qRT-F | GAAAGAACCTATCAGGGCG |
| COM1-qRT-R | GTTTGCGATTGGCATTAGC |
| STU1-qRT-F | CTACGTTAAGTCCGAGATGG |
| STU1-qRT-R | CGTGATCAGCCTCATCTTCC |
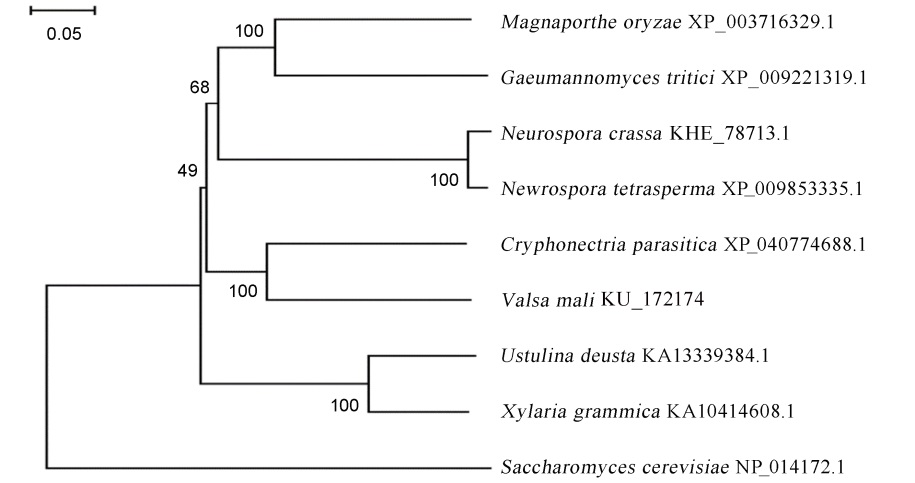
Fig. 1. Phylogenetic analysis of MoMhf6 and its orthologues from several fungal species. The phylogenetic tree was constructed by MEGA version 7.0. Numbers at nodes of the branch represent bootstrapping value in 1000 replications. The length of the branches represents genetic distance. The distance scale=0.05.
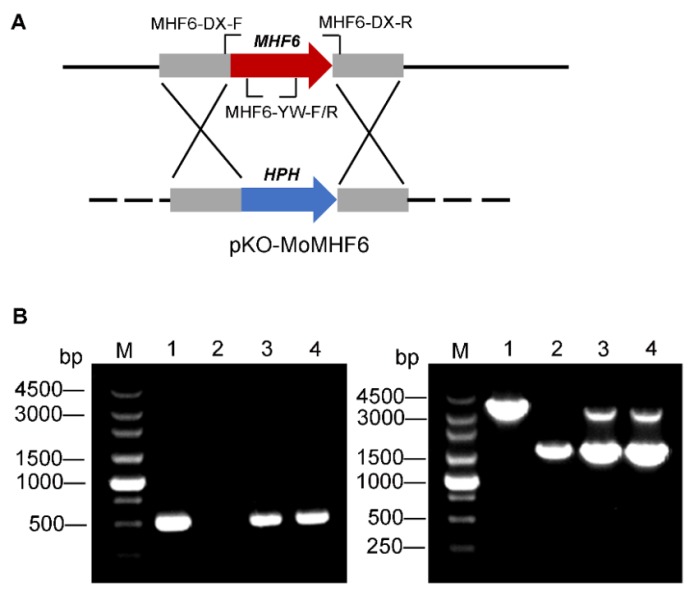
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of gene knockout of MoMHF6 and confirmation of ΔMomhf6 mutants and complemented transformants by PCR. A, Knockout vector pKO-MoMHF6 and target gene deletion of MoMHF6. The red arrow represents the target gene MoMHF6. The blue arrow represents the hygromycin resistant gene. The location of primers is indicated; B, Confirmation of the deletion mutant ΔMomhf6 and the complemented strain ΔMomhf6-C. Left: A 524 bp MoMHF6 gene fragment was amplified by primers MHF6-YW-F/R. Right: the targeted gene deletion or complementation events of different strains were further verified by primers MHF6-DX-F/R. The bands of about 1.5 kb and 3.14 kb were corresponding with HPH and MoMHF6 genes respectively. M, Marker; Lane 1, Guy11; Lane 2, ΔMomhf6; Lane 3, MoMHF6-ect (ectopic); Lane 4, ΔMomhf6-C (complemented).
