
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2016, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 653-660.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.6032
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Long-fei CHEN1, Pin-jun WAN2, Wei-xia WANG2,*( ), Qiang FU2, Ting-heng ZHU1,*(
), Qiang FU2, Ting-heng ZHU1,*( )
)
Received:2016-03-01
Revised:2016-04-21
Online:2016-11-10
Published:2016-11-10
Contact:
Wei-xia WANG, Ting-heng ZHU
陈龙飞1, 万品俊2, 王渭霞2,*( ), 傅强2, 朱廷恒1,*(
), 傅强2, 朱廷恒1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
王渭霞,朱廷恒
基金资助:CLC Number:
Long-fei CHEN, Pin-jun WAN, Wei-xia WANG, Qiang FU, Ting-heng ZHU. Molecular Cloning and Functional Analysis of NlTgo in the Rice Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae)[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(6): 653-660.
陈龙飞, 万品俊, 王渭霞, 傅强, 朱廷恒. 褐飞虱NlTgo基因的克隆及功能研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2016, 30(6): 653-660.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2016.6032
| 引物名称 Primer name | 正向引物(5'-3') Forward sequence(5'-3') | 反向引物(5'-3') Reverse sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| 基因克隆 Gene cloning | ||
| NlTgo | GGCTGTTGCGCATATGAAGG | ATGTCGGACAACTCCTGCTG |
| 双链RNA合成 dsRNA synthesis | ||
| dsNlTgo | T7-ACCGACGAGGTCGAGTACAT | T7-GTGTGTAGGTGGGTGACCTG |
| dsGFP | T7-AGATTTGTATAGTTCATCCATGCCATGT | T7-AGAATGAGTAAAGGAGAAGAACTTTTCA |
| 定量PCR qPCR | ||
| qNlTgo | GGAGGAGGATGGTTCACACT | GGTCCACAAACGTGAACTTG |
| qNl18s | CGCTACTACCGATTGAA | GGAAACCTTGTTACGACTT |
Table 1 Primers used for RT-PCR, qPCR and dsRNA synthesis.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 正向引物(5'-3') Forward sequence(5'-3') | 反向引物(5'-3') Reverse sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| 基因克隆 Gene cloning | ||
| NlTgo | GGCTGTTGCGCATATGAAGG | ATGTCGGACAACTCCTGCTG |
| 双链RNA合成 dsRNA synthesis | ||
| dsNlTgo | T7-ACCGACGAGGTCGAGTACAT | T7-GTGTGTAGGTGGGTGACCTG |
| dsGFP | T7-AGATTTGTATAGTTCATCCATGCCATGT | T7-AGAATGAGTAAAGGAGAAGAACTTTTCA |
| 定量PCR qPCR | ||
| qNlTgo | GGAGGAGGATGGTTCACACT | GGTCCACAAACGTGAACTTG |
| qNl18s | CGCTACTACCGATTGAA | GGAAACCTTGTTACGACTT |

Fig. 1. Alignment of amino acid residues of Tgo in Nilaparvata lugens and other insects. Insect species and GenBank accession numbers of Tango: Ph,Pediculus humanus corporis (XP_002430960.1); Cl, Cimex lectularius (XP_014259945.1); Cm, Callosobruchus maculatus (AFL70632.1); Ld,Leptinotarsa decemlineata (AKG92750.1); Pa,Pyrrhocoris apterus (AGI17574.1); Tc, Tribolium castaneum (TC004710); Ac, Acyrthosiphon pisum (XP_008180102.1).
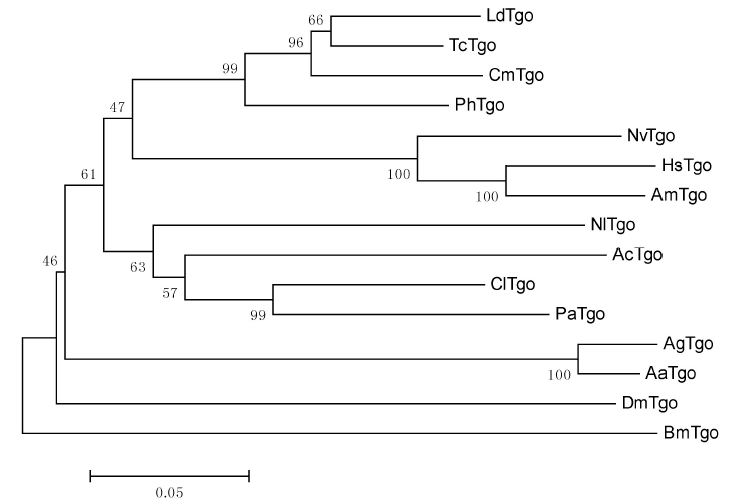
Fig. 2. Phylogenetic relationship of Nilaparvata lugens Tgo and insect homologues. Insect species and GenBank accession numbers of Tango: Ph, Pediculus humanus corporis (XP_002430960.1); Cl, Cimex lectularius (XP_014259945.1); Cm, Callosobruchus maculatus(AFL70632.1); Ld, Leptinotarsa decemlineata (AKG92750.1); Pa, Pyrrhocoris apterus (AGI17574.1); Tc, Tribolium castaneum (TC004710); Ac, Acyrthosiphon pisum (XP_008180102.1); Dm, Drosophila melanogaster (FBgn0264075); Nv, Nasonia vitripennis (Nasvi2EG004242); Bm, Bombyx mori (BGIBMGA003472); Hs,Harpegnathos saltator (HSAL22140); Ag, Anopheles gambiae (AGAP009748); Am, Apis mellifera (GB44259); Aa, Aedes aegypti (AAEL010343).