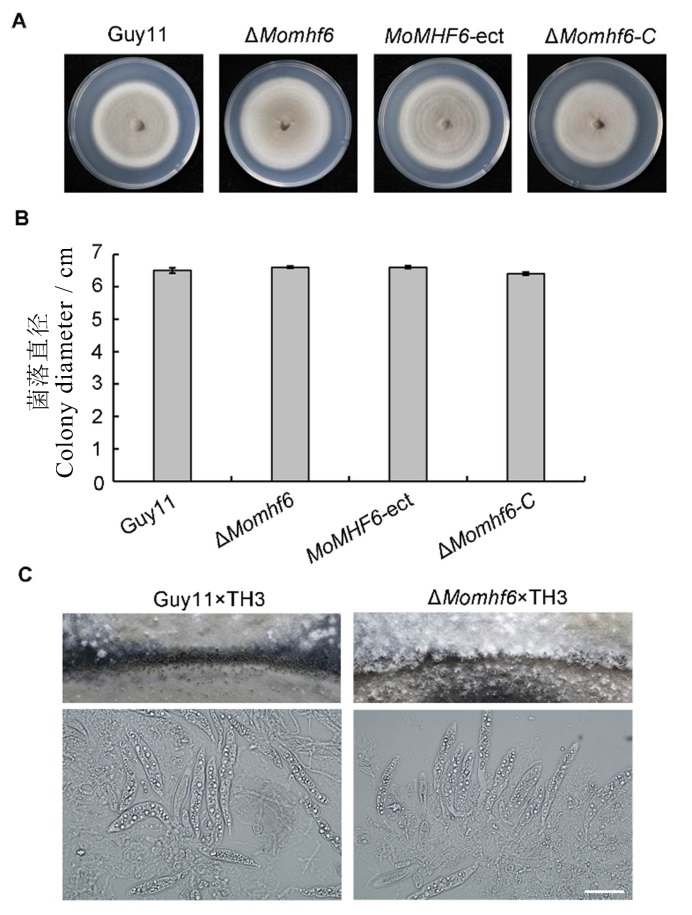
Fig. 3. MoMHF6 is required for aerial hypha growth and perithecia production. A, The wild type Guy11, the ΔMomhf6 mutant, the ectopic insertion strain MoMHF6-ect and the complemented strain ΔMomhf6-C were cultured on CM plates at 25 ℃ for 10 days and photographed at 10 days after inoculation; B, The bar graph shows radical growth of different strains on CM plates. Error bars represent standard error; C, Perithecia production was severely reduced for the ΔMomhf6×TH3 cross. Asci and ascospores in perithecia of both crosses were observed. Bar=20 μm.
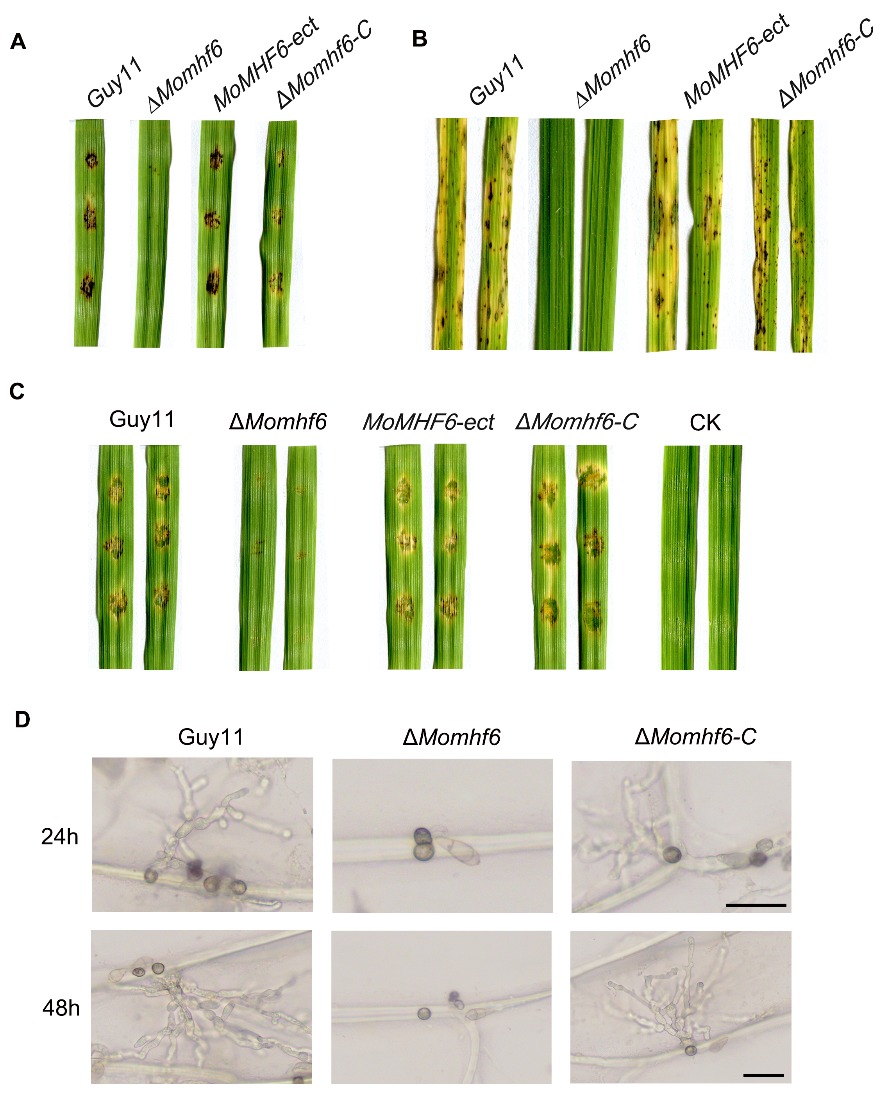
Fig. 4. MoMHF6 plays important roles in pathogenesis by M. oryzae. A, The ΔMomhf6 mutant is nonpathogenic to susceptible barley leaves. Conidial suspension (5×104 conidia/mL) of different tested strains were drop-inoculated onto barley leaf segments and photographed at 5 dpi (days post inoculation); B, The ΔMomhf6 mutant is nonpathogenic to susceptible rice leaves. Rice seedlings were sprayed with conidial suspension (5×104 conidia/mL) of different strains and photographed at 5 dpi; C, Invasive growth of the ΔMomhf6 mutant was severely impaired on wounded barley leaf segments. Conidial suspension (5×104 conidia/mL) of different strains was dropped on wounded barley leaf segments. CK represents H2O. Photographs were taken at 5 dpi; D, The ΔMomhf6 mutant was unable to penetrate onion cuticle and cell wall. Conidial suspension (2×104 conidia/mL) of different strains was dropped on onion epidermis. After 24 h and 48 h of incubation in darkness, the onion epidermis was examined and photographed under a light microscope. Bars=20 μm.
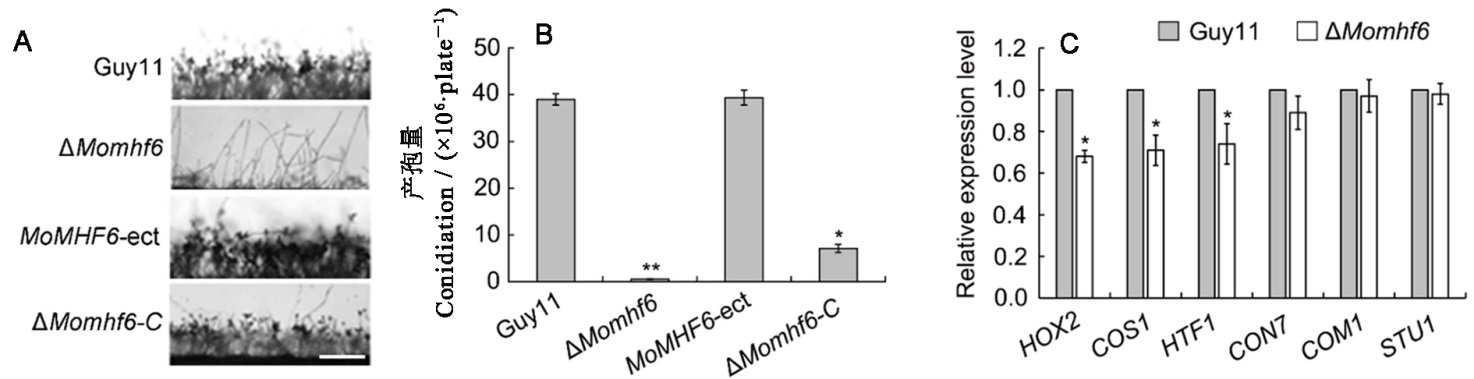
Fig. 5. MoMHF6 is important for asexual sporulation. A, Microscopic observation of aerial hypha growth and conidiophore development. Bars=100 μm; B, Statistical analysis of conidiation on CM at 25 ℃ for 12 days; C, qRT-PCR analysis of transcriptional expression of several sporulation related genes. Error bars represent standard error. Asterisks indicate significant difference (*P<0.05; **P<0.01).
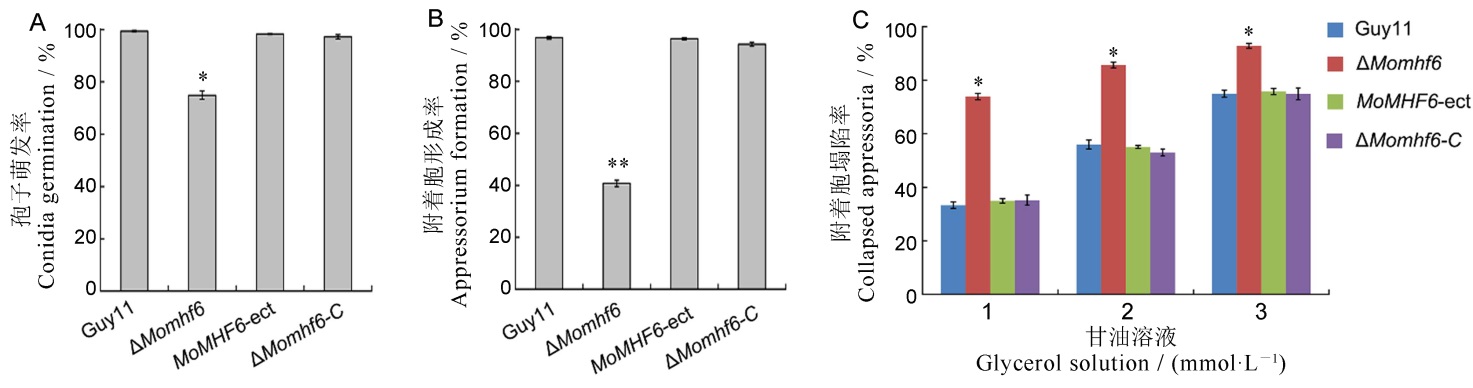
Fig. 6. Deletion of MoMHF6 results in significant reduction of conidium germination, appressorium formation and appressorium turgor generation A, Statistical analysis of conidium germination. Conidia were allowed to germinate on hydrophobic surface for 6 hours; B, Statistical analysis of appressorium formation. Conidia were placed on the hydrophobic surface to induce appressorium formation and incubated for 24 hours; C, Statistical analysis of collapsed appressoria. Appressoria induced for 24 hours were incubated in 1 mol/L, 2 mol/L or 3 mol/L glycerol solution for 10 minutes. Error bars represent standard error. Asterisks indicate significant difference (*P<0.05; **P<0.01).
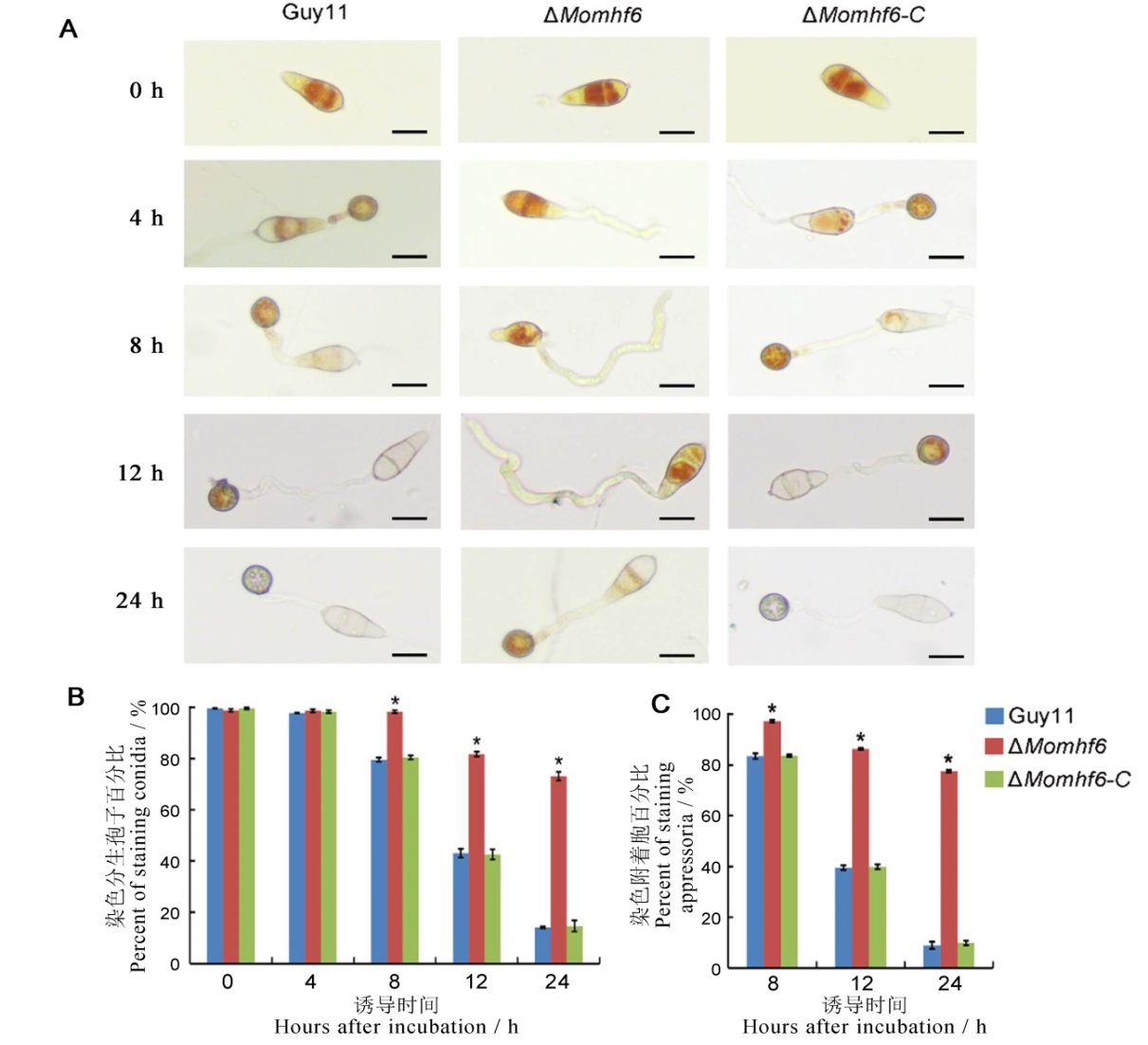
Fig. 7. Deletion of MoMHF6 delays glycogen transportation and degradation during appressoria development in M. oryzae. A, Conidial suspension (5×104 conidia/mL) of the wild type Guy11, the mutant ΔMomhf6 