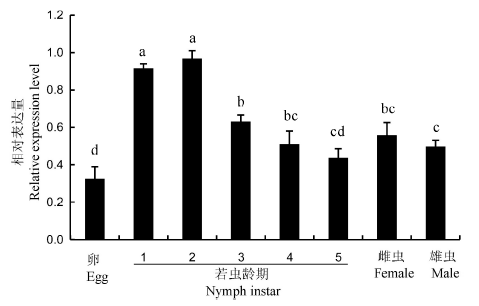
Fig. 3. Relative expression level of NlTgo in different development stages of Nilaparvata lugens. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at the 0.05 level between different groups. n=3
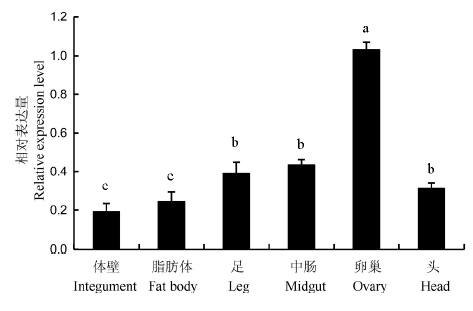
Fig. 4. Relative expression level of NlTgo in different tissues of Nilaparvata lugens. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at the 0.05 level between different groups.n=3.
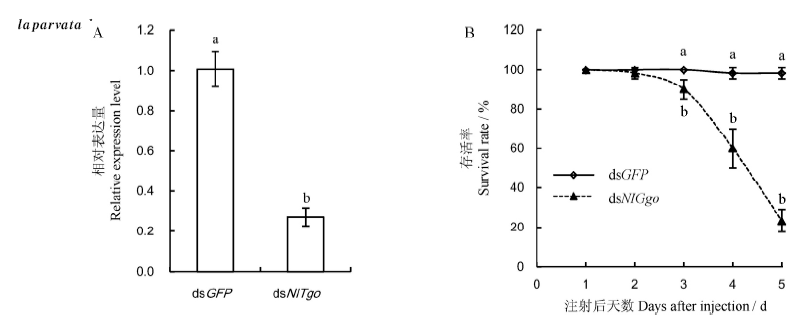
Fig. 5. Relative expression level of NlTgo at 4th day injection with dsRNA(A) and survival rate of Nilaparvata lugens after injection dsRNA of NlTgo(B). n=3. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at the 0.05 level between different groups.