and the complemented strain ΔMomhf6-C was incubated on hydrophobic surface for 4, 8, 12, 24 hours respectively and then stained with KI/I2 solution. Photographs were taken at different time intervals. Bars=20 μm. B, Statistical analysis of glycogen mobilization in conidia of different tested strains; C, Statistical analysis of glycogen degradation in appressoria of different tested strains. Error bars represent standard error. Asterisks indicate significant difference (P<0.05).
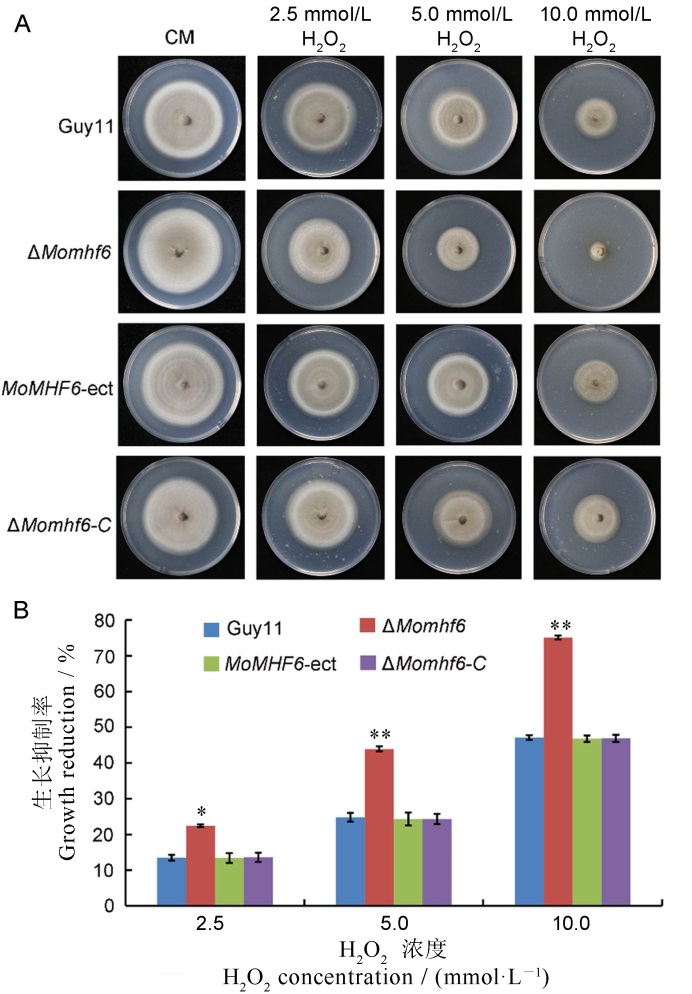
Fig. 8. Deletion of MoMHF6 increases sensitivity of M. oryzae to oxidative stress. A, The different tested strains were inoculated on CM supplemented with 2.5, 5 and 10 mmol/L H2O2, respectively. Growth of various tested strains after 10 days is presented; B, Colony diameters were measured and growth inhibition rates were calculated. Error bars represent standard deviation. Asterisks indicate significant difference (*P<0.05; **P<0.01).
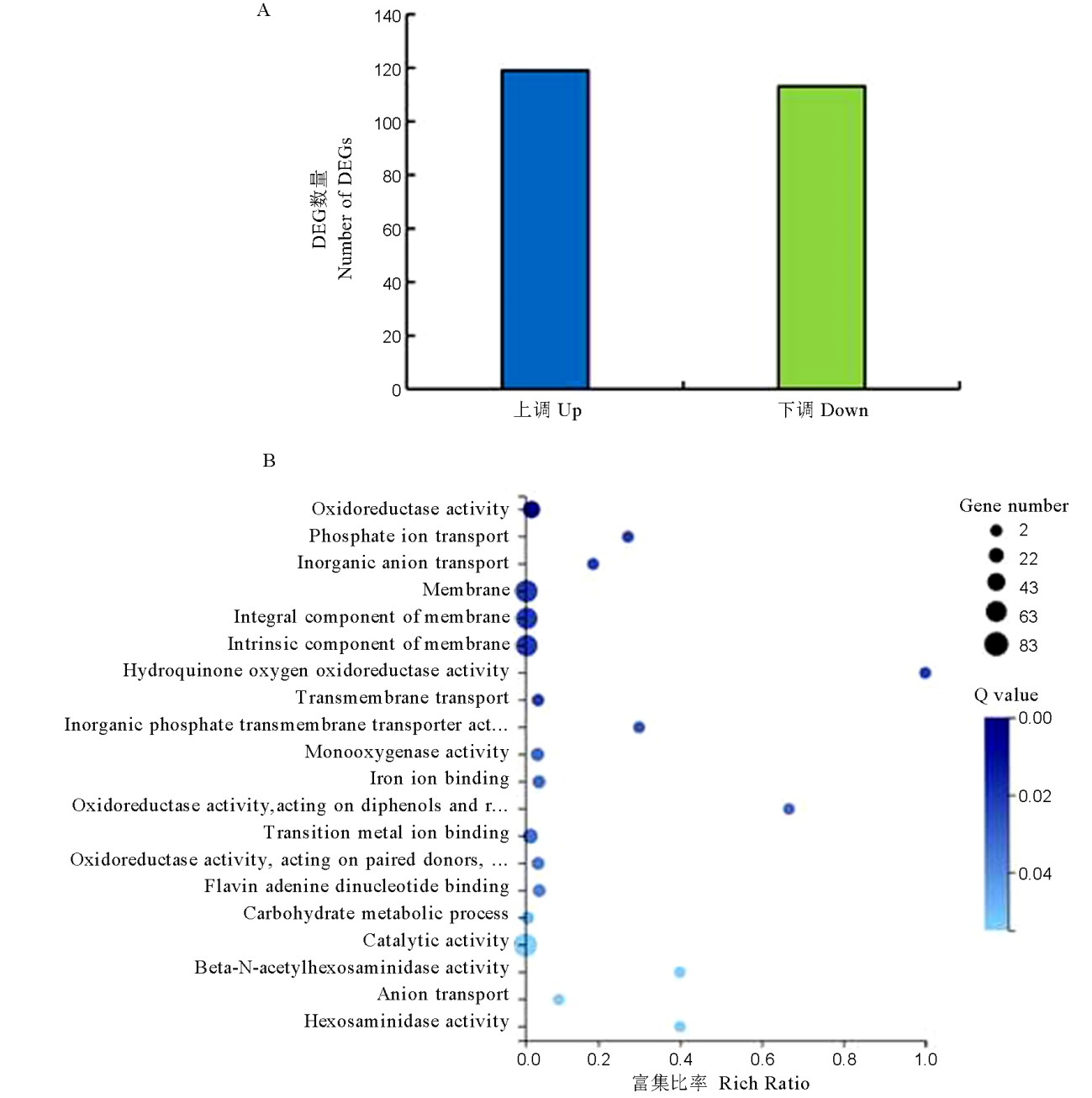
Fig. 9. Transcriptome analysis of the ΔMomhf6 mutant for differentially expressed genes. A, Statistical analysis of numbers of differentially expressed genes in the ΔMomhf6 mutant in comparison to the wild type strain Guy11; B, Scatter plot of GO term enrichment of DEGs in the ΔMomhf6 mutant. Rich ratio represents the ratio of numbers of DEGs annotated in the GO term to the numbers of all genes annotated in the same GO term. The q-value is corrected p value, with lower value means greater intensiveness.