| [1] | Atchley W R, Fitch W M.A natural classification of the basic helix-loop-helix class of transcription factors.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1997, 94(10): 5172-5176. |
| [2] | Massari M E, Murre C.Helix-loop-helix proteins: Regulators of transcription in eucaryotic organisms.Mol Cell Biol, 2000, 20(2): 429-440. |
| [3] | Kadesch T.Consequences of heteromeric interactions among helix-loop-helix proteins.Cell Growth Differ, 1993, 4(1): 49-55. |
| [4] | Reyes H, Reisz-Porszasz S, Hankinson O.Identification of the Ah receptor nuclear translocator protein (Arnt) as a component of the DNA binding form of the Ah receptor.Science, 1992, 256(5060): 1193-1195. |
| [5] | Jan Y N, Jan L Y.HLH proteins, fly neurogenesis, and vertebrate myogenesis.Cell, 1993, 75(5): 827-830. |
| [6] | Weintraub H.The MyoD family and myogenesis: Redundancy, networks, and thresholds.Cell, 1993, 75(7): 1241-1244. |
| [7] | Crews S.Control of cell lineage-specific development and transcription by bHLH-PAS proteins.Genes & Dev, 1998, 12(5): 607-620. |
| [8] | Sonnenfeld M, Ward M, Nystrom G, et al.The Drosophila tango gene encodes a bHLH-PAS protein that is orthologous to mammalian Arnt and controls CNS midline and tracheal development.Development, 1997, 124(22): 4571-4582. |
| [9] | Ghaffar M B, Pritchard J, Ford-Lloyd B.Brown planthopper (N. lugens Stål) feeding behaviour on rice germplasm as an indicator of resistance. PLoS One, 2011, 6(7): e22137. |
| [10] | 李进波, 万丙良, 夏明元, 等. 抗褐飞虱水稻品种的培育及其抗性表现. 应用昆虫学报, 2011, 48(5): 1348-1353. |
| Li J B, Wan B L, Xia M Y, et al.Breeding of the brown planthopper resistant rice varieties.Chin Bull Entomol, 2011, 48(5): 1348-1353. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | Cheng X, Zhu L, He G.Towards understanding of molecular interactions between rice and the brown planthopper.Mol Plant, 2013, 6(3): 621-634. |
| [12] | Yu R, Xu X, Liang Y, et al.The insect ecdysone receptor is a good potential target for RNAi-based pest control.Int J Biol Sci, 2014, 10(10): 1171-1180. |
| [13] | Li K L, Wan P J, Wang W X, et al.Ran involved in the development and reproduction is a potential target for RNA-interference-based pest management in Nilaparvata lugens. Plos One, 2015, 10(11): e0142142. |
| [14] | 王彦华, 王鸣华. 近年来我国水稻褐飞虱暴发原因及治理对策. 农药科学与管理, 2007, 25(2): 49-54. |
| Wang Y H, Wang M H.Factors affecting the outbreak and management tactics of brownplanthopper in China recent years.Pest Sci & Admin, 2007, 25(2): 49-54. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | Long S K, Fulkerson E, Breese R, et al.A comparison of midline and tracheal gene regulation during drosophila development.PLoS One, 2014, 9(1): e85518. |
| [16] | Larkin M A, Blackshields G, Brown N P, et al.Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0.Bioinformatics, 2007, 23(21): 2947-2948. |
| [17] | Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, et al.MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods.Mol Biol Evol, 2011, 28(10): 2731-2739. |
| [18] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D.Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method.RNA, 2001, 9(3): 299-308. |
| [19] | Yuan M, Lu Y, Zhu X, et al.Selection and evaluation of potential reference genes for gene expression analysis in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens(Hemiptera: Delphacidae) using reverse-transcription quantitative PCR. PLoS One, 2014, 9(1): e86503. |
| [20] | Wang W X, Li K L, Chen Y, et al. Identification and function analysis of enolase gene NlEno1 from Nilaparvata lugens (Stal) (Hemiptera:Delphacidae). J Insect Sci, 2015, 15(1): 66. |
| [21] | Li K L, Wan P J, Wang W X, et al.Ran involved in the development and reproduction is a potential target for RNA-interference-based pest management in Nilaparvata lugens. PLoS One, 2015, 10(11): e0142142. |
| [22] | Tang Q Y, Zhang C X. Data Processing System (DPS) software with experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining developed for use in entomological research.Insect Sci, 2013, 20(2): 254-260. |
| [23] | Peyrefitte S, Kahn D, Haenlin M.New members of the Drosophila Myc transcription factor subfamily revealed by a genome-wide examination for basic helix-loop-helix genes.Mech Dev, 2001, 104(1/2): 99-104. |
| [24] | Probst M R, Fan C M, Tessier-Lavigne M.Two murine homologs of the Drosophila single-minded protein that interact with the mouse aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator protein.J Biol Chem, 1997, 272(7): 4451-4457. |
| [25] | Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery M K, et al.Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature, 1998, 391(6669): 806-811. |
| [26] | Bitra K, Tan A, Dowling A, et al.Functional characterization of PAS and HES family bHLH transcription factors during the metamorphosis of the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Gene, 2009, 448(1): 74-87. |