| [1] | Talbot N J. On the trail of a cereal killer: Exploring the biology of Magnaporthe grisea[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2003, 57(1): 177-202. |
| [2] | Muthayys S, Sugimoto J D, Montgomery S, Maberly G F. An overview of global rice production, supply, trade, and consumption[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 2015, 1324(1): 7-14. |
| [3] | 商文奇. 水稻稻瘟病防治方法研究进展[J]. 辽宁农业科学, 2021(1): 33-39. |
| Shang W Q. Advances in research on control methods of rice blast[J]. Liaoning Agricultural Science, 2021(1): 33-39. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | Cyr D M, Lu X, Douglas M G. Regulation of Hsp70 function by a eukaryotic DnaJ homolog[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1992, 267: 20927-20931. |
| [5] | Hennessy F, Nicoll W S, Zimmermann R, Cheetham M E,; Blatch G L. Not all J domains are created equal: Implications for the specificity of Hsp40-Hsp70 interactions[J]. Protein Science, 2005, 14(7): 1697-1709. |
| [6] | Szyperski T, Pellecchia M, Wall D, Georgopoulos C, Wuthrich K. NMR structure determination of the Escherichia coli DnaJ molecular chaperone: Secondary structure and backbone fold of the N-terminal region (residues 2-108) containing the highly conserved J domain[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1994, 91(24): 11343-11347. |
| [7] | Tamadaddi C A, Sahi C. J domain independent functions of J proteins[J]. Cell Stress Chaperones, 2016, 21(4): 563-570. |
| [8] | Kelley W L. The J-domain family and the recruitment of chaperone power[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 1998, 23(6): 222-227. |
| [9] | Liberek K, Lewandowska A, Zietkiewicz S. Chaperones in control of protein disaggregation[J]. EMBO Journal, 2008, 27(2): 328-335. |
| [10] | Meyer A E, Hung N J, Yang P, Johnson A W, Craig E A. The specialized cytosolic J-protein, Jjj1, functions in 60S ribosomal subunit biogenesis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2007, 104(5): 1558-1563. |
| [11] | Lim J G, Lee J G, Kim J M. A DnaJ-like homolog from Cryphonectria parasitica is not responsive to hypoviral infection but is important for fungal growth in both wild-type and hypovirulent strains[J]. Molecules & Cells, 2010, 30(3): 235-243. |
| [12] | Yi M H, Lee Y H. Identification of genes encoding heat shock protein 40 family and the functional characterization of two Hsp40s, MHF16 and MHF21, in Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. The Plant Pathology Journal, 2008, 24(2): 7271-7279. |
| [13] | Yang J, Liu M X, Liu X Y, Yin Z Y, Sun Y, Zhang H F, Zheng X B, Wang P, Zhang Z G. Heat-shock proteins MoSsb1, MoSsz1, and MoZuo1 attenuate MoMkk1-mediated cell-wall integrity signaling and are important for growth and pathogenicity of Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interaction, 2018, 31(11): 1211-1221. |
| [14] | Wang Z Y, Jenkinson J M, Holcombe L J. The molecular biology of appressorium turgor generation by the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea[J]. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2005, 33(2): 384-388. |
| [15] | Badaruddin M, Holcombe L J, Wilson R A, Wang Z Y, Kershaw M J, Talbot N J. Glycogen metabolic genes are involved in trehalose-6-phosphate synthase-mediated regulation of pathogenicity by the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2013, 9(10): e1003604. |
| [16] | Thins E, Weber R W, Talbot N J. MAP kinase and protein kinase A-dependent mobilization of triacylglycerol and glycogen during appressorium turgor generation by Magnaporthe grisea[J]. Plant Cell, 2000, 12(9): 1703-1718. |
| [17] | Guo M, Chen Y, Du Y, Dong Y, Guo W, Zhai S, Zhang H, Dong S, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Wang P, Zheng X. The bZIP transcription factor MoAP1 mediates the oxidative stress response and is critical for pathogenicity of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2011, 7(2): e1001302. |
| [18] | Lin C H, Yang S L, Chung K R. The YAP1 homolog-mediated oxidative stress tolerance is crucial for pathogenicity of the necrotrophic fungus Alternaria alternata in citrus[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2009, 22(8): 942-952. |
| [19] | Molina L, Kahmann R. An Ustilago maydis gene involved in H2O2 detoxification is required for virulence[J]. Plant Cell, 2007, 19(7): 2293-2309. |
| [20] | Liu T B, Liu X H, Lu J P, Zhang L, Min H, Lin F C. The cysteine protease MoAtg4 interacts with MoAtg8 and is required for differentiation and pathogenesis in Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Autophagy, 2010, 6(1): 74-85. |
| [21] | Wegner A, Casanova F, Loehrer M, Jordine A, Bohnert S, Liu X Y, Zhang Z G, Schaffrath U. Gene deletion and constitutive expression of the pectate lyase gene 1 (MoPL1) lead to diminished virulence of Magnaporthe oryzae [J]. Journal of Microbiology, 2022, 60(1): 79-88. |
| [22] | Nguyen Q B, Itoh K, Van V B, Tosa Y, Nakayashiki H. Simultaneous silencing of endo-β-1,4 xylanase genes reveals their roles in the virulence of Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2011, 81(4): 1008-1019. |
| [23] | Qian B, Su X, Ye Z, Liu X Y, Liu M X, Shen D Y, Chen H, ZhangH F, Wang P, Zhang Z G. MoErv29 promotes apoplastic effector secretion contributing to virulence of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. New Phytologist, 2021, 233(3): 1289-1302. |
| [24] | Oh Y, Donofrio N, Pan H, Coughlan S, Dean R A. Transcriptome analysis reveals new insight into appressorium formation and function in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Genome Biology, 2008, 9(5): R85. |
| [25] | Xue C Y, Park G, Choi W B. Two novel fungal virulence genes specifically expressed in appressoria of the rice blast fungus[J]. Plant Cell, 2002, 14(9): 2107-2119. |
| [26] | Geoghegan I A, Gurr S J. Investigating chitin deacetylation and chitosan hydrolysis during vegetative growth in Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Cell Microbiology, 2017, 19(9): e12743. |
| [27] | 邹逸宾. 不同剂型1, 2-苯并异噻唑啉-3-酮对五种镰孢菌的效果评价和稻瘟病菌中MoAop1的功能分析[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2019. |
| Zou Y B. Evaluation of different forms of BIT to five species of Fusarium and functional characterization of MoAop1 in Magnaporthe grisea[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | Zhang H F, Liu K Y, Xing Z, Song W, Zhao Q, Dong Y, Guo M, Zheng X, Zhang Z. A two-component histidine kinase, MoSLN1, is required for cell wall integrity and pathogenicity of the rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Current Genetics, 2010, 56(6): 517-528. |
| [29] | Bekh-Ochir D, Shimada S, Yamagami A, Kanda S, Ogawa K, Nakazawa M, Matsui M, Sakuta M, Osada H, Asami T, Nakano T. A novel mitochondrial DnaJ/HSP40 family protein BIL2 promotes plant growth and resistance against environmental stress in brassinosteroid signaling[J]. Planta, 2013, 237(6): 1509-1525. |
| [30] | Liu J Z, Whitham S A. Overexpression of a soybean nuclear localized type-III DnaJ domain-containing HSP40 reveals its roles in cell death and disease resistance[J]. Plant Journal, 2013, 74(1): 110-121. |
| [31] | Zhong X, Yang J, Shi Y. The DnaJ protein OsDjA6 negatively regulates rice innate immunity to the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2018, 19(3): 607-614. |
| [32] | Saunders D G, Dagdas Y F, Talbot N J. Spatial uncoupling of mitosis and cytokinesis during appressorium-mediated plant infection by the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Plant Cell, 2010, 22(7): 2417-2428. |
| [33] | Fernandez J, Orth K. Rise of a cereal killer: The biology of Magnaporthe oryzae biotrophic growth[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2018, 26(7): 582-597. |
| [34] | Howard R J, Ferrari M A, Roach D H. Penetration of hard substrates by a fungus employing enormous turgor pressures[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1991, 88(24): 11281-11284. |
| [35] | Wilson R A, Talbot N J. Under pressure: investigating the biology of plant infection by Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2009, 7: 185-195. |
| [36] | Nishimura M, Fukada J, Moriwaki A, Fujikawa T, Hayashi N. Mstu1, an APSES transcription factor, is required for appressorium-mediated infection in Magnaporthe grisea[J]. Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 2009, 73(8): 1779-1786. |
| [37] | Liu C, Shen N, Zhang Q. Magnaporthe oryzae transcription factor MoBZIP3 regulates appressorium turgor pressure formation during pathogenesis[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(2): 881. |
| [38] | Qiu X B, Shao Y M, Miao S, Wang L. The diversity of the DnaJ/Hsp40 family, the crucial partners for Hsp70 chaperones[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2006, 63(22): 2560-2570. |
| [39] | Yan W, Schilke B, Pfund C, Walter W, Craig E A. Zuotin, a ribosome-associated DnaJ molecular chaperone[J]. EMBO Journal, 1998, 17(16): 4809-4817. |
| [1] | Xiangyang FENG, Zhen ZHANG, Rongyao CHAI, Haiping QIU, Jiaoyu WANG, Xueqin MAO, Yanli WANG, Guochang SUN. Functional Analysis of MoMET3 in Growth, Development and Pathogenicity of Magnaporthe oryzae [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(5): 542-550. |
| [2] | Xin LIU, Heng ZHANG, Hu-fei KAN, Li-shuai ZHOU, Hao HUANG, Lin-lin SONG, Huan-chen ZHAI, Jun ZHANG, Guo-dong LU. Bioinformatic and Expression Analysis of Rice Ubiquitin-conjugating Enzyme Gene Family [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(3): 223-231. |
| [3] | GUO Qiang,SUN Shu-bin,YU Ling,XU Guo-hua*. Functional Analysis of a Phosphate Transporter from Rice in a Heterologous Expression System [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2008, 22(3): 227-233 . |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||