| [27] | Ohshiro T, Saigo K.Transcriptional regulation of breathless FGF receptor gene by binding of TRACHEALESS/dARNT heterodimers to three central midline elements in Drosophila developing trachea.Development, 1997, 124(20): 3975-3986. |
| [28] | Crews S T, Fan C M.Remembrance of things PAS: regulation of development by bHLH-PAS proteins.Curr Opin Genet Dev, 1999, 9(5): 580-587. |
| [29] | Choi Y J, Kwon E J, Park J S, et al.Transcriptional regulation of the Drosophila caudal homeobox gene by bHLH-PAS proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2007, 1769(1): 41-48. |
| [1] | LUO Ju, YANG Suwen, BEI Wenyong, YU Junwei, TANG Jian, LIU Shuhua. Direct Multiplex TaqMan qPCR Assay for Rapid Detection of Three Sibling Species from Nilaparvata Distant [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2023, 37(3): 329-336. |
| [2] | HE Jiachun, HE Yuting, WAN Pinjun, WEI Qi, LAI Fengxiang, CHEN Xiangsheng, FU Qiang. Effects of Temperature on Biological Traits of the Pincer Wasp [Gonatopus flavifemur (Esaki & Hashimoto)], a Natural Enemy of the Brown Planthopper(Nilaparvata lugens) [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 318-326. |
| [3] | LUO Ju, TANG Jian, WANG Aiying, YANG Baojun, LIU Shuhua. A Rapid Detection Assay of Nilaparvata lugens Based on Recombinase Aided Amplification-lateral Flow Dipstick Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2022, 36(1): 96-104. |
| [4] | Lei PAN, Lihua WANG, Feng ZHU, Yangchun HAN, Pei WANG, Jichao FANG. Expression Profiles and Functions of Small Heat Shock Proteins in Nilaparvata lugens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2020, 34(1): 37-45. |
| [5] | Jiachun HE, Bo LI, Maocheng XIE, Fengxiang LAI, Guowen HU, Qiang FU. Laboratory Bioactivity Study on Neonicotinoid and Other Rice Paddy Used Insecticides Against the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens(Stål) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(5): 467-478. |
| [6] | Juefeng ZHANG, Fang LI, Haiying ZHONG, Jianming CHEN. Effects of Nystatin Treatment on Detoxification Enzymes and Uricase Content in Nymphs of the Brown Planthopper [Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)] [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2019, 33(2): 186-190. |
| [7] | Qiaoli CHEN, Feng WANG, Danlei LI, Yaming LING, Ruizhi ZHANG. Expression Under Hypertonic Osmotic Stress of Ab-lea from Aphelenchoides besseyi [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(6): 652-657. |
| [8] | Huanhuan ZHU, Yang CHEN, Pinjun WAN, Weixia WANG, Fengxiang LAI, Qiang FU. Influence of Symbiotic Bacteria Arsenophonus, Rice Variety and Temperature on the Incidence Rate of Nilaparvata lugens to Metarhizium flavoviride [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(6): 643-651. |
| [9] | Dan SHAN, Lihua WANG, Yueliang ZHANG, Yangchun HAN, Hongtao NIU, Lei PAN, Jichao FANG. Induced Expression Profiles of Hsp70s in Brown Planthoppers, Nilaparvata lugens, Under Different Temperatures [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(5): 533-541. |
| [10] | Chenxing ZHAO, Yewei YU, Yipeng XU, Xiaoping YU. Gene Cloning, Polyclonal Antibody Preparation and Expression Localization of Two dynamin-1-like Genes from Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(4): 345-354. |
| [11] | Yu ZHENG, Jia-chun HE, Pin-jun WAN, Feng-xiang LAI, Yan-qun SUN, Jing-jing LIN, Qiang FU. Virulence Characteristics of Nilaparvata lugens(Stål) Reared on Resistant Rice Variety IR56 [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(5): 552-558. |
| [12] | TANG Yaohua1,2, WAN Pinjun2, HAO Peiying1, FU Qiang2, *, YU Xiaoping1, *. Roles of Two Genes Involved in Histidine Biosynthetic Pathway in YeastLike Symbiont in Development of Nilaparvata lugens (Stl) [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2016, 30(4): 406-416. |
| [13] | Kai LIU, Ya-jun YANG, Jun-ce TIAN, Yan-hui LU, Hong-xing XU, Xu-song ZHENG, Zhong-xian LV. Effects of Bt Rice with cry1C and cry2A on the Ecological Generation Fitness of Rice Brown Planthoppers(Nilaparvata lugens) and Whitebacked Planthoppers (Sogatella furcifera) at Various Nitrogen Rates [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2016, 30(2): 200-209. |
| [14] | Li-hua WANG, Dan SHAN, Ji-chao FANG. Expression Profiling and Function Analyses of LHSC70 in Laodelphax striatellus [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2015, 29(4): 424-430. |
| [15] | AI Liping, SHEN Ao, GAO Zhichao, LI Zhenglong, SUN Qionglin, LUAN Weijiang*. Reverse Genetics Analysis of the Transcription Factor OsHox9, a Member of Homeobox Family, in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2014, 28(3): 223-228. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||